Ch07 Neurons and Electrical Signaling
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
APK2105C @ UF | Dr. Nguyen | Module 2 | Ch06 Neurons and Electrical Signaling
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
False
True or False: Neurons contain only ICF and no organelles.
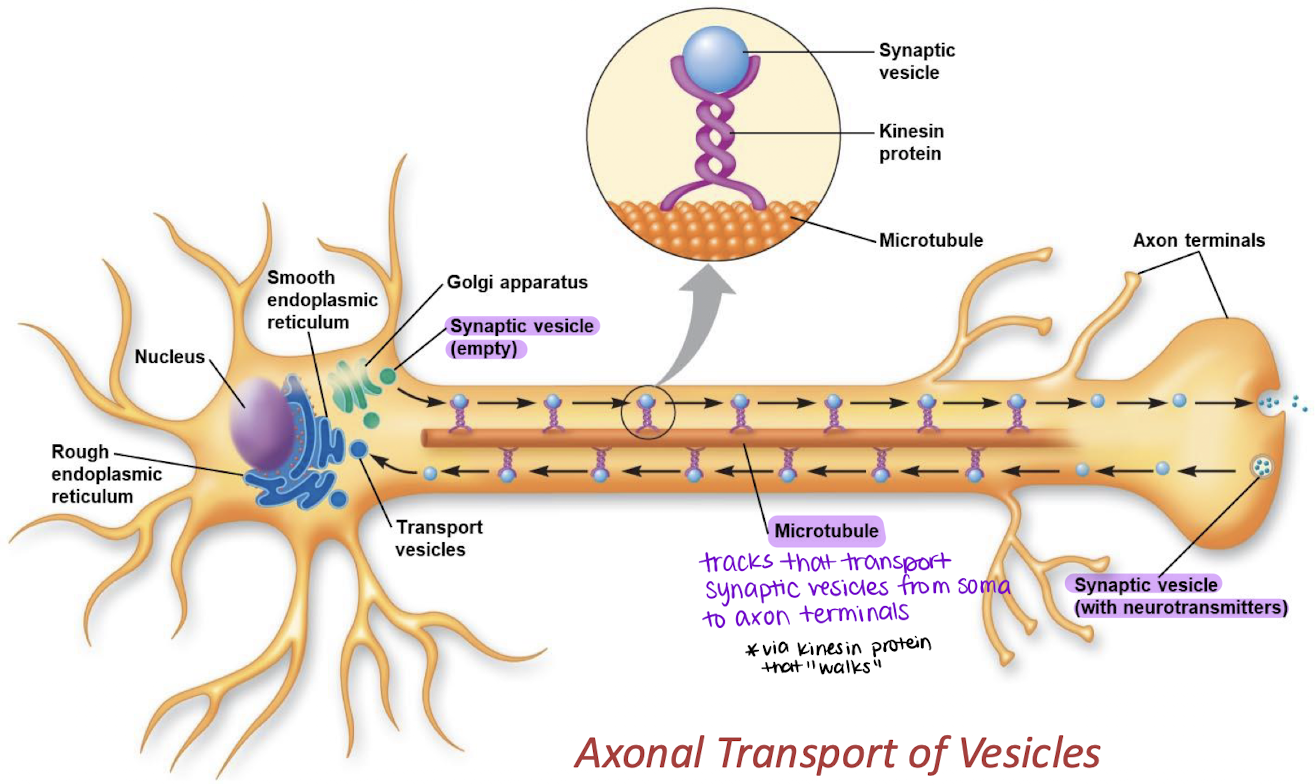
axon
Synaptic vesicles travel along the ______ to release neurotransmitters.
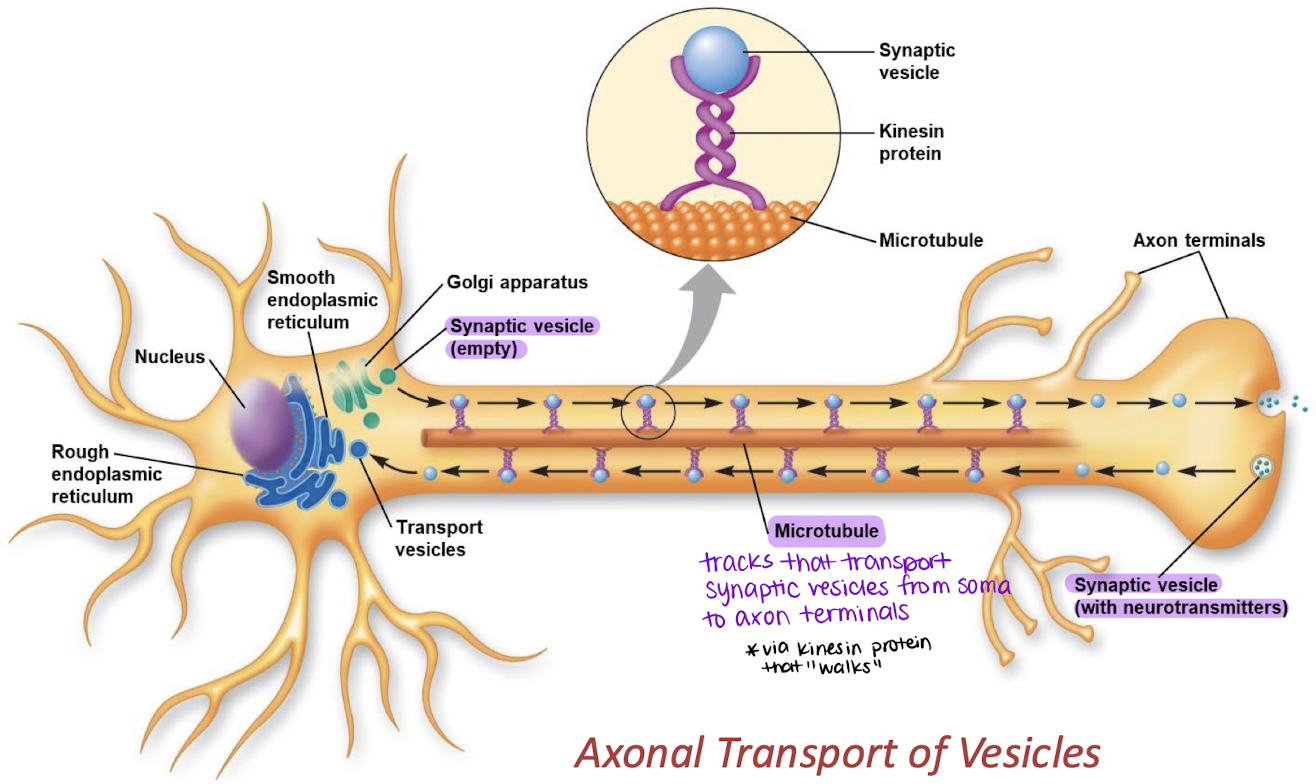
microtubules; soma; axon terminals
Provide structural support and act as “tracks” that transport synaptic vesicles from the _______ to the _______ _______.
ion; electrical
Opening or closing of ____ channels on the neuron changes the _________ properties of the cell.
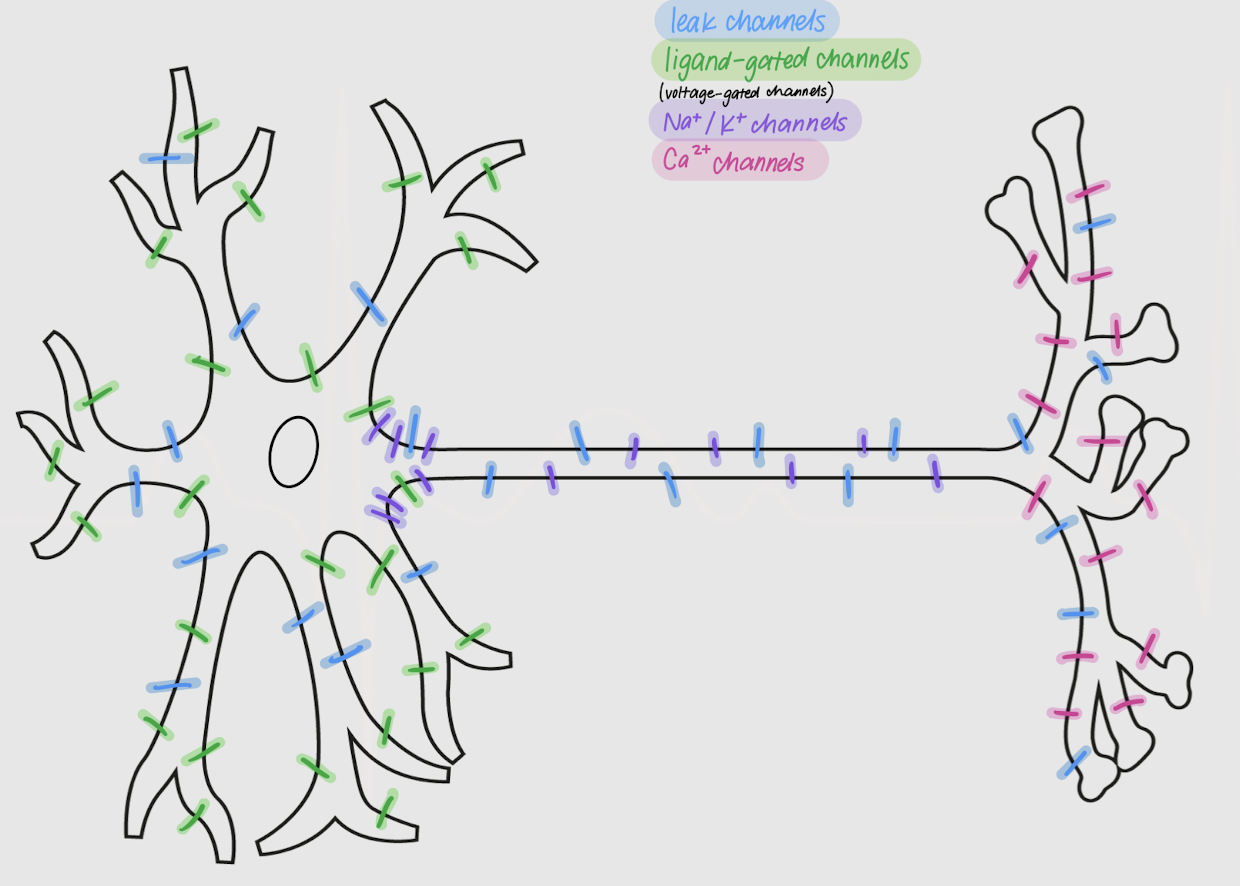
leak channels
Channels in neurons:
allow passive movement of ions across the membrane
always open
located all over the neuron
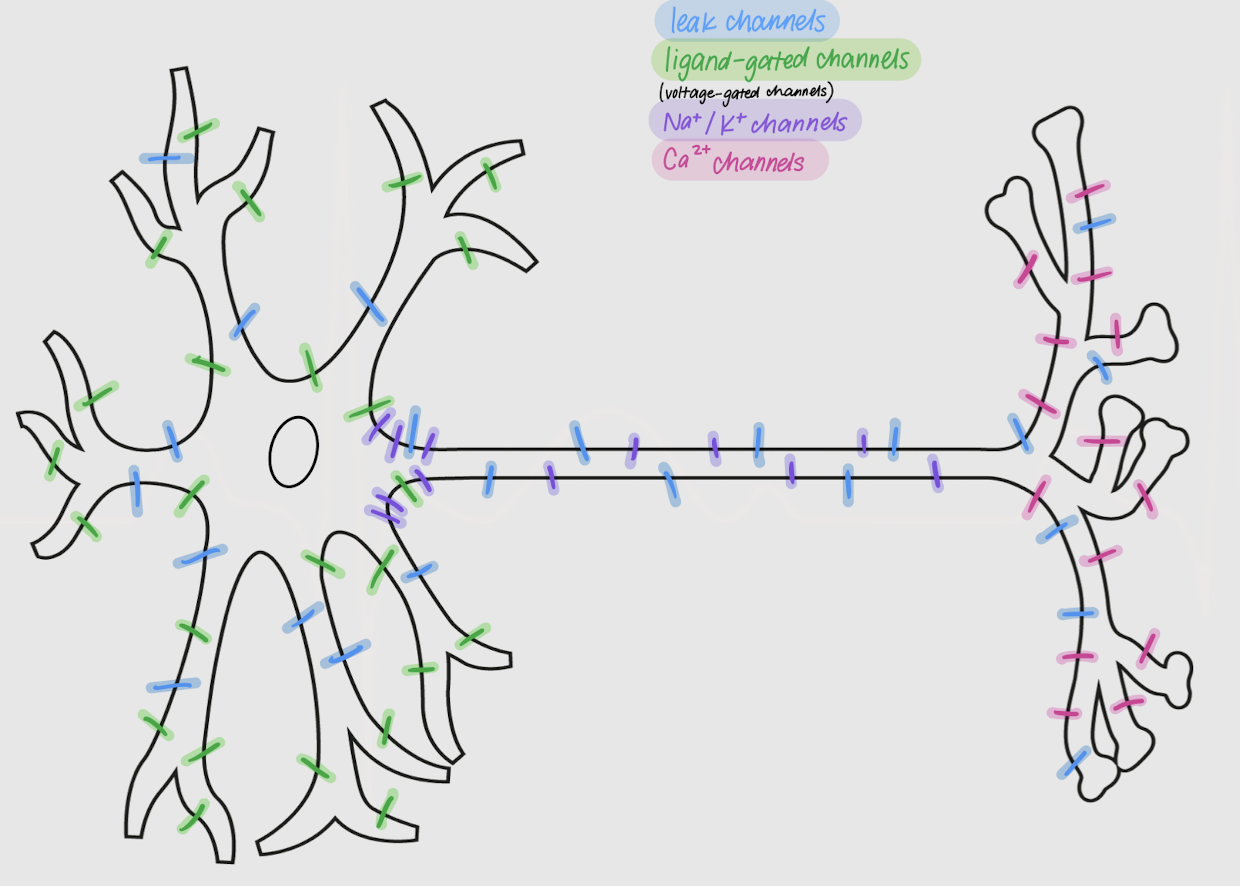
ligand-gated channels
Channels in neurons:
open or close following ligand-receptor binding
densely located in dendrites and soma
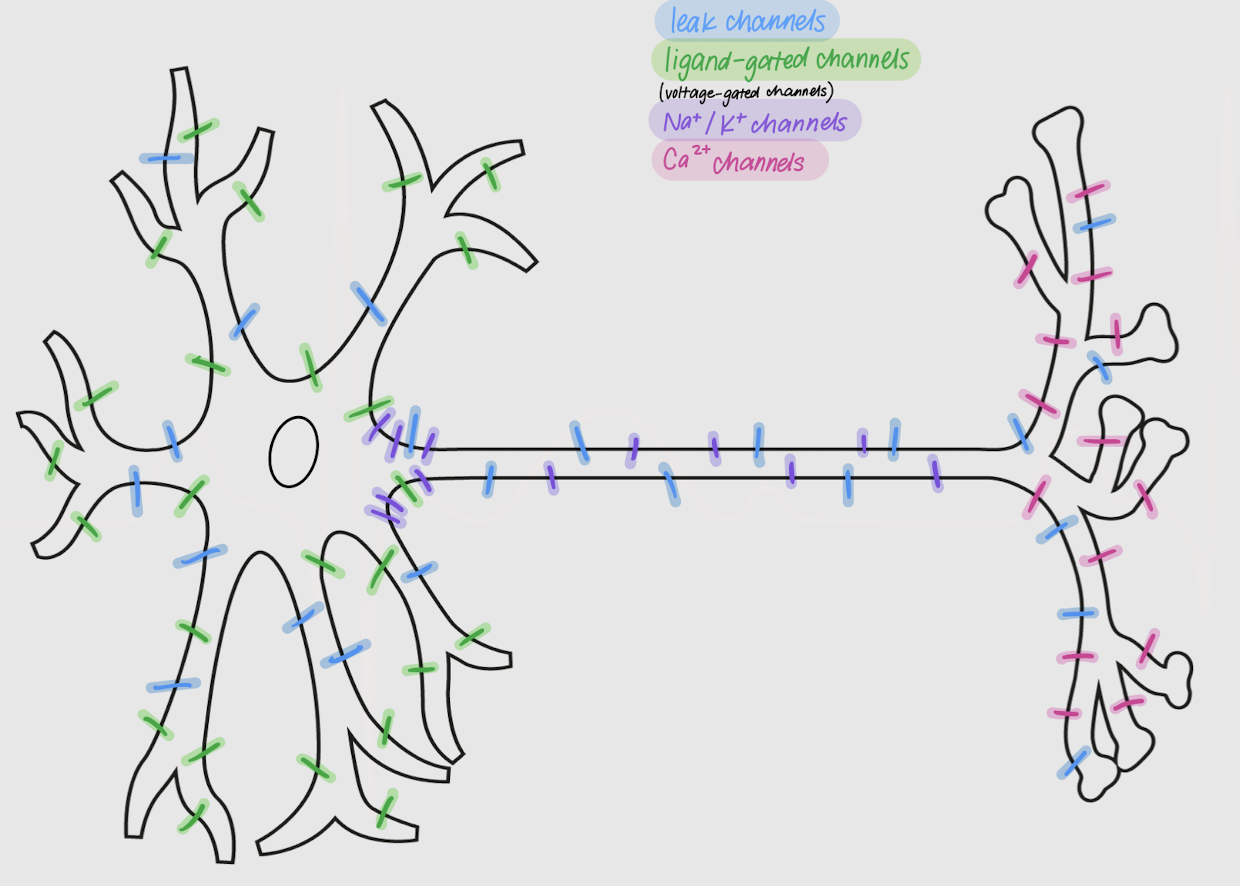
voltage-gated channels
