Swine production final
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
environmental pollution
major concern with waste management
EPA
organization that controls CAFOs
concentrated animal feeding operation
A large indoor or outdoor structure used to raise animals at very high densities
2500 hogs >55 lbs.
45+ days of confinement
requirements for an organization to be considered a CAFO
liquid slurry
semi-solid
dry
forms of manure
water
carbon
nitrogen
phosphorus
potassium
sulfur
nutrients present in manure
10:9:8
ideal N:P:K ratio
phytase
phosphatase (enzyme) is required to liberate phosphorus from phytase molecule
self-distribute
manure collection strategy for dry manure
under-floor storage pit
lagoon
storage tank
manure collection strategy for liquid manure
anaerobic lagoon
cause odor pollution
more shallow
slurry storage tank
manure is collected in large reservoir, allows for improved fertilizer value
9,500 - 11,500 (millions)
estimated number of pigs processed over 1 year
March and October
biggest/highest demand months for hog slaughter
pork checkoff program
established by the national pork board to produce ideal market hogs, set the standard of excellence for quality market hogs in the United States
production, carcass, and meat quality character
areas evaluated in pork checkoff program
auction
direct to buyer (private treaty)
contracts
market channels
contracts
most popular market channel in industry
summer
time of the year when lean hog prices are the highest
corn
resource that lean hog prices are based on
1 boar/20 sows
boar to sow ratio for live cover
1 boar/200 sows
