Unit 3 - Conditions of the Oropharynx, Mouth, and Nasal Regions Exam Review
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Vertigo
Patient experiences a false sense of motion
Bridge
ID A
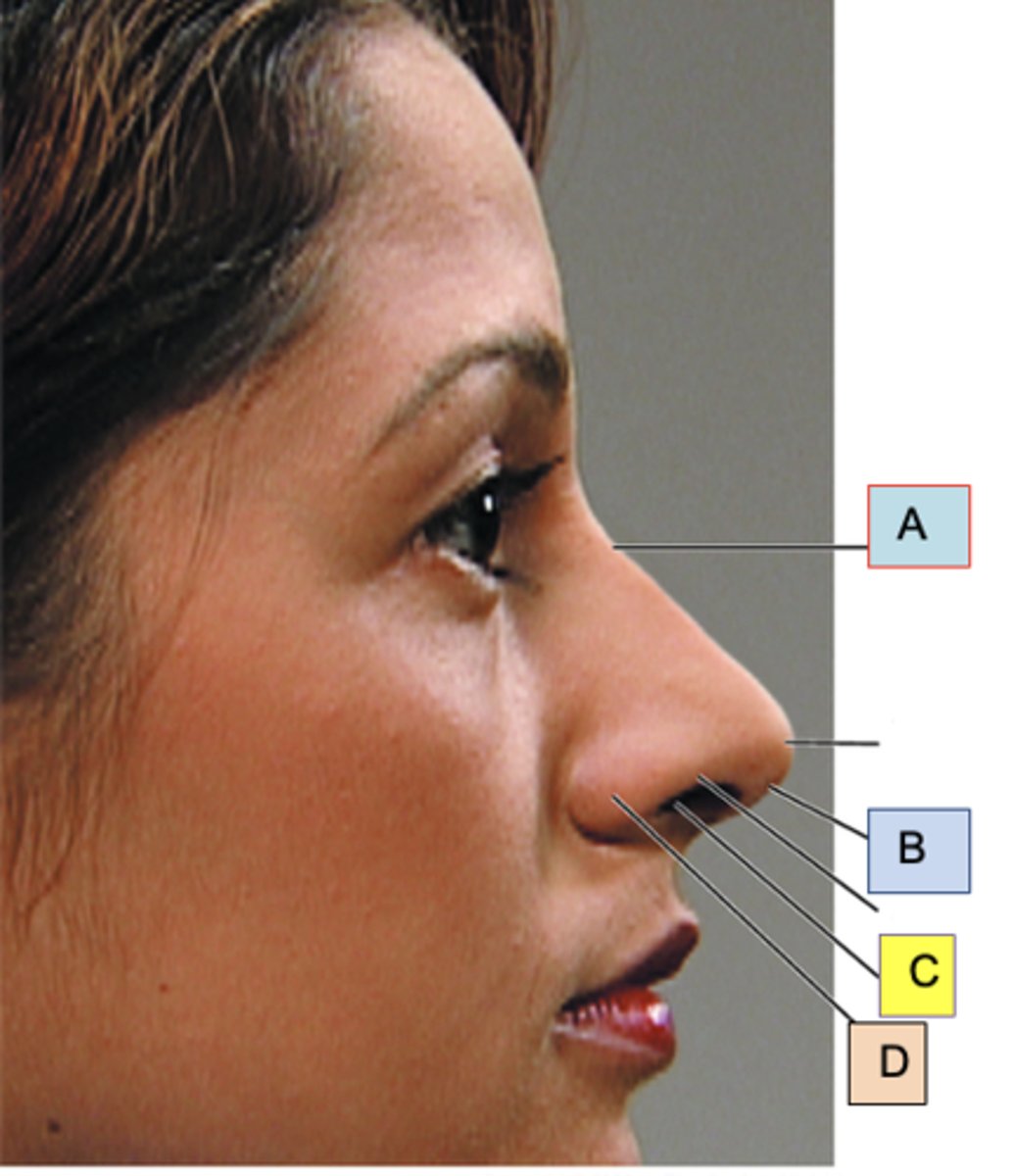
Columella
ID B
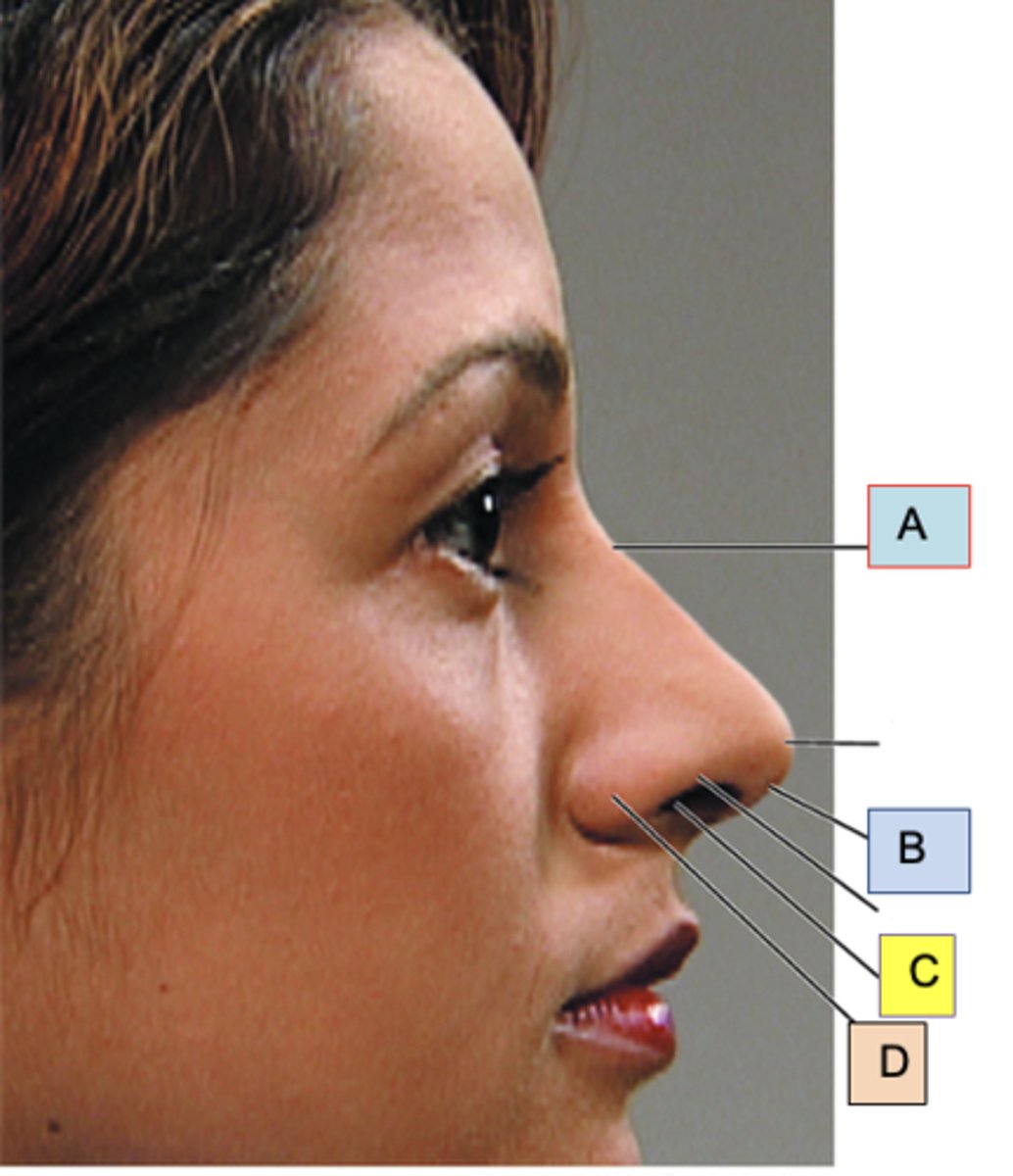
Anterior naris (nostril)
ID C
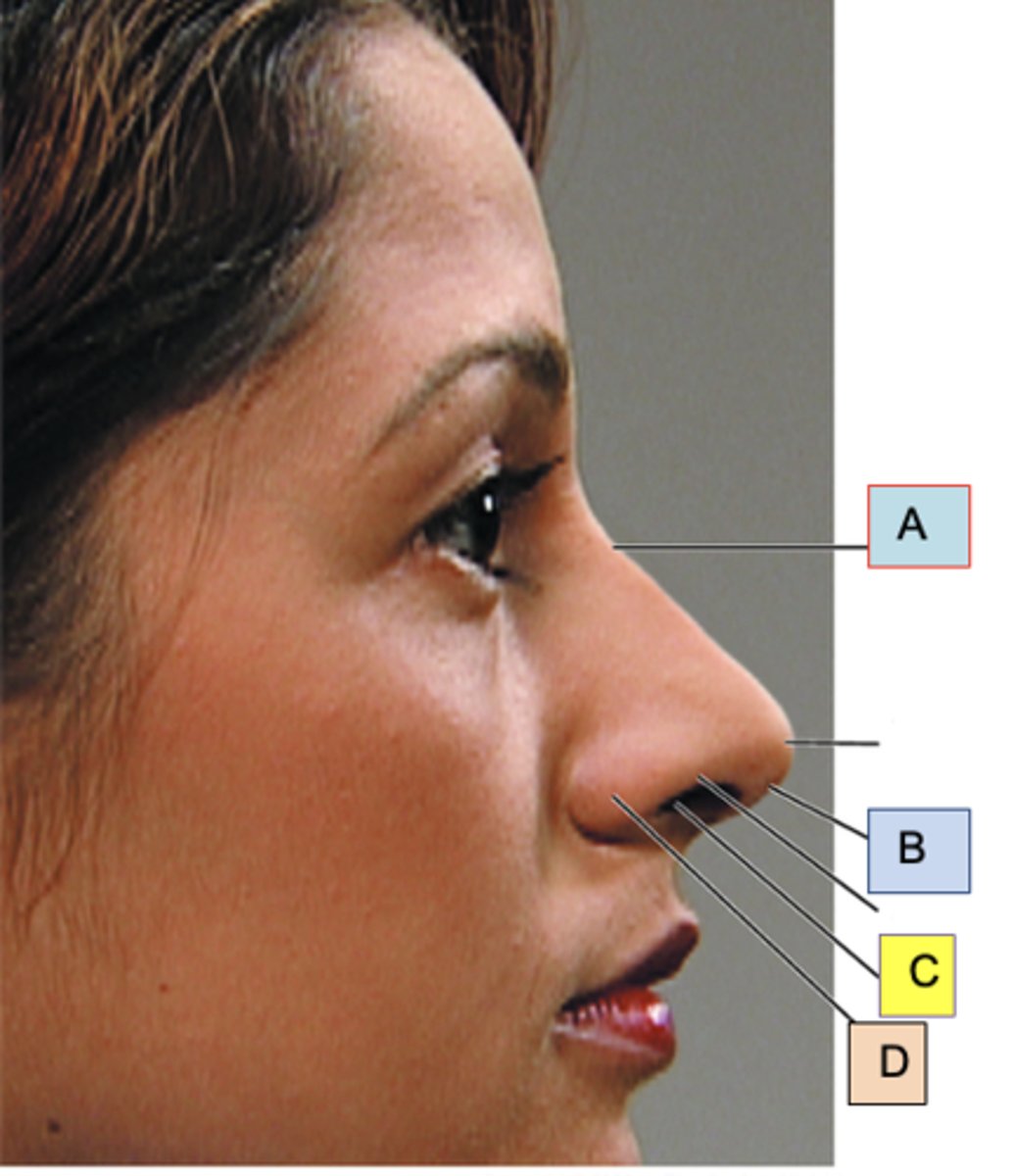
Ala nasi
ID D
