Geo - RANDOM
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
How to find grid reference?
Along then up
Bottom left corner
Split box into 10 across, 10 up smaller boxes
Examples of how the development gap can be closed.
Investment
Micro finance
Debt relief
Fair trade
What is a refugee?
A person who is forced to leave a country
What is illegal immigration?
Moving to a different country illegally
Why are areas like the Maldives most risk of climate change?
Low level island
Could be uninhabitable by 2030
What is global atmospheric circulation?
The pressure around the world
What a natural hazard?
A natural event that puts humans at risk.
What are 3 social effects of climate change?
Less food
Wars
Less fresh water (Less rain)
What are the 3 barriers to development?
Trade
Landlocked
Colonisation
What does the demographic transition model do?
Shows how population changes over time as a country develops
What are 3 natural causes of climate change?
Sunspot theory
Milankovich cycle (orbital)
Continental drift
Eruption theory
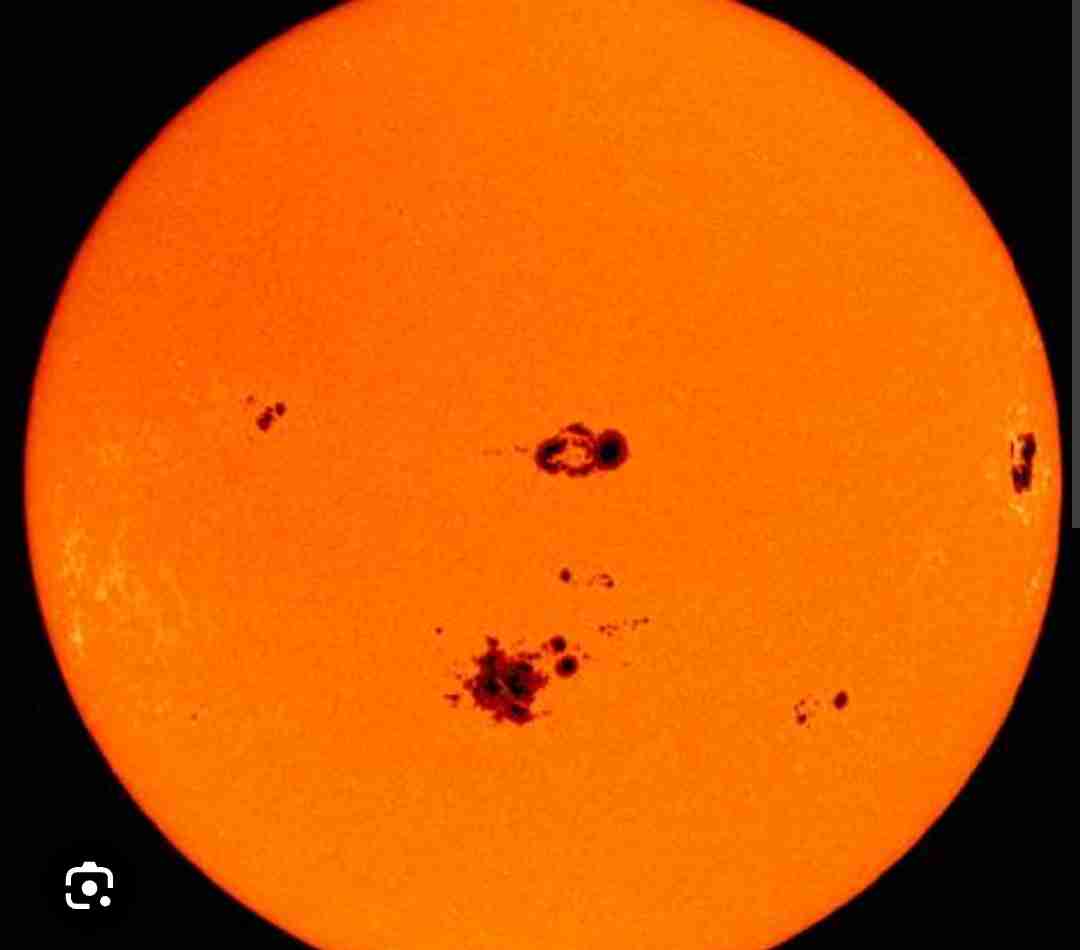
What is the sunspot theory?
Where bursts of hydrogen from the sun radiate to earth because of weak spots in the sun’s surface.

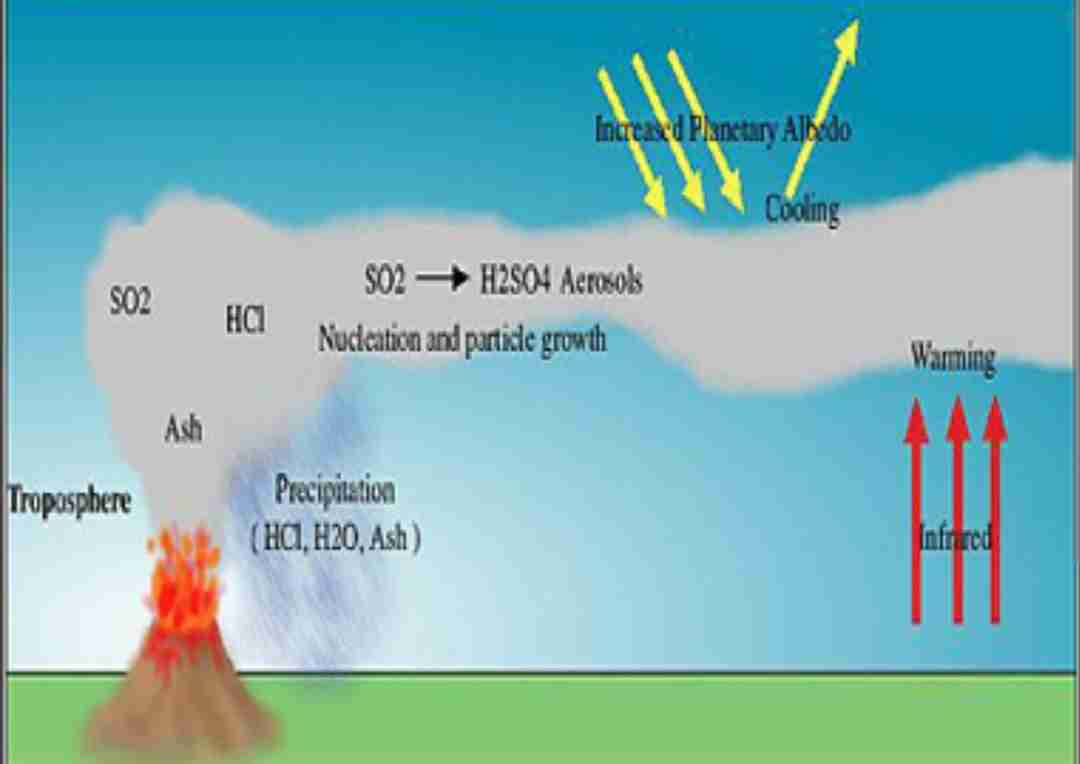
What is eruption theory?
Where it is believed that if a volcano errupts then it could change the earth’s climate
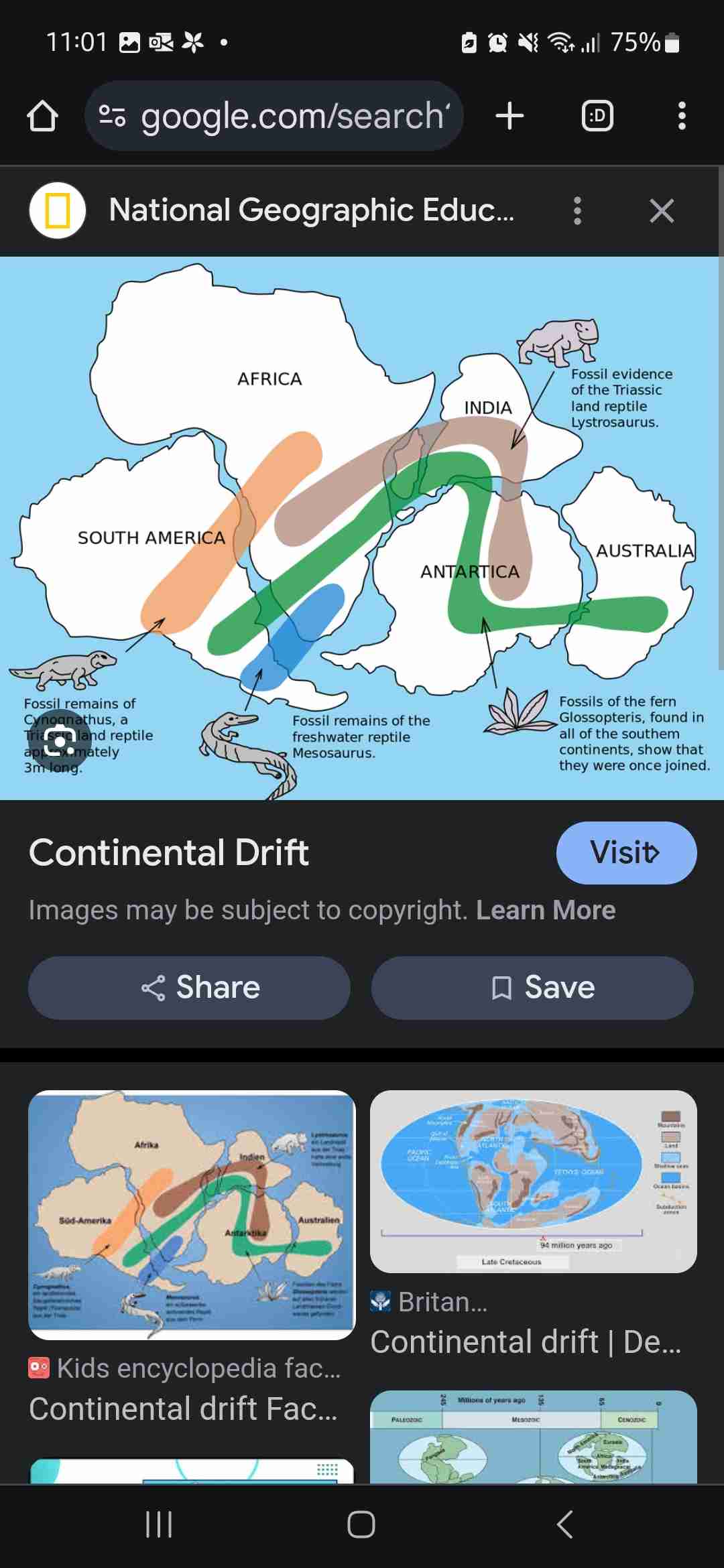
What is continental drift?
