Human Body Organization: Tissues, Systems, and Homeostasis
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
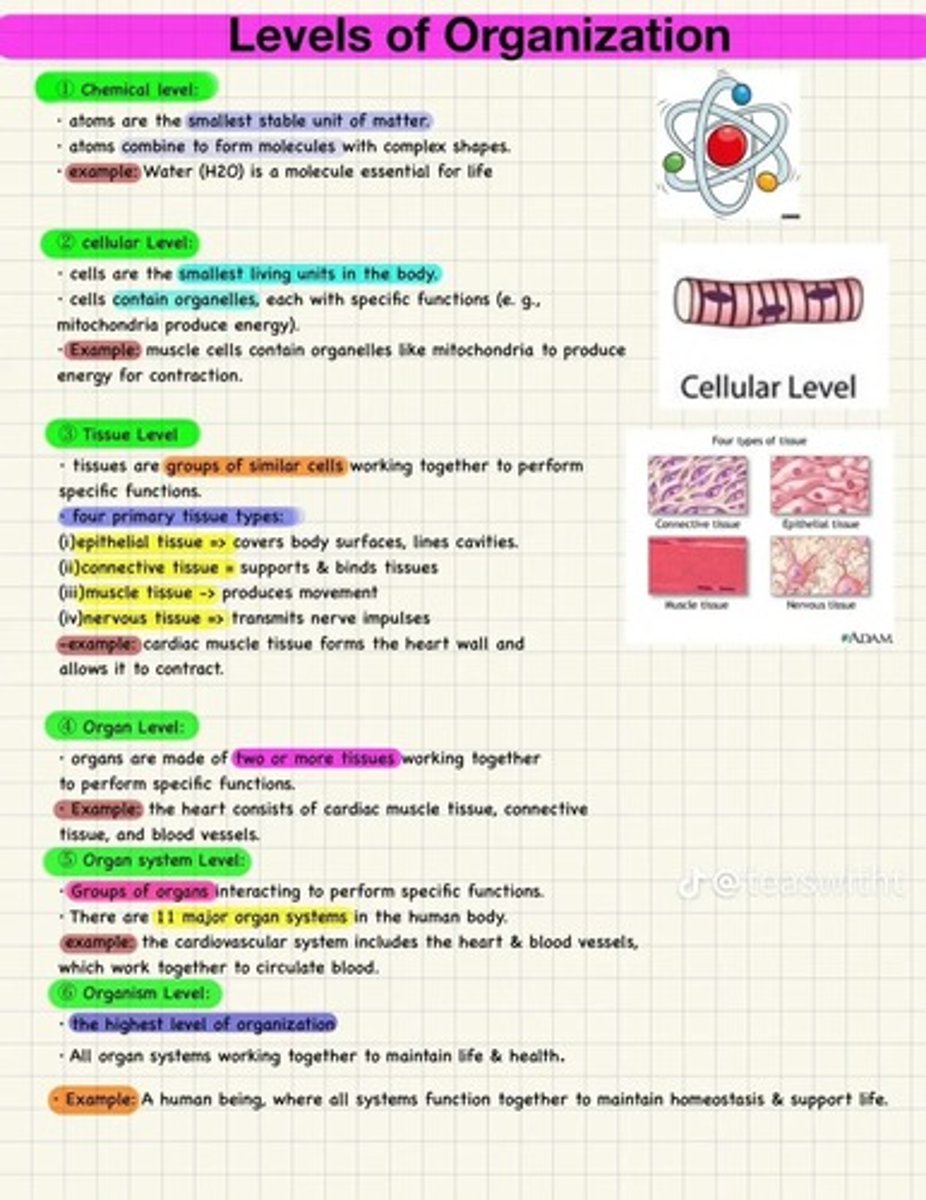
What are the levels of organization in biological systems, in order
Chemical Level,Cellular Level,Tissue Level,Organ Level,Organ System Level,Organism Level
What are the characteristics that qualify an entity as 'alive'?
Organization,Metabolism,Responsiveness,Reproduction,
Growth

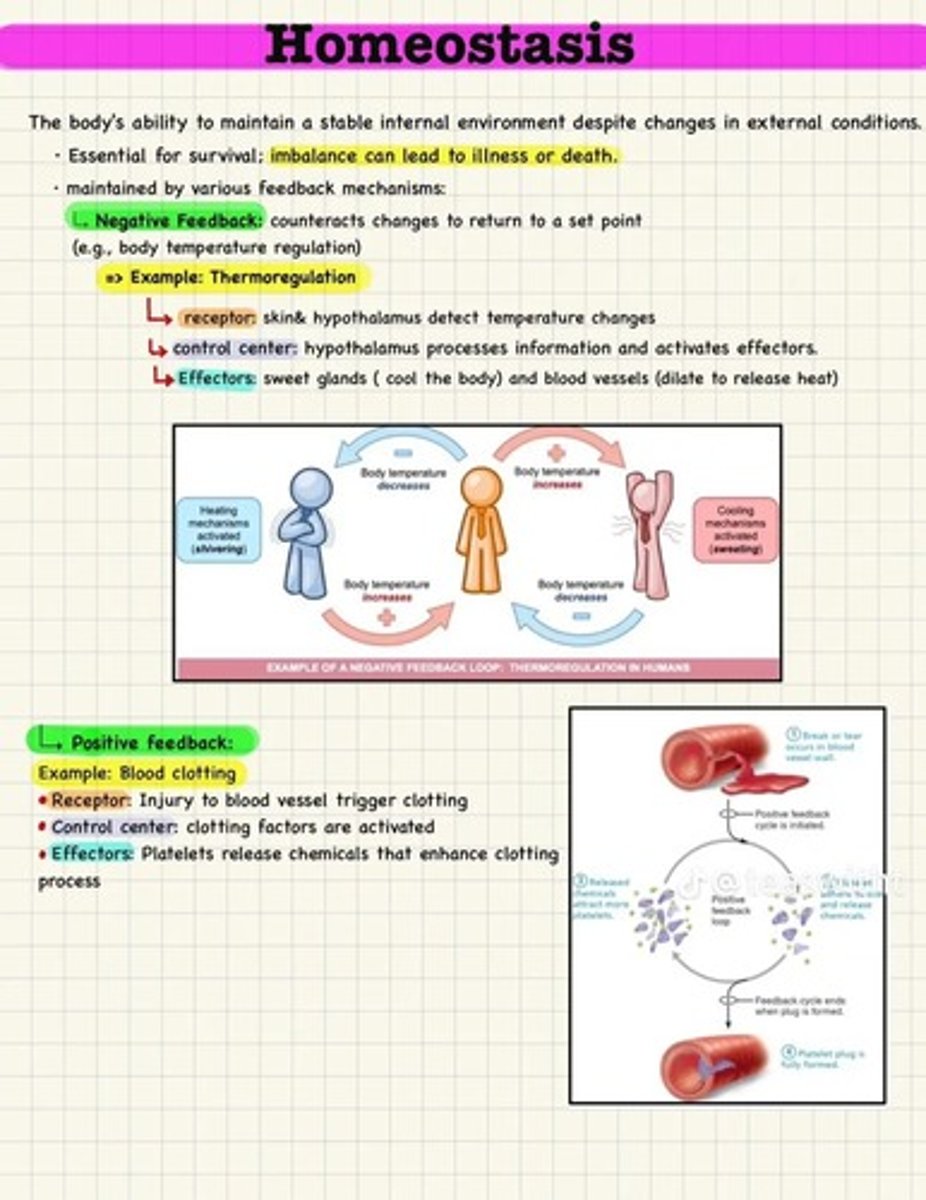
What is homeostasis and how does the body maintain it?
the body's way of maintaining a stable internal environment through negative feedback and positive feedback
What is the role of proteins in the body?
Proteins act as construction workers, building tissues, enzymes, and hormones, such as hemoglobin in red blood cells.
What is the function of carbohydrates in the body?
Carbohydrates serve as quick energy sources, like glucose being a key fuel for brain activity.
What are lipids and their function in the body?
Lipids are used for long-term energy storage, like body fat
What are nucleic acids and their significance?
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, serve as genetic blueprints for living organisms.
What distinguishes anatomy from physiology?
Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body and its parts, while physiology is the study of the functions of those parts.

What does the cell membrane do?
controls what enters and exits the cell.
What is the role of mitochondria in cells?
Mitochondria produce energy for cellular functions, particularly in muscle cells.
What is the function of nervous tissue?
transmits nerve impulses, facilitating communication within the body.
How do tissues work
Tissues are groups of similar cells that collaborate to perform specific functions.
what does cardiac muscle tissue do
Cardiac muscle tissue forms the heart wall and allows it to contract.
What is the relationship between organ systems and homeostasis?
Organ systems work together to maintain homeostasis
How does the body respond to overheating and what is this an example of
the body sweats to cool down and is an example of negative feedback
What is the mnemonic for remembering the four organic compounds?
Proteins Build, Carbs Charge, Lipids Lounge with Nucleic Acids Code.
What is the primary focus of physiology?
The study of how body parts function, the 'how' and 'why' of processes
How does anatomy differ from physiology?
Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body and its parts, while physiology explains how those parts function.
What is the hierarchy of organization in the human body?
Chemical Level, Cellular Level, Tissue Level, Organ Level, Organ System Level, and Organism Level.
What is the chemical level in the hierarchy of organization?
The chemical level consists of atoms and molecules,forming the foundation of the body's structure.
What is the cellular level in the hierarchy of organization?
The smallest unit of life
What is the tissue level in the body?
The tissue level consists of groups of similar cells that perform specific functions
What is the organ level in the body's organization?
The organ level is when of two or more types of tissues work together to perform specific, complex functions.
What is an organ system?
An organ system is a group of organs that work together to carry out more generalized functions
What is homeostasis?
the process that keeps the body's internal environment stable despite external changes.
