U1 P3
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
techinical factors that govern radiation exposure
milliampere (mA), exposure time, mAs (product of mA and exposure time), kVp, SID, filtration
5 factors affecting radiation exposure
mA, time, kilovoltage, distance, thickness and condition of anatomic part
Radiographic variables & affect on x-ray emission casue what changes?
quantitative (mAs) & qaulitative (kVp)
quantitative change
mAs (mA & time), kv, distance, filtration
qaulitative change
kv & filtration; refers to photon energy, & penetrability
quality measured in
HVL (half value life)
xray beam quantity
amount of xray photons; refers to output, intensity, exposure rate
Quantity measured in
Couloumb/kilogram (C/kG) or Air kerma (Gy)
quality or quantity of image represents information that is well visualized for diagnosis?
quality
visibility of the anatomic structures is accomplished by balancing
brightness, contrast, exposure indicator #
A _________ radiographic image accurately represents [records] the anatomic area of interest with high sharpness.
quality
quality criteria for image evaluation
exposure index, brightness, contrast/grayscale, SNR, spatial resolution, artifacts, distortion
expusure index
used to determine incident exposure to the image receptor (S/EI#)
brightness
amount o luminance/light emission of the display monitor
contrast/grayscale
difference in areas of brightness on the display monitor; result of differential absorption of x-ray photons within body tissues
SNR
signal to noise ratio
spatial resolution
sharpness of anatomic details or structural anatomy
quantum noise
described as brightness or density fluctuations (grainy appearance)
quantum noise is caused by?
photon deficiency: too few xray photons reaching IR, decreasing detail visibility
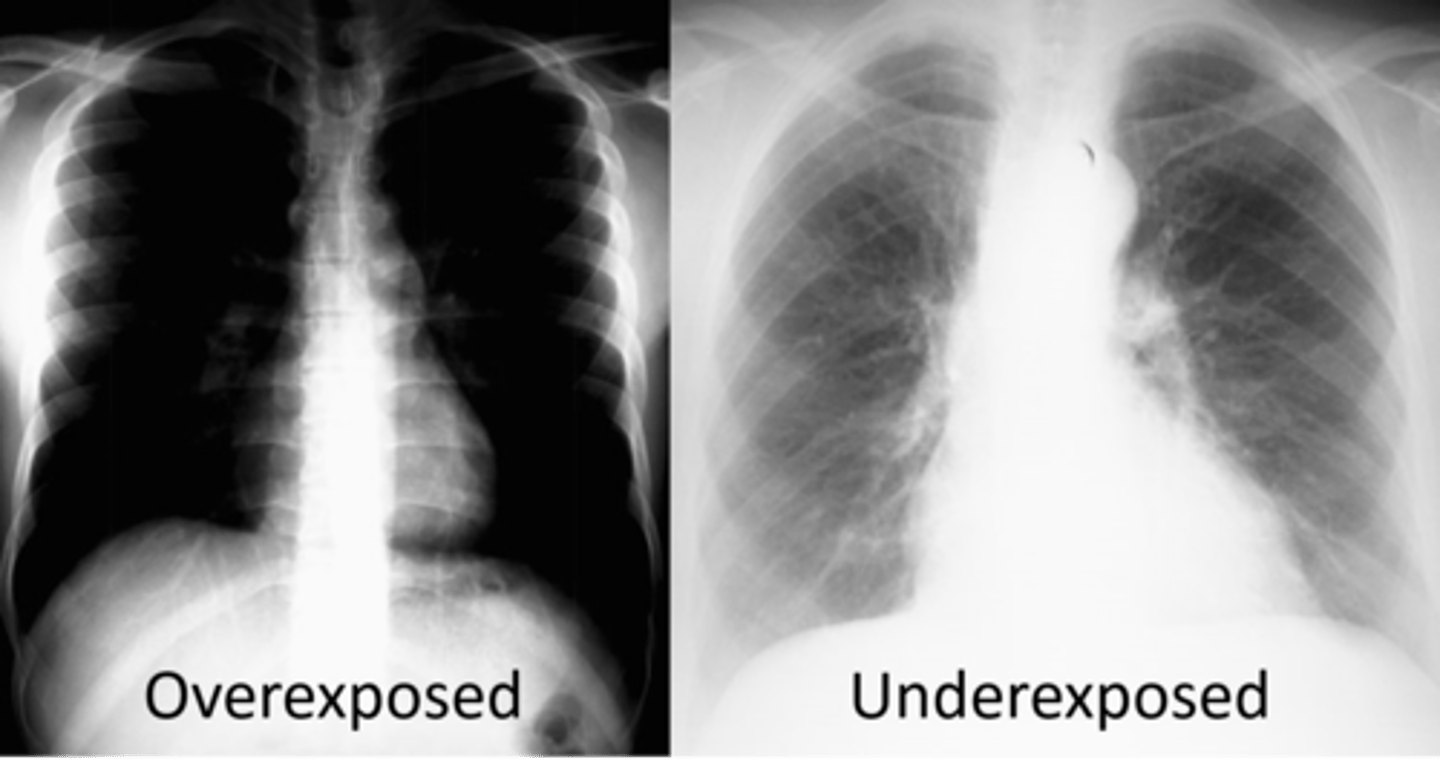
What can be seen on digital images that are underexposed?
