Systemic Anatomy - The Lymphatic System
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture and lab
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Identify the lymphatic vessels.
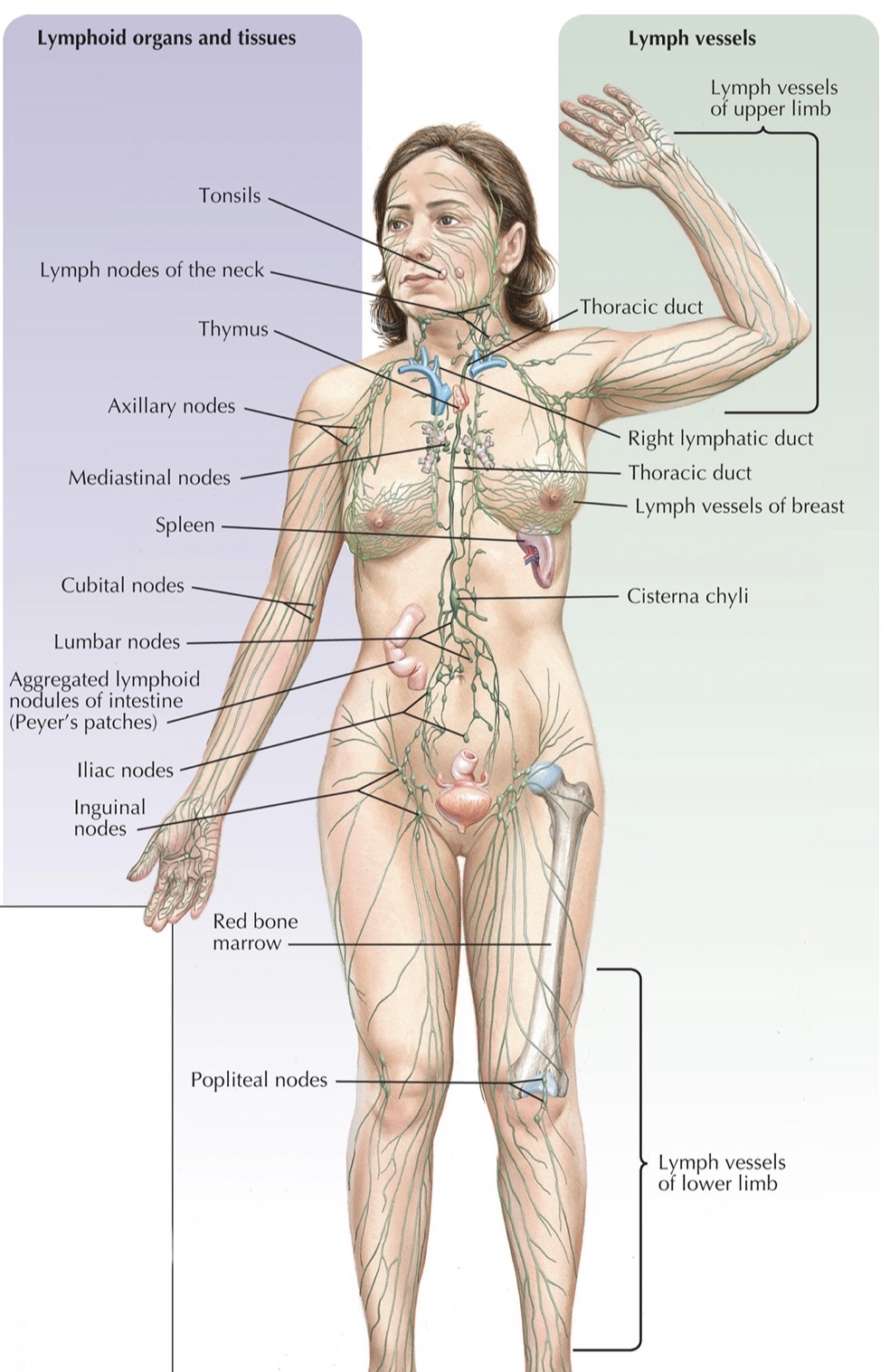
Identify the inguinal lymph node cluster.
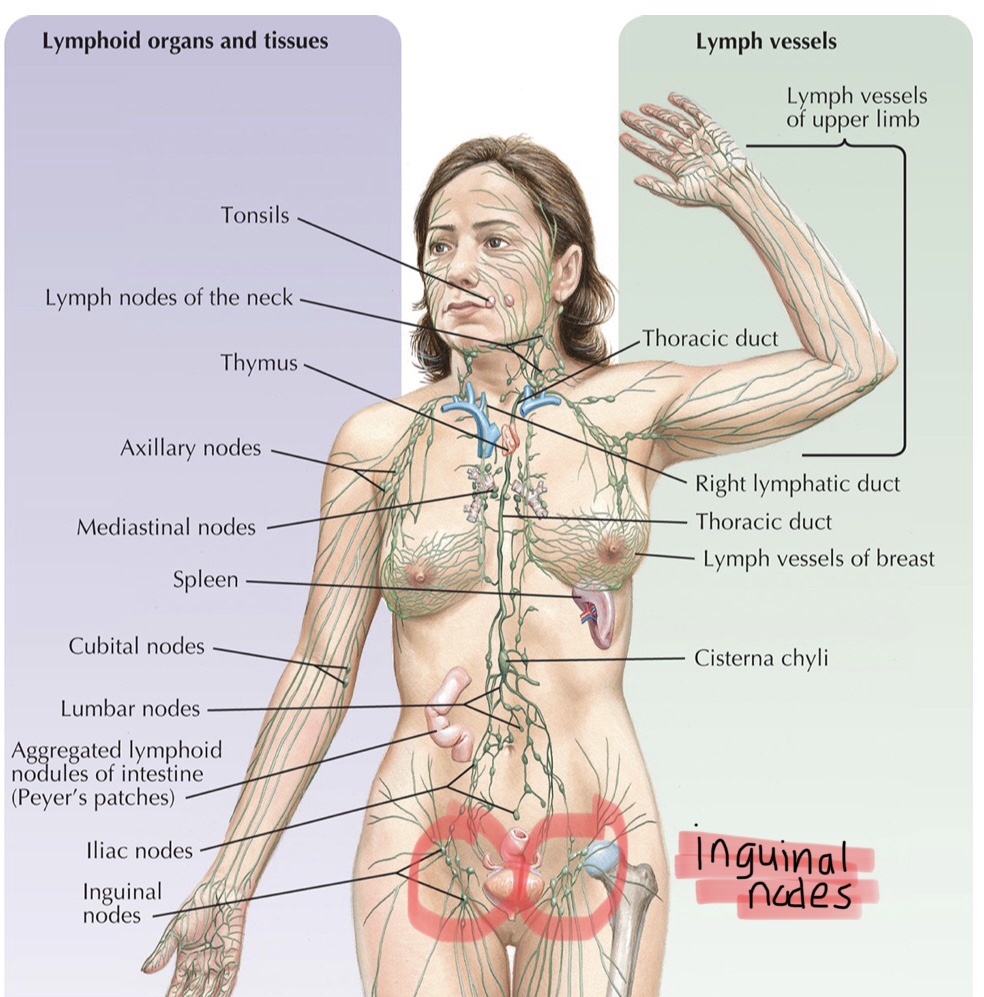
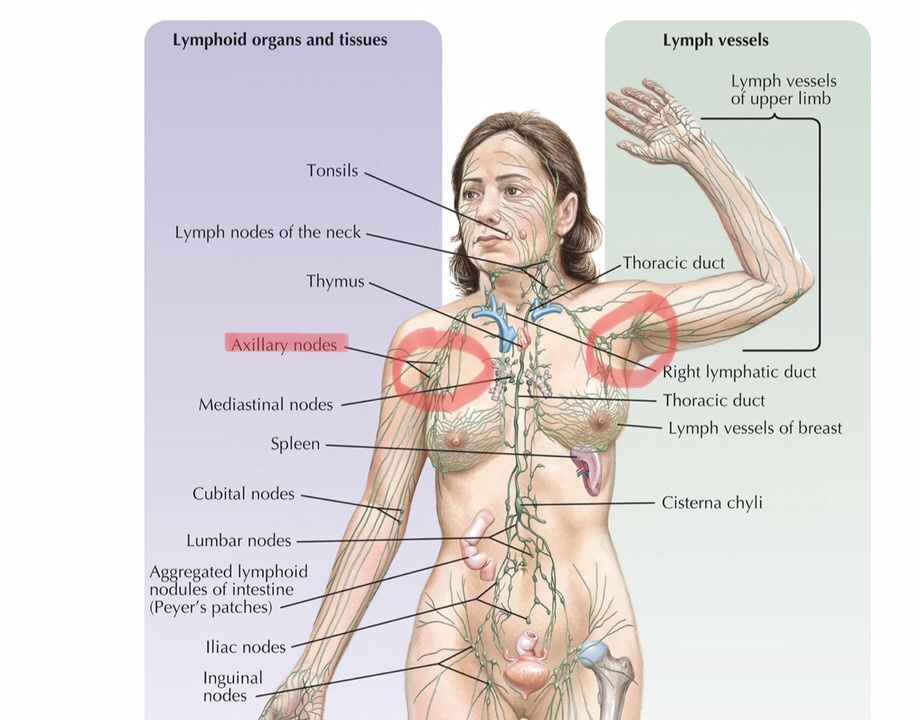
Identify the axillary lymph node cluster.
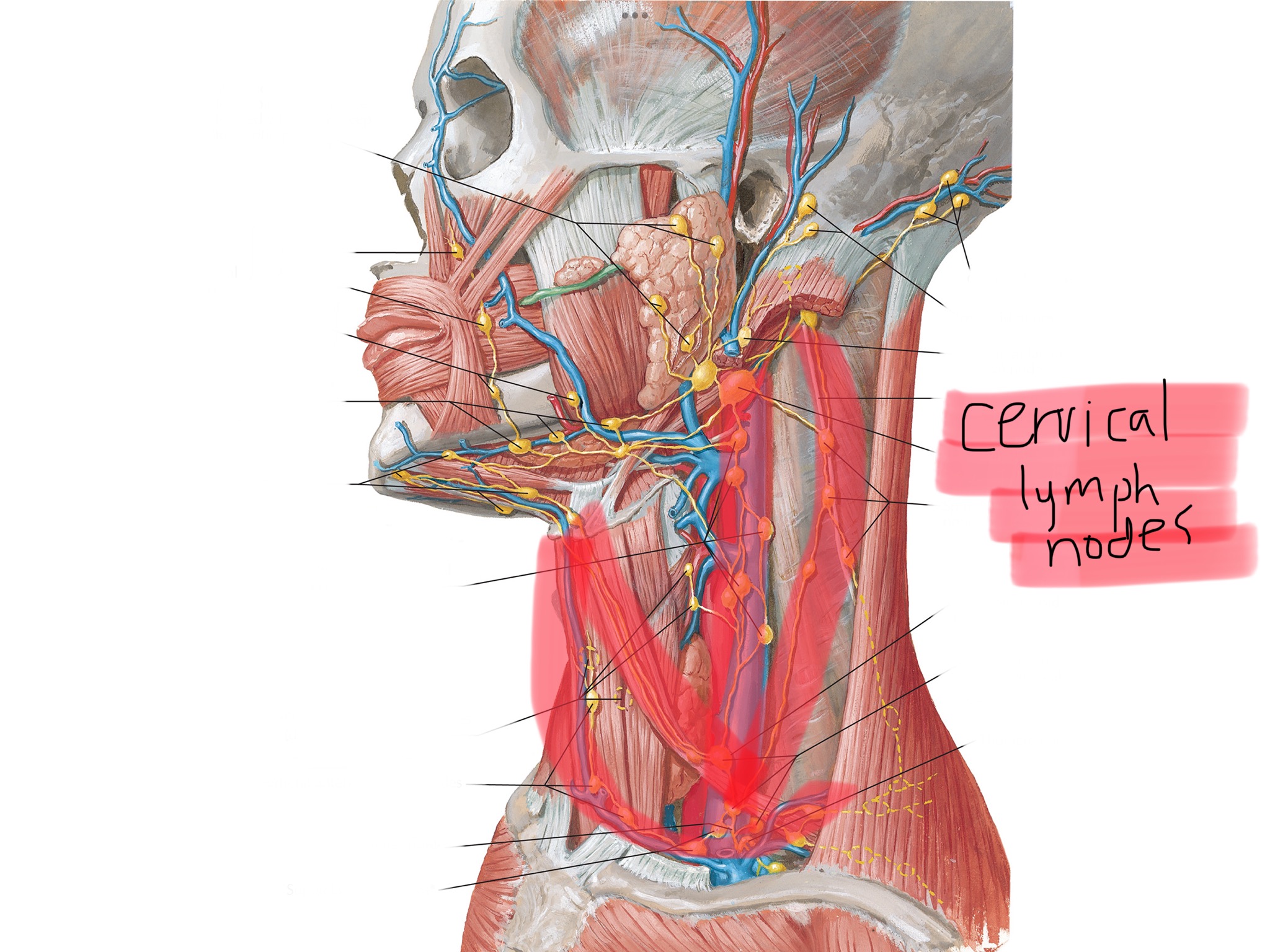
Identify the cervical lymph node cluster.