Channels in neurons that open or close following changes in membrane potential
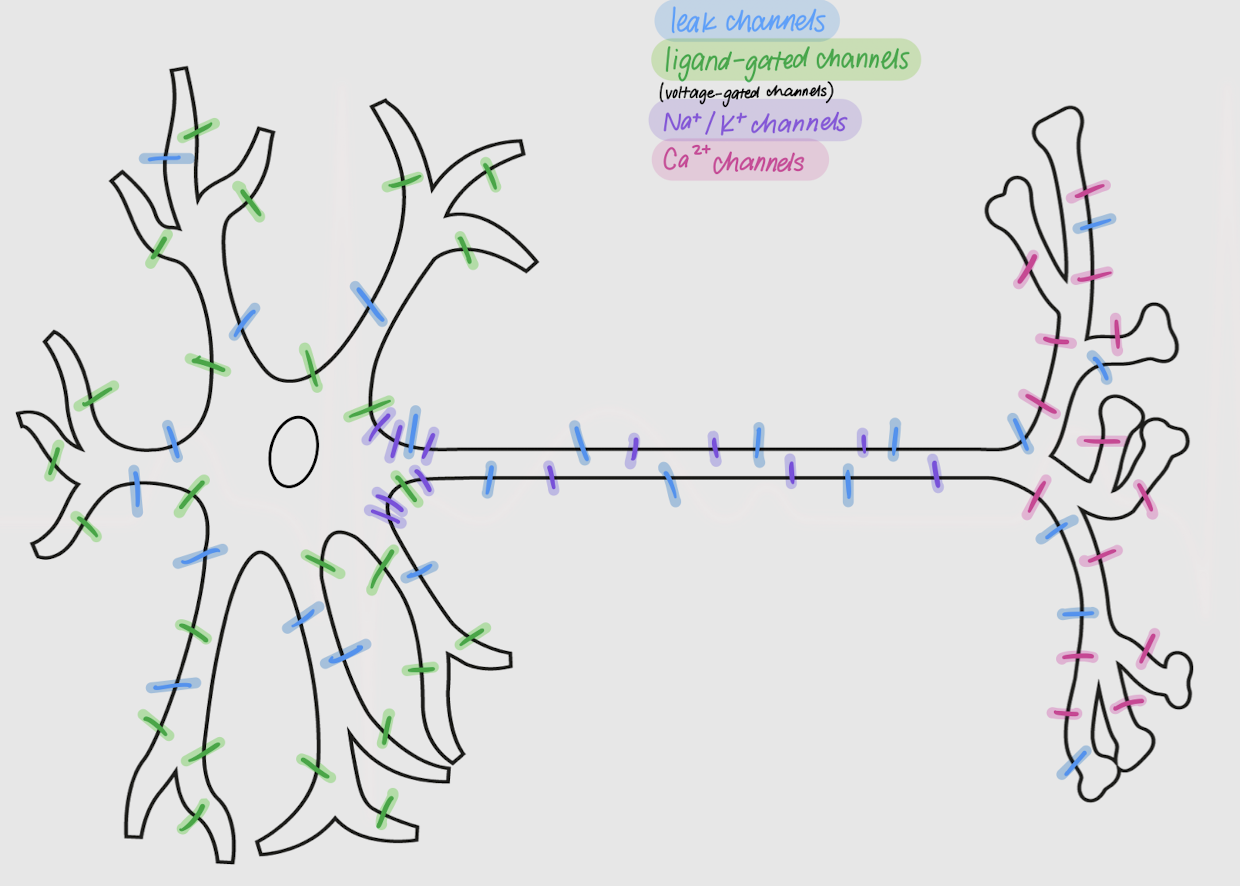
Na+ and K+ channels
Voltage-gated channels that are most dense in the axon and axon hillock
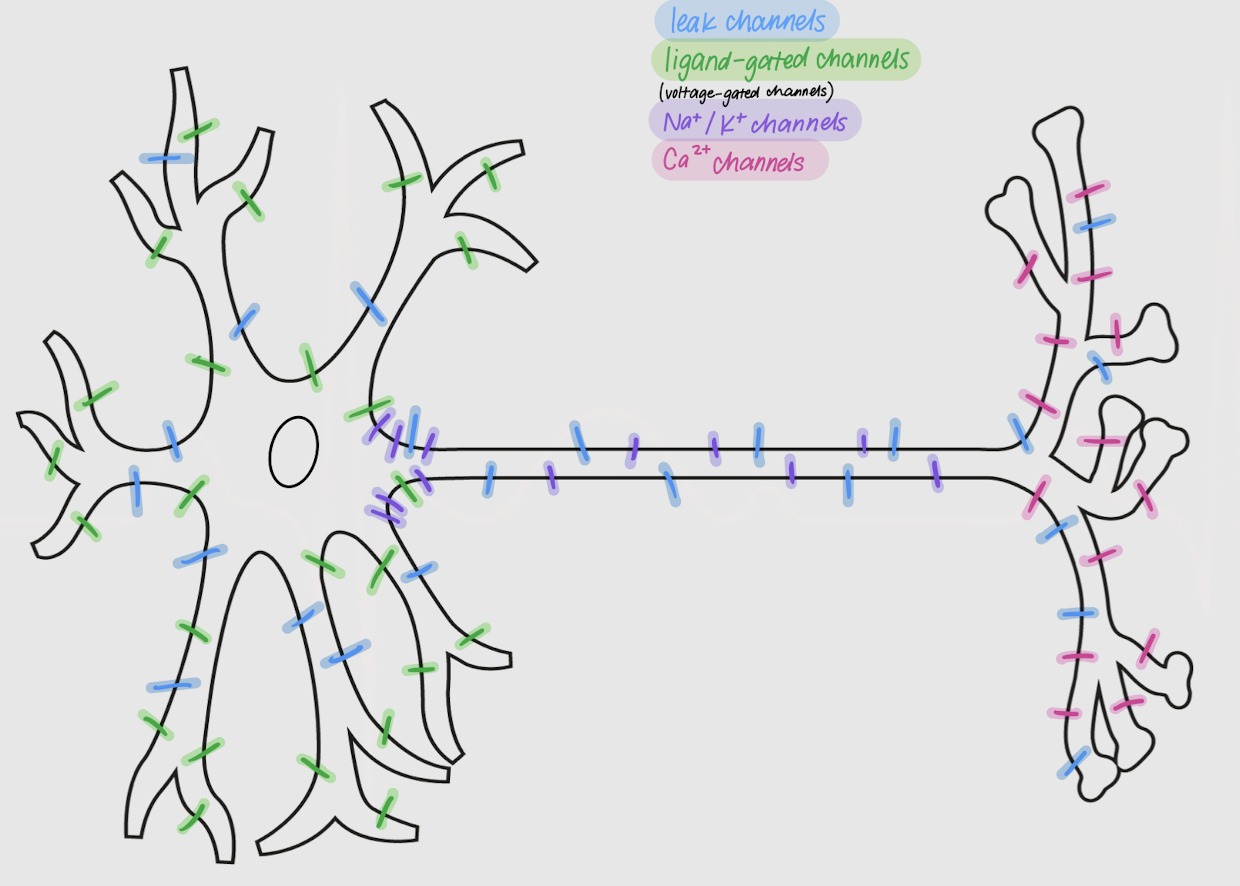
Ca2+ channels
voltage-gated channels that are most dense in the axon terminal
bipolar neuron
Neuron w/ two extensions from the cell body that serves as a sensory neuron for special senses.
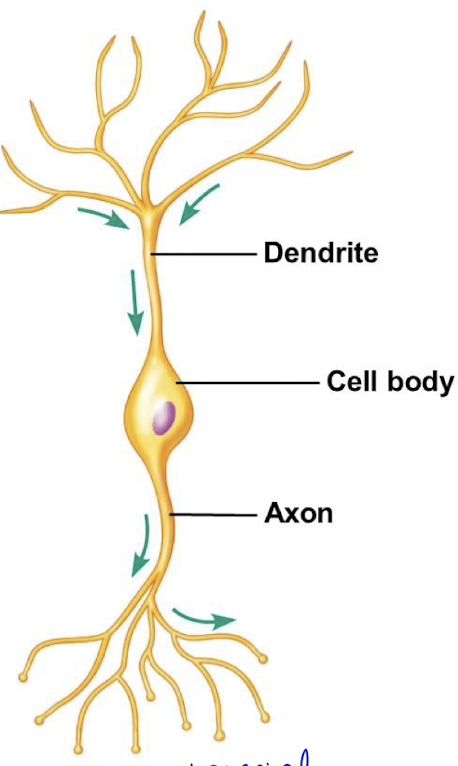
pseudo-unipolar neuron
Neuron w/ only one extension from the soma and that serves as a somatosensory neuron.
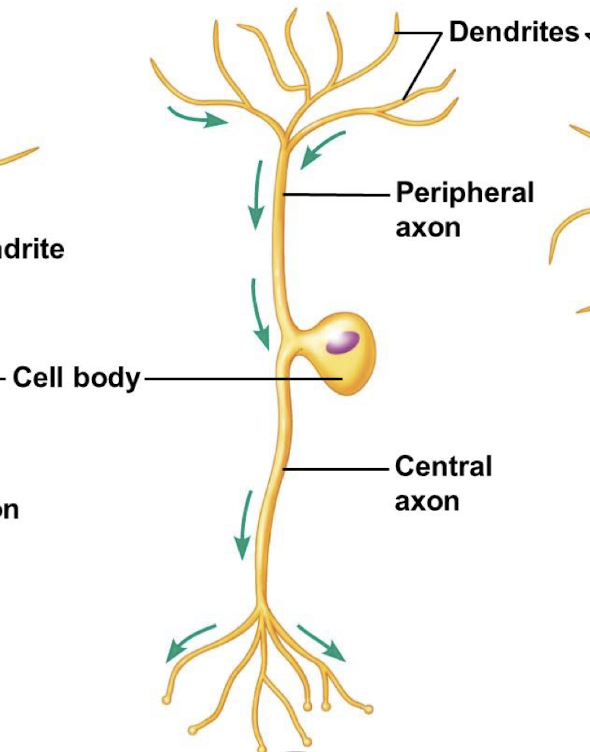
multipolar neurons
Most common neuron in the body.
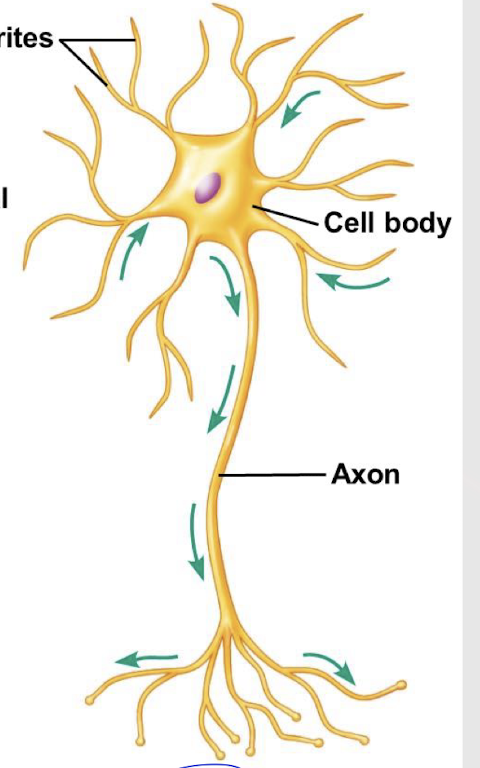
afferent and efferent
What are the functional classes of neurons?
tract
Group of axons traveling together in the CNS (white matter)
nuclei
Group of neurosomas in the CNS (gray matter)
nerve
Group of axons traveling together in the PNS (organs)
ganglion
Group of neurosomas in the PNS
nerves; PNS
Are nerves or tracts organs? Where are they located?
nervous and connective
What two tissues make up nerves in the PNS (making them organs)?
