AP Human Geography Unit 7
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Agglomeration
A cluster of enterprises that can provide assistance to each other through shared talents, services, and facilities.

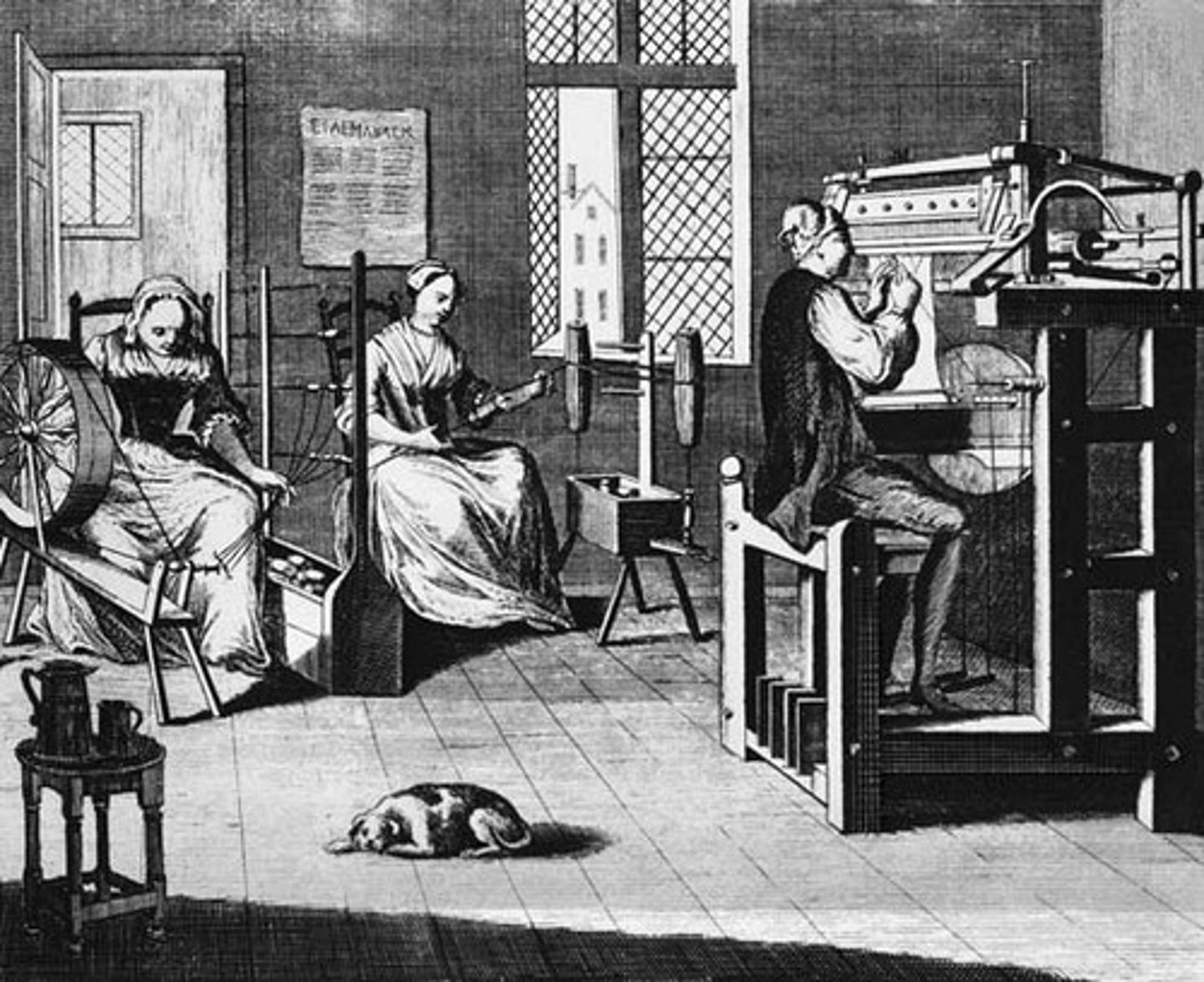
Cottage Industry
Manufacturing based in homes rather than in a factory, commonly found before the industrial revolution.

Deglomeration
The process of industries leaving the crowded urban centers of the U.S. Eastern megalopolis and move to other locations

Deindustrialization
A process by which companies move industrial jobs to other regions with cheaper labor, leaving the newly deindustralized region to switch to a service economy and to work through a period of high unemployment.

Dependency Theory
A theory which holds that the political and economic relationships between countries and regions of the world control, and limit the economic development possibilities of poorer areas.
Ecotourism
Tourism to exotic or threatened ecosystems to observe wildlife or to help preserve nature.

Fordist
Fords idea that the dominant mode of mass production that endured for much of the past century. Fordist also includes a social structures that supported mass production by corporations.

GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
Encompasses only goods and services produced within a country during a given year.

Gini Coefficient
The Gini coefficient's main advantage is that it is a measure of inequality by means of a ratio analysis, rather than a variable unrepresentative of most of the population, such as per capita income or gross domestic product.|

GNI (Gross National Income)
The monetary worth of what is produced within a country plus income received from investments outside the country.