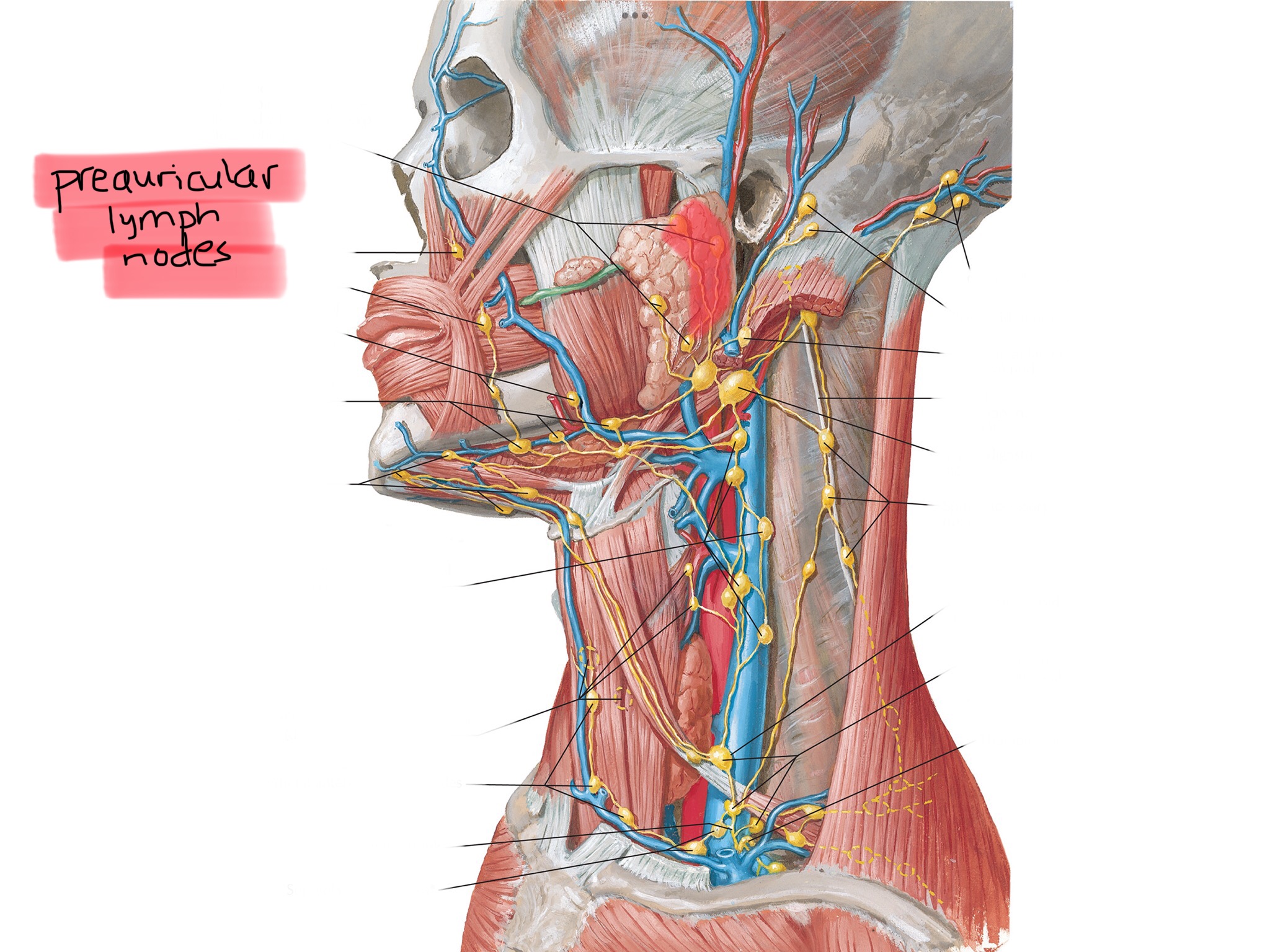
Identify the preauricular lymph node cluster
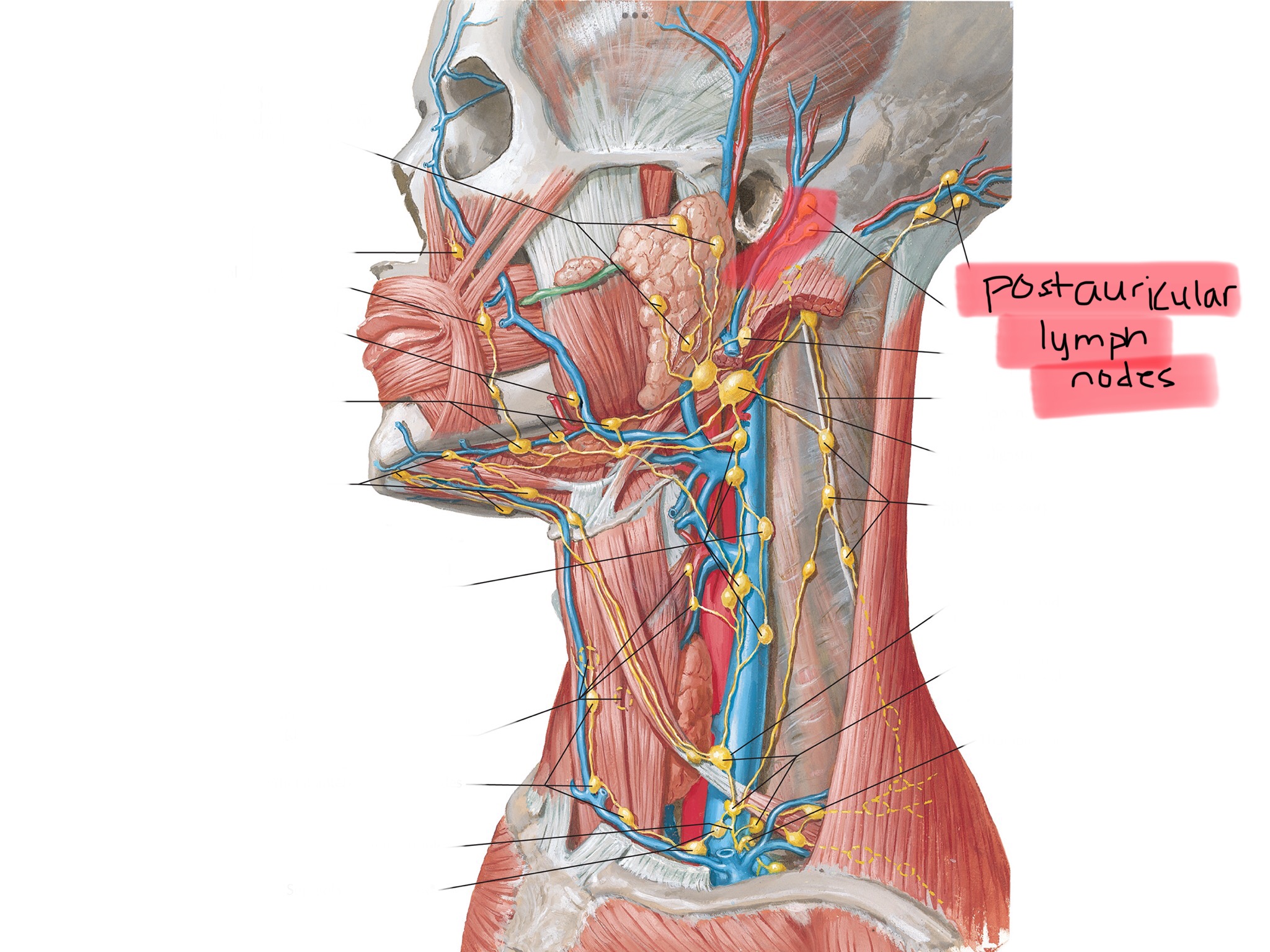
Identify the postauricular lymph node cluster.
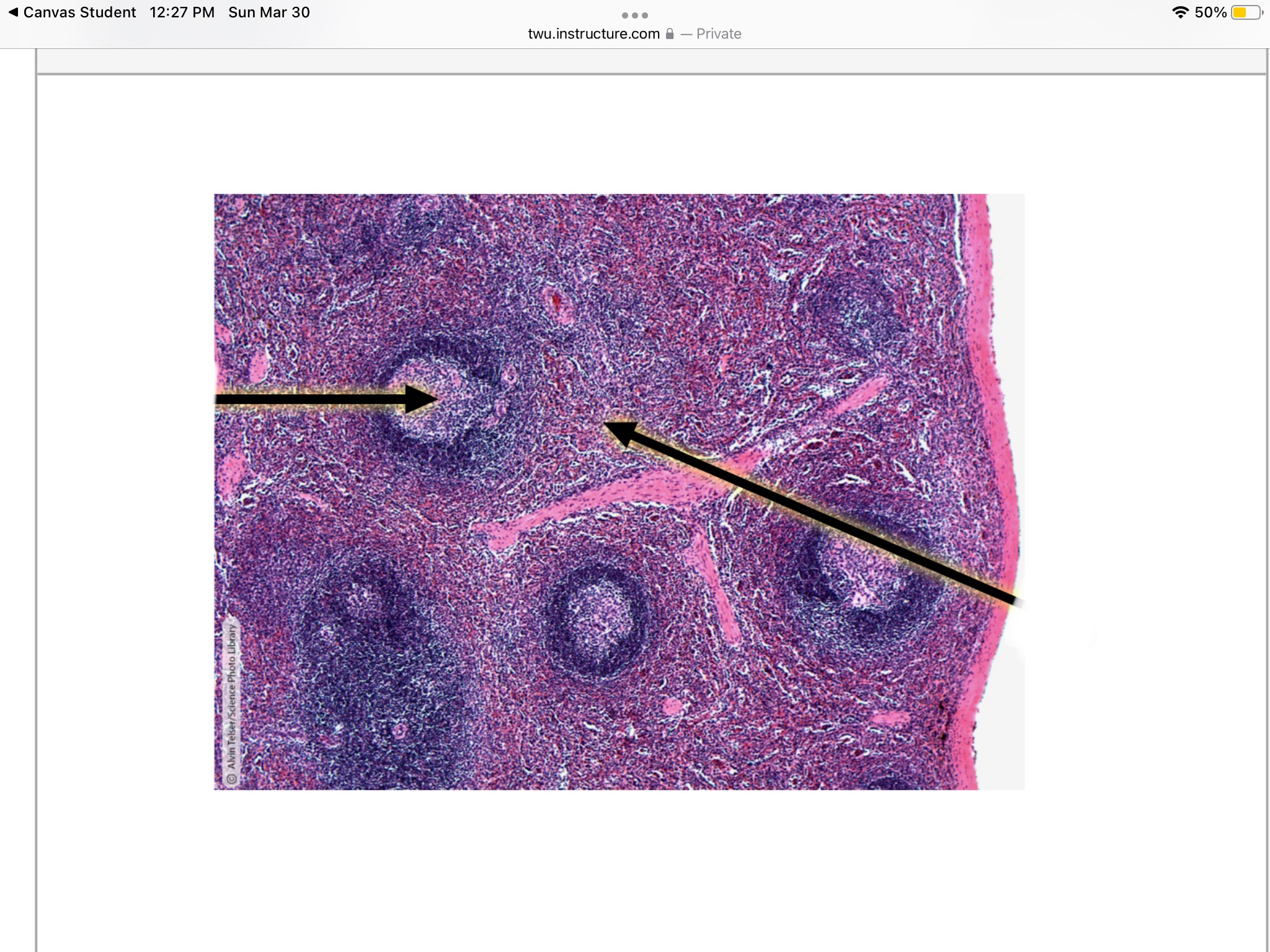
Identify spleen tissue.
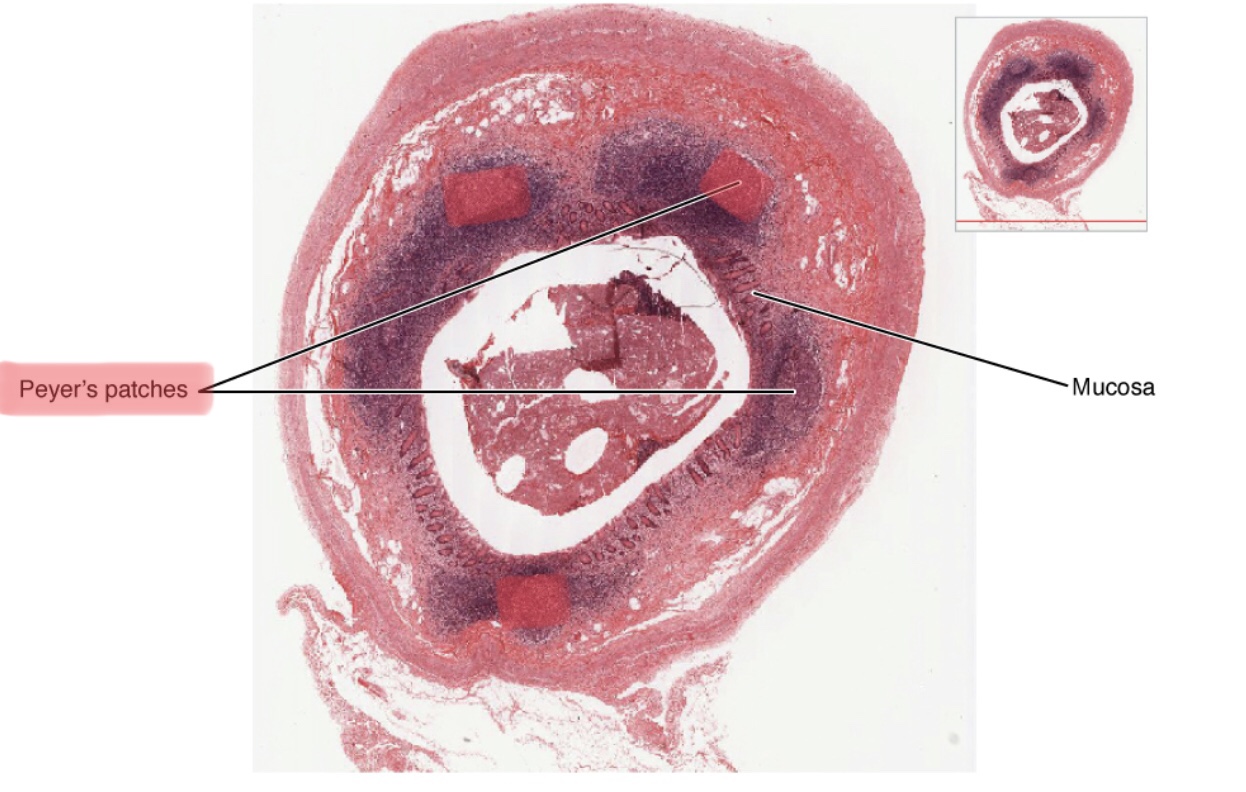
Identify Peyer’s patches.
Identify the tonsils.
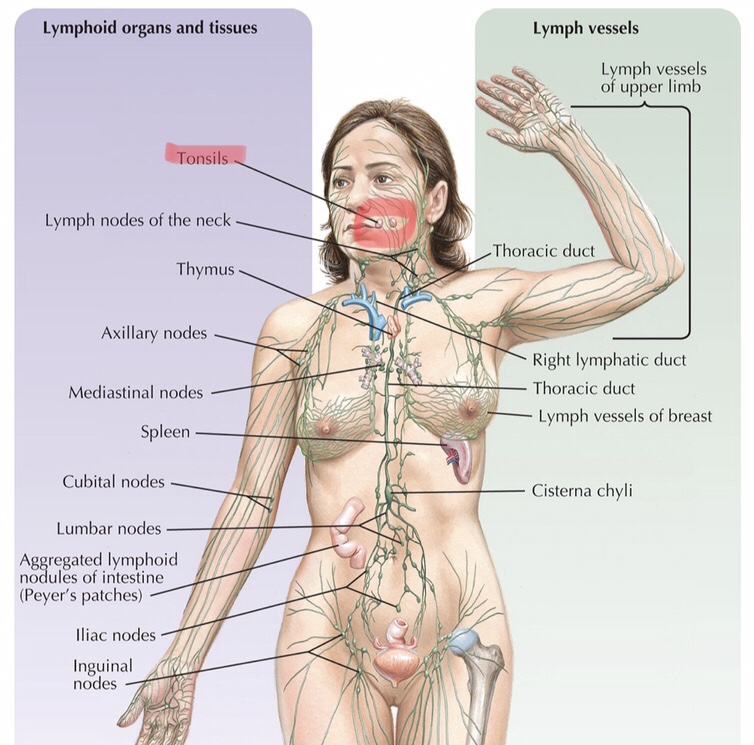
Identify tonsil tissue.
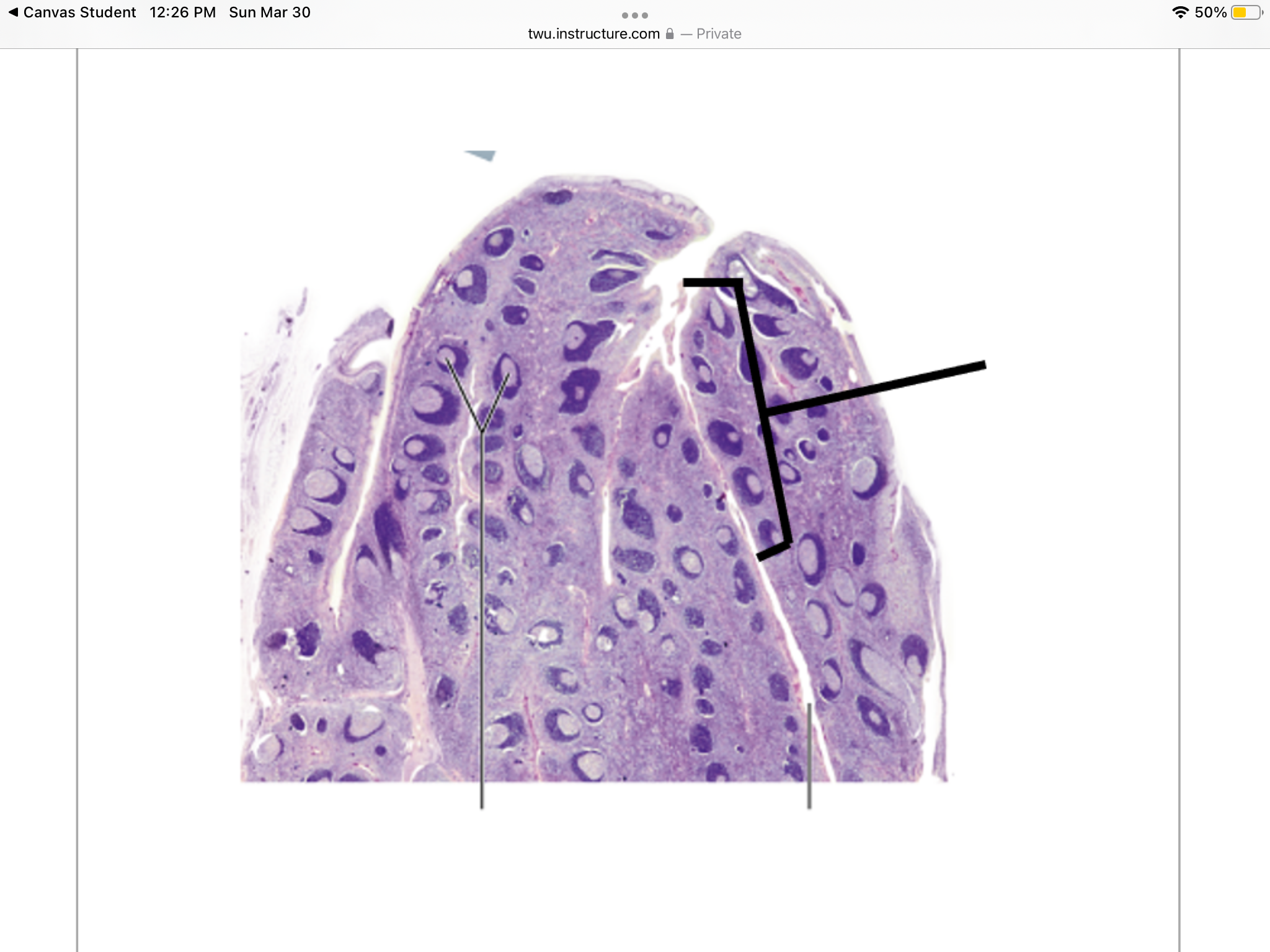
Identify the cisterna chyli.
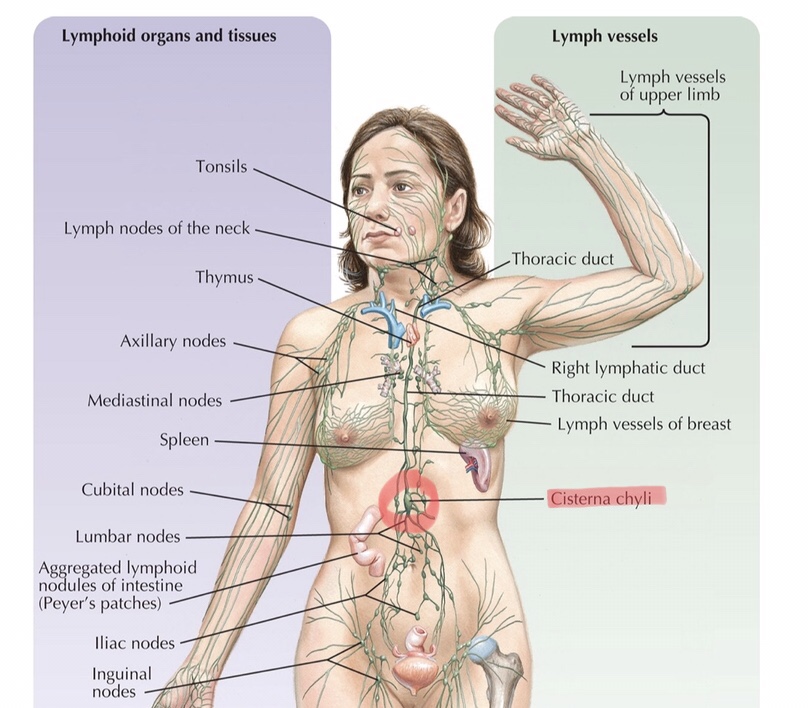
Identify the thoracic duct.
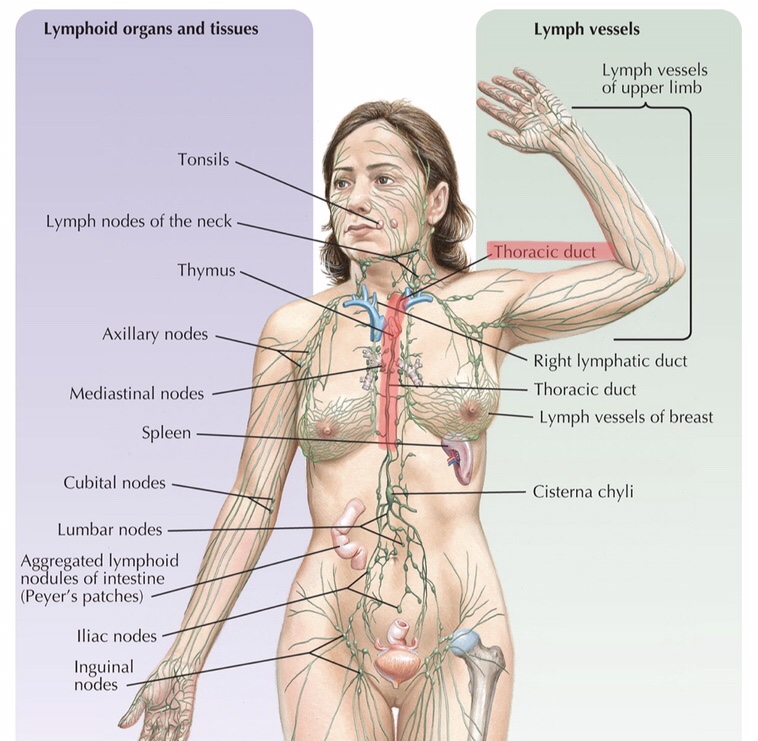
Identify the right lymphatic duct.
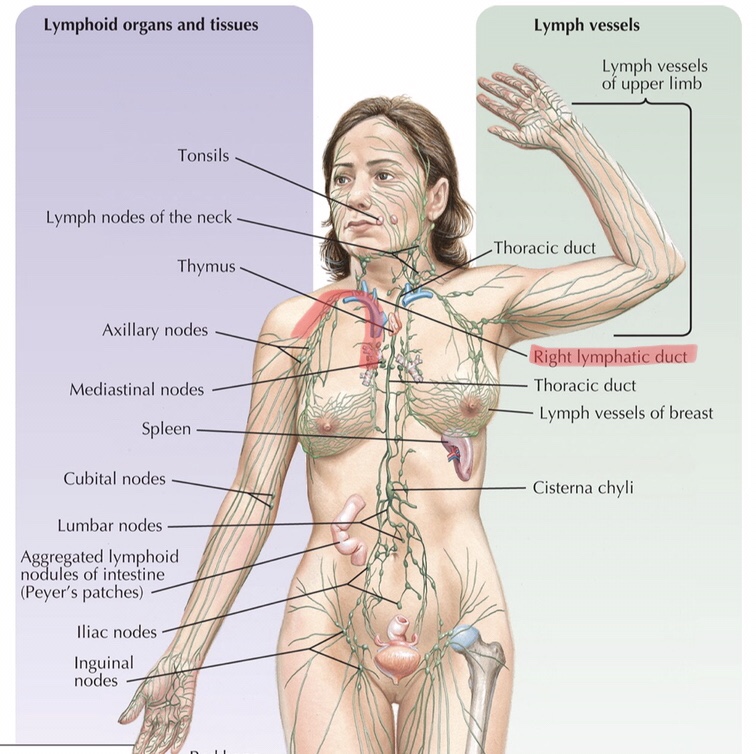
Identify the lymphocytes in a lymph node.
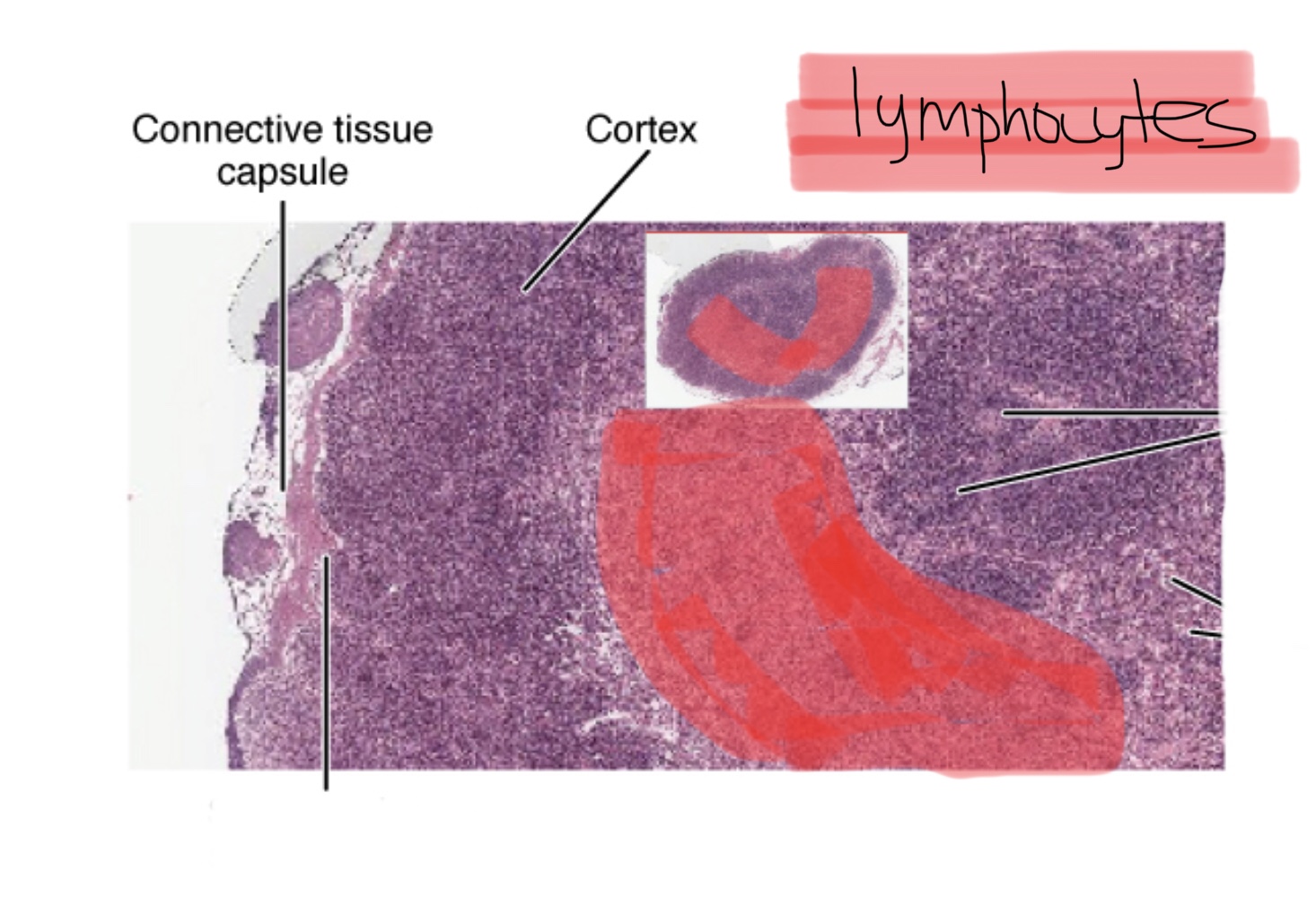
Identify the hilum in a lymph node.
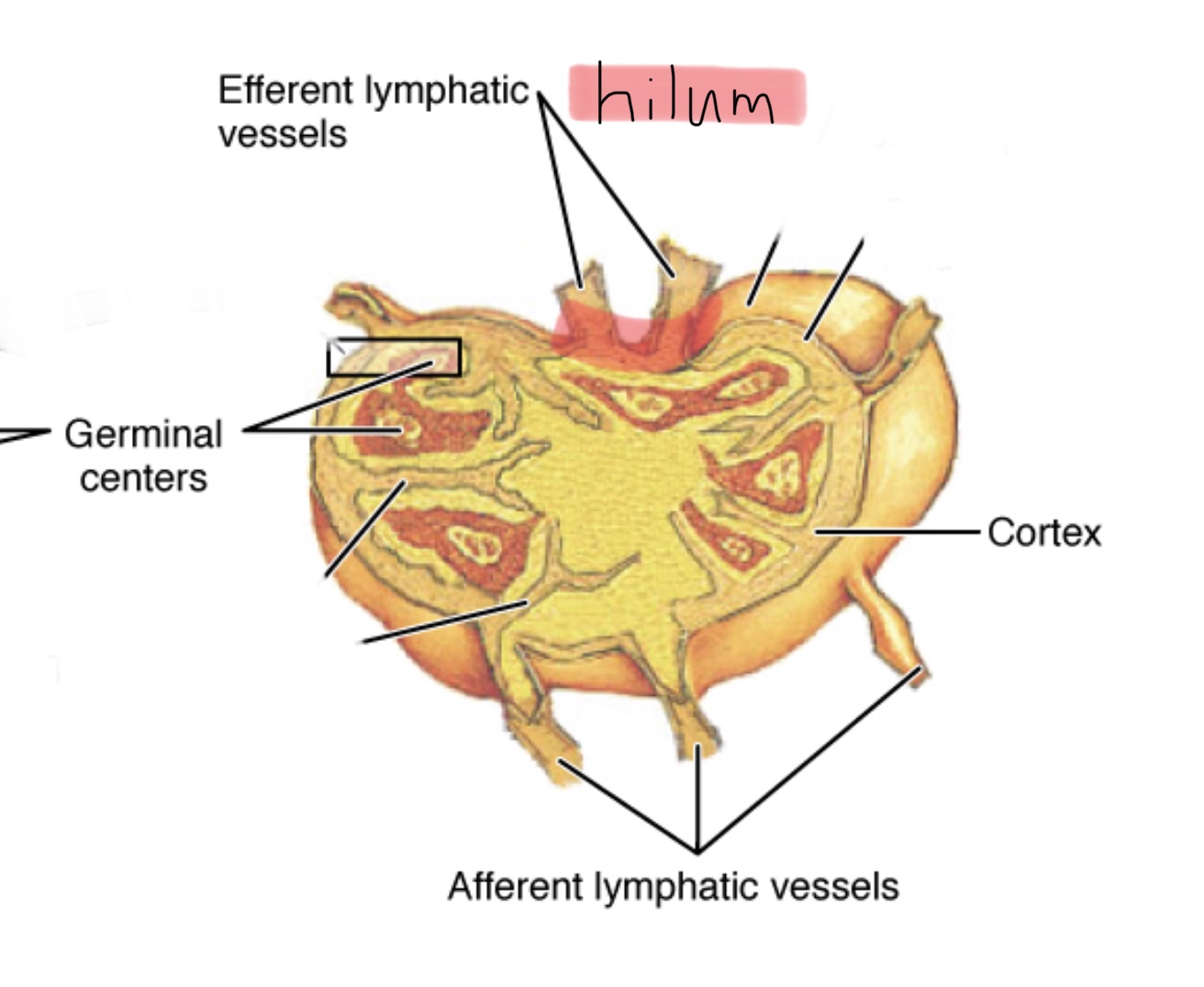
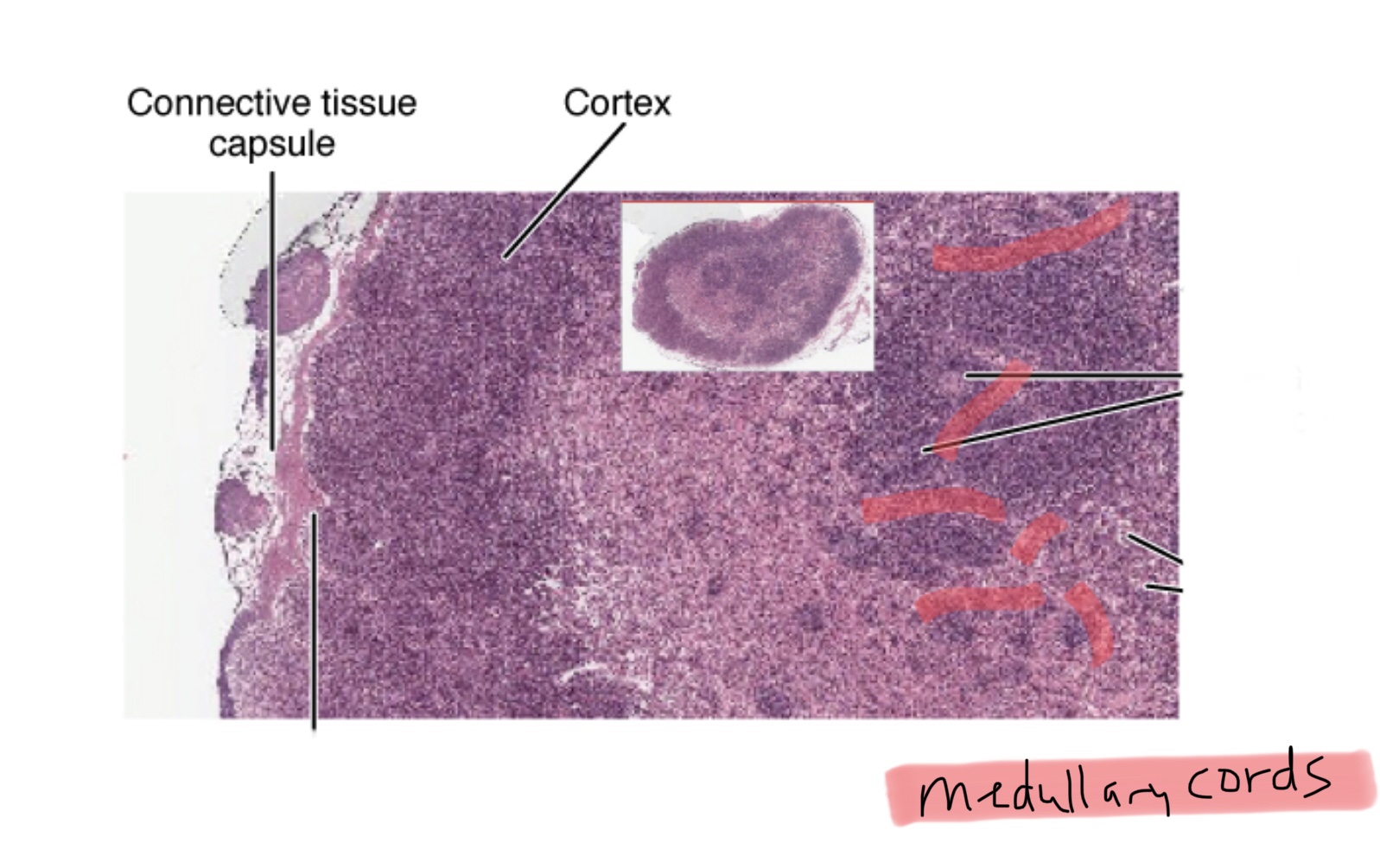
Identify the cortex of a lymph node.
Identify the medulla of a lymph node.
