Ventricles, Choroid, Meninges
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
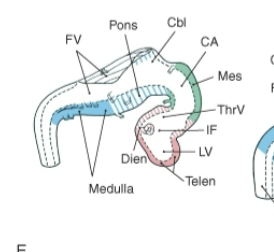
Ventricular System
A network of interconnected cavities within the brain that is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
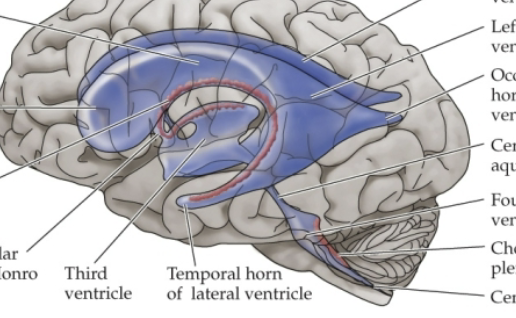
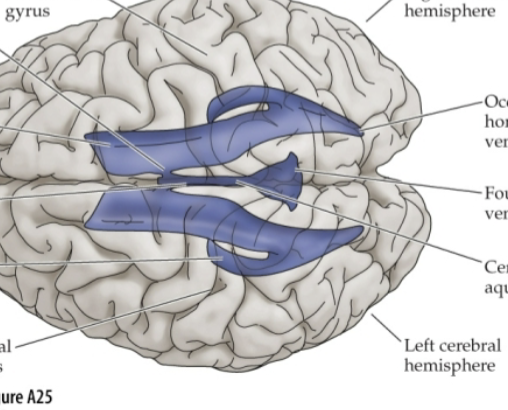
Lateral ventricles
Within and associated to the telencephalon.
Third ventricle
At the center of the brain within the diencephalon.
Fourth ventricle
Associated with the rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
Rhomboid fossa
A diamond-shaped depression located on the floor of the fourth ventricle in the brainstem.
Choroid Plexus
Located within the ventricles and secretes cerebrospinal fluid, filling the ventricles and subarachnoid space.
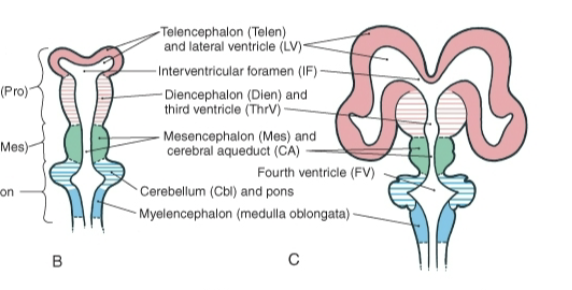
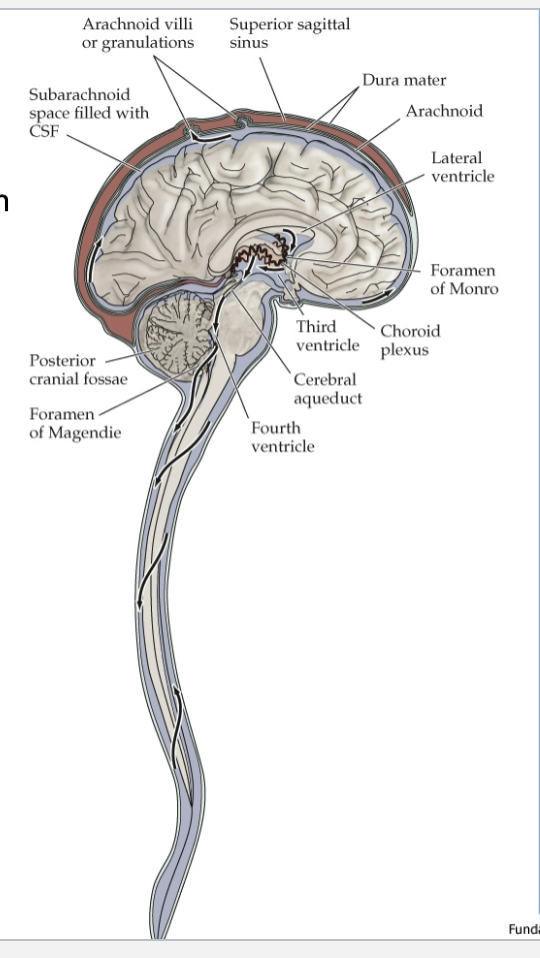
Interventricular foramen
Connects the Lateral ventricle + Third ventrical
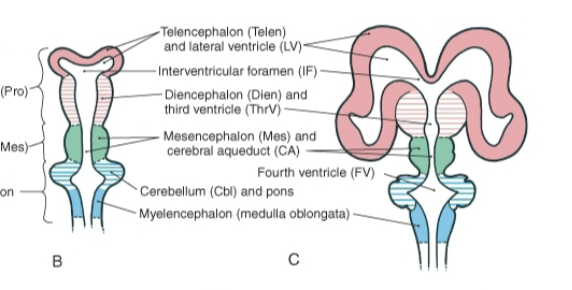
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects the Third and Fourth ventricle.