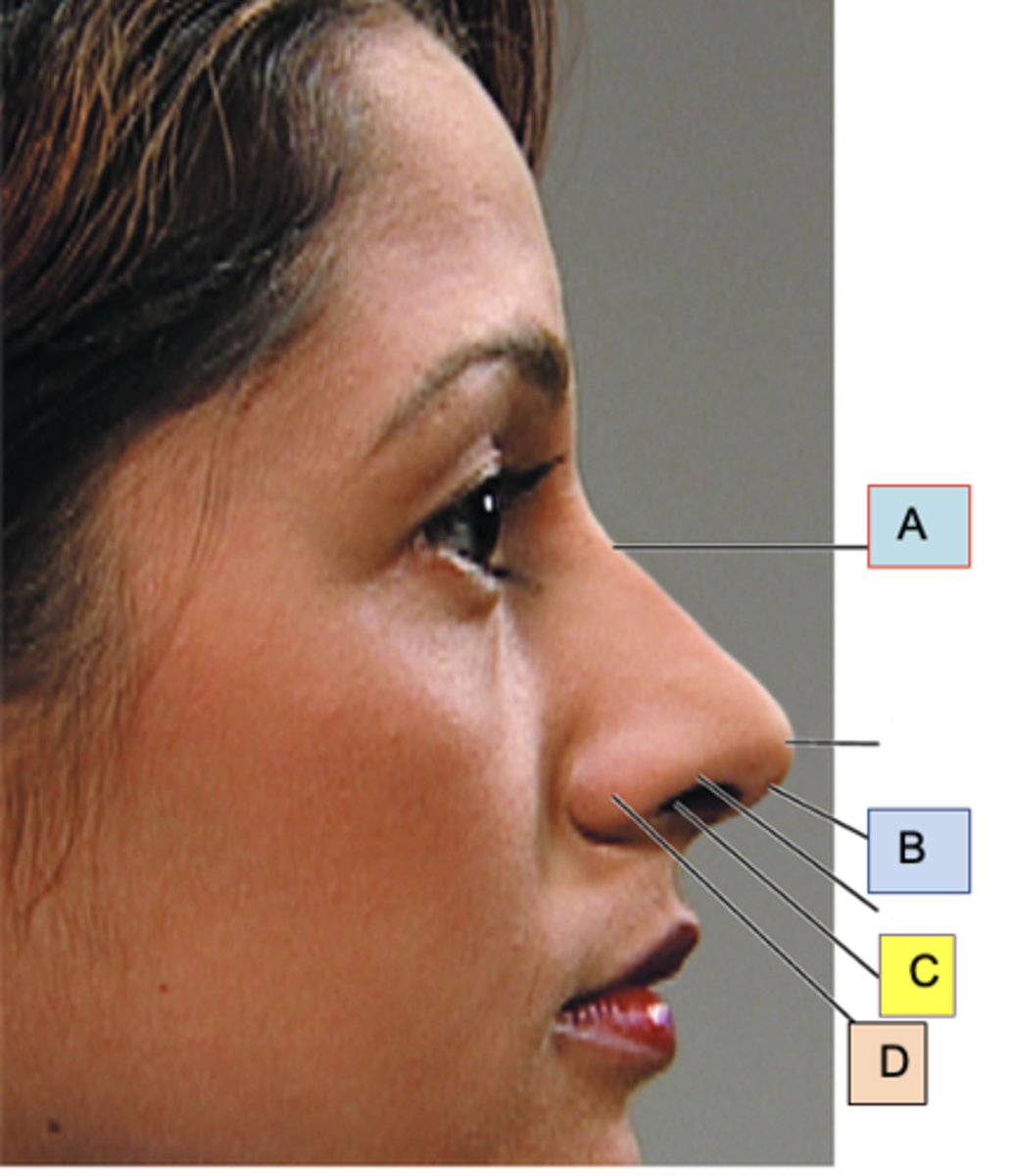
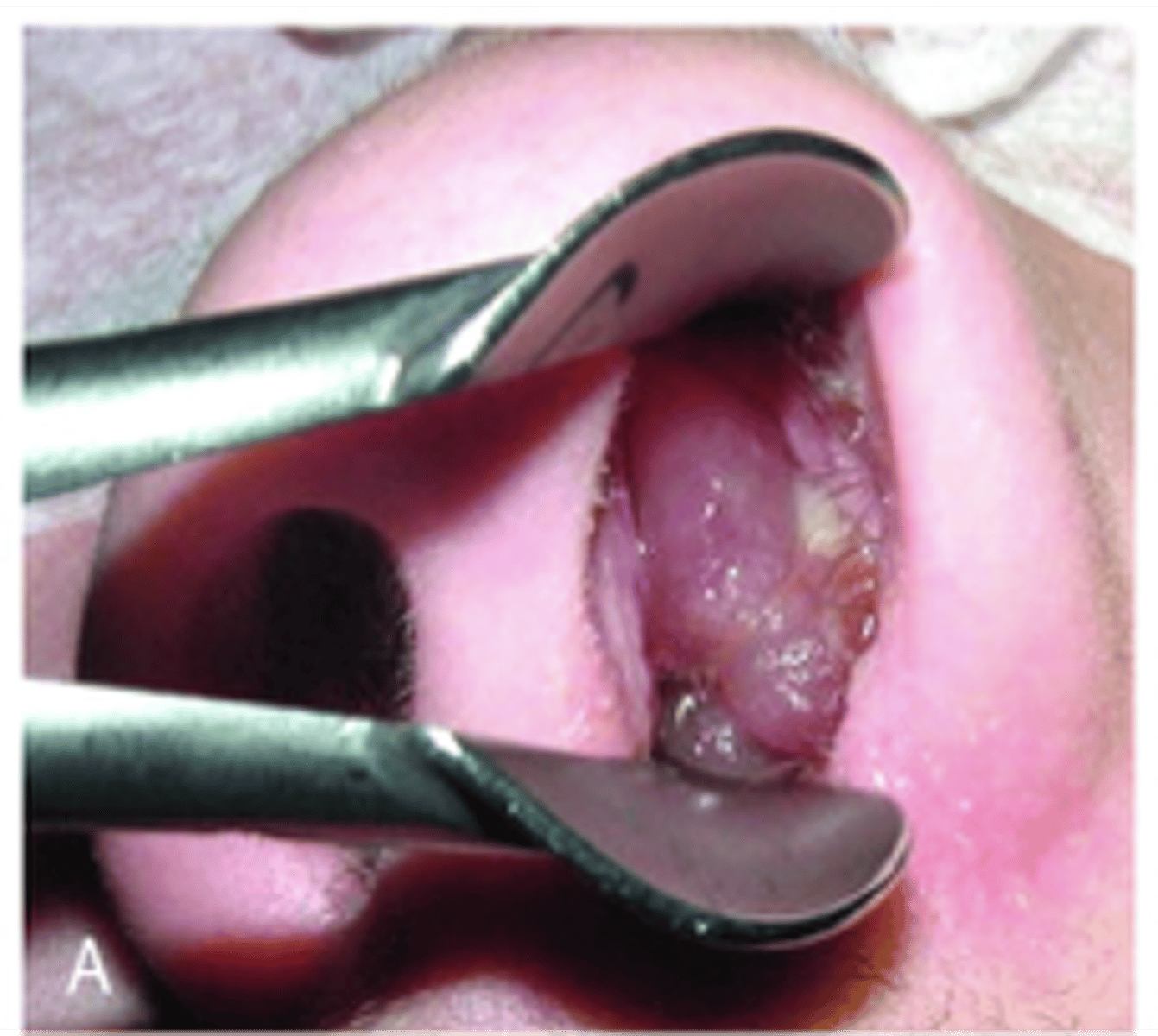
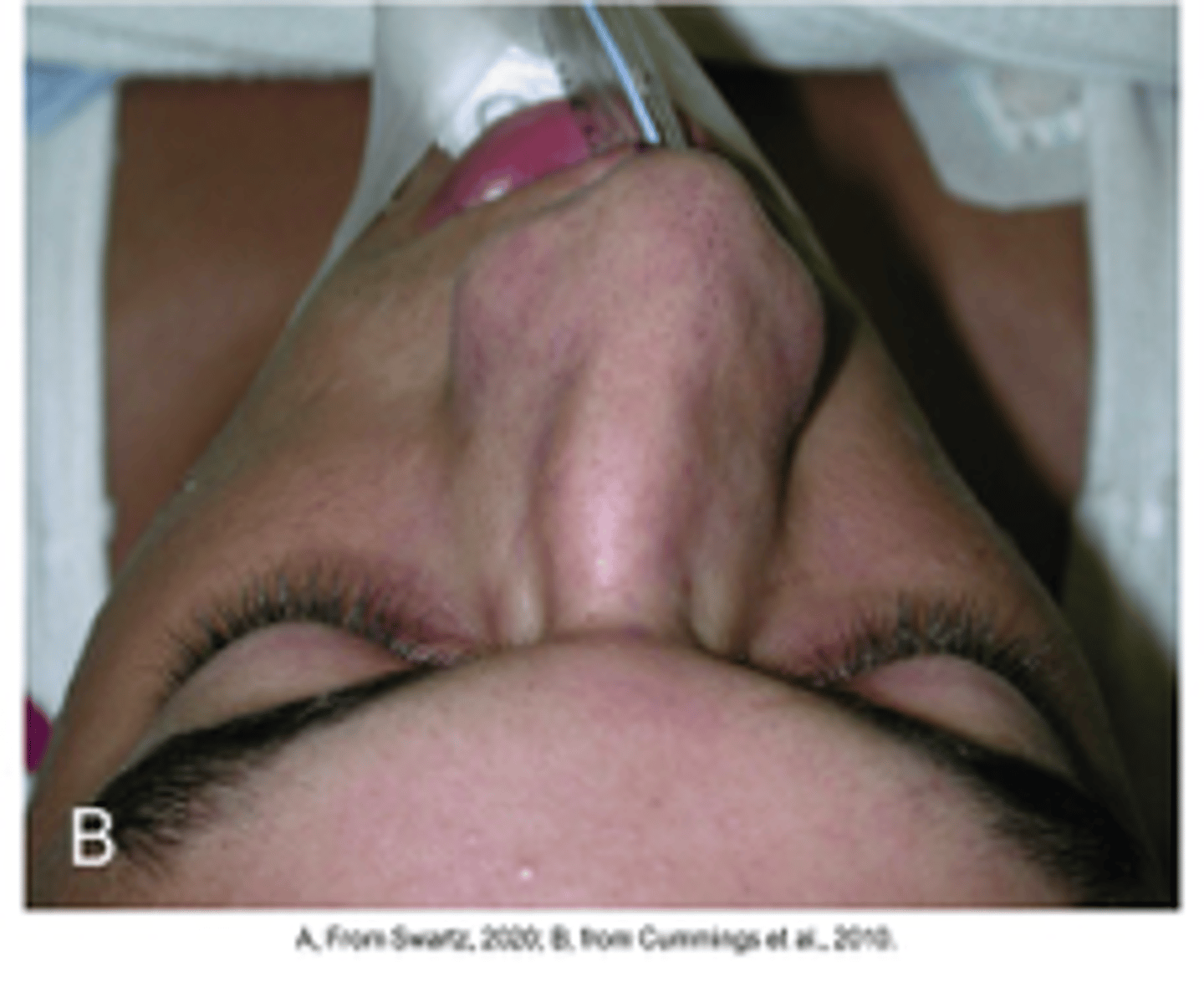
Nasal polyp
Benign mucosal covered mass
- Allergic rhinitis associated
Diagnosis?
