Lecture 18- Metabotropic Receptors
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
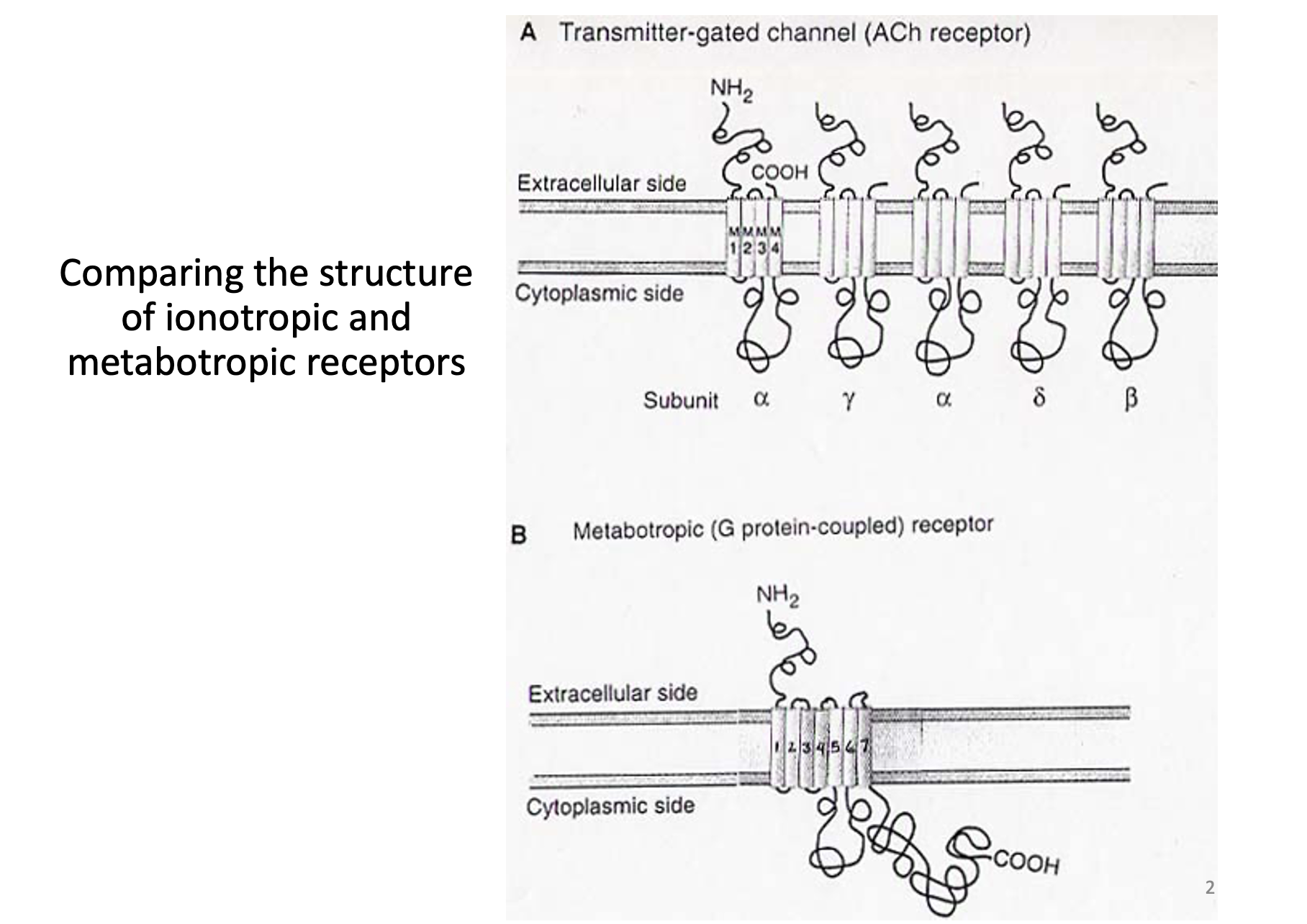
* 7 Transmembrane segments
* Not in subunits
* One protein
* Conserved
* Not in subunits
* One protein
* Conserved
Name three key characteristics of metabotropic receptors
2
New cards
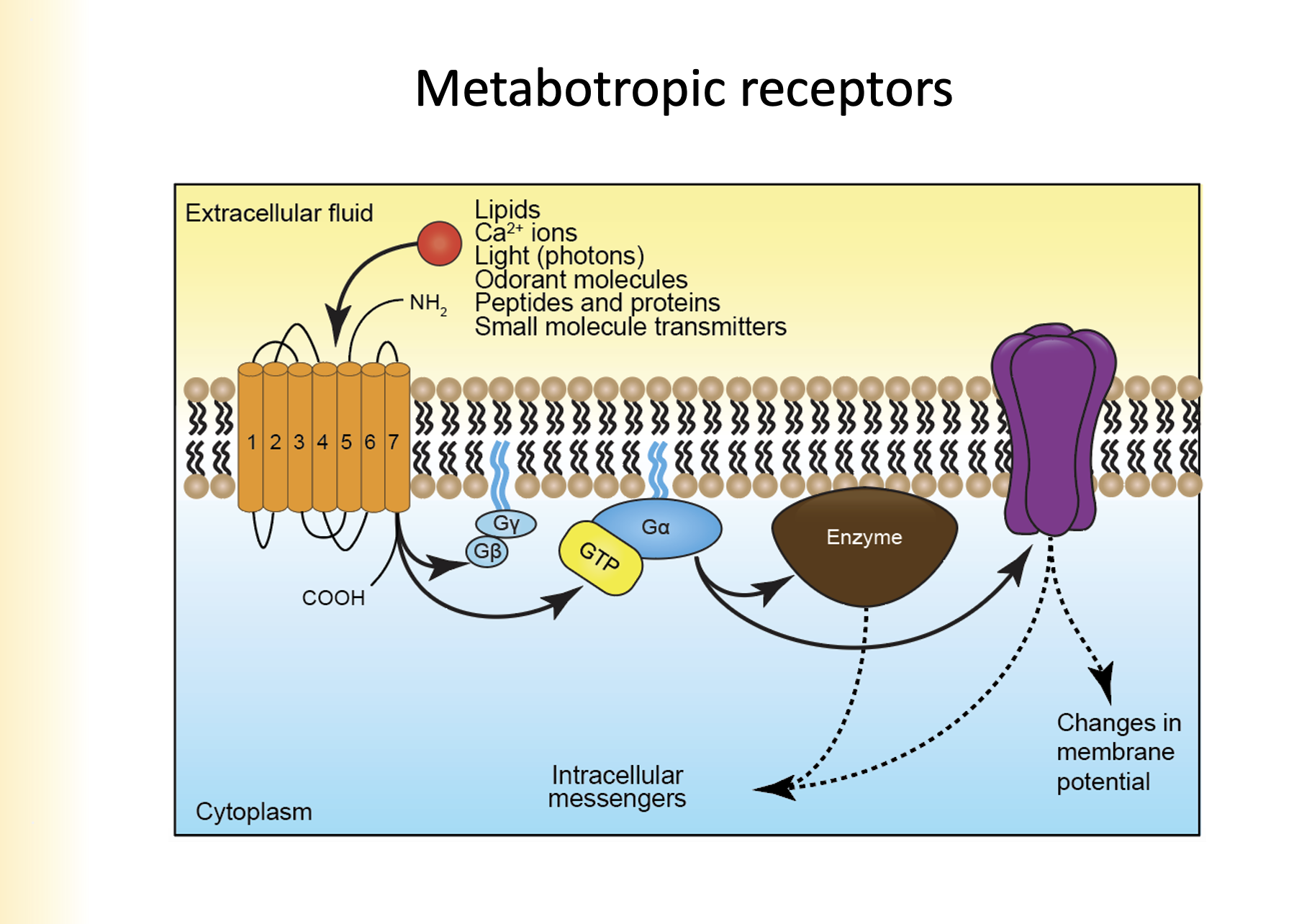
* Lipids
* Ca2+ ions
* Light (photons)
* Odorant molecules
* Peptides and proteins
* small molecule transmitters
* Ca2+ ions
* Light (photons)
* Odorant molecules
* Peptides and proteins
* small molecule transmitters
Name the different types of metabotropic receptors
3
New cards
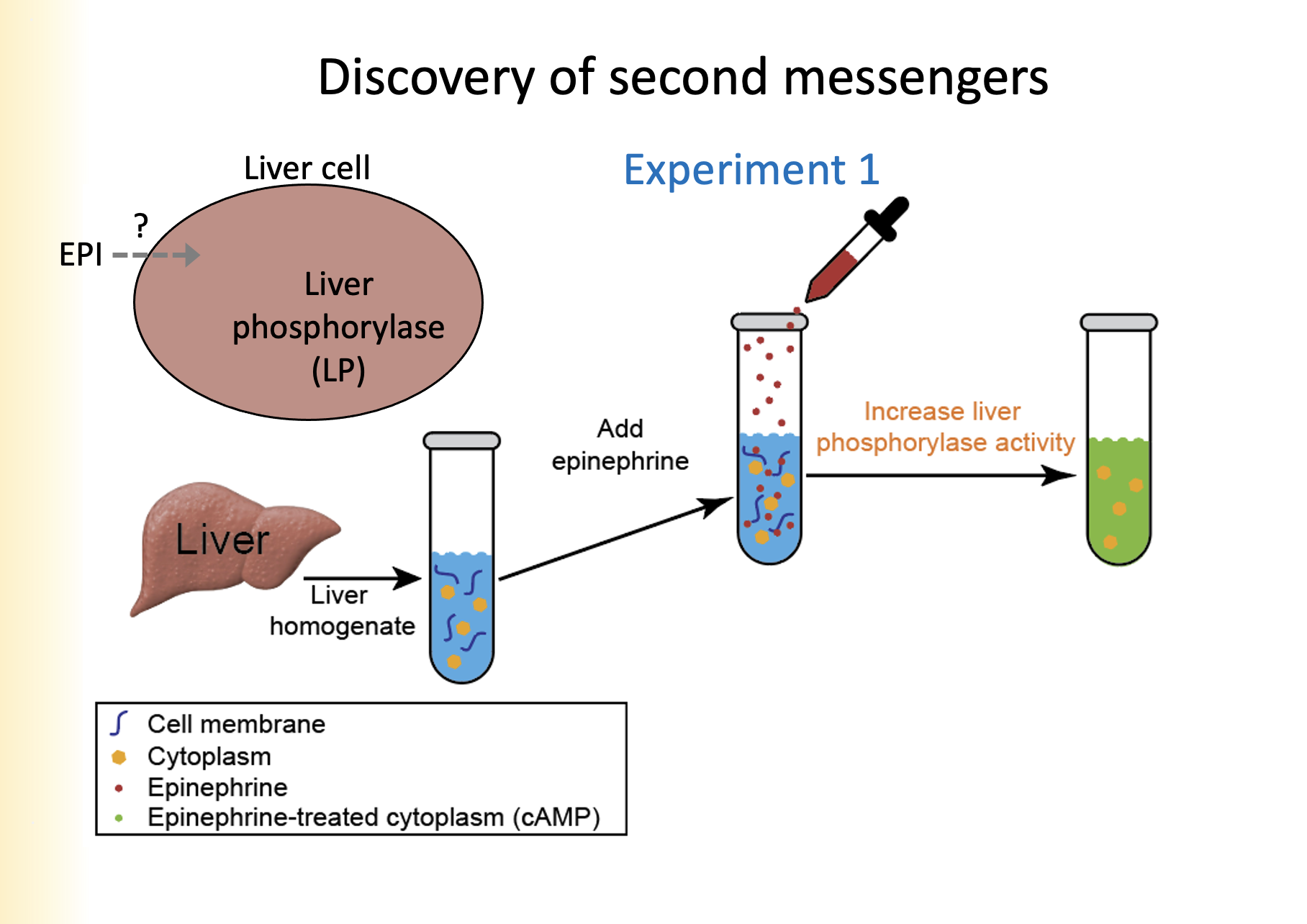
1. Liver homogenate is added to a cell vial
2. Epinephrine is added
3. When epinephrine was added, increased liver phosphorylase activity
Explain the first experiment for the discovery of second messengers
4
New cards
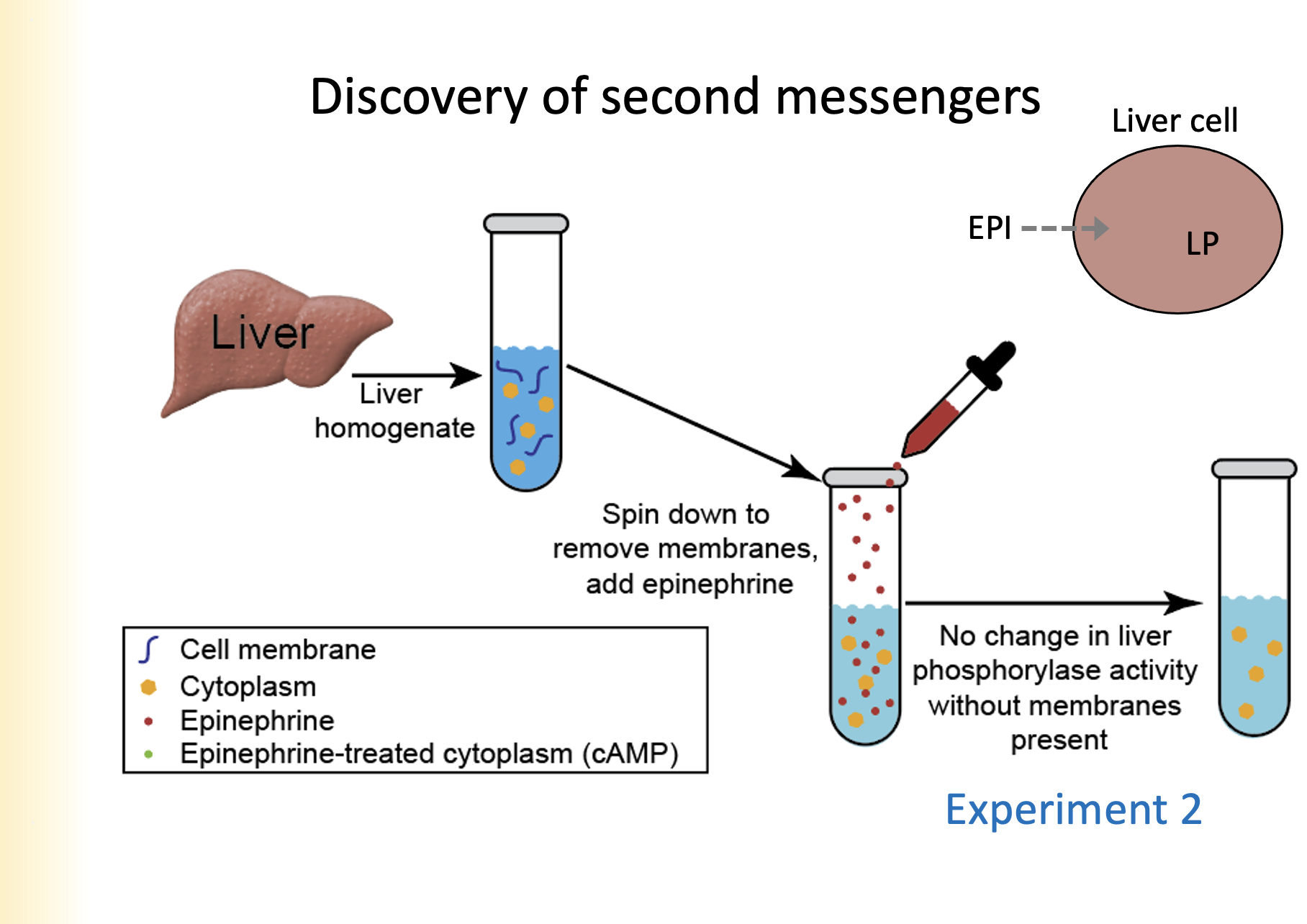
1. Liver homogenate is added to a cell vial
2. The cell is placed through a centrifuge to spin down to remove membranes