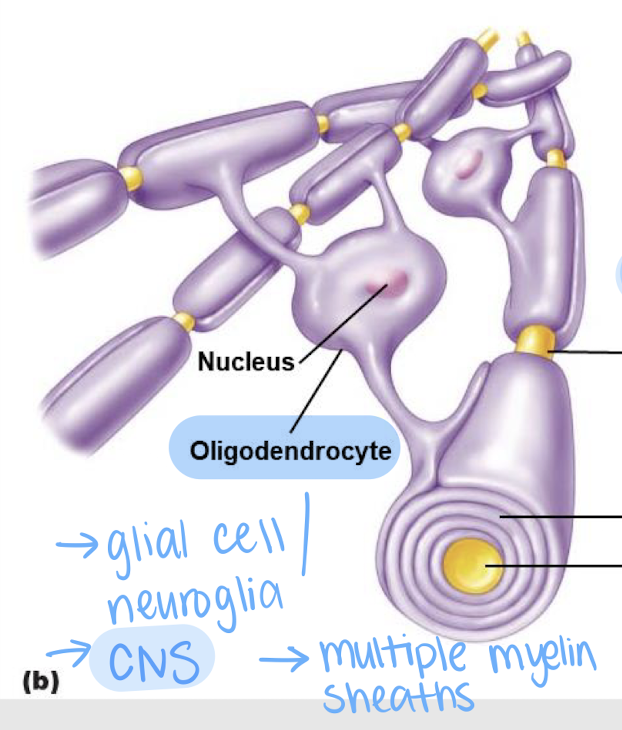
oligodendrocytes
Glial cells in the CNS that form myelin sheaths
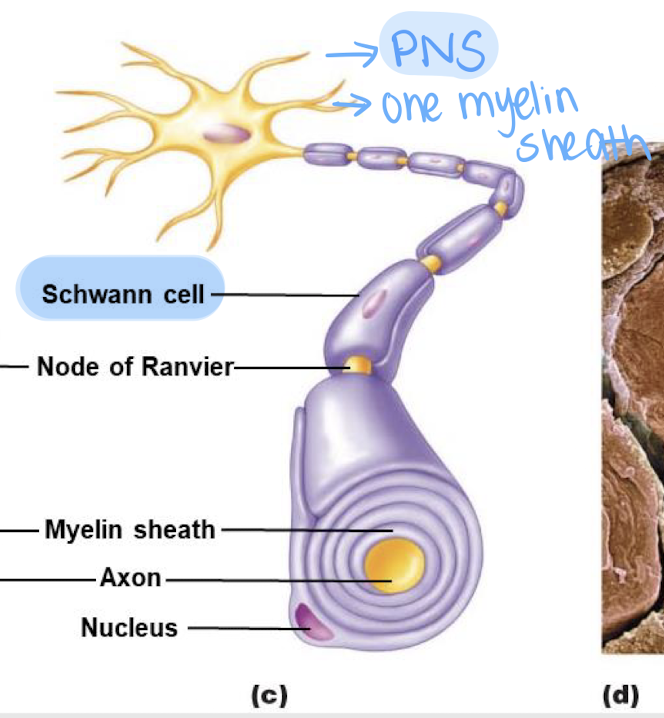
Schwann cells
Glial cells in the PNS that form myelin sheaths
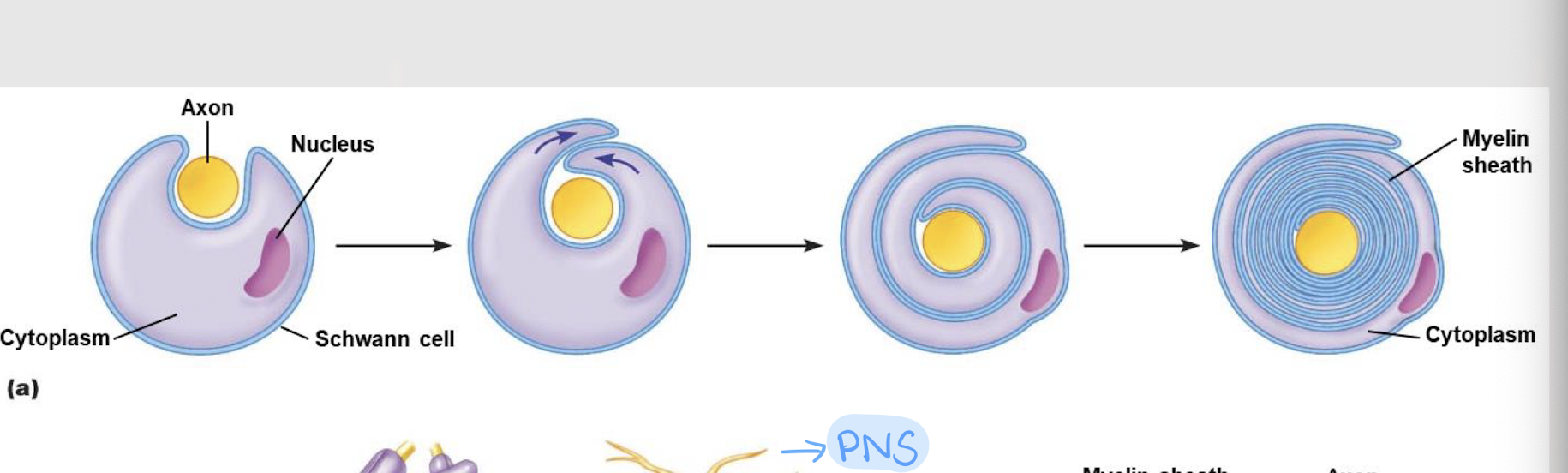
True
True or False: Schwann cells wrap themselves around the axon to form the myelin sheath
membrane potential (Vm)
difference in voltage across the plasma membrane
inside; outside; negative
Membrane potentials are ALWAYS described as the potential inside/outside the cell vs inside/outside the cell. This means the inside of a neuron is 70mV more positive/negative relative to the outside of the neuron.
chemical driving forces (for Na+ and K+), Na+/K+ pump, differences in permeability
What are the 3 contributors to the resting Vm?
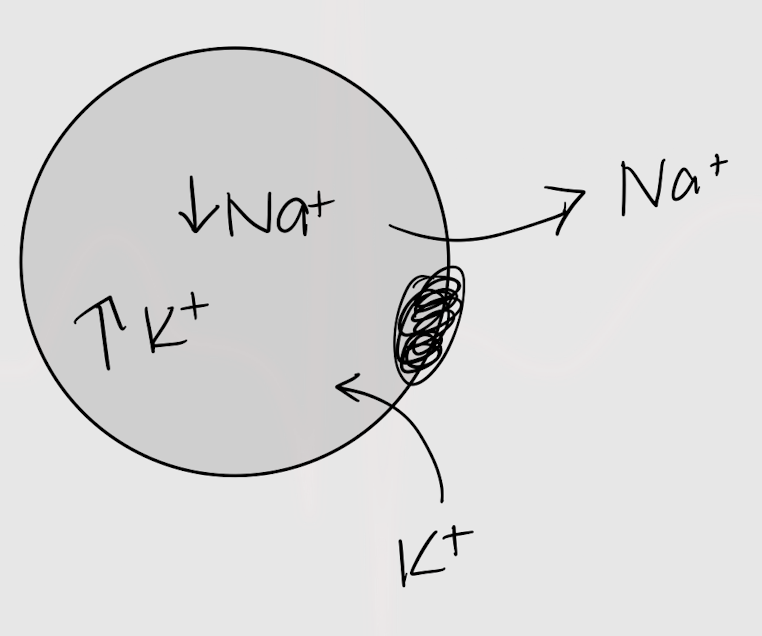
into
Na+ wants to move into/out of the cell.
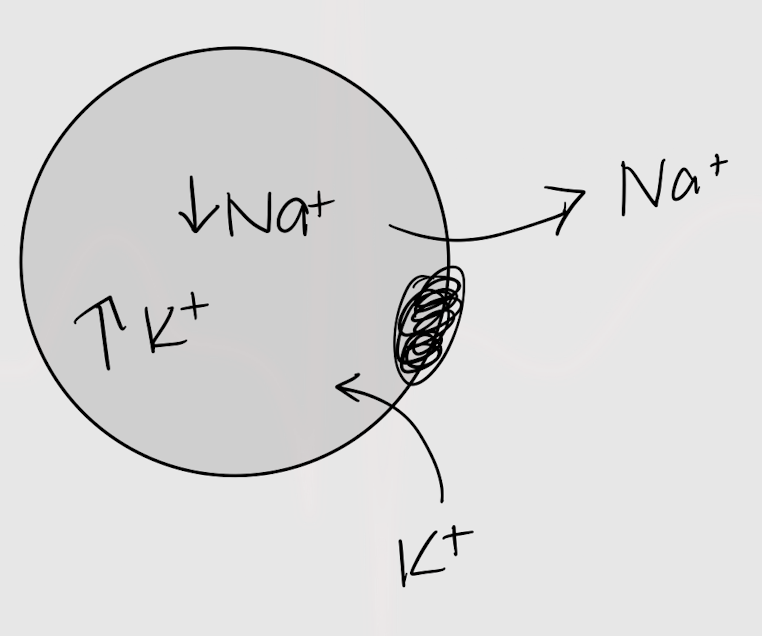
out of
K+ wants to move into/out of the cell.
K+
To which ion is the (neuronal) membrane more permeable to?
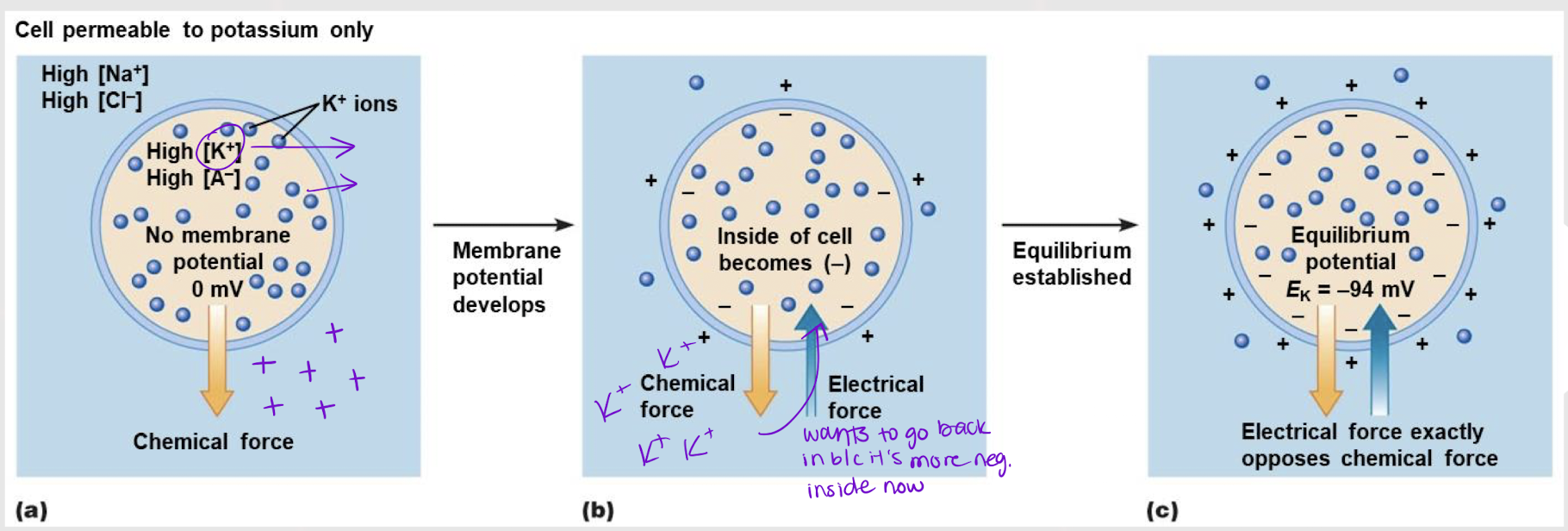
equilibrium potential (Ex)
The Vm that counters the chemical force acting on an ion across the membrane, thereby putting the ion at equilibrium.
electrical; chemical
Vm is an electrical force, so the Ex of an ion is the exact chemical/electrical force needed to equally oppose the chemical/electrical force of an ion.
-94mV
What is EK+ ?
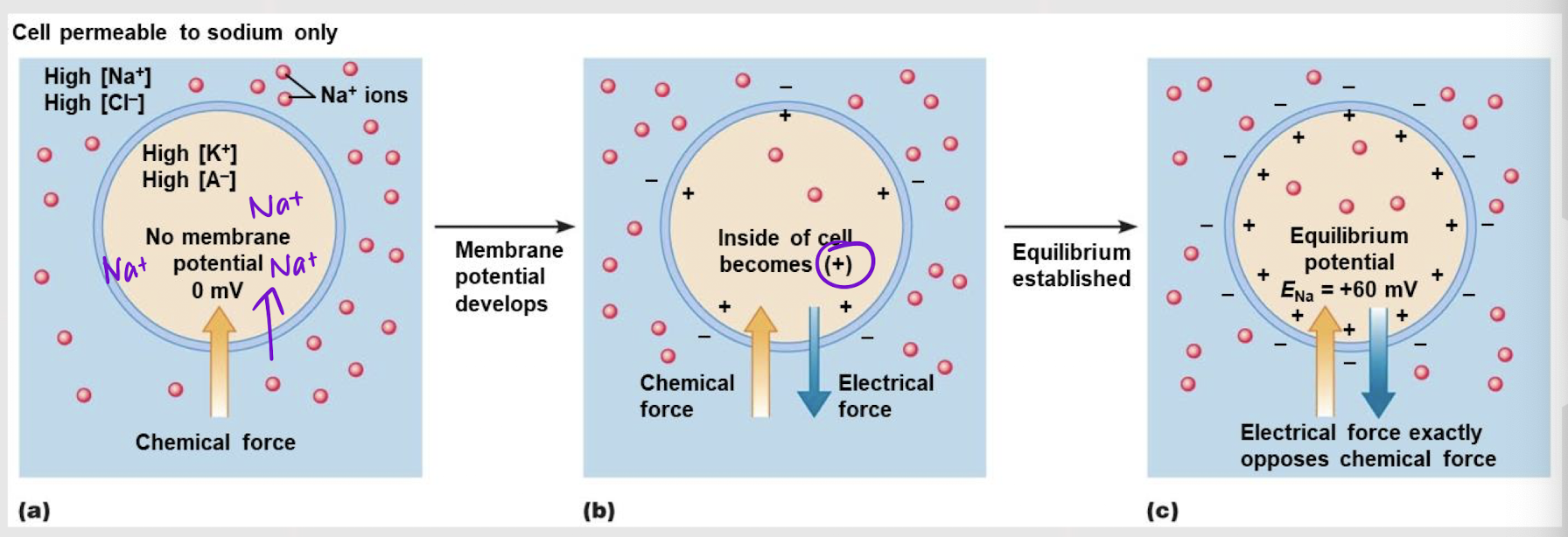
60mV
What is ENa+ ?
closer; Ex
The more permeable the membrane is to an ion, the ______ Vm will be to that ion’s ____.
leak channels
Channels that help establish/keep stable the resting Vm
gated channels
Channels that can be signaled top open or close in order to change the Vm
voltage; ligand
The two types of gated channels are _______- and _______-gated channels.
open; increased; closer to
As ion channels are signaled to open/close, the permeability to that ion is increased/decreased, which will drive the Vm closer to/father from that ion’s Ex
polarized
The plasma membrane is ________ at rest. There is a difference in voltage across the membrane.
