1 Pre-Historic to Bronze Age
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
208 Terms
Art
an aesthetically pleasing & meaningful arrangement of elements, as words, sounds, colors, shapes, etc. Form of human activity whose chief character is determind by such arrangement
architecture
the science or profession of designing and constructing buildings or other structures
decorative arts
Any of the arts pertaining to or referring to the following: painting, sculpture, glass, and glassware, ceramic and pottery, metallurgy and plants.
practical
an approach to historical style analysis that seeks to establish what was built, when, by whom, and for whom
historical
an approach to historical style analysis that seeks the whys and its relationship to the social, economic, political, cultural, and religious environment
aesthetics
an approach to historical style analysis that accounts visual and stylistic differences and to explain how styles change and why they do so
factors of historical development
1) Rational, Technological and Constructional
2) Social and Religious
3) Economic, Cultural and Political
4) Spirit of the Age (Zeitgeist)
post and lintel construction
Wall construction utilizing a framework of vertical posts and horizontal beams to carry floor and roof loads.
arcaded construction
Invented this type of construction to allow bigger and more monumental structures
Paleolithic Age
Old Stone Age or Glacial Age, before written history
Lower Paleolithic
The oldest part of the period during which the first stone tools were created and used.
Oldowan
Lower Paleolithic Culture where the key feature was the method of chipping stones to create a chopping or sharp edged flake
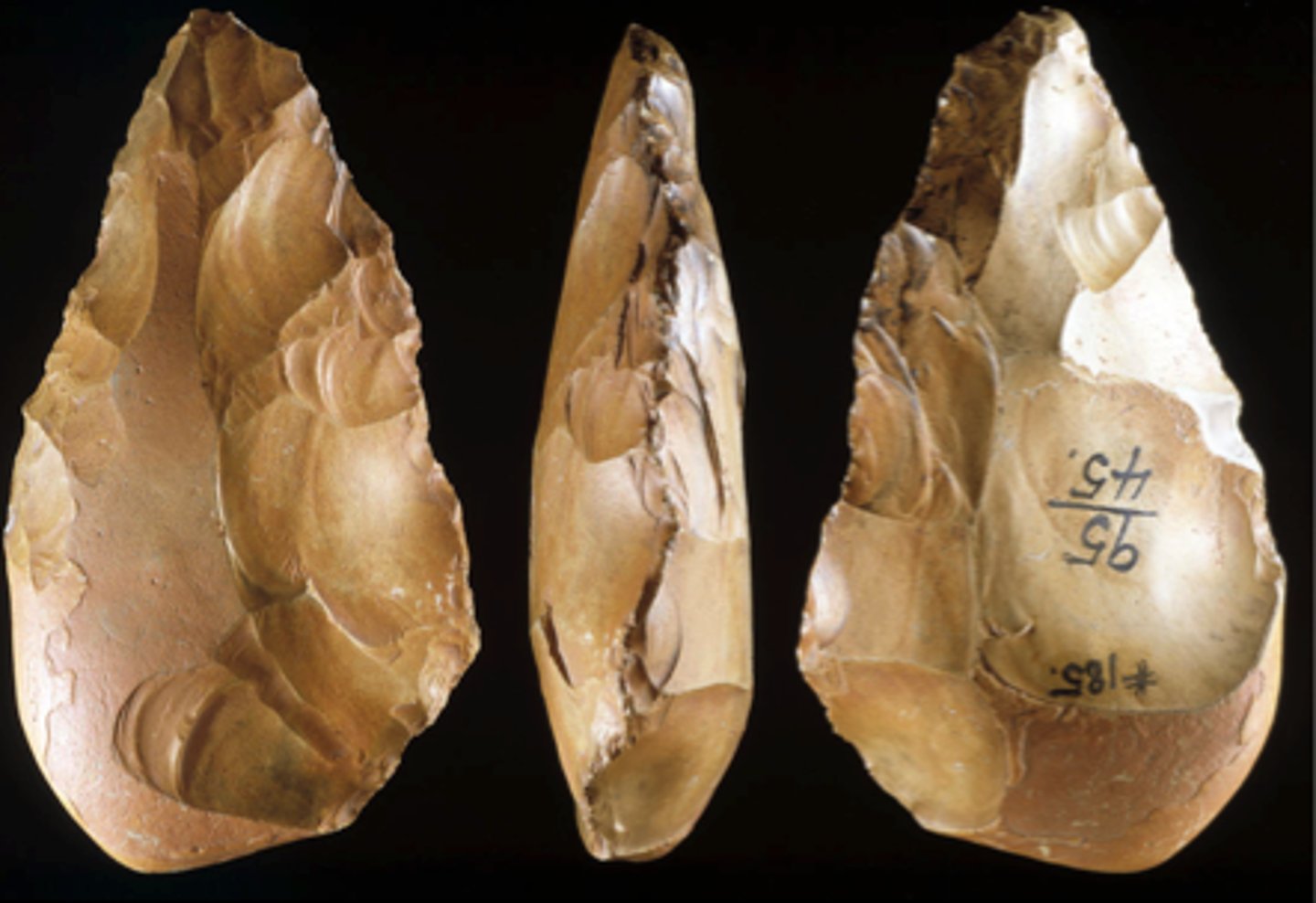
Acheulean
Lower Paleolithic culture that was the most important and dominant tool-making tradition with oval and pear-shaped hand-axes
Shaman of Trois Freres
Paleolithic art shows a Shaman donning an animal suit to absorb the powers of the animal
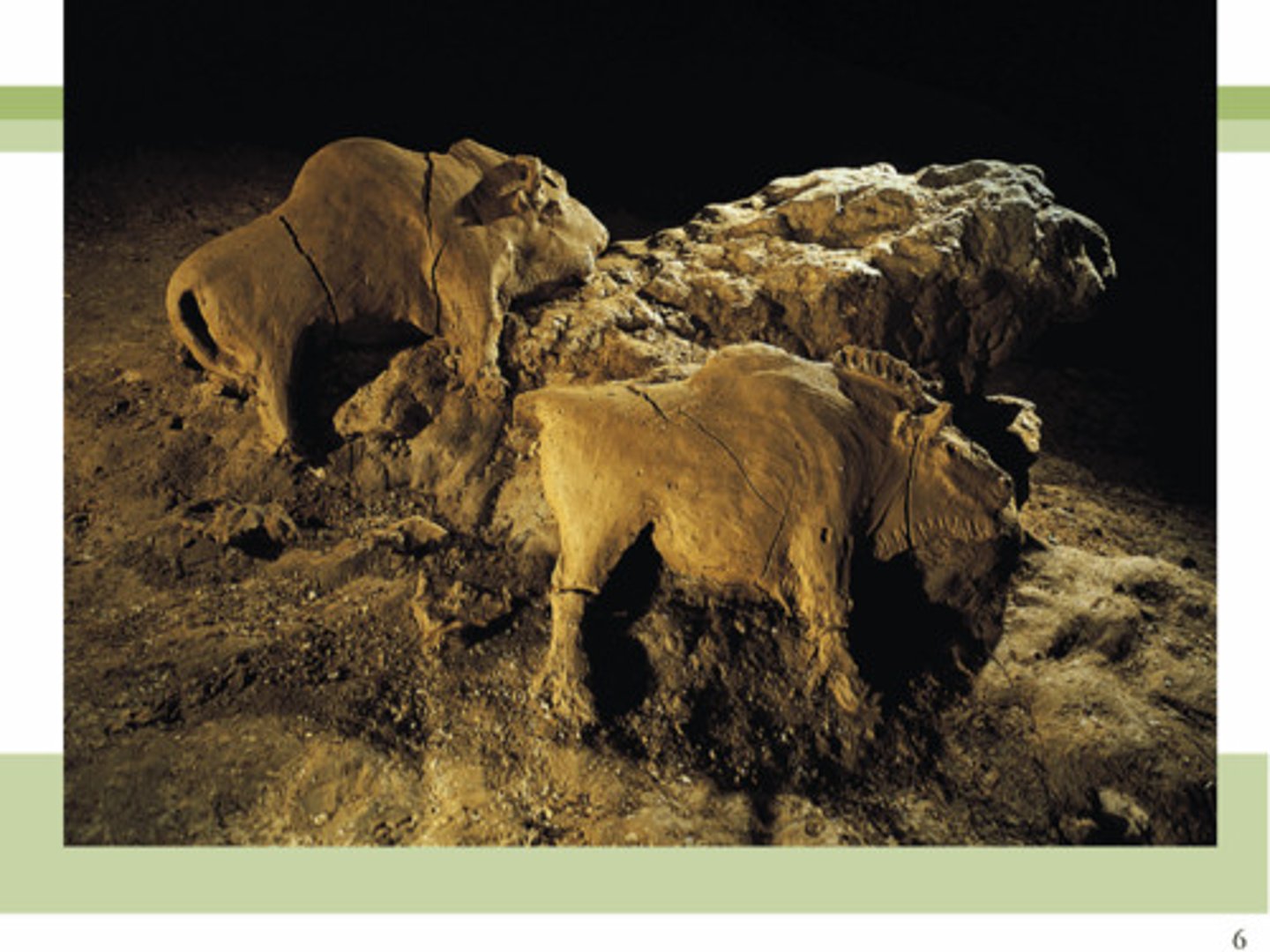
Bison of Tuc D'Audoubert
A paleolithic cave art, constructed in a combination of sculpture in the round and high relief

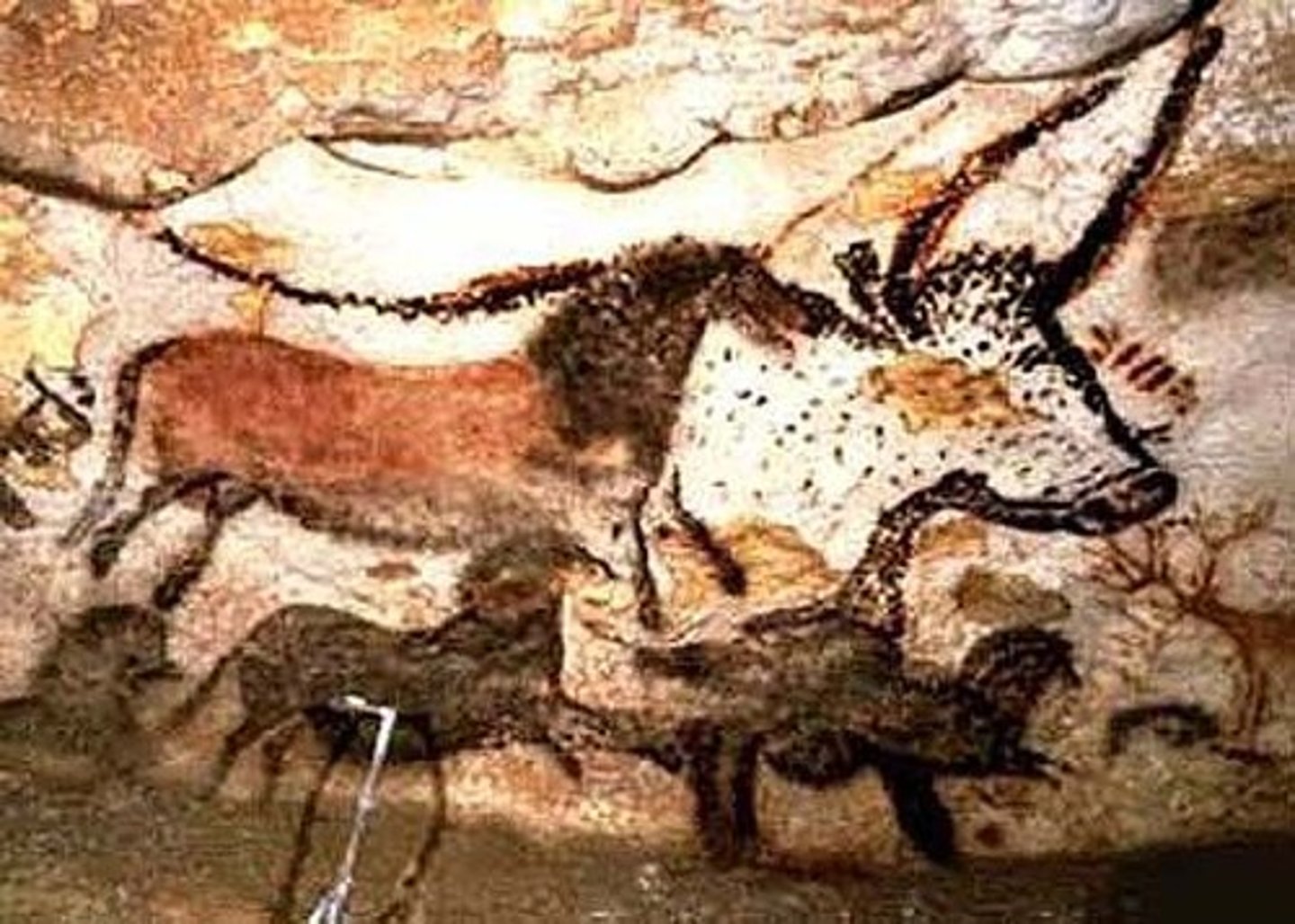
Gallery of The Running Bulls
Cave painting found in Altamira, Spain that tried to achieve realism by creating shadows and overlapping of animals to show perspective. 25 meters long.

cupules
These are round and concave indentions carved into a rock surface by Paleolithic humans. No one is sure of their function.

Clactonian
A term used for assemblages from the Lower Paleolithic, lacking handaxes and characterized by large flakes with heavy retouching and notches.

Middle Paleolithic
The middle part of the Old Stone Age, associated with Mousterian tools, which Neandertals produced using the Levallois technique.

Mousterian
middle paleolithic culture where tools were in specialized shapes, including barbed and serrated edges
Upper Paleolithic
Refers to the most recent part of the Old Stone Age, spawned the first widespread appearance of human painting and sculpture
Perigordian
employed flake-tool technology, producing toothed and serrated stone tools
chatelperron points
Aurignacian
Pertaining to an Upper Paleolithic stone tool industry that witnessed the first significant manifestations of fine art painting and sculpture, cave paintings
el castillo cave
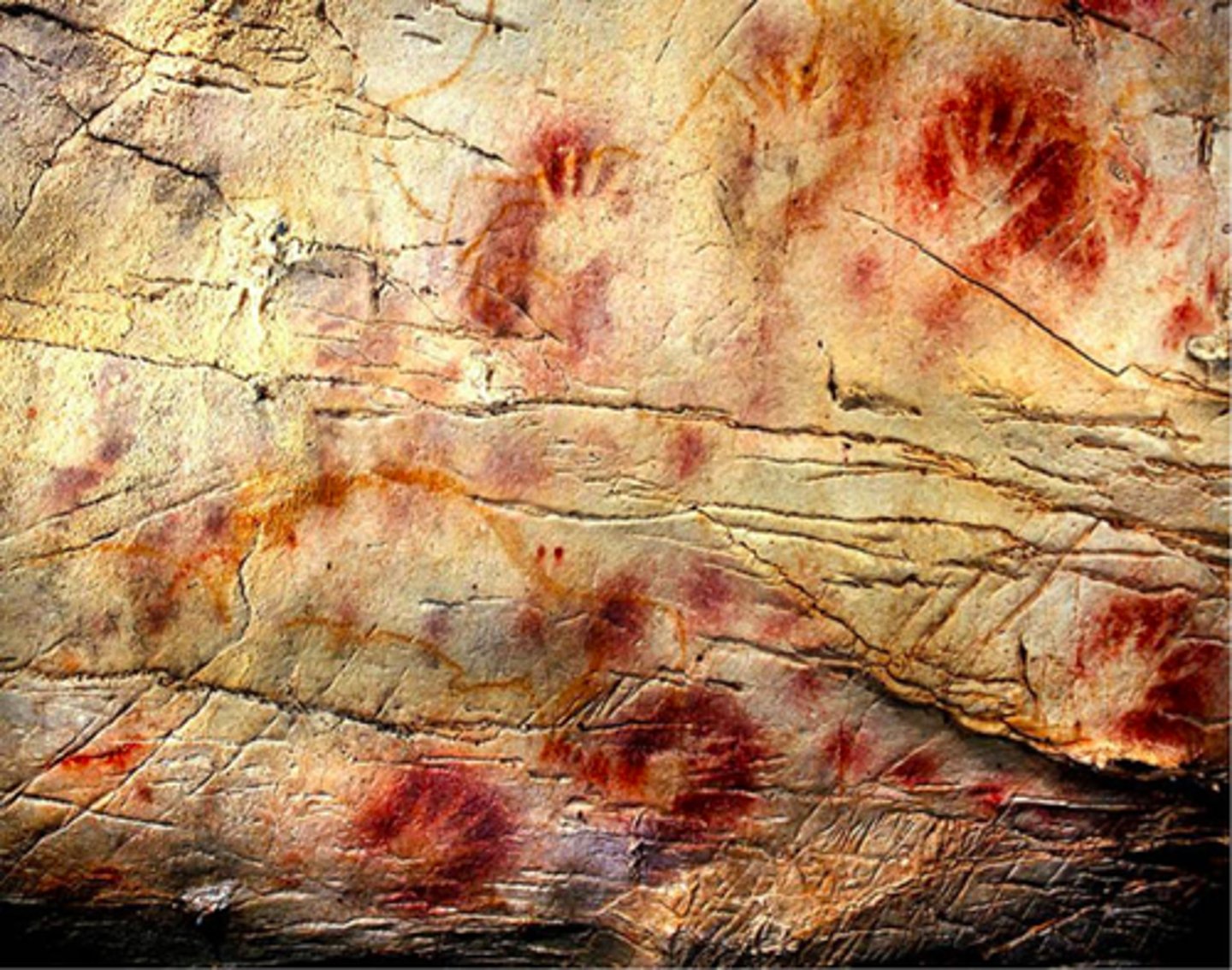
Gravettian
toolmaking tradition of the upper paleolithic, characterized by potable sculpture, the production of small pointed blades with blunt but straight back and denticulate knives
Soultrean
stone-toolmaking tradition of the European Upper Paleolithic. Bifaces are exquisitely made, symmetrical, leaf-shaped projectile points. Finest Paleolithic flint craftsmanship
Magdalenian
Pertaining to the final phase of the Upper Paleolithic defined by smaller and more sophisticated tools (from barbed points to needles). Growing importance to aesthetics
Venuses
Created during prehistoric time to ensure successful childbirth
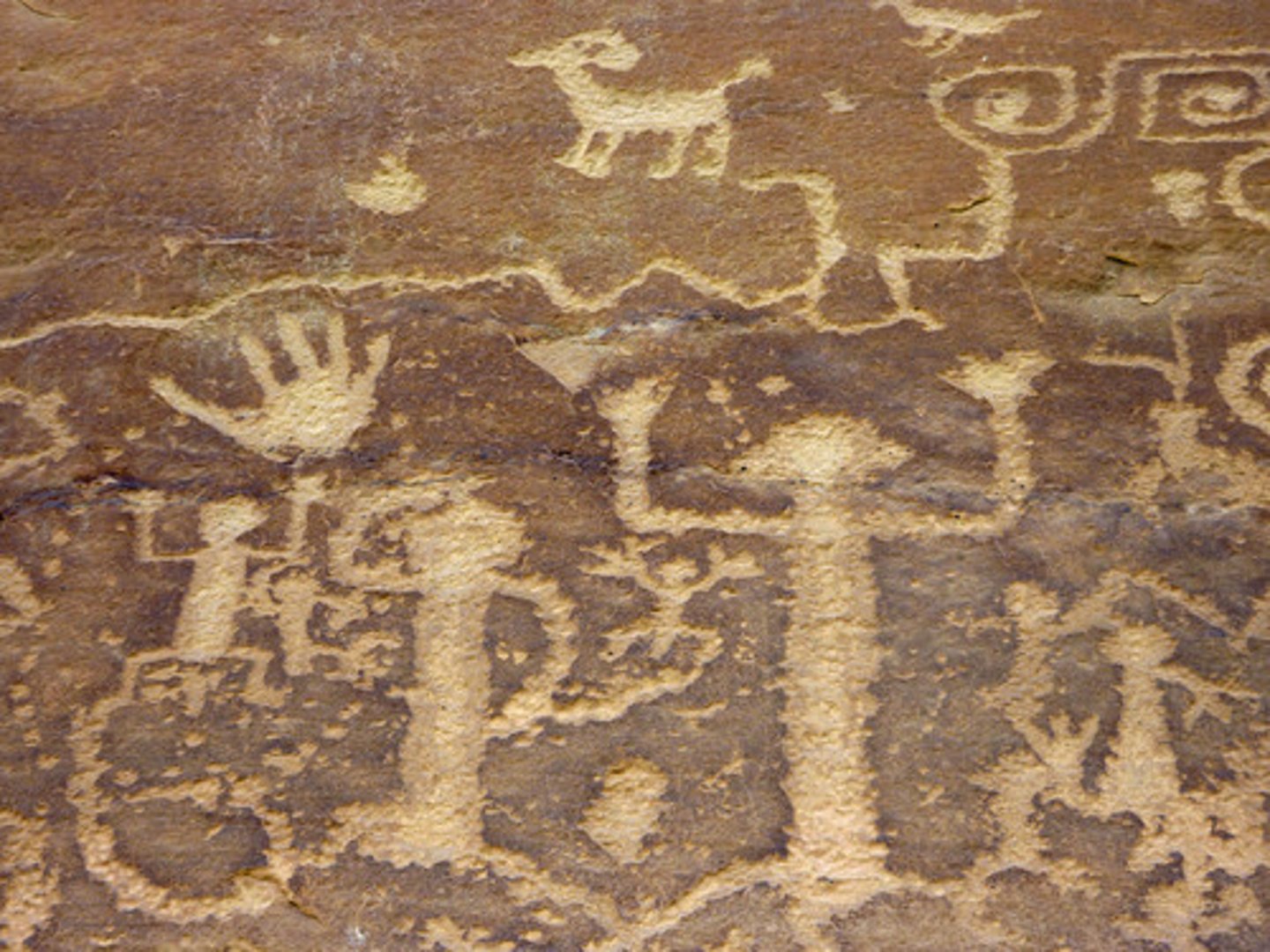
petroglyph
rock carving

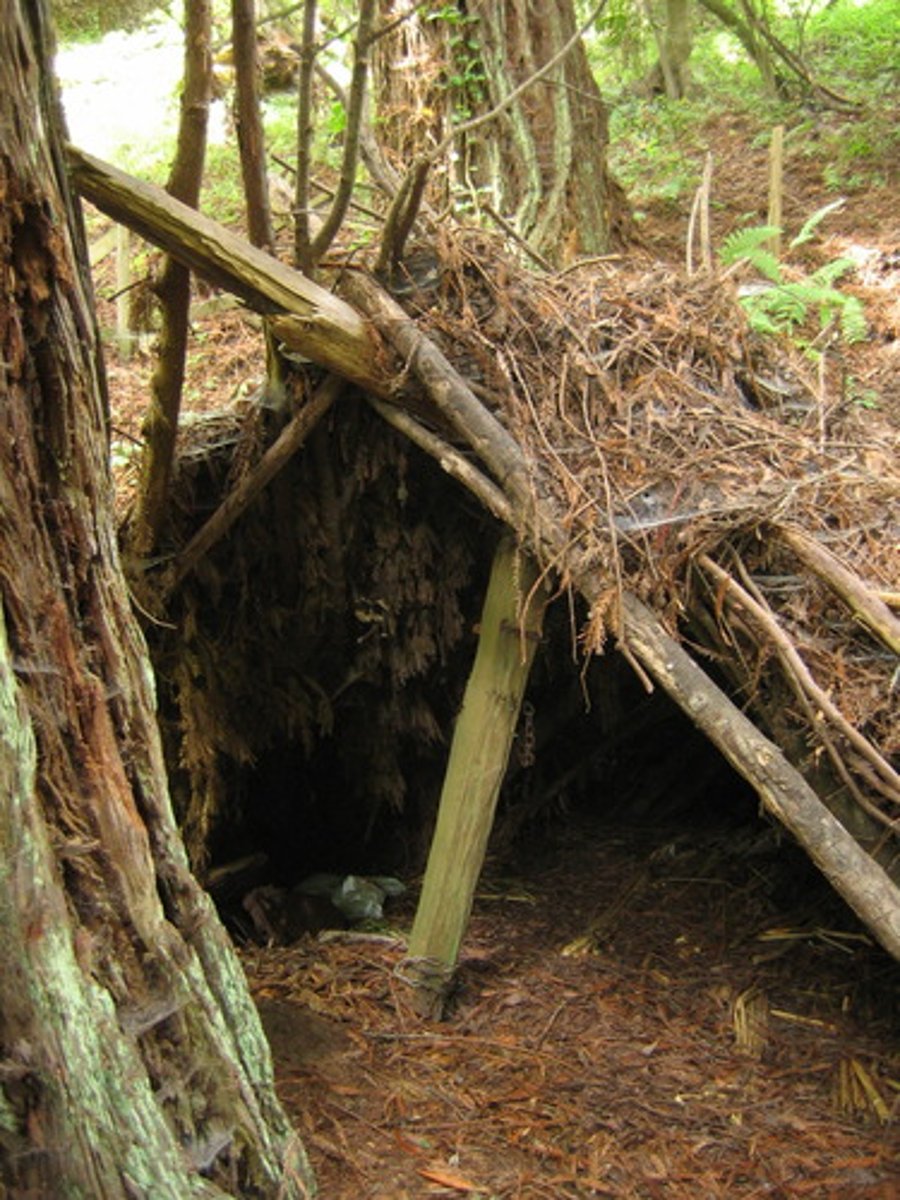
lean-tos
often erected against the wall of a cave

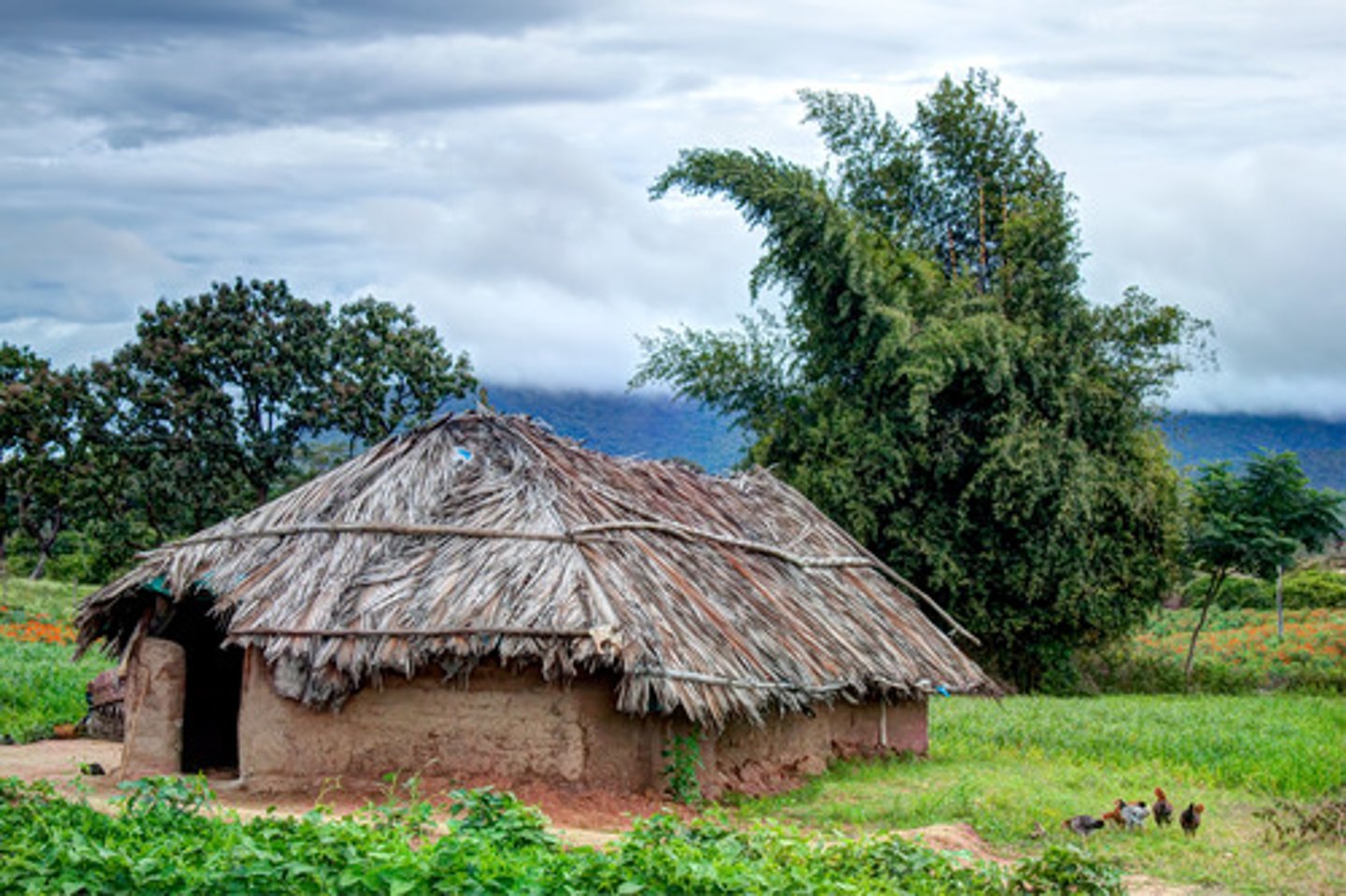
huts
built using stakes with stones as supports, with stouter posts along the axis

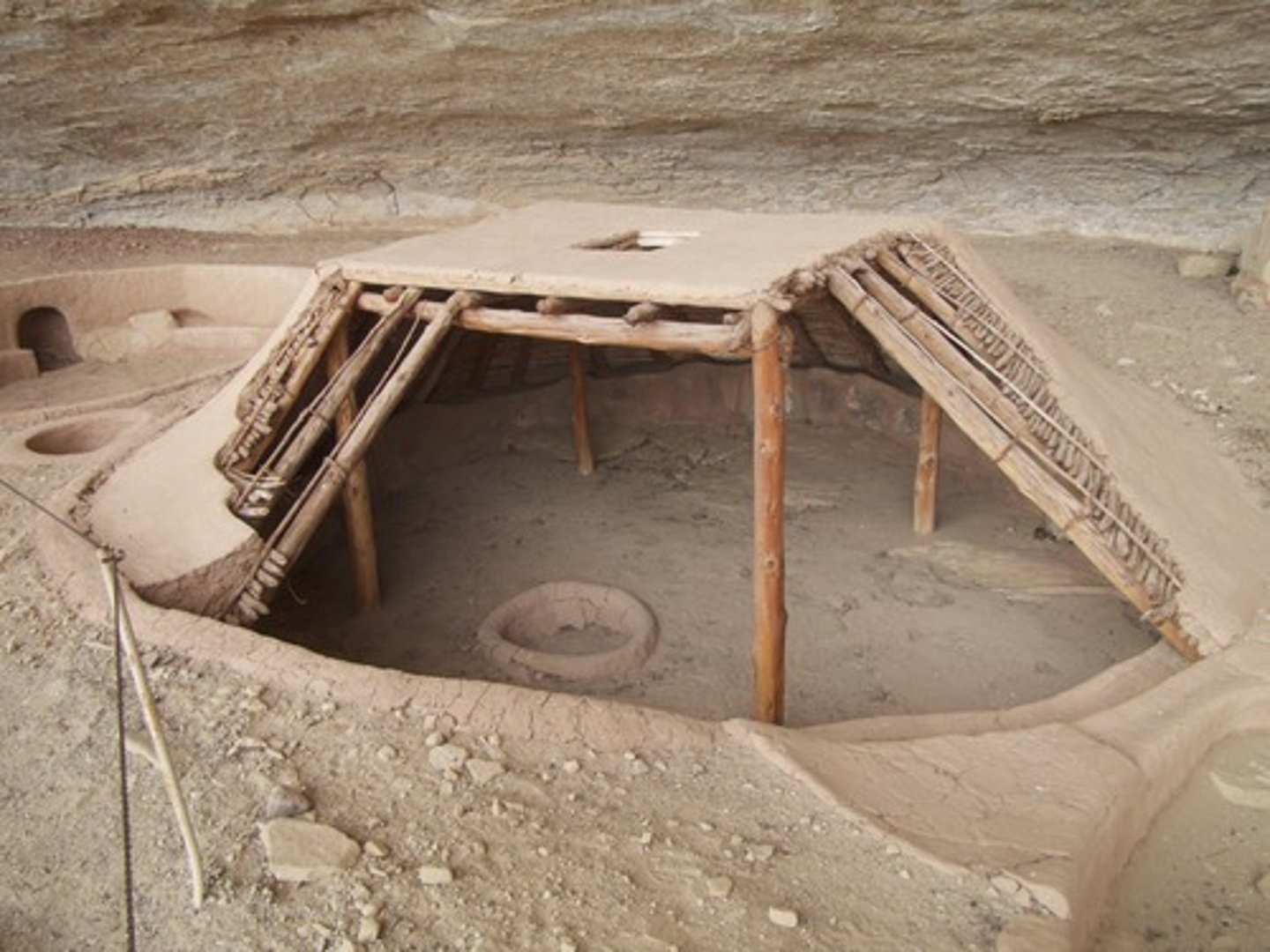
pit houses
houses dug into the ground and covered with wood and skins

tents
made of wooden posts and covered with skins that were weighed down with pebbles
pictograms
A pictorial symbol or sign representing an object or concept. Used by many non-alphabetic written scripts.

Venus of Brassempouy
oldest known prehistoric portrait, carved from mammoth ivory
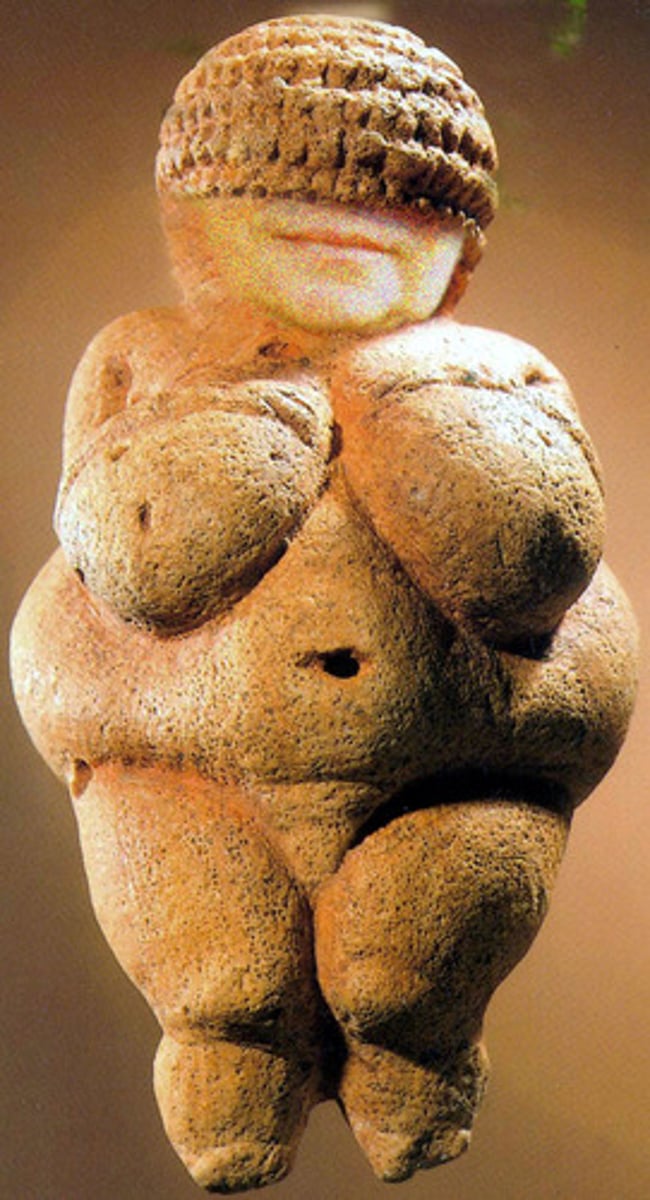
Venus of Willendorf
Austrian painted venus made of limestone; stumpy female figure features pendulous breasts, an obese middle and belly, and pronounced buttocks

Venus of Dolni Vestonice
earliest ceramic artifact found in the Czech Republic
parietal art
paintings and engravings found along cave walls and ceilings
Stationary Art
cave paintings from lascaux, france; great hall of the bulls (belief in the power in animals)
Totemism
the belief that people are related to particular animals, plants, or natural objects by virtue of descent from common ancestral spirits
Shamamism
communication with good and evil spirits
relief sculpture
Sculpture that projects from a flat background
pottery/ceramic art
creation of objects, mainly cooking or storage vessels made out of clay and then hardened by heat
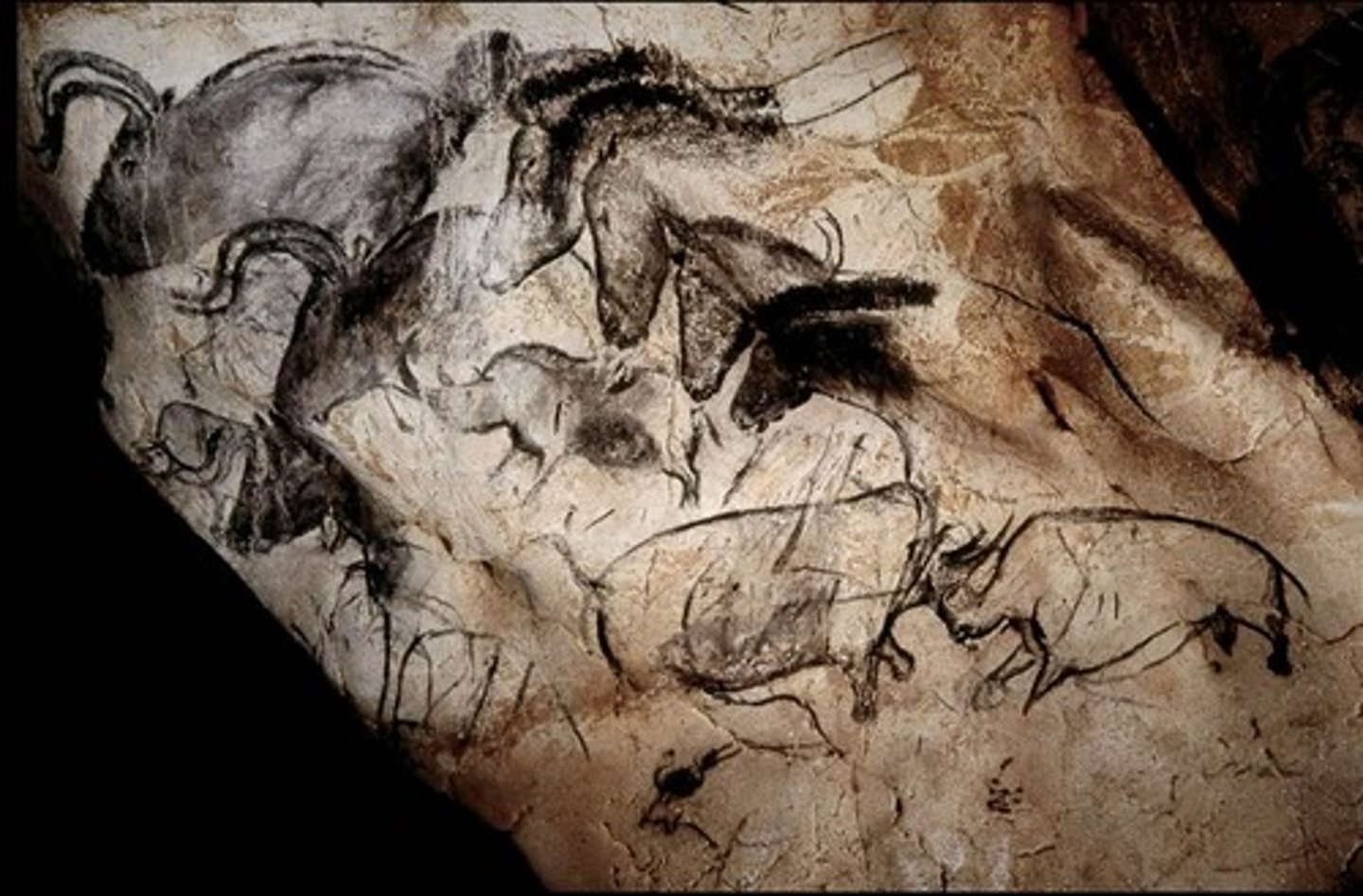
Chauvet-Pont-D'Arc Cave
paintings were more sophisticated, showing shading, perspective, composition, even depictions of movement

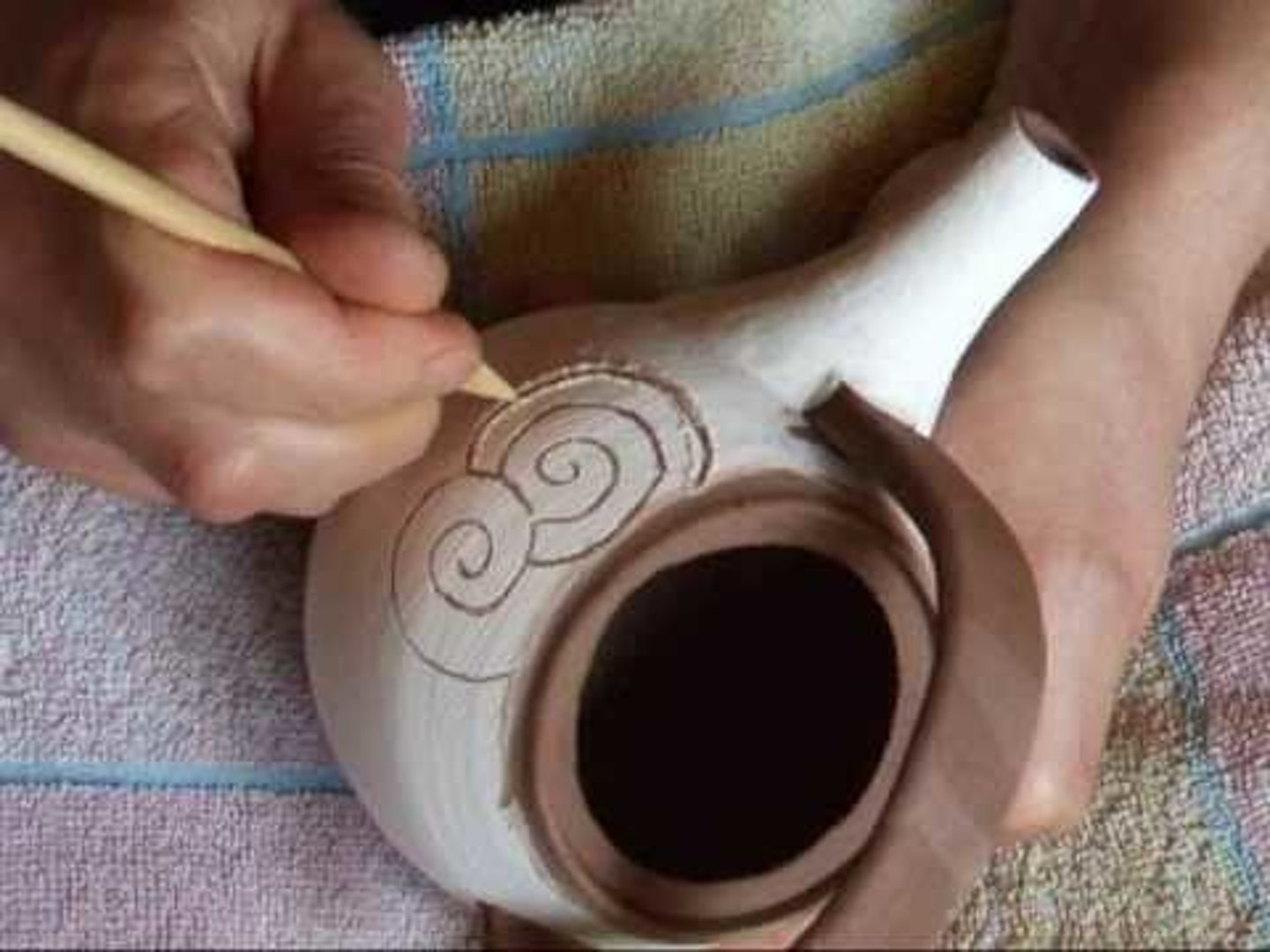
Sgraffito
a ceramic or mural decoration made by scratching off a surface layer to reveal the ground

megalith
a large stone that forms a prehistoric monument
Mesolithic Era
Middle Stone Age
Mesolithic Era
Era that focused from hunting and gathering to farming/agriculture
rock paintings
mesolithic art found outside caves, on vertical cliffs or sheer faces, people became subjects
pottery
art that emerged in the mesolithic era for utilitarian purposes
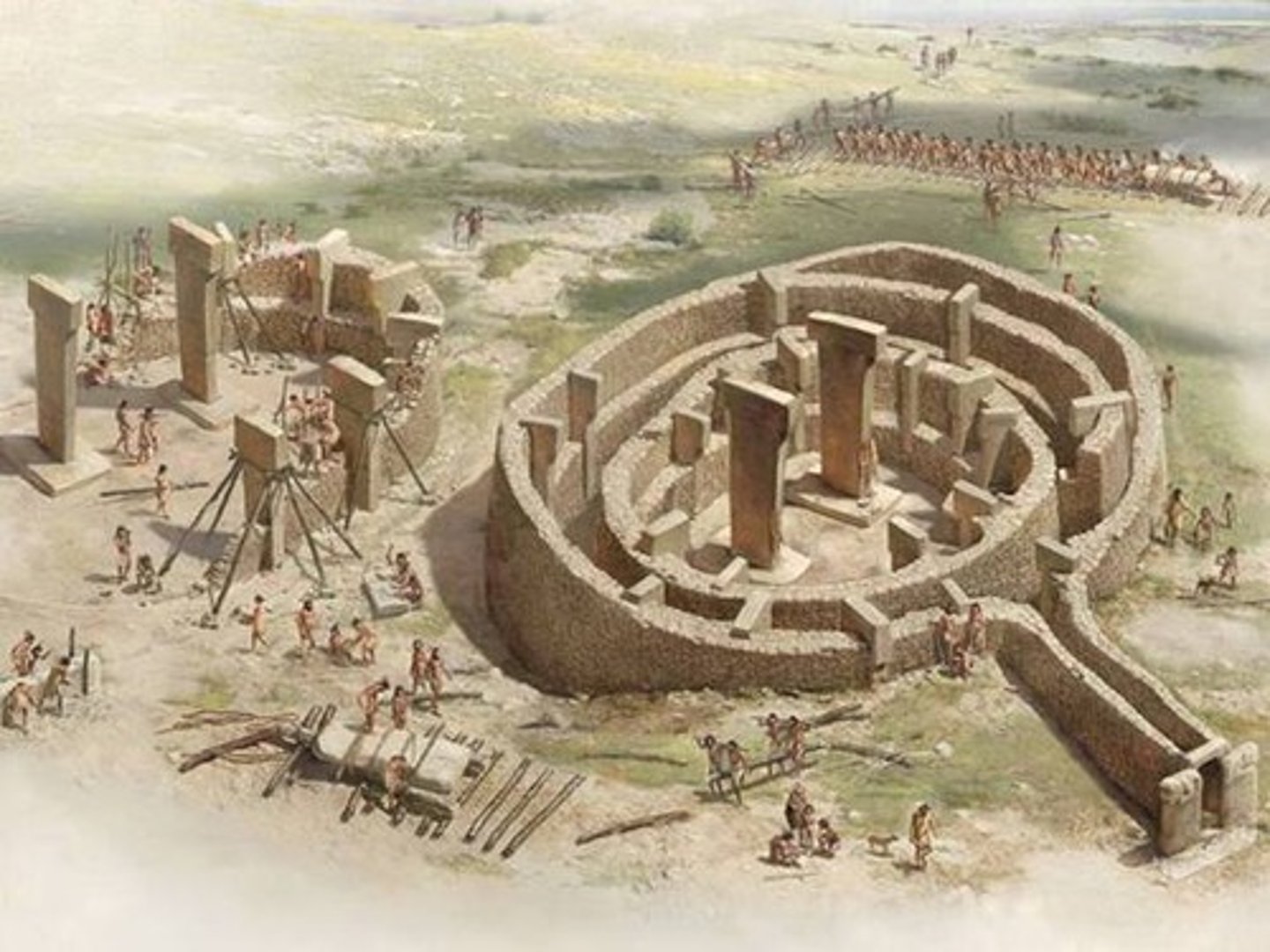
Gobekli Tepe
A ceremonial site of megaliths found in Turkey made by hunting and gathering people.

Neolithic Age
stone tools shaped by polishing or grinding, and farming, led to growth in crafts like pottery and weaving. beginning to civilization. mud bricks were first used
timber-framed houses

longhouses
tripartite, bipartite, single plans
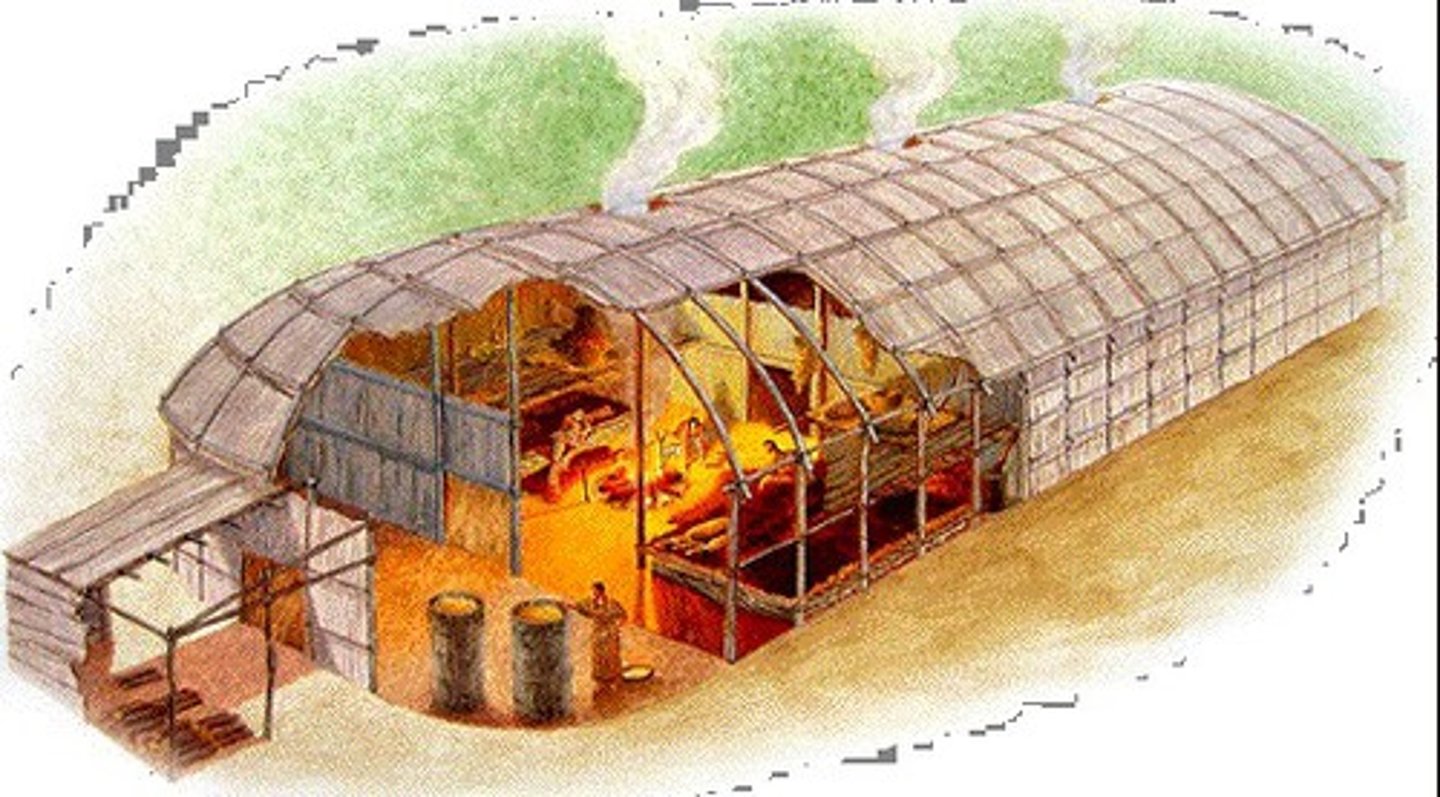
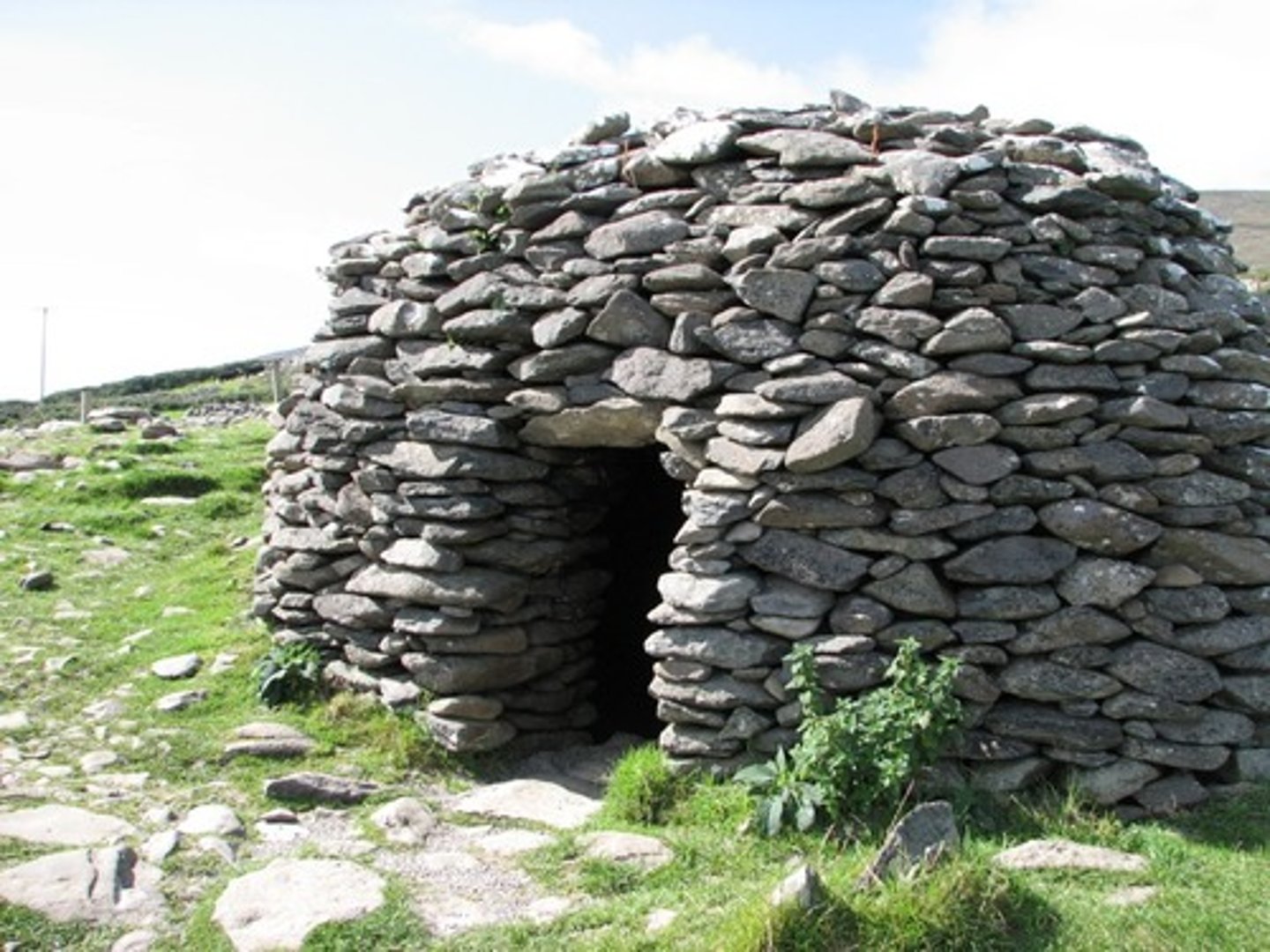
Beehive hut

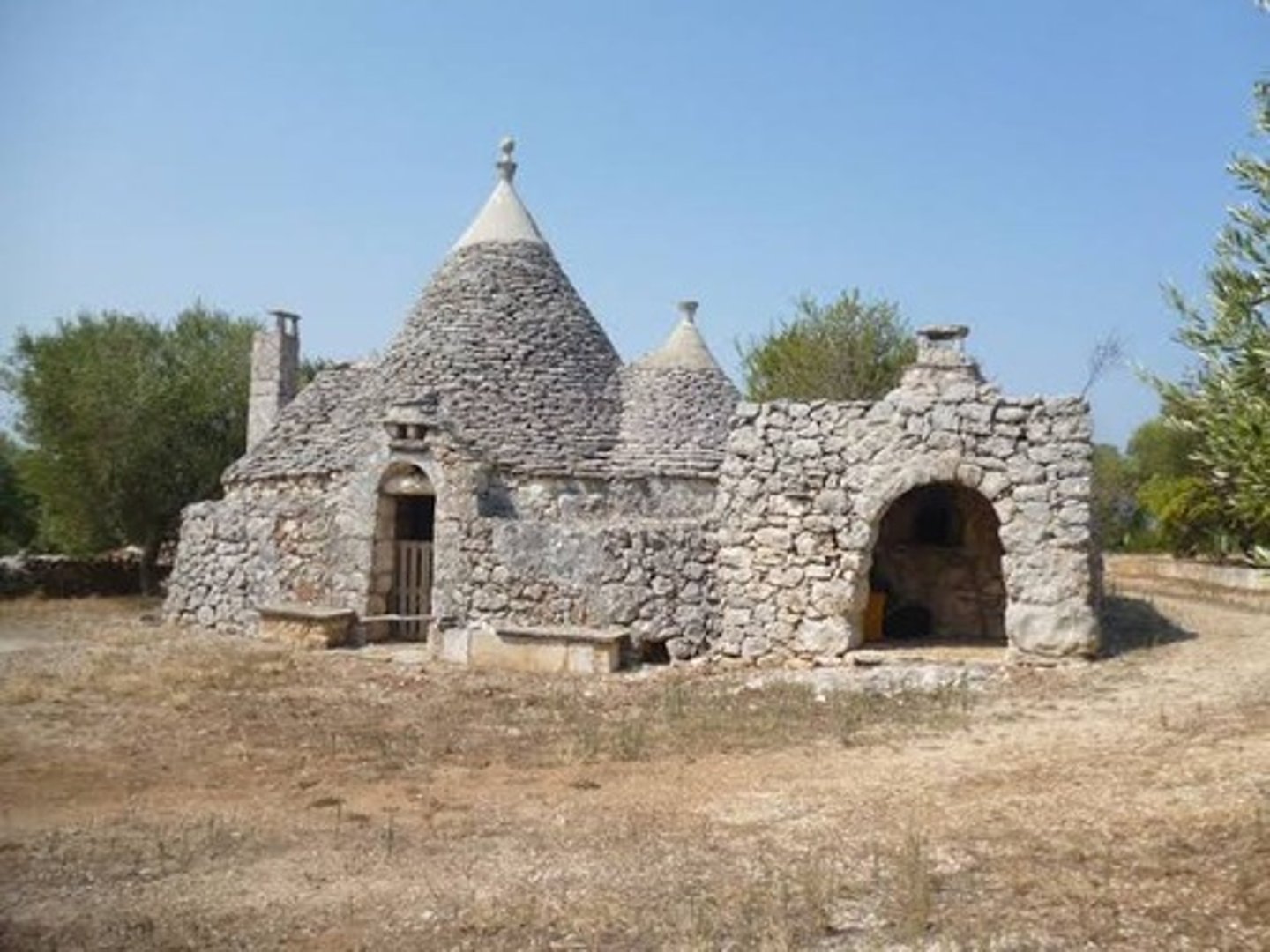
trullo
dry walled rough stone shelter with corbelled roof

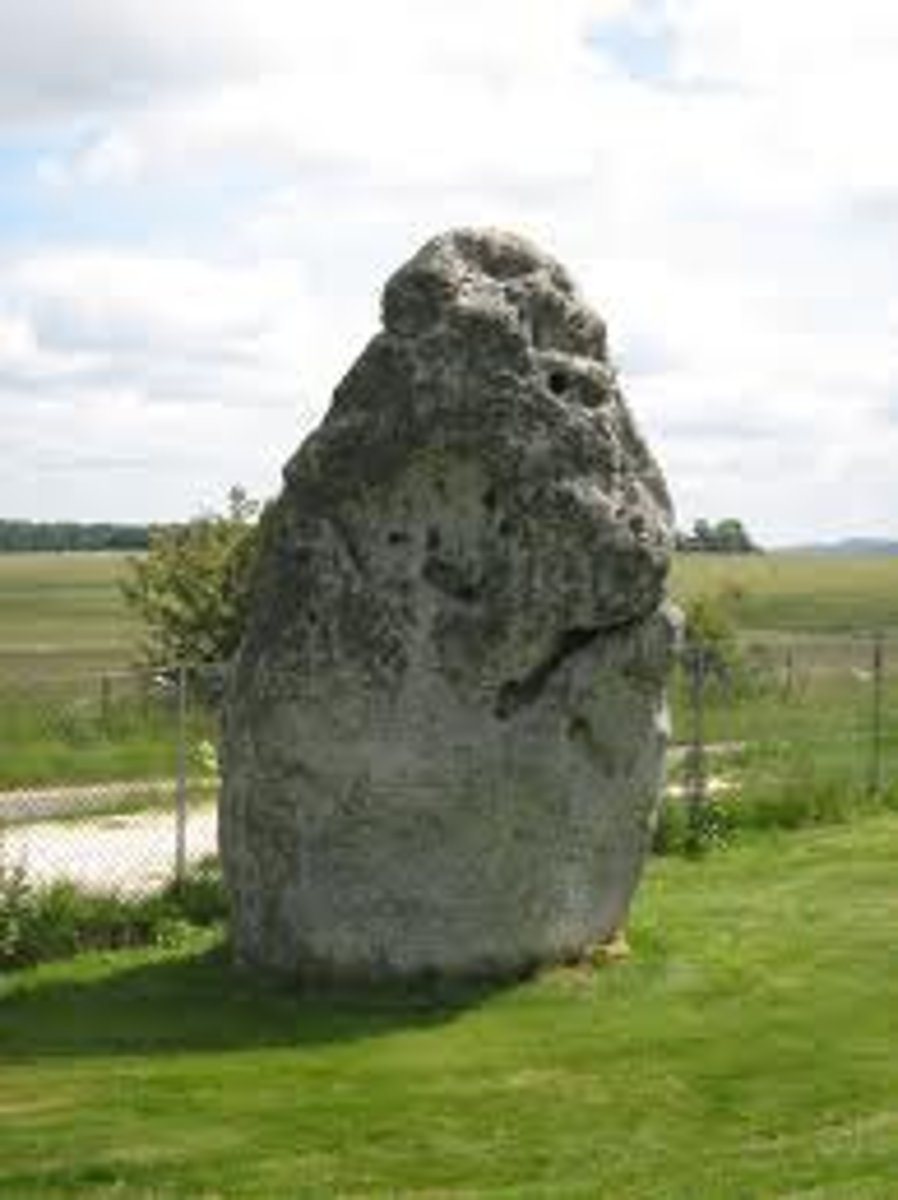
Menhir
a large uncut stone erected as a monument in the prehistoric era; a standing stone
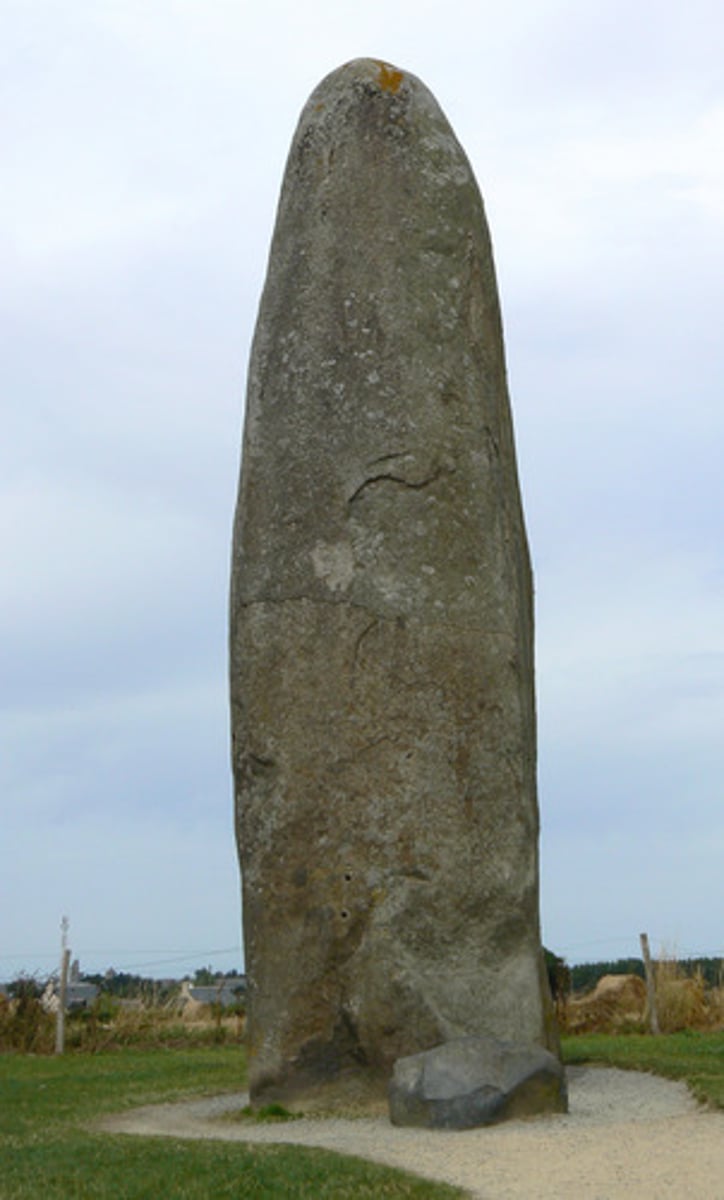

orthostat
An upright slab forming part of a larger structure
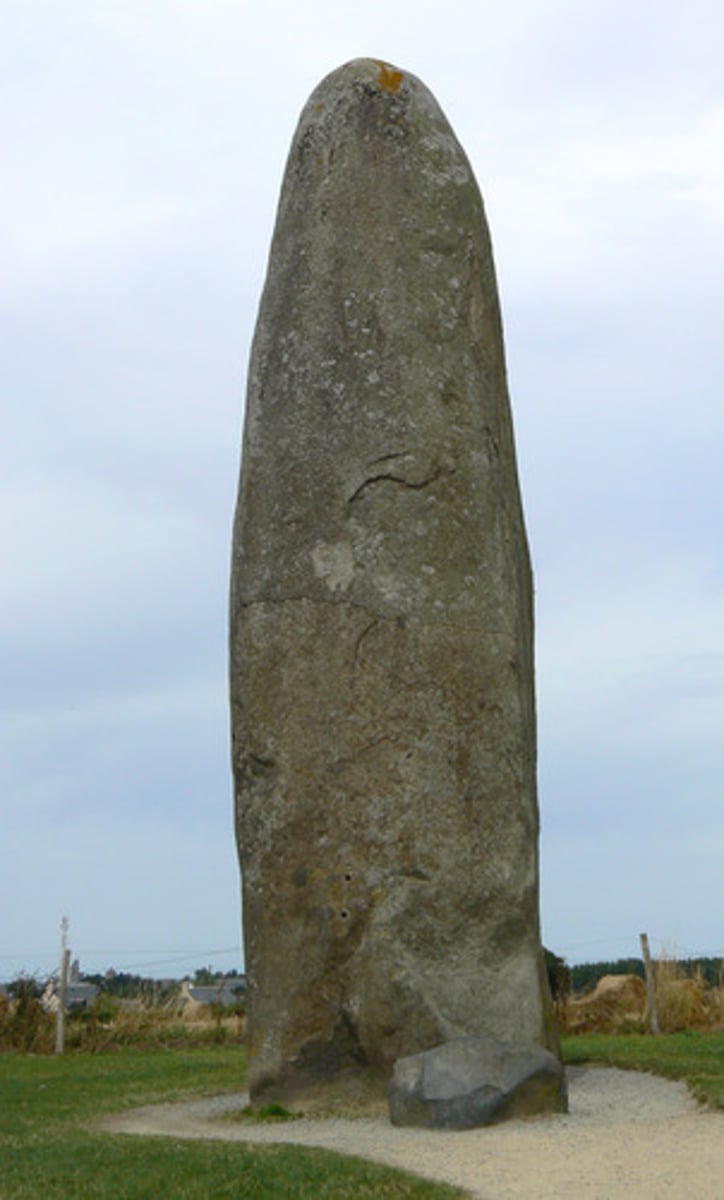

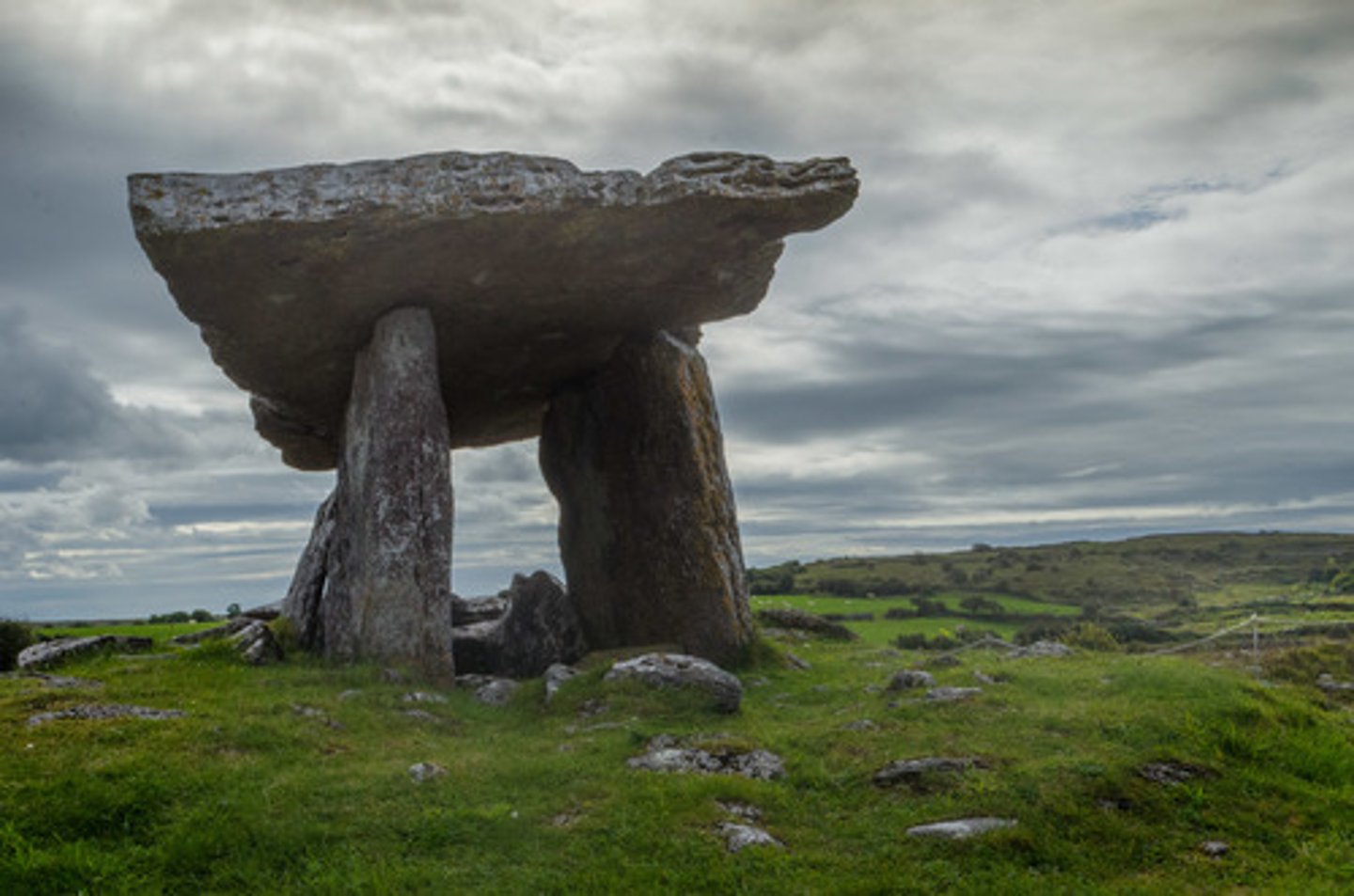
Dolmen
a stone tomb formed by two posts capped by a lintel

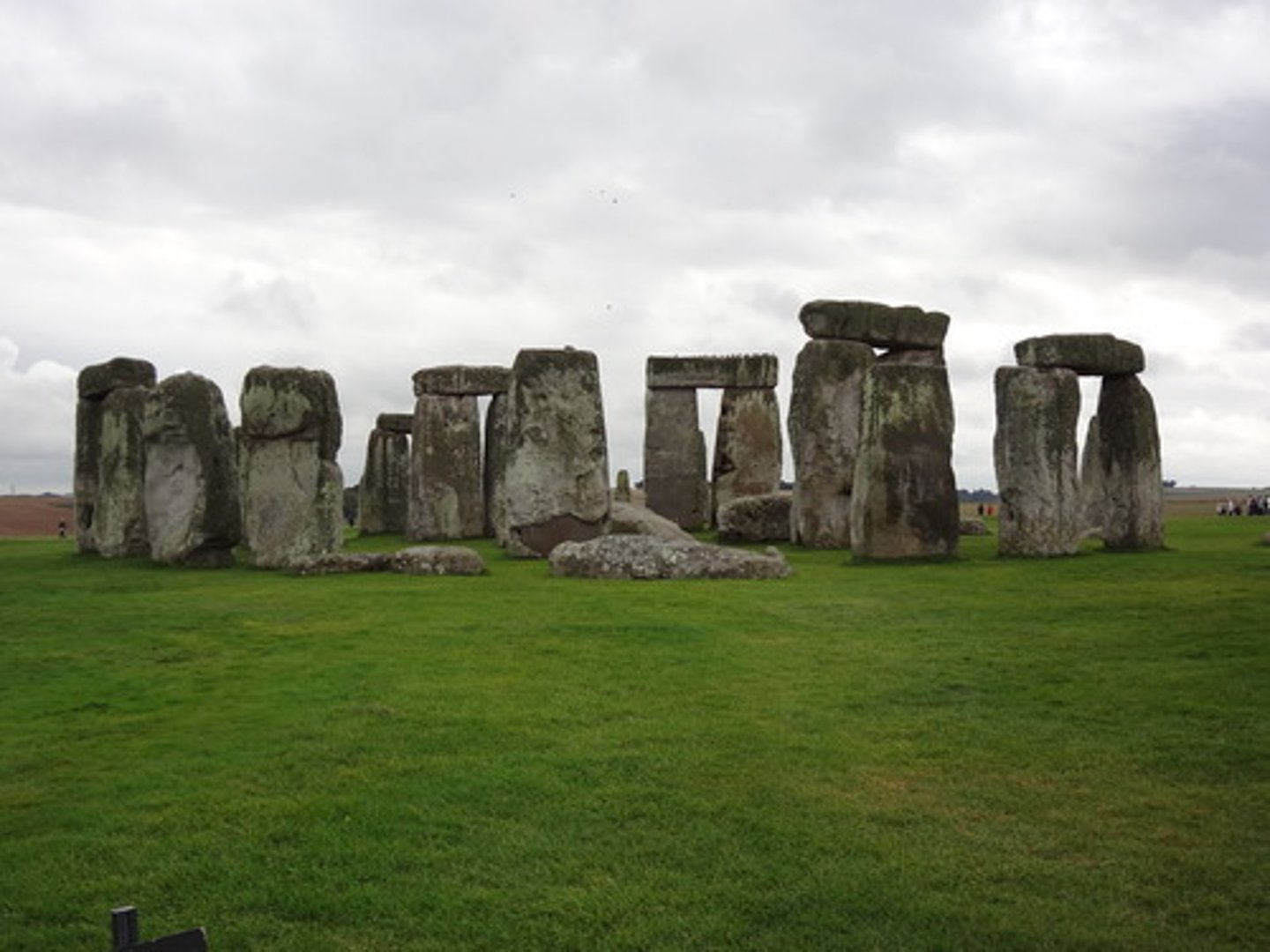
stone circle
Standing stones arranged in a circle

Taulas
consist of a vertical pillar with a horizontal stone lying on it forming a letter T
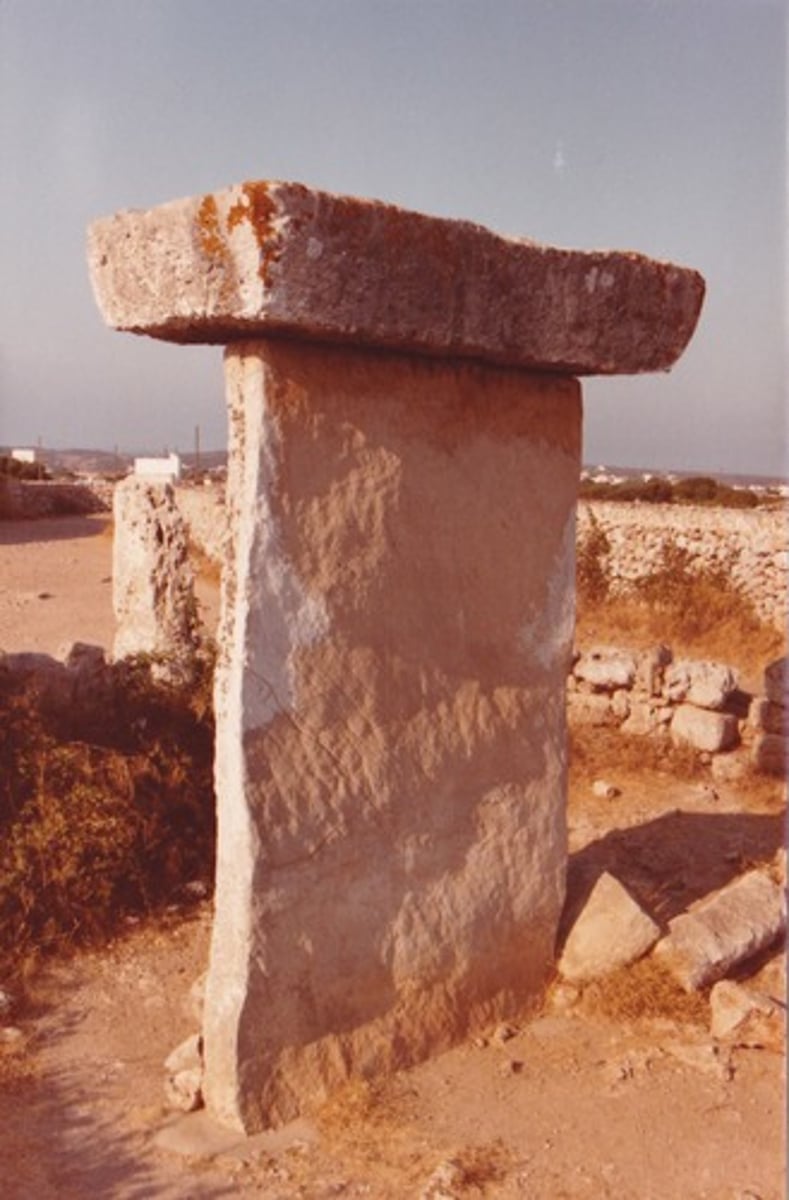

Trilithon
a pair of monoliths topped with a lintel

Kneeling Bull Holding Spouted Vessel
one of the earliest treasures of silver metalwork, crafted by Mesopotamian silversmiths
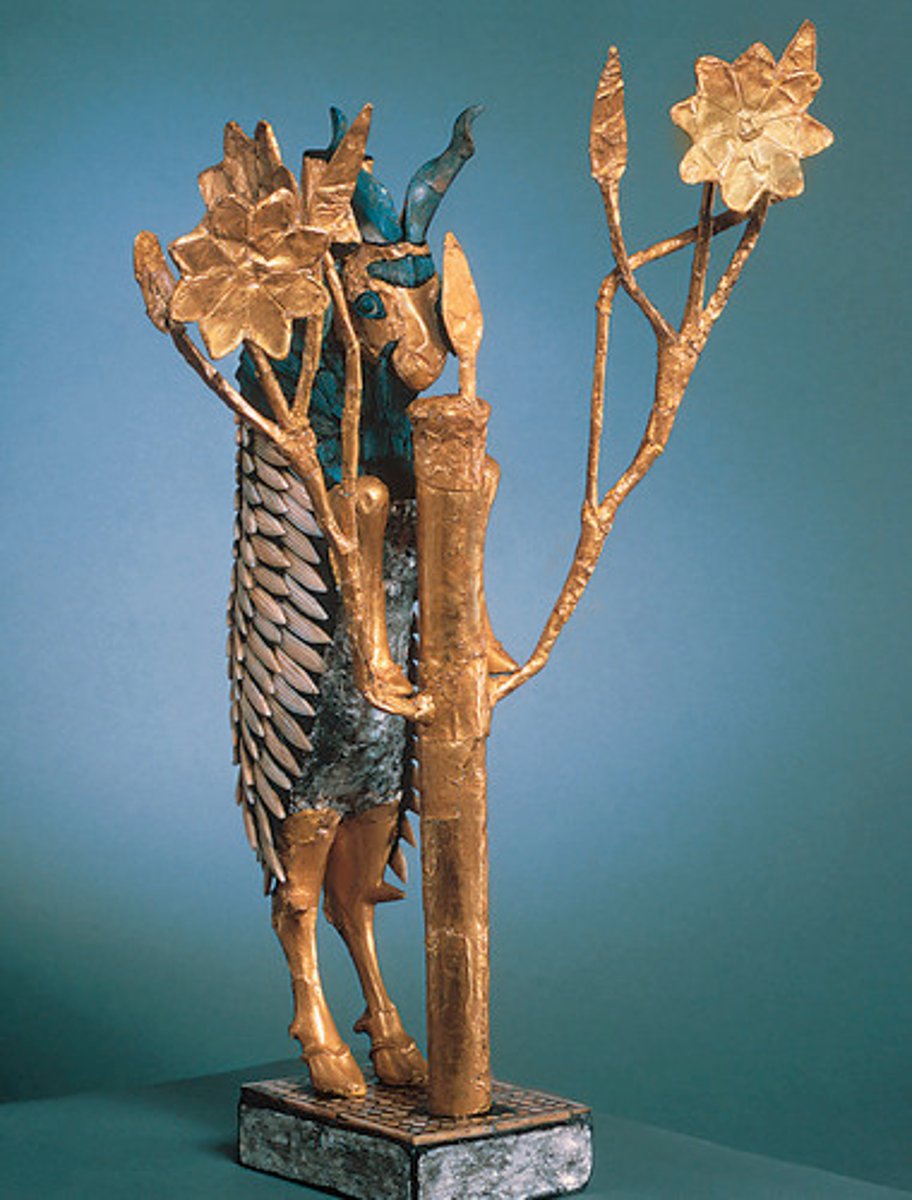
Ram in a Thicket
elaborate gold figurine found at Ur (Mesopotamia), early example of ceramics and art. Statuette of a goat perched against a bush looking for food
Jericho skulls
-took skulls, used plaster to mold their features & shells for eyes
-to preserve the memory of those who have passed on
Catalhuyuk
one of the world's first villages, established in modern-day Turkey. Houses were made of brick, no doors and entered through hatches in roofs. The best examples of an early Neolithic town where the transition to a fully settled existence has been satisfactory achieved.
cromlech
cluster of dolmens arranged in a circle; mark sacred spaces

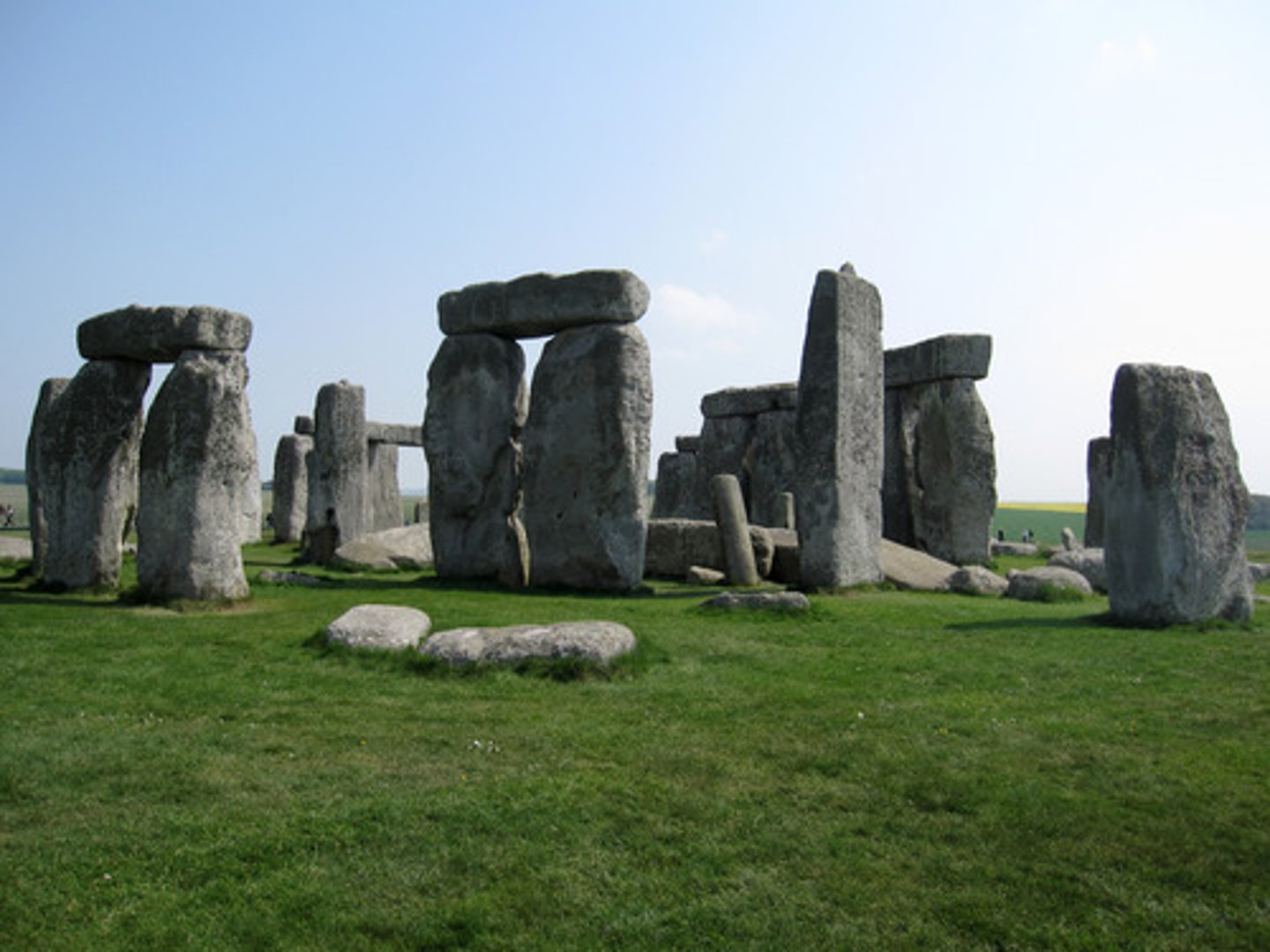
bluestones
A ring of standing stones at the center of Stonehenge. The source of the stones is over 240 kilometers from Stonehenge.

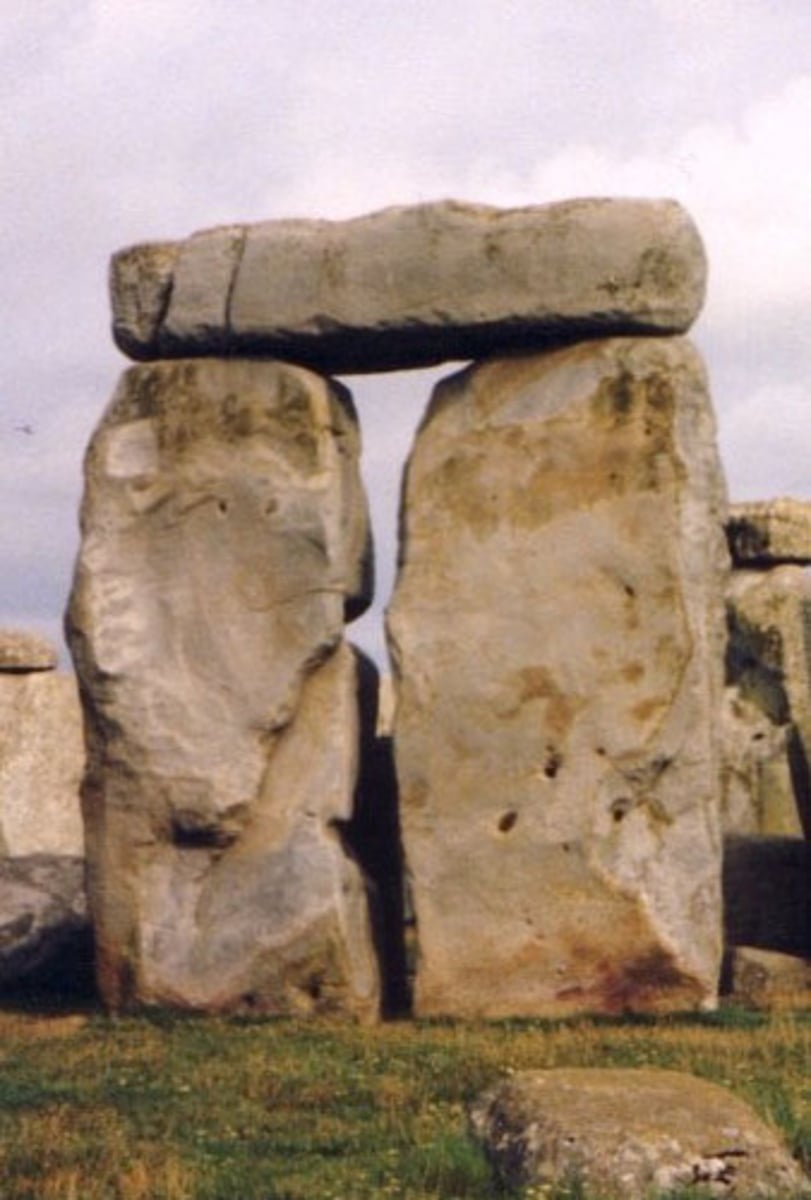
Sarsen Stones
Larger stones of Stonehenge, and similar stone circles; make up the outer ring, and inner U of Stonehenge

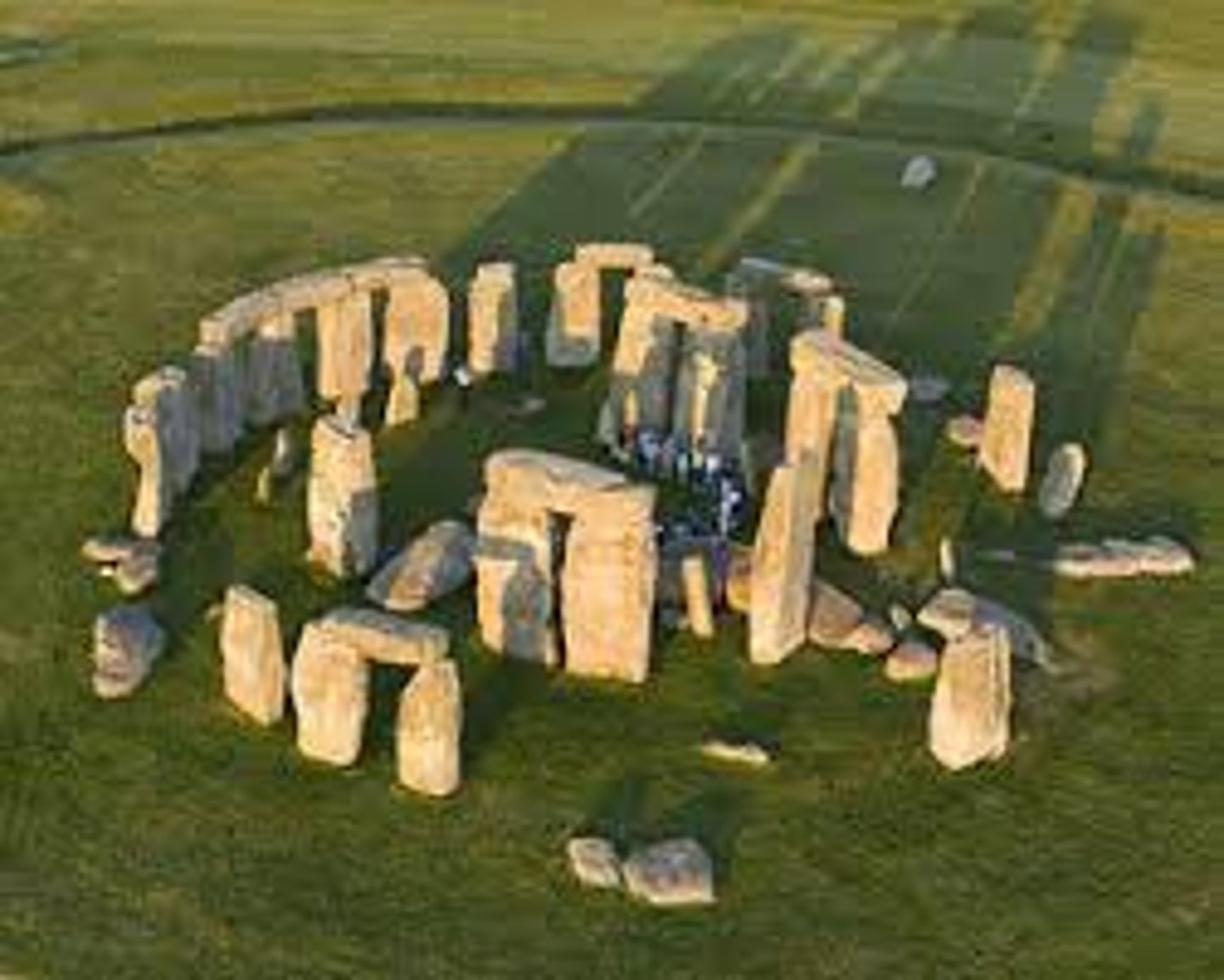
heel stone
The monolith set outside the stone circle of Stonehenge along an axis which marked the rising of the sun on June 21st the mid-summer solstice.

red, black, yellow
prehistoric primary colors
ochre
mineral-based pigment used in parietal art. has yellow from goethite and red from hematite
ochre, umber, sienna, manganese, kaolin
prehistoric mineral-based pigments used in parietal art
sienna
lighter than umber, another earth pigment that contains both iron oxide and manganese oxide (has raw & burnt kind)
manganese
stone age artists obtained their black colors from a range of _______ oxides
kaolin
a fine, pure-white pigment in sotne age art
umber
Bronze Age
the period in ancient human culture when people began to make and use copper and tin
Mesopotamian Civilization
where art history started, cuneiform, first written code, organization into city-states, and astronomy
Anu
Mesopotamian supreme male god that was represented with a bull
Sumerians
Founders of Mesopotamian civilization
Innana
patron goddess of summeria (uruk)
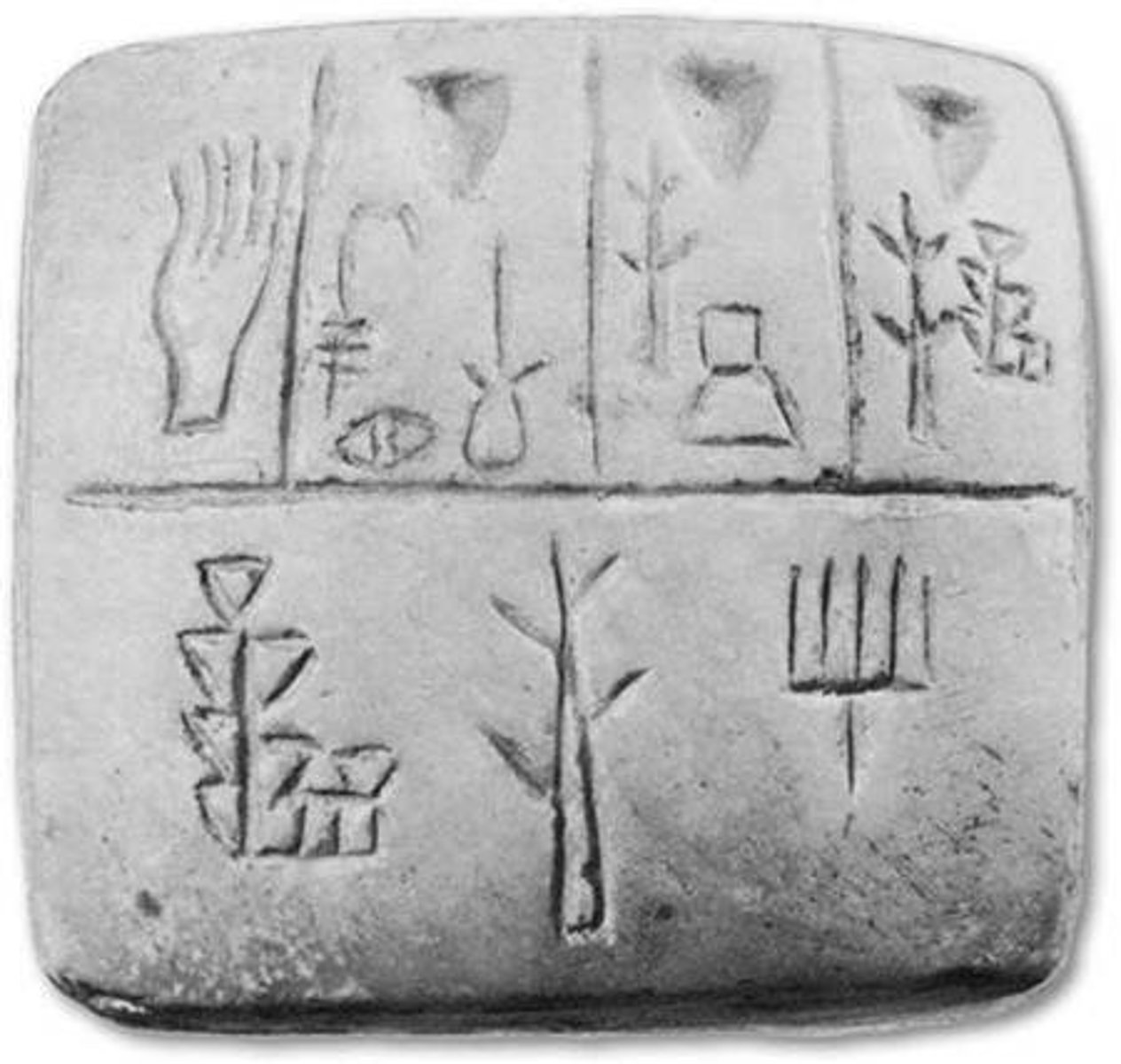
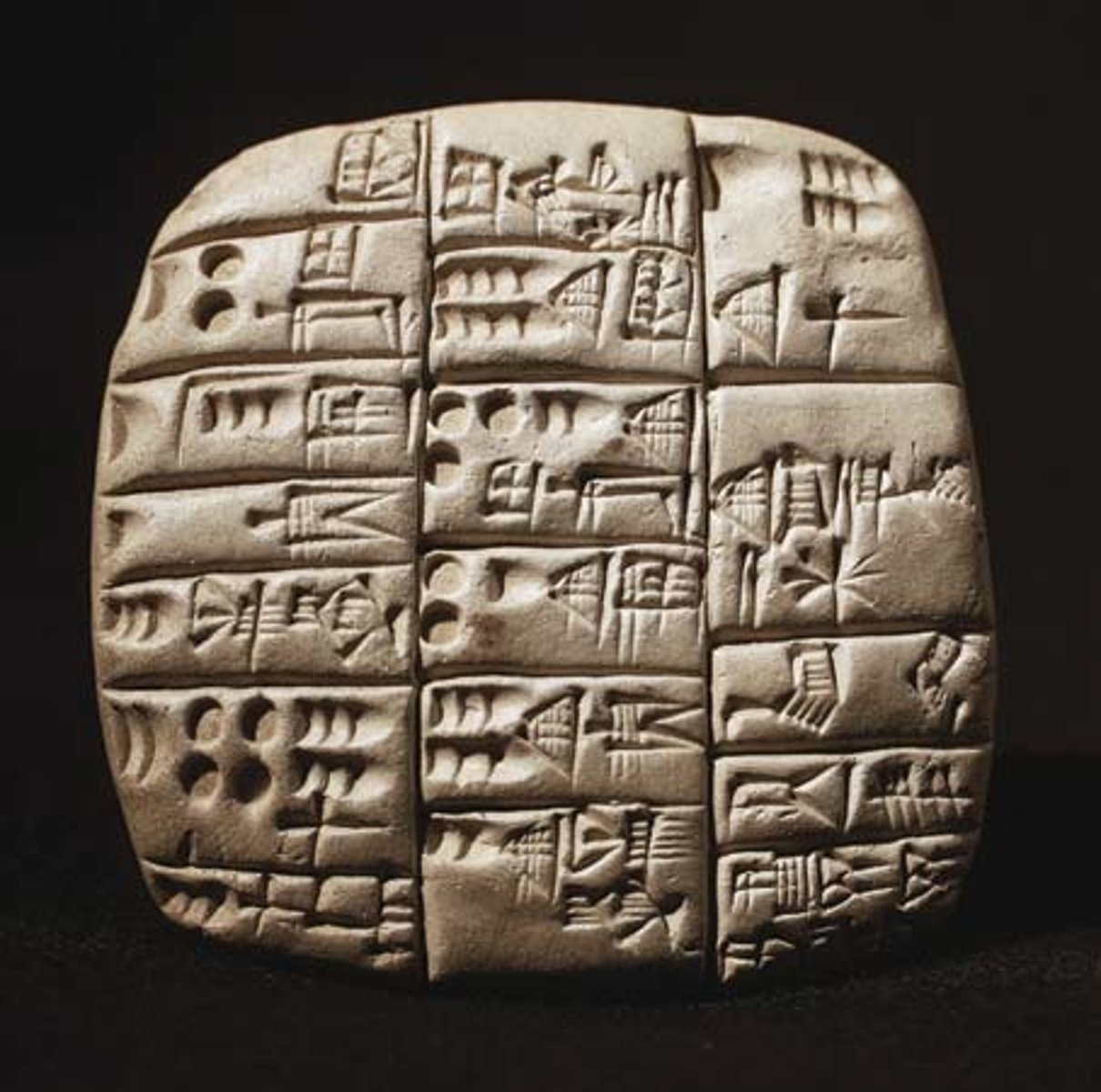
Cuneiform
Earliest form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge shaped stylus and wet clay tablets.

Stylus
Egyptian reed pen
Epic of Gilgamesh
World's first literature by Sumerians, The most famous extant literary work from ancient Mesopotamia, it tells the story of one man's quest for immortality.
the stele of the vultures
a stone tablet sculpted in low relief, had been commissioned as a war memorial by King Eannatum

Standard of Ur
a hollow wooden box with scenes of war and peace represented on each side through elaborately inlaid mosaics of shell, red limestone, and lapis lazuli
Drystone house
stones pilled up on one another, walls were almost a meter thick
bas-relief
low-relief sculpture
Domestic Architecture
mud brick construction with an open courtyard surrounded by the rooms of the house with windows within for ventilation. Roofs were made of reeds
Ziggurat of Ur
a temple to the moon goddess Nanna
Nanna
Sumerian moon god
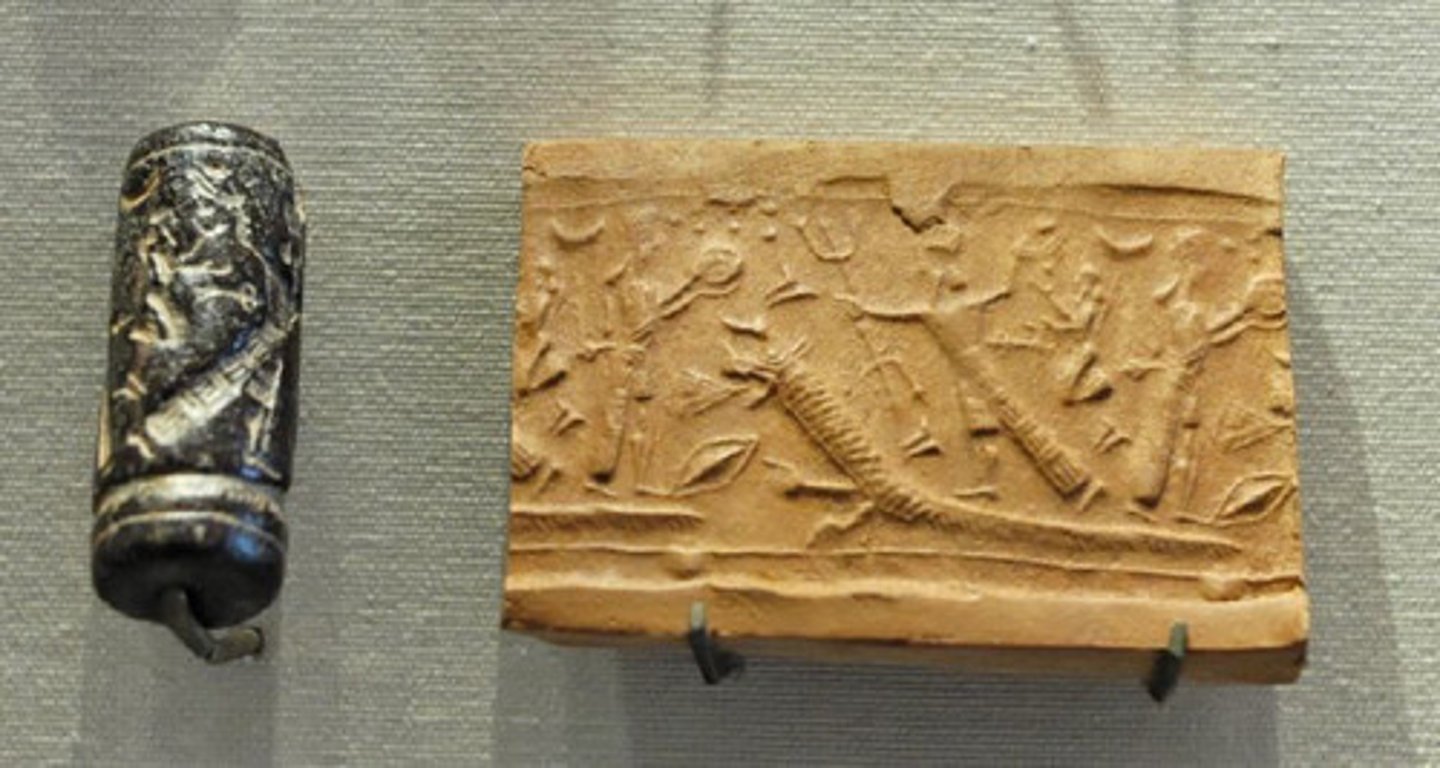
cylinder seal
a round piece of carved stone that when rolled onto clay produces an image; used for business transactions

Glyph
usage of picture symbols for writing
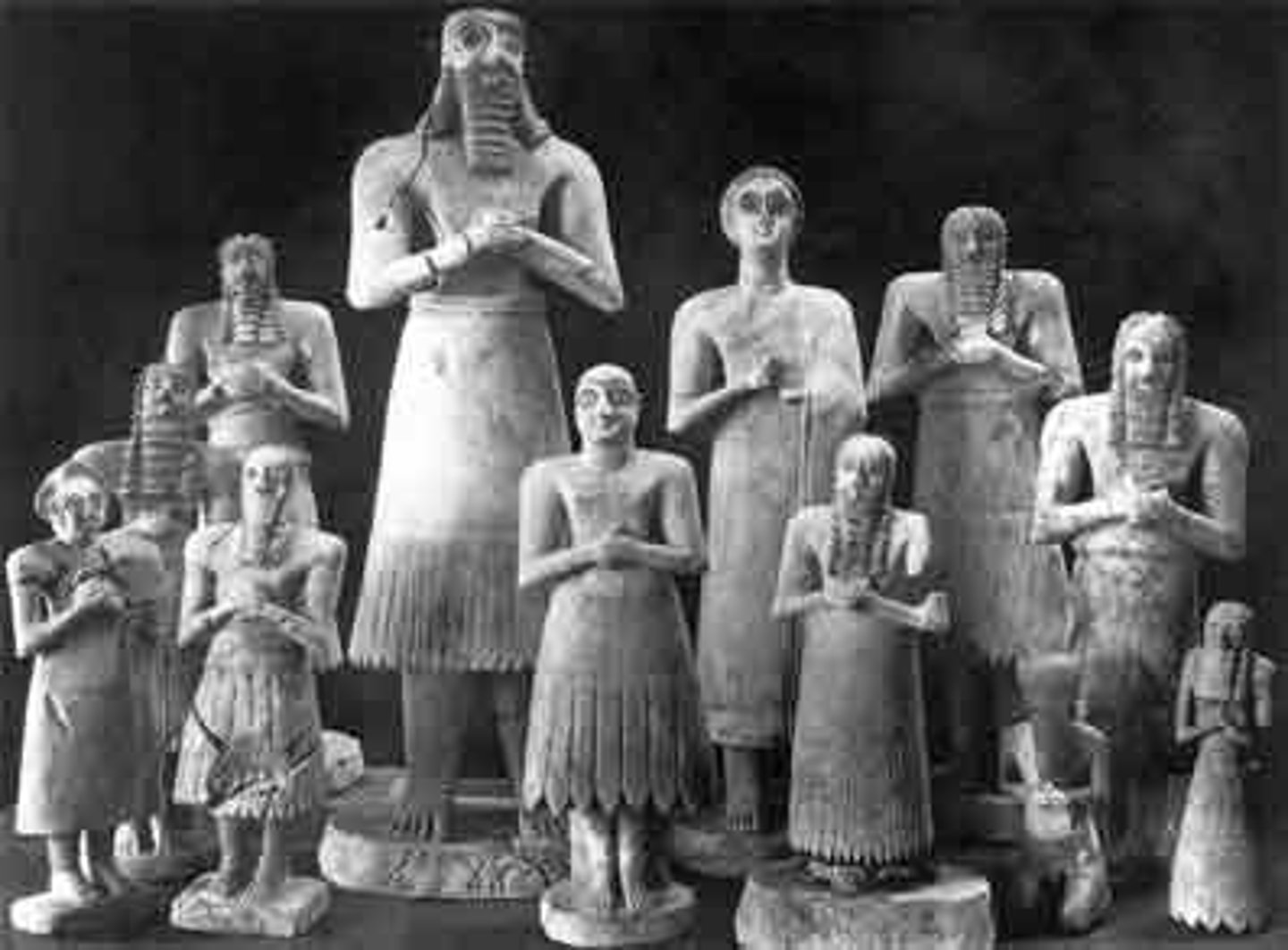
Tell Asmar Figures
30 statuettes made of marble from the mesopotamian period with overwhelmingly large eyes. made from limestone, gypsum, alabaster

cire perdue
the lost wax process. A bronze casting method in which a figure is modeled in clay and covered with wax and then recovered with clay. When fired in a kiln, the wax melts away, leaving a channel between the two layers of clay which can be used as a mold for liquid metal
convention
a stylistic method to make everything standard to be approved as beautiful
lapis lazuli
a semiprecious blue stone
Ziggurat
A pyramid shaped temple tower, seen by leaders as a link to heaven; artificial mountains made of tiered rectangular layers which rose in 1-7; multipurpose
The Ram and Tree
An offering stand from Ur in the 2600 B.C. made of wood, gold, and lapis lazuli
