CBT Nuggets CompTIA Project+ Terminology
1/412
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
413 Terms
-Project
a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique project, service, or result. Generally, this means creating business value or driving change
-Temporary
Indicates a beginning and an end. Refers to the nature of a project, its work, or one of its phases. Not concerned with "how long", but rather the fact that a project will not last forever
-TRUE- projects can exist alone, in a program, or in a portfolio
(T/F) Projects can be stand alone or part of a program or portfolio
-The difference between a project and an ongoing operation
Projects build the thing. Ongoing operations indefinitely maintain the thing (i.e. constructing a building vs regular maintenance / repairs).
-Project Management
the application of knowledge, tools, and techniques, to project activities, to meet project requirements.
-Project Lifecyle
the series of phases that a project goes through from its start through to its finish.
-The Phases of a Project
1. Discovery/Concept Preparation (the Idea); 2. Initiation(the Idea); 3. Planning( the Plan); 4. Execution (Do the thing); 5. Closing (Finish the thing);
-Discovery/Concept Preparation
The phase of a project in which the question, "Is this project a good fit for us right now?" is answered. Deals with ROI analysis, Preparing the Business Case, High level budgeting, and seeing what vendors/contracts already in place that can be utilized.
-Initiation
The phase of a project in which there is formal authorization for the project to begin. Deals with identifying stakeholders, reviewing existing artifacts, and developing project charter.
-Planning
The phase of a project that deals with identifying units of work, determining the budget, assigning resources, and developing a schedule.
-Execution
The phase of a project that deals with actually doing the work. Includes tracking/reporting project work, managing changes, updating the plan, managing conflict, etc.
-TRUE
(T/F) Planning and Execution often function in a cycle with one another
-Closing
The phase of a project that deals with the formal end of a project. Includes the final sign-off of the work, handing over the project to operations, closing contracts, documenting/archiving/collating of lessons learned, and celebrating.
-Product Life Cycle
The entire evolution of a product from concept to market through to retirement.
-The difference between process groups and project lifecycle phases
the PMI's process groups have slightly different names to the lifecycle phases but they look similar. One deals with the phases while the other groups similar work processes together.
-Program
related projects managed in a coordinated manner
-Portfolio
Projects and Programs (and sometimes operations) managed in a coordinated way to achieve the organization's strategic objectives.
-Program management
Focuses on the interdependencies between projects
-Portfolio management
Focuses on the strategic view of whether projects and programs align with the organization's objectives.
-Waterfall/Predictive PMA
a PMA in which each phase of a project cannot start until the previous phase is completed in its entirety. E.G. Gather all requirements-> Design-> Plan-> Build-> Test-> Open/Release
-Benefit of a Waterfall/Predictive PMA
Quite useful when all requirements can be gathered up front, and aren't likely to change, and as a result requires lots of up front effort.
-Downside of a Waterfall/Predictive PMA
Customer sees no value until the end, Not useful in a project that is unpredictable (duh lol), e.g. money runs out, or a chaotic user market (like software).
-Agile/Adaptive PMA
The principle of software development based on iterative and incremental development. Produces working software with each iteration of development.
-Benefit of an Agile/Adaptive PMA
Allows delivery to client/users for the sake of feedback in which to learn what works / doesnt work and changing direction if needed.
-Agile Development Values
People > Processes; Working Software > Comprehensive Documentation; Customer Collaboration > Contract Negotiation; Responding to Change > Following a Plan
-The #1 Goal of Agile Development
To satisfy the customer through early and continuous delivery of valuable software
-Explain considerations involved in choosing between Agile or Predictive Development
Organizational structure, is it stable or unpredictable (software devs or construction company)?; Schedule + Budget Constraints (unpredictable funding)? Stakeholder Expectations (do they want day to day involvement or occasional updates)?
-Scrum
An agile project management methodology involving a small team led by a Scrum master, whose main job is to remove all obstacles to getting work done. Work is done in short cycles called sprints, and the team meets daily to discuss current tasks and any roadblocks that need clearing. Allows for rapid development and testing, especially within a small team.