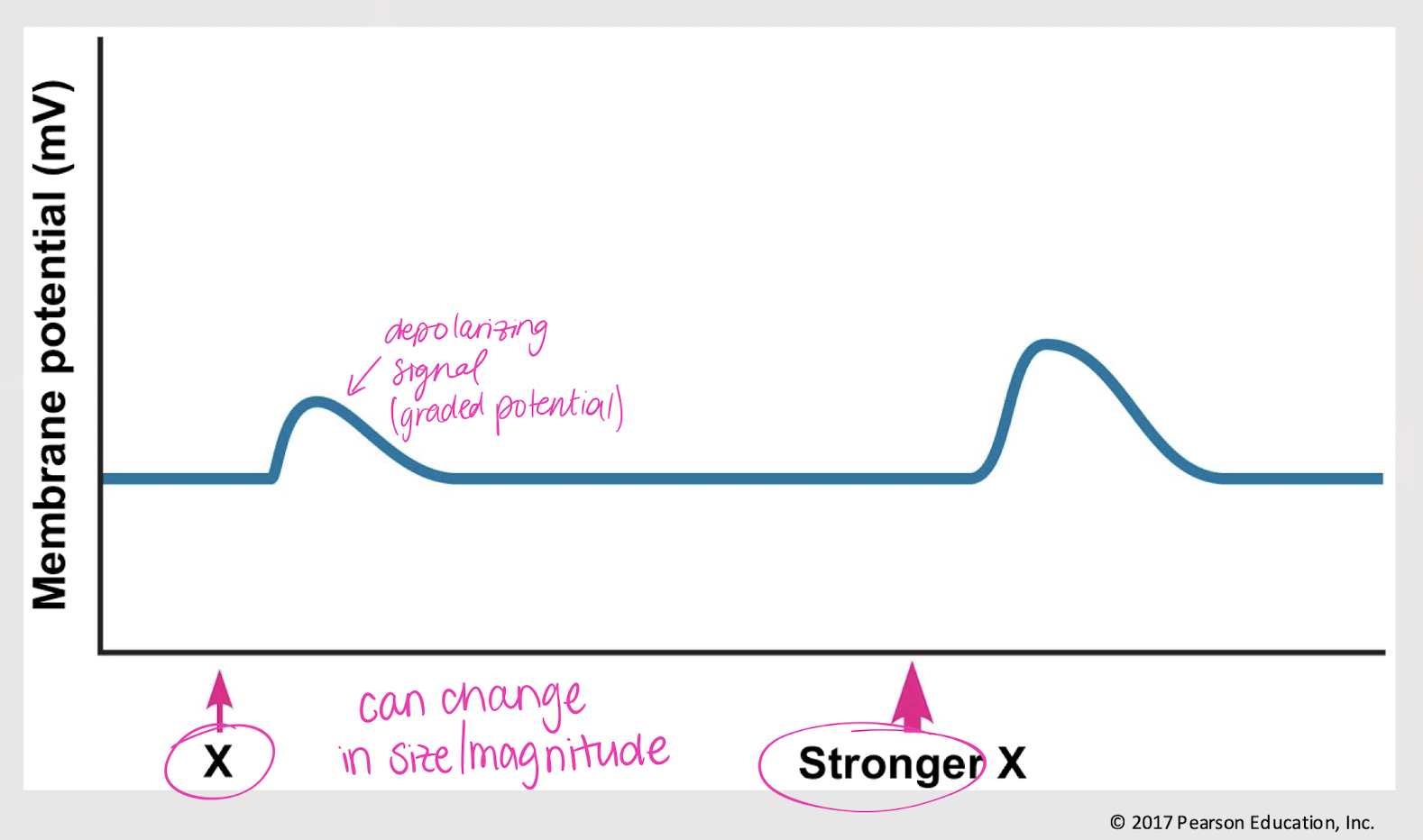
graded potentials
Small, decremental changes in Vm that occur when ion channels are signaled to open or close. Can change in magnitude.
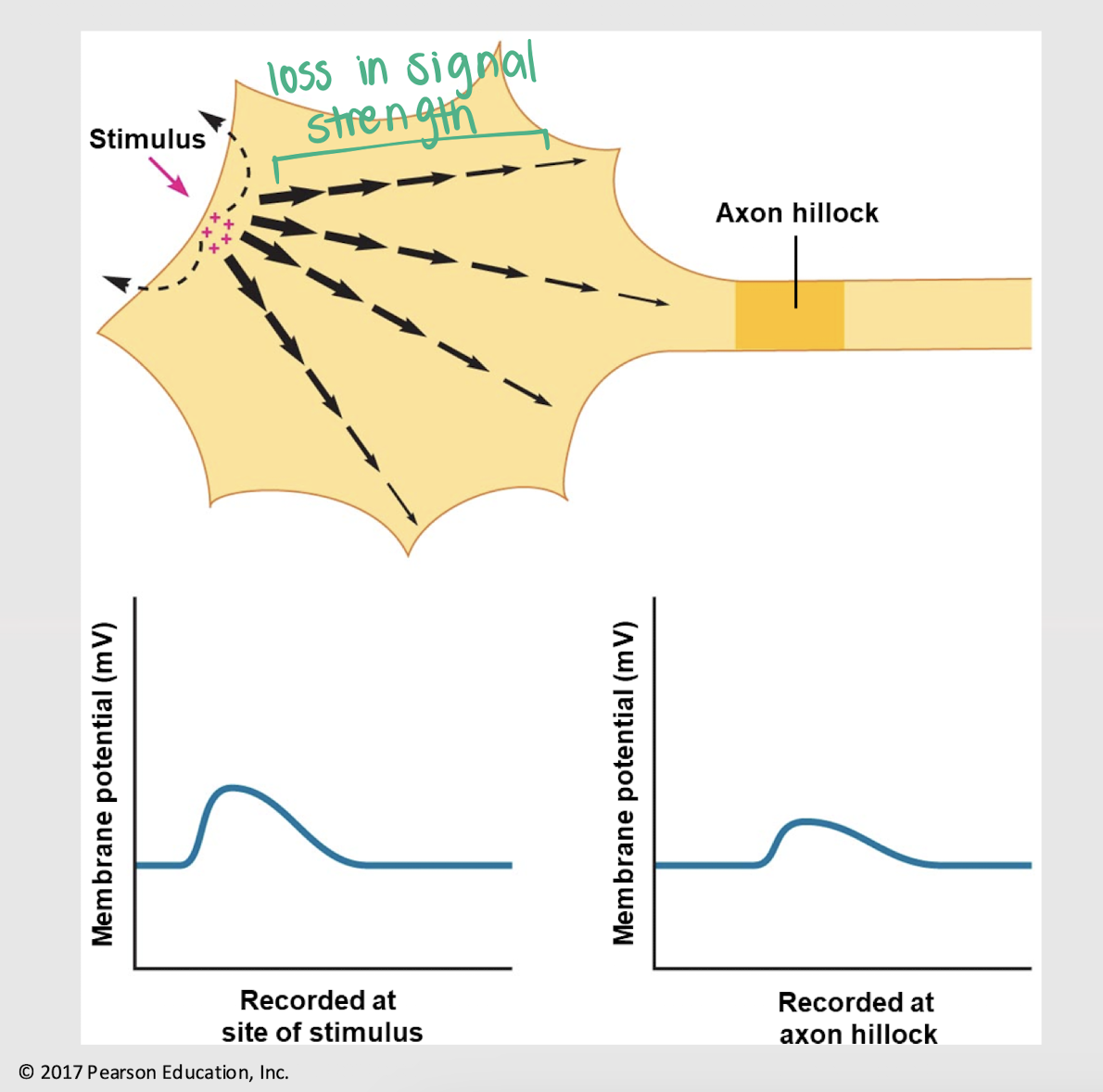
decreases
As the signal moves away from the stimulus site, its Vm increases/decreases.
axon hillock
Where do graded potentials converge?
True
True or False: Graded potentials can be hyperpolarizing or depolarizing.
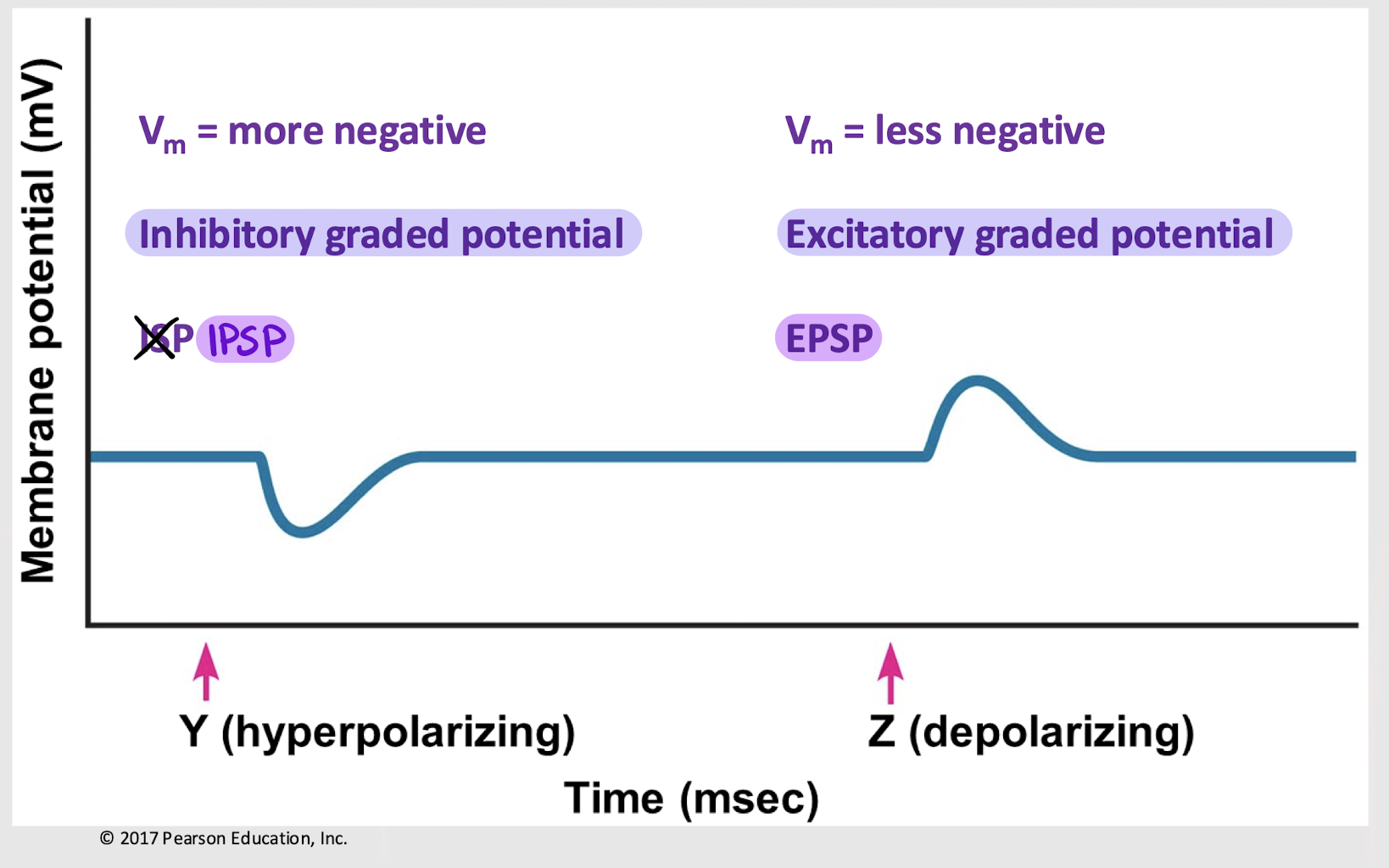
hyperpolarizing
Is an IPSP hyperpolarizing or depolarizing?