3. Epinephrine is added
4. No change in liver phosphorylase activity without membranes present
Showed: membrane is necessary for kinase activity
Explain the second experiment for the discovery of second messengers and state what it showed.
5
New cards
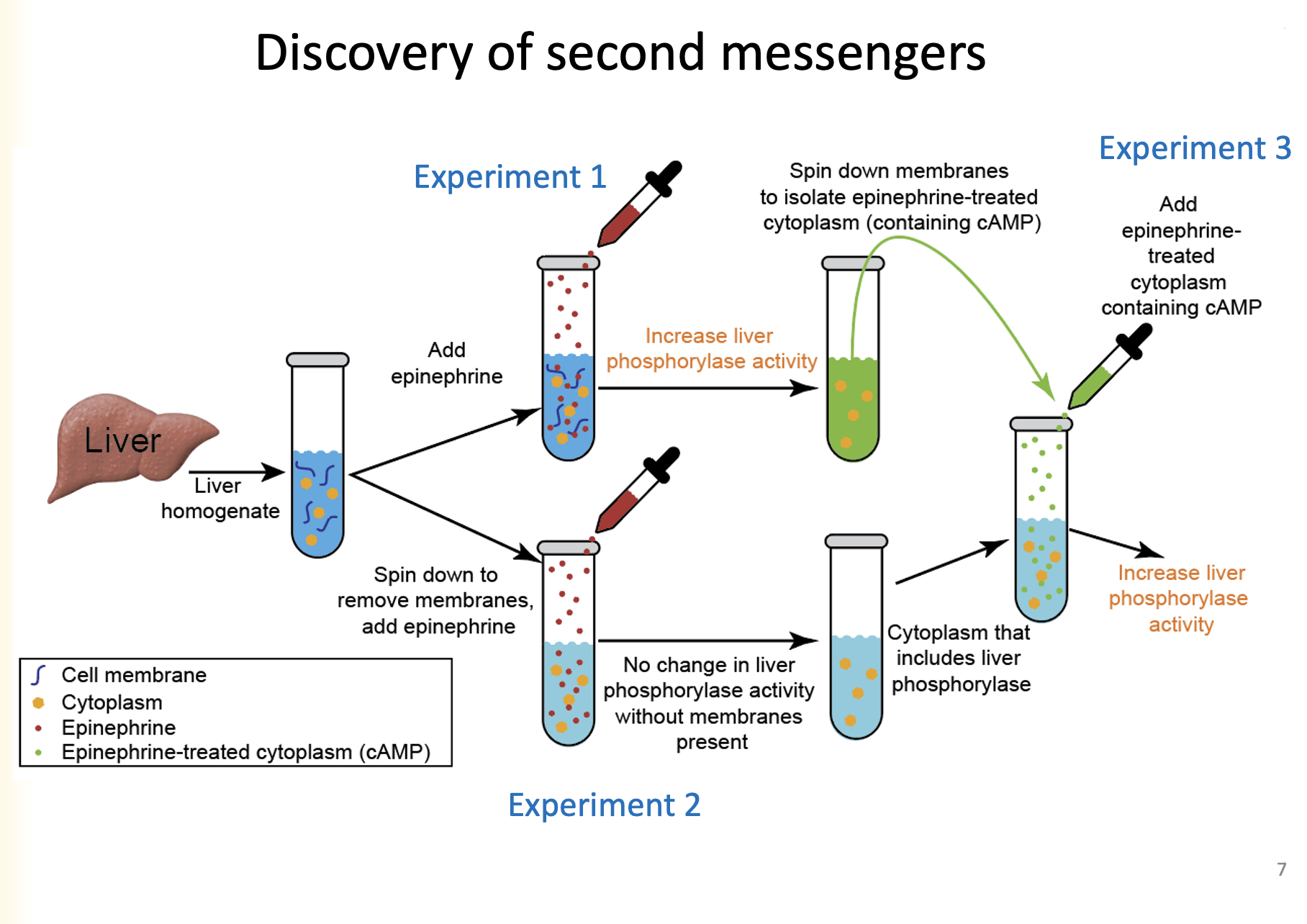
Part 1:
1. Liver homogenate is added to a cell vial
2. Epinephrine is added to cell vial, which increases liver homogenate activity
3. Membrane is spun down to isolate epinephrine-treated cytoplasm (containing cAMP)
Part 2:
1. Spin down to remove membranes, add epinephrine (no change in liver phosphorylase activity without membranes present.
2. Add epinephrine treated cytoplasm containing cAMP to cytoplasm that includes liver phosphorylase
1. Increase liver phosphorylase activity
1. Liver homogenate is added to a cell vial
2. Epinephrine is added to cell vial, which increases liver homogenate activity
3. Membrane is spun down to isolate epinephrine-treated cytoplasm (containing cAMP)
Part 2:
1. Spin down to remove membranes, add epinephrine (no change in liver phosphorylase activity without membranes present.
2. Add epinephrine treated cytoplasm containing cAMP to cytoplasm that includes liver phosphorylase
1. Increase liver phosphorylase activity
Explain the third experiment for the discovery of second messengers
6
New cards
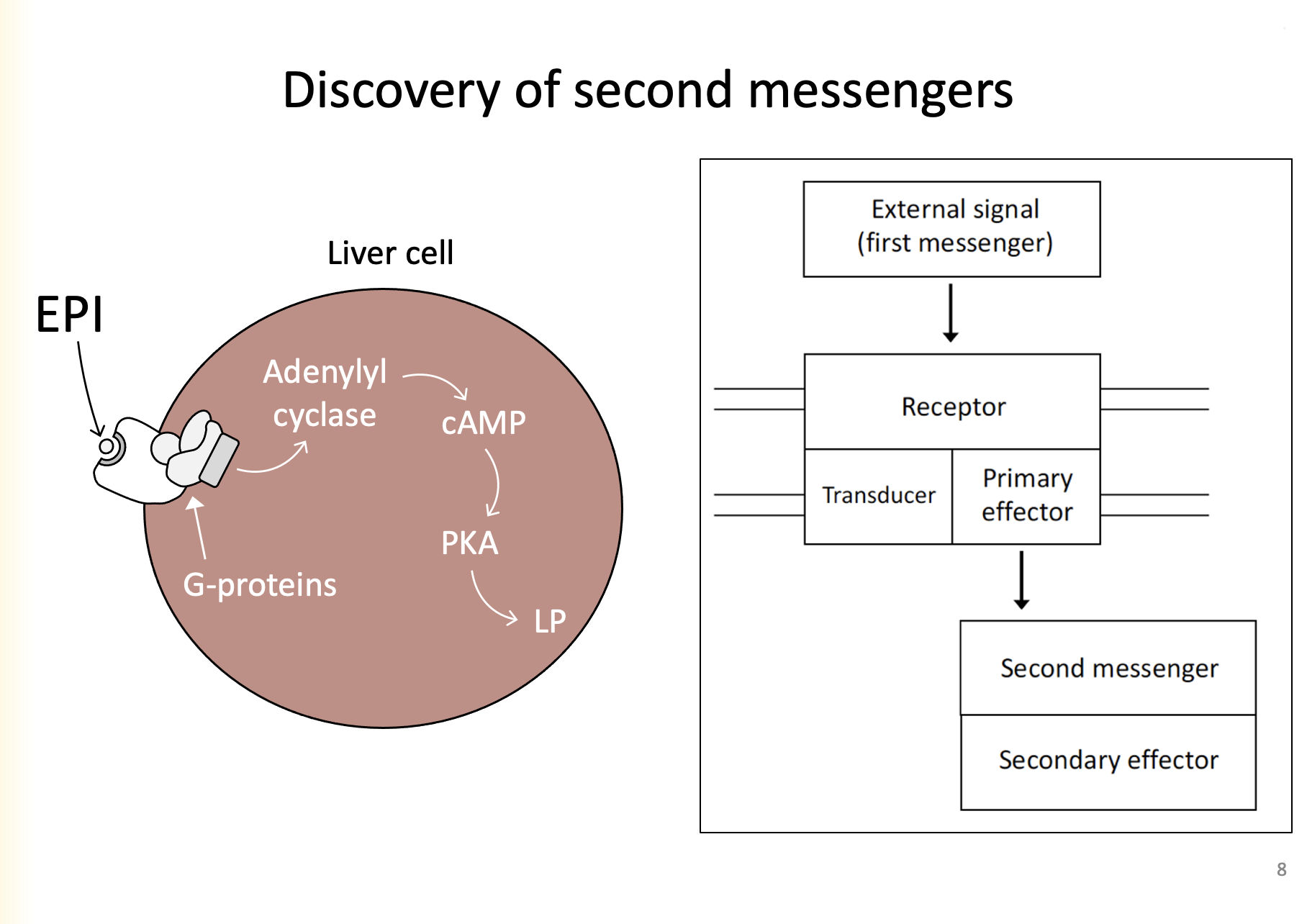
1. External signal (ligand, first messenger) binds to receptor
2. Receptor includes transducer
3. Transducer incudes primary effector
4. Primary effectors turns on second messenger
5. Second messenger turns on secondary effector
6. Secondary effector produces cellular response
Explain the pathway from ligand to secondary effector
7
New cards
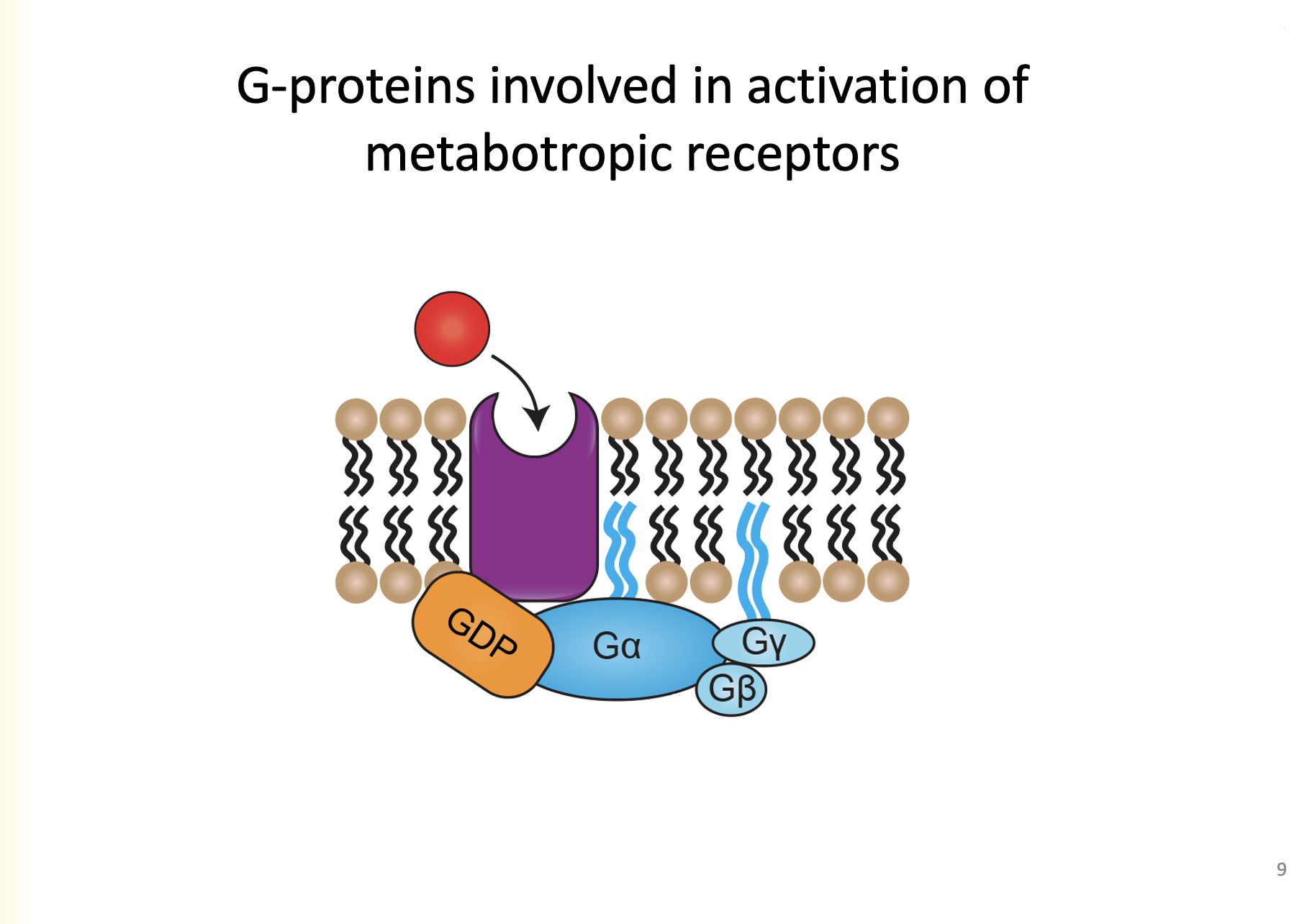
1. Ga is bound to GDP- considered inactive
2. Ga is bound to GyGb
What is considered the “resting” state for G-Proteins?
8
New cards
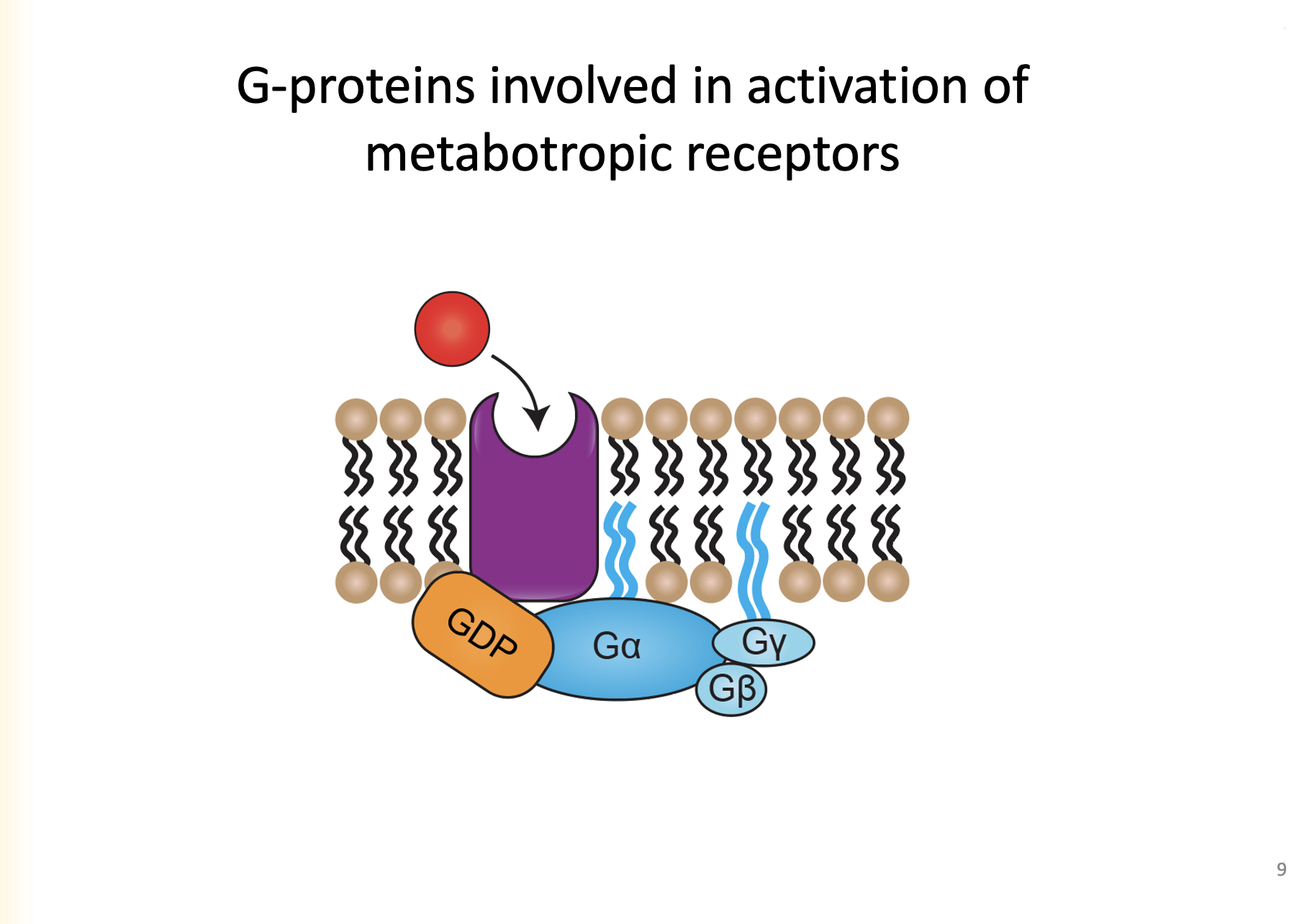
always bound to lipids that are embedded in the membrane- helps to keep associated with the membrane
What are GyGb bound to and why?
9
New cards
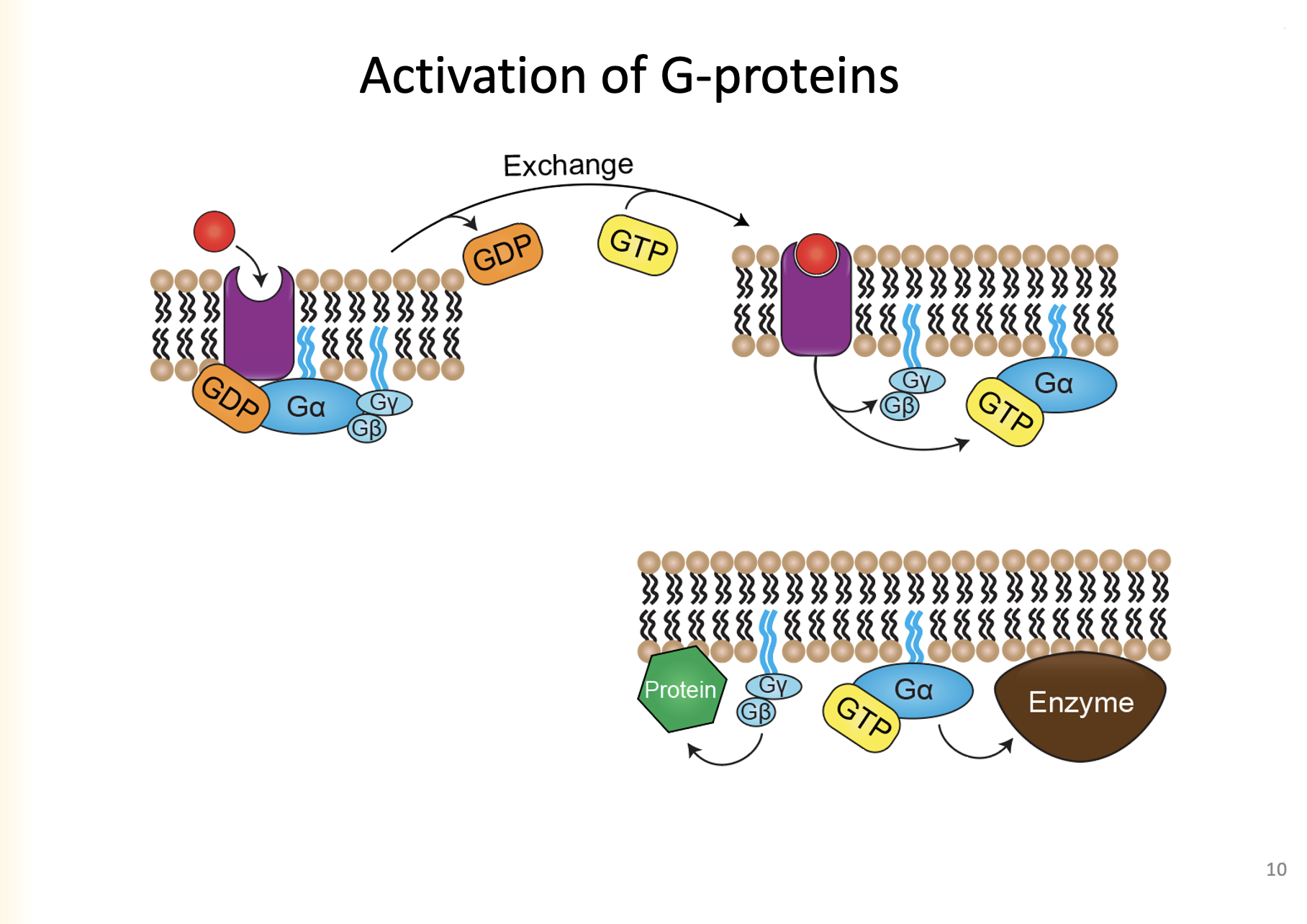
1. A ligand binds to the receptor
2. Receptor changes confirmation, Ga has a lower affinity for GDP and a higher affinity for GTP
3. GDP to GTP exchange
4. When ligand is bound, breaks into two dimers: GyGb and Ga+GTP, which acts as a transducer
Explain the activation of G-Proteins
10
New cards
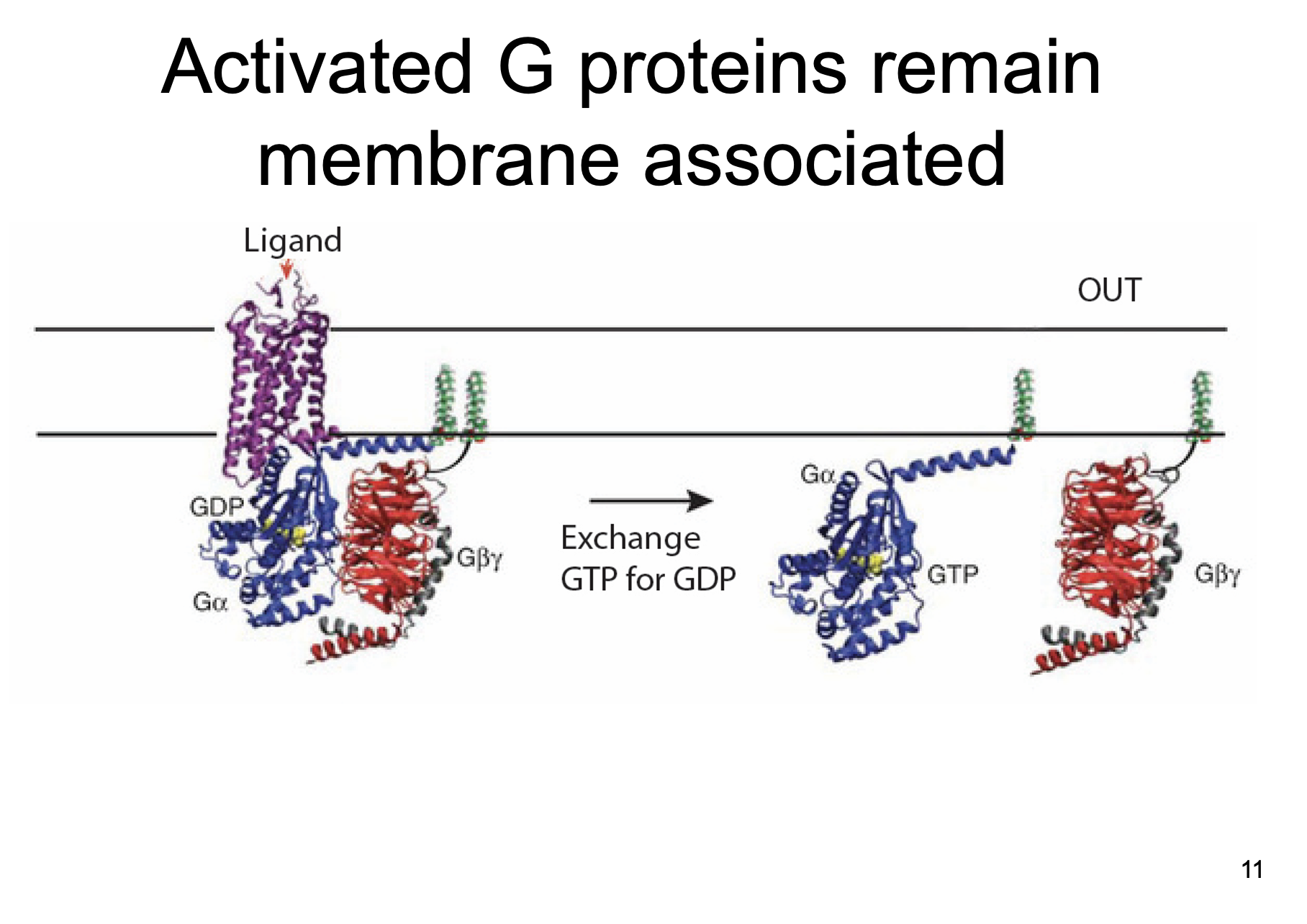
membrane
Activated G-Proteins remain ____________ associated
11
New cards
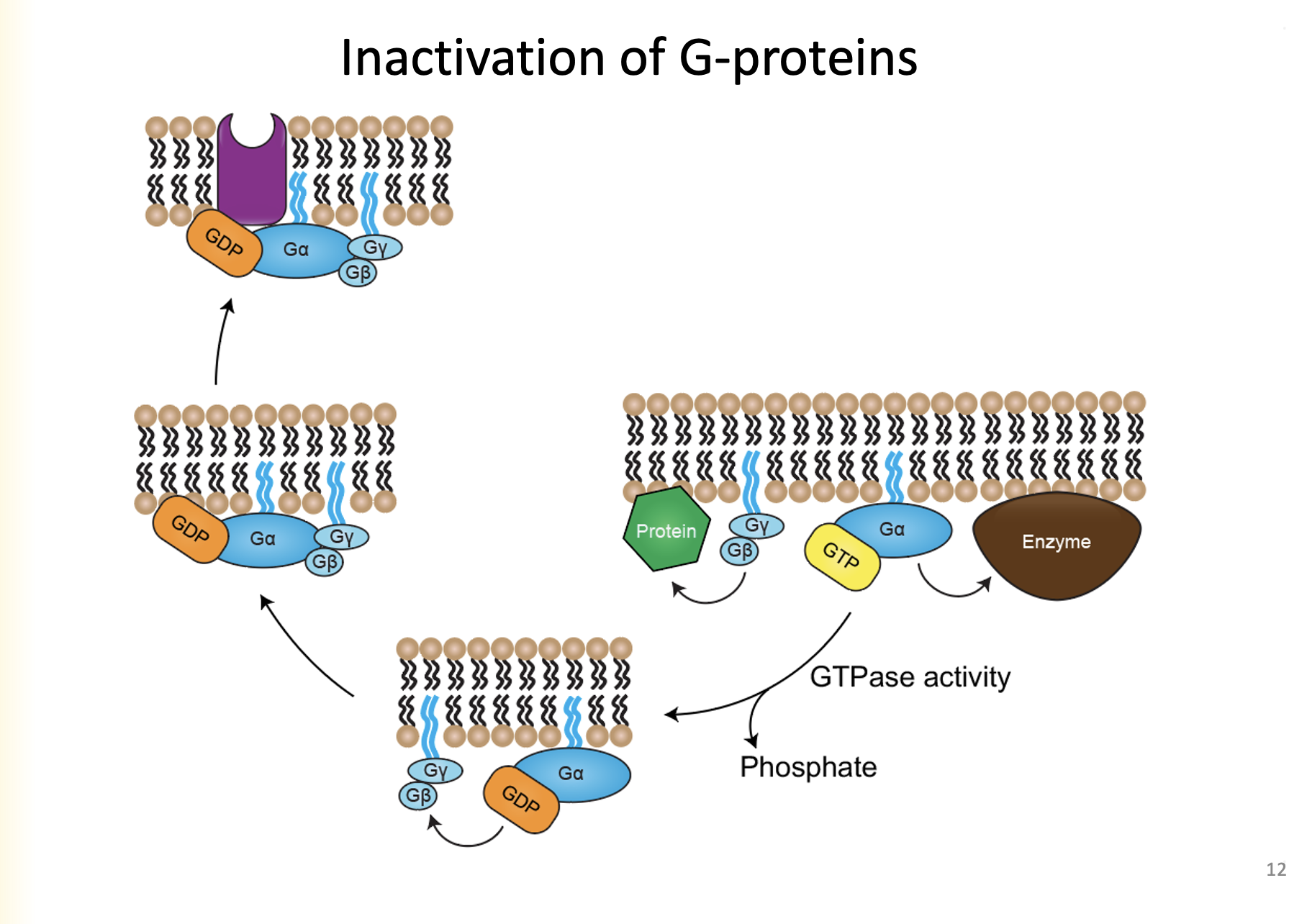
1. Ga hydrolyzes GTP into GDP, phosphate group is removed
2. Ga binds to GyGb as Ga has a high affinity
3. Re-association with receptor
Explain the inactivation of G-Proteins
12
New cards
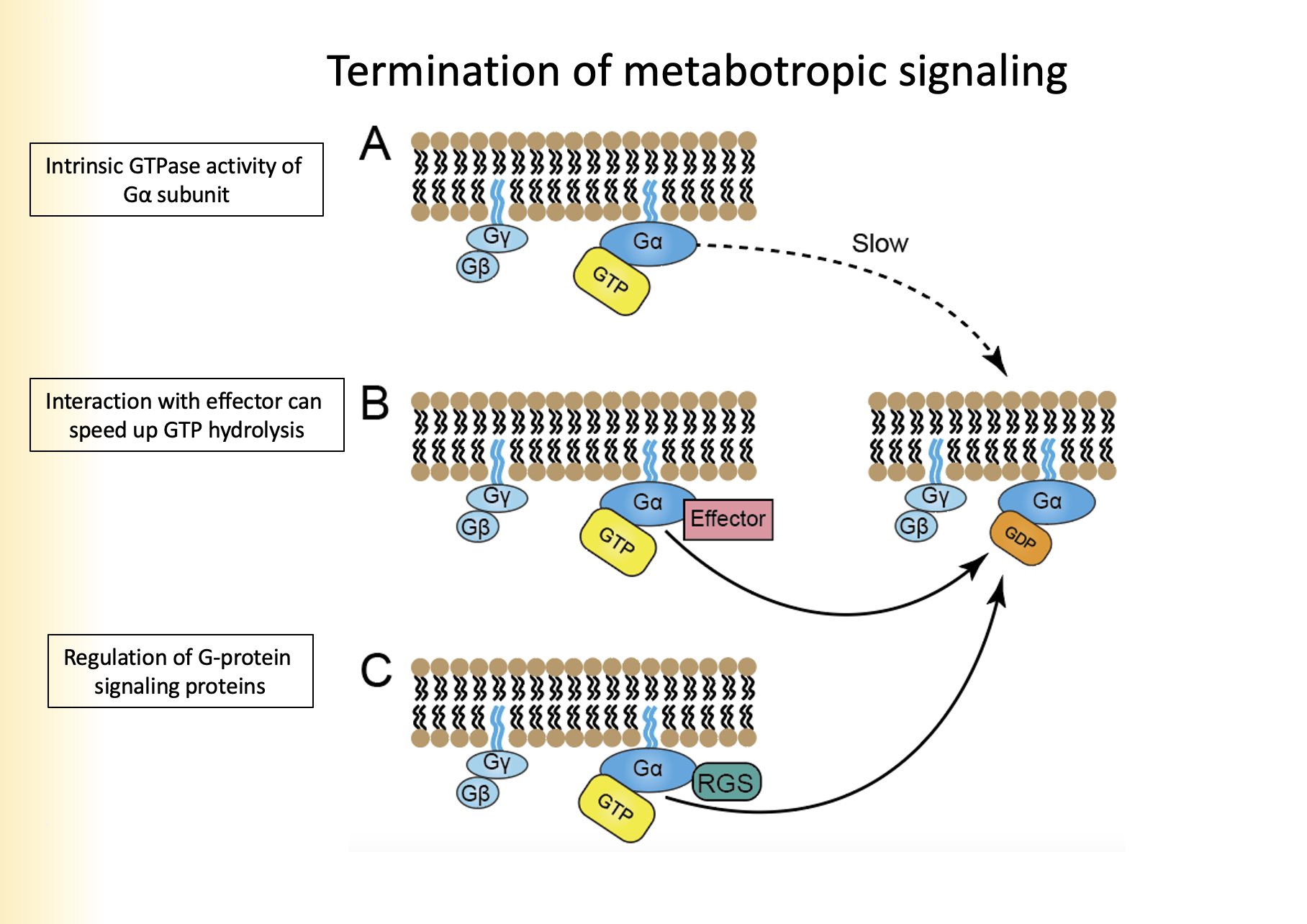
1. Instrinsic GTPase activity of Ga subunit
2. Interaction with effector
3. Regulation of G-Protein signaling proteins
Name the three types of termination of metabotropic signaling
13
New cards
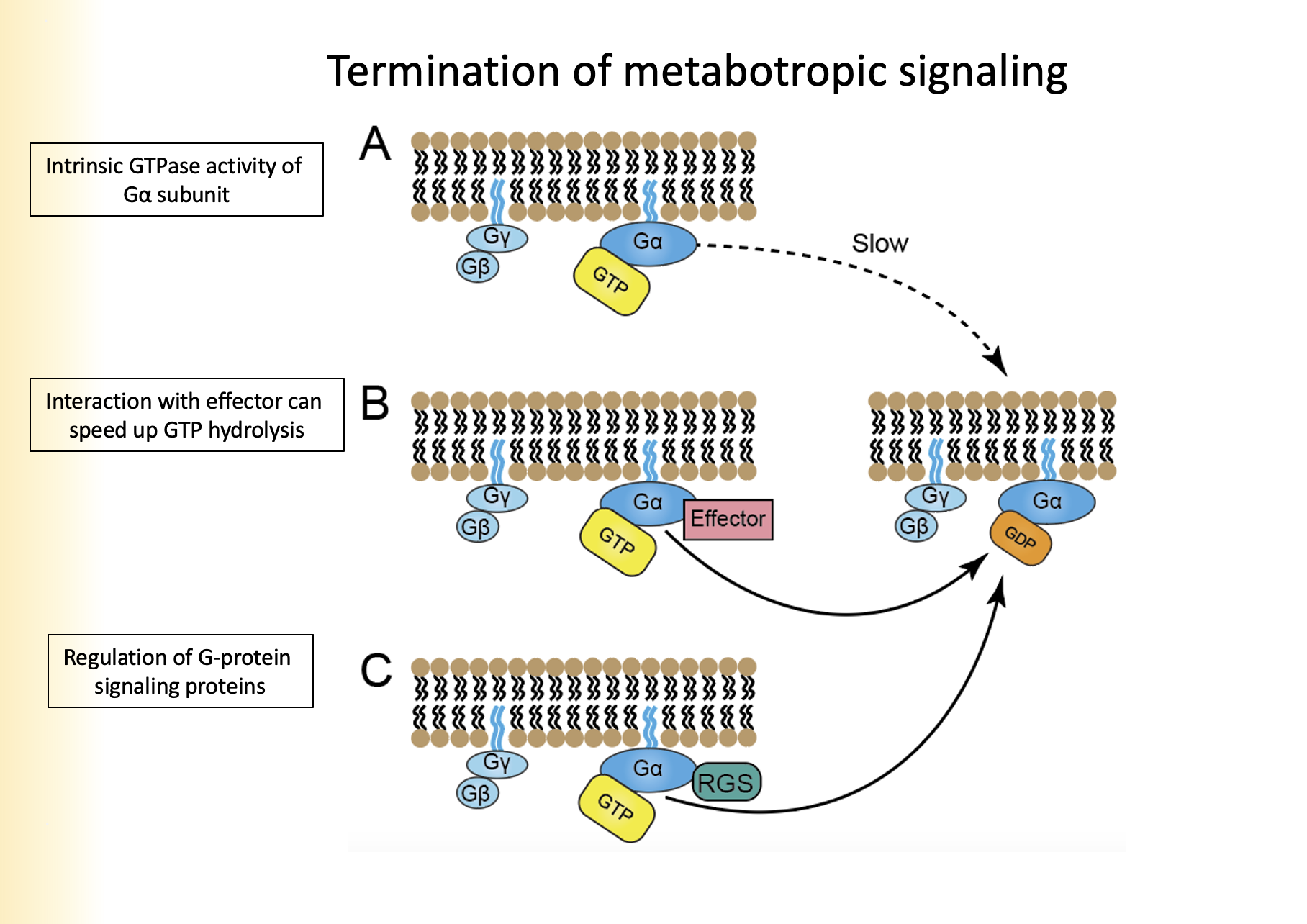
1. Ga hydrolyzes GTP to GDP, removes phosphate group
2. Ga binds to GyGb as Ga has a high affinity
3. Re-association with receptor