GNP (Gross National Product)
A measure of the total value of the officially recorded goods and services produced by the citizens and corporations of a country in a given year.

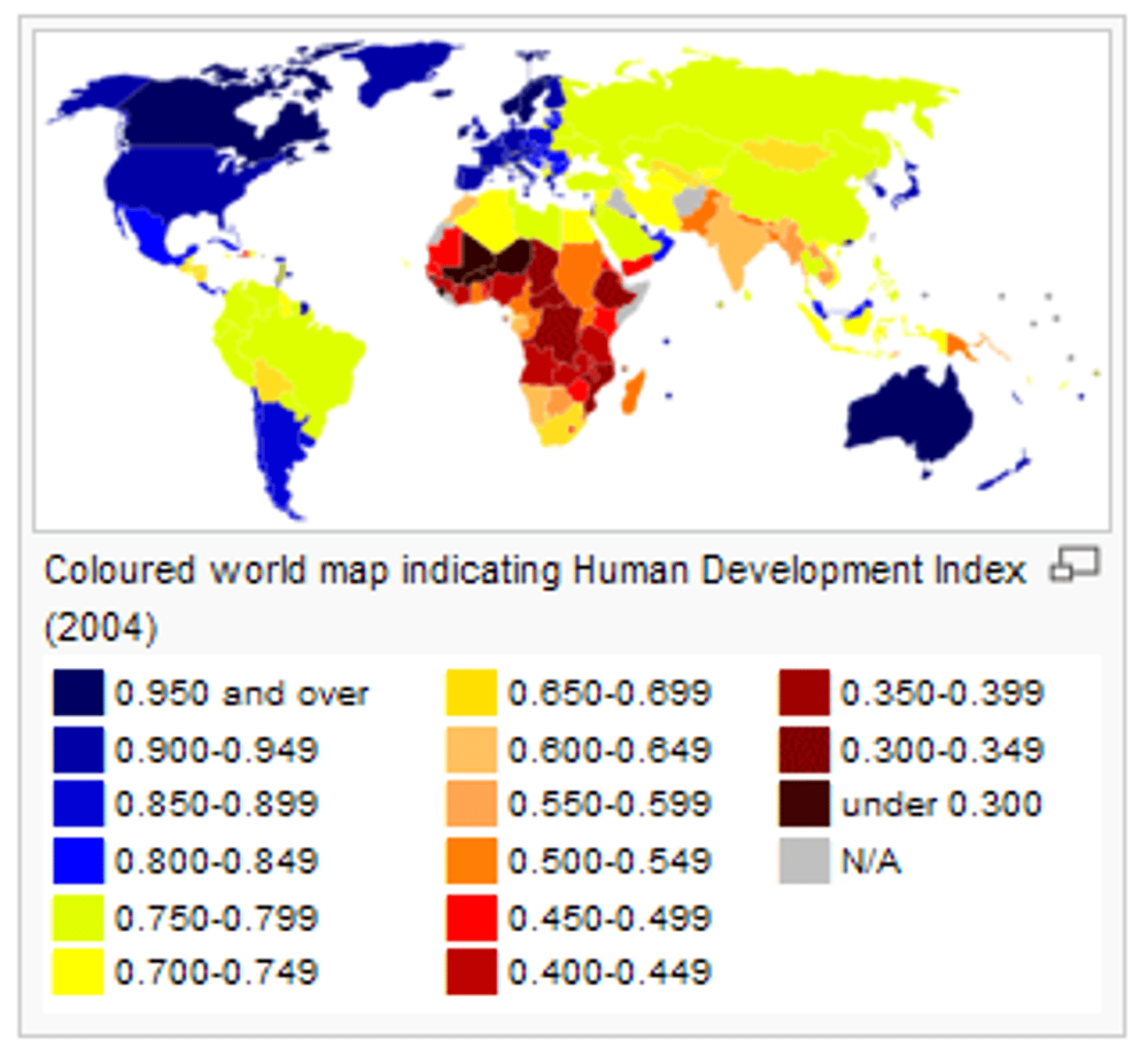
HDI
Human development issue
IMF (International Monetary Fund)
The lending of massive amounts of money to peripheral and semi-peripheral countries with restriction strings attached.

Industrial Revolution
A series of inventions that brought new uses to known energy sources, and new machines to improve efficiency, and enable other new inventions.

Just in Time Delivery
Rather than keeping a large inventory of components or products, companies keep just what they need for short term production and new parts are shipped quickly when needed.

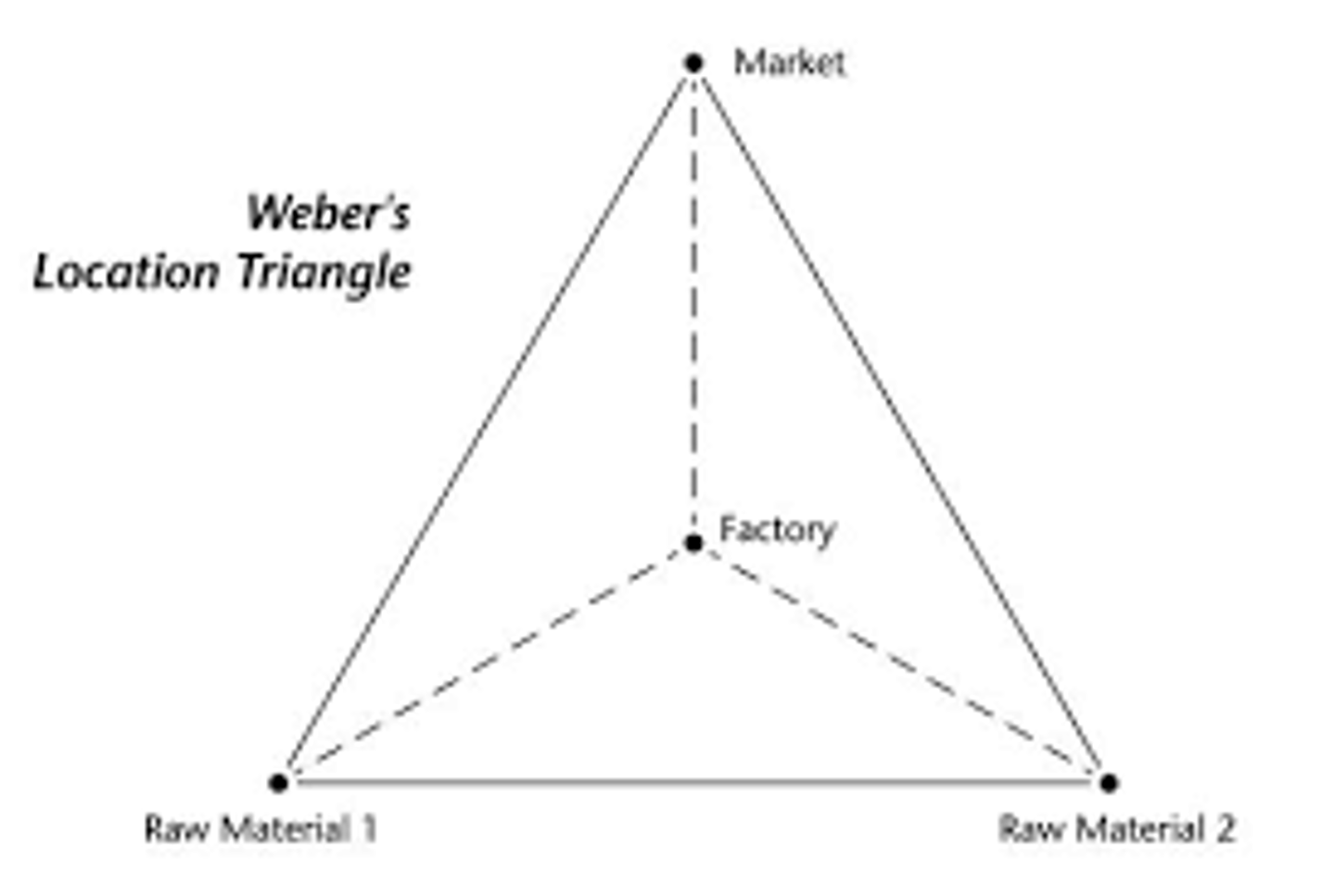
Least Cost Theory (Weber)
A theory that accounted for the location of a manufacturing plant in terms of the owner's desire to minimize three categories of cost. Transportation, labor, agglomeration. DISTANCE
Microcredit Program
A program that gives money to the poor, particularly women, to encourage the developement of businesses.

NIC (Newly Industrialized Country)
Newly industrialized country
Offshore
When outsourced work is located outside a country.

Outsource
A single factory is outsourced to suppliers, who focus their production and offer cost savings.

Post-Industrial
The rapid growth of the Quaternary, and Quinary sectors.

Primary Sector
The part of the economy that draws raw materials from the natural environment.

Quaternary Sector
Industries for the collection, processing, and manipulation of information and capital.

Quinary Sector
Industries for the actives the facilitate complex decision making and the advancement of human capacities.