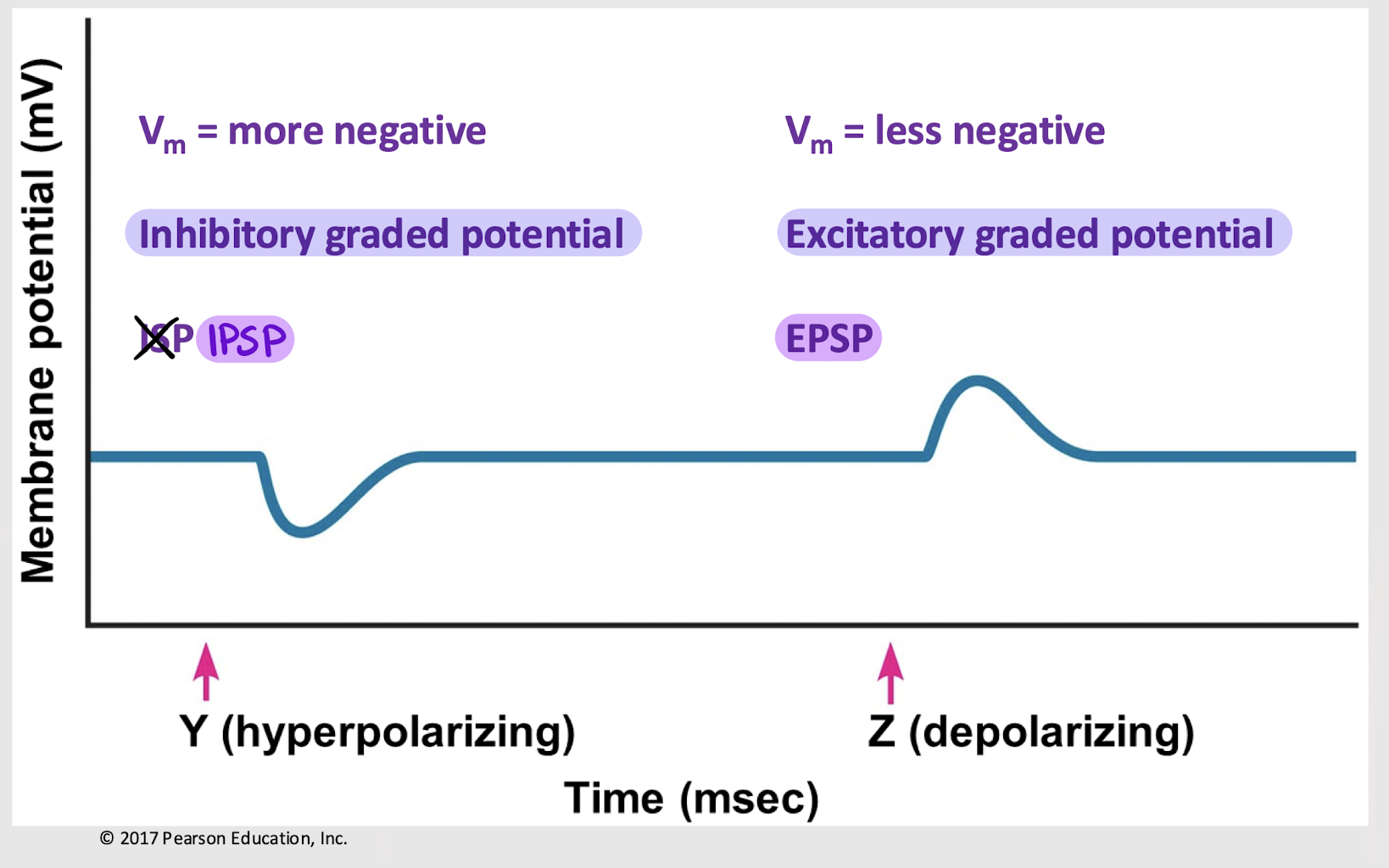
depolarizing
Is an EPSP hyperpolarizing or depolarizing?
axon hillock
Where does graded potential summation occur?
False
True or False: One stimulus is usually enough to meet threshold and trigger an action potential.
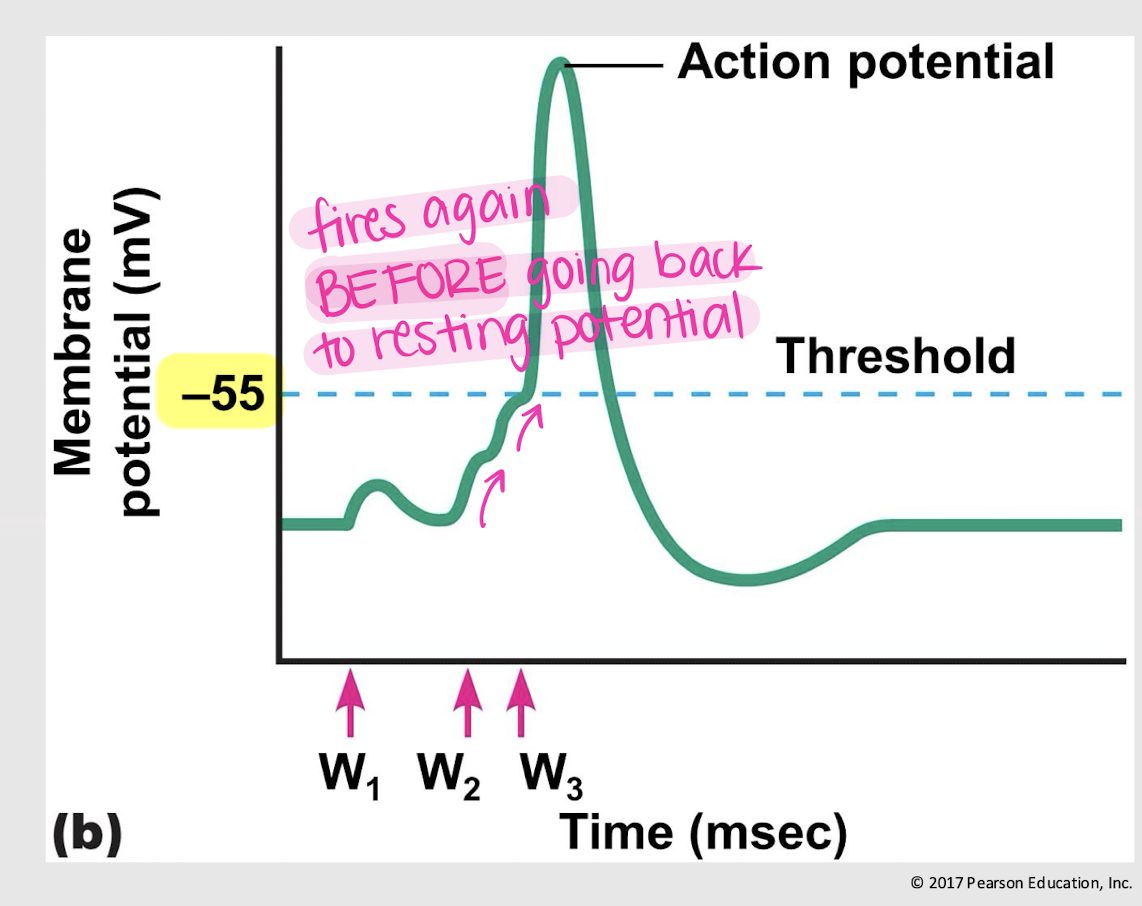
temporal summation
process of adding together multiple graded potentials that occur at the same synapse in rapid succession, leading to a greater chance of reaching threshold for action potential generation.
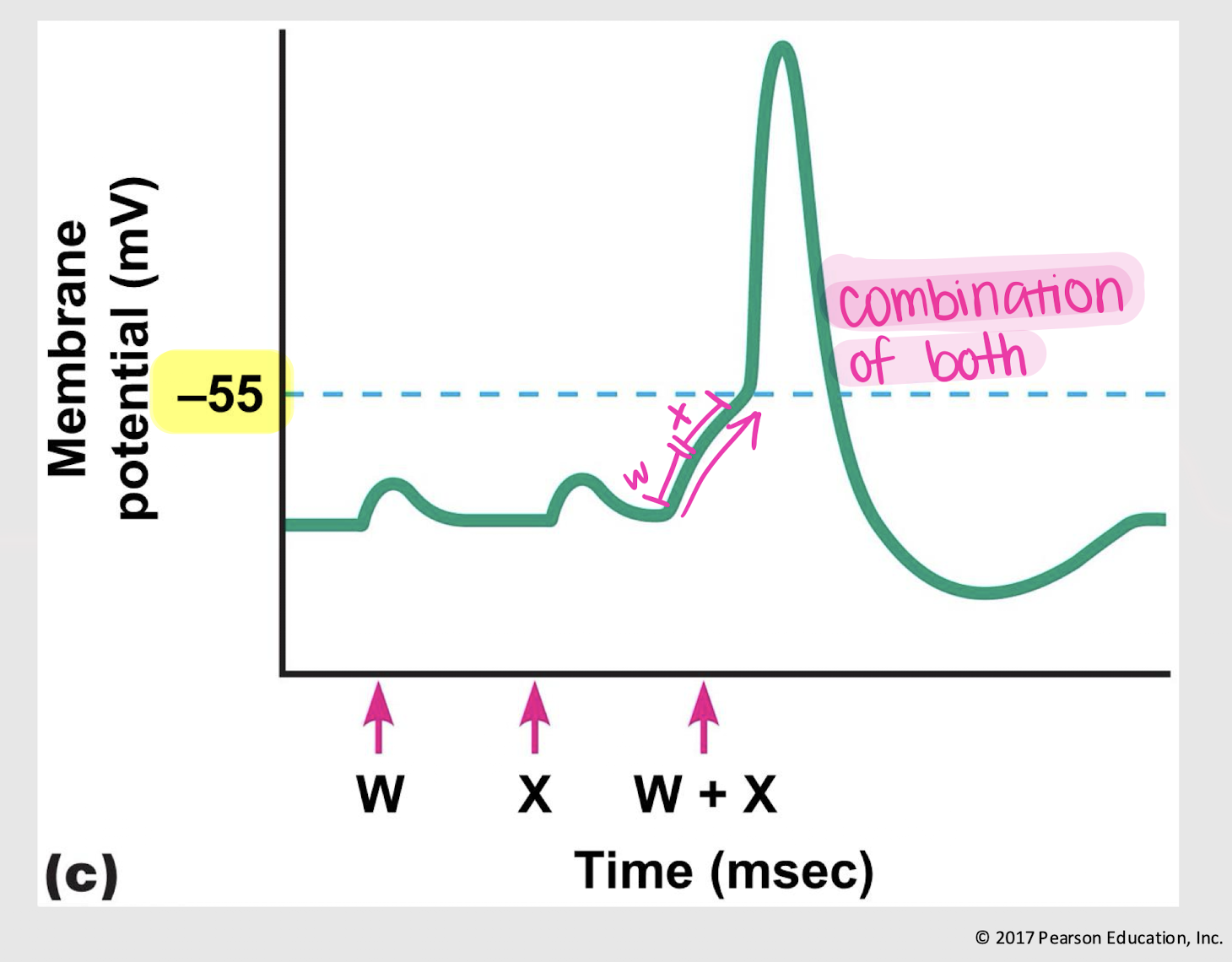
spatial summation
process of adding together graded potentials from multiple synapses at different locations on the neuron, increasing the likelihood of reaching the threshold for action potential generation.
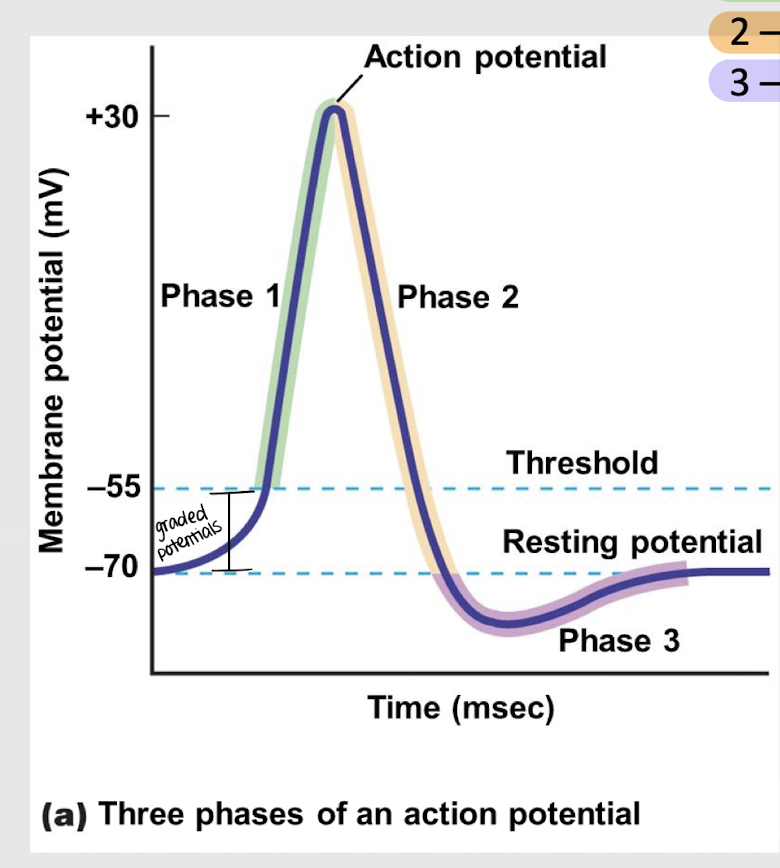
depolarization
What is phase 1 of an action potential?
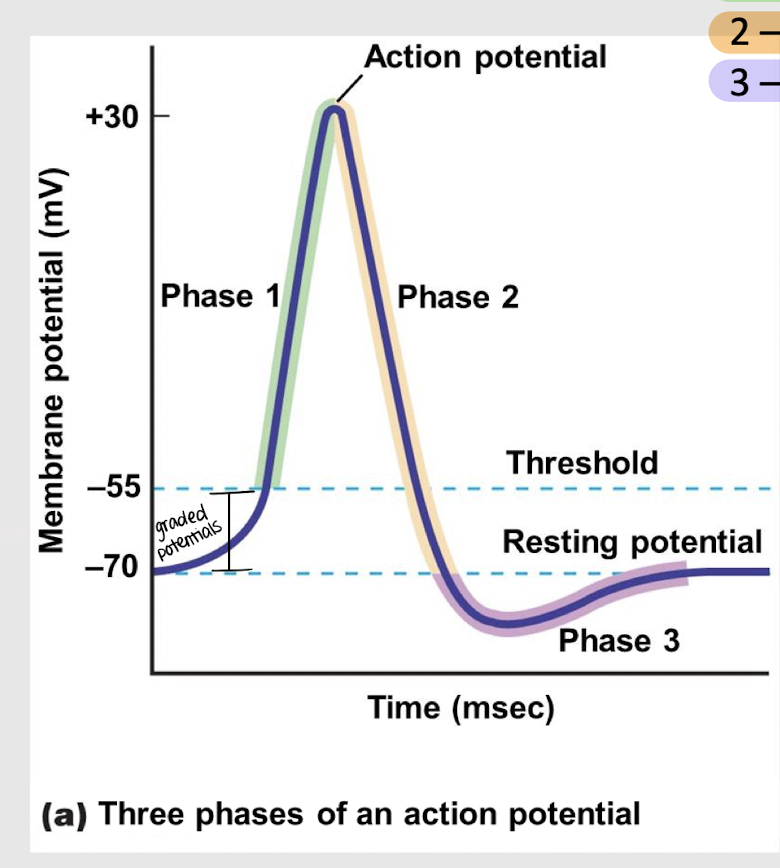
repolarization
What is phase 2 of an action potential?
