Genomics Homework Exam #3
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
_______ is the isolation and amplification of a given gene
Gene cloning
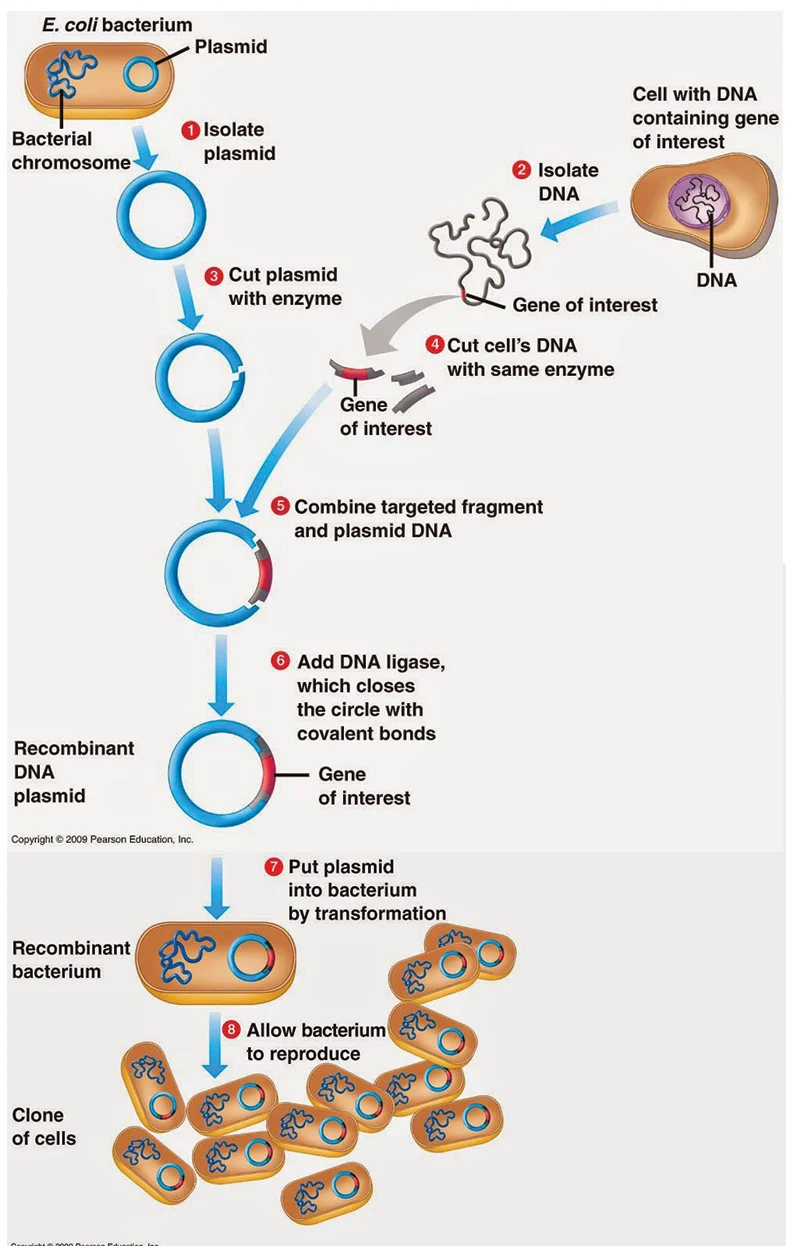
What is gene cloning?
Gene cloning is a process where a specific DNA fragment (often a gene) is isolated, replicated, and manipulated for various purposes, like gene expression, research, or genetic engineering. It involves inserting the gene into a vector (like a plasmid) that can replicate within a host cell, allowing for the production of multiple copies of the gene and potentially the protein the protein it encodes
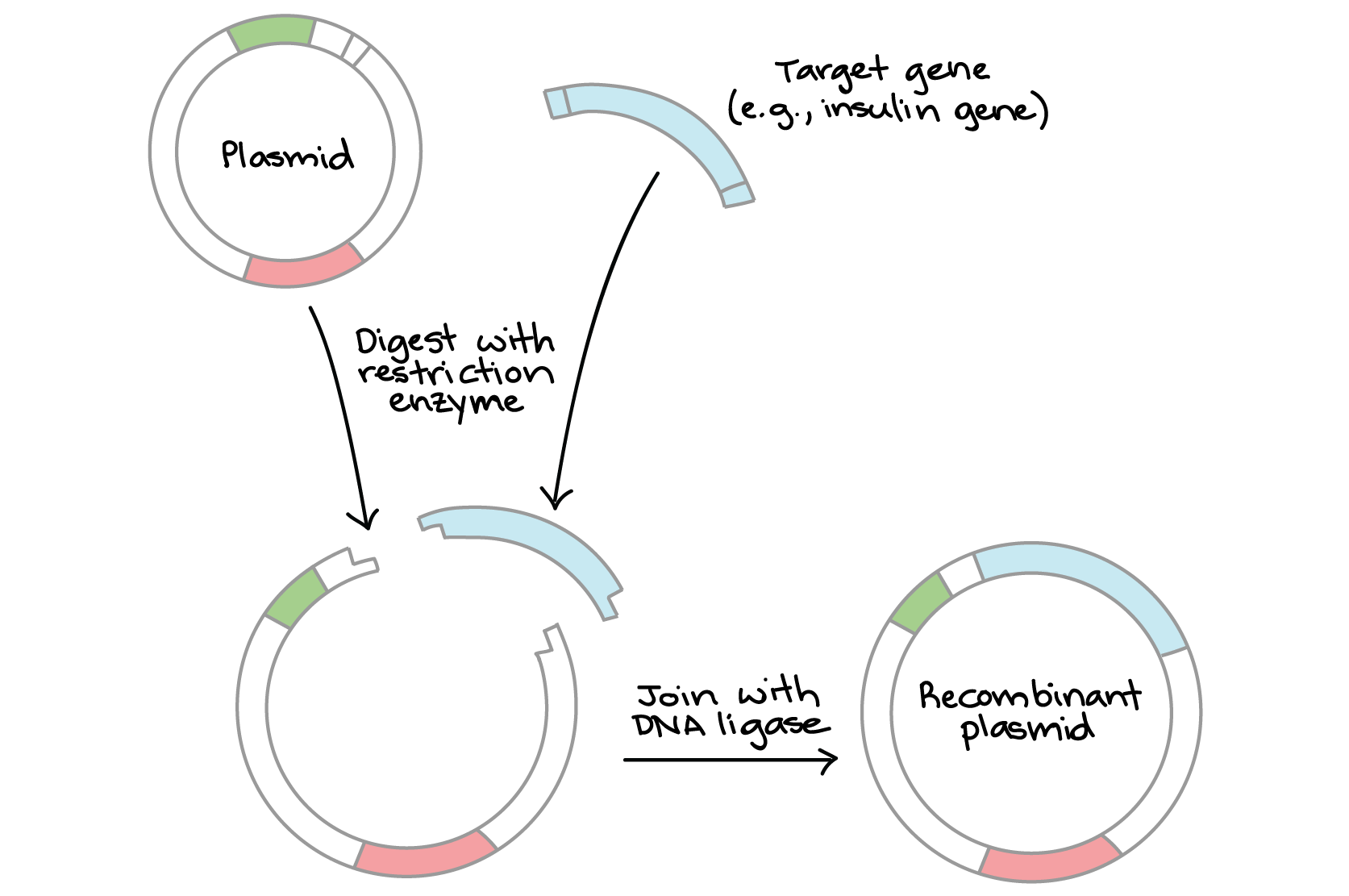
What is southern blotting?
A procedure for identifying specific sequences of DNA, in which fragments seperated on a gel are transferred directly to a second medium on which detection by hybridization may be carried out
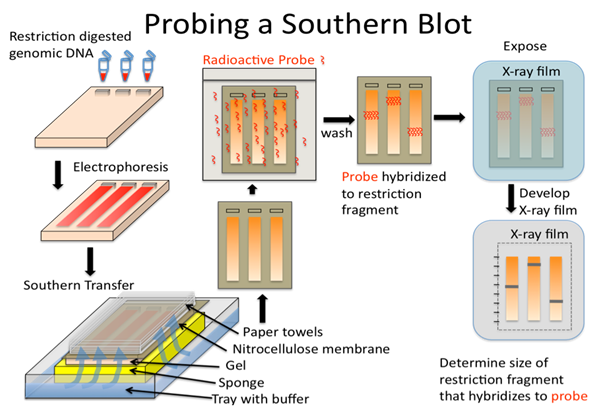
What is the difference between southern and western blotting?
Then southern and northern blotting method can be used to identify specific DNA and RNA sequences respectively, while the Western blotting method can be used to identify a specific protein
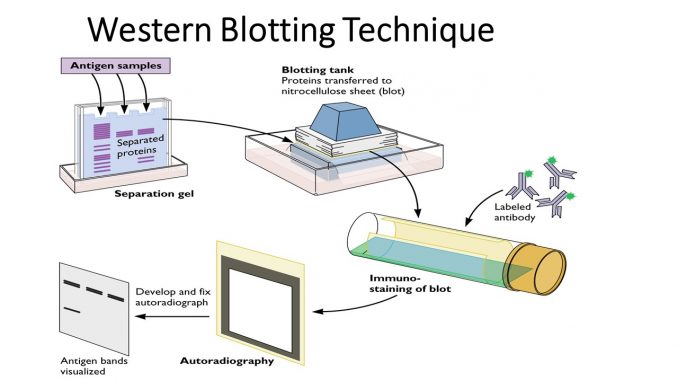
What is western blotting?