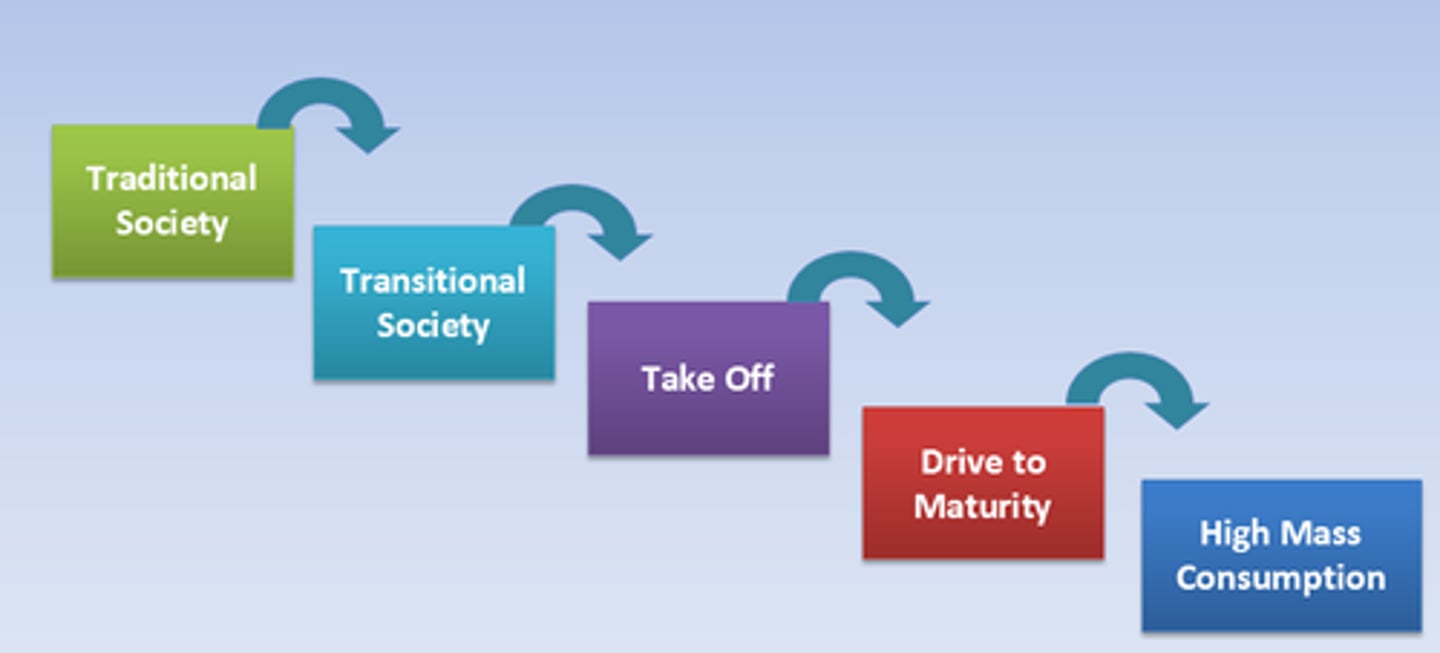
Rostow's Developement Model
The classic development model.
Secondary Sector
The portion of the economy concereced with manufacturing useful products through processing, transforming, and assembling raw materials

Tertiary Sector
Services related to transportation and communication.

Trafficking
Adults and children fleeing poverty or seeking better prospects are manipulated, decieved, and bullied into working conditions the would otherwise not choose.

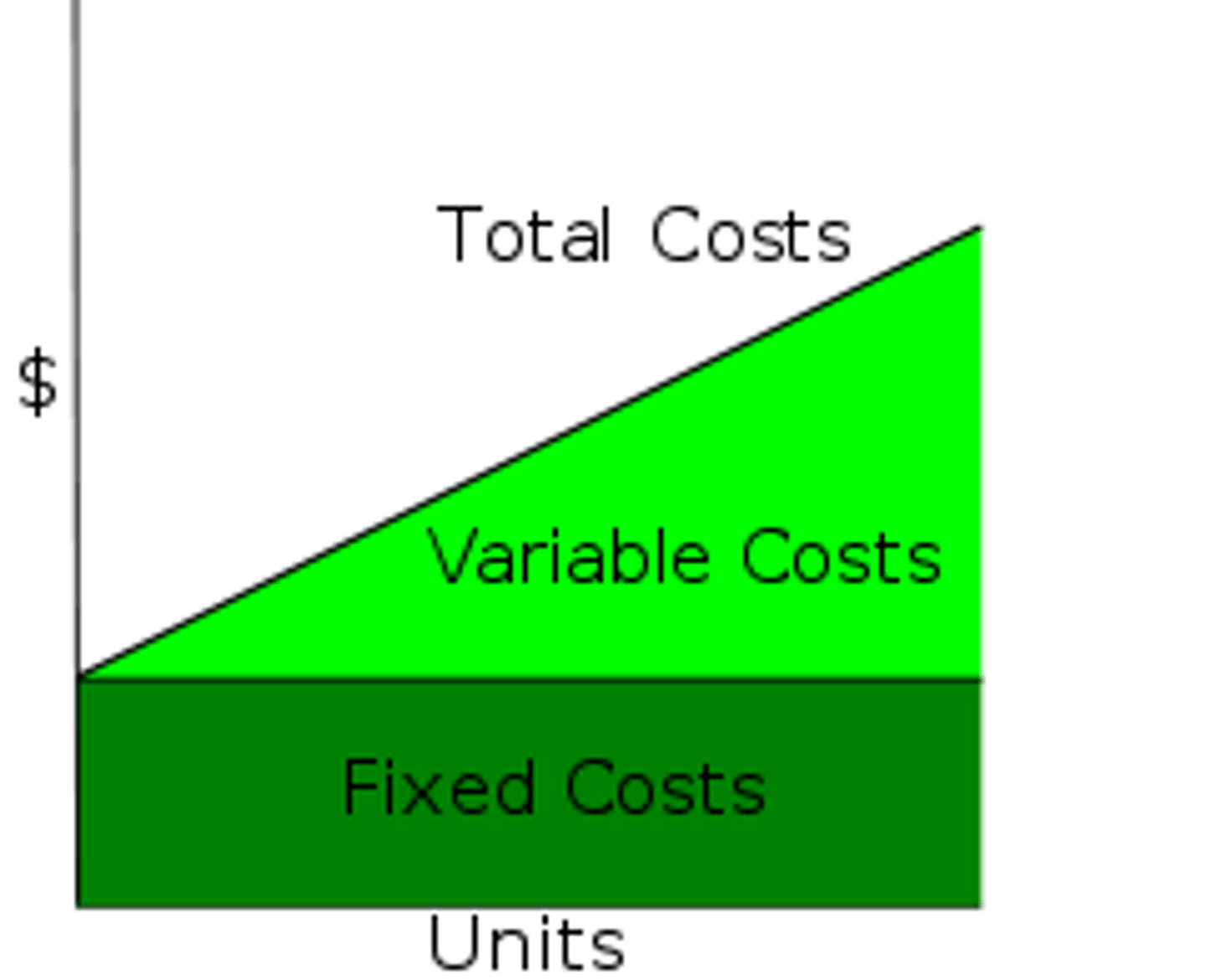
Variable Costs
Costs such as energy supply, transport expenses, labor costs, and other costs relating to the industrialiazation of an area.
WTO
World Trade Organization works to negotiate rules of trade among the member states

