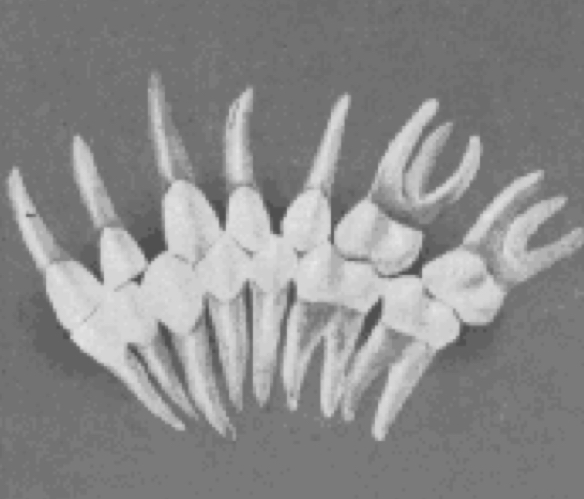
6 keys to normal occlusion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
The six keys
Molar relationship
Crown Angulation
Crown Inclination
Rotations
Spaces
Occlusal plane
Molar relationship
Distal surface of the distobuccal cusp of the upper first permanent molar
occludes with the mesial surface of the mesiobuccal cusp of the lower second molar

Molar relationship
Better opportunity for normal occlusion
The closer the distal surface of the distobuccal cusp of the upper first permanent molar approaches the mesial surfaces of the mesiobuccal cusp of the lower second molar
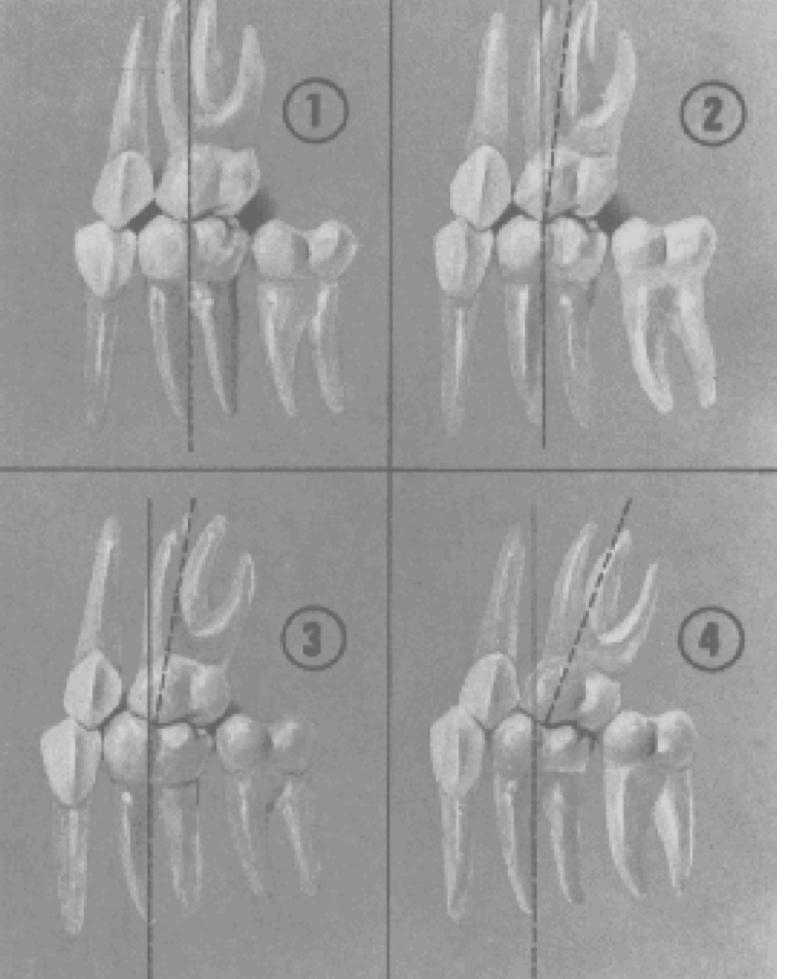
Crown angulation (tip)
Distal than incisal
gingival portion of the long axes of all crowns was more…
