Endocrine Structures
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What gland is this?
hypothalamus
What hormones does the hypothalamus produce?
oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Where is oxytocin sent to?
uterus muscles and breast tissue
What actions does oxytocin perform?
causes contractions to start childbirth
causes milk to flow from the breasts during nursing
Where is ADH sent to?
kidneys
What actions does ADH perform?
triggers to reabsorb water (instead of making it into urine)
helps to hold in urine through the night
What gland is this?
anterior pituitary gland
What hormones are produced in the anterior pituitary gland?
Prolactin, growth hormone (GH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinizing hormone (LH), Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and adrenocorticotropic hormone
Where is prolactin sent to?
breast tissue
What action does prolactin perform?
stimulates milk production for breastfeeding
Where is GH sent to?
the liver, which releases a second hormone that targets the bones and muscles
What action does GH perform?
Tells the bones, muscles, and other organs to grow by doing mitosis
Where is FSH sent to?
ovaries in females
testes in males
What actions does FSH perform?
stimulates egg production in ovaries
stimulates sperm production in testes
Where is LH sent to?
ovaries in females
testes in males
What actions does LH perform?
Ovaries
triggers ovulation each month
stimulates the ovaries to produce estrogen and progesterone
Testes
stimulates testosterone production
Where is TSH sent to?
Thyroid gland
What action does TSH perform?
regulates when the thyroid releases its own hormones
Where is adrenocorticotropic hormone sent to?
Adrenal cortex
What action does adrenocorticotropic perform?
Triggers the adrenal cortex to produce its own hormones
What gland is this?
pineal gland
What hormone is produced in the pineal gland?
Melatonin
Where is melatonin sent to?
nervous tissue
What actions does melatonin perform?
causes feelings of calm and sleepiness
biological clock
What gland is this?
Thyroid gland
What hormones are produced in the thyroid gland?
Triiodo-thryonine (T3), Thyroxine (T4), Calcitonin
Where are T3 and T4 sent to?
most organs
What actions does T3 perform?
increase metabolic rate (how quickly the body uses energy)
high levels = fast metabolism
What action does T4 perform?
Gets converted into T3 which regulates metabolism
Where is Calcitonin sent to?
bones
What action does calcitonin perform?
triggers calcium ions to EXIT the bloodstream and ENTER the bones (so the calcium can build the bones)
What gland is this?
parathyroid gland
What hormone are produced in the parathyroid gland
parathyroid hormone
Where is parathyroid hormone sent to?
bones
What action does parathyroid perform?
triggers calcium ions to EXIT the bones and ENTER the bloodstream (so that calcium is available for other functions)
What gland is this?
thymus
What hormone is produced in the thymus?
Thymosin
Where is thymosin sent to?
T cells and immune system
What action does thymosin perform?
Triggers T cells to mature
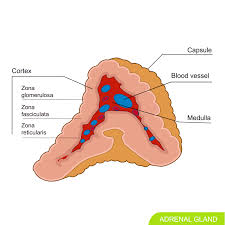
What glands are these?
Adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex
What hormones are produced in the adrenal medulla
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Where is epinephrine and norepinephrine sent to?
most organs
What actions do epinephrine and norepinephrine perform?
recognizes stress and helps with the “fight or flight” response
increases heart and lungs
causes the bronchioles in the lungs to enlarge and the pupils to dilate
What hormones are produced in the medulla cortex?
Cortisol and Aldosterone
Where is cortisol sent to?
All tissues
What actions does cortisol perform?
important in the production of glucose
released in stressful situations
Where is aldosterone sent to?
kidneys
What actions does aldosterone perform?
stimulates the kidneys to keep salt and water in the blood (rather than excreting them)
causes blood pressure to rise
What gland is this?
ovaries
What hormones are produced in the ovaries?
Estrogen and Progesterone
Where is estrogen sent to?
Many targets in the female reproductive system
What actions does estrogen perform?
triggers the uterine lining to build up in preparation for pregnancy
Regulates secondary female characteristics such as breast development
Where is progesterone sent to?
Uterus
What actions does progesterone perform?
triggers the uterine lining to build up in preparation for pregnancy
Triggers the uterine lining to stay thick during pregnancy
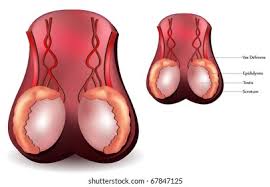
What gland is this?
testes
What hormone is produced in the testes?
Testosterone
Where is testosterone sent to?
Male reproductive system
What actions does testosterone perform?
stimulates the production of sperm
Responsible for male secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair, muscle development, and sex drive
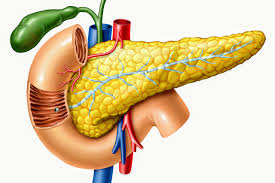
What gland is this?
Pancreas
What hormones are produced in the pancreas?
Insulin and glucagon
Where is insulin sent to?
Many organs
What actions does insulin perform?
helps to regulate blood sugar, along with glucagon
released when blood sugar is too high
stimulates body cells to suck up sugar from the blood and store it
causes blood sugar levels to drop
Where is glucagon sent to?
Liver cells
What actions does glucagon perform?
helps to regulate blood sugar along with insulin
released when blood sugar is too low
stimulates liver cells to release sugar into the bloodstream
caused blood sugar levels to raise