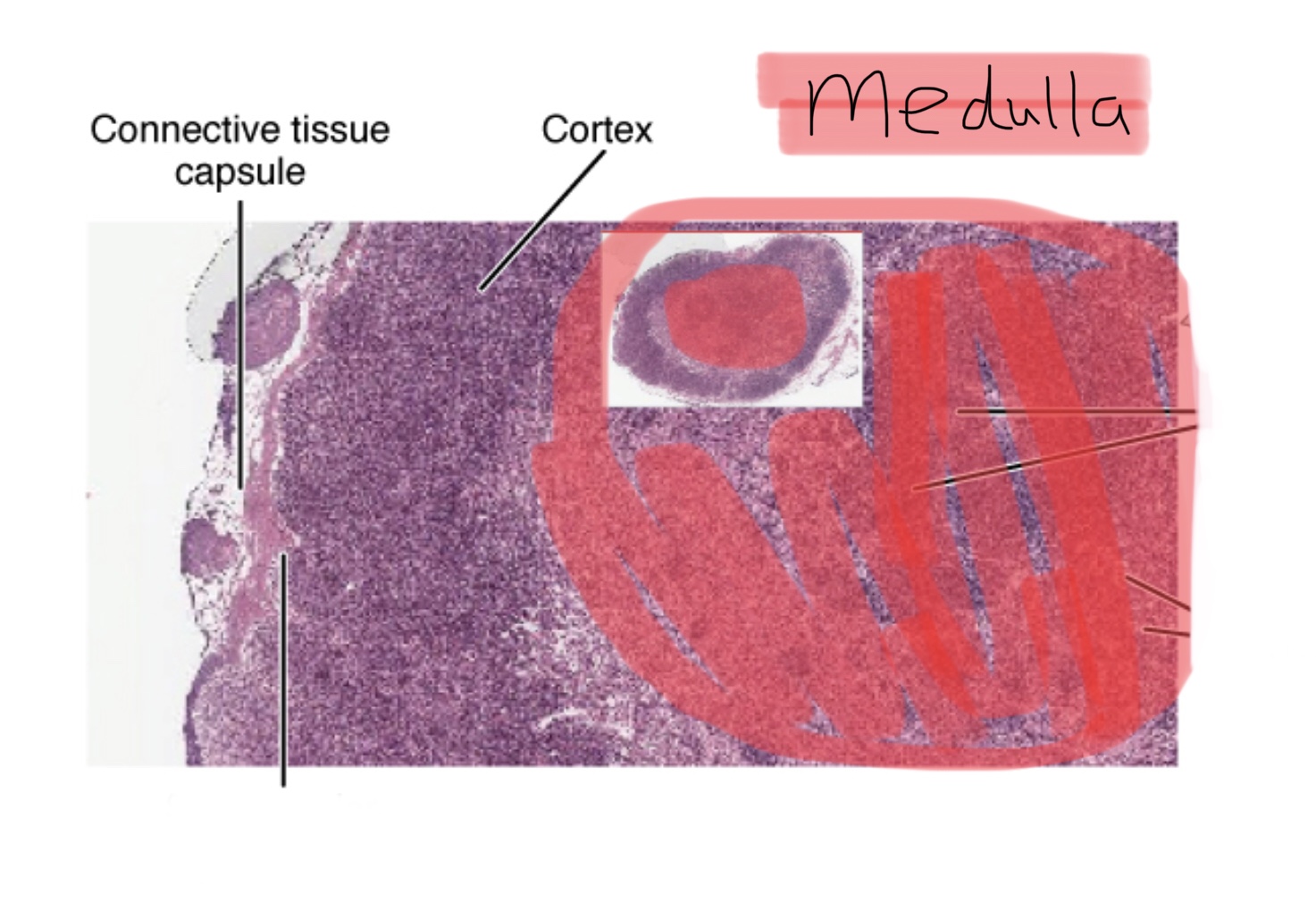
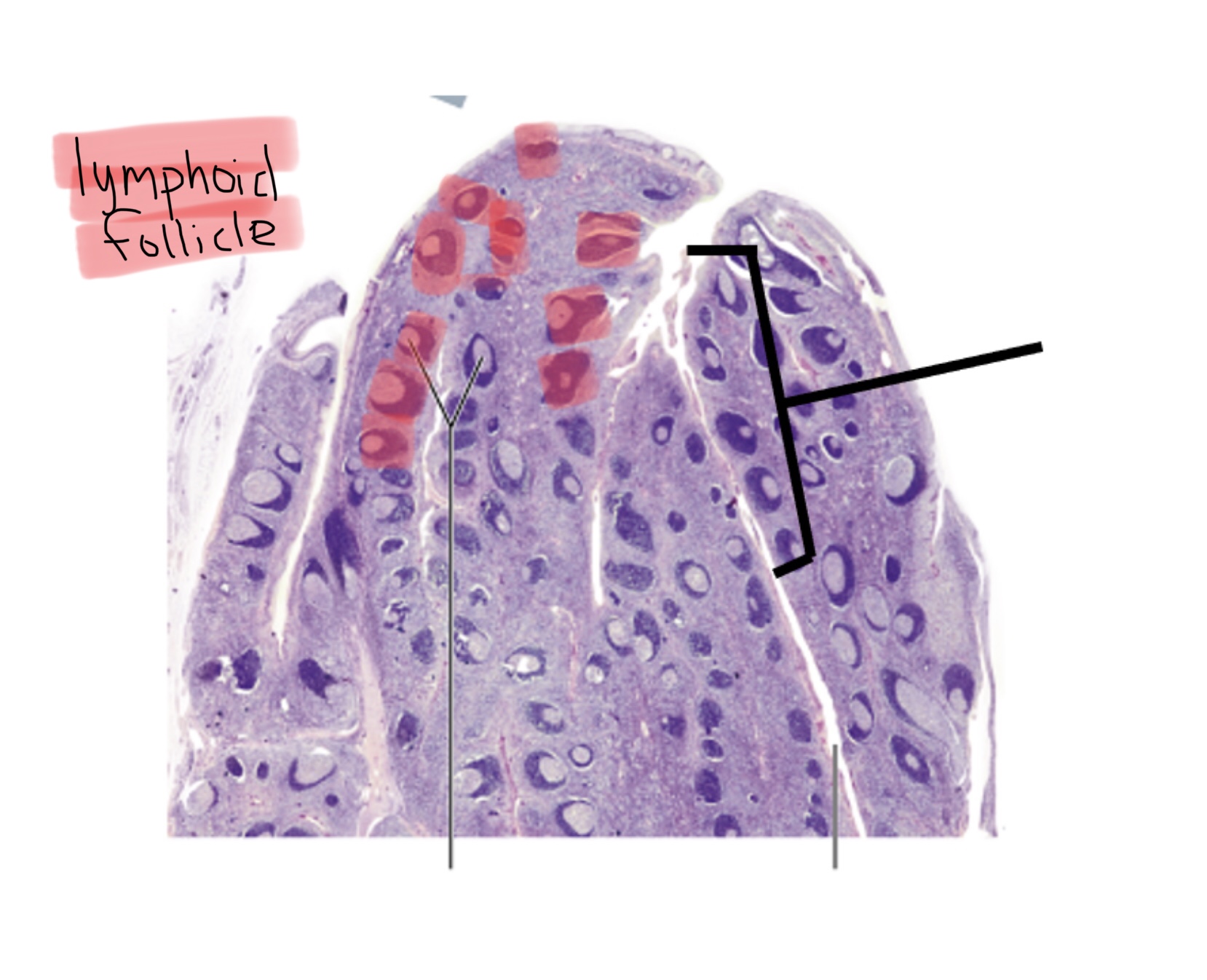
Identify the lymphoid follicles of a lymph node.
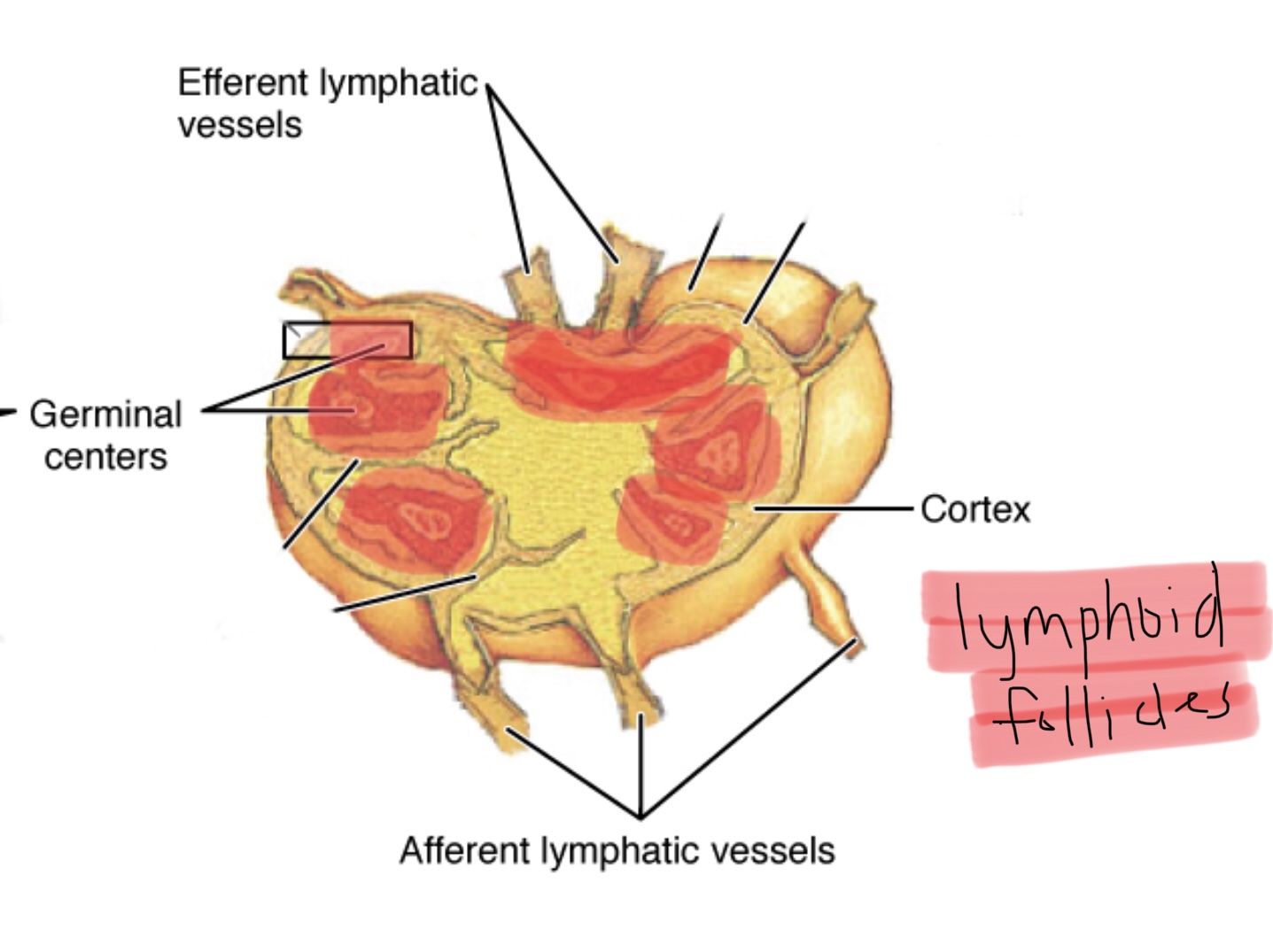
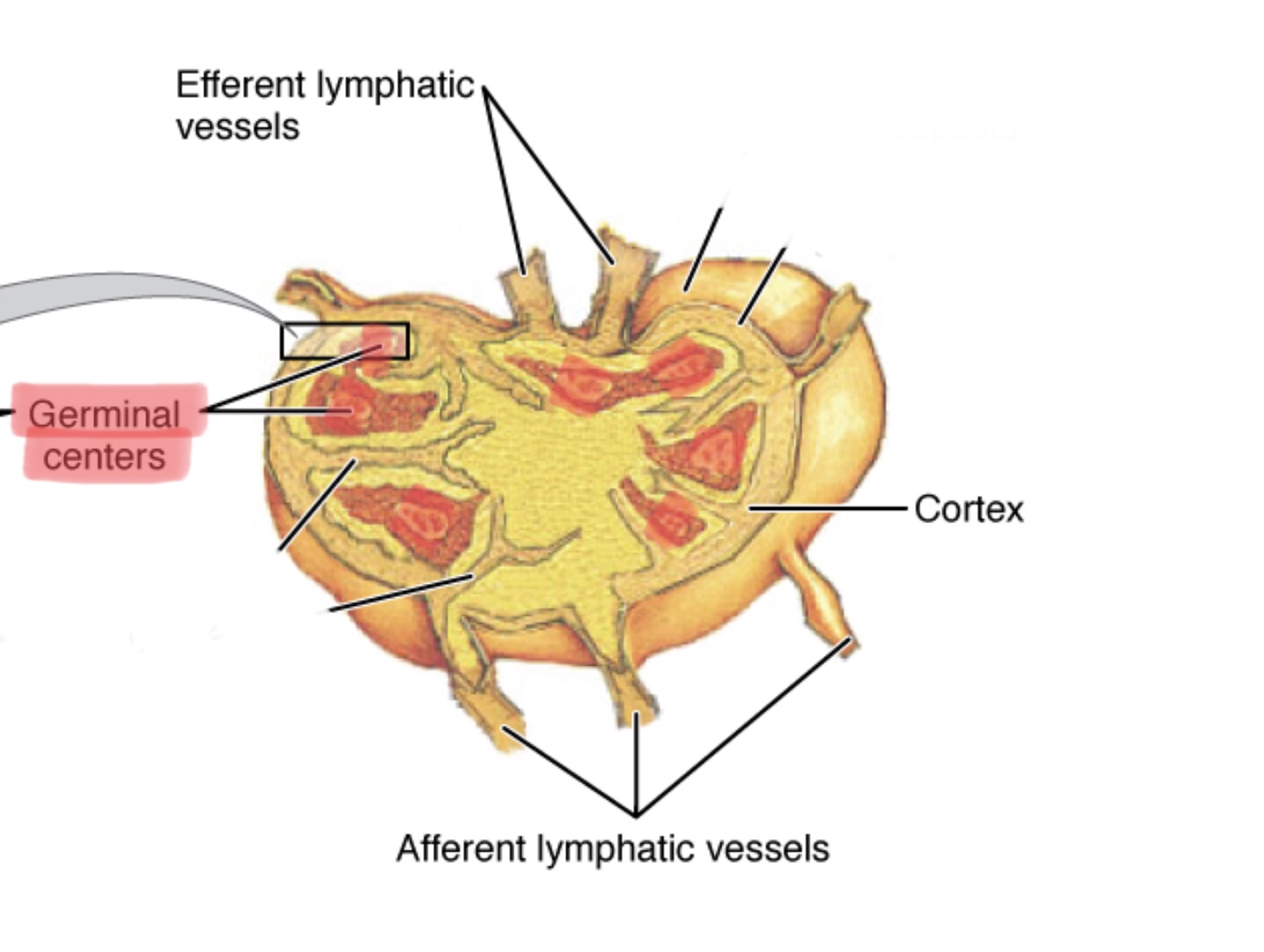
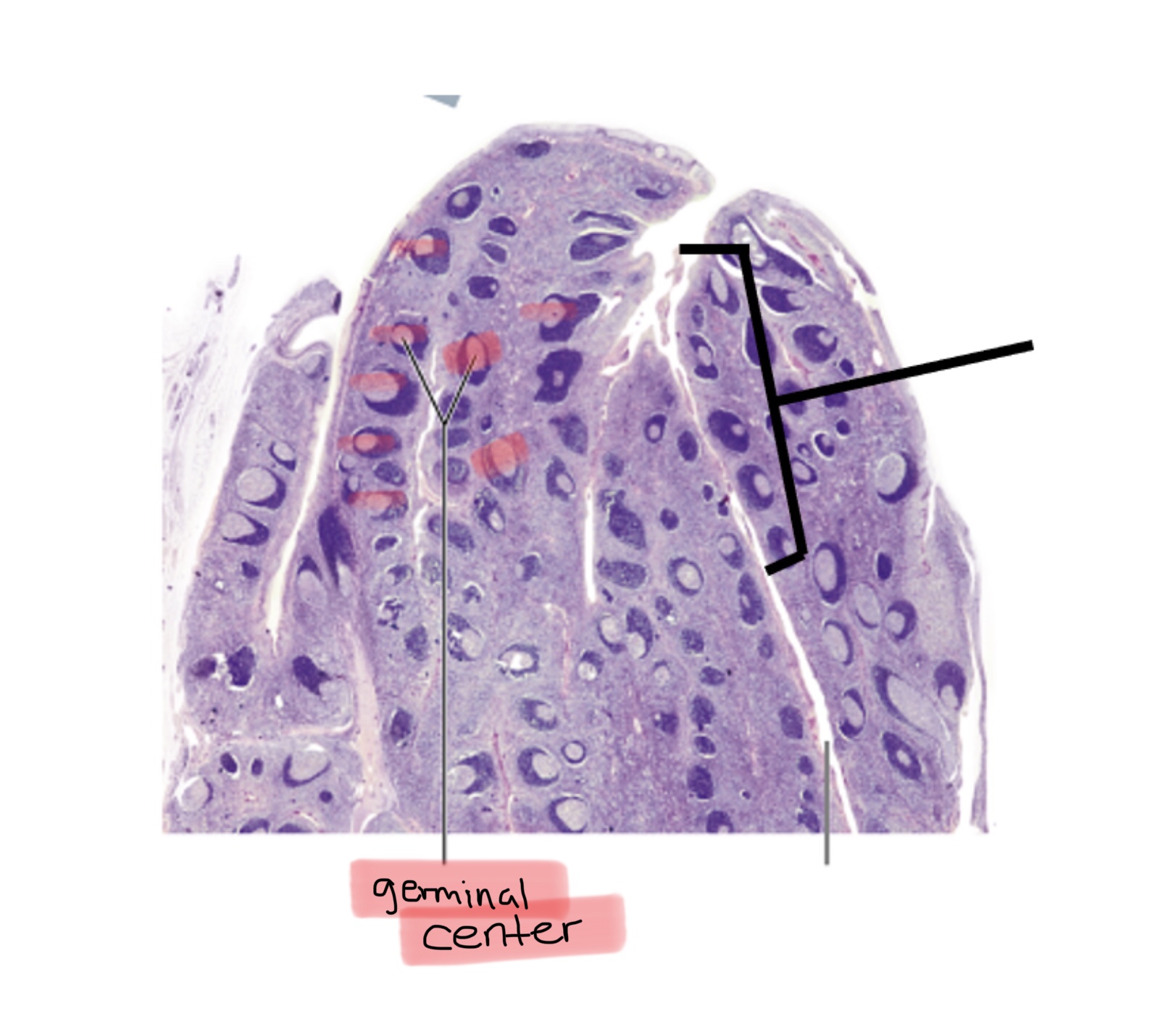