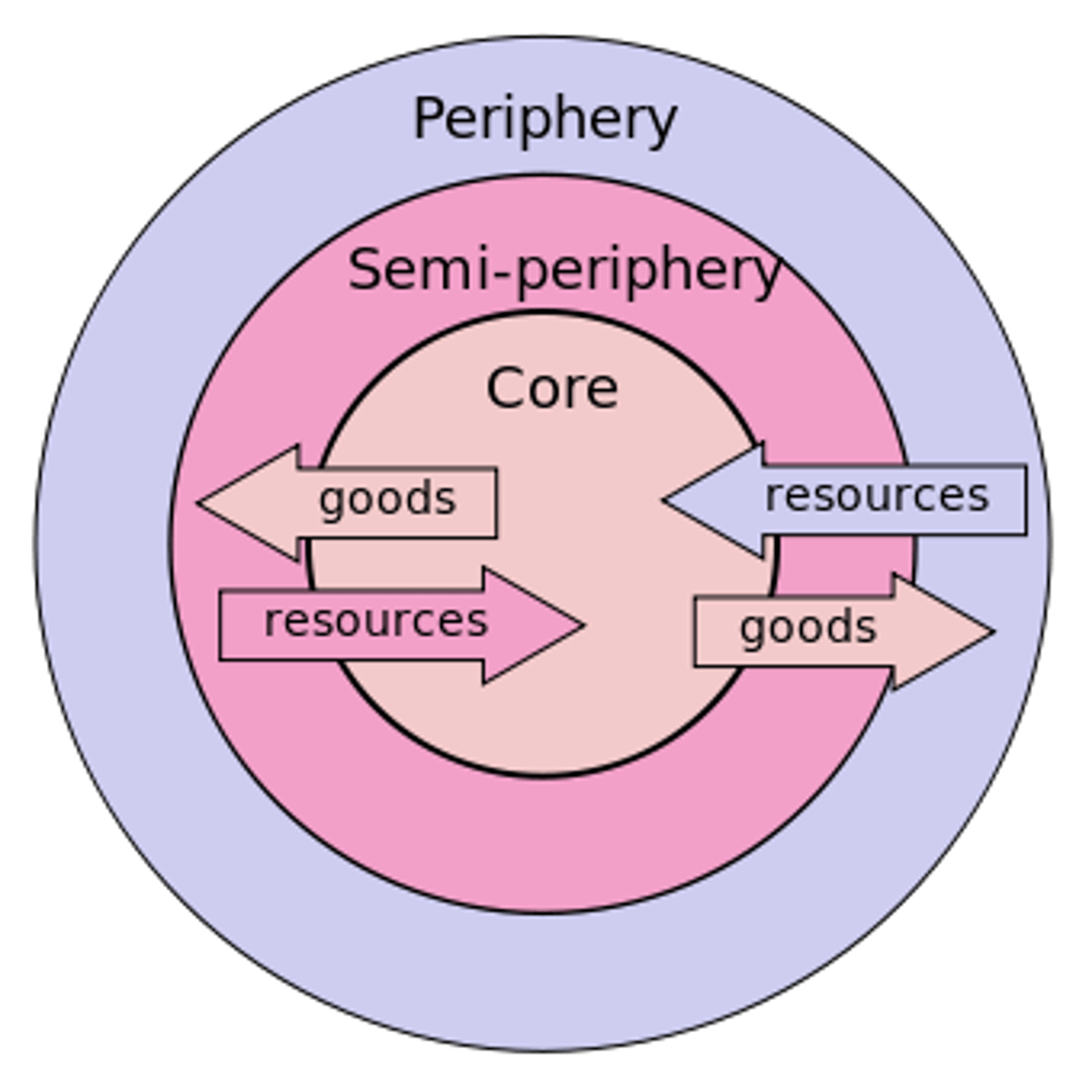
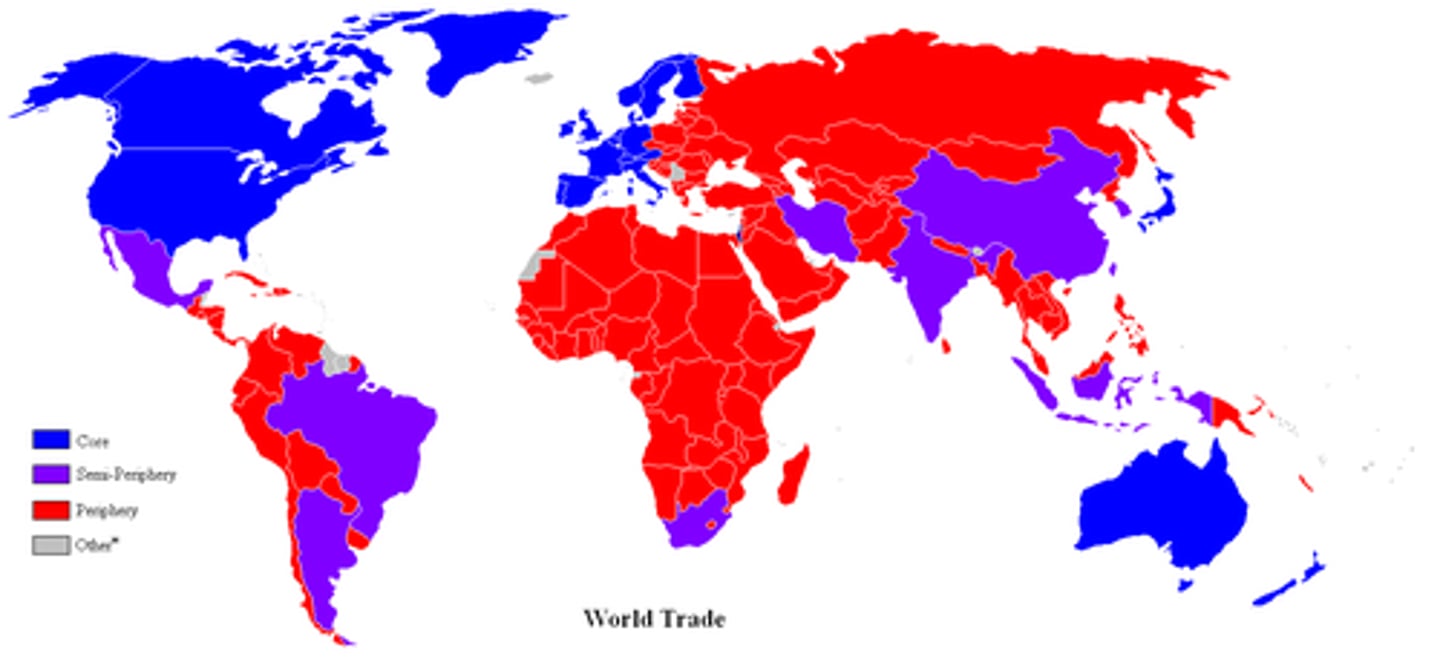
core countries
industrialized former colonial states that dominate the world economic system
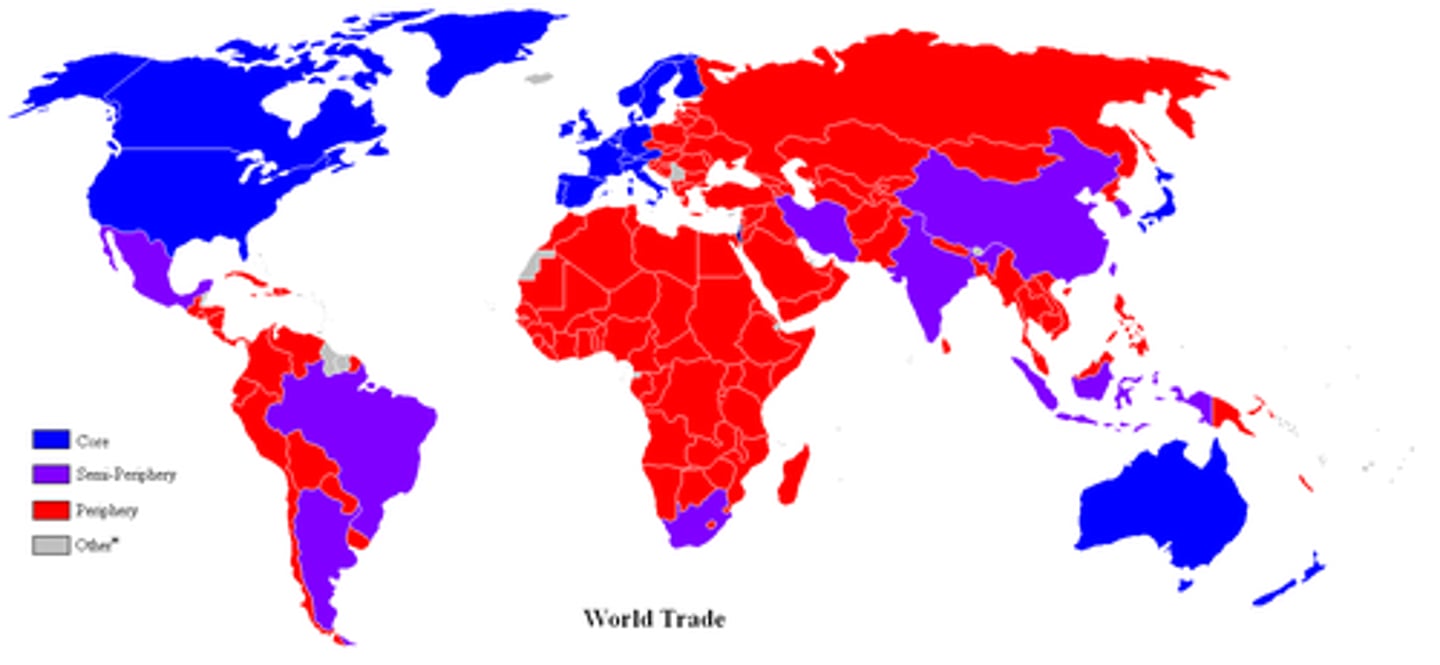
Periphery
