apwh unit 4
1/175
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
176 Terms
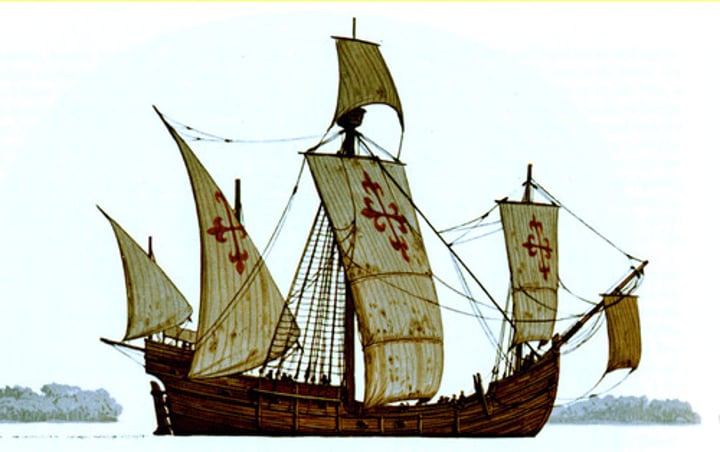
Caravel
A small, highly maneuverable three-masted ship used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic; used for long voyages at great speed from 15th to 17th centuries; used for exploration, not trade

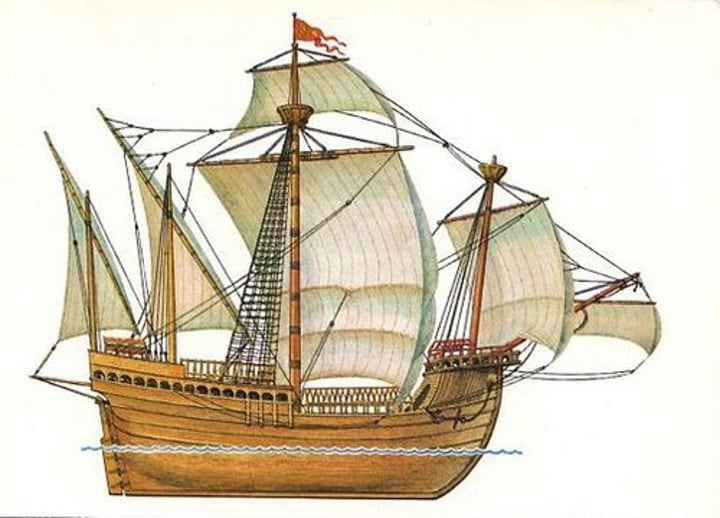
Carrack
a large trading merchant ship operating in European waters (especially by the Portuguese) in the 14th to the 17th century.

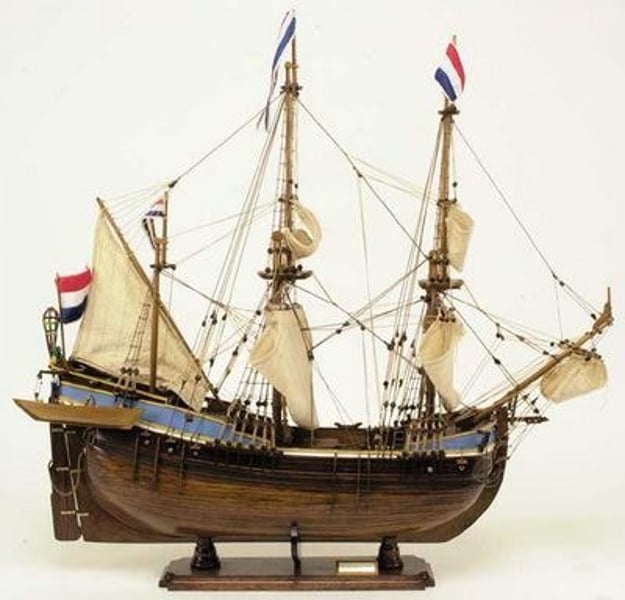
Fluyt
Dutch sailing vessel that allowed them to control the Baltic trade; designed to facilitate transoceanic delivery with max space and crew efficiency; used from 16th to 17th centuries

Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Portuguese prince who promoted the study of navigation and directed voyages of exploration down the western coast of Africa; sponsored seafaring expeditions to search for an all-water route to the east; imported enslaved Africans via the sea

Vasco da Gama
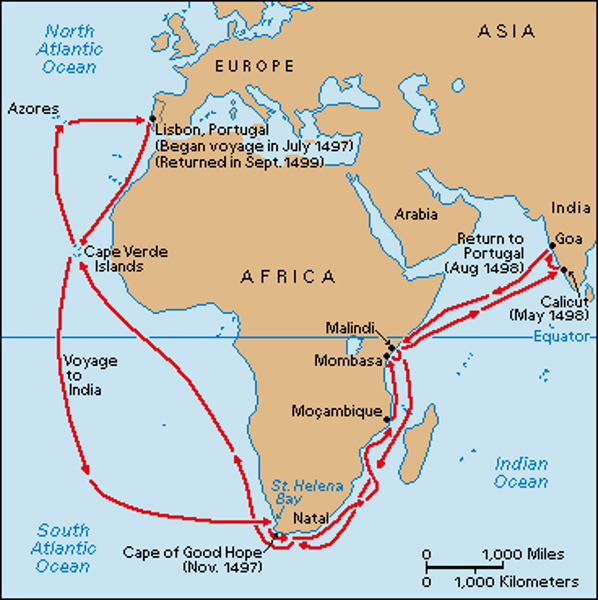
Portuguese explorer. In 1497-1498 he led the first naval expedition from Europe to sail to India, opening an important commercial sea route for Europeans
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese navigator who led the Spanish expedition of 1519-1522 that was the first to sail around the world.
trading post empire
Form of imperial dominance based on control of trade rather than on control of subject peoples; practiced by Europeans in the Indian Ocean as they took over trade from Arab and Muslim merchants
Christopher Columbus
Italian navigator who discovered the New World in the service of Spain while looking for a route to China (1451-1506)
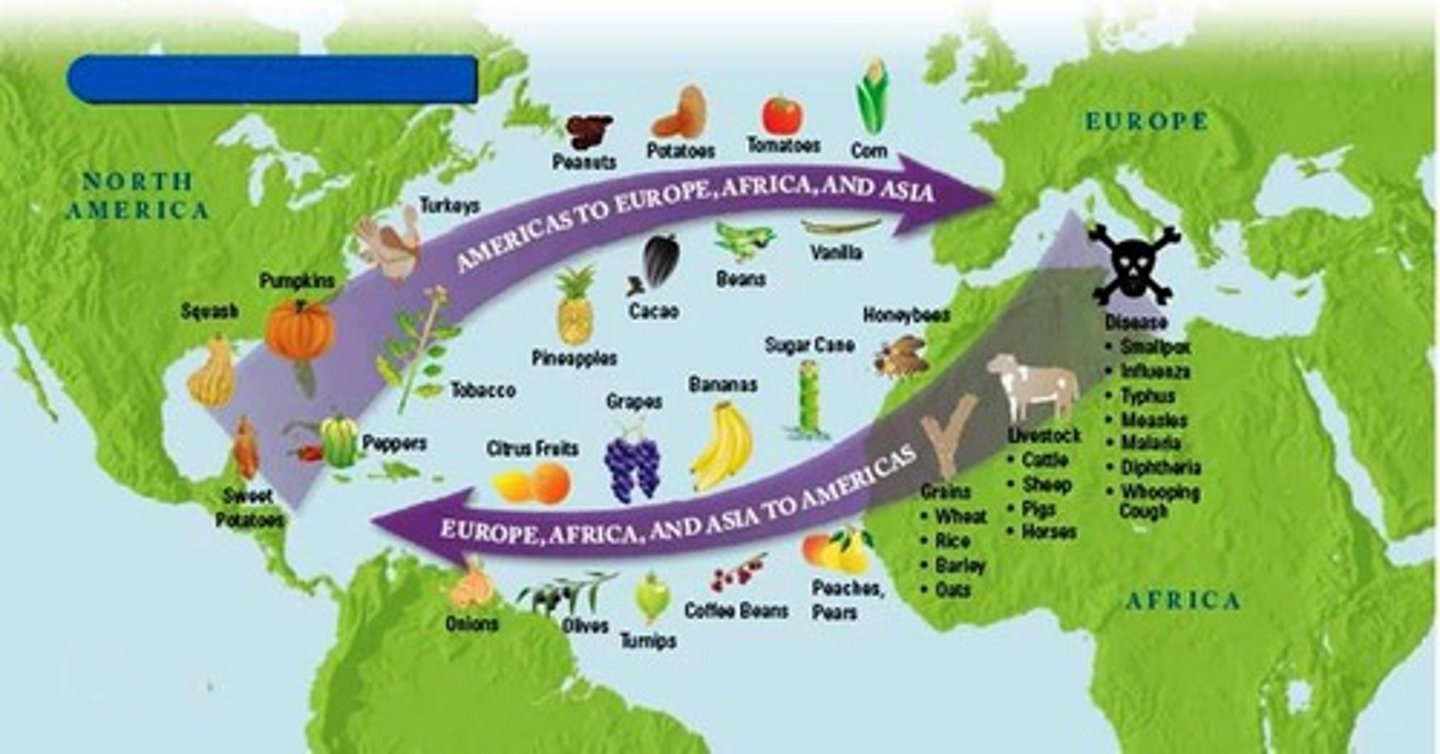
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus' voyages.
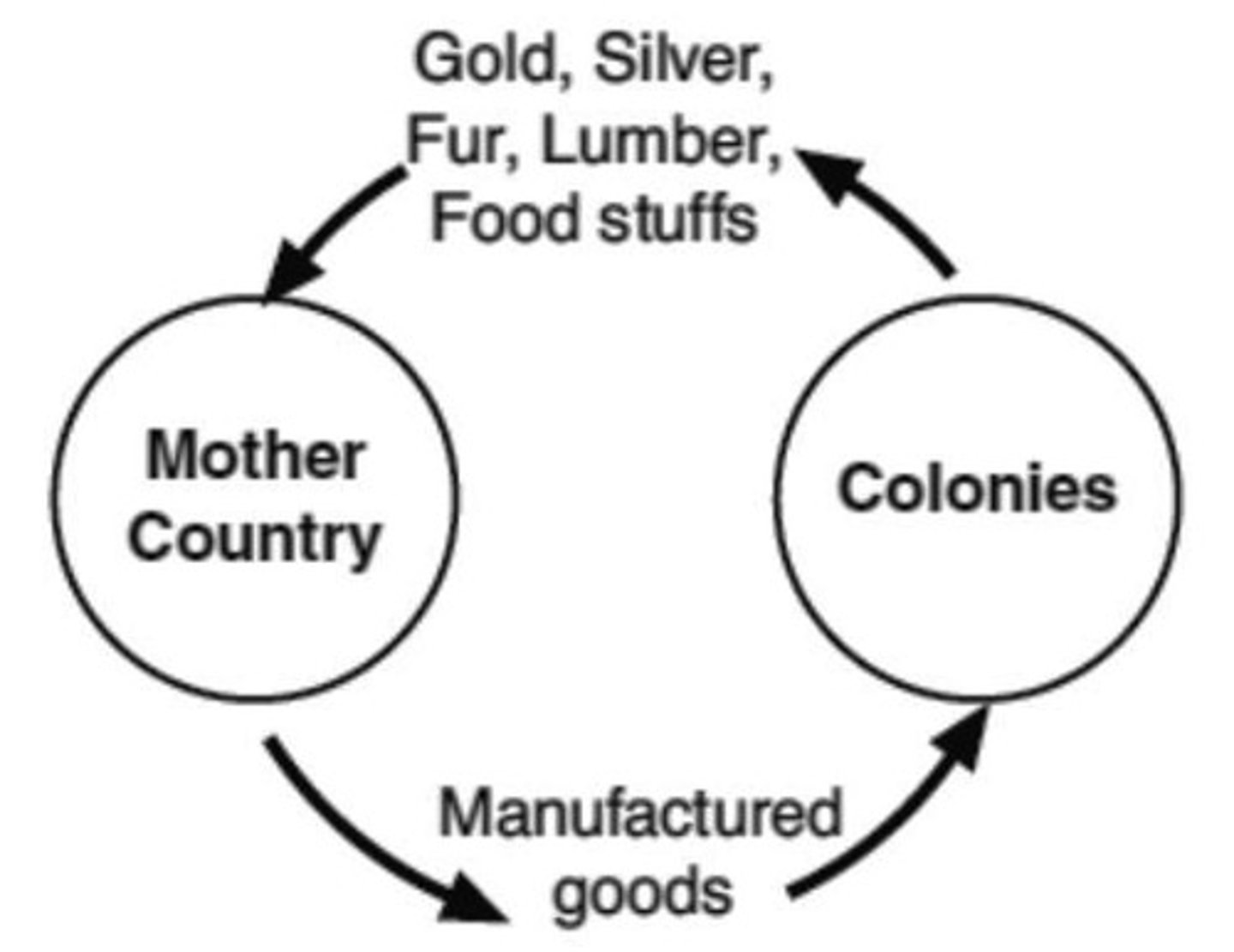
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought; colonies were crucial in the accumulation of wealth
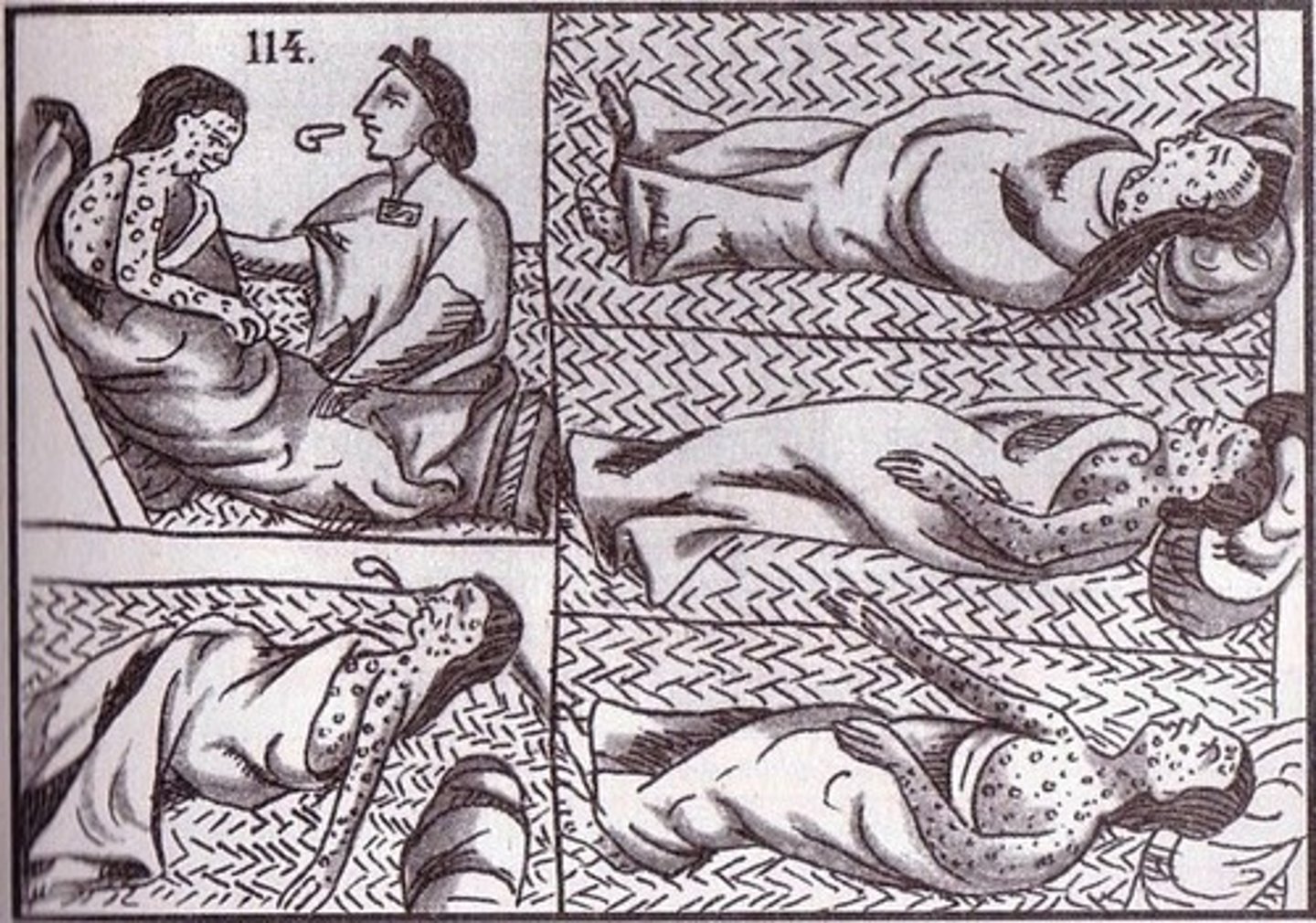
The Great Dying
Term used to describe the devastating demographic impact of European-borne epidemic diseases on the Americas.
Chattel Slavery
Absolute legal ownership of another person, including the right to buy or sell that person; the form of slavery utilized in the Americas during the trans-Atlantic slave trade
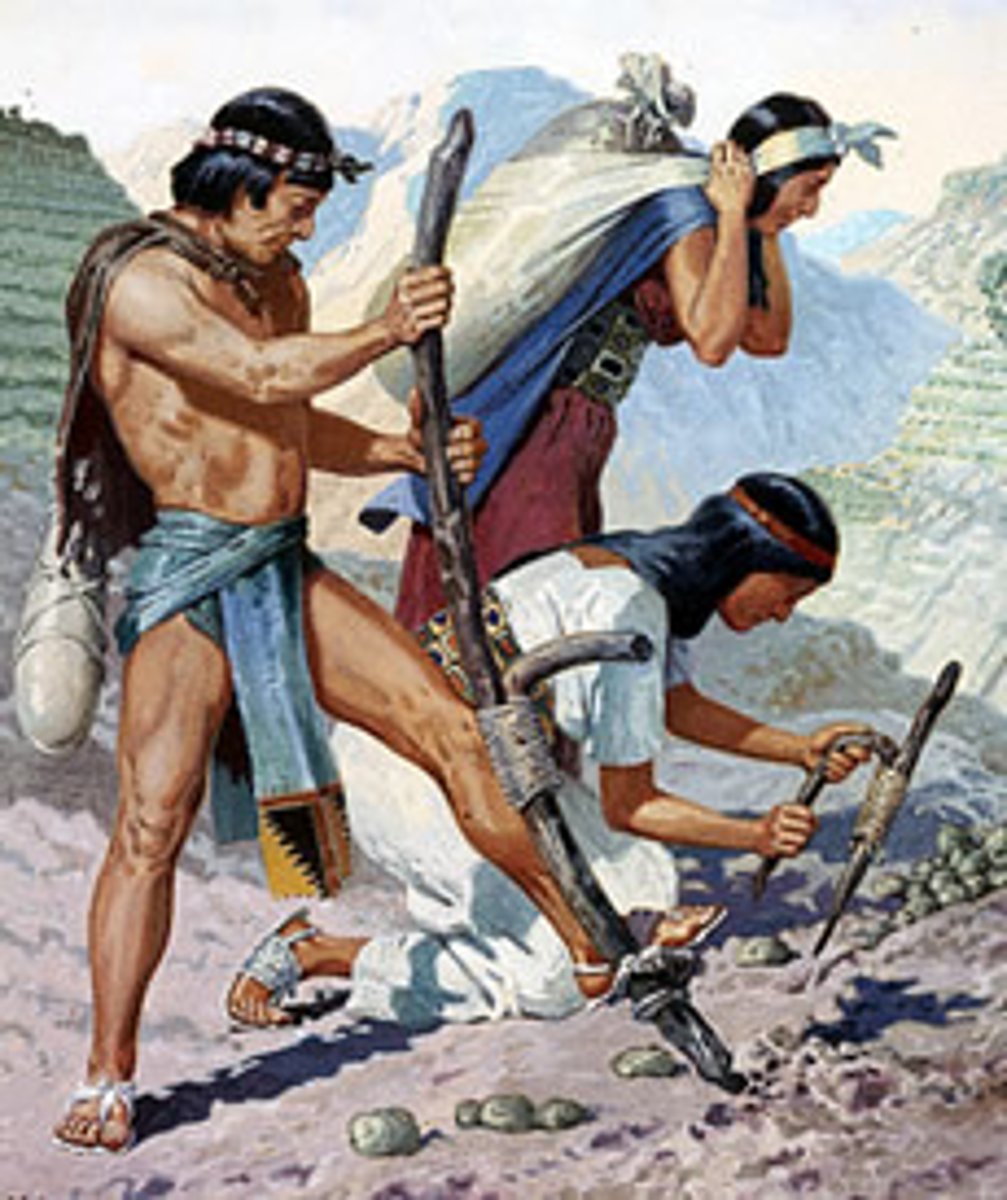
Mita System
economic system in Inca society where people paid taxes with their labor and what they produced; later exploited by the Spanish as they forced Incas to mine silver

Indentured Servitude
A worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination. Before 1800 most were Europeans; after 1800 most indentured laborers were Asians.

Encomienda
A grant of land made by Spain to a settler in the Americas, including the right to use Native Americans as laborers on it

Hacienda
Spanish estates in the Americas that were often plantations. They often represent the gradual removal of land from peasant ownership and a type of feudalistic order where the owners of would have agreements of loyalty but would retain control over the actual land. This continued into the 20th century.
joint-stock company
A company made up of a group of shareholders. Each shareholder contributes some money to the company and receives some share of the company's profits and debts; used by European rulers to finance exploration and were used by rulers to compete against one another in global trade
Royal chartered monopoly companies
Groups of private investors who paid an annual fee to France and England in exchange for a monopoly over trade to Indian Ocean colonies
Casta Paintings
Paintings that show the racial mixing of a family. Shows hierarchy of society.
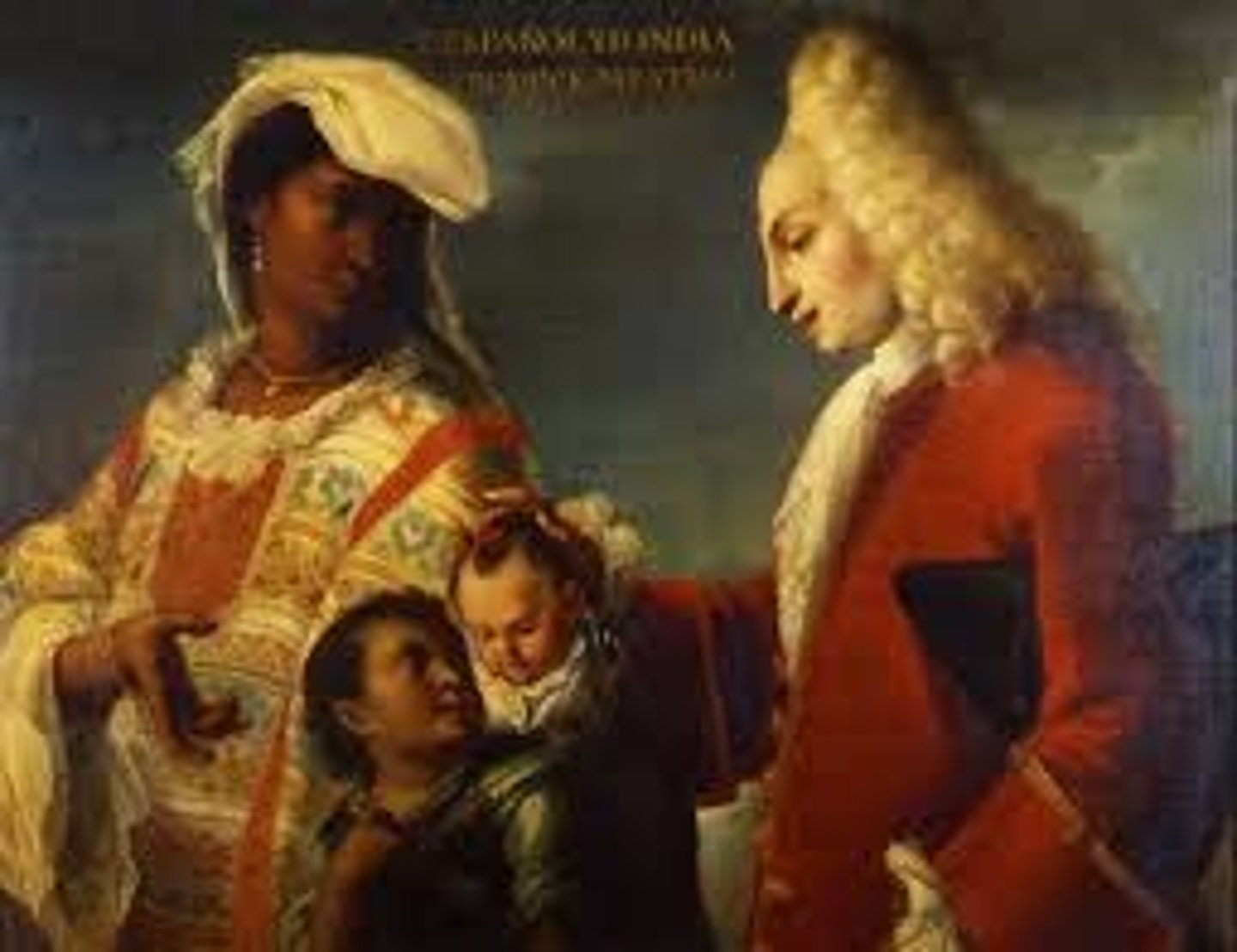

Mestizo
The term used by Spanish authorities to describe someone of mixed native American and European descent.
Mulatto
The term used in Spanish and Portuguese colonies to describe someone of mixed African and European descent.
Creoles
Descendants of Spanish-born but born in Latin America; resented inferior social, political, economic status.
Peninsulares
Spanish-born, came to Latin America; ruled, highest social class.
Fronde
A series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV triggered by growing royal control and increased taxation

Nat Turner's Rebellion
a slave rebellion led by Nat Turner that took place in Virginia in 1831; one example of slave resistance challenging existing authorities in the Americas
British East India Company
A British joint stock company that controlled most of India during the period of imperialism. This company controlled the political, social, and economic life in India for more than 200 years.

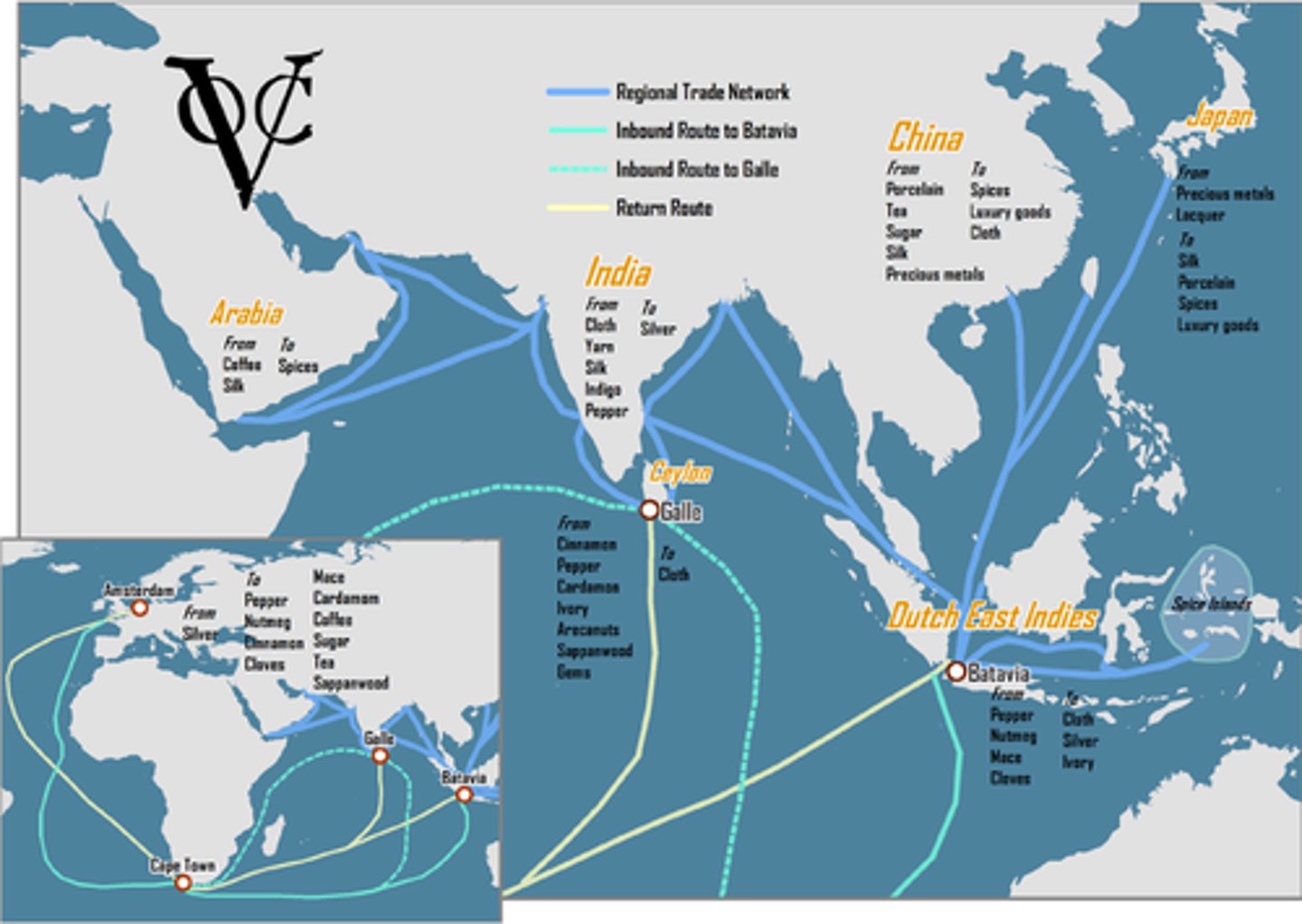
Dutch East India Company
Government Dutch-chartered joint-stock company that controlled the spice trade in the East Indies.
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s whereby Africa sent slaves to the Americas, the Americas sent raw materials to Europe, and Europe sent guns and rum to Africa in exchange for slaves
Cartography
science or art of making maps
Primogeniture Laws
the right, by law or custom, of the firstborn male child to inherit the family estate, in preference to siblings. In the absence of children, the inheritance is passed to collateral relatives, usually males, in order of seniority of their lines of descent
Omani-European Rivalry
A trade rivalry over the Muslim-controlled Indian Ocean trade between the Omani of the Middle East and the European traders.
Maritime Empires
empires based on sea travel
Astronomical Charts
Charts of the sky that divides up constellations and astronomical bodies by location for navigational purposes
Lateen Sail
triangular sail that made it possible to sail against the wind; used in the Indian Ocean trade
compass
an instrument containing a magnetized pointer that shows the direction of magnetic north and bearings from it.
Okra
a flowering plant in the mallow family. It is valued for its edible green seed pods.
Rice
One of the most lucrative crops in the region in early colonial America yielding up to 25% profit
Swahili Arabs
Arab Africans operating outside of the East coast of Africa and trading in the Indian ocean
Omanis
Arabs operating between Swahili, Africa, and Gujarat
Gujaratis
Merchants operating from the north west coast of India, close to the Omani coast on the Arabic penninsula
Javanese
Merchants operating East southeast
Competition over trade routes
Muslim-European rivalry in the Indian Ocean
Pueblo Revolts
a successful native revolt against Spansh settlers in Santa Fe de Nuevo, Mexico, killing hundreds of the Spanish & driving out the remaining of the region
Cossack Revolts
autonomous, democratic, militant communities of the East Slavic people that continuously rebelled against the states that claimed to control them. Normally Russia or Poland-Lithuania
Maratha Conflict with the Mughals
The mughal emperors broke their streak of tolerance with emperor Aurangzeb( he was a staunch Islamist and was incredibly intolerant to non-muslims). This produced an inordinate series of uprising across the Mughal territory. Worst of these enemies were the Indian Marathas, who would fight the Mughals asymmetrically until their numbers dwindled, their treasury was empty, and their emperor was dead.
Ana Nzinga's Resistance
was a politically savvy noblewoman who proved to be a remarkable military commander who fought back against the colonization efforts of the Portuguese.
Metacom's War
Natives that attacked English colonies in North America and the colonists had to join together to fight back. It was the greatest conflict in English colonization history, and the colonials fought back with no help from the English crown.
Establishment of Maroon Societies in the Caribbean and Brazil
Maroons in the Caribbean. Communities formed by self-liberated slaves dotted the fringes of plantation America, from Brazil to the southeastern United States, from Peru to the American Southwest for more than four centuries
North American Slave Resistance
were common across the Americas because many Africans were selected for slavery based on physical prowess and would later join together with native resistance fighters
Different Treatment of Groups in Society
Expulsion of Jews from Spain and Portugal; the acceptance of Jews in the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Timars
A timar was land granted by the Ottoman sultans with a tax revenue annual value of less than 20 000 akçes. The revenues produced from land acted as compensation for military service.
Russian Boyars
the boyars were a privileged class of rich landowners; they served the prince as his aides and councillors but retained the right to leave his service and enter that of another prince without losing their estates.
European Nobility
European nobility originated during the feudal/ seigneurial system that arose in Europe during the Middle Ages; knights or nobles were mounted warriors who swore allegiance to their sovereign and promised to fight for him in exchange for an allocation of land
Smallpox
A highly contagious viral disease characterized by fever, weakness, and skin eruption with pustules that form scabs; responsible for killing 90% Native Americans after contact with Europeans.
Conquistadores
Spanish 'conqueror' or soldier in the New World. They were searching for the 3-G's: gold, God, and glory.
Galleons
Large, heavily armed ships used to carry silver from New World colonies to Spain or to China; basis for convoy system utilized by Spain for transportation of bullion (silver) from the New World.
maize
corn
cacao
Tropical tree that originates in the Americas whose seeds are used to make chocolate and cocoa
Lateen sail
triangular sail that made it possible to sail against the wind; used in the Indian Ocean trade.
sugarcane
A tall grass with a thick, woody stem containing a liquid that is a source of sugar. Originated in Southeast Asia. Grown as a cash crop in plantations in the Caribbean and American continents.
Bartholomew Diaz
Portuguese explorer, first European to reach the southern tip of Africa in 1488.
creole
A language that results from the mixing of a colonizer's language with the indigenous language of the people being dominated.
gumbo
a traditional Louisiana dish; a hearty Creole soup made of seafood, chicken, okra, and other vegetables.
Jacques Cartier
French explorer who explored the St. Lawrence river and laid claim to the region for France (1491-1557).
transatlantic slave trade
The brutal system of trading African Slaves from Africa to the Americas. It changed the economy, politics, and environment. It affected Africa, Europe, and America. It implies that slaves were used for cash crops and created a whole new economy.
Samuel de Champlain
French explorer in Nova Scotia who established a settlement on the site of modern Quebec (1567-1635).
engenhos
A plantation or estate dedicated to the production of sugar in Brazil. These made use of slave labor in order to maximize profits. The conditions of slavery on these types of plantations were among the harshest in the Americas.
Manila
Capital of the Spanish Philippines and a major multicultural trade city that already had a population of more than 40,000 by 1600.
Northwest Passage
A water route from the Atlantic to the Pacific through northern Canada and along the northern coast of Alaska. Sought by navigators since the 16th century. Only possible to navigate with special ice-breaking ships but that did not stop many from trying to make the voyage in wooden vessels who were hoping for a short-cut to China.
Quebec
First permanent French settlement in North America, founded by Samuel de Champlain.
New France
French colony in North America, with a capital in Quebec, founded 1608. New France fell to the British after the Seven Years War in 1763.
Jamestown
1603 - The first permanent English settlement in North America, founded in East Virginia.
New Amsterdam
1625 - Dutch colonial settlement that served as the capital of New Netherland. This later became "New York City"
colonies
Lands that are controlled by another nation (located somewhere else).
encomenderos
Spanish settlers who were in charge of the natives working on the encomiendas.
coercive labor system
An institution in which workers are compelled to work by force, intimidation, or authority, often against their will (ex. serfdom, slavery).
Middle Passage
The route across the Atlantic Ocean from Africa to the Caribbean and American continents that enslaved peoples were forced to make. Conditions on these voyages were almost always inhumane.
Asante Empire
Africa - Established in Gold Coast among Akan people settled around Kumasi; Grew wealthy from trading with Europeans.
Kingdom of the Kongo
Africa - Basin of the Congo river, conglomeration of several village alliances. Participated actively in trade networks. Royal currency: cowrie shells. Ruled 14th-17th century until undermined by Portuguese slave traders.
Hernan Cortes
(1485-1547)Spanish conquistador who defeated the Aztecs and conquered Mexico. Arrived in present-day Mexico in 1519 with 600 men and by 1521 deposed the Aztec king and took the capital Tenochtitlan with help from native allies and disease.
Aztec Empire
Central American empire constructed by the Mexica and expanded greatly during the fifteenth century. Conquered in 1521 by Cortes.
Moctezuma
Aztec emperor defeated by the Spanish conquistador Hernando Cortes. Was either killed by the Spanish or by his own people depending on who you believe. His sudden death and disease destabilized the empire.
Inca Empire
The vast and sophisticated Peruvian empire centered at the capital city of Cuzco that was at its peak from 1438 until 1532. Conquered by Pizarro in 1533.
Francisco Pizarro
(1475-1541) Spanish explorer (conquistador) who conquered the Inca with only 180 men in what is now Peru and founded the city of Lima.
Atahualpa
Last ruling Inca emperor of Peru. He was executed by the Spanish in 1533.
New Spain
After the defeat of the Aztecs, it was a Spanish colony. Its capital was Mexico City (Tenochtitlan).
Mexico City
Capital of New Spain; built on ruins of Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan.
Hispaniola
First island in Caribbean settled by Spaniards; settlement founded by Columbus on second voyage to New World; Spanish base of operations for further discoveries in New World. Where Haiti and Dominican Republic are located today.
Treaty of Tordesillas
A 1494 agreement between Portugal and Spain, declaring that newly discovered lands to the west of an imaginary line in the Atlantic Ocean would belong to Spain and newly discovered lands to the east of the line would belong to Portugal.
monopoly
The exclusive possession or control of the supply or trade in a commodity or service.
syncretism
The unification or blending of opposing people, ideas, or practices, frequently in the realm of religion. For example, when Christianity was adopted by people in a new land, they often incorporate it into their existing culture and traditions.
Santeria
Originating in Cuba, a syncretic religion that blends African traditions and Christian (Catholic) beliefs
Vodun
African religious ideas and practices among descendants of African slaves in Haiti. (sometimes mistakenly called voodoo)
Candomble
New World syncretic religion with roots in West Africa - particularly Yoruba culture - which is prominent in Brazil
Virgin of Guadalupe
An apparition of the Virgin Mary said to have appeared to a Mexican farmer (Juan Diego) in 1531. Diego discovered her image on his cloak as proof of her visit to him. This image is enshrined in the cathedral in Guadalope. She exerted a powerful attraction to Mesoamerica's surviving Amerindians and became an icon of Mexican identity. Mexicans visit Guadalupe on December 12th for her saints holiday.
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower.
Viceroy
A governor or ruler exercising authority on behalf of a sovereign in a province or colony.
African Diaspora
The separation of Africans from their homeland through centuries of forced removal to serve as slaves in the Americas and elsewhere. This was the fate of approximately 12-15 million Africans.
audiencias
Courts appointed by the king who reviewed the administration of viceroys serving Spanish colonies in America.
Dahomey
West African kingdom that became strong through its rulers' exploitation of the slave trade.