Identify the germinal center of a lymph node.
Identify the medullary cords of a lymph node.
Identify spleen tissue.
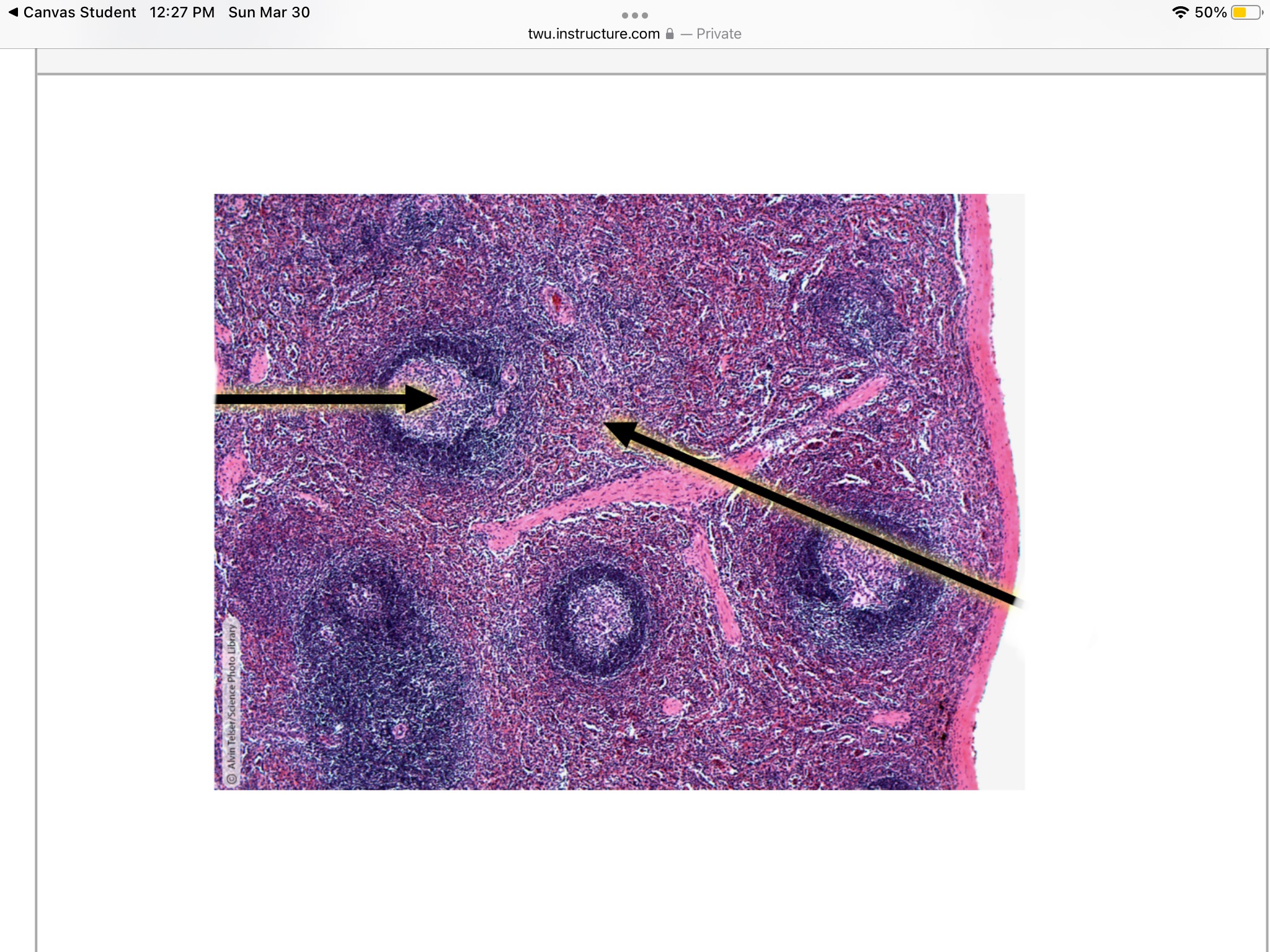
Identify the white pulp of the spleen.
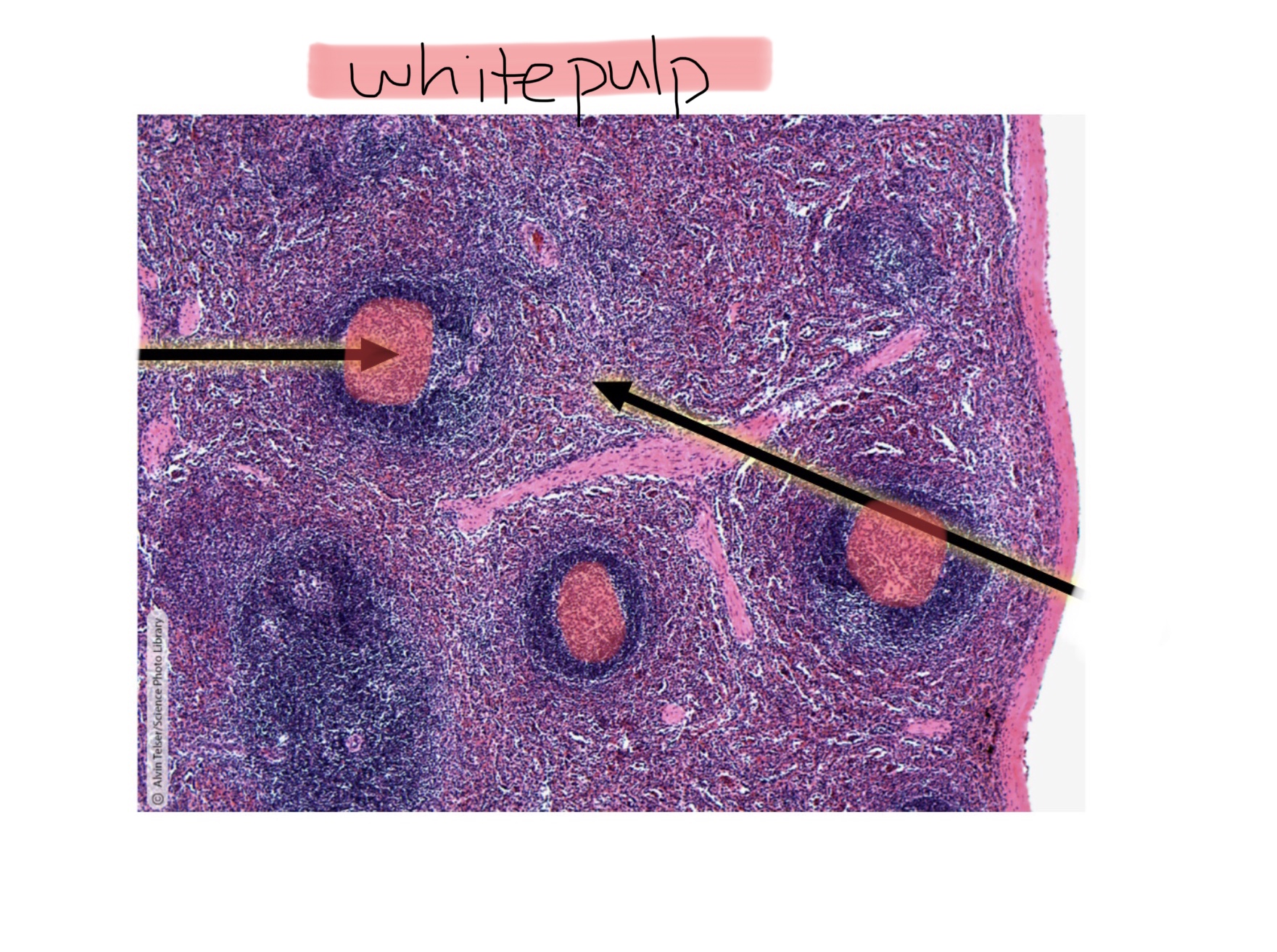
Identify the red pulp of the spleen.
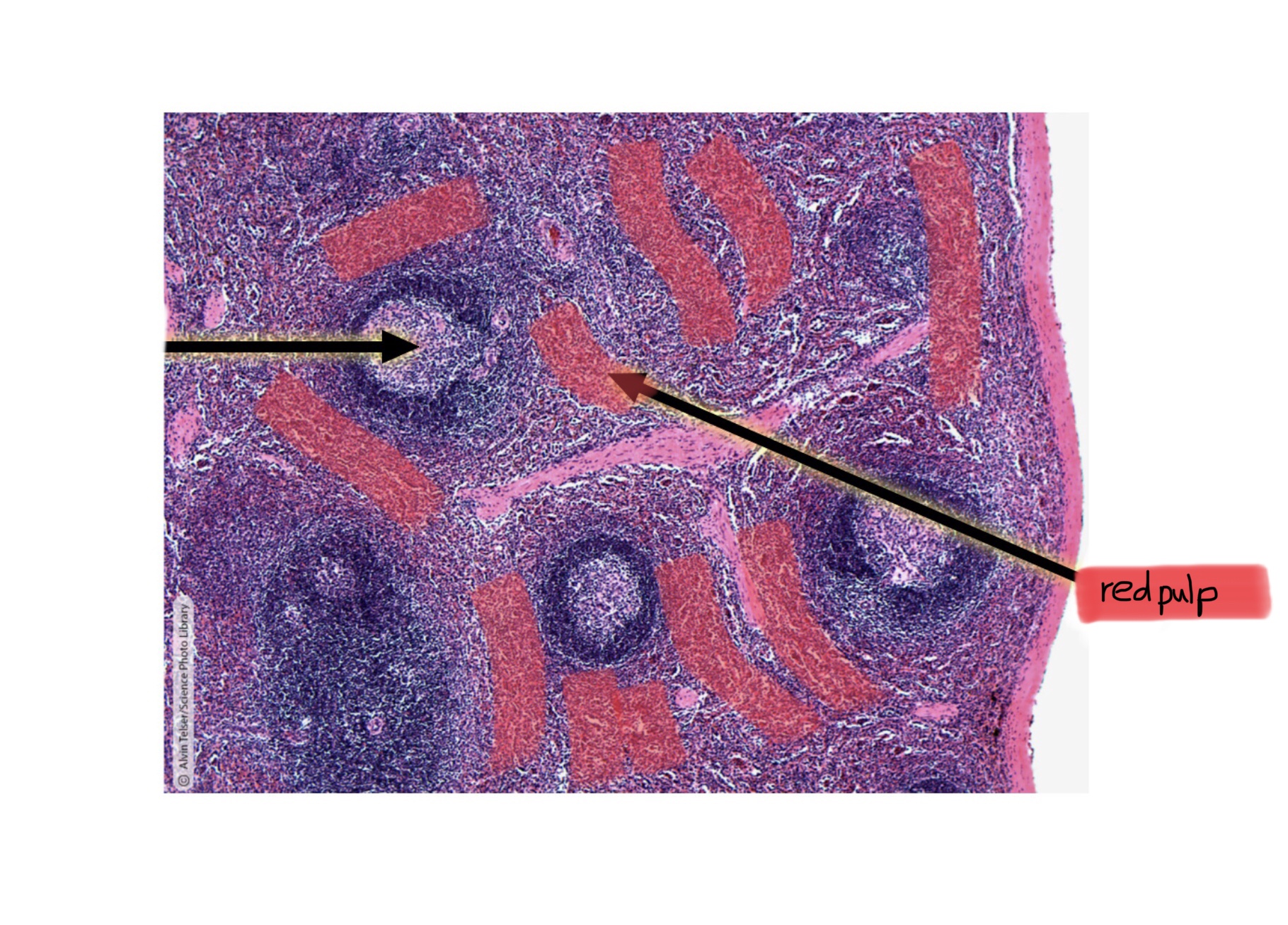
Identify the trabeculae of the spleen.
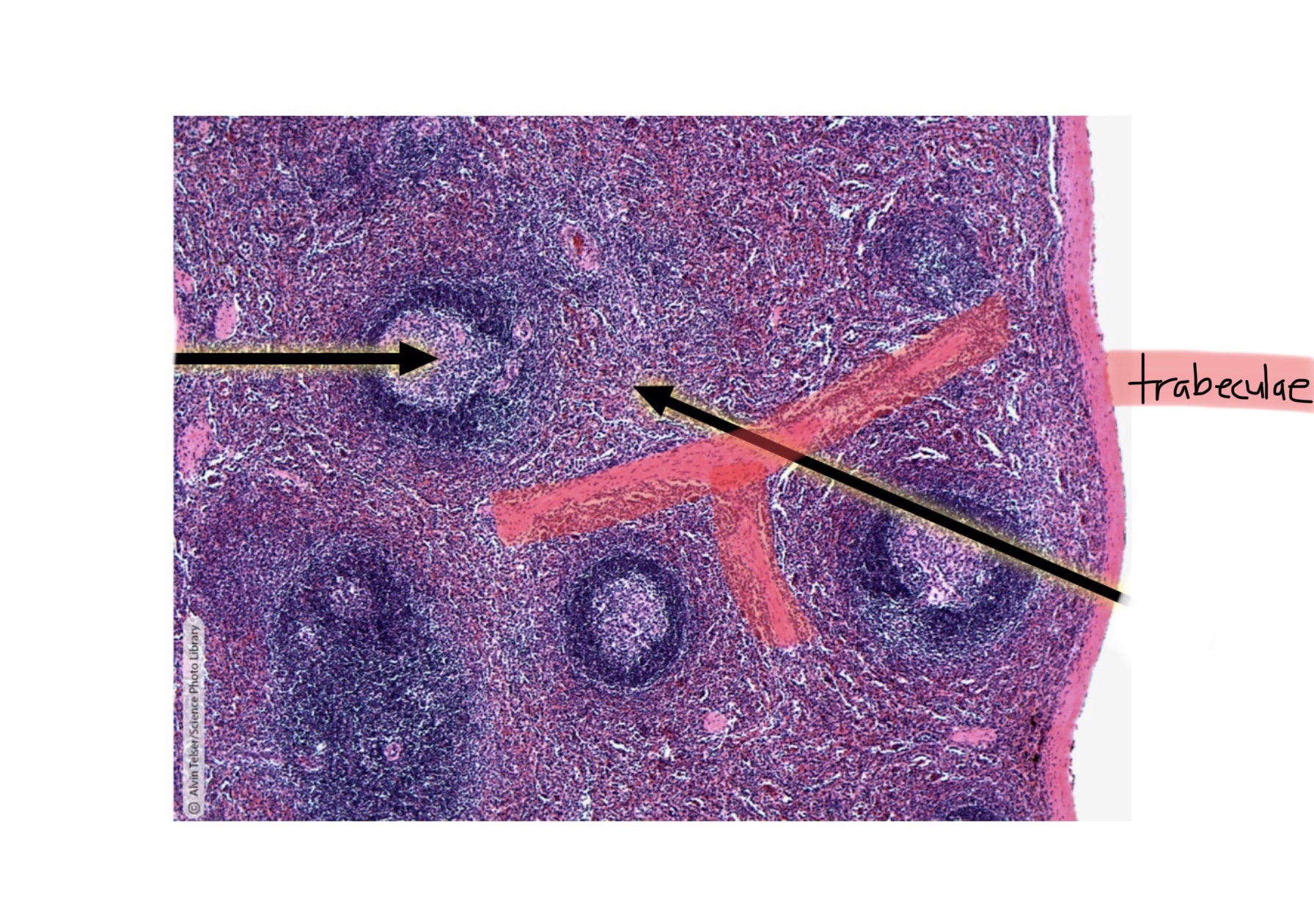
Identify the central artery of the spleen.
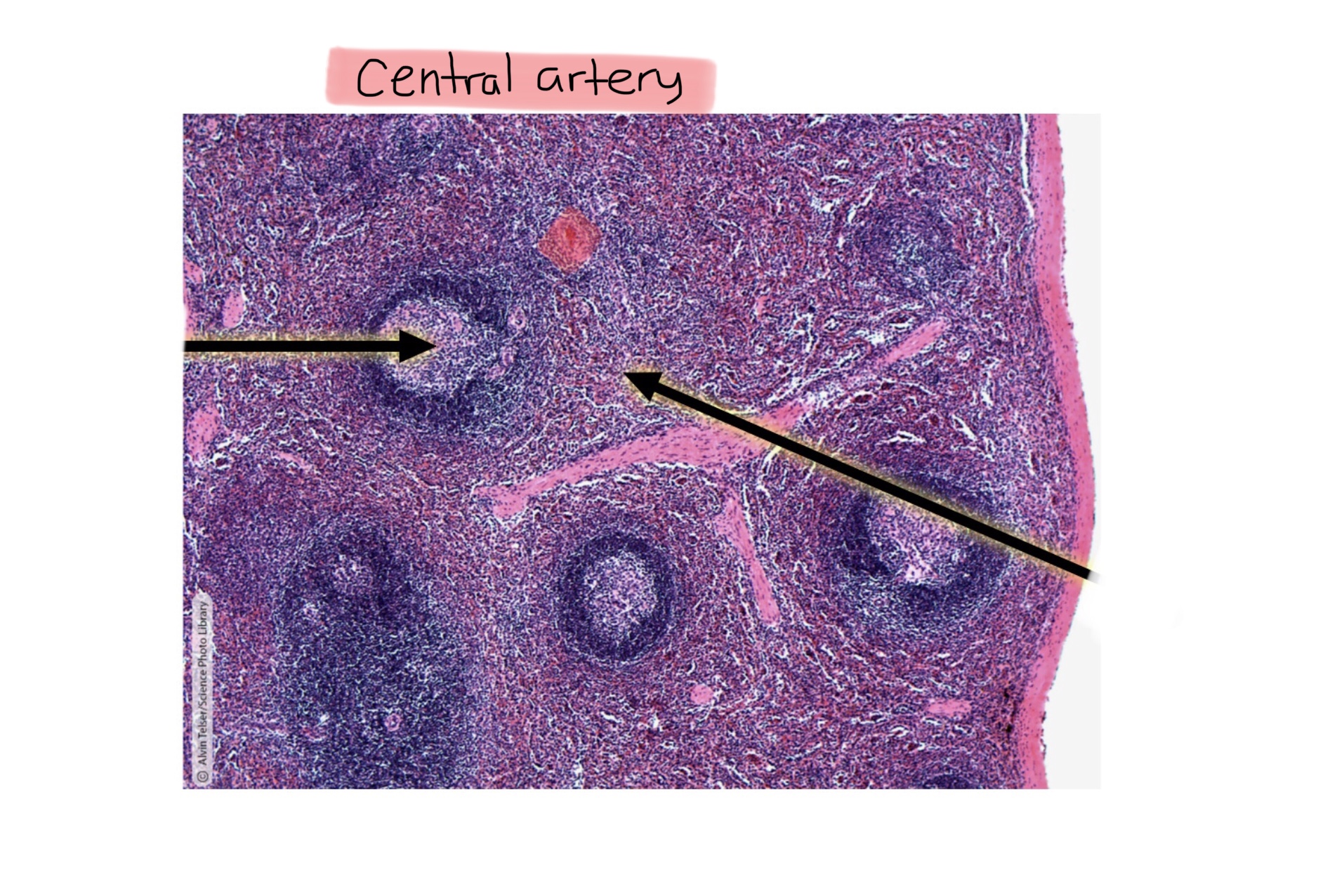
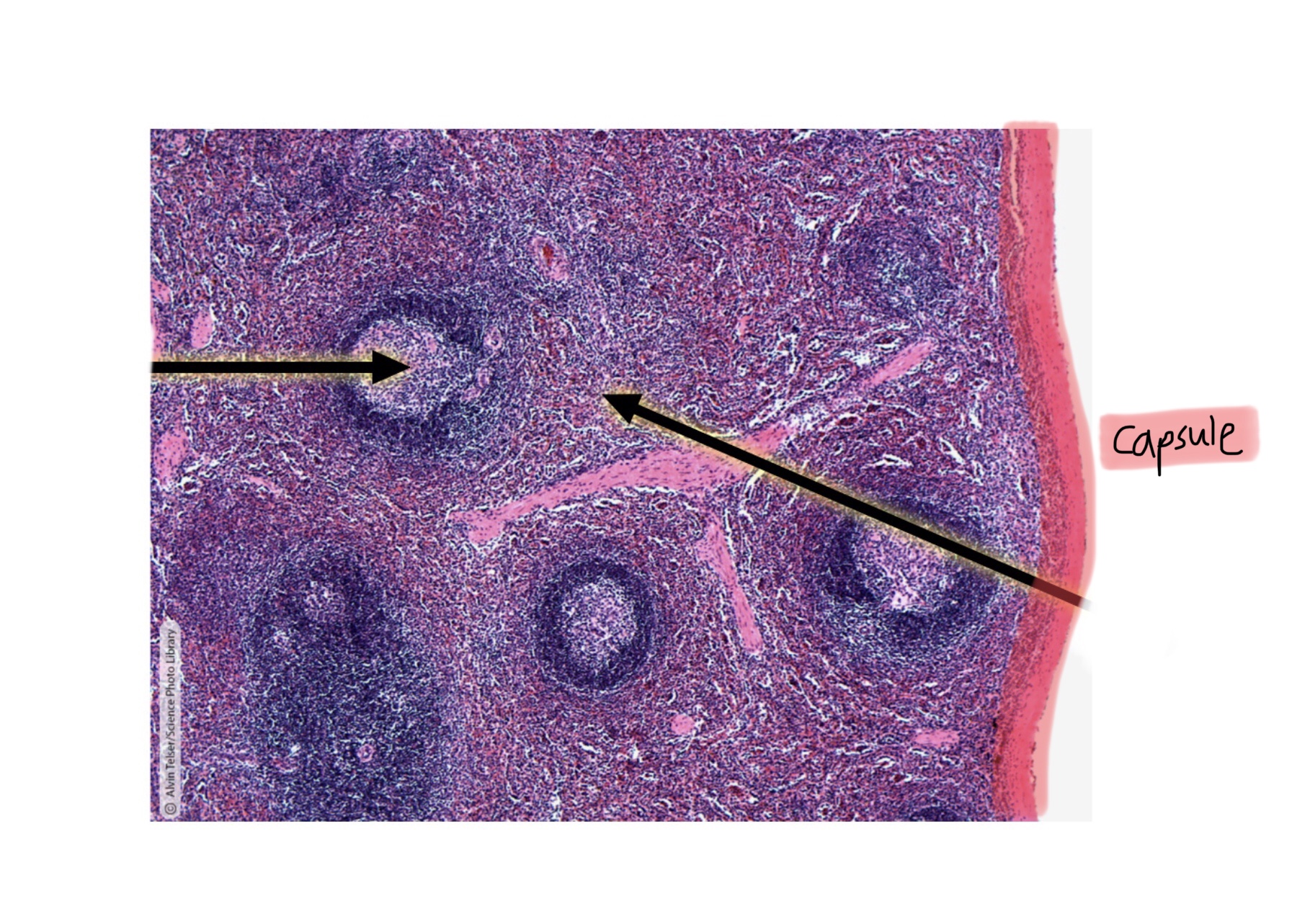
Identify the capsule of the spleen.
