Lipids
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This deck contains content from 3.1.3 Lipids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Are lipids polymers?
No
What elements are lipids made of?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Phosphorous(Phospholipids)
What bonds join the components of lipids?
Ester bonds
How is the proportion of O to C & H in lipids compared to that of in carbohydrates?
It is smaller
Are lipids soluble in water?
No
Are lipids soluble in organic solvents?
Yes
Give examples of organic solvents…
Alcohols
Acetone
What are the two types of lipids?
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
What do saturated fatty acids generally make?
Fats
What do unsaturated fatty acids make?
Oils
What are the 4 functions of lipids?
Source Of Energy
Waterproofing
Insulation
Protection
What makes lipids a good source of energy?
When they are oxidised, they provide more than twice the energy as the same mass of carbs & release H2O
What makes lipids good in waterproofing?
They are insoluble in water
What makes lipids good insulators?
They are slow conductors of heat and electricity, making them good in myelin sheath around nerve cells.
What makes lipids good for protection?
They can be stored around the organs.
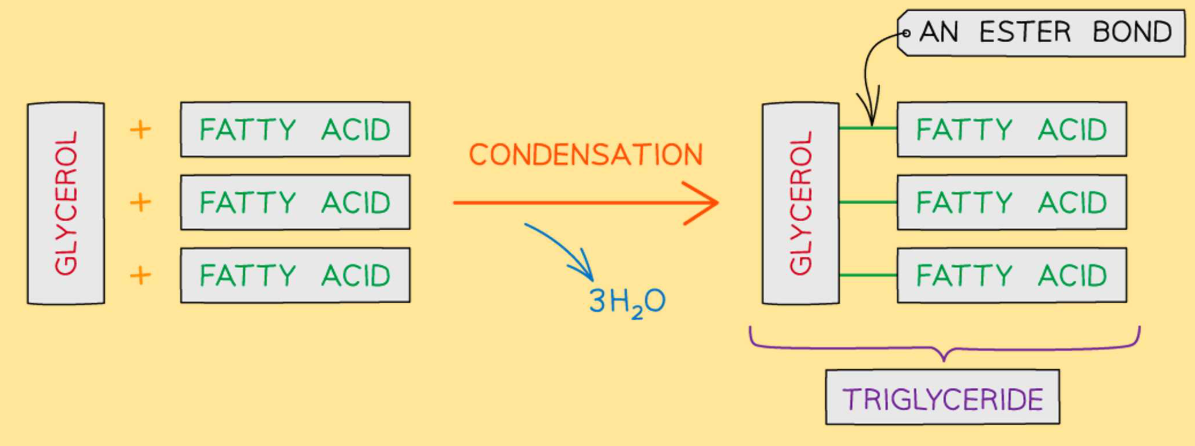
What are triglycerides made up of?
A glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Where does the ester bond form?
Between the hydroxyl group of the glycerol & the carboxyl group of the fatty acid.
Are triglycerides polar?
No
Are triglycerides hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic
What does the condensation of a triglyceride look like?
What makes up a fatty acid?
A methyl group at one end
Hydrocarbon chain(unsaturated or saturated)
A carboxyl group at the other end
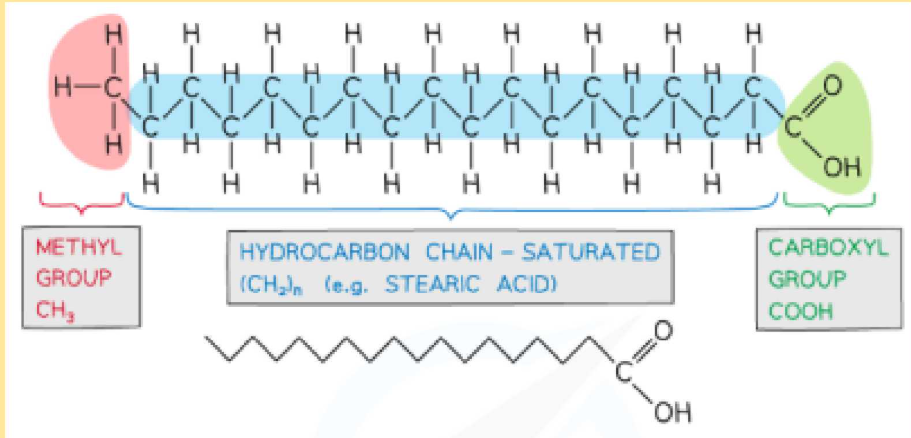
What may the hydrocarbon chain in a fatty acid be?
Saturated/unsaturated
What does saturated mean?
There are no carbon-carbon double bonds in the hydrocarbon chain
What does unsaturated mean?
There is at least one carbon-carbon double bond in the hydrocarbon chain.
What are the two types of unsaturated?
Monounsaturated - one double bond
Polyunsaturated - more than one
What are the 4 relationships between structure and function in triglycerides?
High-ratio of energy-storing carbon-hydrogen bonds to carbon atoms, so a great source of energy
Low mass to energy ratio, so a good storage molecule as a lot of energy can be stored in a small volume
Large, non-polar molecule that is insoluble in water, so their storage doesn’t affect osmosis in cells or the water potential of them
High ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, so release water when oxidised and provide an important source of water
What is a phospholipid made up of?
Two fatty acids
A glycerol molecule
A phosphate molecule
Are phospholipids polar?
Yes
What makes phospholipids polar?
Fatty acids are hydrophobic, so repel water
Phosphate is hydrophilic, so interacts with water
How does a phospholipid look?
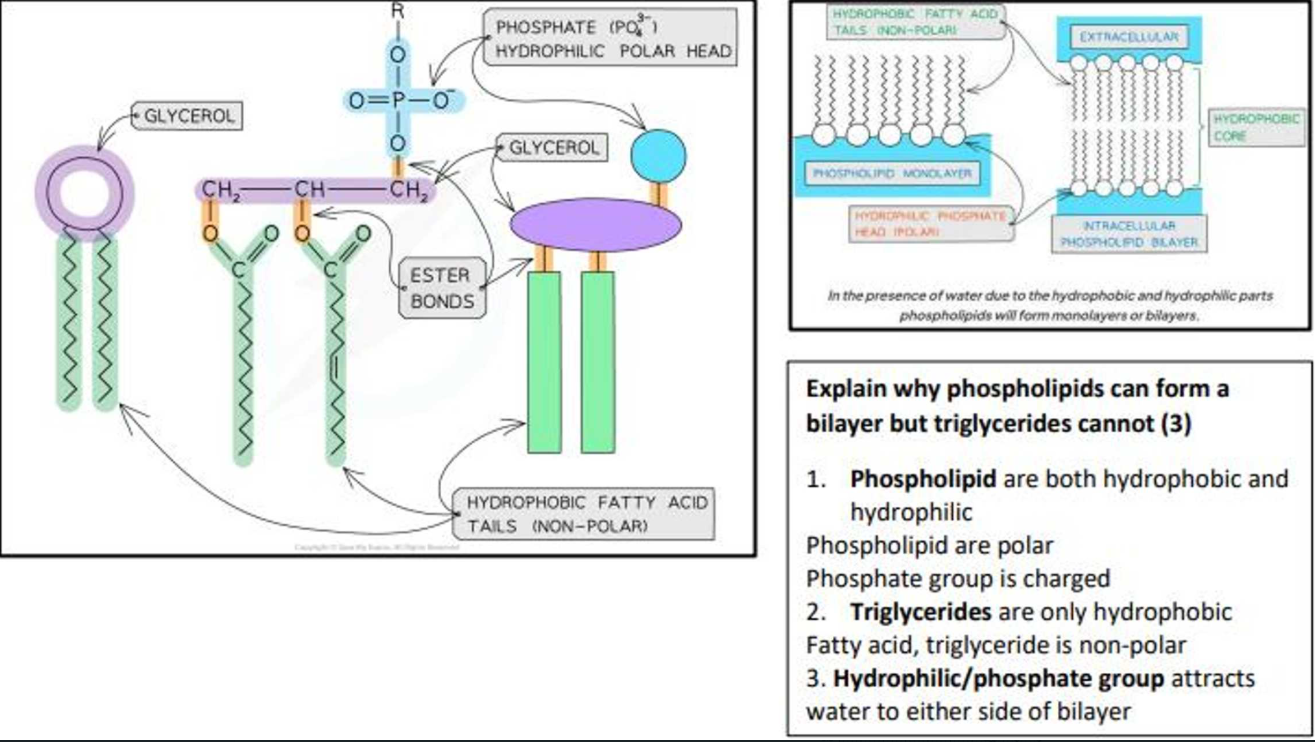
What are the 3 relationships between structure and function in phospholipids?
Polar molecules, so in an aqueous environment, phospholipid molecules form a bilayer within cell-surface membranes, hydrophobic barrier is formed between the inside and outside of the cell
Hydrophilic phosphate ‘head’ help to hold at the surface of the cell-surface membrane
Form glycolipids by combining with carbohydrates within the cell-surface membrane. These are important for cell-recognition
What is the test for lipids called?
The emulsion test
What is the method for the emulsion test?
Add ethanol
Shake - dissolves and lipid in sample
Add water
Shake gently
What is the positive result for the emulsion test?
A white emulsion indicates the presence of a lipid