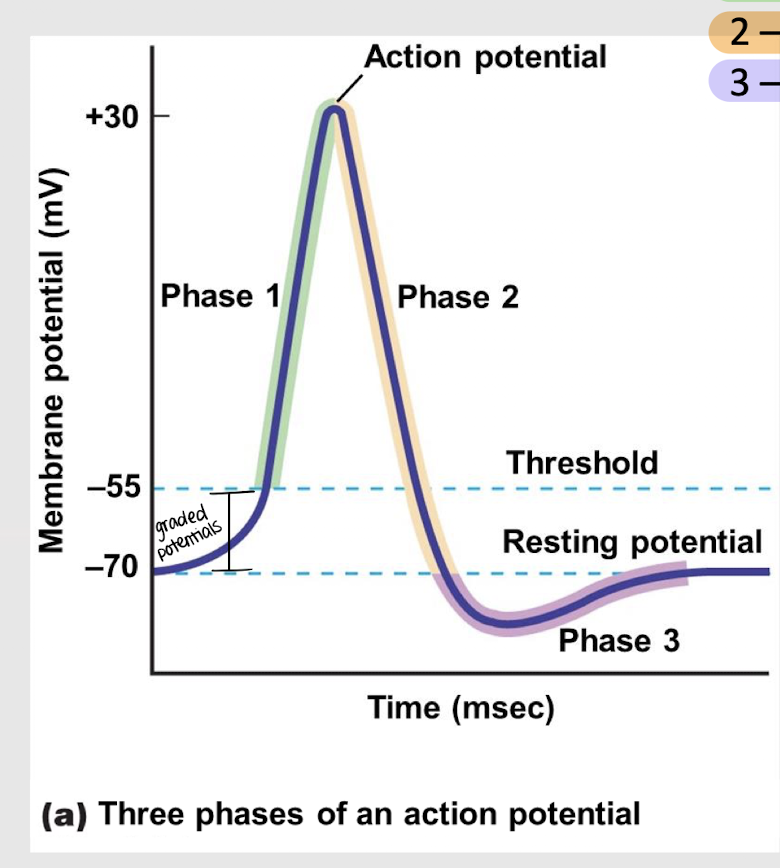
hyperpolarization
What is phase 3 of an action potential?
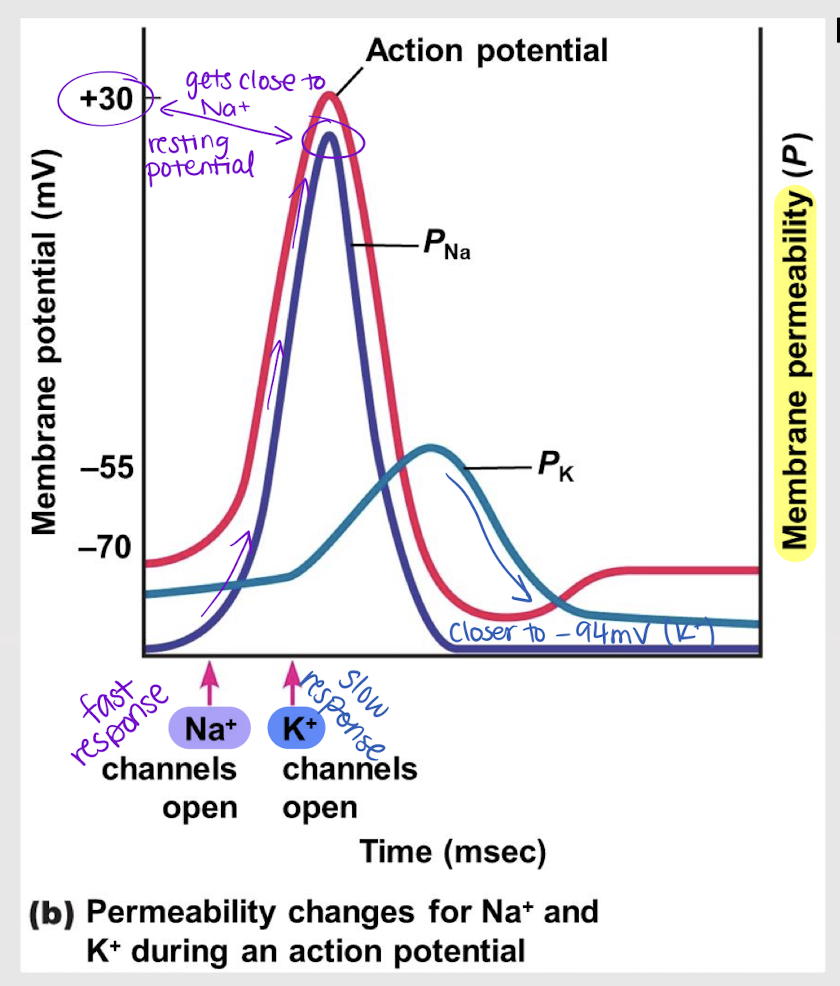
fast
During an action potential, the influx of Na+ ions is slow/fast.

slow
During an action potential, the efflux of K+ ions is slow/fast.
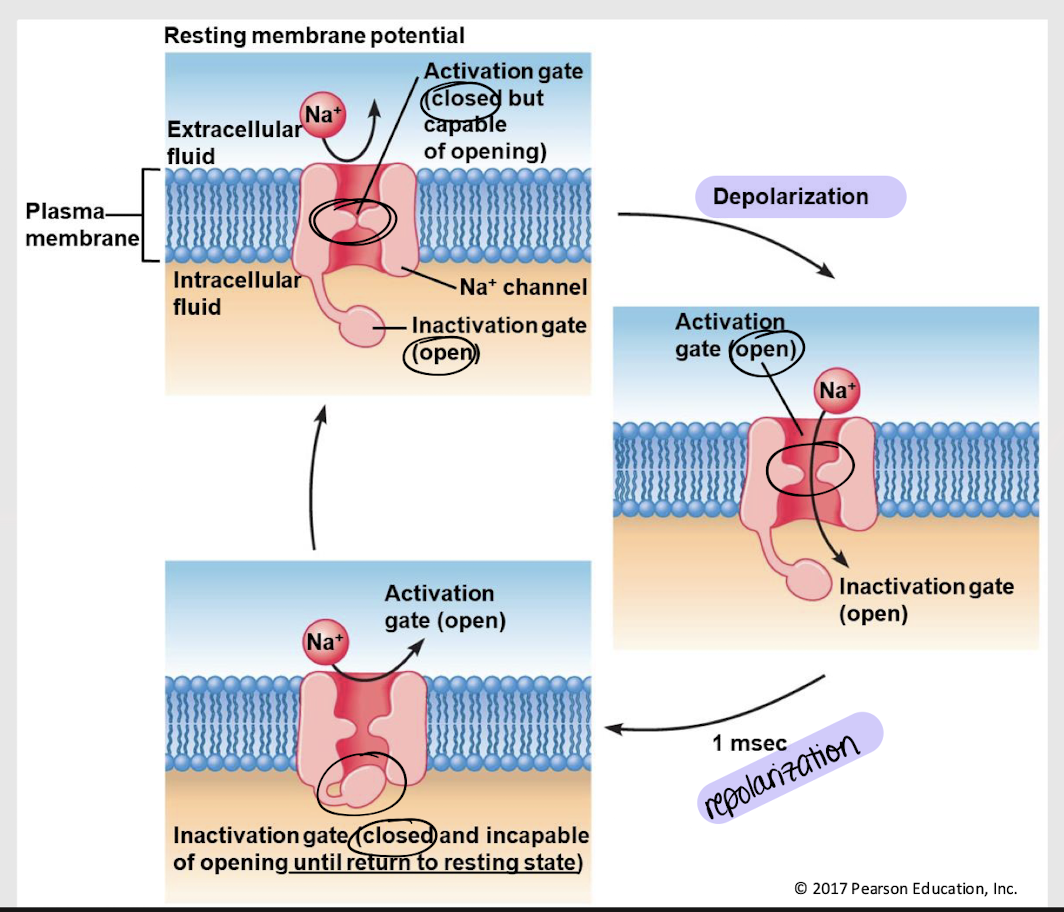
closed; open; open; open; open; closed
In voltage-gated Na+ channels (ONLY)…
At resting membrane potential, the activation gate is open/closed and the inactivation gate is open/closed
During depolarization, the activation gate is open/closed and the inactivation gate is open/closed.
During repolarization, the activation gate is open/closed and the inactivation gate is open/closed.
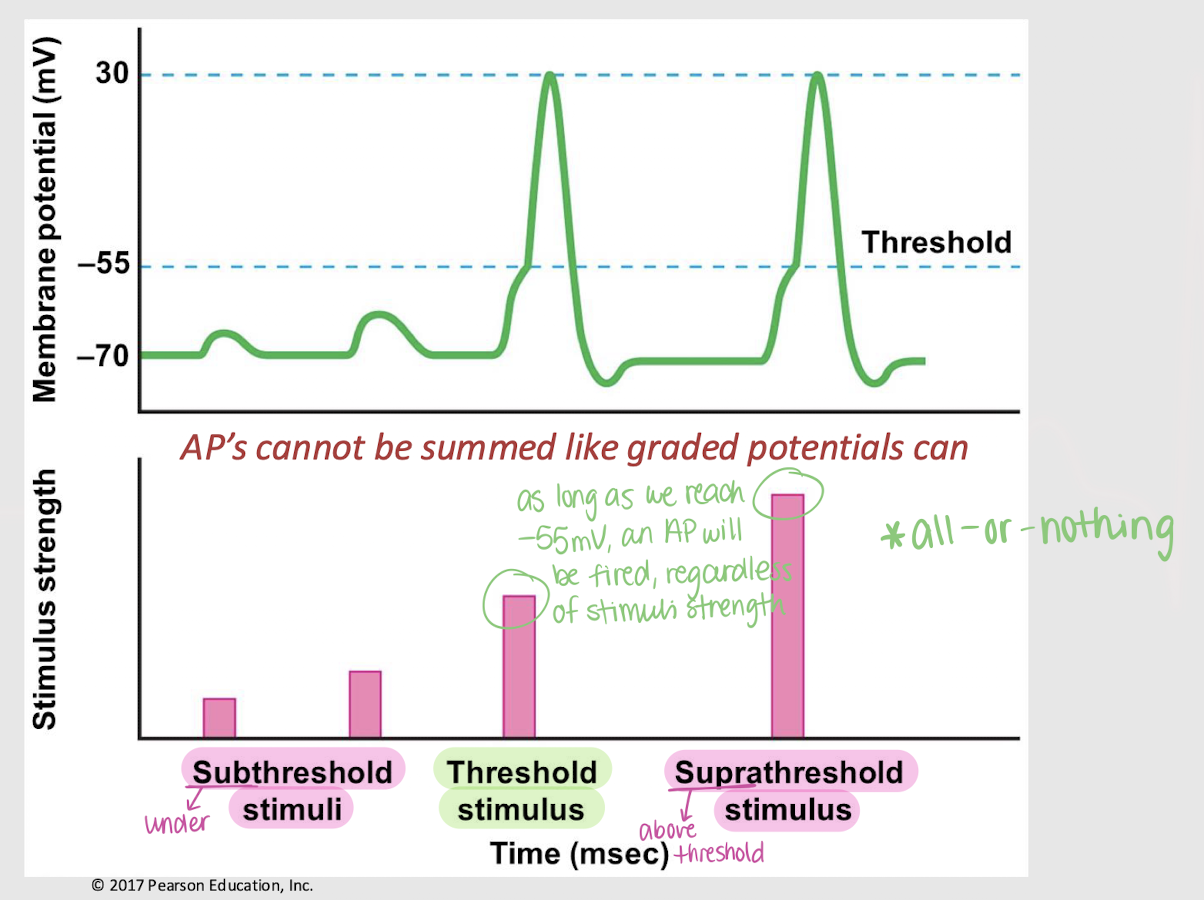
subthreshold stimulus
A stimulus that is below the threshold and therefore unable to trigger an action potential.
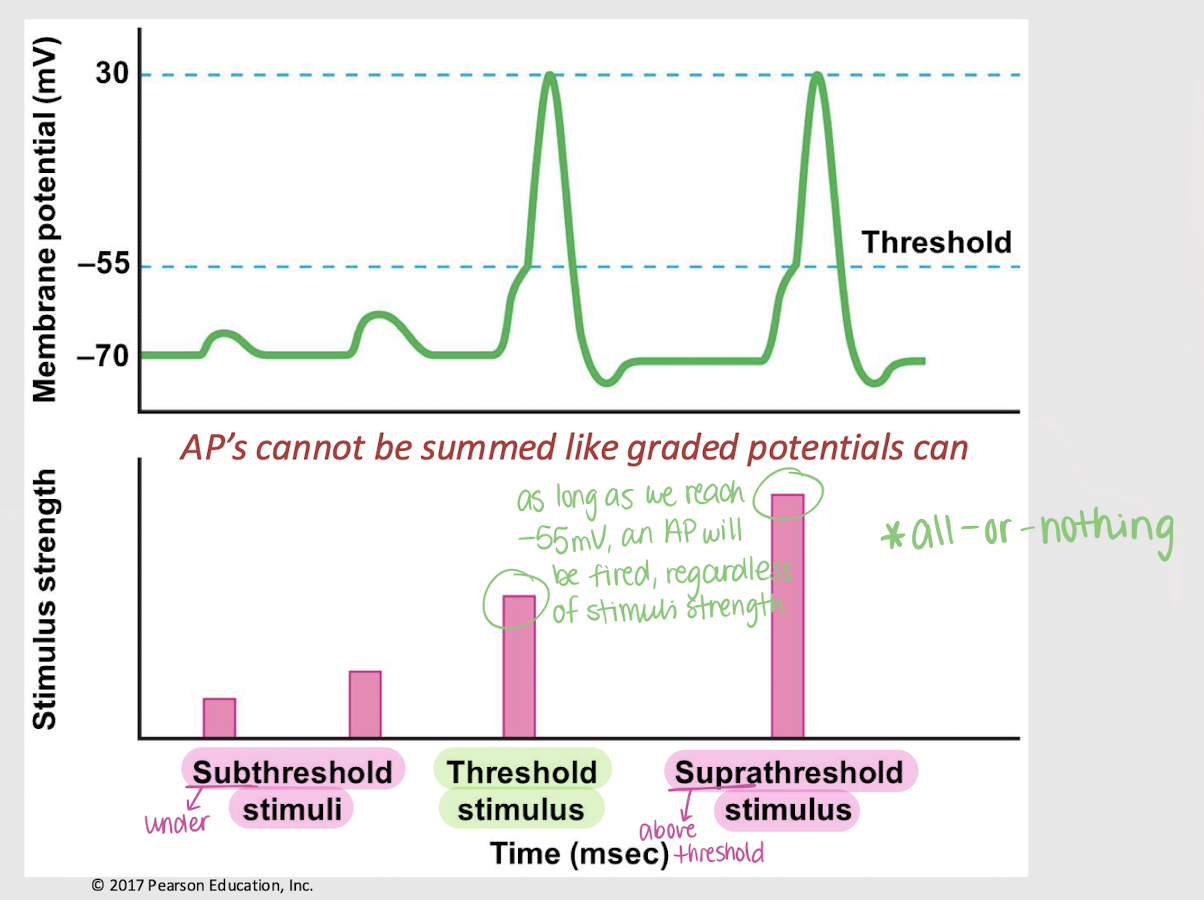
threshold stimulus
A stimulus that is at the threshold and therefore triggers an action potential.