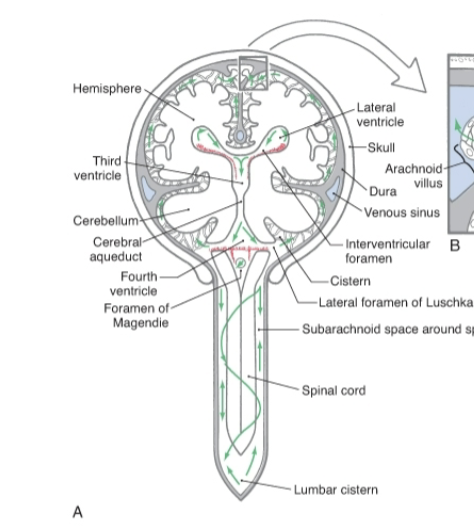
Cerebrospinal fluid
Produced within the ventricles by choroid plexus and serves to cushion and nourish the brain.
Foramen of Lushka and Magendie
The caudal part of the roof is deficient centrally as the median aperture of the fourth ventricle through which cerebrospinal fluid, formed in the ventricular system, escapes into the subarachnoid space.
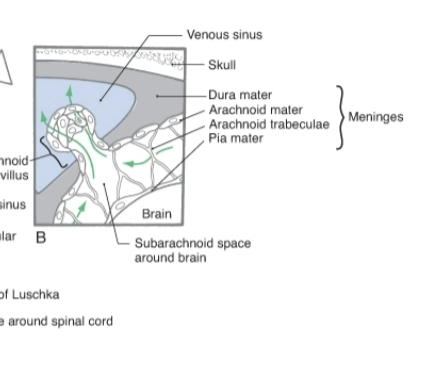
Arachnoid villa
Small projections act as one-way valves to drain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain into the venous system.
Dura mater
A tough, fibrous membrane that forms the outermost layer of the meninges, which are the protective coverings of the brain and spinal cord.
Separated by epidural space from vertebrate.
Epidural space
The area between the spinal dura mater and the vertebral column. Contains fat, blood vessels, and other tissues.
Arachnoid space (Spinal cord)
A spiderweb-like middle layer filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and contains blood vessels.
Contains arachnoid villa in brain
Pia mater
The innermost layer of the meninges, the membrane that directly covers and protects the brain and spinal cord.
surface of brain
pial specializations
Superior sagittal sinus
Large venous channel located along the midline of the brain within the dura mater, primarily responsible for draining venous blood from the brain.
Faix cerebri
A sickle-shaped fold of the dura mater that extends into the longitudinal fissure between the two hemispheres of the brain, providing support and separation for the cerebral hemispheres. It contains important structures such as the superior sagittal sinus.
Faix cerebelli
A vertical fold of dura mater that separates the two lobes of the cerebellum.
Astrocyte
Star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord that play a key role in supporting neurons. They are involved in maintaining the blood-brain barrier, supplying nutrients to nervous tissue, repairing brain injuries, and regulating blood flow.
Blood-Brain Barrier
A selective barrier formed by specialized endothelial cells of the brain capillaries, surrounded by a basal lamina, that controls the movement of substances between the bloodstream and the brain, protecting it from potentially harmful components. Also maintains a constant environment for the brain, slowing molecules with high electrical charge.
Brain glymphatic system
A waste clearance system in the central nervous system (CNS) that utilizes astrocytes to facilitate the exchange of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and interstitial fluid.
Arterial perivascular space
A region surrounding blood vessels in the brain where cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) exchanges with interstitial fluid.