-Product Owner
The individual (single person not group!) within a scrum who owns the vision of the product, has the authority to decide what features and functionality get built (and in what order), and is responsible for the Product Backlog
-Product Backlog
A continually evolving prioritized list of work that needs to be done. Associated with Scrum frameworks.
-Artifacts
Any project documents, templates, or outputs.
-Kanban
Focuses on workflow (not sprints) using a "pull-based" approach and a board (rather than time-boxed sprints) so that work flows continuously
-Lean
Agile method that Removes anything that doesn't add value
-XP
Focuses on technical excellence via pair programming (2 people one workstation), collective code ownership ("our code"), test-driven development (automated tests before creating code). Spiking (set aside time to explore solutions), refactoring(remove clutter from code), continuous integration (commit code into repository every couple hours to avoid fragmented dev)
-SAFe
Scaled Agile Framework, focuses on implementing Agile ideals at scale
-Prince2
Projects In Controlled Environments. Flexible enough to fit in agile or waterfall approaches Process based approach that says any project should have a controlled start (organize and plan then leap in), middle (keep everything organized controlled), and end (tidy up loose ends).
-SDLC
Requirement Analysis-> Plan-> Design-> Build-> Test-> Deploy-> Maintain-> Repeat
-DevOps
Practices that combine software development (Dev) and IT Operations (Ops)
-DevSecOps
Software development (Dev) and IT Operations (Ops) with integrated security (Sec)
-Hybrid Approach
A mixture of different frameworks / methodologies
-Project Business Case
A value proposition for a proposed project that may include financial and non-financial benefits. Often Includes business needs, analysis, strategic alignment, options, recommendation, and/or a feasibility study.
-TRUE
(T/F) Value is the ultimate indicator of project success
-Linear + Nonlinear Programming
Project selection method using mathematical modeling known as "constrained optimisation"
-Constrained Optimization
the process of optimizing an objective function with respect to some variables in the presence of constraints on those variables
-Net Present Value (NPV)
Project selection method providing a value based on the assumption that money is worth more today than tomorrow. You want projects with a high value of this
-Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Project selection method based on the idea that if this project was an interest rate %, what would it be? You want projects with a high value of this
-Return on Investment (ROI)
A % value that shows how much money will be made when Investing. You want projects with a high value of this
-Benefit to Cost Ratio (BCR)
How many X$ do I get back for every Y$ I invest? X:Y Only invest in projects where X is higher than Y
-Pay Back Period (PBP)
How long will it take us to pay back what we invested in the project? Shorter durations preferred
-Scoring Model
A matrix where projects are rated by criteria which are weighted by importance
-Opportunity Cost
What's the cost of other opportunities that were given up by investing in this one?
-Procurement
The process of purchasing goods and services.
-Name the four common Procurement Methods
Build/Make(build inhouse), Buy(outsource), Lease(Hire/Rent instead of buying), Subscription/Pay-as-you-go(e.g. Cloud services)
-Capital Expenditures
Major investments which are depreciated over time
-Operation Expenditures (OpEx)
Relates to ongoing expenses, which are often tax deductible
-Pre-Qualified Vendors
A list of approved suppliers
-Pre-Determined Clients
Partner organizations we already have agreements with
-Pre-Existing Contracts
Will speed up procurement processes
-Request for Information (RFI)
Used to narrow down the list of possible suppliers. Asks, "does the vendor have the skills/capacity?"
-Request for Proposal (RFP)
Evaluates factors beyond just the price of a service. Detailed + complex design approach + timelines + costs
-Request for Quote (RFQ)
Used for cost of a predetermined list of items (e.g. I want these 10 items, how much is that?)
-Request for Bid (RFB)
Similar to RFQ (it's used for a set list of items) but offers are submitted in sealed envelopes to the client (like a govt dept) and the lowest bid is accepted.
-Fixed Price Contracts
A Total Fixed Price is set for the product or service. Appropriate when the scope is well defined, and no significant changes are expected.
-Firm Fixed Price (FPP)
Price Fixed at outset and wont change unless scope changes
-Fixed Price Incentive Fee (FPIF)
Fixed Price plus bonus if target is met
-Fixed Price with Economic Price Adjustments (FPEPA)
Fixed Price with adjustments to cover cost changes (e.g. for currency exchange rates or cost of oil)
-Cost Plus Contracts
The buyer pays the seller for the actual costs, plus a fee representing profit for the seller. Appropriate when the scope is expected to change slightly.
-Cost Plus Fixed Fee (CPFF)
Costs paid by buyer, and then a fixed fee paid on completion
-Cost Plus Incentive Fee (CPIF)
Costs paid by buyer plus bonus if target is met
-Cost Plus Award Fee (CPAF)
Costs paid by buyer, plus a performance-based bonus at buyer's discretion
-Time and Materials Contracts
The vendor charges for time spent (generally at an agreed hourly rate), plus the cost of any materials.
-Statement of Work (SOW)
The details of the services or goods we want to purchase, so that the vendor knows what we're asking them to provide, similar to TOR, generally used for procuring material goods or to help vendors put together a proposal for goods or services.
-Scope Statement
Describes what we're going to create in the project, providing a common understanding for all involved, and will enable us to do more detailed planning.
-Terms of Reference (TOR)
The description of the work requirement including the scope, timeline, resources, etc. Similar to SOW. Generally used for procuring services.
-Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)
Get your vendor to sign this if they'll be exposed to sensitive information or trade secrets that you don't want shared outside of your organization.
-Cease and Desist Letter (C&D)
Used to stop somebody doing something immediately and never do it again. E.G. if they are violating copyright/patent.
-Memorandum of Understanding
Not legally enforceable, but might be useful for outlining terms when it's not possible to create a legal agreement between parties.
-Letter of Intent (LOI)
Describes the intention of what the buyer and vendor are going to do, usually before they enter into a contract. Not always legally binding, but can carry weight.
-Master Service Agreement (MSA)
A kind of umbrella agreement to set general terms between parties, which can help streamline future contracts.
-Service Level Agreement (SLA)
Defines expectations of the level of service provided by the vendor E.G. how quickly issues will be responded to.
-Maintenance Agreement
Describes what the vendor is expected to do in order to keep the goods or service you purchased up and running
-Warranty
The Vendor's guarantee that the product will perform as expected for a specific period of time
-Purchase Order (PO)
The official document issued by a buyer committing to pay the vendor for the sale of the specified products or services.
-Key Purpose of the Business Case
Should the Project Proceed?
-The Project Charter
Provides high level information to define project objectives, set boundaries, align expectations, and describe success. Created at an early stage to reflect stakeholders' common understanding of what will be performed in the project. Covers general project info, project vision, org (people), implementation overview.
-Key Purpose of the Project Charter
Authorize the Project to Begin
-Project Sponsor
The person / group who provides resources and support for the project (is also a stakeholder)
-Stakeholder
anyone who can affect or is affected by our project (or who thinks so). Provides feedback, input, requirements, but typically do not have decision making authority.
-FALSE; Identify stakeholders early on!
(T/F) There is no need to identify stakeholders early in a project.
-TRUE
(T/F) Different stakeholders have different levels of priority/influence in a project
-Describe ways to identify stakeholders
Review other projects, ask around, brainstorm.
-Techniques used to assess stakeholders
Power/Influence classification grid, stakeholder cube, salience model.
-Classification Grid
stakeholder assessment technique that involves 2d graph of power and influence (can also be interest or impact) used to plot each stakeholder's relative power (vertical) and influence (horizontal)
-Stakeholder Cube
Stakeholder assessment technique that builds upon the classification grid, adding an impact or interest as a third criteria and creating a 3d graph, where the third criteria is the Z axis
-Salience Model
stakeholder assessment technique that essentially venn diagrams stakeholders along relative criteria (e.g. power, urgency, legitimacy)
-Directions of Influence
stakeholder assessment technique that places stakeholders in a table along with their direction of influence in a neighboring column (e.g. downwards and sideways means they influence their employees and coworkers)
-Stakeholder Register
The main output of all stakeholder identification efforts. This is a document that includes main identification, assessment information, and classification for all stakeholders related to a project.
-Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM)
Assigns project deliverables to the key stakeholder who will be responsible for them, providing clarity and structure. Looks like a table with two columns.
-RACI
A kind of responsibility assignment matrix that identifies the Responsible, Accountable, Consulting, and Informed.
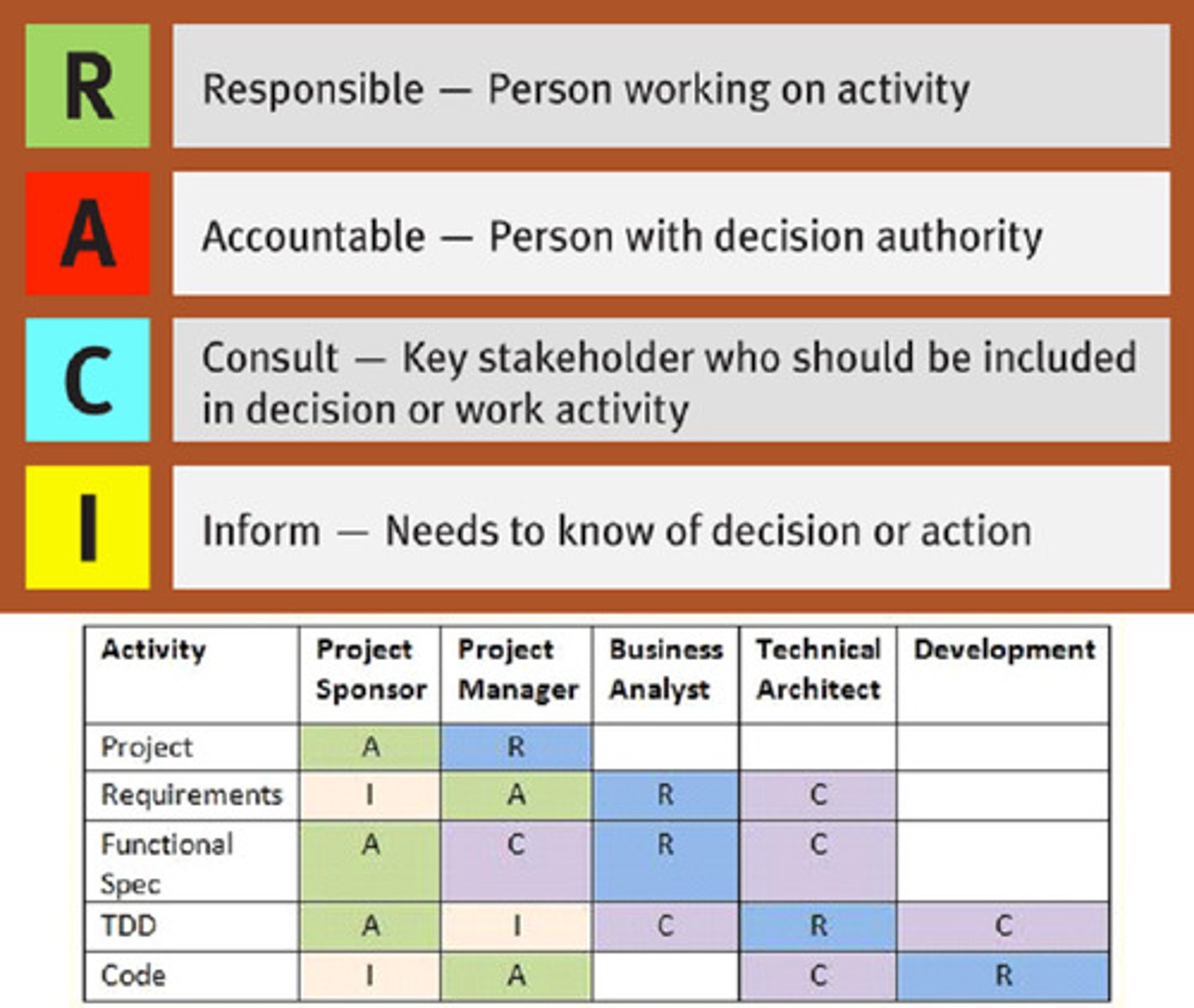
-The Responsible Person in a RACI
The person who's actually responsible for doing the work, only 1 name.