boar to sow ratio for AI
replacement gilts
terminal market hogs
purpose of boars in the herd
8 months
age at which a boar can be used for breeding
12 even teats
no genetic abnormalities
strong feet/legs
wide stance
ability to move freely
features of reproductive soundness
body length/depth
height
size
features of conformation
10+ farrowed
8+ weaned
type of litter that boar should be selected from
250 lbs. at 155 days
2.75lbs. feed/1lb gain
gain 2+ lbs./day
performance requirements when selecting boars
ideal backfat measure
EPD
estimate of how future progeny of sire will perform
selection index
incorporates genetic evaluation of performance record, includes multiple traits
overall BV in terms of money
values based on 100
number born alive (NBA)
Number of live pigs born per litter, expressed as number of individuals, 10% heritability
21 day litter weight
weight in pounds of total litter adjusted to 21 days, 15% heritability
days to 250
number of days it takes a hog to reach market weight, reflects feed efficiency and intake, 35% heritability
backfat depth
measured at 10th rib, amount adjusted to 250lbs., negative correlation to muscle, 40% heritability
terminal sire index
swine- Ranks hogs on DAYS, LBS, F/G and BF only and does not include any maternal information
16 sq ft
size of housing crates
42 sq ft
size of housing pens
penned separately
crates
pens
housing options for boars
common area
flooring highly important
breeding area
>85% F
temperature at which semen quality begins to decrease
limit-fed at 6 months to prevent over-fattening
feed based on BCS
boar nutrition
