Waves
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the three types of mechanical waves?
Longitudinal, transverse, and torsional (rotational).
What is required for a mechanical wave to travel?
A medium (solid, liquid, or gas).
In a longitudinal wave, how do particles move relative to the wave?
In the same direction as the wave travels (parallel).
In a transverse wave, how do particles move relative to the wave?
Perpendicular (90°) to the direction of wave travel.
What is a torsional wave?
A wave that twists or rotates the medium around its axis (e.g., twisting a rope).
What are the three essential properties of a wave?
Wavelength, frequency (or period), and amplitude.
What does amplitude represent?
The maximum displacement from the rest position — relates to wave energy.
What is wavelength (λ)?
The distance between two identical points on adjacent waves (e.g., crest to crest).
What is frequency (f)?
The number of cycles (waves) that pass a point in one second; measured in Hz.
What is period (T)?
The time it takes to complete one full wave cycle; measured in seconds.
How are frequency and period related?
They are reciprocals: f = 1/T and T= 1/f
What is the equation for wave speed?
v=fλ
How does wave speed change with temperature?
As temperature increases, wave speed increases (directly proportional).
In which medium do waves travel fastest: solid, liquid, or gas?
Solid (because particles are closer together).
How does string length affect wave speed?
Longer string = higher wave speed.
How does tension affect wave speed?
Greater tension = higher wave speed.
How does mass per unit length affect wave speed?
Lower mass = higher wave speed.
What is Snell's Law formula?
n1sin(θ1)=n2sin(θ2)
What does Snell’s Law calculate?
The angle of refraction when a wave passes from one medium to another.
What happens to wave speed when moving to a denser medium (higher index)?
Wave slows down, and the angle of refraction bends toward the normal.
What do compressions and rarefactions represent?
Compressions = high pressure areas, Rarefactions = low pressure areas in longitudinal waves.
What unit is frequency measured in?
Hertz (Hz) or 1/s.
What unit is wave speed measured in?
Usually m/s or cm/s.
What unit is wavelength measured in?
Metres (m) or centimetres (cm).
What is one complete wave cycle?
A crest and a trough in transverse, or a compression and rarefaction in longitudinal.
A light wave passes from air (n1=1.00) into water (n2=1.33n) at an angle of incidence of 30. What is the angle of refraction?
The angle of refraction is approximately 22°.
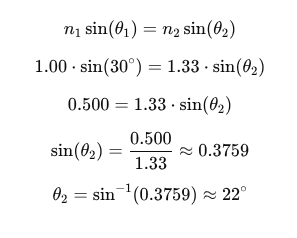
What is the difference between a mechanical wave and an electromagnetic wave?
A mechanical wave requires a medium (solid/liquid/gas); an electromagnetic wave does not (can travel in a vacuum).
What shape do wave graphs usually follow?
Sinusoidal (sine wave), representing periodic motion.
What are compressions and rarefactions?
In a longitudinal wave: compressions = particles pushed together; rarefactions = particles spread out.
What’s the difference between transverse and longitudinal wave diagrams?
Transverse: shows crests/troughs. Longitudinal: shows compressions/rarefactions.
What causes wave speed to increase in a string?
Higher tension, lower mass, or longer string length.
What is the standard unit for wave period?
Seconds (s).
What is one complete wave cycle?
One full crest and one full trough, or one compression and one rarefaction.
What does it mean if a wave has a high frequency?
More wave cycles per second; shorter wavelength.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
They are inversely proportional: as frequency increases, wavelength decreases (if speed is constant).