7. small animal med- disease of the large intestine
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
what structures make up the large intestine?
colon, small cecal diverticulum, and rectum
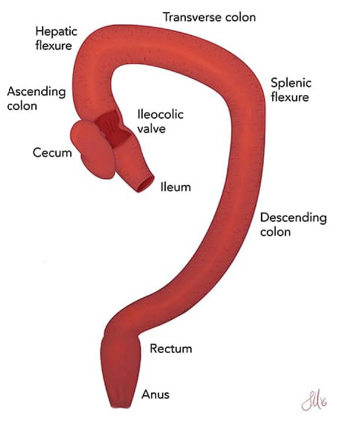
what are the major functions of the colon?
1. absorption of water and electrolytes (proximal colon) to produce normal consistency of feces
2. storage of feces (distal colon)
the colon is not a digestive organ
what are the clinical features of large intestinal disease?
1. large bowel diarrhea
2. constipation/obstipation
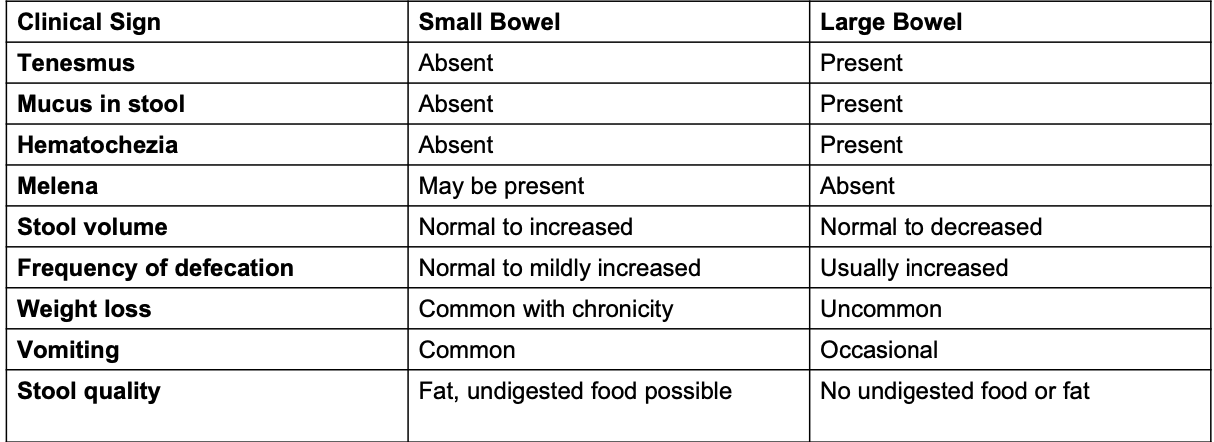
what are characteristics of large bowel diarrhea?
tenesmus, mucus in stool, hematochezia
-melena is not present
-normal to decreased stool volume
-frequency of defecation usually increased
-weight loss is uncommon
-occasional vomiting
-will not see undigested food/fat in stool
what are clinical signs of constipation/obstipation?
-tenesmus (may pass small amounts of liquid stool)
-dry, hard pelleted feces

what abnormalities may be felt when doing a digital rectal exam?
-colonic mucosa
-anal sac abnormalities
-rectal or anal strictures
-mass
-urethra
-pelvic fracture
-sacral disease
-prostate disease

what is included in the diagnostic approach for acute large bowel diarrhea?
1. history and physical exam (determine if self-limiting or life-threatening)
2. diagnostic testing
3. treatment of acute colitis
what diagnostic testing should be done for diagnosis of acute large bowel diarrhea?
fecal flotation at minimum
further testing if warranted:
-abdominal imaging
-rule out secondary GI disease (CBC/chem/UA)
what is acute colitis?
large bowel diarrhea with normal appetite and no vomiting
what is the treatment for acute colitis?
1. short-course of high-fiber diet (or psyllium husk supplementation)
2. empirical deworming (fenbendazole x3d or pyrantel)
3. probiotic
4. consider anti-diarrheal
what are the 2 antidiarrheals used for treatment of acute colitis?
1. loperamide (immodium)
2. kaolin-pectin (pro-pectalin by Vetoquinol)
what is the MOA of loperamide?
opioid antidiarrheal that acts by decreasing peristaltic activity and inhibiting small intestinal secretion
what are contraindications of loperamide use?
-toxigenic intestinal infections (salmonella)
-hemorrhagic gastroenteritis
-intestinal obstruction
-GI perforation
-causes profound sedation in dogs with MDR1 mutation
what is the MOA of kaolin-pectin?
used as GI adsorbents and demulcents that improve stool consistency and increase stool bulk
does not alter fluid/electrolyte loss nor shorten duration of diarrhea
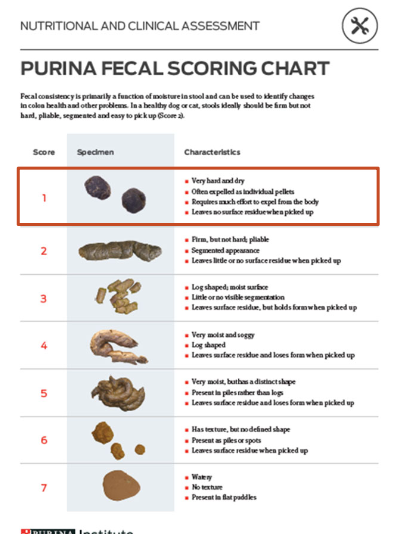
what is constipation?
-infrequent or difficult evacuation of feces
-having difficult time passing stool
-passing fewer than 3 stools/week
-hard, dry stool
what is obstipation?
intractable constipation that is refractory to cure or control
obstruction that prevents passage of feces (anatomical vs functional)
what is megacolon?
hypomotility and severe dilation of colon
what are causes of constipation/obstipation?
1. medical conditions that cause dehydration
2. pain or discomfort
3. neuropathy
4. mechanical obstruction
5. lack of physical activity (obesity)
6. medications
what medical conditions causing dehydration may lead to constipation/obstipation?
-chronic kidney disease
-diabetes mellitus
-hypothyroidism
what conditions causing pain/discomfort may lead to constipation/obstipation?
-OA (sacrum, pelvis, femoral heads)
-anal sacculitis
-proctitis
-bite wounds
what neuropathies may cause constipation/obstipation?
-sacral spinal cord disease/injury
-hypogastric (L2-L5) or pudendal nerve (S1-S2) disorders
-manx cat syndrome (sacrocaudal dysgenesis)
-feline dysautonomia syndrome (myenteric plexus neuropathy)
-feline idiopathic megacolon (colonic smooth muscle disorder)
what mechanical obstructions can cause constipation/obstipation?
-mass, FB, stricture
-pelvic fracture with narrowing of canal
-perineal hernia
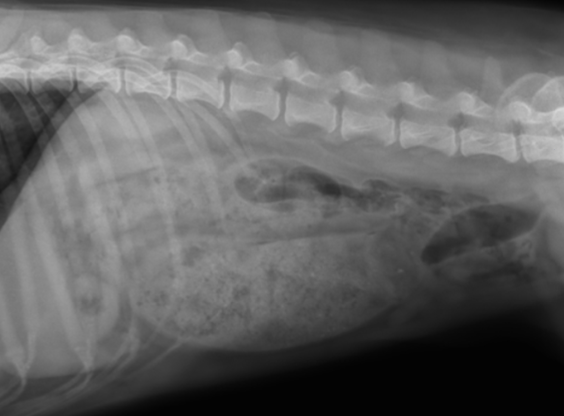
what medications can cause constipation/obstipation?
opioids, diuretics
what is the approach to diagnosing constipation?
1. clinical suspicion based on history and PE
2. digital rectal exam
3. abdominal, sacral, and pelvic rads
4. abdominal U/S (intramural/intraluminal lesions, wall layering)
what are obvious clinical signs of constipation?
-tenesmus
-vocalization while defecating
-vomiting while defecating
-decreased frequency of defecation
what are subtle clinical signs of constipation?
fecal score, passing small amounts of liquid stool/mucus (O may confuse this with diarrhea)
what are the physical exam findings of animals with constipation?
-hard feces in descending colon
-distended colon
-abdominal distention
what can digital rectal exams help with diagnosis of constipation?
may be able to identify:
-sacral protrusion/pain
-pelvic fracture malunion
-neoplasia
-stricture
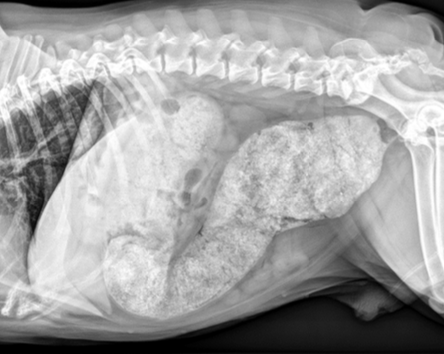
what is the normal colon diameter in dogs and cats as measured on radiographs?
dogs: normal colon diameter less than L7 length
cats: ratio maximal colonic diameter to length of L5 <1.28
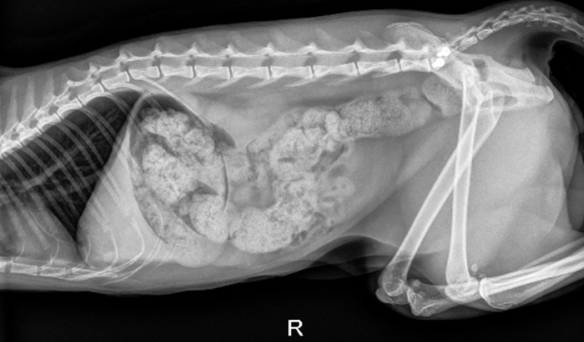
What may be seen on AUS with constipation?
intramural or intraluminal lesions, wall layering
what is the treatment for acute constipation?
-warm water enemas
-psyllium husk fiber (metamucil)
-laxatives (miralax, lactulose)
what is the treatment for chronic constipation?
-diet (canned food, fiber-enhanced diet and/or insoluble fiber diet)
-laxatives
-cisapride to promote colonic motility
what is the treatment for obstipation?
1. manual extraction under anesthesia
2. treat for constipation after relieving fecal obstruction
What are major diseases of the large intestine?
Granulomatous colitis
Tritrichomonas foetus
Feline idiopathic megacolon
what is granulomatous colitis?
formerly known as histiocytic ulcerative colitis
predominantley diagnosed in boxers and frenchies (rare in cats) younger than 4 years of age
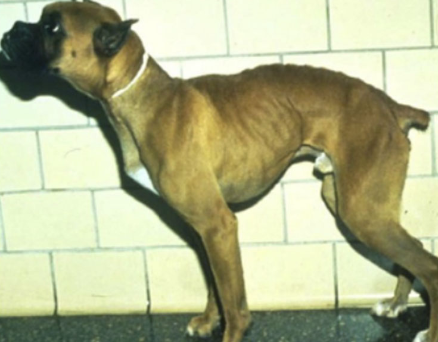
what are the clinical signs of granulomatous colitis?
typical signs of colitis: large bowel diarrhea, hematochezia (may be severe)
in severe cases: weight loss, cachexia, iron deficiency anemia
what is the etiology of granulomatous colitis?
invasive e. coli
how is granulomatous colitis diagnosed?
-clinical signs of chronic colitis
-endoscopic colonic biopsies (min. 10 biopsies)
-histopath (granulomatous inflammation)
-invasive e. coli documented on FISH
what is FISH?
fluorescent in situ hybridization
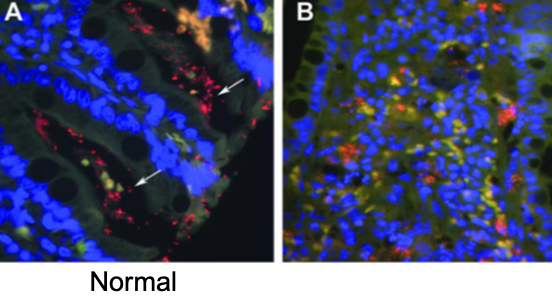
how can FISH be used to diagnose granulomatous colitis caused by invasive e. coli?
FISH detect enteroinvasive e. coli by using genetic probes directed against a specific section of the DNA of e. coli that has be fluorescently labeled
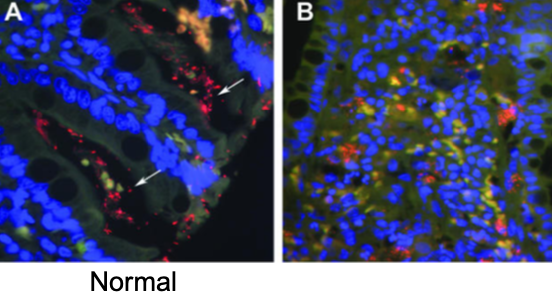
what is the treatment for granulomatous colitis?
use of an antibiotic that penetrates macrophages (enrofloxacin) for 8 weeks
alt. options: chloramphenicol, rifampicin, TMS, tetracycline, clarithromycin
antibiotic resistance is common so best to select based off C&S
why should you not give a ___ before definitive diagnosis of granulomatous colitis?
fluoroquinolone
associated with antimicrobial resistance and poor outcome
what is the prognosis of granulomatous colitis?
good with eradication of invasive e. coli
clinical improvement seen within 1-2 weeks
what is tritrichomonas foetus?
flagellate protozoan with undulating membrane
looks like giardia but differs by motility pattern
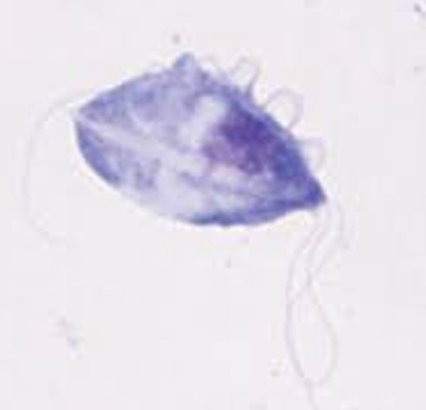
which is the typical signalment of tritrichomonas foetus infections?
causes chronic large bowel diarrhea in cats:
-<1 year old, pedigree cats in multi-cat households or catteries
-any age, breed, and sex can be infected
how is tritrichomonas foetus transmitted?
oral-fecal routes
what are the clinical signs of cats with tritrichomonas foetus infections?
waxing and waning large bowel diarrhea
- +/- fecal incontinence
- +/- proctitis
-usually normal appetite and body condition (no weight loss)
how are tritrichomonas foetus infections diagnosed?
no method is 100% sensitive, fresh fecal sample is best sample to submit (by fecal loop or colonic flush)
-visualization on direct wet mount
-fecal PCR
-have to differentiate from giardia
how are tritrichomonas foetus infections treated?
this organism is resistant to all commonly used anti-protozoal drugs, have to use ronidazole (has neurologic side effects)
may also resolve w/o treatment within 9 months of diarrhea onset
what is the goal of treatment for tritrichomonas foetus?
resolution of diarrhea
-60% of cats will have complete resolution of diarrhea
-may not be able to obtain negative PCR
what is the typical signalment of feline idiopathic megacolon?
middle-aged male cats
what is feline idiopathic megacolon?
severe, pathological dilation of the colon w/o impaction
includes entire colon, or only the descending colon
what is the etiology of feline idiopathic megacolon?
etiology is not completely understood
results in permanent loss of function of colonic smooth muscle
how is feline idiopathic megacolon diagnosed?
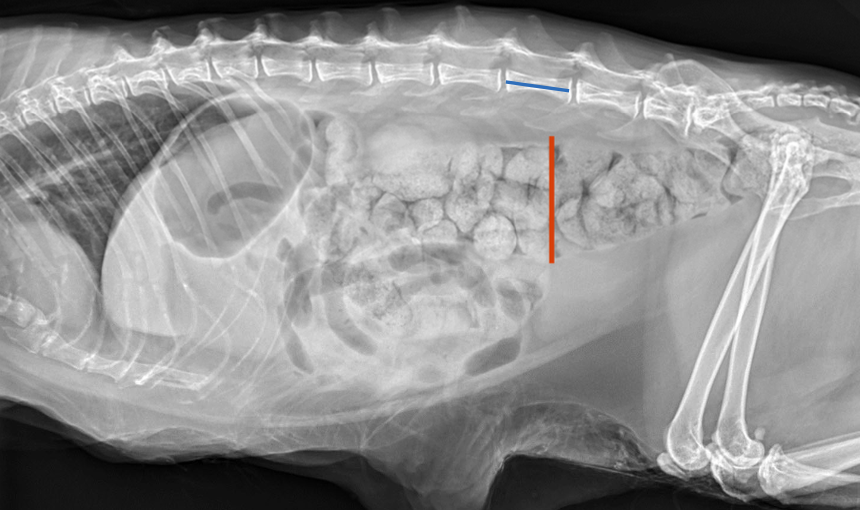
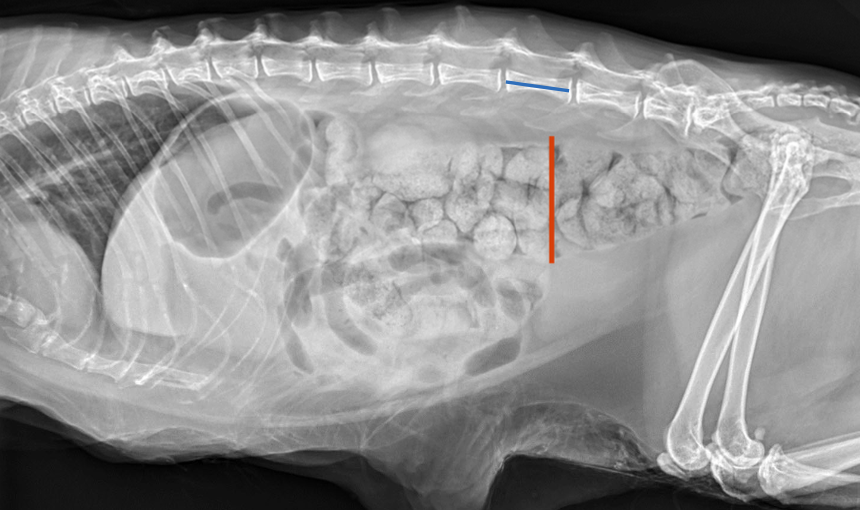
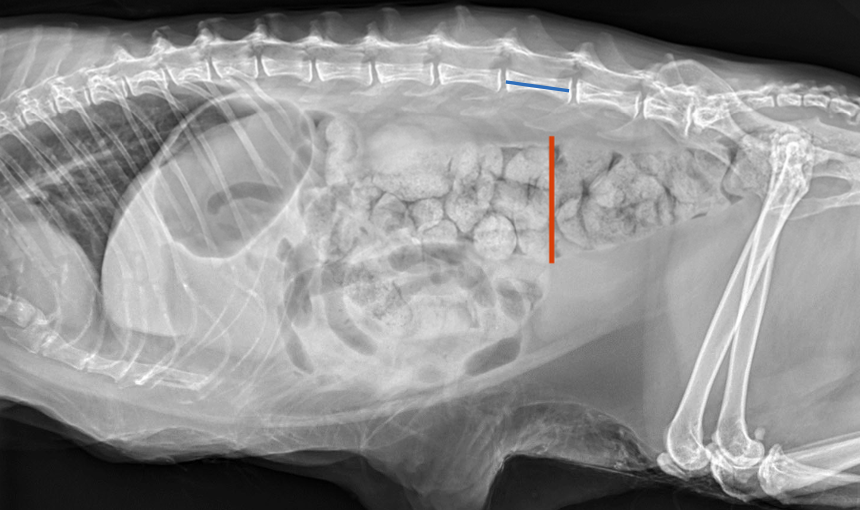
radiographs--> ratio of maximal diameter of the colon to L5 length:
ratio <1.28=normal
ratio >1.48= megacolon
diagnosis of exclusion
what is the treatment for feline idiopathic megacolon?
-same tx for constipation/obstipation
-subtotal colectomy in refractory cases
what is the prognosis after subtotal colectomy to treat cats with feline idiopathic megacolon?
good prognosis if ileocolic valve is preserved
mild to moderate diarrhea 1-6 weeks post-op and may persist