BCEM 393 - Lipids
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This folder contains flashcard sets based on material from "Biochemistry, A Short Course Fourth Edition" by Tymoczko, Berg, Gatto, and Stryer designed for undergraduate introductory biochemistry. These sets follow University of Calgary BCEM 393 course content
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Define: lipids
Water-insoluble molecules that are highly soluble in organic solvents
What are the 5 classes of lipids?
Free fatty acids
Triacylglycerols
Phospholipids
Glycolipids
Steroids
Define: free fatty acids
The simplest type of lipid, most commonly used as fuel. Vary in hydrocarbon chain length, which has important ramifications when they are used as fuels and as components of membrane lipids
Define: triacylglycerols
Storage form of fatty acids
Define: phospholipids
Membrane lipids that consist of fatty acids attached to a scaffold that also bears a charged phosphoryl group, creating a macromolecule with a polar head and nonpolar tail
Define: glycolipids
Lipids bound to carbohydrates and are important membrane constituents
Define: steroids
Polycyclic hydrocarbons that function as hormones that control a variety of physiological functions. The most common type is cholesterol, which is a vital membrane component
Describe: fatty acid structure
Hydrocarbon chain with a terminal carboxylic acid group
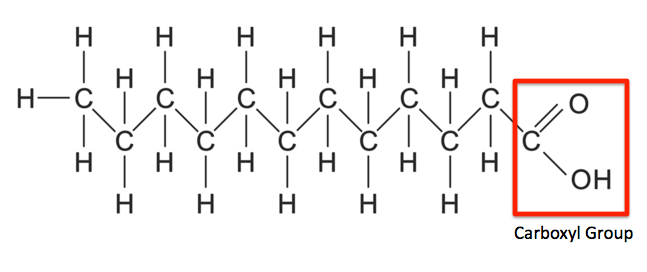
Fill in the blanks: the two key roles for fatty acids are as _______ and as ________.
Fuels, building blocks for membrane lipids
Fill in the blanks: fats are good fuels because the carbon atoms are bonded to _______ atoms and other _______ atoms rather than to _______ atoms, as is the case for carbohydrates. Because of this greater reduction, fats yield more energy than carbohydrates do when undergoing combustion to carbon dioxide and water.
Hydrogen, carbon, oxygen
Why are fats better fuels than carbohydrates?
Because they are more reduced than carbohydrates (C bonded to H and other C rather than O (partially oxidized) in carbohydrates. This greater reduction allows fats to yield more energy than carbohydrates do when undergoing combustion to CO2 and H2O. Fats are like fully charged batteries (more reduced) and carbohydrates are like half-used batteries (partially oxidized))
Fill in the blanks: saturated molecules have ___ double/triple bonds, while unsaturated molecules have ___ double/triple bonds.
Zero, at least one
Define: saturated molecules
Molecules with all the possible H
Define: unsaturated molecules
Molecules with at least one double/triple bond or ring
What are the steps to naming a saturated fatty acid?
Count the carbons (determine hydrocarbon name)
Count the double bonds (Carbon : Double Bonds ; for saturated, there will be zero DBs)
Name is hydrocarbon name minus e (e.g., decane) plus oic acid (e.g., decanoic acid)
What are the steps to naming an unsaturated fatty acid?
Count the carbons (determine hydrocarbon name)
Count the double bonds (Carbon : Double Bonds)
Identify if the double bonds are cis or trans
Identify the location of double bonds - carbon 1 is at the carboxyl terminus with Δ marking the location (e.g., cis-Δ9)
Name is hydrocarbon name minus e (e.g., octadecane) plus oic acid (e.g., octadecanoic acid) with location of double bond (e.g., cis-Δ9-octadecenoic acid)
Fill in the blank: when naming fatty acids, carbon 1 is at _______.
The carboxyl terminus
Fill in the blank: when naming fatty acids, carbon 1 is called __.
α
Fill in the blank: when naming fatty acids, carbon 2 is called __.
β
Fill in the blank: when naming fatty acids, the last carbon is called __.
ω
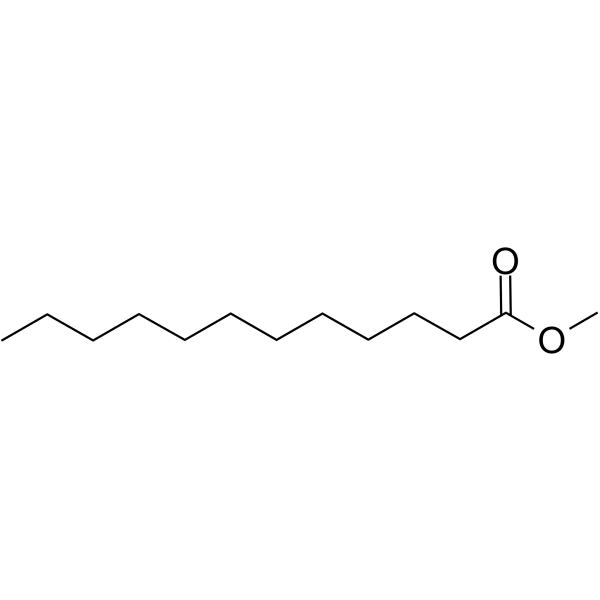
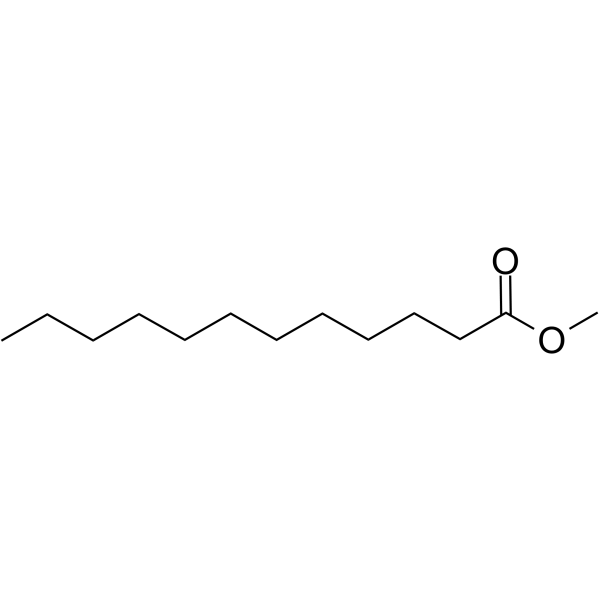
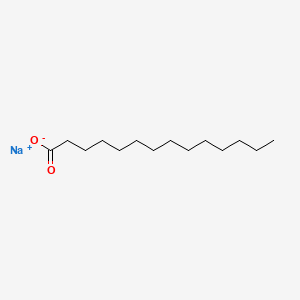
What is the common name of n-Dodecanoate?
Laurate
What is the systematic name of laurate?
n-Dodecanoate
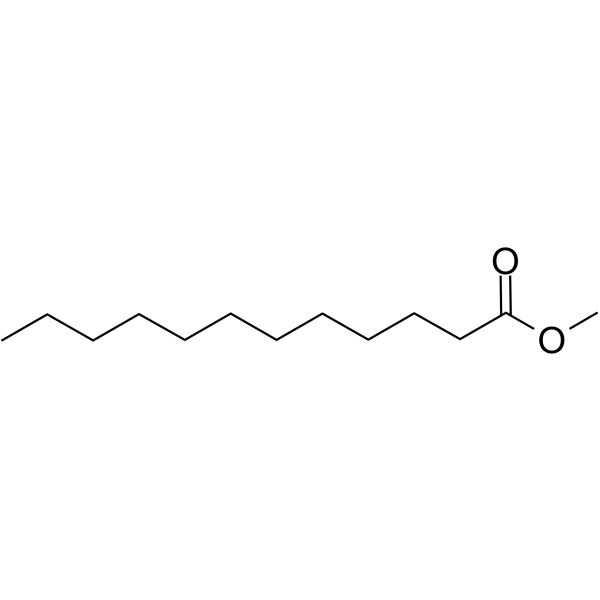
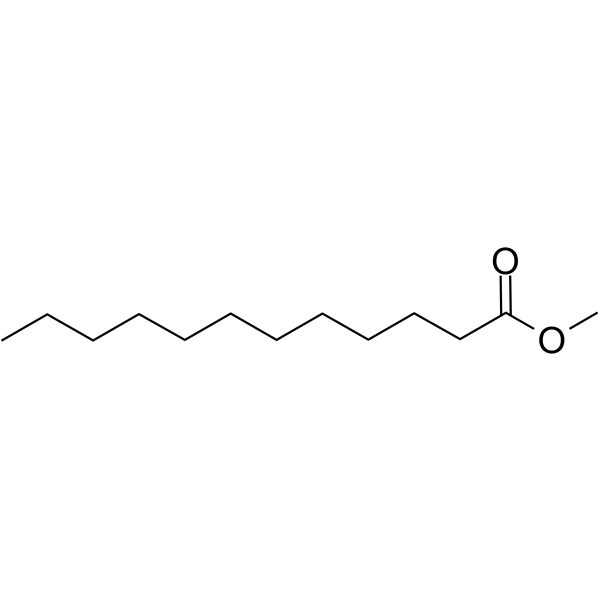
Name this fatty acid
Laurate (n-Dodecanoate)
Identify laurate (n-Dodecanoate)
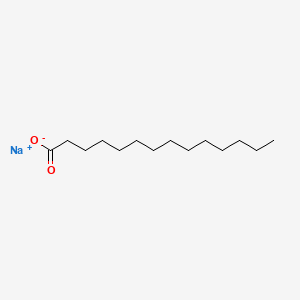
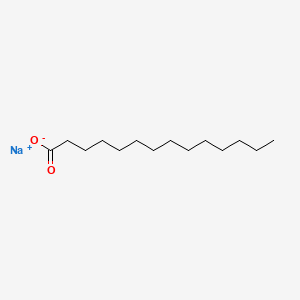
What is the common name of n-Tetradecanoate?
Myristate
What is the systematic name of Myristate?
n-Tetradecanoate
Name this fatty acid
Myristate (n-Tetradecanoate)
Identify myristate (n-Tetradecanoate)
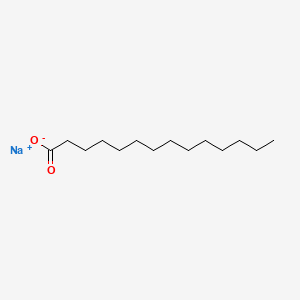
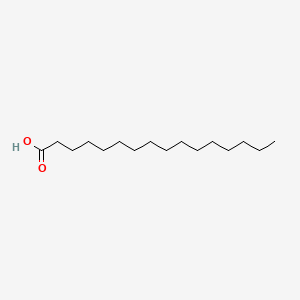
What is the common name of n-Hexadecanoate?
Palmitate
What is the systematic name of Palmitate?
n-Hexadecanoate
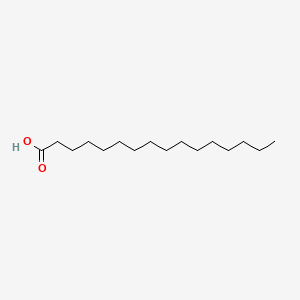
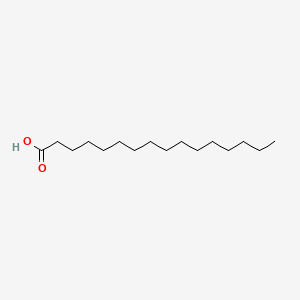
Name this fatty acid
Palmitate (n-Hexadecanoate)
Identify palmitate (n-Hexadecanoate)
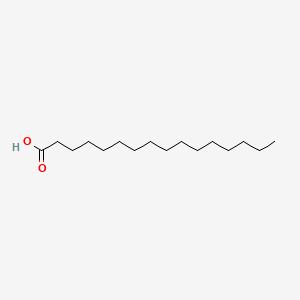
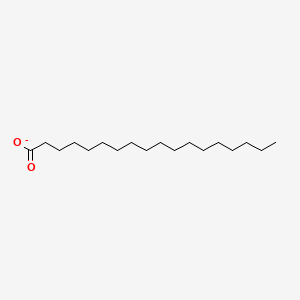
What is the common name of n-Octadecanoate?
Stearate
What is the systematic name of Stearate?
n-Octadecanoate
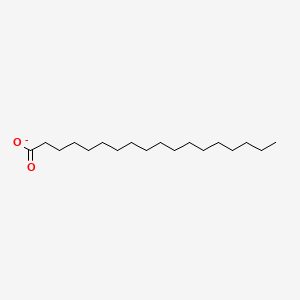
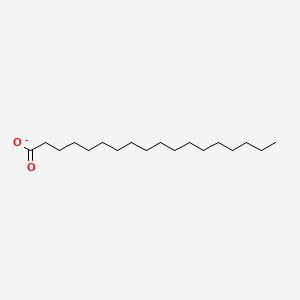
Name this fatty acid
Stearate (n-Octadecanoate)
Identify stearate (n-Octadecanoate)
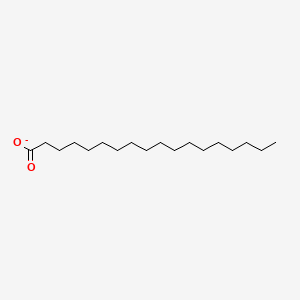
What is the common name of cis-Δ9-Hexadecenoate?
Palmitoleate
What is the systematic name of Palmitoleate?
cis-Δ9-Hexadecenoate
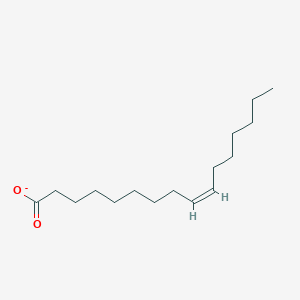
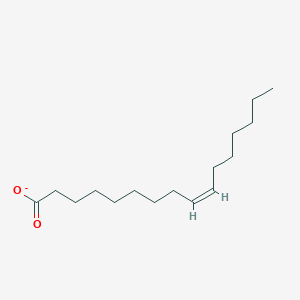
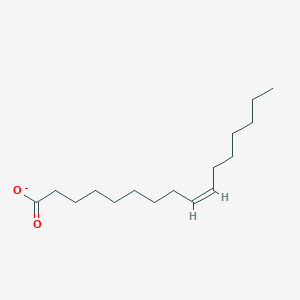
Name this fatty acid
Palmitoleate (cis-Δ9-Hexadecenoate)
Identify palmitoleate (cis-Δ9-Hexadecenoate)
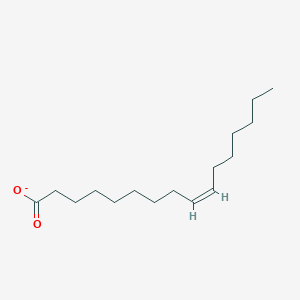
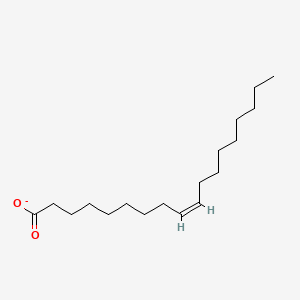
What is the common name of cis-Δ9-Octadecenoate?
Oleate
What is the systematic name of Oleate?
cis-Δ9-Octadecenoate
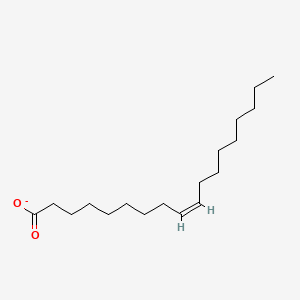
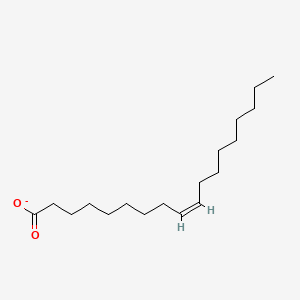
Name this fatty acid
Oleate (cis-Δ9-Octadecenoate)
Identify oleate (cis-Δ9-Octadecenoate)
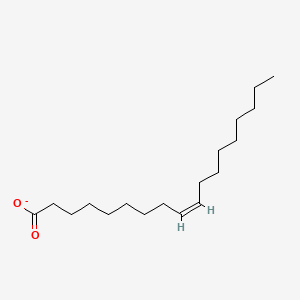
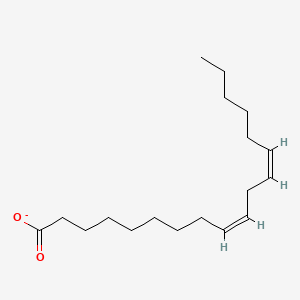
What is the common name of cis,cis-Δ9-Δ12-Octadecadienoate?
Linoleate
What is the systematic name of Linoleate?
cis,cis-Δ9-Δ12-Octadecadienoate
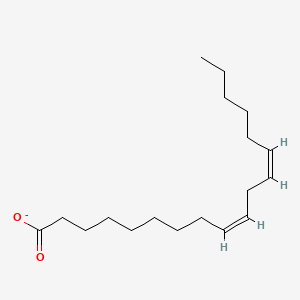
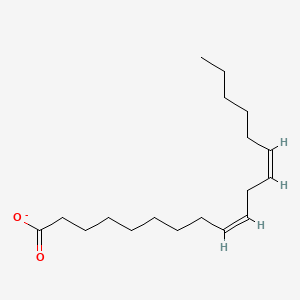
Name this fatty acid
Linoleate (cis,cis-Δ9-Δ12-Octadecadienoate)
Identify linoleate (cis,cis-Δ9-Δ12-Octadecadienoate)
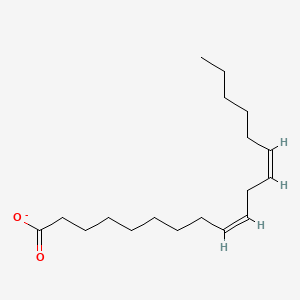
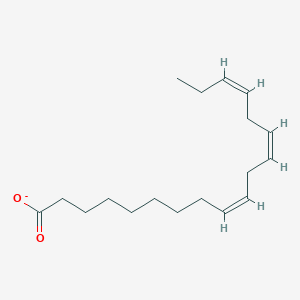
What is the common name of all-cis-Δ9-Δ12-Δ15-Octadecatrienoate?
Linolenate
What is the systematic name of Linolenate?
all-cis-Δ9-Δ12-Δ15-Octadecatrienoate
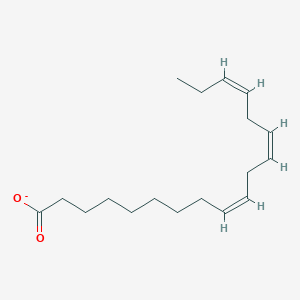
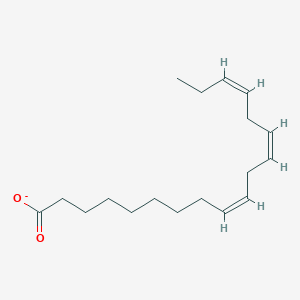
Name this fatty acid
Linolenate (all-cis-Δ9-Δ12-Δ15-Octadecatrienoate)
Fill in the blanks: melting point of fatty acids is dependent on ________ and ________.
Degree of saturation and chain length
Fill in the blank: unsaturated fatty acids have a _______ melting temperature than saturated fatty acids of the same length.
Lower
Fill in the blank: longer carbon chains have a _______ melting temperature than shorter carbon chains.
Higher
Why do unsaturated fatty acids have a lower melting point than saturated fatty acids?
The presence of a cis double bonds introduces a kink in the fatty acid and makes tight packing between the chains impossible. The lack of tight packing limits the van der Waals interactions between chains, lowering the melting temperature
Fill in the blanks: Melting temperatures of fatty acids are key elements in the control of the fluidity of cell membranes, and the proper degree of fluidity is essential for membrane function. Thus, _______ and _______ enhance the fluidity of fatty acids and of their derivatives.
Short chain length, cis unsaturation
True or False: animal fatty acids typically have an even number of carbon atoms.
True
True or False: 16- and 18-carbon fatty acids are most common (in animals).
True
True or False: the configuration at an animal fatty acid is usually trans.
False; usually cis
True or False: double bonds in polyunsaturated fatty acids are separated by at least one methylene group.
True
True or False: it is common to have triple bonds in fatty acids.
False; it is rare
True or False: despite fatty acids being our principal energy source, the concentration of free fatty acids in cells or the blood is low because free fatty acids are strong acids.
True
Fill in the blank: fatty acids required for energy generation are stored as _______, which are formed by the attachment of three fatty acid chains to a glycerol molecule.
Triacylglycerols
Fill in the blanks: in triacylglycerols, fatty acids are attached to the glycerol through _______ in a process known as _______.
Ester linkages, esterification
Fill in the blanks: when energy is required during a fast (for instance, while sleeping), the fatty acids are cleaved from the _______ and carried to the cells. The ingestion of food replenishes the ______ stores.
Triacylglycerol, triacylglycerol
Fill in the blank: fatty acids store energy more efficiently in the form of _______.
Triacylglycerols
Fill in the blanks: fatty acids store energy more efficiently in the form of triacylglycerols, which are _______ and so are stored in a nearly ______ form.
Hydrophobic, anhydrous
True or False: triacylglycerols are an efficient form of stored energy because they are able to pack tightly together due to being hydrophobic and thus are stored with almost no water.
True
Fill in the blanks: triacylglycerols are ______ and are not stored with water molecules, while ______ carbohydrates bind to water molecules. Because of this, a gram of nearly anhydrous fat stores more than six times as much energy as a gram of hydrated glycogen.
Hydrophobic, polar
Triacylglycerols are used for fuel storage in both plants and animals. The triacylglycerols from plants are often liquid at room temperature, whereas those from animals are solid. Suggest some chemical reasons for this difference.
Triacylglycerols from plants may have many cis double bonds or have shorter fatty acid chains than those from animals
Why are lipids a more efficient storage form than glycogen?
Lipids are more reduced than glycogen, and they are stored in an anhydrous form
Small mammalian hibernators can withstand body temperatures of 0 degrees C to 5 degrees C without injury. However, the body fats of most mammals have melting temperatures of approximately 25 degrees C. Predict how the composition of the body fat of hibernators might differ from that of their nonhibernating cousins.
Hibernators selectively feed on plants that have a high proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids with lower melting temperature
Explain why oleic acid (18C, 1 cis bond) has a lower melting point than stearic acid, which has the same number of carbon atoms but is saturated. How would you expect the melting point of trans-oleic acid to compare with that of cis-oleic acid?
The presence of a cis double bond introduces a kink in the fatty acid chain that prevents tight packing and reduces the number of atoms in van der Waals contact. The kink will lower the melting point compared with that of a saturated fatty acid. Trans fatty acids do not have the kink, so their melting temperatures will be higher and more similar to those of saturated fatty acids
Explain why the melting point of palmitic acid (C16) is 6.5 degrees lower than that of stearic acid (C18).
Palmitic acid is shorter than stearic acid. Thus, when the chains pack together, there is less opportunity for van der Waals interactions and the melting point will thus be lower than that of the longer stearic acid