daily observation
vaccination
treat for mange/lice
tusk trimming
features of routine management
loss of appetite
listlessness
lameness
features to look for during daily observation
2x per year
frequency of tusk trimming
erysipelas
a contagious disease of the skin and subcutaneous tissues caused by infection with streptococci organisms
infection by ingestion
edema of nose
snoring
diamond skin lesions
clinical signs of erysipelas
leptospira pomona
reproductive disease caused by infection by contact
show no external symptoms
mange
scabies, 15 day life cycle, lay eggs under skin
causes irritated crusty skin
ear --> neck --> body
pathway of infection of mange
insecticides
treatment of mange
lice
sucking and biting insect, lay eggs on hair near body, affects all parts of the body
causes irritated skin and decreased weight
insecticides
sanitation
treatment of lice
sperm and testosterone production
function of the testes
stores sperm (maturation)
function of epididymis
transports sperm during ejaculation
function of ductus deferens
produce seminal fluid
function of vesicular and prostate glands
produce gel
function of bulbourethral gland
individual mating
one boar with one female, requires a lot of labor and time
increased conception rates
pen mating
boar in pen with random females, boars rotated every couple days
training
facilities
requirements for collection for AI
safety
most important aspect of semen collection for AI
200 mL
average amount of ejaculate of mature boar
100 mL
3 billion cells
1 dose of sperm =
70-90%
ideal motility of sperm for insemination
7 days