AKA immunoblotting, it is a laboratory technique used to detect specific proteins within a complex mixture of proteins. It involves seperating proteins based on size using gel electrophoresis, transferring them to a membrane, and then using antibodies to specifically detect they target protein
Bacteria use methylation of DNA sequences for what purpose?
Methylation of DNA can mask a restriction enzyme cleavage site
What is DNA methylation?
DNA methylation is an epigenetic process where a methyl group (CH3) is added to a cytosine base within the DNA molecule, specifically at the C5 position, forming 5-methylcytosine (5mC). This modification alters gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence.
In simpler terms: Imagine the DNA as a book with a sequence of letters (genes). Methylation is like adding a small sticker (methyl group) to a specific letter (cytosine base). This sticker can change how the page (gene) is read, either making it easier or harder to read, and thus affecting the gene's expression.
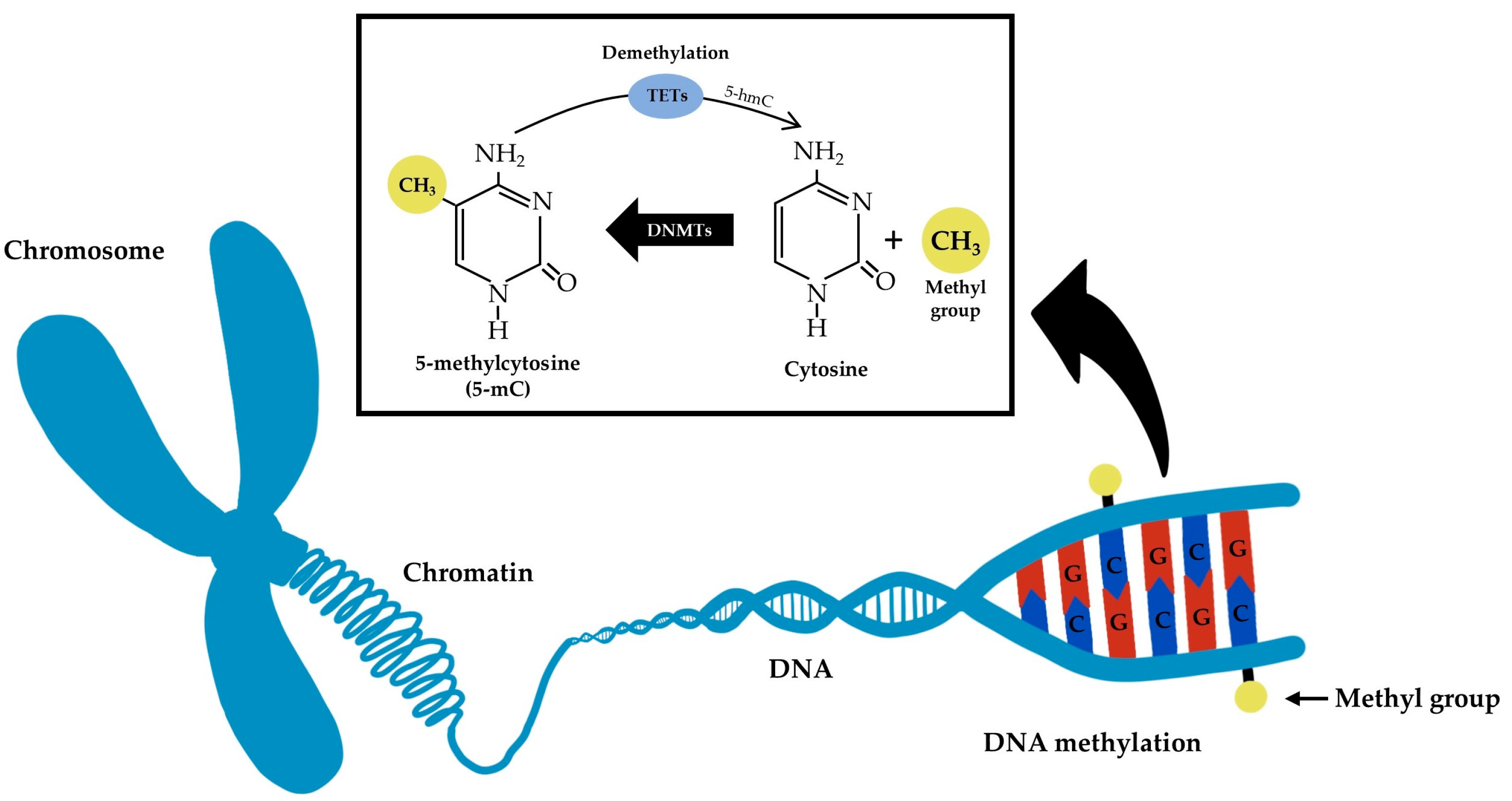
What is an enzyme cleavage site?
