Diuretics- Prof K
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
What are the main functions of the kidney?
regulate ECF vol
regulate osmotic pressure thru urine excretion
regulate conc of electrolytes
regulate bp
eliminate waste
remove drugs/foreign components
filters around 180L of blood a day
What are the board indications for diuretics?
Edema
Hypertension
CHF
Prevent renal damage
General actions of diuretics:
increase urine output
increase/decrease electrolyte excretion
3 thiazide diuretics to know:
hydrochlorothiazide
chlorothiazide
chlorthalidone
Do thiazides have a small, moderate, or severe diuretic action?
moderate
What part of the nephron do thiazides effect?
distal tubule
A thiazide diuretic has what 3 main structural components?
benzo ring
dioxide
thiadiazine
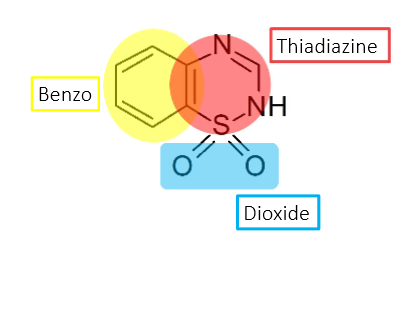
How does the structure of Chlorothiazide/Hydrochlorothiazide differ from chlorthalidone?
No thiadiazine ring in chlorthalidone
What group is absolutely necessary in the structure for thiazide function?
sulfonamide
An electron-_________ group on position 6 would decrease reactivity.
donating
An electron-donating group like a -Cl group on position ____ would increase reactivity of a thiazide.
6
On position 2 of a thiazide diuretic, what increases the duration of action?
alkyl substitution
Ex: methyl, ethyl, propyl (a carbon chain)
On position 3 of a thiazide diuretic, what would increase potency and duration of action?
hydrophobic group
Ex: methyl, benzene ring, haloalkyl
Does saturation of the 3-4 bond of a thiazide increase or decrease potency?
increase
Which is more potent, Hydrochlorothiazide or Chlorothiazide?
Hydrochlorothiazide
MOA of thiazide diuretics
inhibits Na/Cl symporter in distal tubule
Indications of Thiazides
Edema
Hypertension
Heart Failure
Nephrolithiasis due to excess Ca
Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus
What are the Acute Antihypertensive effects of thiazide diuretics?
increase Na excretion
decrease intravascular vol, cardiac output, and BP
What are the chronic antihypertensive effects of thiazide diuretics?
vol and cardiac output returns to normal
BP stays decreased
decrease vascular resistance
What are the ADRs on electrolytes for thiazide diuretics?
HYPO
hypomagnesemia
hyponatremia
hypokalemia
HYPER
hypercalcemia
What are the metabolic changes seen with thiazides diuretics?
Think: Hyper everything
hyperuricemia
hyperglycemia
hyperlipidemia
What group on the structure of the thiazide diuretics has the potential to cause hypersensitivity reactions? (Hives, swelling, N/V, HA, etc.)
sulfonamide
Thiazides are contraindicated in anyone with…
sulfonamide allergy.
What drugs interact with thiazides in an additive/synergistic way?
Loop diuretics
Antihypertensive drugs
What drugs interact with loop diuretics in an additive/synergistic way?
thiazide diuretics
Antihypertensive drugs
What drugs interact with thiazides in a way that we want to watch/avoid the drug altogether?
lithium
seizures, shakes
NSAIDs
makes thiazides not work
Dofetilide
severe arrythmias
What drugs interact with loop diuretics in a way that we want to watch/avoid the drug altogether?
lithium
NSAIDs
Digoxin
arrythmias
Aminoglycosides
may induce hearing loss
Names of the 4 loop diuretics to know:
furosemide
torsemide
bumetanide
ethacrynic acid
Site of Action of loop diuretics:
ascending limb of loop of henle
How does the structures of the other loop diuretics differ from Ethacrynic acid?
Ethacrynic acid has no sulfoamide
Loop Diuretics block what transporter?
NKCC
How does Loop diuretics effect magnesium, calcium, and potassium?
Think: HYPOOOOOOO
hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
hypomagnesemia
hypocalcemia
Loop Diuretics and Thiazide diuretics all have similar effects on electrolytes and metabolic changes EXCEPT FOR:
calcium
loop- hypocalcemia
thiazides- hypercalcemia
Why does hypokalemia caused by loop diuretics cause metabolic alkalosis?
bc increased excretion of K and H causes a bicarb buildup. Bicarbonate is a base, so a lot of base= alkalosis
Can ototoxicity caused by diuretics be reversed?
yes- usually
Loop Diuretics are contraindicated in pts with:
Sulfonamide allergy
except ethacrynic acid
severe Na or volume depletion
pretty obvious
anuria
Indications of Loop Diuretics:
Edema
pulmonary, hepatic, cardiac, renal
hypertension
acute renal failure
hyperkalemia
hypercalcemia
What diuretic has the possibility of causing hearing issues? (otoxicity)
loop diuretics
4 Potassium sparing diuretics to know:
spironolactone
eplerenone
triamterene
amiloride
What are the 2 MOAs for Potassium sparing diuretics?
Inhibit ENac
Inhibit Aldosterone
Site of action of potassium sparing diuretics:
cortical collecting duct
(principal cells)
Which Potassium sparing diuretics act as aldosterone antagonists?
Spironolactone
Eplerenone
Which potassium sparing diuretics act as ENac inhibitors?
Triamterene
Amiloride
If Aldosterone works to increase sodium resorption and increase potassium excretion, Aldosterone Antagonists do what?
decrease sodium resorption
decrease potassium excretion
How do Potssium sparing diuretics that are Aldosterone Antagonists inhibit aldosterone? (MOA)
competitively bind to the receptor where aldosterone would bind (mineral corticoid receptor)
causes less ENac and Na/K pumps to work
end result: less Na reabsorbed and less K excreted
Which Potassium Sparing diuretic is a prodrug?
What is the active metabolite of this diuretic called?
How does the structures of these 2 differ?
Spironolactone
Active metabolite- Canrenone
Structurally- Spironolactone has a thio-acetyl, canernone doesn’t
ADRs of Potassium Sparing Diuretics that are Aldosterone Antagonists:
hyperkalemia
metabolic acidosis
endocrine effects (only spironolactone)
Which diuretic has the potential to cause gynecomastia, an endocrine problem?
spironolactone
Which diuretic would I chose if I didn’t want the potential endocrine side effects that spironolactone has?
eplerenone
Indications of Potssium Sparing Diuretics:
Aldosterone Antagonists
ENac Inhibitors
BOTH:
CHF
Hypertension
Hypokalemia
JUST Aldosterone Antagonists:
Edema
Primary Aldosteronism
Femal Hirsutism
only spironolactone
Contraindications of Aldosterone Antagonists:
K supplements
other K sparing diuretics
Hyperkalemia
decreased renal function
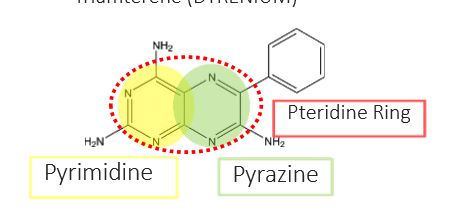
Recognize the components of Potassium Sparing Diuretics that are ENac inhibitors:
pyrimidine
pyrazine
pterdine ring
Common ADRs of Potassium Sparing Diuretics that are ENac Inhibitors:
Hyperkalemia
Metabolic Acidosis
N/V, HA
Name of an osmotic diuretic:
mannitol
Site of action of osmotic diuretics:
proximal tubule
descending limb of loop of henle
Mannitol has no other effects other than attracting _______.
water
Mannitol is classified as what?
sugar alcohol
How does mannitol attract water out of the cells?
it’s structure- it has a bunch of alcohol groups and that attracts water
ADRs of osmotic diuretics:
hyperkalemia
hypernatremia
N/V, HA
Contraindications of osmotic diuretics:
anuria
dehydration
Indication of osmotic diuretics:
acute renal failure
reduces intracranial or intraocular pressures
What is the name of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitor we have to know?
Acetazolamide
Acetazolamide inhibits reabsorption of what 2 things?
Na
Bicarbonate
Acetazolamide acts on what part of the nephron?
proximal tubule
ADRs of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Metabolic acidosis
hypokalemia
vomiting
Indications of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors:
glaucoma
metabolic alkalosis
moutain sickness