Clover Questions need to review
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What type of consent occurs during a standard outpatient two-view chest x-ray examination?
Implied
Informed
Legal
Written
Implied
After the injection of contrast for an intravenous urogram, it is noticed that the patient is suffering from hydronephrosis. To ensure adequate filling of the ureters with contrast medium, which of the following positions might be added to the examination?
LPO
Prone
RPO
Supine
Prone
Which of the following age groups may have unpredictable reactions during an X-ray exam, sometimes behaving in a mature fashion and other times in a more childlike manner?
Infants (age 0-1)
Toddlers (age 1-3)
Young Children (age 4-11)
Teens (age 12-17)
Teens (age 12-17)
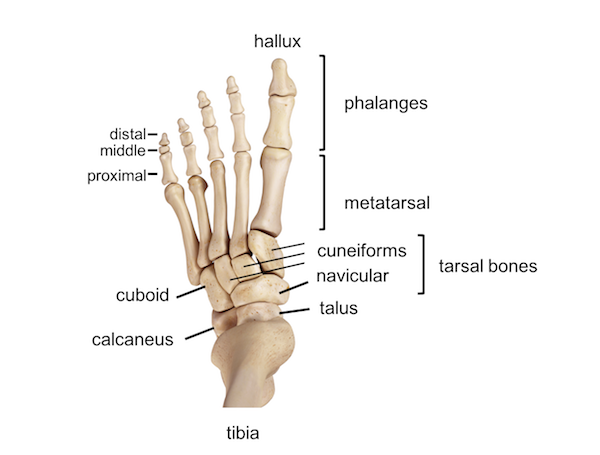
The cuboid bone articulates with which of the following bones?
5th metatarsal
Medial cuneiform
3rd metatarsal
Talus
5th metatarsal
What is the proper method of preparing the skin surface with an antiseptic prior to a surgical procedure?
Beginning at the center of the region of interest and moving in a circular motion toward the outside
Beginning in one corner of the region of interest and moving in a linear pattern
Beginning in the center and moving toward each corner of the region of interest in a linear pattern
Beginning outside the area and moving in a circular motion toward the center of the region of interest
Beginning at the center of the region of interest and moving in a circular motion toward the outside
Which of the following components should alert a technologist during a fluoroscopic x-ray production after a preset period of time?
Cumulative dose timer
Cumulative timer
Deadman switch
Fluorescent timer
Cumulative timer
According to the ACR, if cumulative air kerma or air kerma area-product data are not available during a fluoroscopic procedure, which two (2) of the following can be used? (Select two)
Cumulative exposure time
The amount of contrast media used
The type of procedure
The number of images taken
Cumulative exposure time
The number of images taken
The average normal range of creatinine in an adult is:
0.1-1.1 mg/dl
0.7-1.5 mg/dl
2.0-3.4 mg/dl
4-5.5 mg/dl
0.7-1.5 mg/dl
Which three of the following are included in a personnel monitoring report? (Select three)
Lifetime-to-date dose equivalent
Quarter-to-date dose equivalent
Total effective dose equivalent
Year-to-date dose equivalent
Lifetime-to-date dose equivalent
Quarter-to-date dose equivalent
Year-to-date dose equivalent
What portion of the x-ray circuit must use alternating current (AC) in order to function correctly?
Circuit breakers
Kilovoltage peak (kVp) meter
Transformers
X-ray tube
Transformers
Limb-stunting, microcephaly, and genital defects are all examples of:
Carcinogenic effects
Cerebral effects
Lethal effects
Teratogenic effects
Teratogenic effects
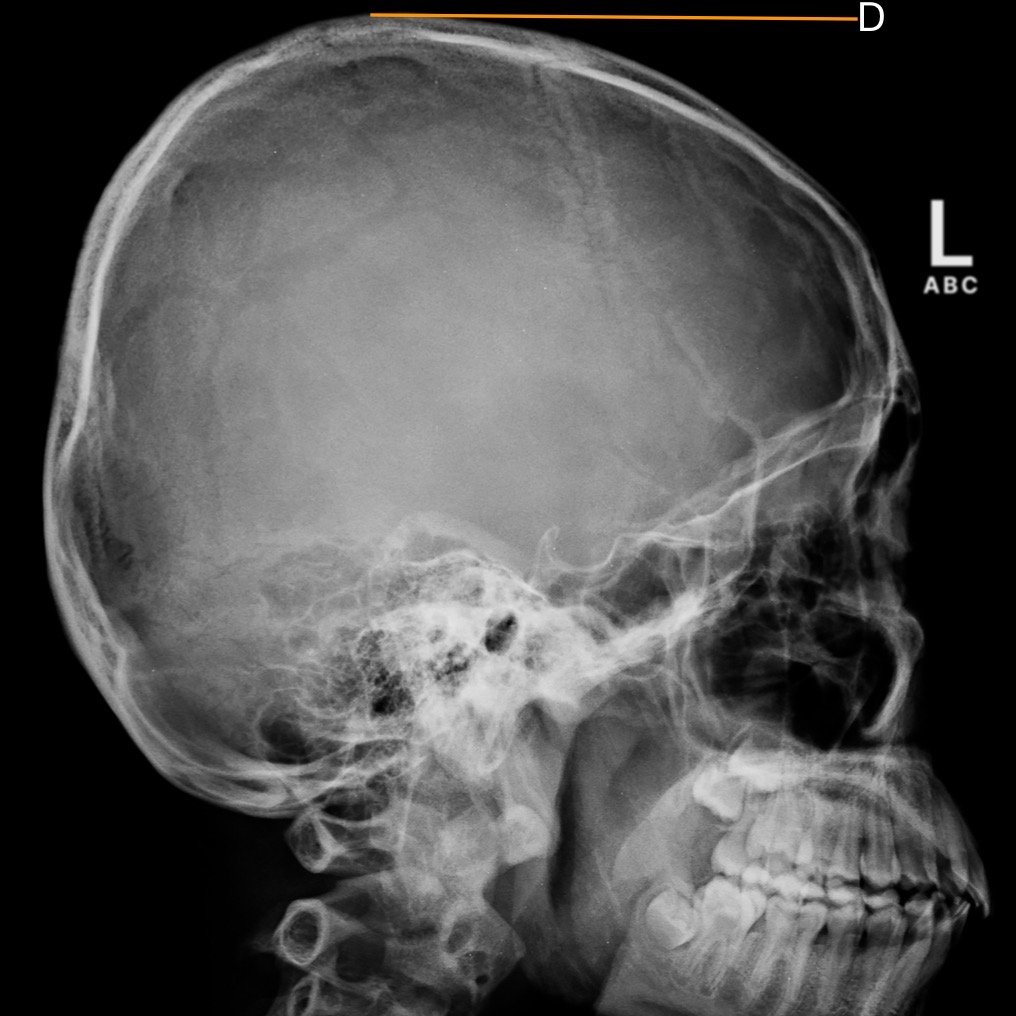
Identify the structure that is represented by the letter (D):
Occipital bone
Lambdoidal suture
Sella turcica
Vertex
Vertex
Which of the following methods may be used when anatomy or the area of interest is too large to fit on one image receptor?
Appending
Multiplanar reconstructions
Stitching
Volume rendering
Stitching
Which three of the following statements are true when describing the female pelvis? (Select three)
It is heavier than the male pelvis
It is wider than the male pelvis
The pubic arch forms an acute angle
The sacrum has a more pronounced posterior curve
The superior aperture (inlet) is oval-shaped
It is wider than the male pelvis
The sacrum has a more pronounced posterior curve
The superior aperture (inlet) is oval-shaped
What percentage of the beam would remain after the application of two half-value layers?
25%
50%
75%
100%
25%
In quality control of imaging equipment, what does the term "linearity" refer to?
The ability to produce images with consistent brightness
The uniformity of images across various monitors
The consistency of radiation output relative to mA settings
The precision of geometric representation on images
The consistency of radiation output relative to mA settings
What is the primary purpose of performing a daily quality control check on digital radiography systems?
To ensure patient information is input correctly
To verify the functioning of imaging plates
To minimize radiation exposure to patients
To check the system's ability to reproduce image contrast
To check the system's ability to reproduce image contrast
How many shades of gray can be produced by an 8-bit digital radiography system?
8 shades of gray
64 shades of gray
256 shades of gray
1,024 shades of gray
256 shades of gray
28=256
Which patient position would best demonstrate small amounts of fluid in the pleural cavity?
Anteroposterior (AP) chest with patient in Trendelenburg position
Anteroposterior (AP) supine chest
Lateral decubitus position with affected side down
Lateral decubitus position with affected side up
Lateral decubitus position with affected side down
What term refers to an acute infection of the lung parenchyma or supportive tissue?
Asthma
Atelectasis
Emphysema
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
What is the degree difference between the orbitomeatal line (OML) and the infraorbitomeatal line (IOML)?
3 degrees
5 degrees
6 degrees
7 degrees
7 degrees
Air kerma is expressed in units of:
Coulomb/kilogram
Gray
Roengten
Sievert
Gray
Which of the following is considered a tort?
Act that results in an injury
Misdemeanor
Type of fracture
Viral infection
Act that results in an injury

If the distance between the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) and the tabletop is 22 cm, what central ray angle and direction should be used for an anteroposterior (AP) knee radiograph?
0 degrees (perpendicular)
5 degrees cephalad
10 degrees cephalad
15 degrees cephalad
0 degrees (perpendicular)
Which two of these processes corrects for slight underexposure or overexposure errors caused by incorrect technical factors settings? (Select two)
Histogram analysis
Look-up table (LUT) adjustments
Quantization
Rescaling
Look-up table (LUT) adjustments
Rescaling
The lifetime whole-body dose limit for a radiographer is calculated as:
5 millisieverts (mSv) + 0.5 millisieverts (mSv) per month
Age + 20 millisieverts (mSv)
Age x 10 millisieverts (mSv)
Age x 50 millisieverts (mSv)
Age x 10 millisieverts (mSv)
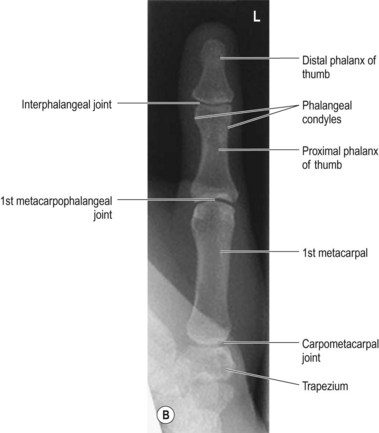
Where is the proper central ray entrance point for an anteroposterior (AP) projection of the thumb?
Base of first metacarpal
Distal interphalangeal joint of first digit
First metacarpophalangeal joint
Interphalangeal joint of first digit
First metacarpophalangeal joint
Which of the following situations would be an example of libel?
Describing the patient condition with your assigned radiography student
Discussing the x-ray results of a patient with your co-worker in the hospital cafeteria
Noting the location of a suspicious bruise in a potential child abuse case
Writing a negative comment about the patient in the chart
Writing a negative comment about the patient in the chart

Walls that are considered to be secondary barriers should consist of:
0.8 mm (1/32 in) of lead thickness
1.6 mm (1/16 in) of lead thickness
3.2 mm (1/8 in) of lead thickness
4.8 mm (3/16 in) of lead thickness
0.8 mm (1/32 in) of lead thickness
Surgical aseptic technique should be used during which of the following procedures?
Double-contrast barium enema
Intravenous urogram
Myelogram
Pediatric UGI
Myelogram
A technologist is accidentally punctured by a used hypodermic needle. What is the mode of disease transmission in this situation?
Airborne
Fomite
Enteric
Vector
Fomite

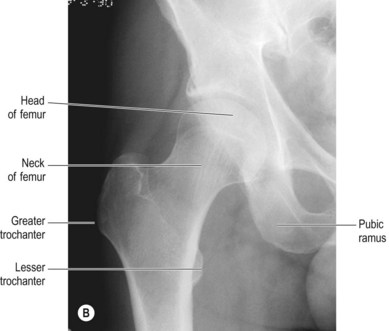
Where should the central ray enter for an anteroposterior (AP) radiograph of the hip?
Acetabulum
Femoral neck
Greater trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Femoral neck
Who is required to wear a personnel dosimeter?
Anyone who may be occupationally exposed to more than 5% of the annual dose limit
Anyone who may be occupationally exposed to more than 10% of the annual dose limit
Anyone who works exclusively in non-ionizing imaging modalities
Anyone who is occupationally exposed to any amount of ionizing radiation
Anyone who may be occupationally exposed to more than 10% of the annual dose limit
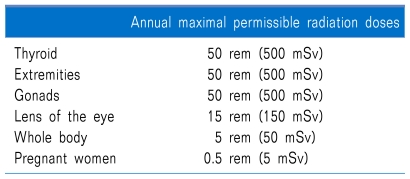
What is the annual dose equivalent limit for a radiographer’s hands?
50 millisieverts (mSv)
150 millisieverts (mSv)
250 millisieverts (mSv)
500 millisieverts (mSv)
500 millisieverts (mSv)
Consider a technologist that accidentally uses a higher kVp setting than needed for a radiograph of the chest. Which of the following is used to display the image as if it was exposed using proper technical factors?
Histogram analysis
Edge enhancement
Quantization
Rescaling
Rescaling
What is the annual effective dose limit for a radiographer?
150 millisieverts (mSv)
250 millisieverts (mSv)
50 millisieverts (mSv)
500 millisieverts (mSv)
50 millisieverts (mSv)
Which three of these changes will improve the spatial resolution recorded in the radiographic image? (Select three)
Decreased focal spot size (FSS)
Decreased object-to-image distance (OID)
Increased focal spot size (FSS)
Increased object-to-image distance (OID)
Increased source-to-image distance (SID)
Decreased focal spot size (FSS) [SMALL FOCAL SPOT]
Decreased object-to-image distance (OID)
Increased source-to-image distance (SID)
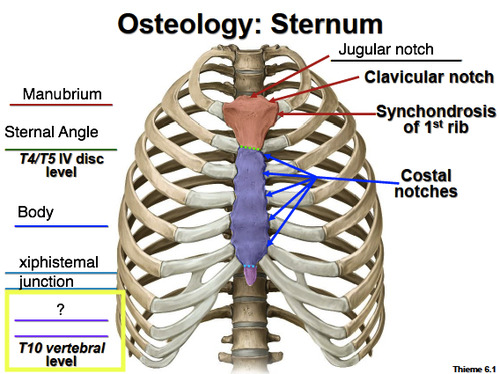
Which of the following structures is located at the level of the interspace between T4 and T5?
Jugular notch
Manubrium
Sternal angle
Xiphoid
Sternal angle
An “apple core” lesion typically is related to which of the following pathologies?
Chondrosarcoma
Cirrhosis
Colon cancer
Renal calculi
Colon cancer
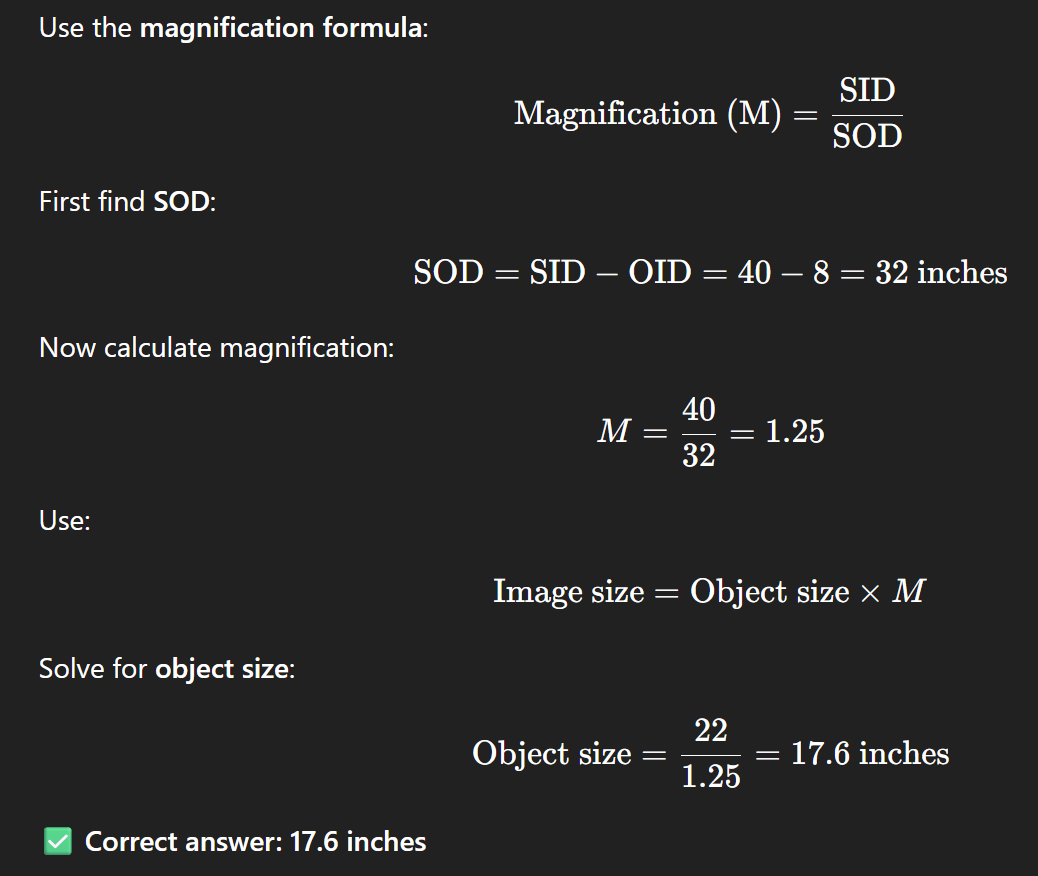
A radiograph of the femur is produced using 12 milliampere-seconds (mAs), 70 kilovoltage peak (kVp), 40-inch source-to-image distance (SID), and an 8-inch object-to-image distance (OID). If the image of the femur measures 22 inches, what is the actual length of the femur?
4.4 inches
15.8 inches
17.6 inches
32 inches
17.6 inches
What is the most likely effect of a large radiation exposure during the first few days of pregnancy?
Anencephaly
Intellectual disability
Preterm birth
Death of the embryo
Death of the embryo
Which chamber of the heart is responsible for pumping blood to the lungs?
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Right ventricle
“A = Arrive, V = Venture out”
Atria = Arrive
Right atrium → blood arrives from the body
Left atrium → blood arrives from the lungs
Ventricles = Venture out (pump out)
Right ventricle → pumps blood to the lungs
Left ventricle → pumps blood to the body