countries with low levels of economic productivity and a disproportionately small share of the world's wealth with weaker state institutions, lower standards of living and are often dependent on the core
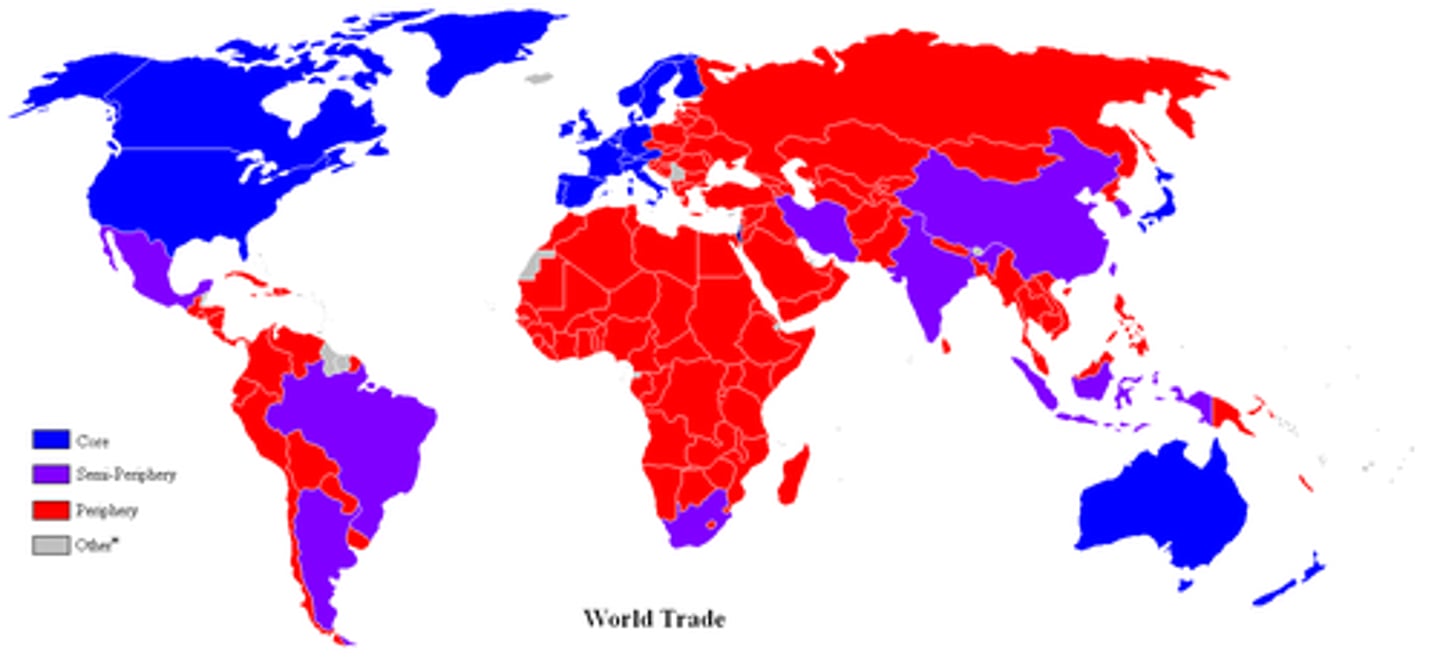
semi-periphery
places where core and periphery processes are both occurring; places that are exploited by the core but in turn exploit the periphery
Post-Fordist Production
Adoption by companies of flexible work rules, such as the allocation of workers to teams that perform a variety of tasks.

comparative advantage
the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer

complimentary
When one country has the goods and services that another country desires

Tariffs
Taxes on imported goods

multiplier effect
An effect in economics in which an increase in spending produces an increase in national income and consumption greater than the initial amount spent.
Horrizontal integration
In business, horizontal integration is a strategy where a company creates or acquires production units for outputs which are alike - either complementary or competitive. One example would be when a company acquires competitors in the same industry doing the same stage of production for the creation of a monopoly.
Vertical Integration
Practice where a single entity controls the entire process of a product, from the raw materials to distribution
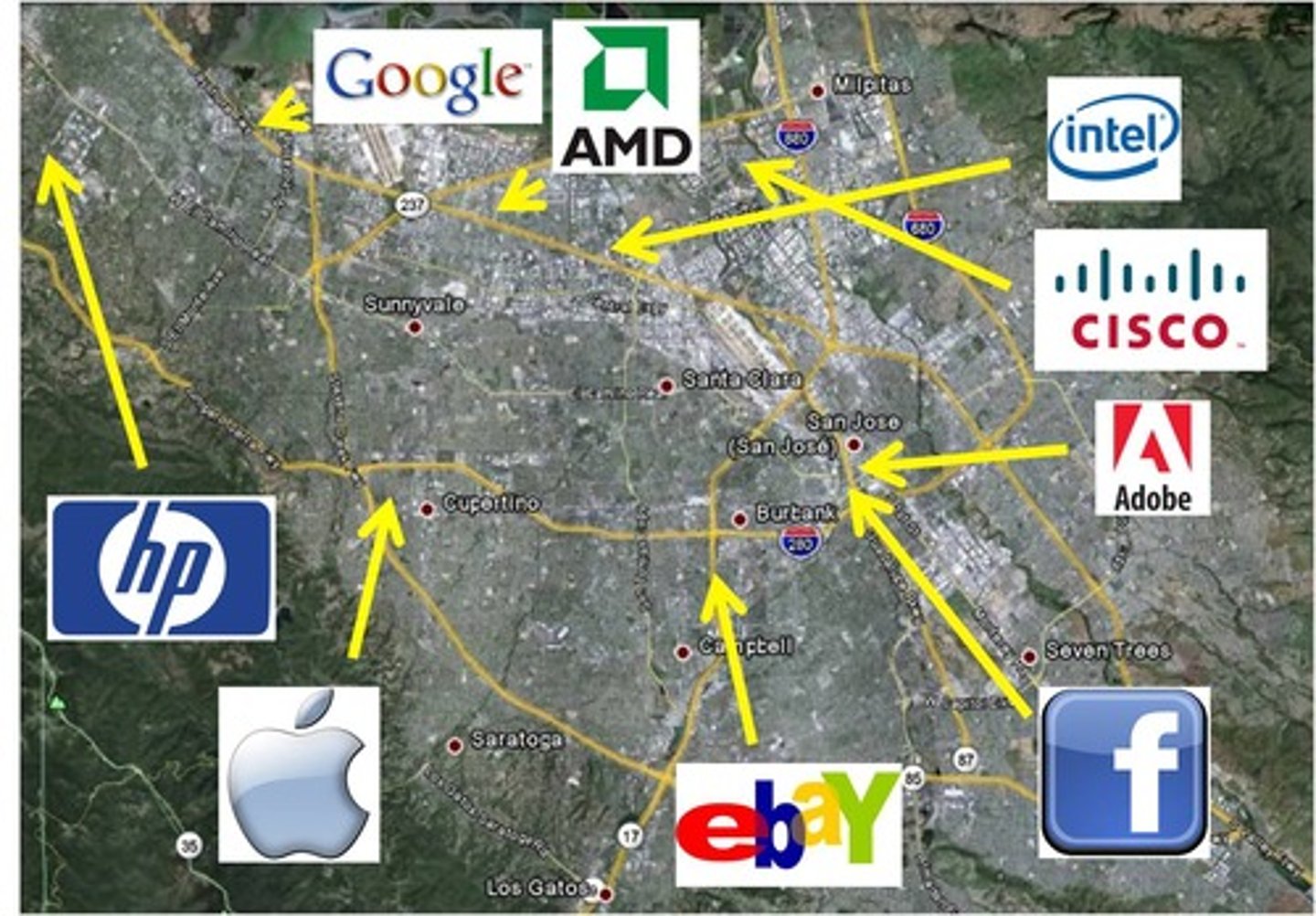
techno poles/growth pole
A center of high-tech manufacturing and information-based industry.
Break-of-bulk point
A location where transfer is possible from one mode of transportation to another.

GII (Gender Inequality Index)
A measure of the extent of each country's gender inequality
