Momentum and Impulse
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1008: Dynamic Systems - Lecture 17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Law of conservation of momentum
The momentum of a system is constant if no external forces are acting on the system.
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
Conservation of momentum and Newton’s First Law
An object that continues to maintain its state of rest or motion unless or until it is acted upon by an external force.
Conservation of momentum and Newton’s Third Law
A force applied by an object A on object B, object B exerts back an equal force in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
Change in momentum
m(v - u)
Conservation of momentum equations
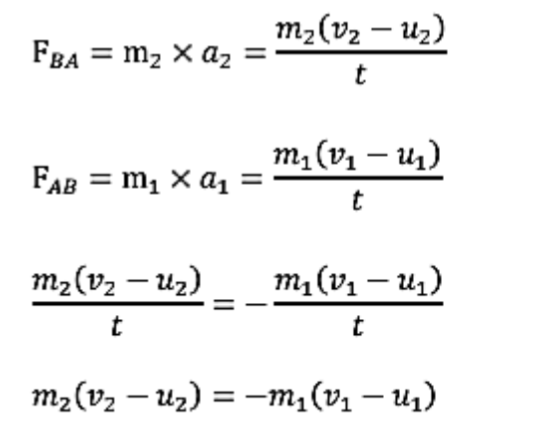
Impulse
The force acting on an object and the time interval the force is exerted.
Impulse - momentum theorem
The impulse applied to an object will be equal to the change in its momentum.
Faverage = m(v2 - v1)/Δt
Newton’s Second Law and linear momentum
The resultant (net) force is proportional to an object’s rate of change in linear momentum.
Linear momentum
G = mv
Resultant force and linear momentum
ΣF = d(mv)/dt = dG/dt
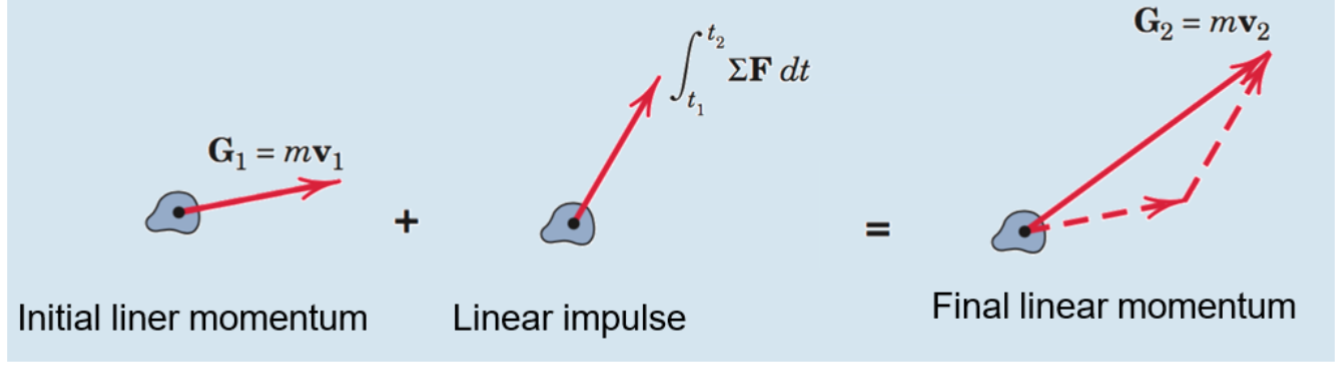
Linear impulse-momentum principle
G1 + ∫ΣF dt = G2
where the integral is constrained by t1 and t2.
Linear impulse - momentum principle in components
m(v1)x + ∫ ΣFx dt = m(v2)x
m(v1)y + ∫ ΣFy dt = m(v2)y
m(v1)z + ∫ ΣFz dt = m(v2)z
Use of the linear impulse - momentum principle
Provides a direct means of obtaining the particle’s final velocity v2 after a specified time period when the particle’s initial velocity v1 is known and the forces acting on the particle are either constant or can be expressed as functions of time.
Finding v2
Apply ΣF = ma to obtain a, then integrate a = dv/dt to obtain v2.
Impulse - momentum diagram
Conservation of linear momentum
If the resultant force on the particle is zero, i.e. ΣF = 0.
G1 = G2
In this case, the linear momentum of the particle is said to be conserved.
Applications of impulse momentum
Pitching machine
Crane mounted hammer