Explain intrinsic GTPase activity of Ga subunit for termination of metabotropic signaling
14
New cards
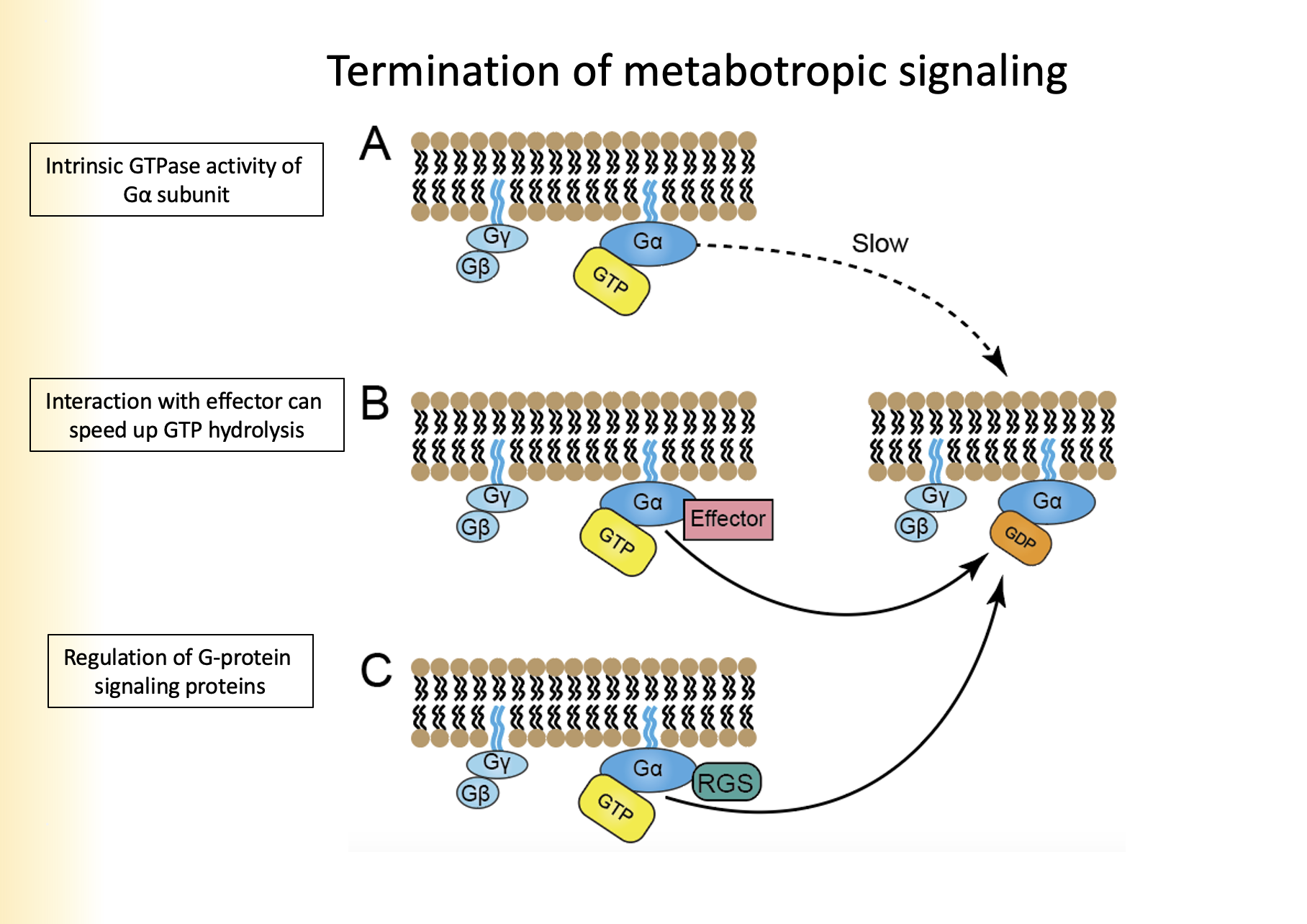
Effector will speed up the rate of hydrolysis by a subunit allowing Ga to bind faster to GDP
Explain interaction with effector for termination of metabotropic signaling
15
New cards
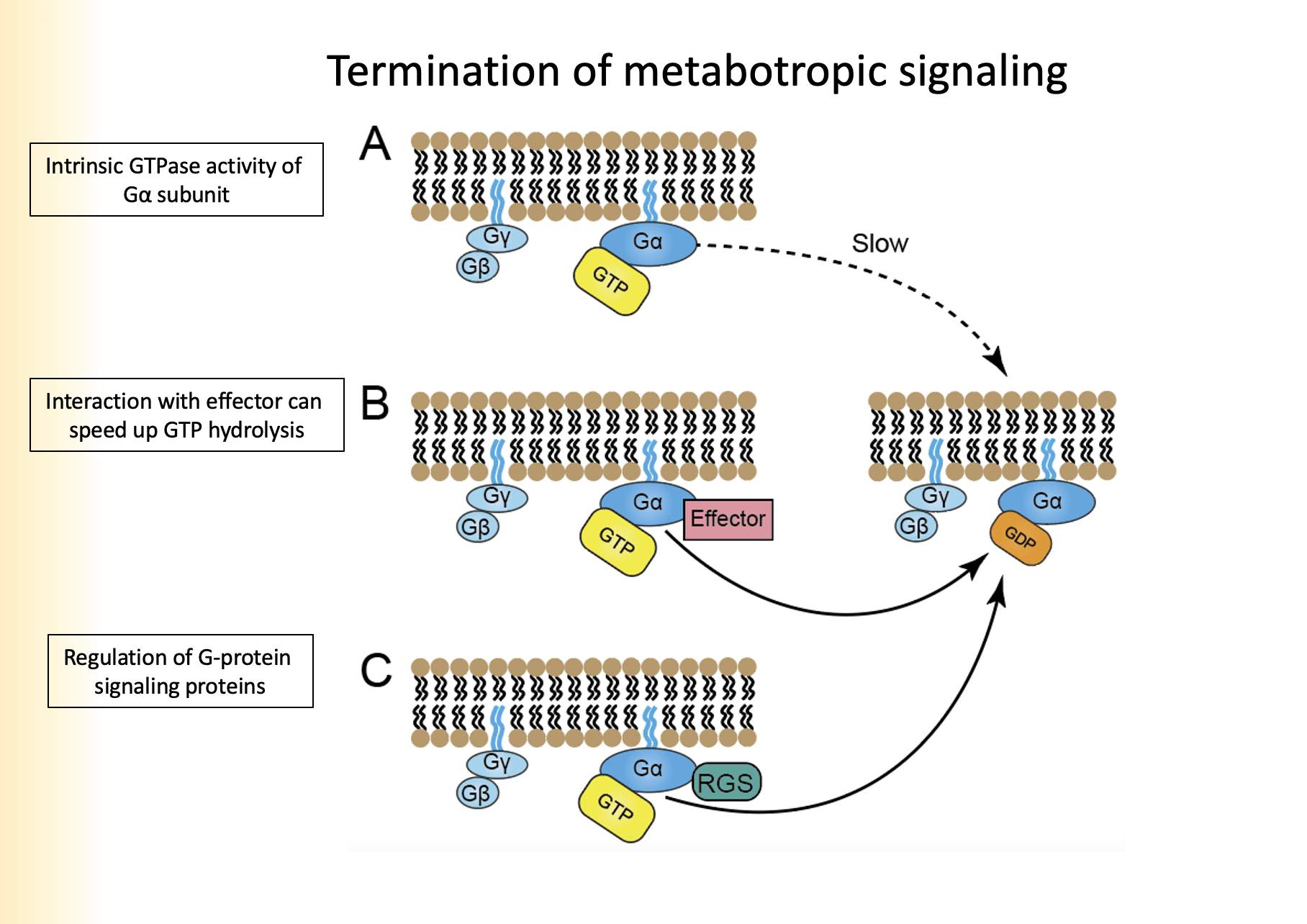
terminate the action of Ga subunit
* are not effectors
* are not effectors
Explain regulation of G-Protein signaling proteins for termination of metabotropic signaling
16
New cards
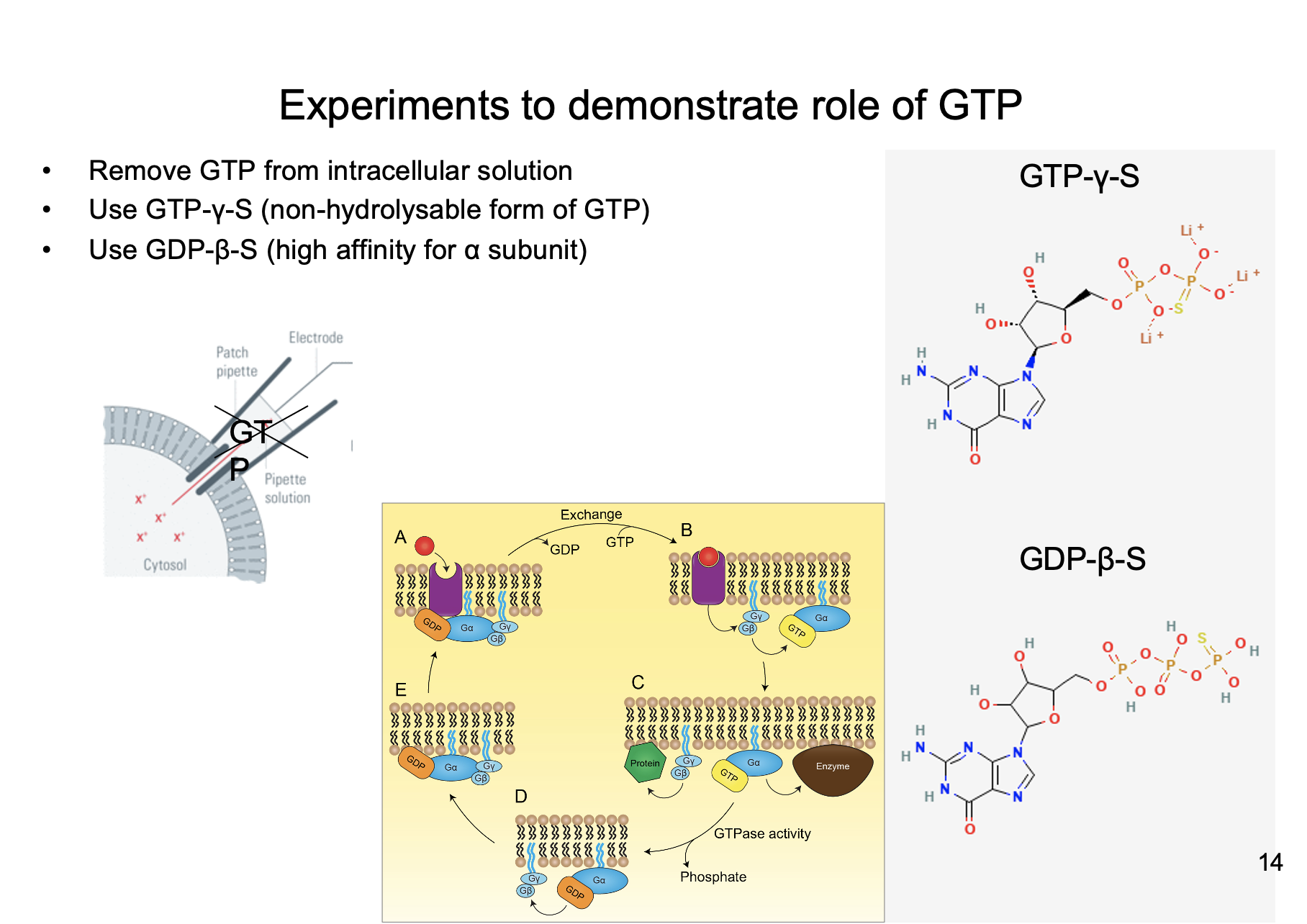
1. Remove GTP from intracellular solution
2. Use GTP-y-S
3. Use GDP-B-S
Name the three experiments to demonstrate the role of GTP
17
New cards
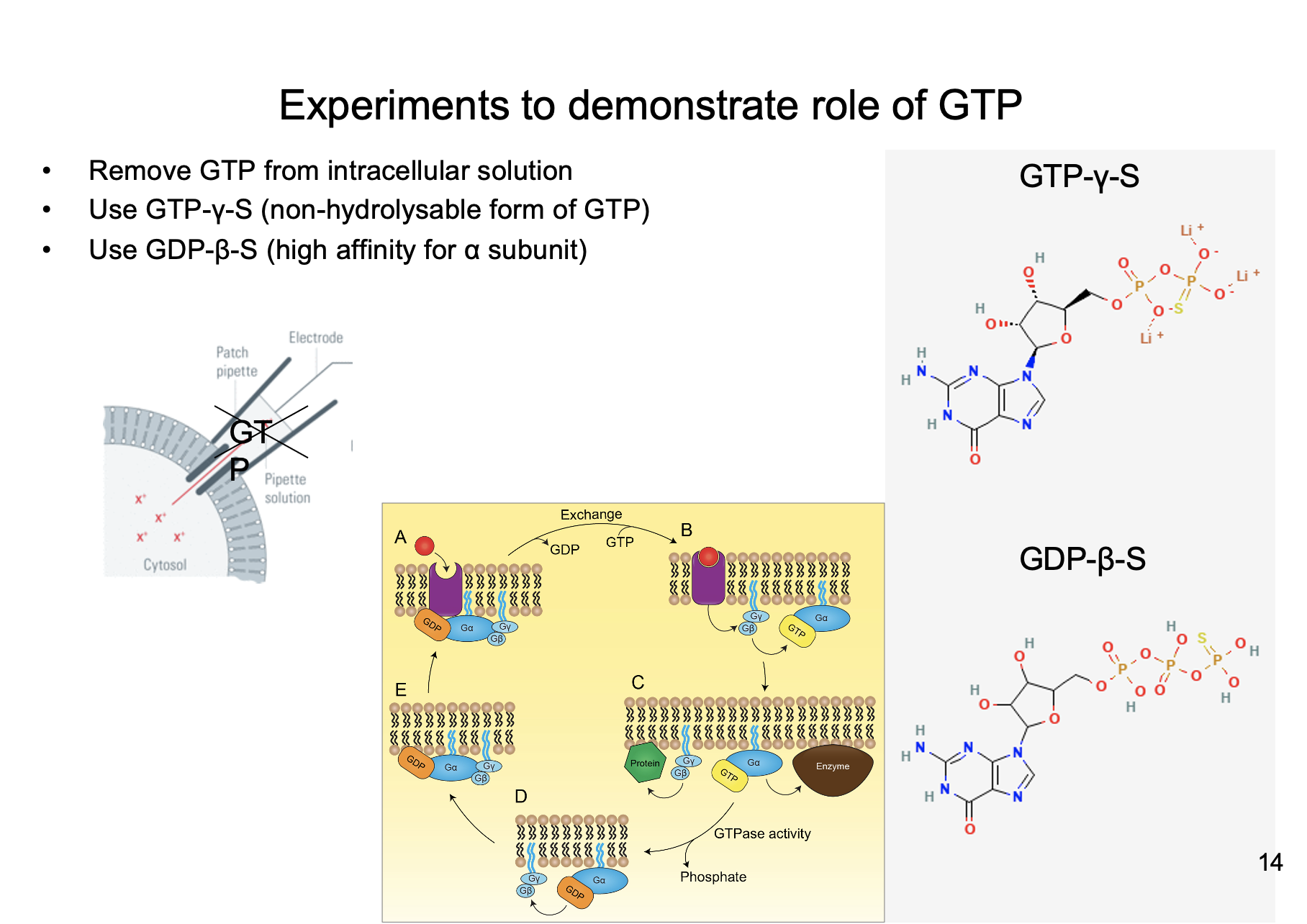
* Use whole cell recording
* wash out all GTP
* Place in NT
* Nothing happens
* wash out all GTP
* Place in NT
* Nothing happens
Explain the experiment that removes GTP from intracellular solution to demonstrate role of GTP
18
New cards
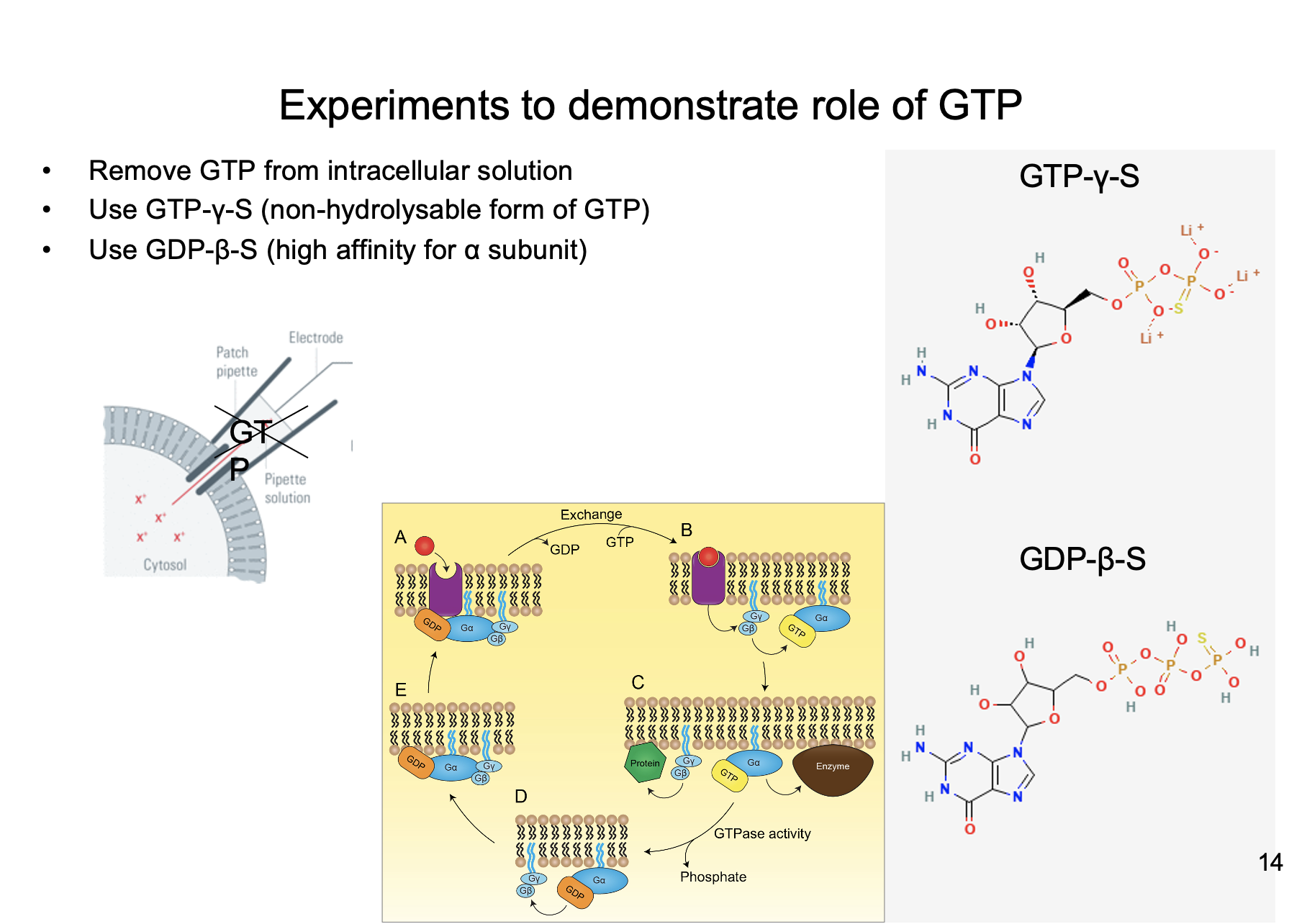
* Non-hydrolysable from of GTP
* Permanately active
* Permanately active
Explain the experiment that uses GTP-y-S to demonstrate the role of GTP
19
New cards
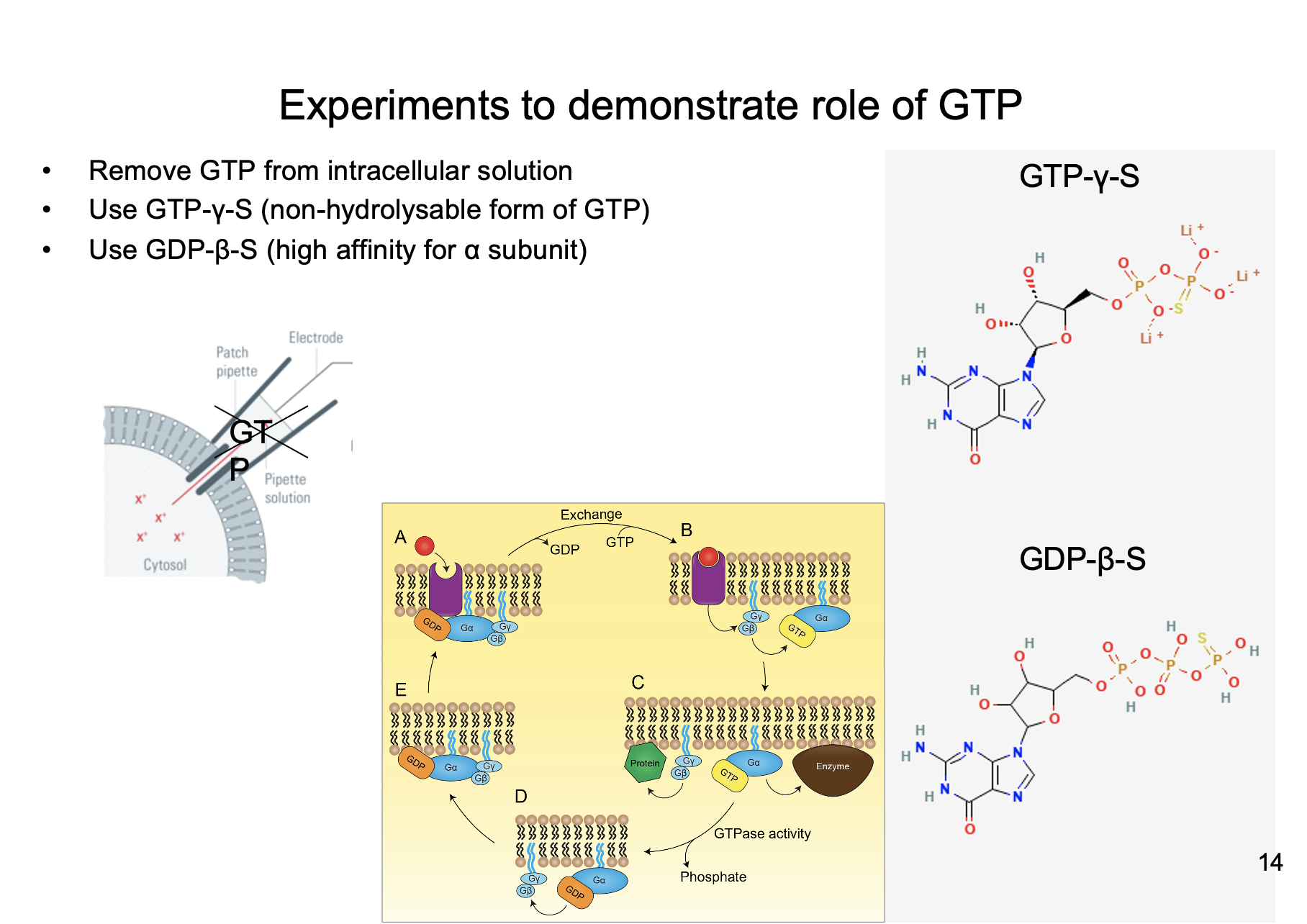
* GTP cannot compete with GDP-B-S
Explain the experiment that uses GDP-B-S to demonstrate role of GTP
20
New cards
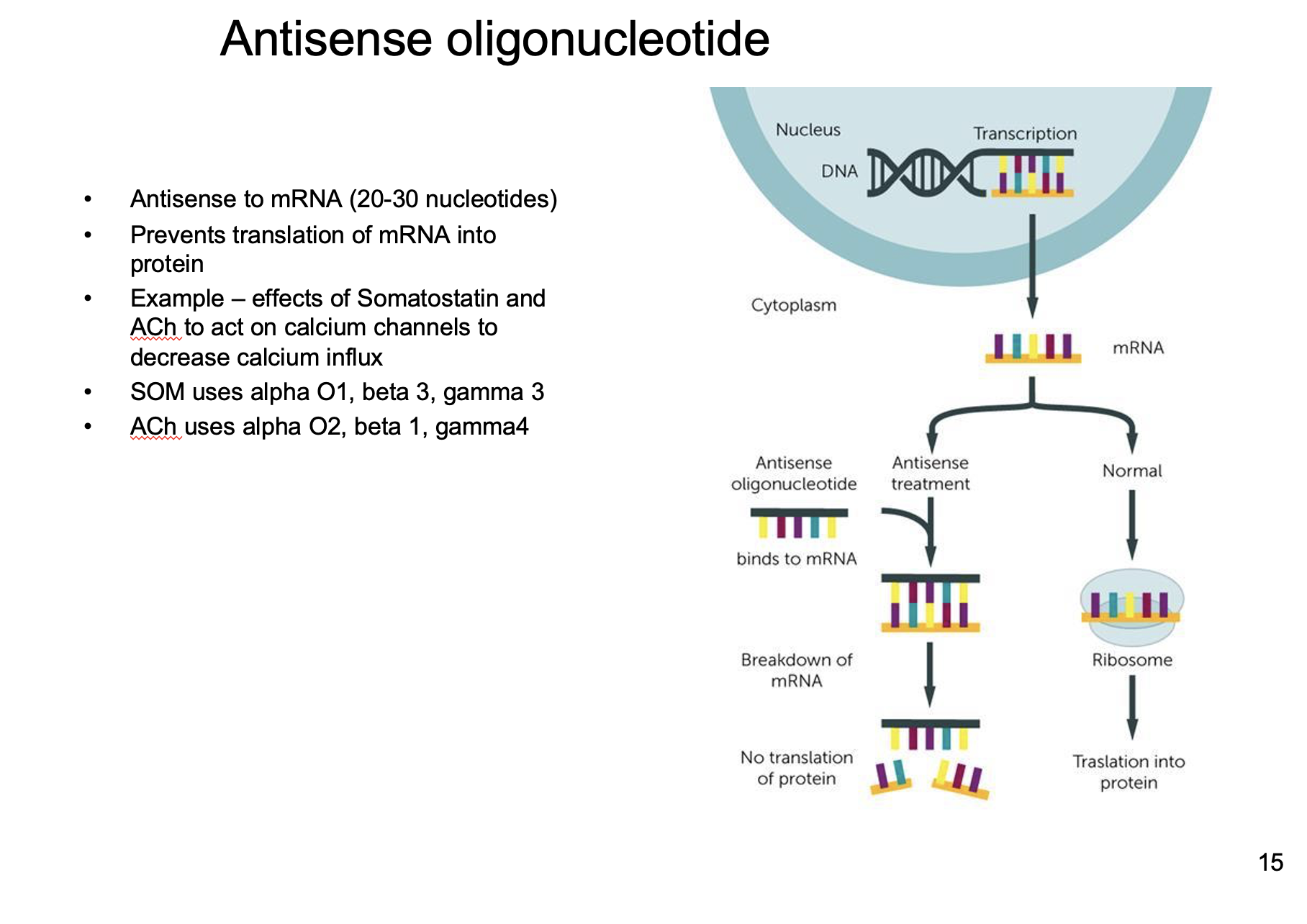
Prevents translation of mRNA to protein
(Which G-Protein is related to which receptor)
(Which G-Protein is related to which receptor)
What is the goal/role of an antisense oligonucleotide?
21
New cards
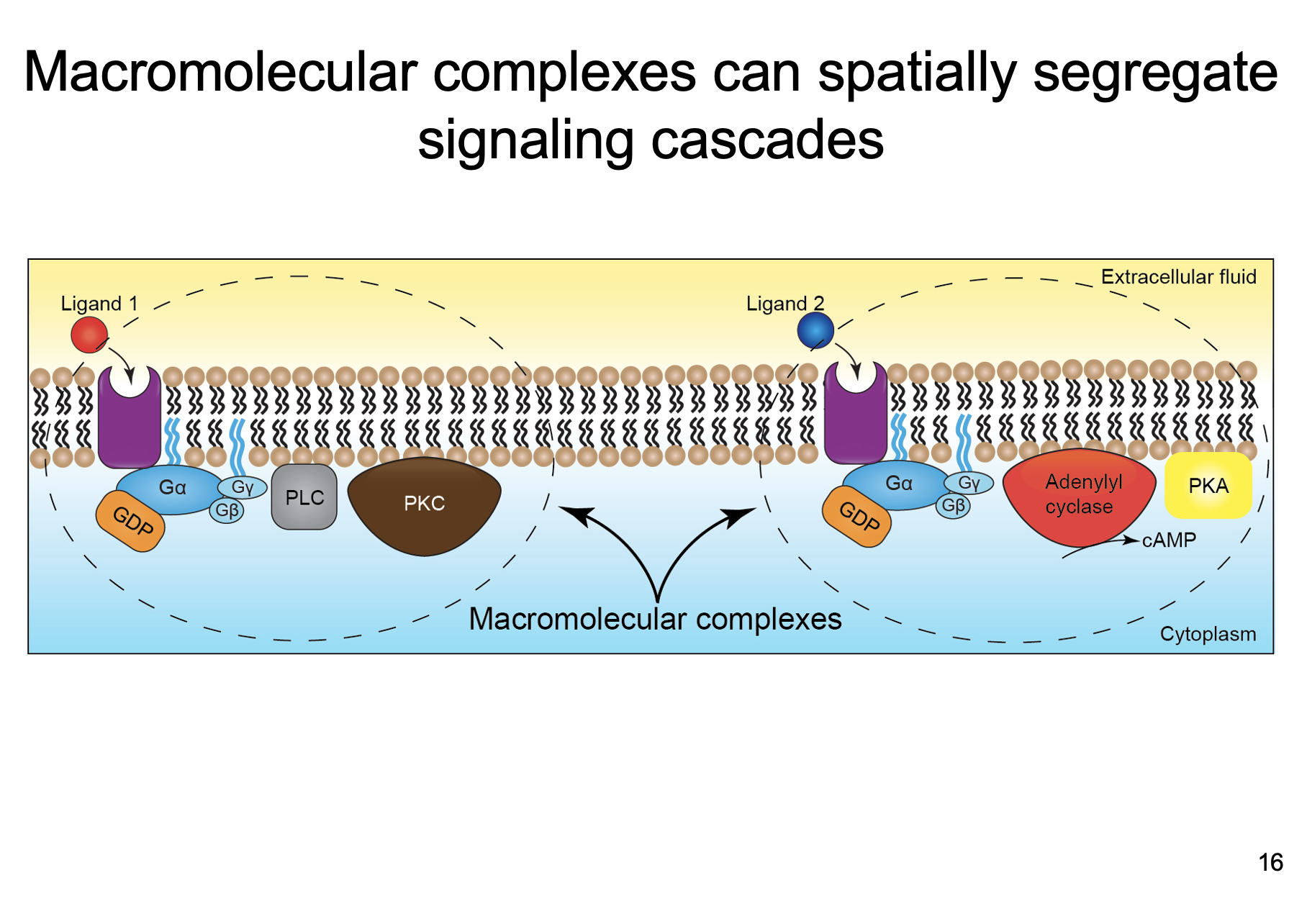
spatially segregate
Macromolecular complexes can_________________ signaling cascades