quantum noise
scatter radiation (a form of noise)
a type of secondary radiation produced when the useful x-ray beam intercepts any object, causing some x-rays to scatter (change direction)
most significant source of scatter radiation on patients?
x-ray exposure or fluoroscopic exam
Scatter degrades what?
image quality decreasing visibility of anatomic details
increase/decrease?
⬆/⬇ scatter production = ⬆/⬇ receptor exposure
increase; increase
subject contrast is produced by
differential absorption
How do x-ray photons interact with the digital receptor?
They pass through anatomic tissues to interact with the IR.
beam attenuation
reduction in number/intensity of x-ray photons as the beam passes through matter
beam attenuation proccesses include:
absorption and scattering
transmission
xray photons pass through matter without interaction with tissue atoms
Receptor Exposure (RE) is dependent upon?
the amount of exposure
S#
- inverse relationship
- Fuji and Konica
- S# of 200 = 1mR exposure to the IR
An increase in the S# from 200 to 400 indicates a decrease in RE Solution: to lower S# by one half, do what?
double mAs
EI#
- direct relationship
- Carestream and Kodak
An increase in the E# by 300 indicates a doubling of the RE Solution: to lower EI# by 300 points, do what?
1/2 mAs
LgM#
- direct relationship
- Agfa
What is the primary controller of receptor exposure?
mAs
underexposed or overexposed
underexposed appear whiter; overexposed appear darker
mA: directly proportional to? inversely related to?
direct: radiation quantity
inverse: exposure time to maintain exposure to IR
exposure time: directly proportional to? inversely related to?
direct: radiation quantity
inverse: mA to maintain exposure to IR
exposure time equation
mA × time (seconds) = mAs
kVp: directly related to? inversely related to?
direct: radiation quality & quantity
inverse: radiographic contrast
Milliampere (mA)
measure of the quantity of electrons or electrical current flowing per second
Doubling mA = 2x what 3 things?
#electrons produced, # of x-rays produced, receptor exposure
Changing the mA station on control panel changes what?
amount of electrical current delivered to filament wire (cathode)
Inverse Square Law
the intensity of radiation at given distance is inversely related to square of distance between object & source
inverse square law formula
I₁(D₁)² = I₂(D₂)²
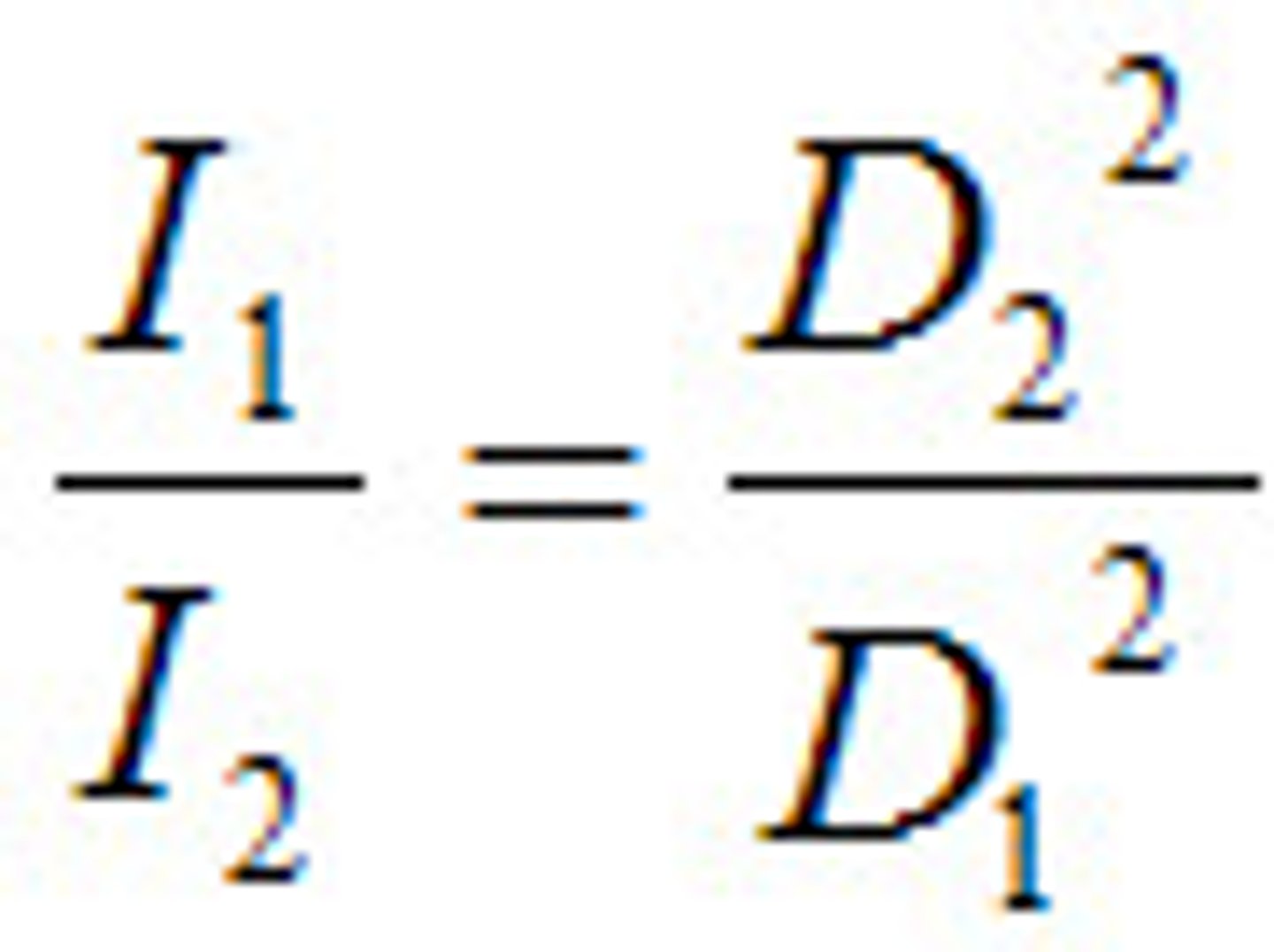
inverse square law:
↓SID = ?
↑SID = ?
- more radiation exposure/intensity to IR
- less radiation exposure/intensity to IR
to maintain xray intensityt (quantity) use?