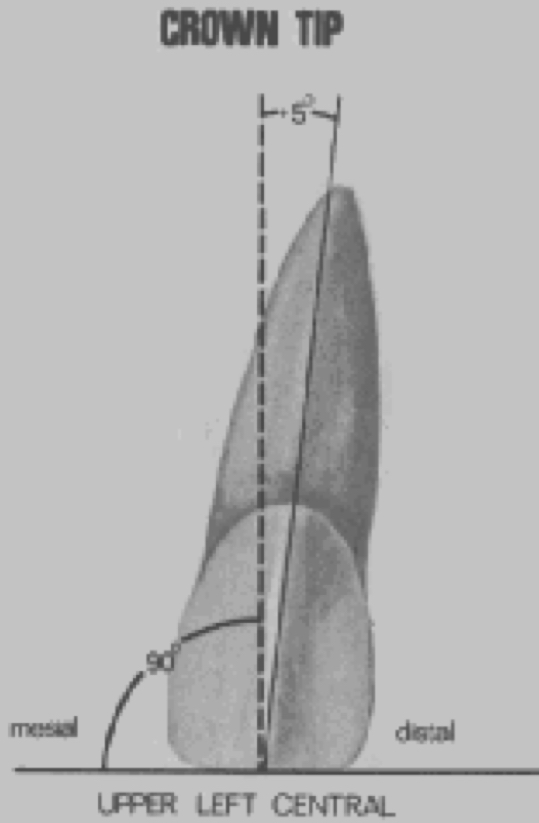
Crown angulation (tip)
Degree of crown tip
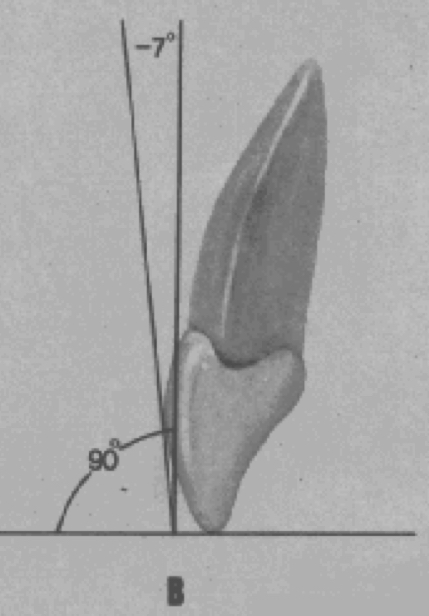
angle between the long axis of the crown and a line bearing 90 degress from the occlusal plane
Crown angulation (tip)
Plus reading
gingival portion of the long axis of all crown is distal to the incisal portion
Crown angulation (tip)
Minus reading
gingival portion of the long axis of the crown is mesial to the incisal portion
Crown angulation (tip)
Normal occlusion
dependent upon proper distal crown tip, especially of the upper anterior teeth since they have the longest crowns
Crown angulation (tip)
Degree tip of incisiors
determines the amount of mesiodistal space they consume and, therefore, has a considerable effect on posterior occlusion as well as anterior esthetics.
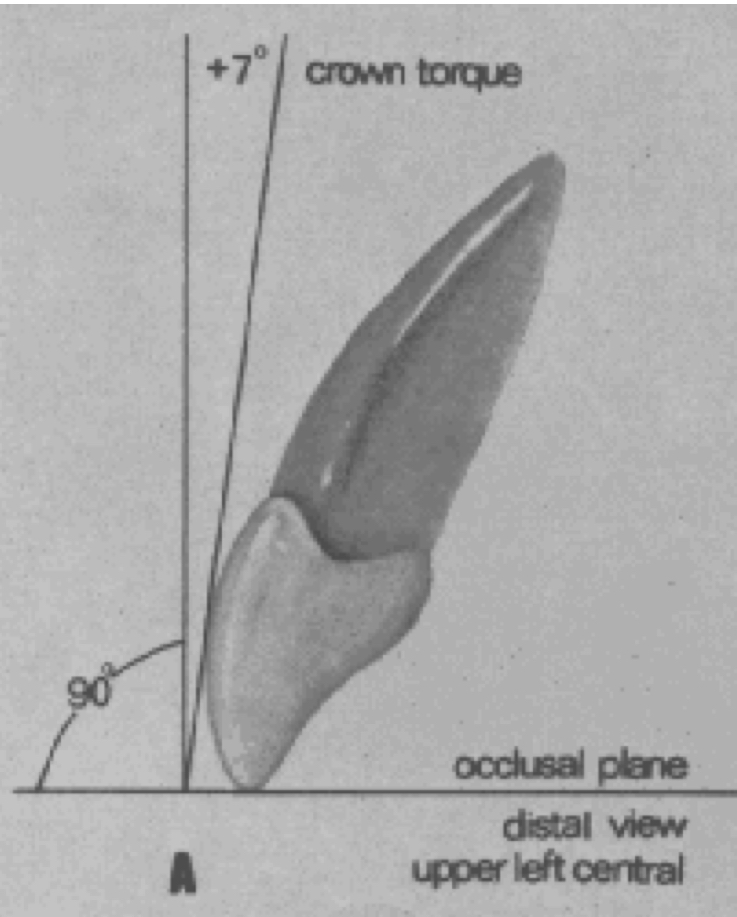
Crown inclination
Plus reading
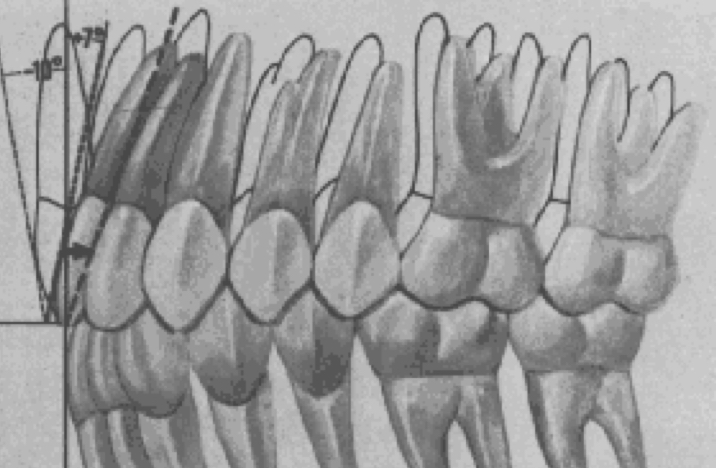
the gingival portion of the tangent line (or of the crown) is lingual to the incisal portion
Crown inclination
Minus reading
the gingival portion of the tangent line is labial to the incisal portion
Crown inclination
Anterior Crown
upper and lower anterior crown inclinations are intricately complementary and significantly affect overbite and posterior occlusion
positive upper anterior crown inclination
Crown inclination
Posterior crown (upper)
minus crown inclination existed in each crown from the upper canine through the upper second premolar
Crown inclination
Posterior Crown (lower)
progressively greater “minus” crown inclination existed from the lower canines through the lower second molars
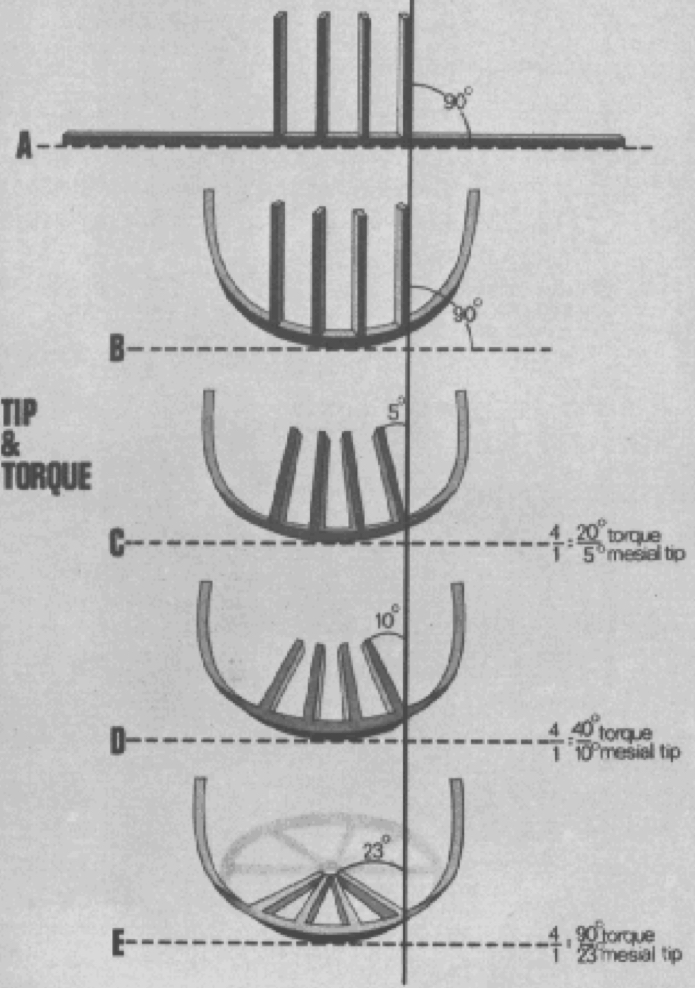
Tip and torque
Anterior portion of an upper rectangular arch
lingually torqued, a proportional amount of mesial tip of the anterior crowns occurs
Rotations
teeth should be free of undesirable rotations
Tight contacts
contact points should be tight (no spaces)
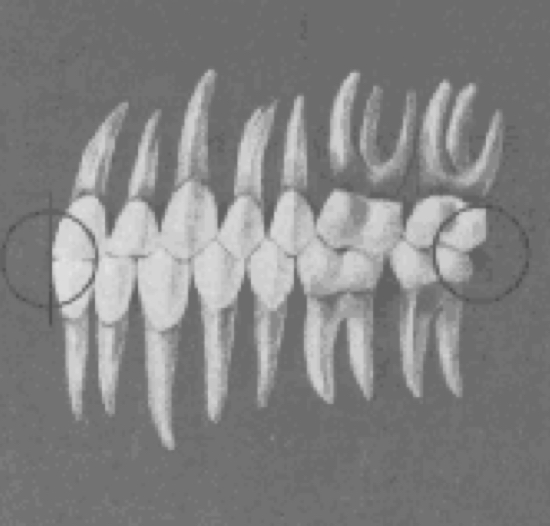
Occlusal plane
Planes of occlusion
flat to slight curves of spee
Occlusal plane
Intercuspation of teeth
best when the plane of occlusion is relatively flat
Occlusal plane
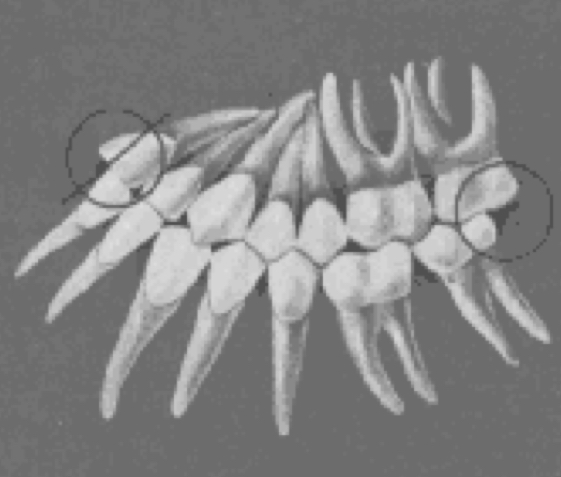
Deep curve of spee
more contained area for the upper teeth, making normal occlusion impossible
Occlusal plane
reverse curve of Spee
extreme form of overtreatment, allowing excessive space for each tooth to be intercuspally placed