AKA recognition or scissile bond, it is the specific location within a molecule (like DNA or protein) where an enzyme will cleave or cut
Name the essential component of a cloning vector:
restriction endonuclease cleavage site
A dominant selectable marker gene
An origin of replication
All cloning vectors have what in common?
The ability to self-replicate
What method of gene cloning is best suited to making copies of a gene in vitro?
Polymerase chain reaction is best suited to making copies
What organelles can carry a genome?
Plastids, nucleus and mitochondria
What is a cloning vector?
A cloning vector is a DNA molecule, often a plasmid or virus, used to carry a piece of foreign DNA into a host cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed
Humans vary in their genome sequences. The type of variance that is a single base pair substitution is also know as:
A SNP
What is an SNP?
Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), commonly know as snips, are the most frequent type of genetic variation found in humans
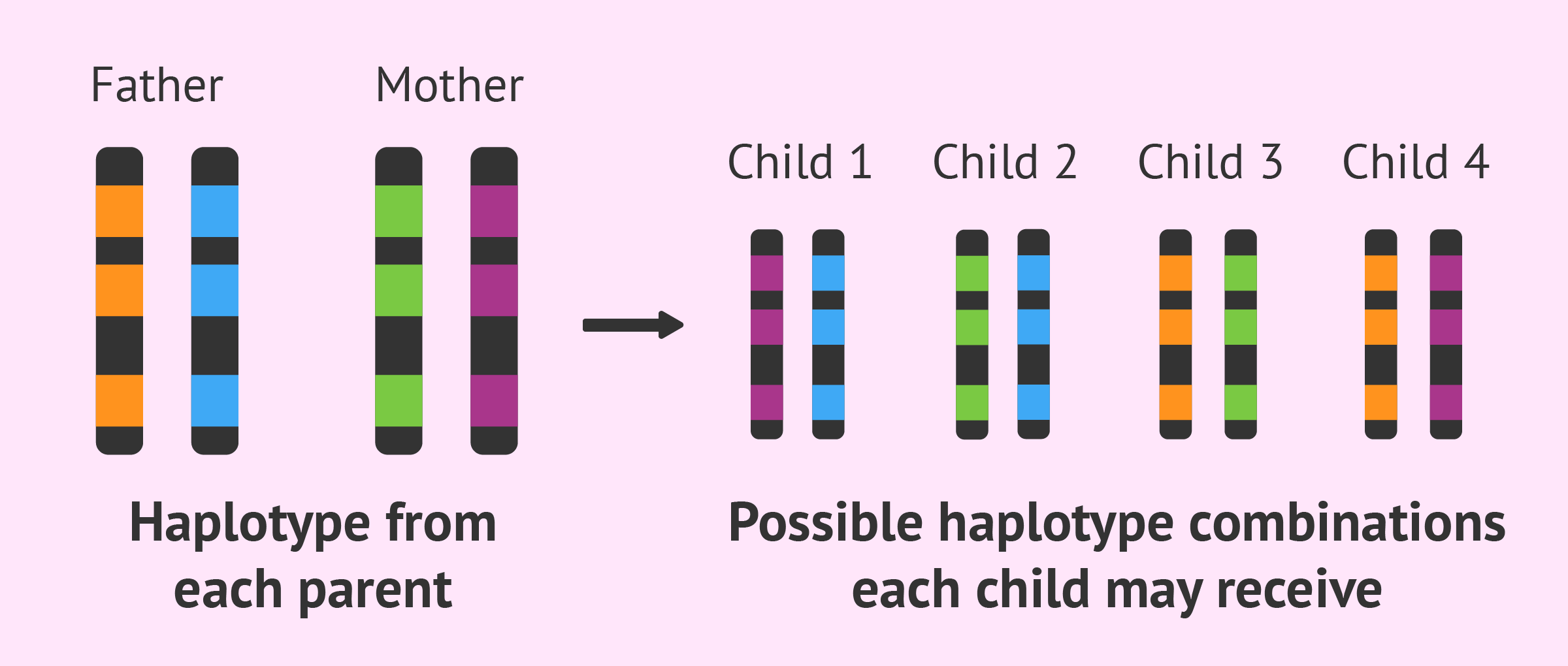
A collection of SNPs on a chromosome that tend to be inherited together is called:
A haplotype
The technology that can analyze gene expression of all genes in a genome is called:
Microarray analysis
What are cytological maps based upon?
Cytological maps are based upon banding patterns of chromosome