Where it is believed that the world land mass was once a place called pangea (one large land mass) and then due to the earth’s plate movement the climates have changed.
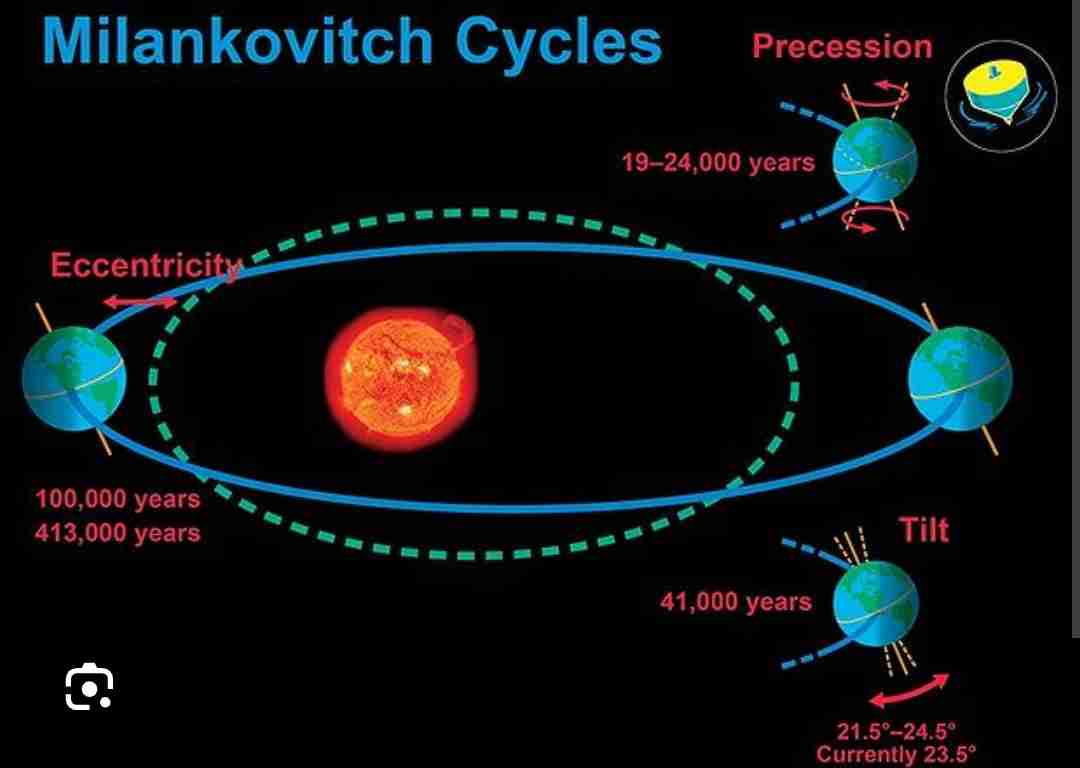
What are the milankovich cycles?
Where the earth’s orbit changes with eccentricity. (The elongation of the earths orbit) which effects the climate of the earth.
What are 3 human causes of climate change?
Deforestation
Agriculture
Fossil fuel
What ate 3 sources of evidence for climate change?
☆ Ice cores
☆ pollen cycles
☆ fossils (link to pangea)
What are examples of the UKs airmass? (2 examples)
♡ polar maritime
♡ artic maritime
♡ tropical continental
What is mitigation? + one example
Reduce or prevent climate change
Afforestation
What is adaption? + one example
◇ adapting to climate change
◇ adapting agriculture
What are the CATT statements?
Consequently
As a result
Therefore
This means that
How does development make inequalities?
♤ disparity in health
♤ disparity in wealth
3 factors that influence development-
♧ trade
♧ colonisation
♧ geographical location
What’s GNI?
Gross National Income - the aggregate value of the gross balances of primary incomes for all sectors
What are the 3 cells of global atmospheric circulation?
Polar, Hadley and ferrel
What is sustainability?
Development that meets the needs of the present without limiting the ability of the future Generations
What is globalisation?
Is the growth and spread of ideas around the world. This can involve the movement or spread of cultures, people, money ect.
What is deindustrialisation?
The reduction of industrial activity of capacity in a region or economy.