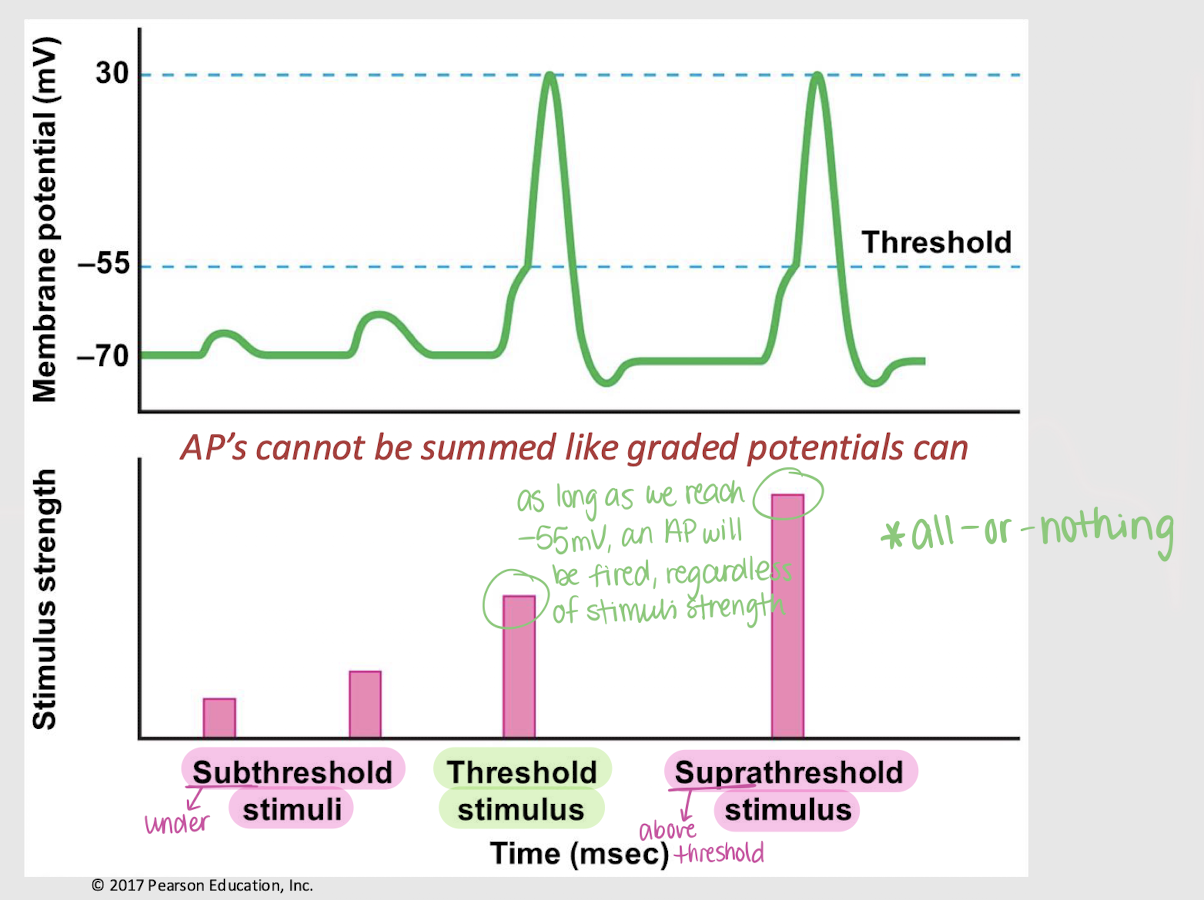
suprathreshold stimuli
A stimulus that is above the threshold and therefore triggers one or multiple action potentials
refractory period
Period during and immediately after an action potential in which the membrane is less excitable than at rest.
refractory; overlap
In comparison to graded potentials, action potentials cannot sum due to _________ periods that prevent ________ in APs.
frequency
Since action potentials are not graded, they “code” for the strength of a stimulus through their…
False
True or False: Action potentials can travel in either direction on an axon.
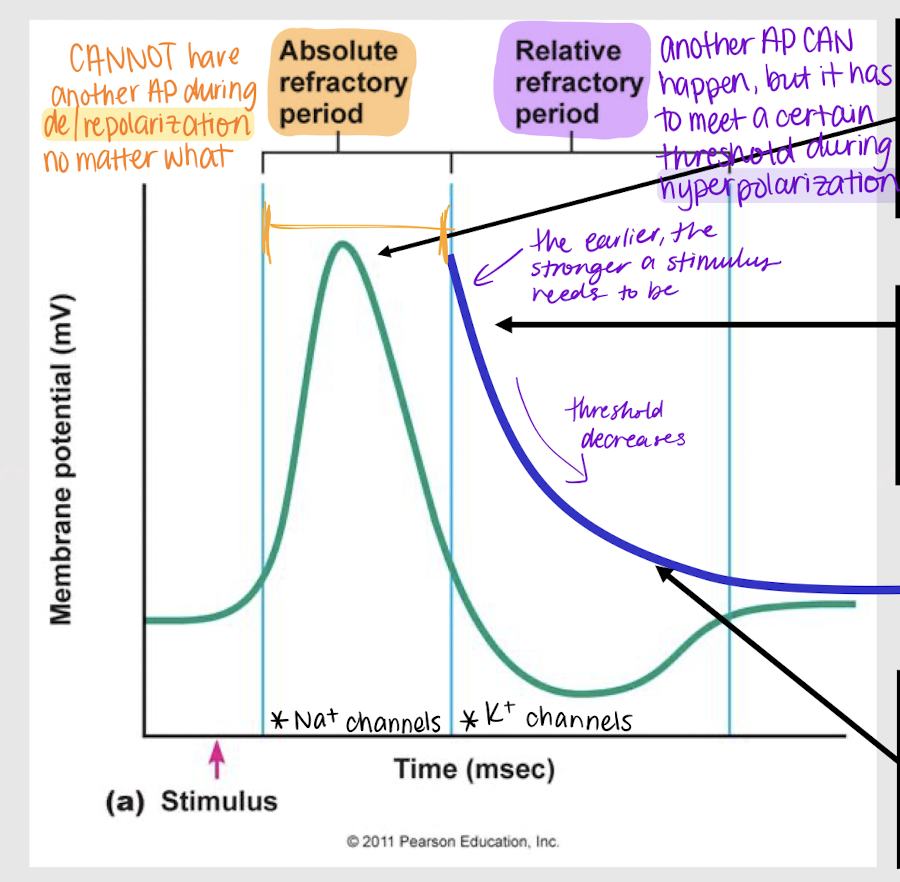
absolute refractory period
Period where a neuron CANNOT have another action potential during depolarization and repolarization no matter what.
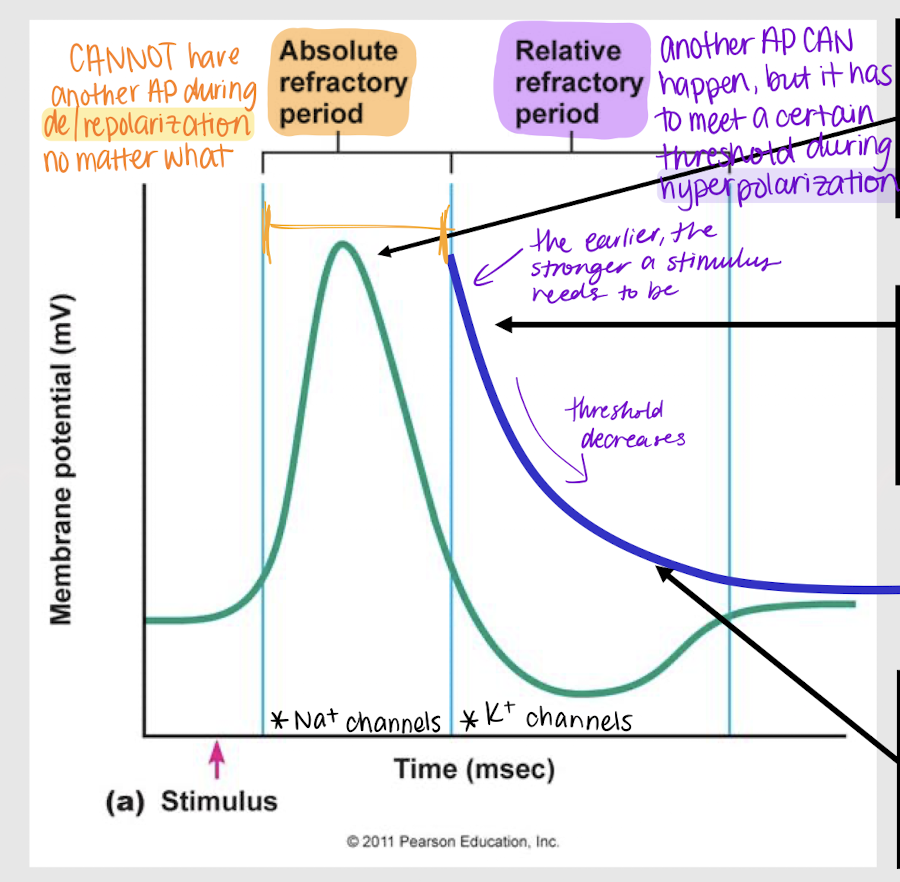
relative refractory period; stronger; weaker
Period where a neuron CAN have another action potential BUT a stimulus must meet a certain threshold during hyperpolarization.
The earlier during hyperpolarization that a stimulus wants to produce an action potential, the stronger/weaker it has to be. The later, the stronger/weaker it has to be.
True
True or False: During hyperpolarization/relative refractory period, the threshold will ALWAYS have to be greater than -55mV.
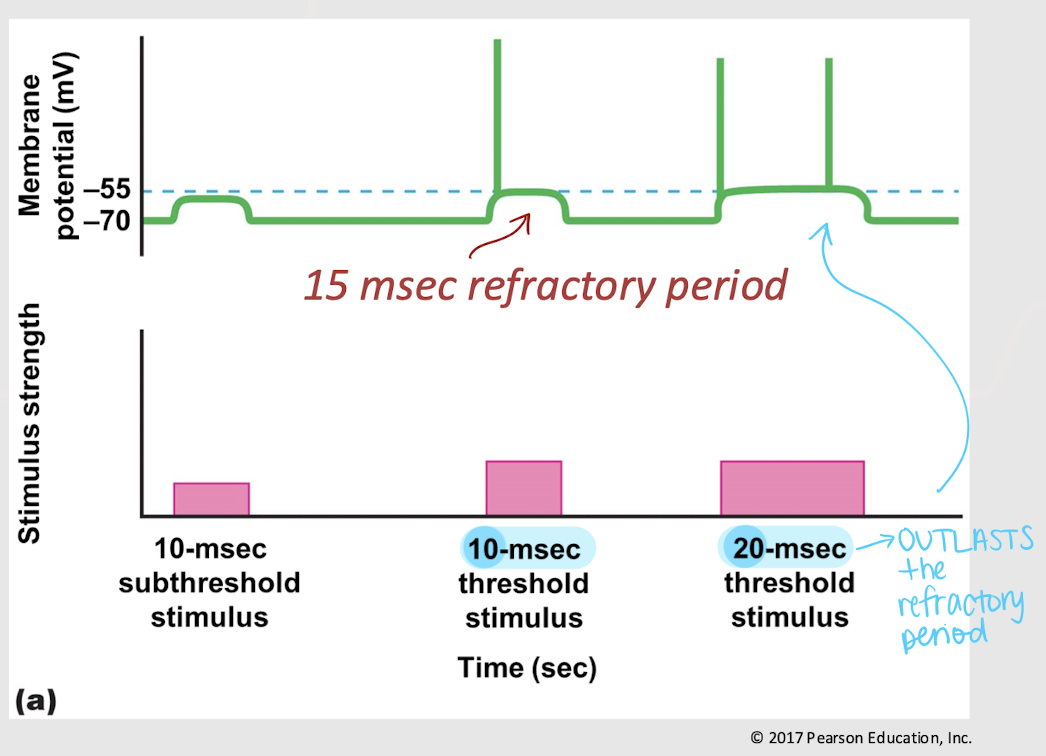
True
True or False: If a threshold stimulus outlasts the refractory period, another action potential can occur.
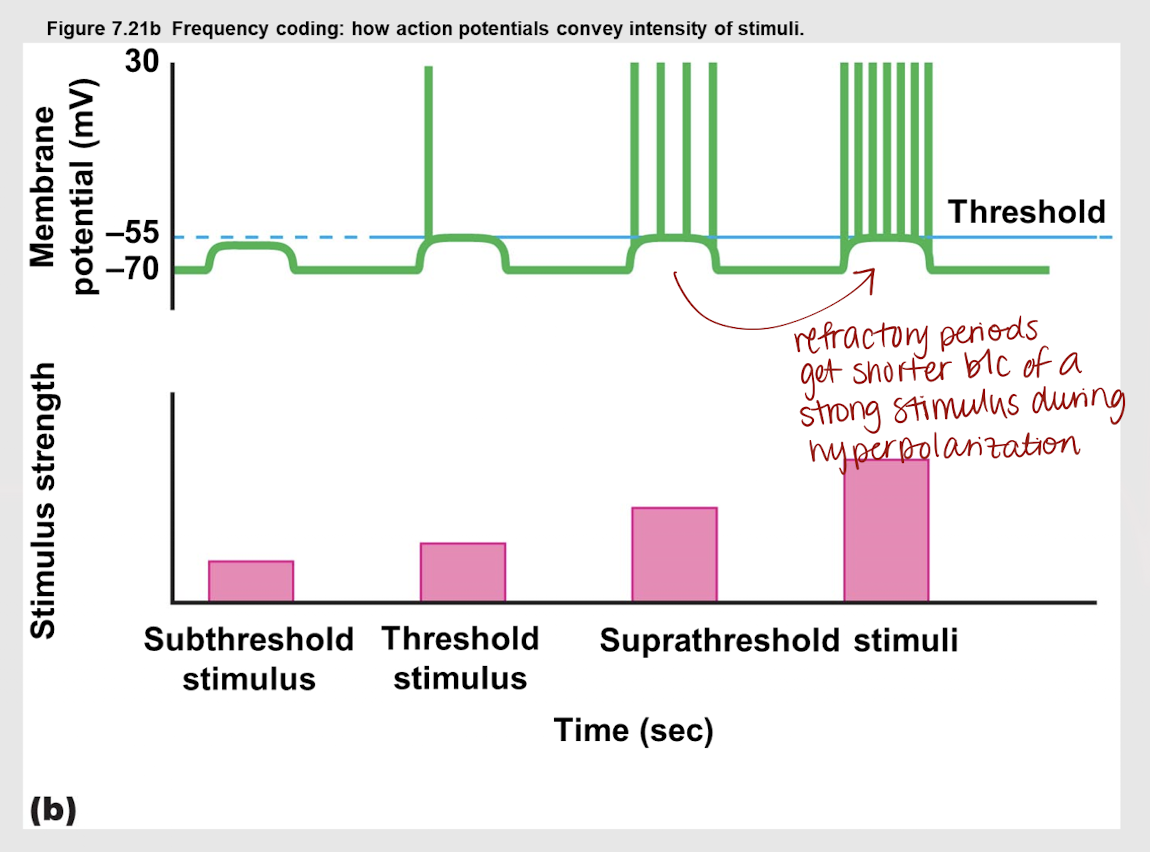
more; supra; relative
Firing occurs ______ frequently w/ increasing ______-threshold stimuli b/c action potentials can be generated earlier and earlier in the _______ refractory period.