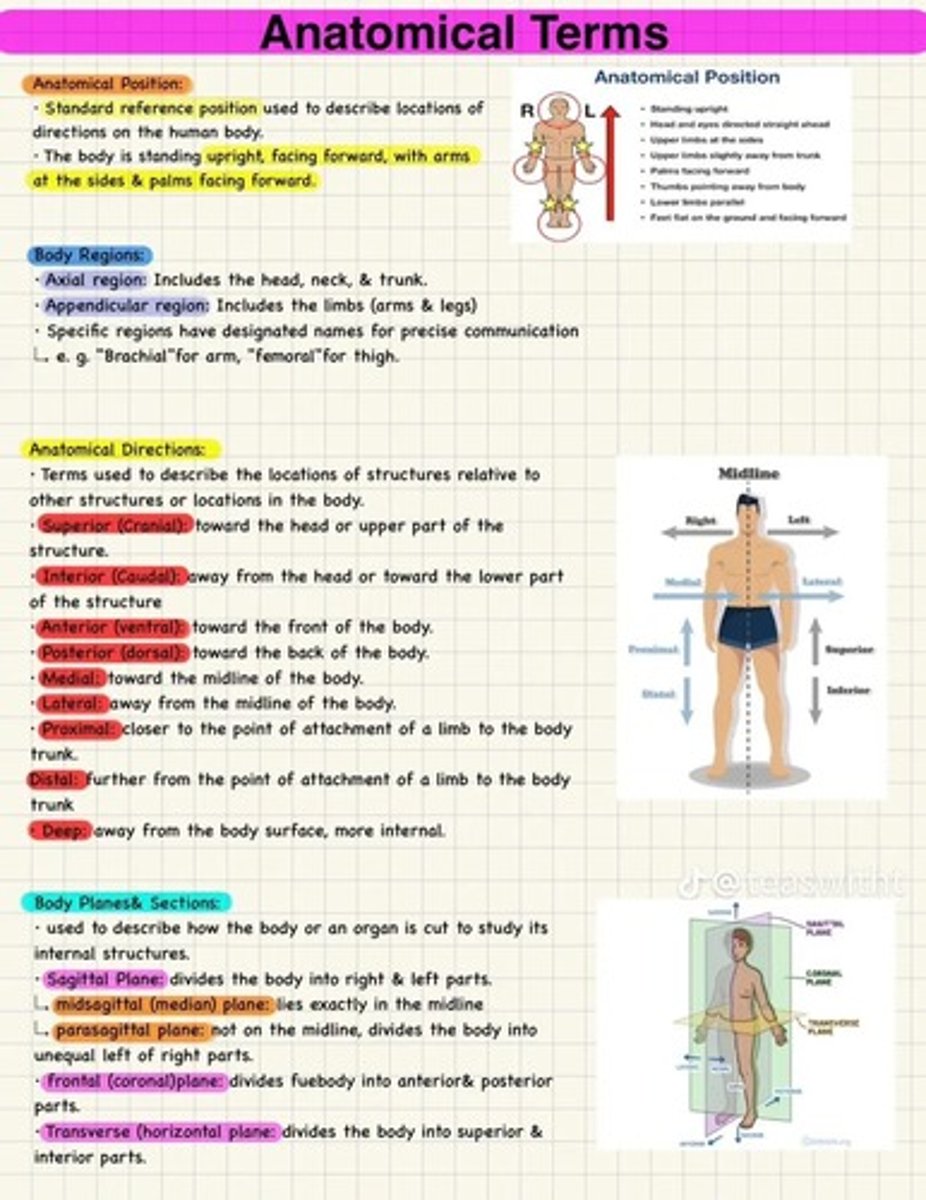
What are the directional terms used in anatomy?
Superior (above) vs. Inferior (below), Anterior (front) vs. Posterior (back), Medial (toward the midline) vs. Lateral (away from the midline).
What are the main body regions mentioned?
Thoracic (chest), Abdominal (stomach area), Cranial (head).
What are the planes of the body?
Sagittal (divides left/right), Coronal (divides front/back), Transverse (divides top/bottom).

What is gross anatomy?
The study of large, visible structures in the body
What is microscopic anatomy?
The study of structures that require magnification to be seen
What is negative feedback?
A mechanism that counteracts changes to return to a set point
Give an example of a negative feedback loop.
Thermoregulation in humans, where the hypothalamus detects temperature changes and activates effectors like sweat glands.
What happens during positive feedback?
It enhances changes and drives processes to completion, such as blood clotting.
Describe the anatomical position.
The body is standing upright, facing forward, with arms at the sides and palms facing forward.
What are the two main body regions?
Axial region (head, neck, trunk) and appendicular region (limbs).
What does the term 'superior' refer to in anatomical directions?
Toward the head or upper part of the structure.
What does 'inferior' mean in anatomical terms?
Away from the head or toward the lower part of the structure.
What is the meaning of 'medial'?
Toward the midline of the body.
What does 'lateral' indicate in anatomical directions?
Away from the midline of the body.
Define 'proximal'.
Closer to the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
What does 'distal' mean?
Further from the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk.
What is the sagittal plane?
A plane that divides the body into right and left parts.
What is the difference between midsagittal and parasagittal planes?
Midsagittal lies exactly in the midline, while parasagittal divides the body into unequal left and right parts.
What does the frontal (coronal) plane do?
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
What is the transverse plane?
A plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts.