05.E BIO, HN Light Dependent Reactions (PART E)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Photosystem
Consists of proteins and pigments found in the thylakoid membrane that capture and trap light energy; the reaction center contains a special pair of chlorophyll a molecules where the captured energy is transferred and excites an electron
Photosystem II (PS II)
A photosystem that is best at absorbing a wavelength of 680 nm so the reaction-center chlorophyll a of PS II is called P680
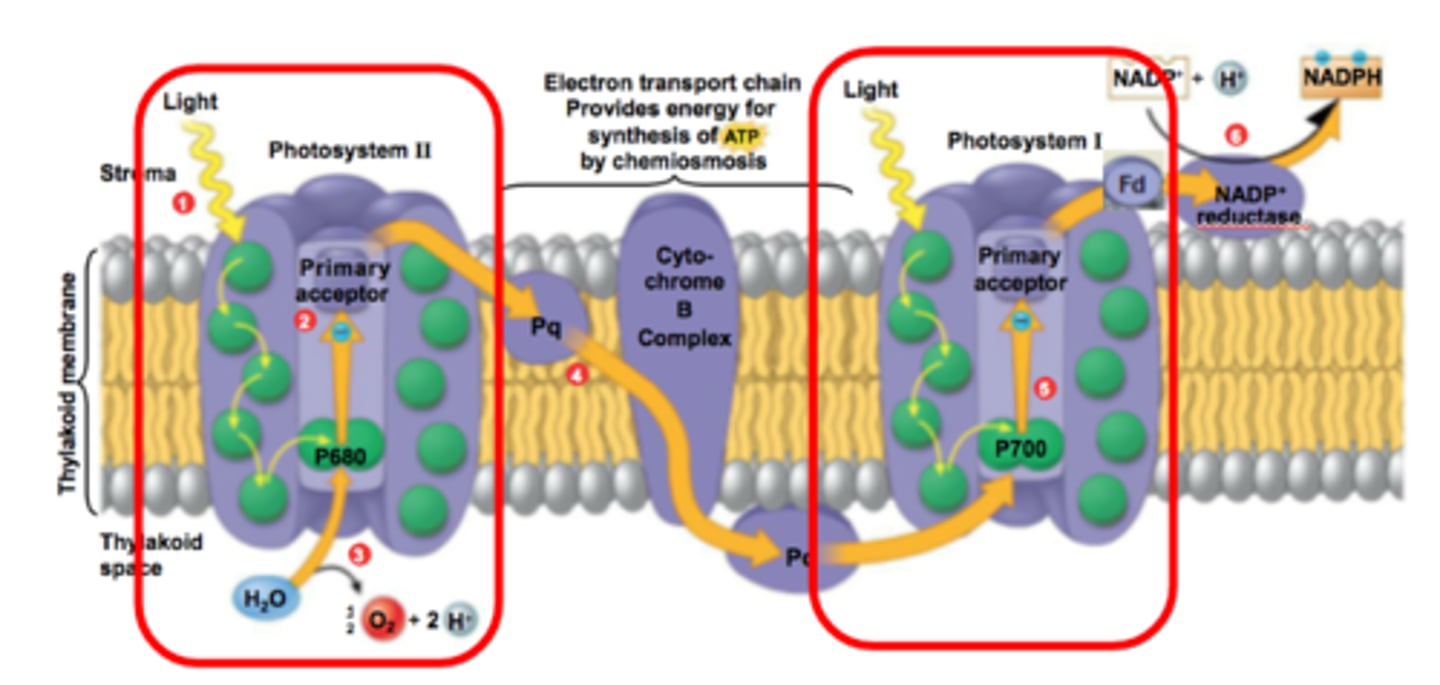
Photosystem I (PS I)
A photosystem that is best at absorbing a wavelength of 700 nm so the reaction-center chlorophyll a of PS I is called P700
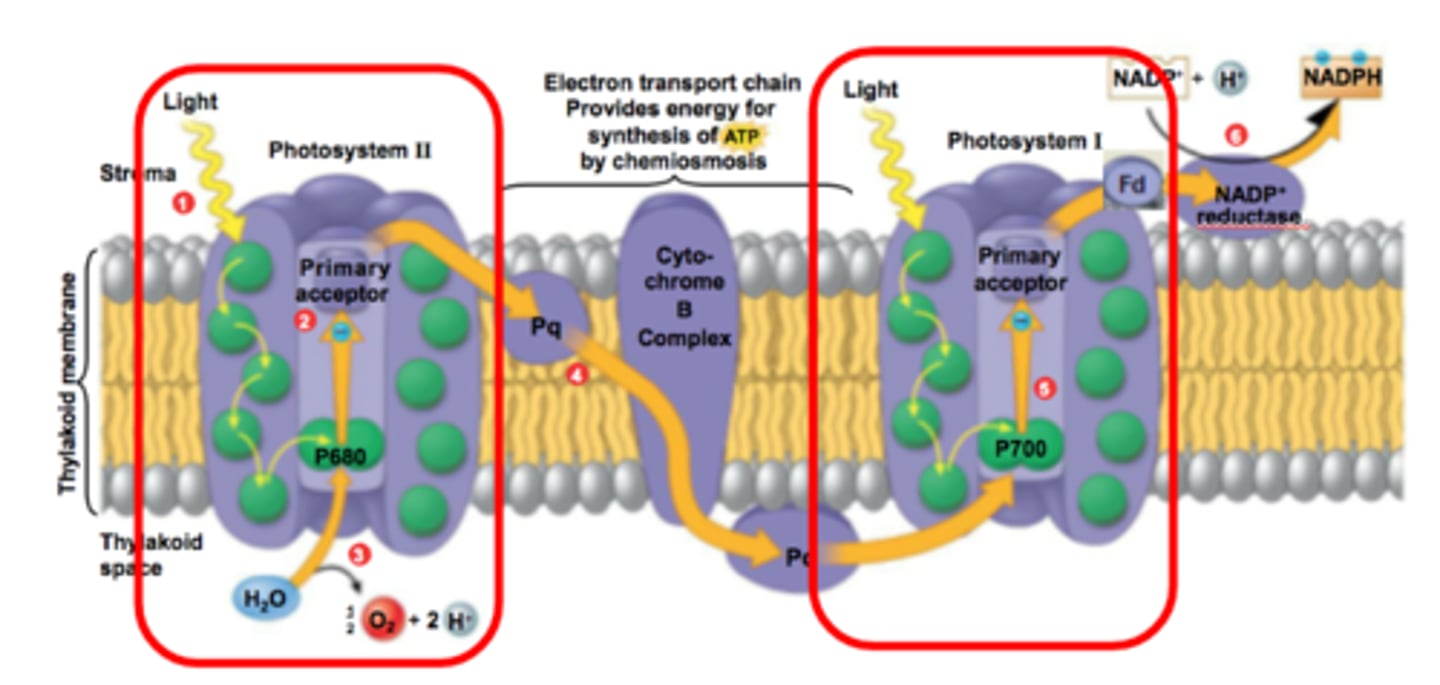
Primary electron acceptor
Accepts excited electron from chlorophyll a and transfers the electrons to a mobile electron carrier in the ETC
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
A series of proteins in the thylakoid membrane that absorbs light energy that is then used to excite electrons; energy released by electron as it travels along ETC is used to transport H+ from the stroma into the thylakoid against the concentration gradient; hydrogen ions then move back out through ATP synthase and generate ATP; at the end of the ETC the electrons join with NADP+ to produce NADPH
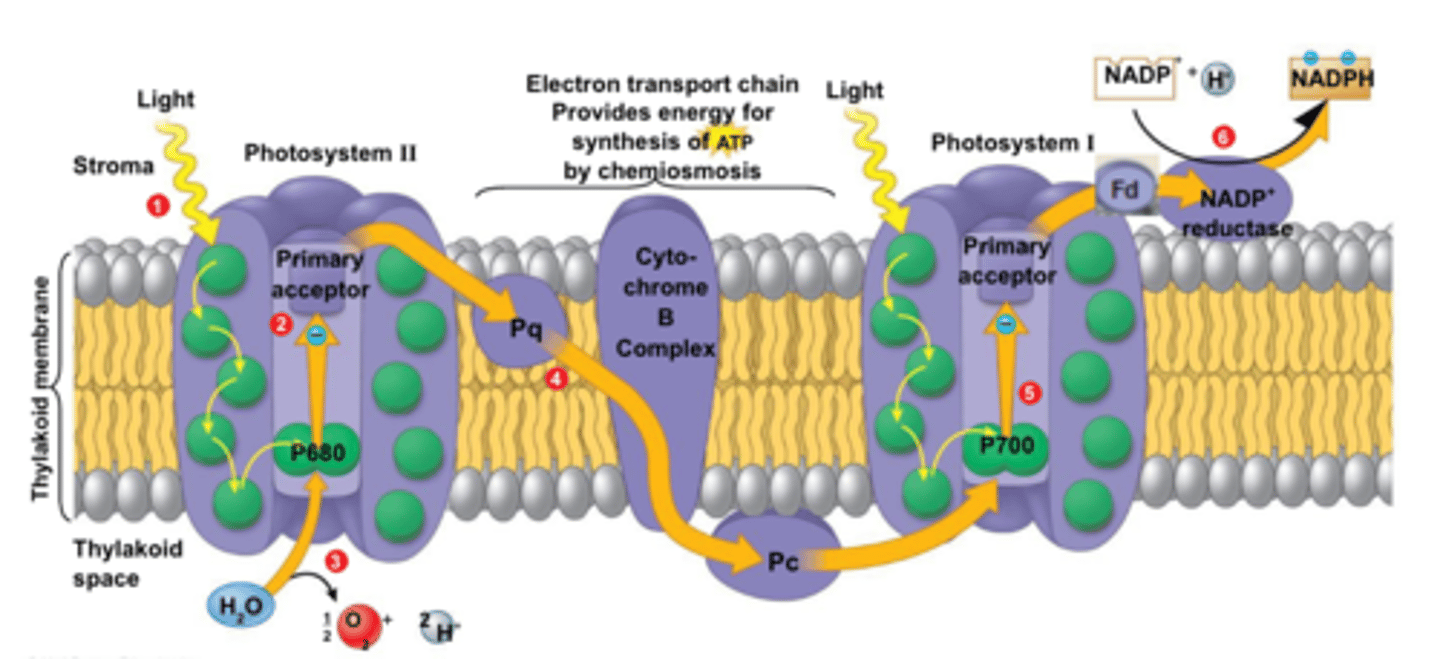
Mobile electron carriers (Description)
Proteins found within the electron transport chain that move or "shuttle" the "excited" electrons from one protein to another within the electron transport chain
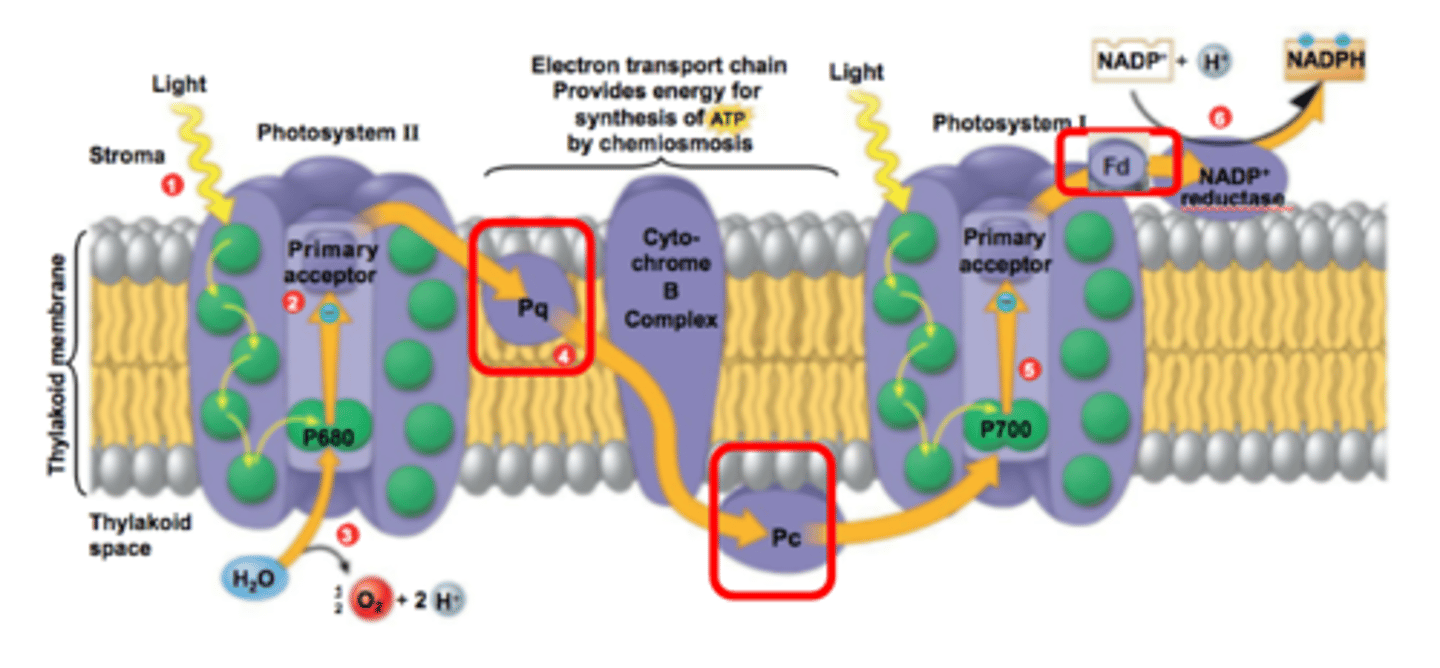
Mobile electron carriers (Examples)
Examples include:
Plastoquinone (Pq), Plastocyanin (Pc) & Ferredoxin (Fd)
Transport proteins in the ETC (Description)
Transport proteins move materials across the membrane; Cytochrome Complex B actively pumps hydrogen ions from the stroma to the thylakoid space; ATP synthase transports hydrogen ions into the stroma via facilitated diffusion from the thylakoid space
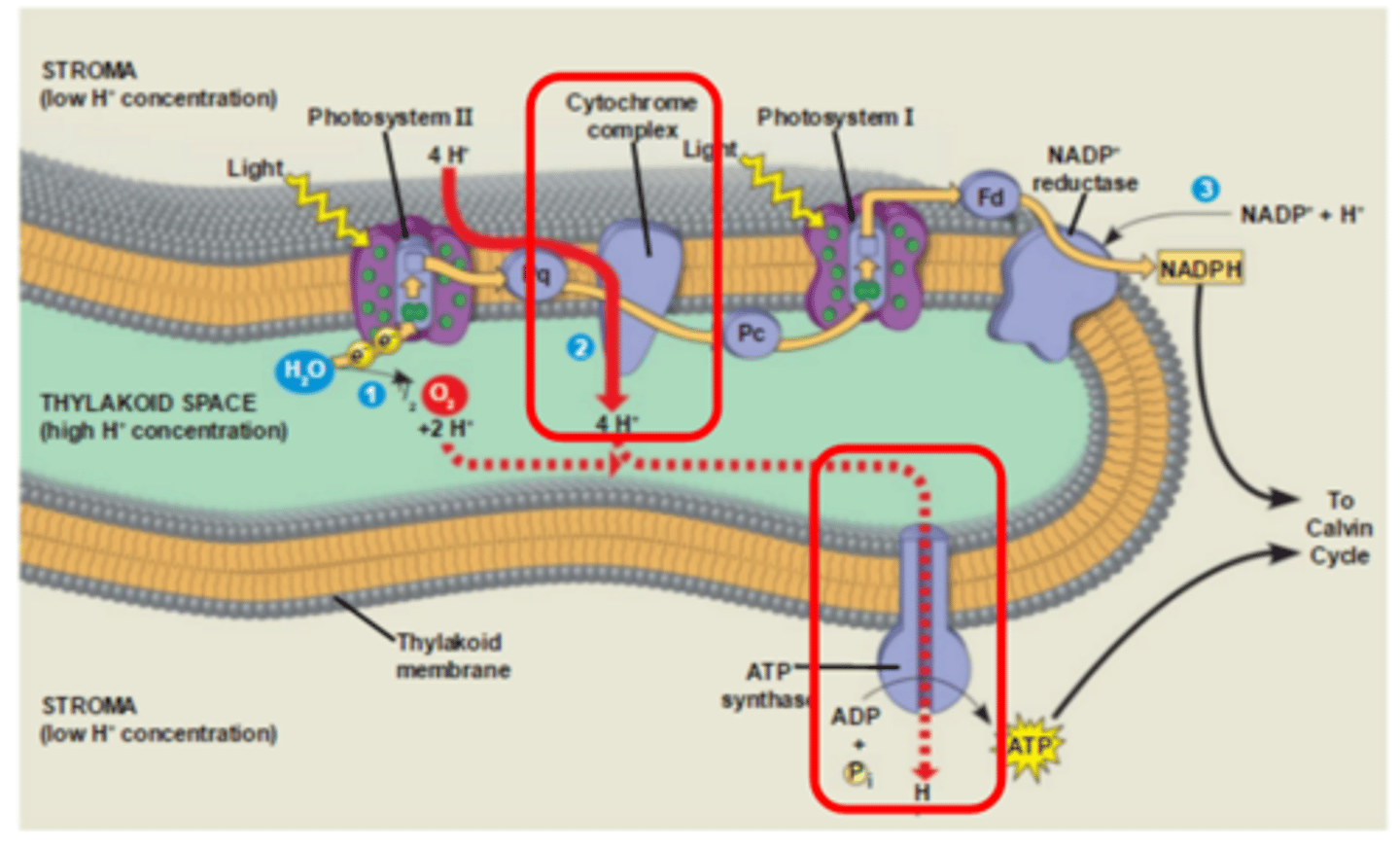
Transport proteins in the ETC (Examples)
Examples include:
Cytochrome B
ATP Synthase
Photolysis (Description)
A process in which water absorbs light energy and is split to form hydrogen ions, electrons and oxygen
2H2O → 4H+ + 4e- + O2
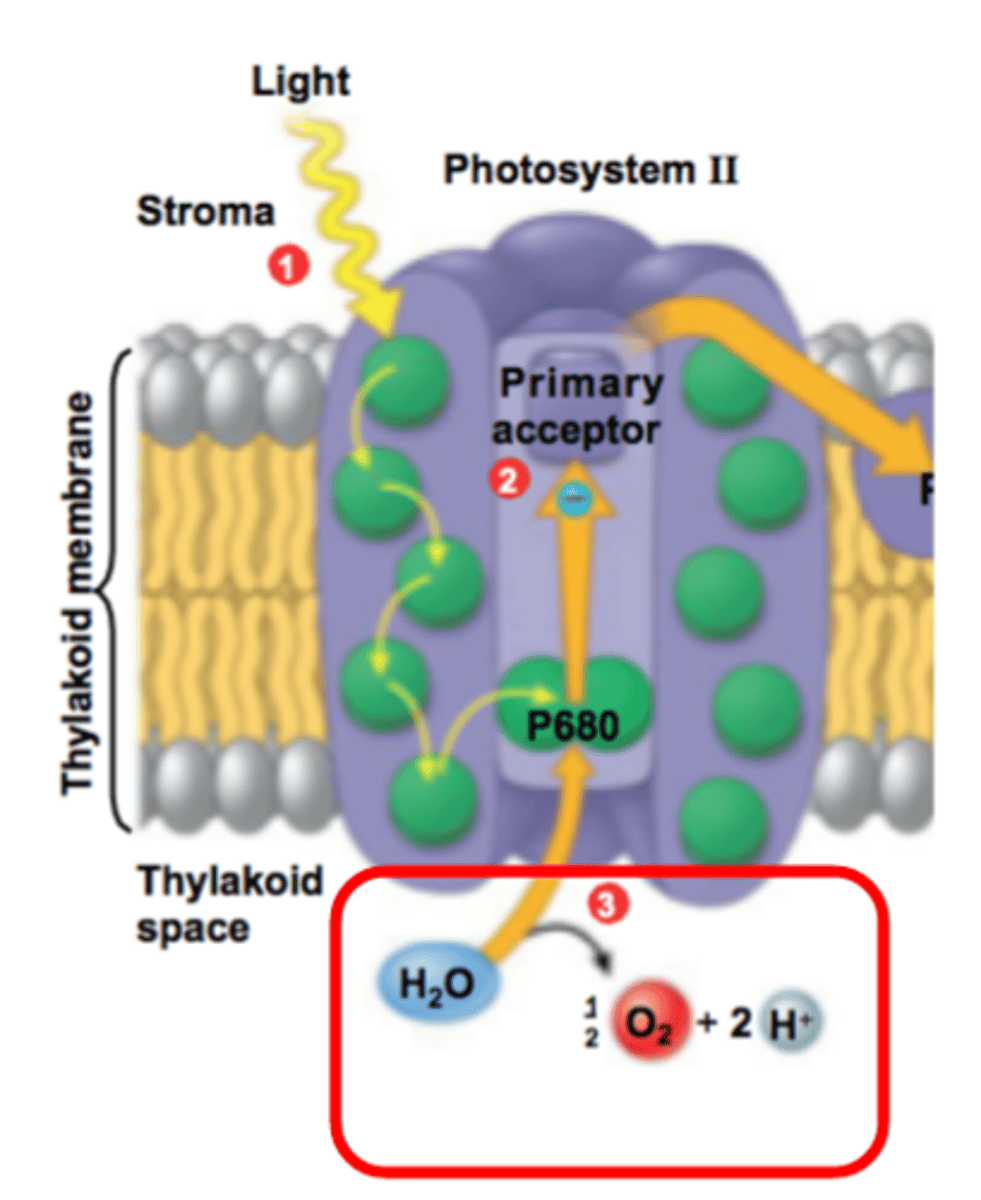
Photolysis (Role in Light Reactions)
Process in which the splitting of water generates electrons (e-) and hydrogen ions (H+); electrons generated replenish excited electrons that travel along the ETC; hydrogen ions (H+) generated help to maintain the high concentration of H+ inside the thylakoid
Chemiosmosis (Role in Light Reactions)
The process in which energy from excited electrons is used to pump protons (H+ ions) into the thylakoid space which creates a concentration gradient. The H+ ions then suddenly reverse their direction and escape back across the membrane and out of the thylakoid space through the ATP synthase channel protein, releasing energy that is used by ATP synthase to unite ADP with phosphate to form ATP
Production of NADPH
A reaction in which NADP+ which is found in the stroma accepts or "catches" the electrons from the electron transport chain to become NADPH; the enzyme NADP+ reductase found in the thylakoid membrane helps the reaction to occur at a faster rate
NADP+ + 2e- + H+ → NADPH
NADP+
An electron acceptor found in the stroma that accepts electrons that leave the electron transport chain
NADP+ Reductase
An enzyme found in the thylakoid membrane that speeds up the reduction of NADP+ to produce NADPH
Enzymes in the ETC (Description)
Enzymes found in the ETC that help to speed up chemical reactions that produce NADPH and ATP
NADP+ + 2 electrons + H+ → NADPH
ADP + phosphate → ATP
Enzymes in the ETC (Examples)
Examples include:
NADP+ Reductase
ATP Synthase
Light Dependent Reactions (Chemical Reactions)
2H2O → 4H+ + 4e- + O2
ADP + phosphate → ATP
NADP+ + 2 electrons + H+ → NADPH