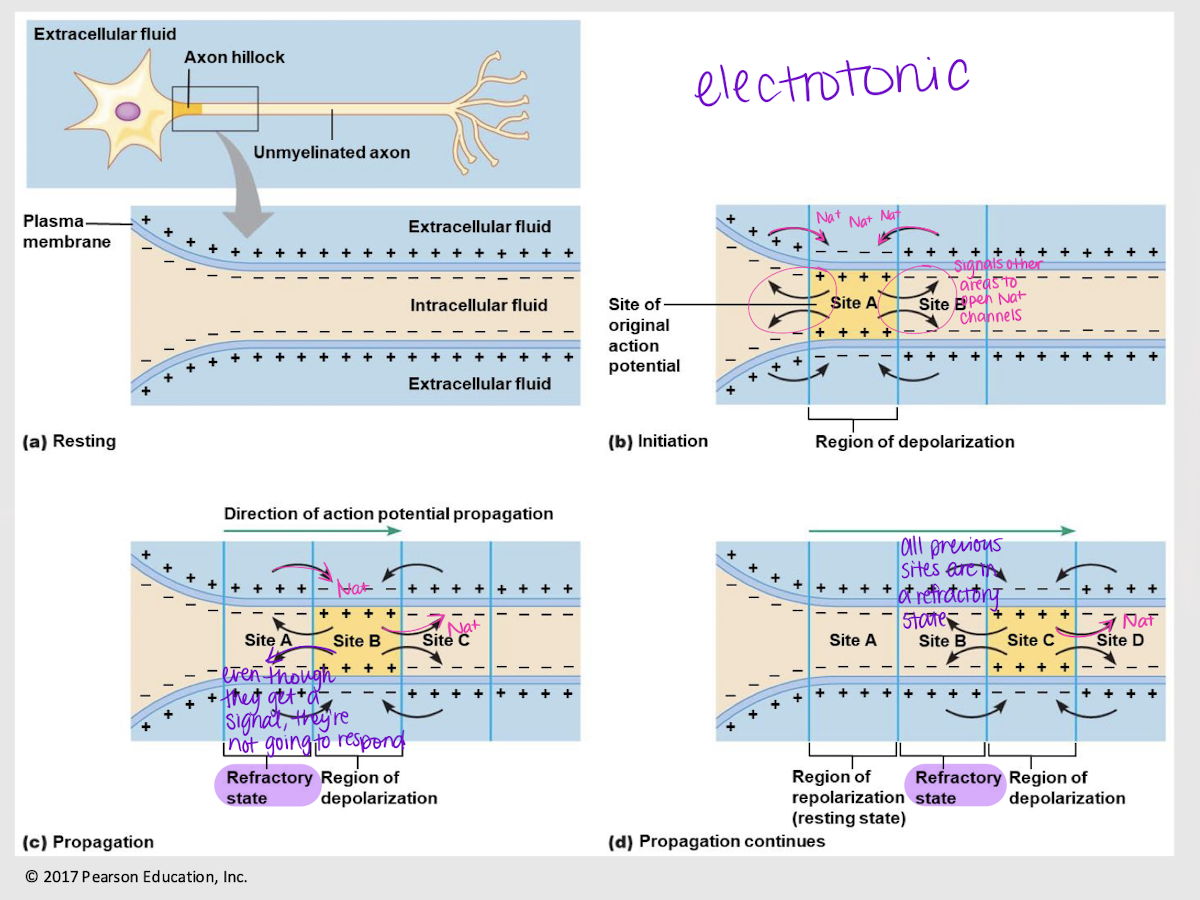
electrotonic propagation; Na+
Process where a nerve impulse travels along the neuron. When one site has an action potential, it signals the following area to open ____ channels, and so on.
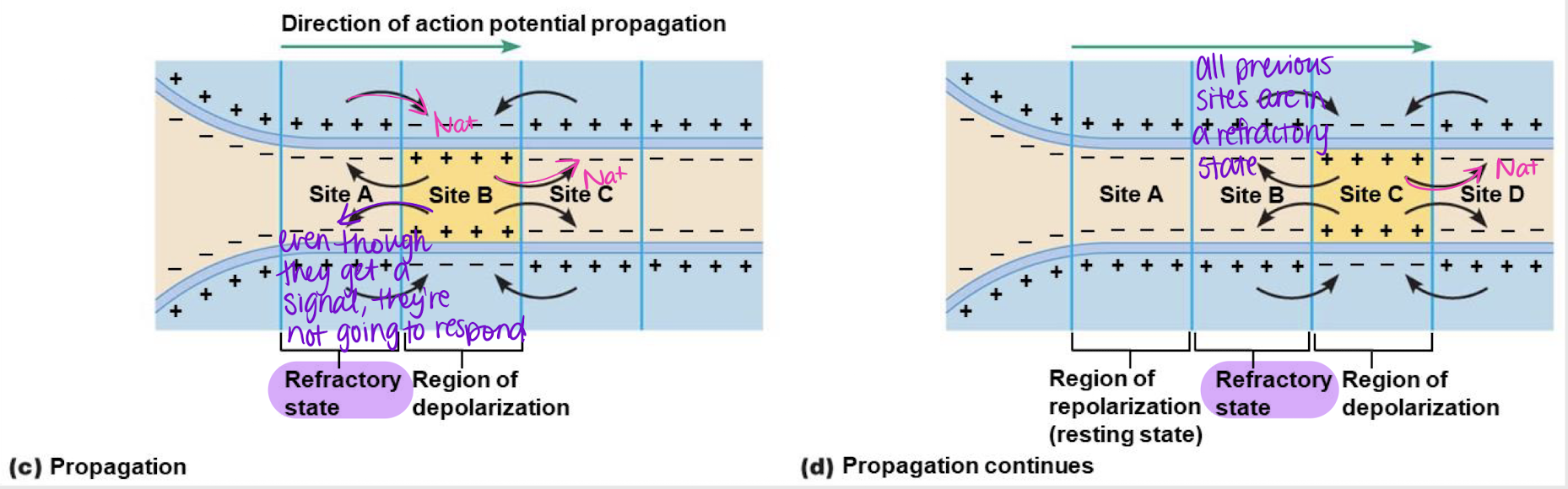
False
True or False: When a subsequent site releases Na+, this will signal the previous site to open their channels again.
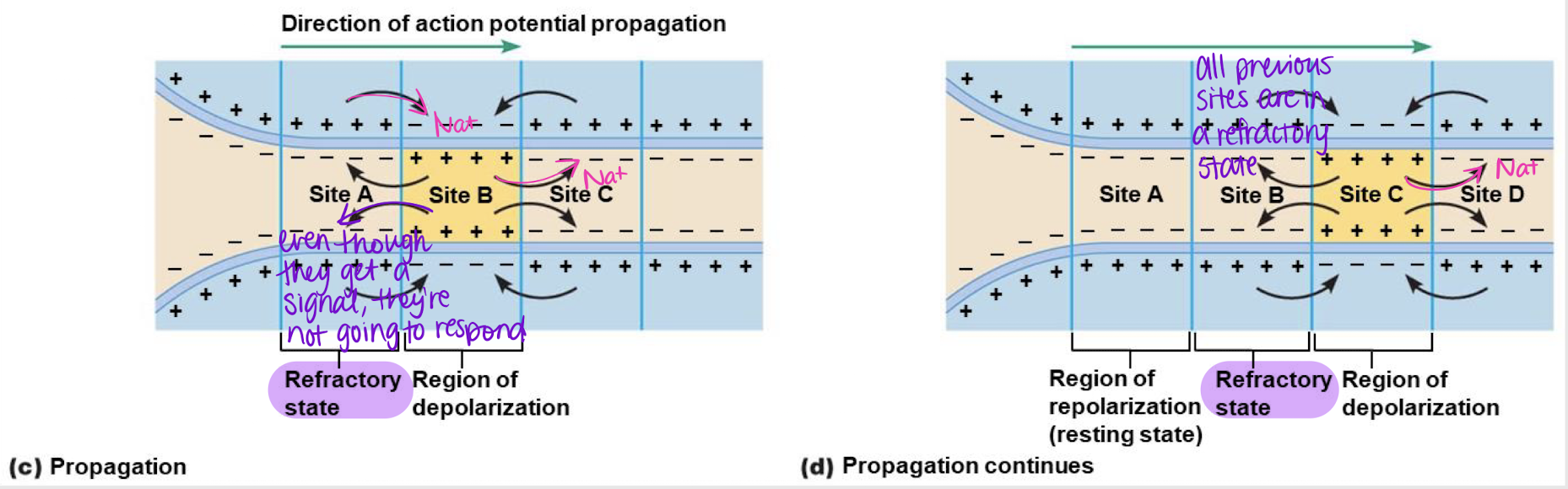
relative refractory state/period
Previous sites on a neuron will not respond to Na+ coming from subsequent site b/c they are in a…
False
True or False: Saltatory propagation can occur in both myelinated and unmyelinated axons.
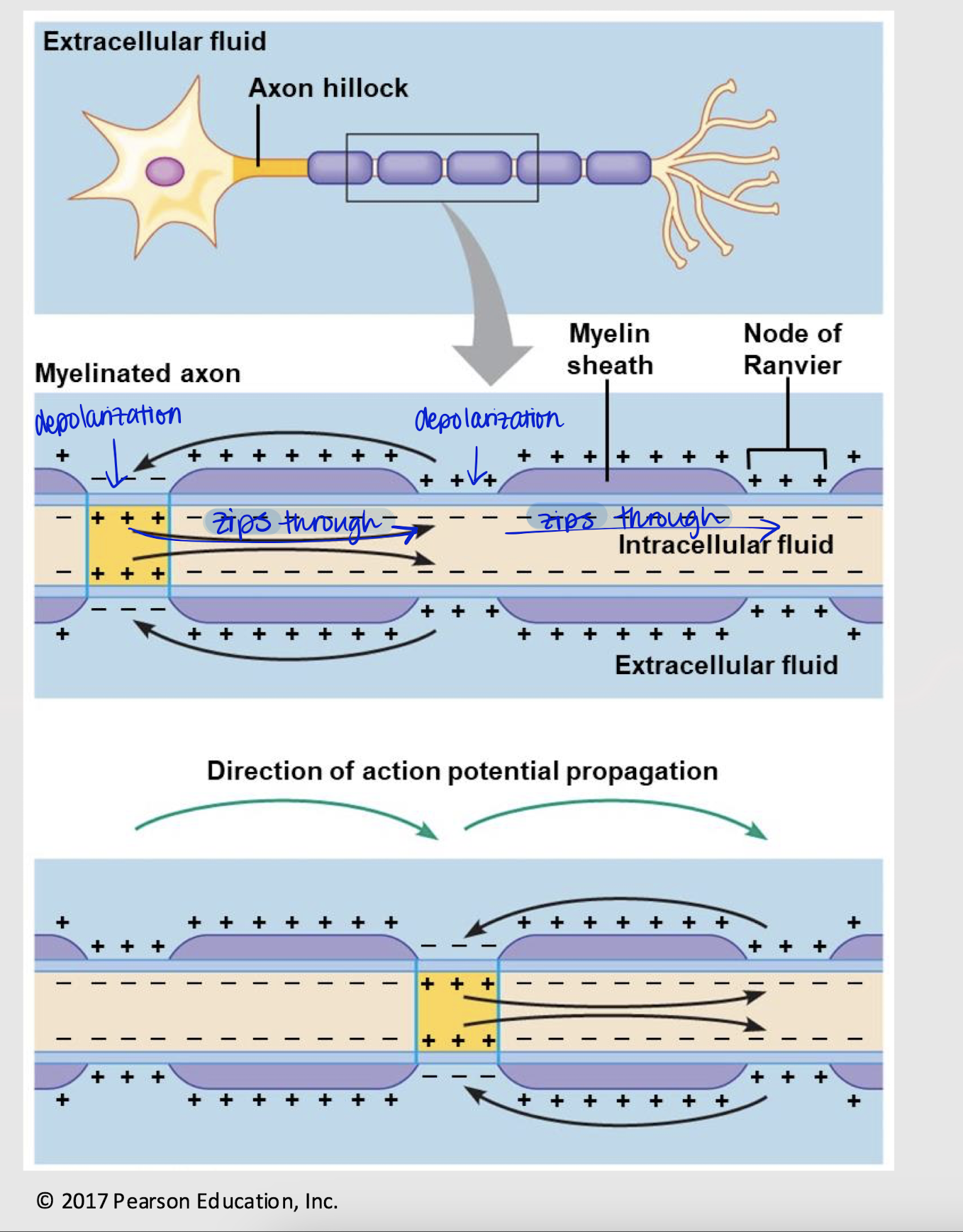
saltatory propagation
Rapid transmission of electrical impulses on a myelinated neuron. Characterized by Na+ “zipping through” myelinated areas on the axon after depolarization at Nodes of Ranvier.
axon diameter and myelination
What are two factors affecting speed of propagation?
True
True or False: The larger an axon’s diameter, the faster the propagation.
A fibers
? fibers — large diameter, myelin present
B fibers
? fibers — small diameter, myelin present
C fibers
? fibers — small diameter, no myelin present
A fibers
Which nerve fibers are the fastest?
C fibers
Which nerve fibers are the slowest?
Tetrodotoxin (TTX)
Neurotoxin that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels, which can be fatal
Novocaine
Local anesthetic that blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels