cell growth and division
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
sexual production
between two different organisms
creates offspring that are hybrids of two parents who gave 50% of DNA
increases genetic diversity
asexual reproduction
occurs within a single organism
creates genetically identical offspring (all DNA came from one parent)
simpler and takes less time
chromosome and chromatid relationship
chromosome is made up of two strands that are identical to eachother (called a chromatide)
made up of two identical sister chromatids
INTERPHASE
G1 (Gap 1): cell growth —> cytoplasm and organelles increase in size
S (synthesis): DNA replication
G2 (Gap 2): cell growth and prep for cell division
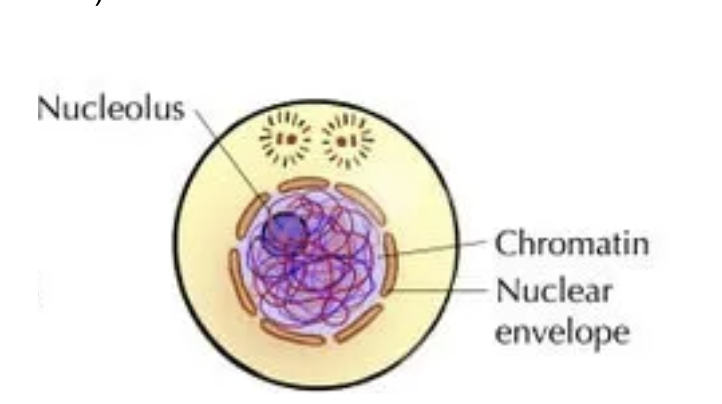
CELL DIVISION: Mitosis —> Prophase
Chromosomes become visible and nucleus dissolves
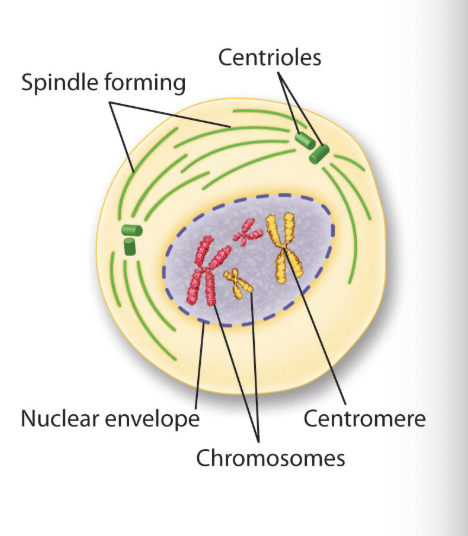
CELL DIVISION: Mitosis —> Metaphase
Chromosomes are lined up in the center of the cell by the spindle fibers.
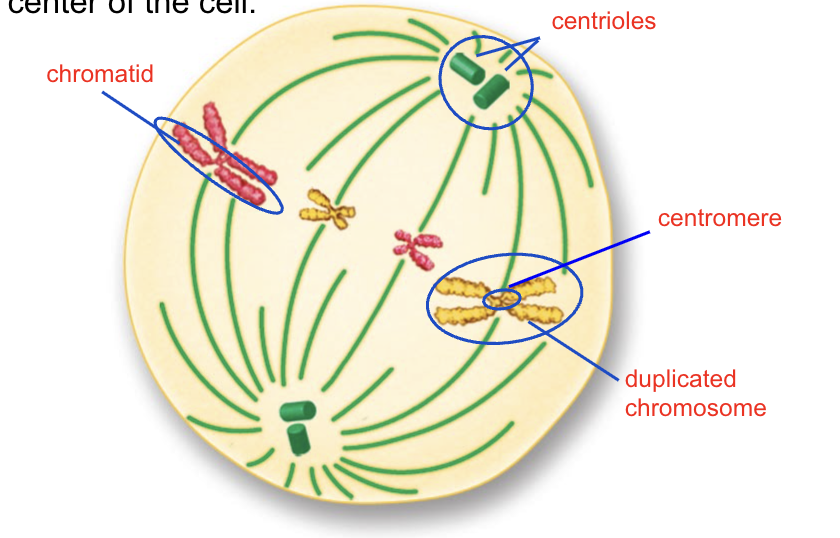
CELL DIVISION: Mitosis —> Anaphase
Spindle fibers pull chromosomes apart and pull them towards two ends of the cell
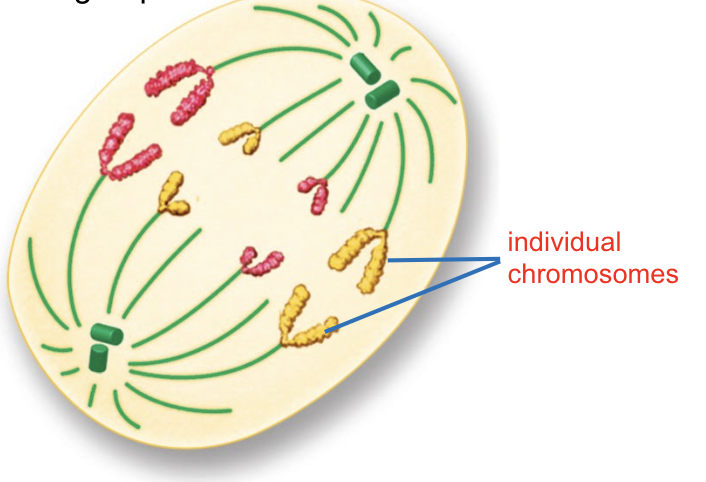
CELL DIVISION: Mitosis —> Telophase
Two new nuclei form around the two groups of chromosomes
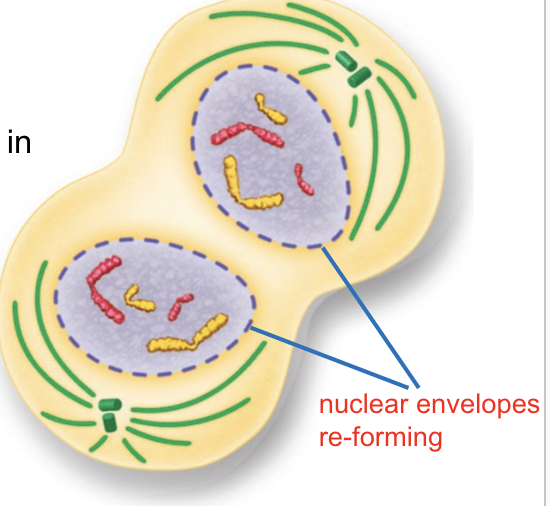
CYTOKINESIS
The cytoplasm of the original cell splits to form two new identical daughter cells.
how are cancer cells different than other cells
CANCER CELLS
keep dividing and spreading, ignoring the body’s signals —> creating tumors in the body
don’t mature because they reproduce very quickly
NORMAL CELLS
respond to the body’s signals to stop growing and reproducing + regulated by cyclins
grow at a normal pace and can carry out bodily functions