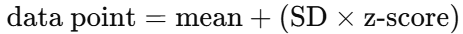Exam Revision
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Types of evidence
Personal testimony
Reputable research journal
Reproducible research
Nature of the data collection
Selection bias
When participants are more likely to be chosen than others
Randomised controlled trial
One group receives the intervention (the experimental group), while the other (the control group) receives a placebo, standard treatment, or no treatment at all.
Randomised controlled double-blind trial
A research study where neither the participants nor the researchers know who is receiving the intervention or placebo, reducing bias in results.
Consent bias
When participants choose whther or not they take part in the experiment
Survivior bias
Only happens after the study
An observed "improvement" may happen because there are dropouts of the sickest subjects

Adherer bias
Certain participants (adherers) keep taking treatment (placebo) as opposed to non-adherers = "improvement" in treatment group due to the adherers
3 precautions of observational studies
Obsevational studies can’t establish causation only association
Observational studies may present as an RCT
Confounding variables may influence results if not properly controlled.
Observational studies
An observational study is one in which the investigator cannot use randomisation for allocation to groups. The assignment of subjects is outside the control of the investigator.
Contemporaneous control
A contempoaneous control group occurs at the same time as the treatment group.
What is the simpson's paradox?
It’s when a trend appears in separate groups of data but reverses or disappears when the groups are combined, often due to a confounding variable. It highlights how misleading conclusions can arise if data isn't properly stratified.
What is data in statistics?
Data is information about the subjects being studied, usually referring to a sample rather than the whole population.
What does IDA stand for and what is it?
Initial Data Analysis – a first look at the data before answering research questions. It checks quality, structure, and suggests patterns or new questions.
What are the key steps in IDA?
A variable measures or describes an attribute of the subjects; each column in a tidy dataset is a variable.
What does high dimensional data mean?
There are more variables (p) than subjects (n), common in big data.
What are the two main types of variables?
Quantitative (numerical) and qualitative (categorical)
How is one qualitative variable visualised?
With a single barplot, where categories are on the x-axis.
How are two qualitative variables visualised?
With a double barplot using colour to show the second variable.
What is a histogram used for?
To visualise the distribution of a quantitative variable across class intervals.
What’s the difference between a standard and density histogram?
Standard shows counts; density shows percentages (area = 100%).
What is the rule of thumb for number of histogram intervals?
Use 10–15 class intervals to avoid over/under condensing data.
What is a sliced histogram?
A histogram where a qualitative variable is shown by slicing each bar with colour.
What do the edges of a boxplot represent?
The 25th and 75th percentiles; the box shows the middle 50% of the data.
How are outliers identified in a boxplot?
They are outside the thresholds:
LT = Q1 − 1.5×IQR
UT = Q3 + 1.5×IQR
What is a comparative boxplot?
A boxplot comparing a quantitative variable across levels of a qualitative variable.
What is a filtered scatterplot?
A scatterplot with more variables shown using colour or shape to distinguish them.
Why is age usually treated as quantitative?
Because it's easier to convert from quantitative to qualitative, not the other way around.
What is the purpose of numerical summaries?
To reduce all data to a single statistic, making it easier to communicate and compare key features like centre and spread.
What are the main types of numerical summaries?
Maximum, minimum, centre (mean, median), and spread (standard deviation, range, IQR).
What is the mean?
The balancing point of a distribution, where the sum of deviations on both sides equals zero.
What is the median?
The middle value of an ordered dataset; 50% of values lie above and 50% below it.
When is the median more useful than the mean?
When the data is skewed or contains outliers, because the median is robust and unaffected by extreme values.
When is the mean more useful than the median?
For symmetric data with few outliers; e.g., calculating averages for prediction or reporting.
How do mean and median behave with skewed data?
Left skew: mean < median
Right skew: mean > median
Symmetric: mean ≈ median
What is robustness in statistics?
A property of a summary (like the median or IQR) where it remains reliable even with outliers or skewed data.
Why must the mean gap always equal zero?
Because the mean is the balancing point; all positive and negative deviations from the mean cancel out.
What does standard deviation measure?
The average spread or dispersion of data points from the mean.
What is the RMS (root mean square) in standard deviation?
It calculates the square root of the average squared deviations from the mean.
When is it okay to treat a dataset as a population vs. a sample?
If the dataset includes all subjects of interest (e.g. all house sales in one suburb in one month), it's a population; otherwise, it's a sample.
What percentage of data falls within 1, 2, and 3 standard deviations of the mean?
68% within 1 SD
95% within 2 SDs
99.7% within 3 SDs
What is the interquartile range (IQR)?
The range of the middle 50% of the data, calculated as Q3 − Q1; it's robust against outliers.
What is the difference between quartiles and quantiles?
Quartiles divide data into 4 parts, while quantiles divide data into q equal parts.
What are standard units (z-scores)?
The number of standard deviations a data point is from the mean: