Oral Histology LO 2
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
5th week
The formation of the palate starts during what week of prenatal development? This is within the embryonic period.
Primary and secondary
In the 5th week of prenatal development, the palate is formed from 2 separate embryonic structures: ——————— and ——————— palate.
12th week
What week of prenatal development is the palate COMPLETED?
Intermaxillary segment
The development of the —————————— ——————— is from the fused medial nasal process on the inside of the stomodeum. This is an internal wedge shaped mass that extends inferiorly and deep to the nasal pits on the inside of the stomodeum. This develops the primary palate, floor of the nasal cavity and the nasal septum.
Primary (or primitive) palate
The intermaxillary segment gives rise to the ————— palate, the ————— palate will form the pre maxillary part of the maxilla. This is the anterior one third of the final palate. Part of the hard palate that is anterior to the incisive foramen. At this stage of development, the ————— palate serves only as a partial separation between the developing oral cavity proper and the nasal cavity. The formation of this completes the first stage of palate development.
Oronasal membrane
The deepening of the nasal pits produces a nasal sac. This membrane disintegrates. The nasal and oral cavities open posterior to developing the primary palate.
6
Secondary palate formation begins at week:
Palatal shelves (or lateral palatine processes)
In week 6 of prenatal development the bilateral maxillary processes give rise to 2 of ————— —————. These grow inferiorly and deep on the inside of the stomodeum in a vertical direction, along both sides of the developing tongue.
8
In week —, the developing tongue muscles begin to function, the tongue contracts and moves out of the way of the developing palatal shelves.
Secondary
-palatal shelves move into a horizontal position, now superior to developing tongue.
-during week 9, 2 palatal shelves elongate and move medially towards each other, meeting and joining to form the ——————— palate.
- during week 12, the posterior part of the primary palate meets the ——————— palate, and gradually fuses together in an anterior to posterior direction. This gives rise to the posterior 2/3 of the hard palate.
Nasal septum
Growth of the fused medial nasal process (week 9-12).
Median palatine suture
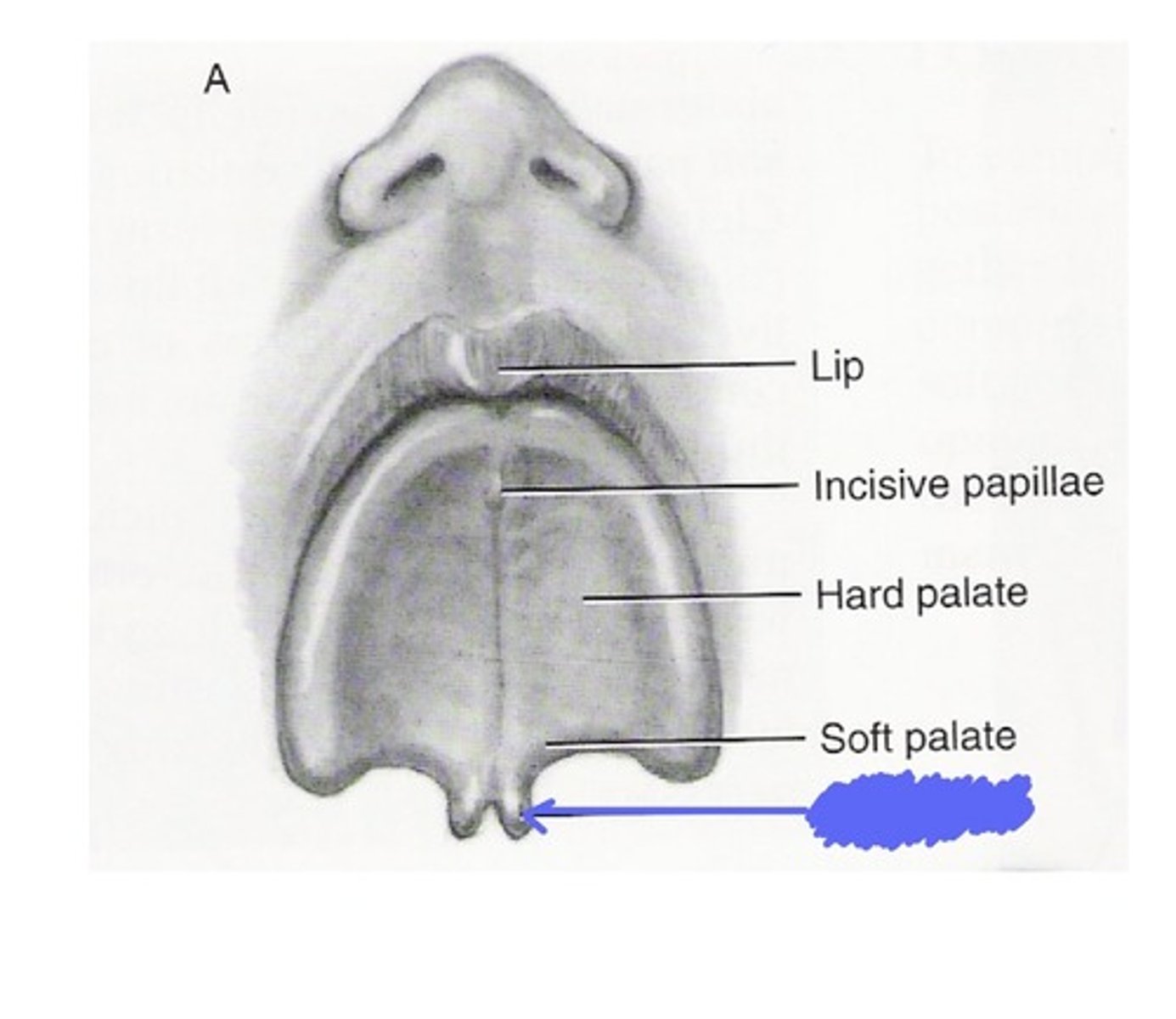
This is on the hard palate, it indicates the line of fusion of the palatal shelves.
Epstein's pearl
This is a developmental disturbance of the palate. A small white papule seen in the midline of the palate of an infant. This represents epithelial tissue that becomes trapped during the palatal fusion.
Cleft uvula (bifid uvula)
This is the least complicated example of cleft palate.
Orofacial clefts.
These are the second most congenital defect. Approximately 1 case of this occurs in every 700 births. There is a 2x higher incidence in males than females. There are 300 identifiable syndromes that are associated with this.
5-12
The nasal cavity forms in the same time frame as the palate, from the — week to the —— week of prenatal development.
Medial nasal processes
The future nasal septum of the nasal cavity is also developing when the palate is forming. The structure of the nasal septum is similar to the primary palate in that they are both a growth from the fused ————— ————— ———————.
Deviated septum
This occurs when the thin wall that makes up the nasal septum inside the nose is displaced to one side.
4-8
The tongue develops during the — to — week of prenatal development. It develops on the floor of the primitive pharynx, formed by the first 4 bronchial arches.
Tuberculum impar
initial part of developing tongue located in midline, on the floor of the primitive pharynx.
1st
In week 6, two oval lateral lingual swellings or copula (from which branchial arch) develop on each side of the tuberculum impar.
Median lingual sulcus
This is a superficial demarcation of the line of fusion of the 2 lateral lingual swellings during the development of the tongue. (as well as of a deeper fibrous structure).
2nd branchial arch or hyoid arch
During the formation of the base of the tongue, the copula gradually overgrows which branchial arch, to form the base of the tongue or posterior one third.
Epiglottic swellings
From the 4th branchial arch, there are ——————— ———————, which develop the most posterior region of the tongue and future epiglottis.
Sulcus terminalis
As the tongue I develops further, the copula of the tongue base, merges with the anterior swellings of the first branchial arch of the tongue body during the 8th week of prenatal development. The fusion is superficially demarcated by the ————— ——————— in the mature dorsal surface of the tongue. An inverted V-shaped groove marking the border between the base of the tongue and its body.