average amount of time an extender can preserve sperm
within herd
Where most replacement gilts are found
well-developed underline
sound feet/legs
fast growing
from large litters
from high producing mothers
guidelines for selecting replacement gilts
structural soundness
volume/body capacity
muscling
leanness
underline quality
visual evaluation for replacement gilt selection
number born alive (NBA)
number of offspring born in a litter
expressed as number of individuals
10% heritability
21 day litter weight
weight in pounds adjusted to 21 days
15% heritability
maternal line index
index which includes TSI and maternal traits (SPI)
BF, Days, LBS, NBA, LWT, NW
maternal traits weighted 2x as much
sow productivity index
index which includes NBA, LW, and NW
indicates reproductive ability
based on average (100)
HAL gene
porcine stress syndrome
pigs have PSE pork
originally selected for lean meat
ESR gene
estrogen sulfate receptor
increased ovulation rate
K88 gene
- e. coli binds to the K88 receptor in gut
- no K88 = no e. coli = no scours
white skin
trait that packer prefer
5-8 months
180 lbs
age and weight of puberty
2-3 days
length of estrus
20-22 days
length of estrous
12 hrs before end of estrus
time of ovulation
114 days
length of gestation
3-7 days
amount of time post-weaning that cycling occurs again
level of fatty acids
level of carbs
level of leptin
factors that may affect onset of puberty
boar exposure
PG600
technique to bring prepubertal gilts into heat
Matrix
oral progesterone fed for 14 days to synchronize cycling females
group weaning
technique used to synchronize weaned sows
suckling
releases opioids that inhibit GnRH release --> prevents cycling
pure breeding
crossbreeding
types of breeding systems
purebreeding
eligible for breed registration, lineage, line purity and promotion
necessary to maintain genetic diversity and progress
crossbreeding
mating of animals of different breeds, aims to capture additive/nonadditive gene action
additive gene action
occurs when each gene has an expressed phenotypic effect
offspring exhibit phenotype that is the average of the parent's
nonadditive gene action
offspring traits differ from average of parent's
heterosis present
individual heterosis
how much hybrid vigor is in the offspring
increased performance traits due to crossbreeding
maternal heterosis
increased performance in sows and progeny from crossbred dam
increased litter size and rebreeding rates
paternal heterosis
increased performance in boars and progeny from crossbred sire
increased libido, breeding, and longevity
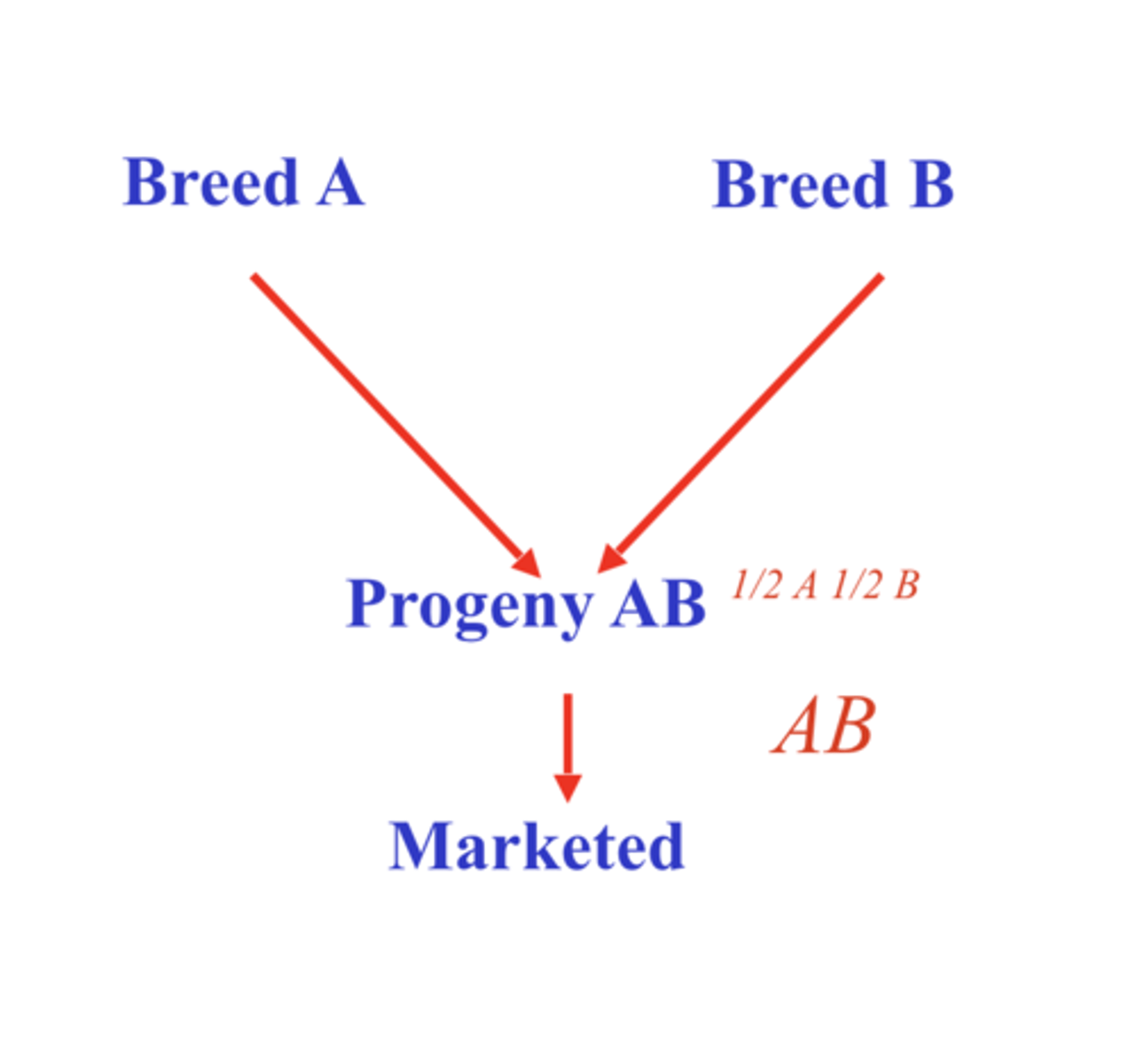
2 breed terminal cross
100% heterosis
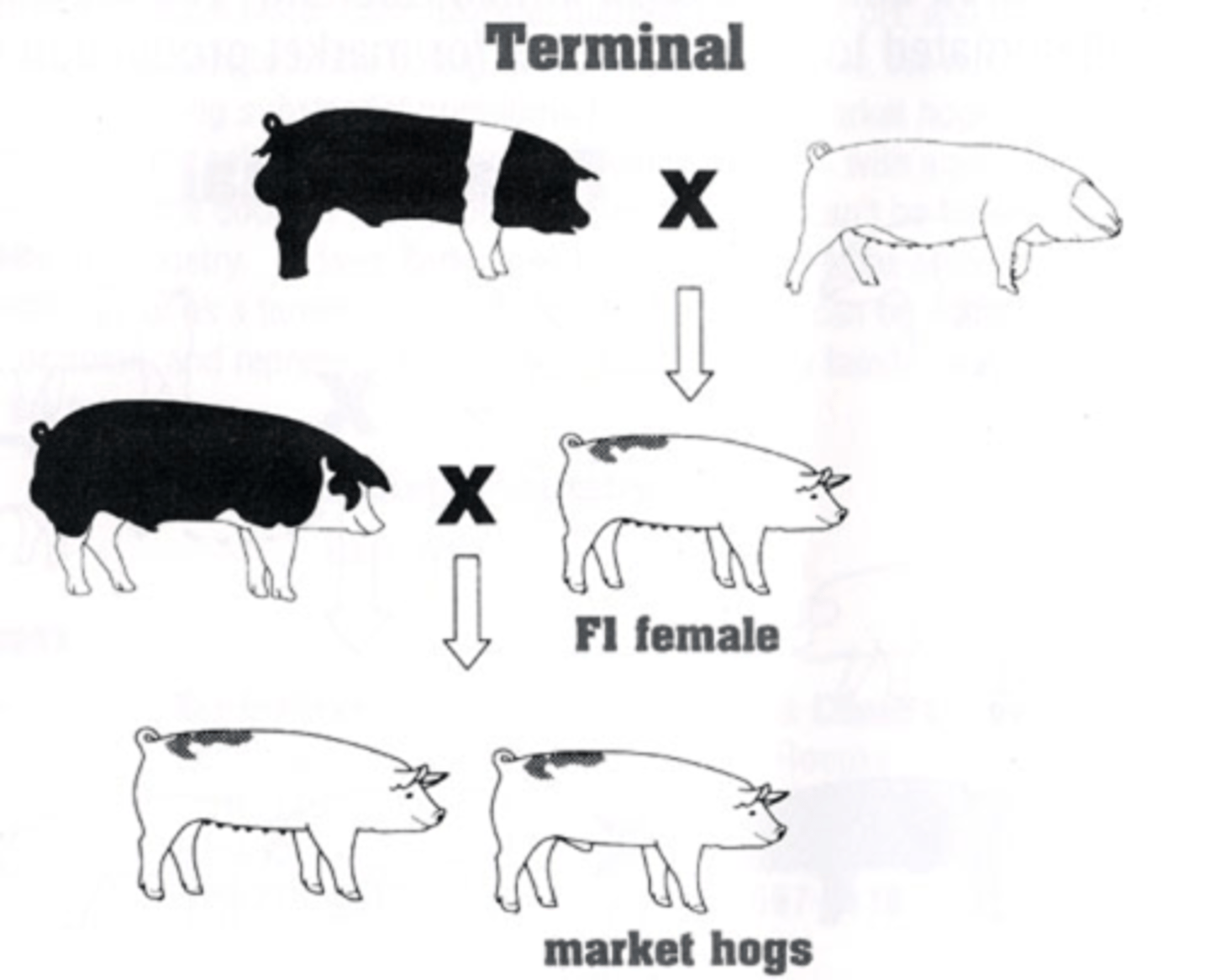
3 breed terminal cross
maintain 100% heterosis
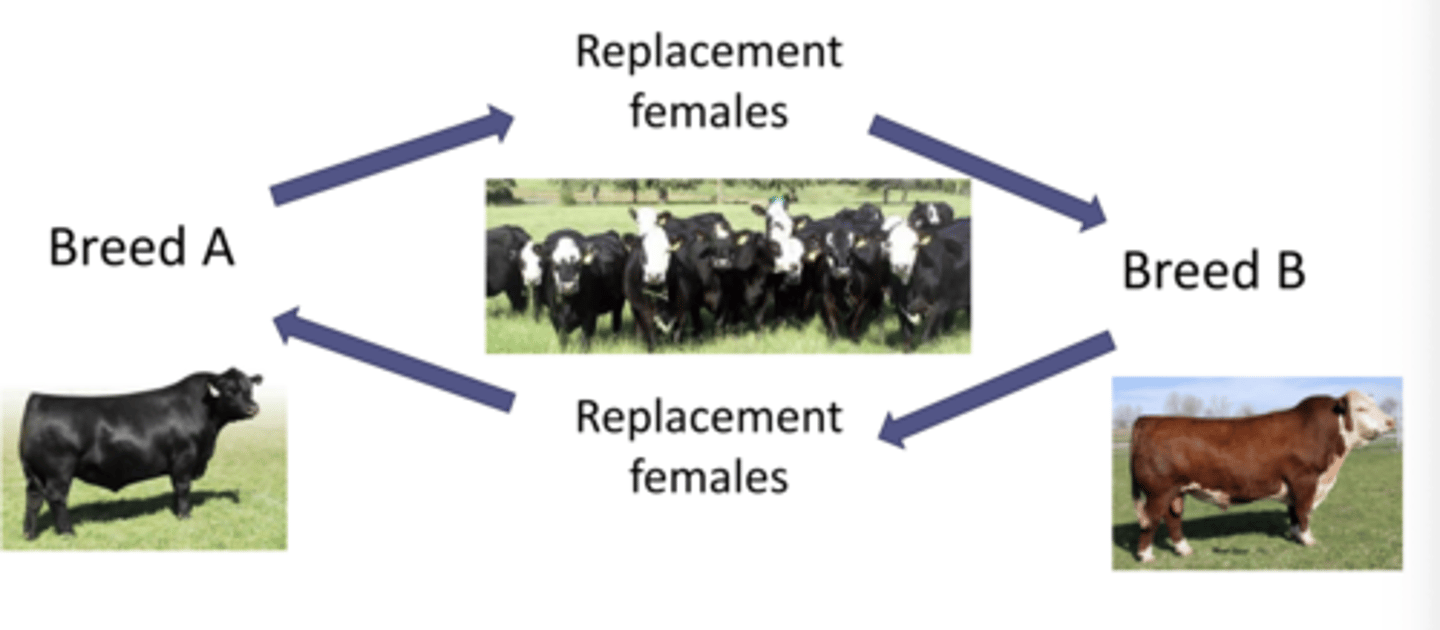
2 breed rotational cross
- Mate straight-bred sires of 2 different breeds to dams that are a mix of the two breeds
- Female progeny from one group transferred to the other group. All crossbred males are sold
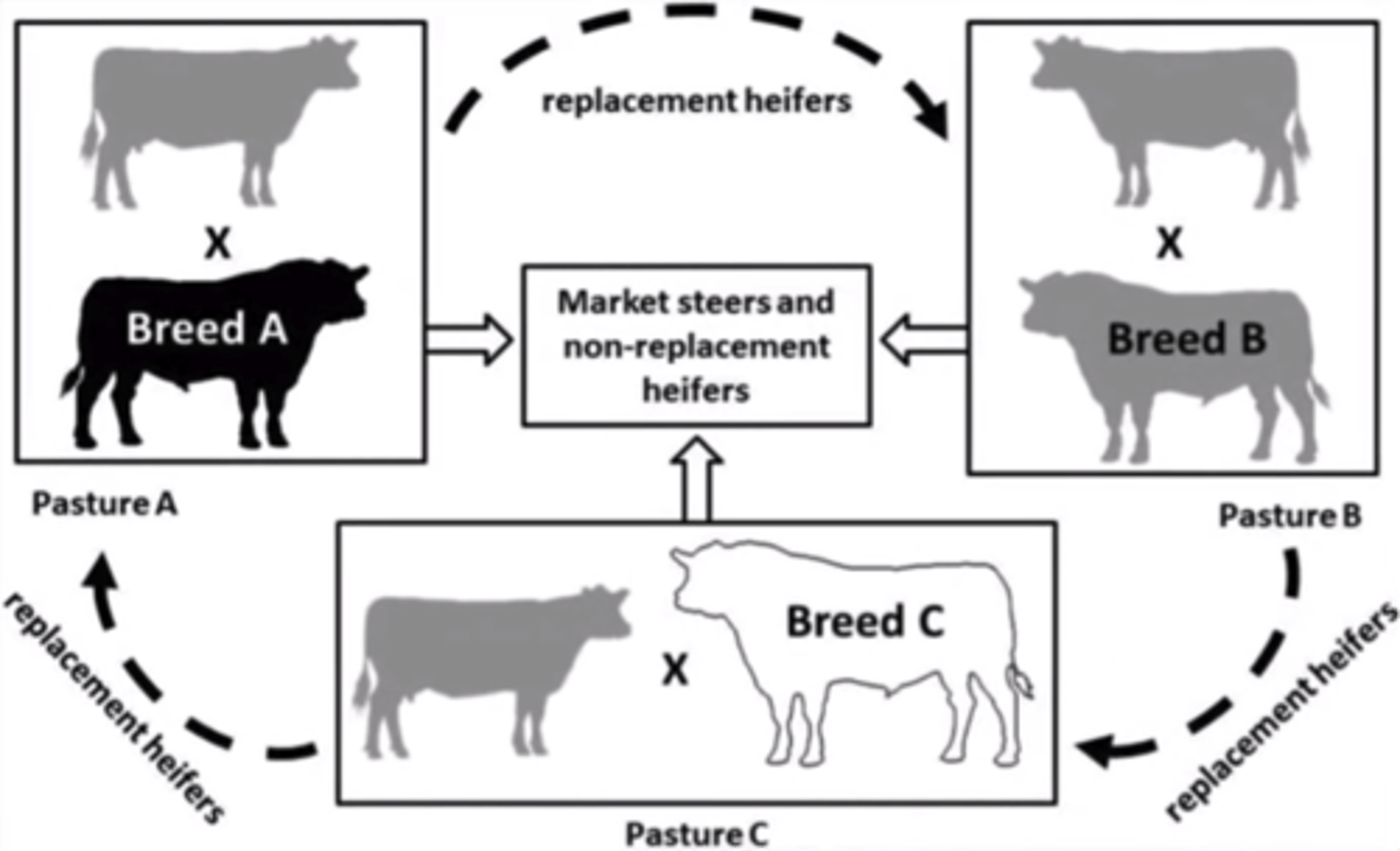
3 breed rotational cross
- Three different sire breeds are mated to females that are a mixture of the three breeds
- Crossbred dams are mated with the breed of sire to which they are least related.