direct square law
mAs-distance compensation
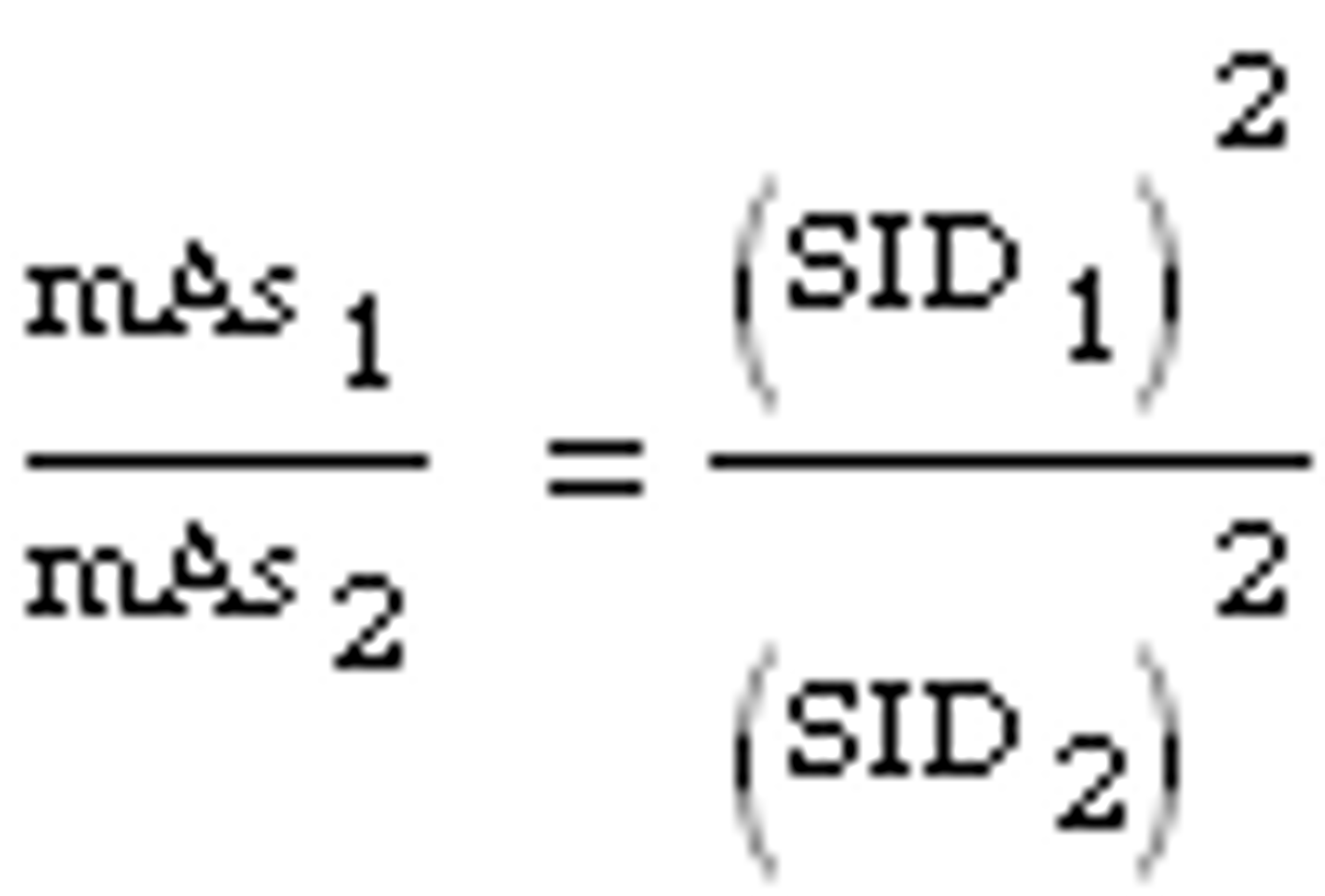
direct square law:
↓SID = ?
↑SID = ?
- decrease mAs/mA
- increase mAs/mA
2x SID gives you?
1/2 SID gives you?
1/4 intensity ∴ use 4x mAs
4x intensity ∴ use 1/4 mAs
Reciprocity Law
exposure on x-ray should remain unchanged as long as intensity & duration of x-ray exposure remains unchanged
Reciprocity Law fails for?
extremely short exposures
15% rule of kVp
⬆kVp 15% = RE doubles (100% or 2)
⬇kVp 15% = RE halves (50%)
(kVp & RE have direct but not proportional relationship)
Maintenance of Receptor Exposure using 15% Rule:
⬆kVp 15% (1.15) & ⬇mAs by 1/2
⬇kVp 15% (0.85) & ⬆mAs by 2x
How will changing kVp affect beam quality and quantity?
⬆kVp: ⬆beam penetrability & quantity
⬇kVp: ⬇beam penetrability & quantity