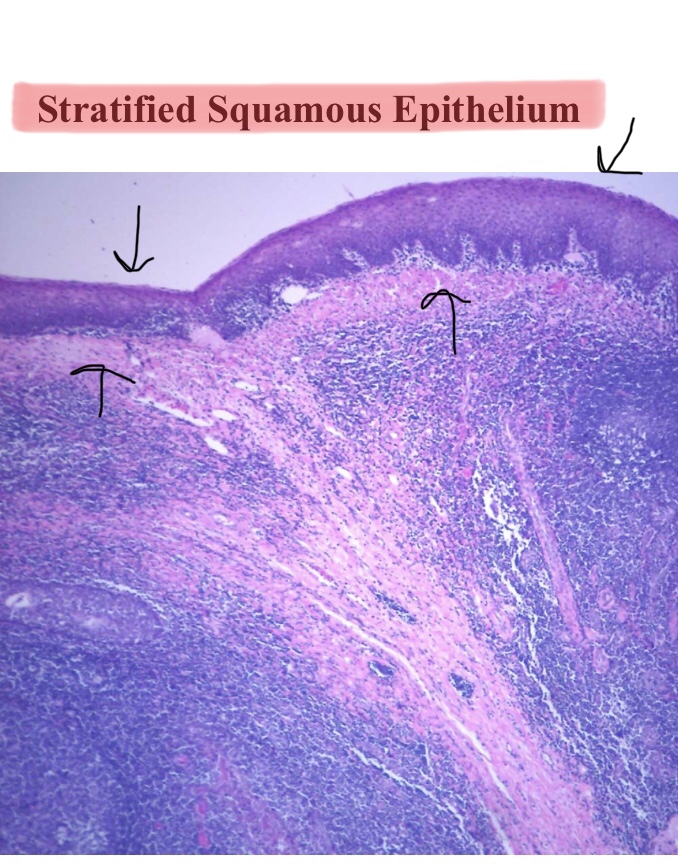
Identify the stratified squamous epithelium of the tonsils.
Identify the tonsilar crypts.
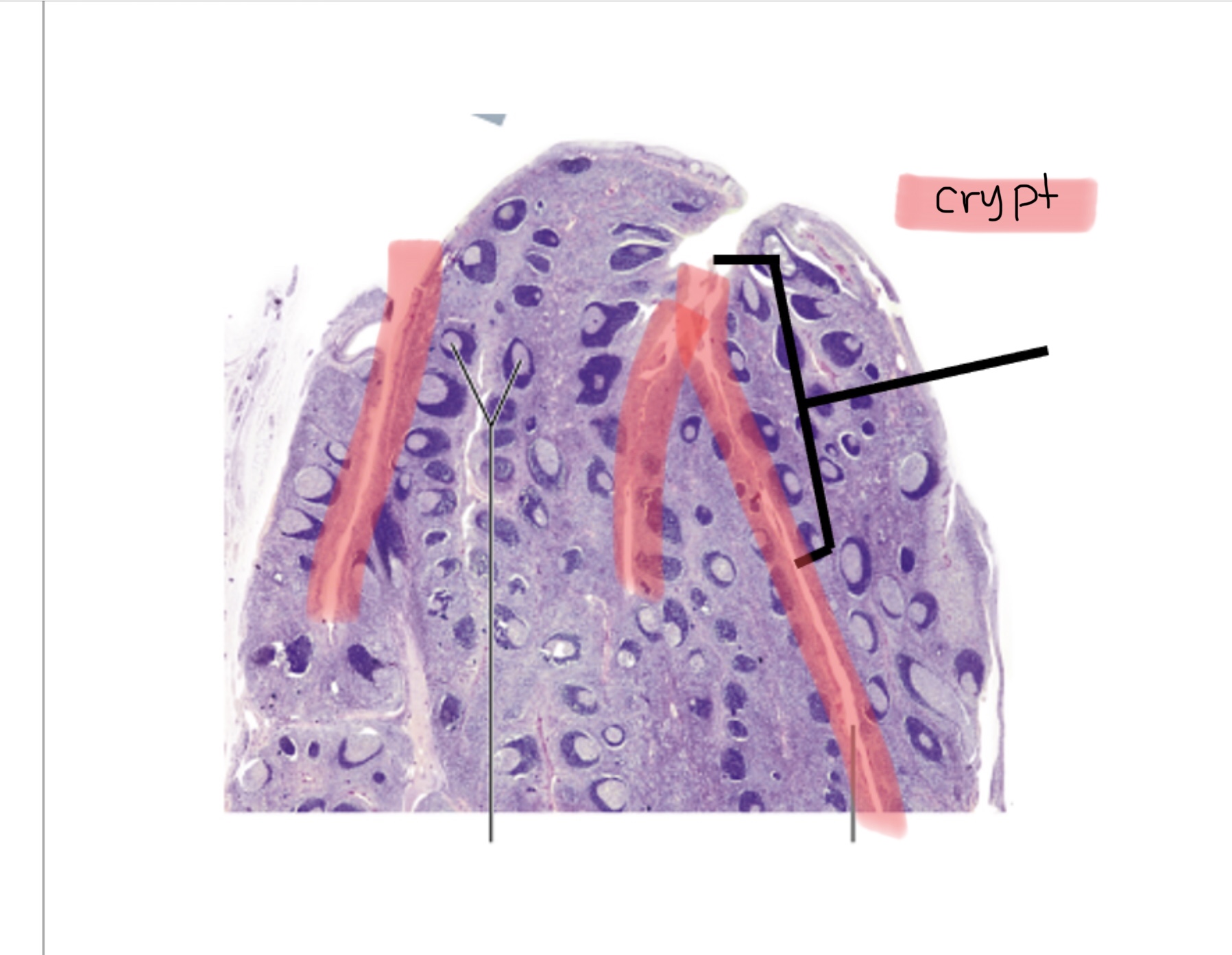
Identify the lymphoid follicles of the tonsils.
Identify the germinal centers of the tonsils.
What is the immune system?
The immune system comprises of a complex collection of cells and organs that destroy or neutralize pathogens that would otherwise cause disease or death.
What is the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system is a collection of vessels, cells, and organs that carry excess fluids from tissues to the bloodstream and filters pathogens from the blood.
What is lymph?
Lymph is used to refer to the interstitial fluid that has entered the lymphatic system.
What is a lymph node?
A lymph node is a small bean-shaped organ throughout the lymphatic system that connects multiple lymphatic vessels.
How is lymph forced through lymphatic vessels throughout the body?
Lymph is moved through the body by body movement, unlike blood which flows due to pressure from the heart pumping.
Describe the general flow of lymph through the body.
Lymph enters the lymphatic system at lymphatic capillaries. It then flows into lymphatic vessels toward the heart, eventually getting dumped into the circulatory system at the junction of the jugular and subclavian veins.
How does lymph enter lymphatic capillaries.
Lymphatic capillaries comprise of overlapping endothelial cells that separate/open due to the swelling of surrounding tissues.
What parts of the body drain into the right subclavian vein?
Only lymphatic vessels on the right side of the head, right side of the thorax, and the right upper limb drain into the right subclavian vein.
What parts of the body drain into the left subclavian vein?
Other than the upper right side of the body, the entire body’s lymphatic vessels drain into the left subclavian vein.
What is the right lymphatic duct?
The right lymphatic duct is the final lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the upper right side of the body.
What is the thoracic duct?
Most of the body’s lymphatic vessels converge on the thoracic duct to be drained into the left subclavian vein.
What is the cisterna chyli?
The cisterna chyli is a sac-like chamber that receives lymph from the lower half of the body.
What constitutes the body’s barrier defenses?
This skin and mucous membranes are our primary barrier defenses against pathogens.
What is the role of our innate immune response?
Our innate immune response is fast but non-specific to pathogens.
What is the role of our adaptive immune reponse?
Our adaptive immune response is slower but provides memory to the immune system and specific antibodies to pathogens.
What is the main difference between B and T cells?
B and T cells are both a type of lymphocyte of the adaptive immune response that originate in bone marrow, but B cells mature in the bone marrow while T cells mature in the thymus. While B cells differentiate to create antibodies, T cells focus on killing cells infected with intercellular pathogens.
What are plasma cells?
When a B cell is activated, it differentiates into a plasma cell to provide antibodies.
What are natural killer (NK) cells?
Natural killer cells are a part of our innate immune system and provide non-specific protection against pathogens. They excrete cytotoxic granules.
What are afferent lymphatic vessels?
Afferent lymphatic vessels carry lymph toward lymph nodes.
What are efferent lymphatic vessels?
Efferent lymphatic vessels carry lymph away from lymph nodes.
What is the role of the spleen?
The spleen filters blood to remove microbes and other materials, including dying blood cells. Separating them from the blood stream allows macrophages and dendritic cells to destroy them.
What is the difference between red pulp and white pulp within the spleen.
White pulp consists of the lymphatic follicles whereas the red pulp has the red blood cells within the spleen.
What is the main function of the tonsils.
Tonsils provide oral pathogen immunity.
What are the four types of tonsils.
There are palatine tonsils on the sides of the back of your mouth, the lingual tonsils at the back of your tongue, the adenoid at the back of your mouth, and the tubal tonsils at the opening of the Eustachian tube.
What are mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALTs)?
MALTs consist of lymphoid follicles that are directly associated with mucous epithelia. They are often found in the gastrointestinal tract, the lungs, in breast tissues, and in the eyes. One example is Peyer’s patches.
What are the five classes of antibodies?
The five classes of antibodies include IgM, IgG, IgE, IgA, and IgD.
What is the role of IgM antibodies?
IgM antibodies are the main antibody of primary immune responses.
What is the role of IgG antibodies?
IgG antibodies are the main antibody of secondary immune responses.
What is the role of IgA antibodies?
IgA antibodies are often found in mucus, tears, colostrum, and breast milk.
What is the role of IgE antibodies?
IgE antibodies function in allergies and parasitic activity.
What is the role of IgD antibodies?
IgD antibodies are a type of B cell receptor.