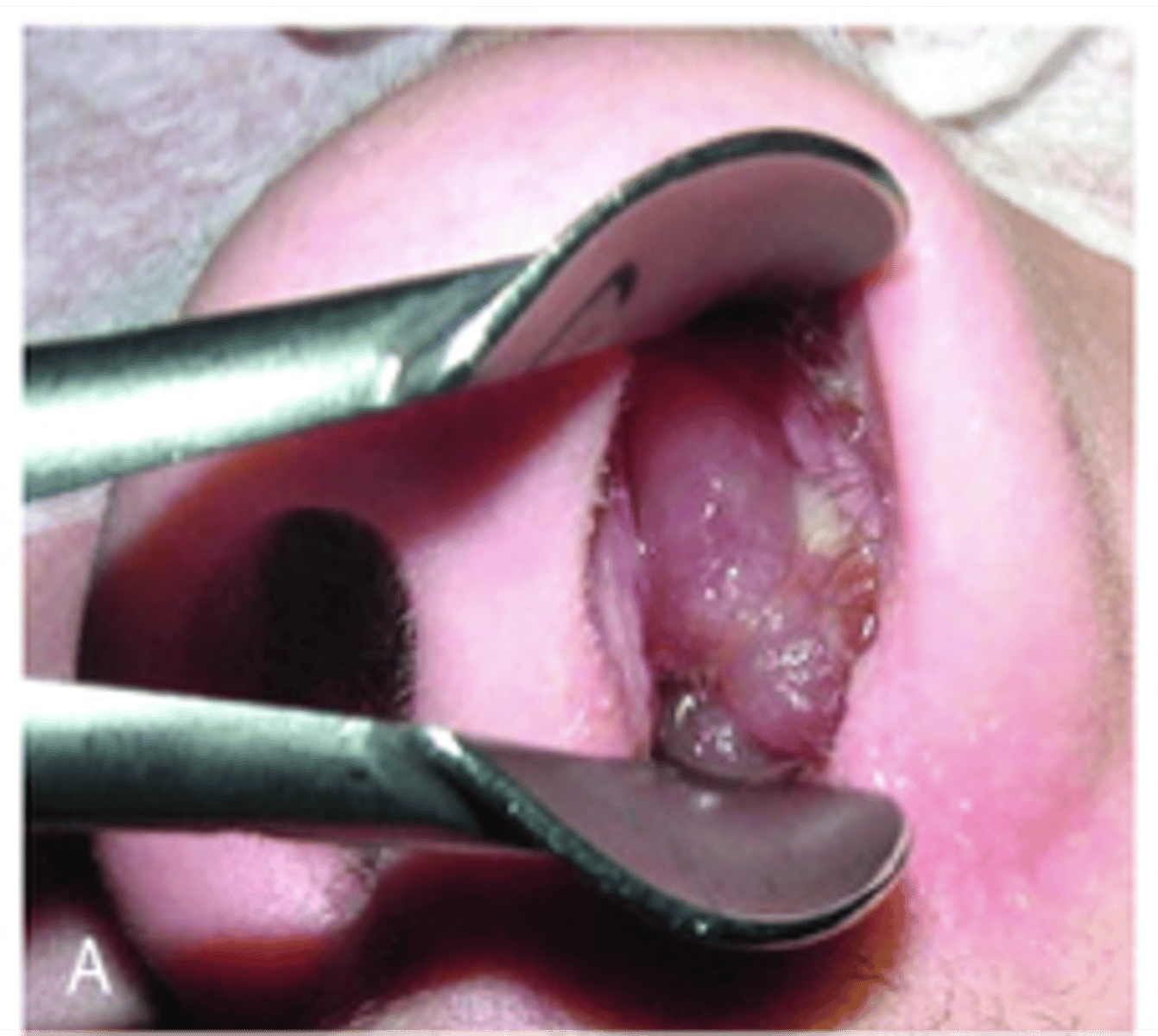
- Nasal corticosteroids, oral as well
- Endoscopic removal surgery
Nasal polyp treatment?
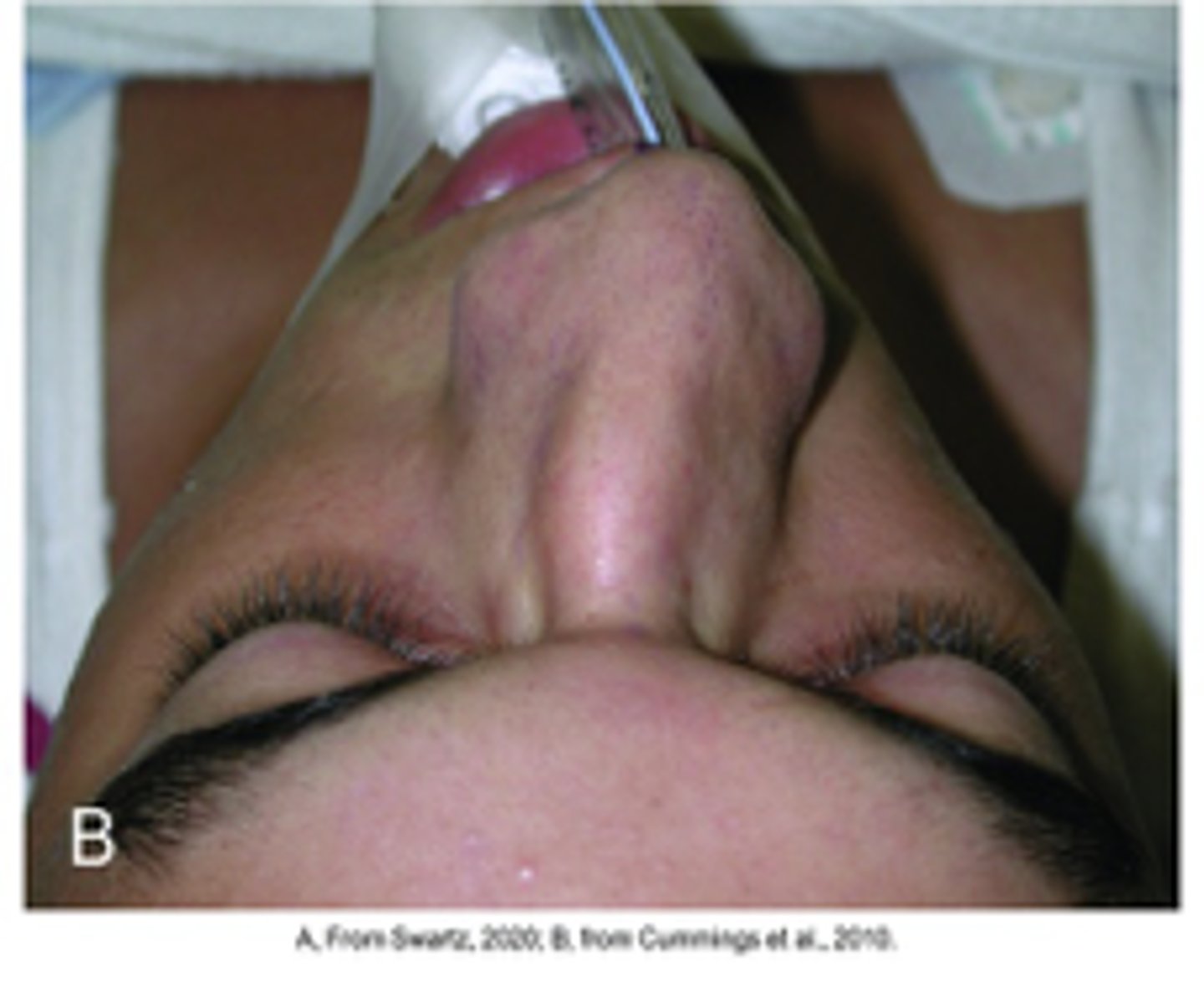
Deviated septum
Diagnosis?
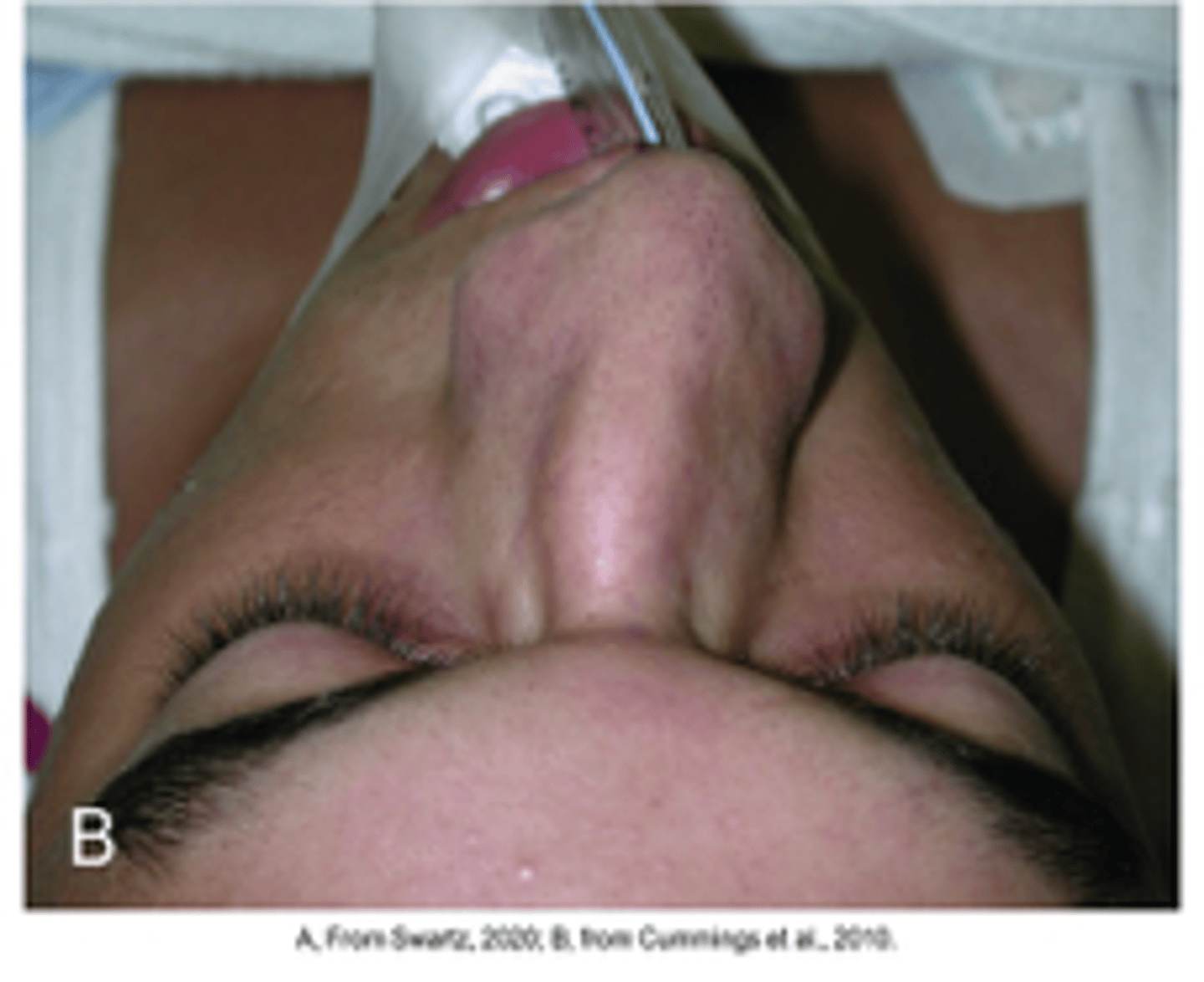
Trauma, developmental
A deviated septum results from _____ or is _____
Surgery to straighten to clear the airway if obstructive
Deviated septum treatment?
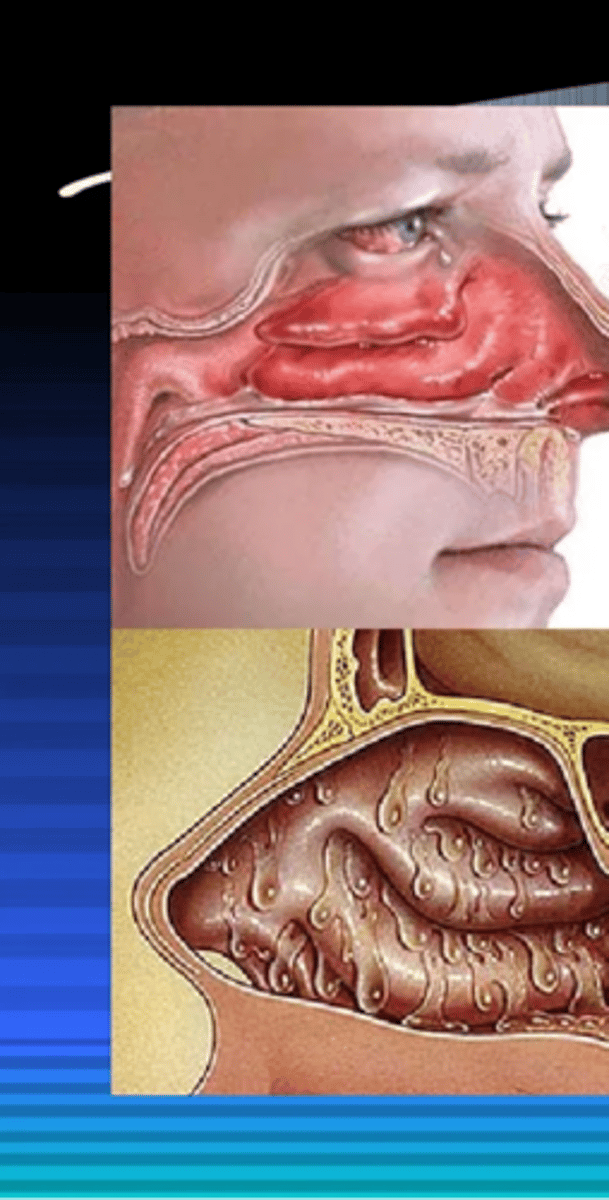
Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Acute
- Bacterial infection of one or more of the paranasal sinuses
- Accumulation of mucus in the sinus cavity that becomes infected
- Yellow-green discharge
- Facial pain over sinuses
- Nasal obstruction
- Cough
- Fever
- Malaise
State symptoms of Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Acute
- NSAIDS, antihistamines, nasal spray
- Antibiotics if persists beyond 10 days
- Endoscopy if persists beyond 12 weeks
- Otolaryngologist referral due to intracranial extension
Bacterial Rhinosinusitis Acute treatment?
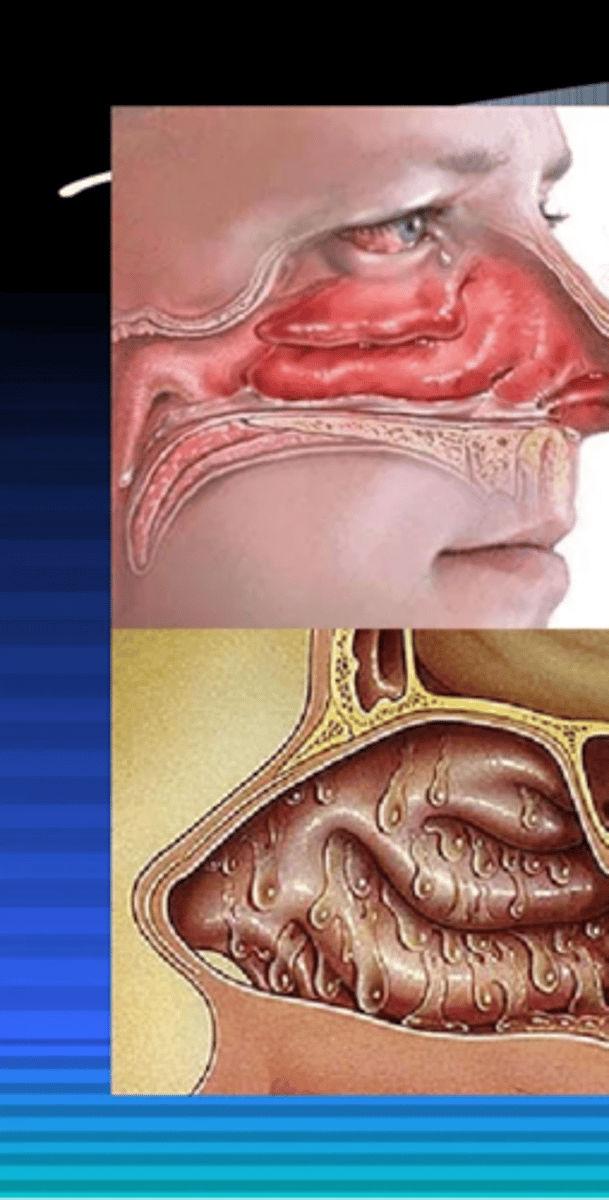
Allergic rhinitis
Diagnosis?
- Clear rhinorrhea
- Sneezing
- Tearing/itching eyes
- Blue gray turbinates
- Cough
- Dermatitis
- Environmental allergen
- 20-30% of adults in US
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis
- Intra nasal corticosteroids
- Sinus drainage massage
- Adjustment
Allergic rhinitis treatment?
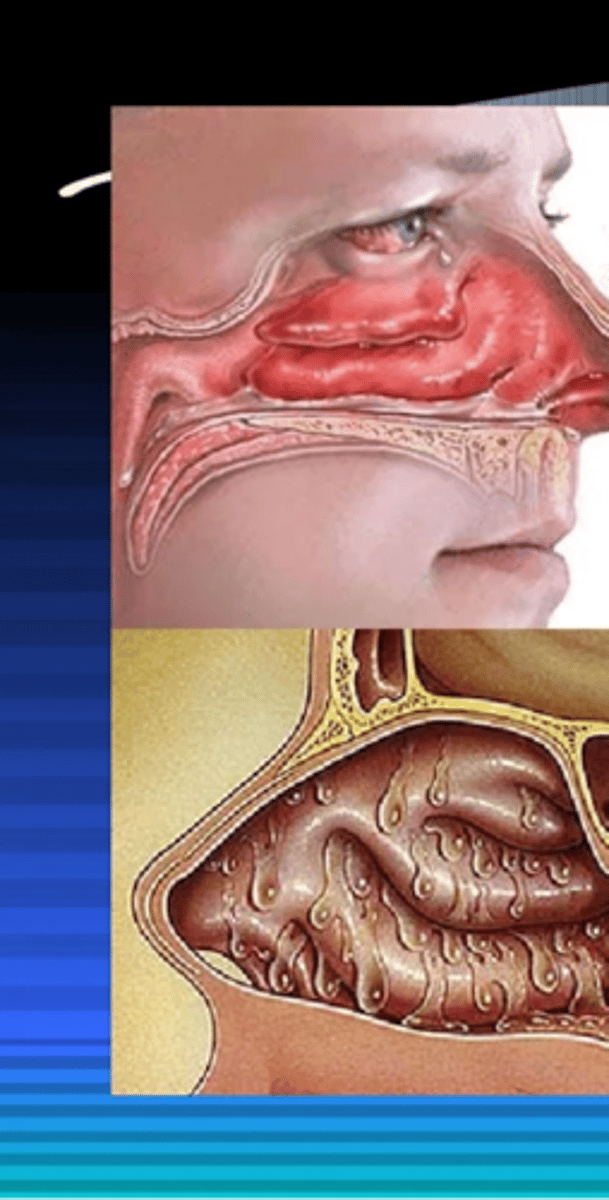
Acute allergic rhinitis
Your patient has clear rhinorrhea, sneezing, tearing, itching, blue gray turbinates. What is the diagnosis?
- Nasal polyp
- Rhinosinusitis
- Deviated septum
- Acute allergic rhinitis
Epistaxis
Which of the following describes as a nose bleed?
- Fordyce spots
- Epstein Pearls
- Epistaxis
- Xerostomia
Cerumen
What is the term for earwax secreted by the apocrine glands in the distal third of the ear canal; provides an acidic pH environment that inhibits the growth of microorganisms?
- Fordyce spots
- Epstein Pearls
- Epistaxis
- Cerumen
Epstein Pearls
Which is described as small whitish-yellow masses at the juncture between the hard and soft palate?
- Fordyce spots
- Epstein Pearls
- Epistaxis
- Xerostomia
Cocaine
Mr. Sprat is a 21-year-old patient who complains of nasal congestion. He admits to using recreational drugs. On examination, you have noted a septal perforation. Which of the following recreational drugs is commonly associated with nasal septum perforation?
- Heroin
- Cocaine
- PCP
- Ecstasy
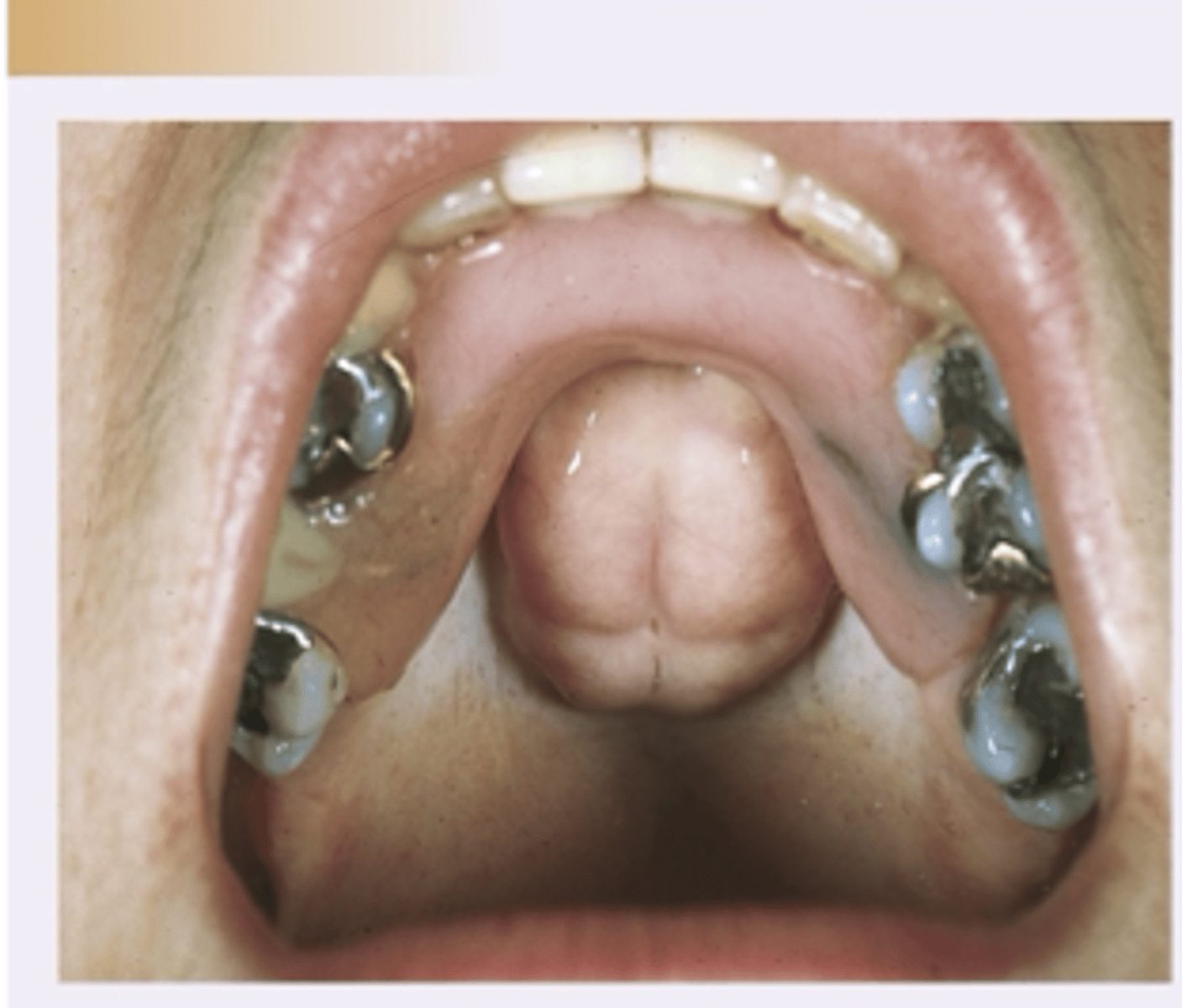
Torus Palatinus
Diagnosis?
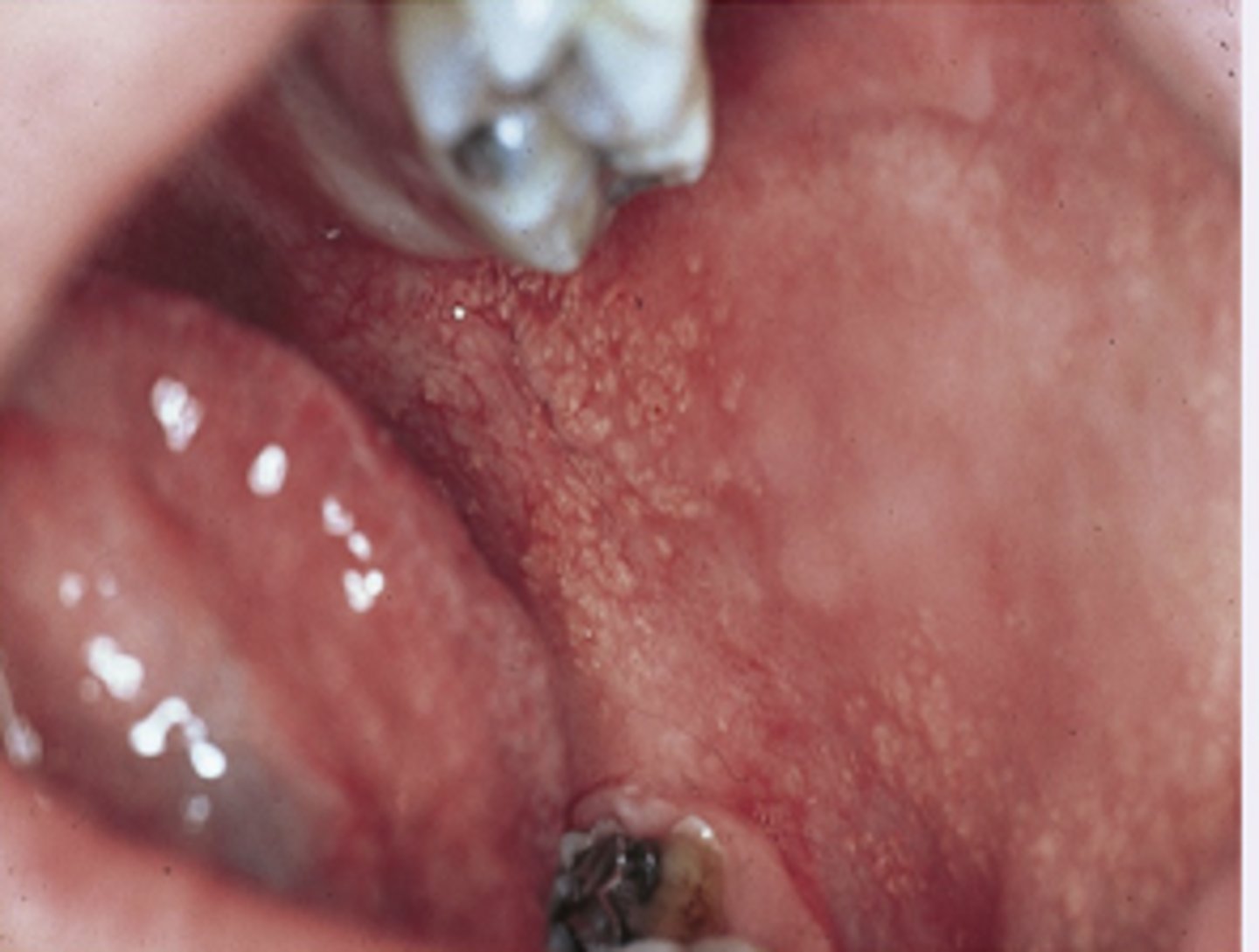
Koplik Spots
Diagnosis?
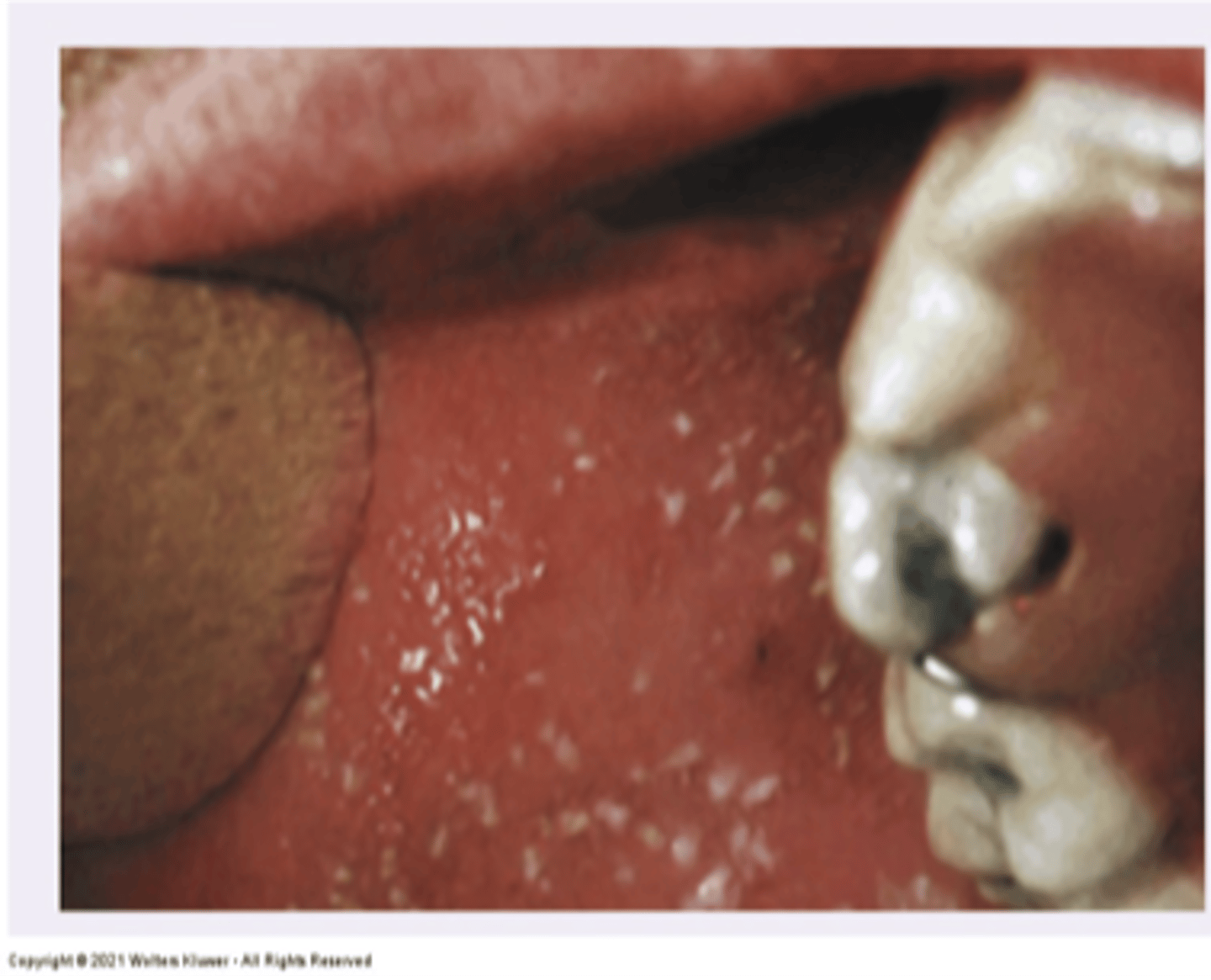
Fordyce Spots
Diagnosis?
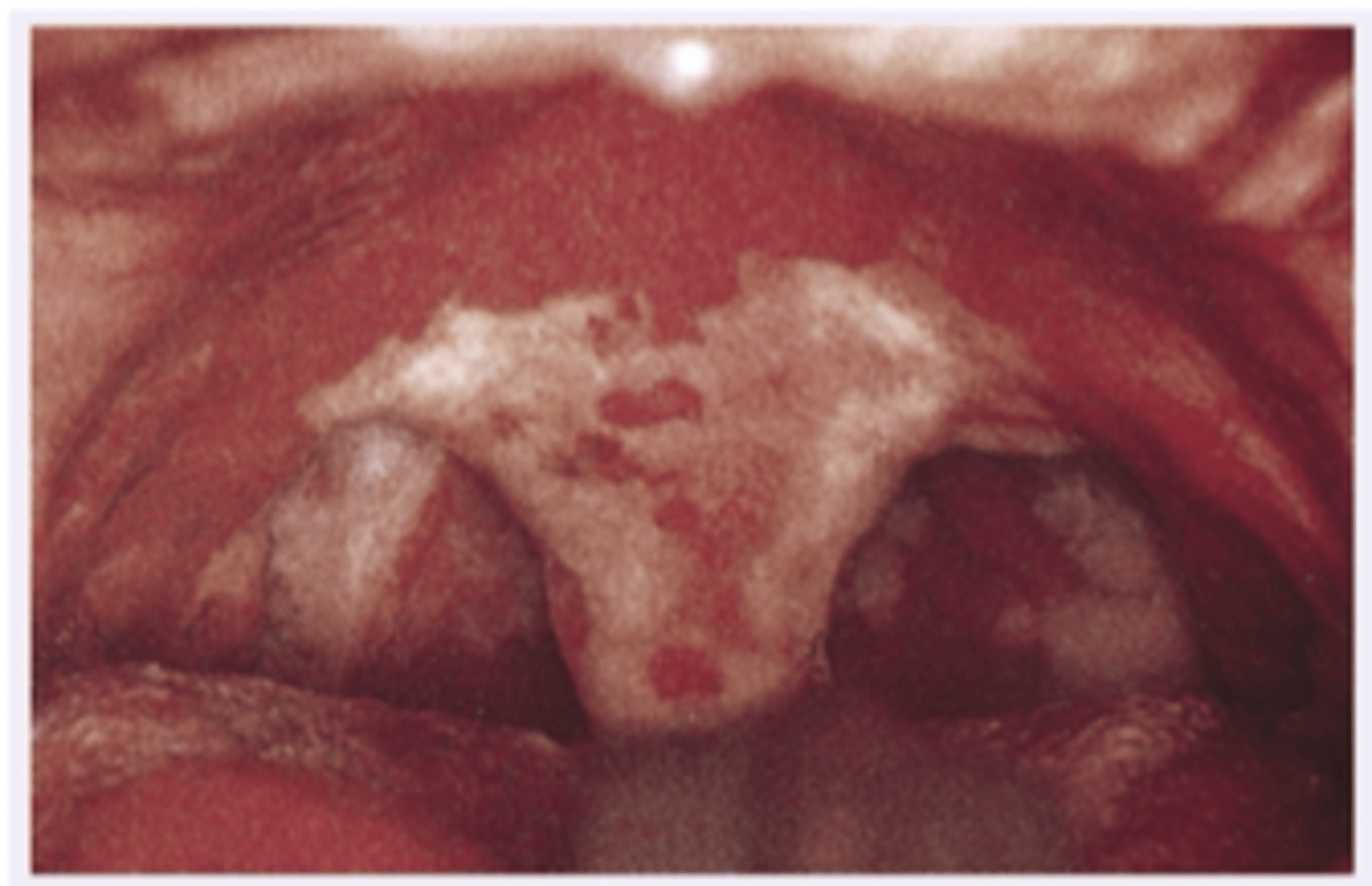
Diphtheria
Diagnosis?
- Most children are vaccinated against this
Thrush on the palate (candidiasis)
This patient is immunocompromised and has been on antibiotics recently. He is on corticosteroids frequently. Diagnosis?
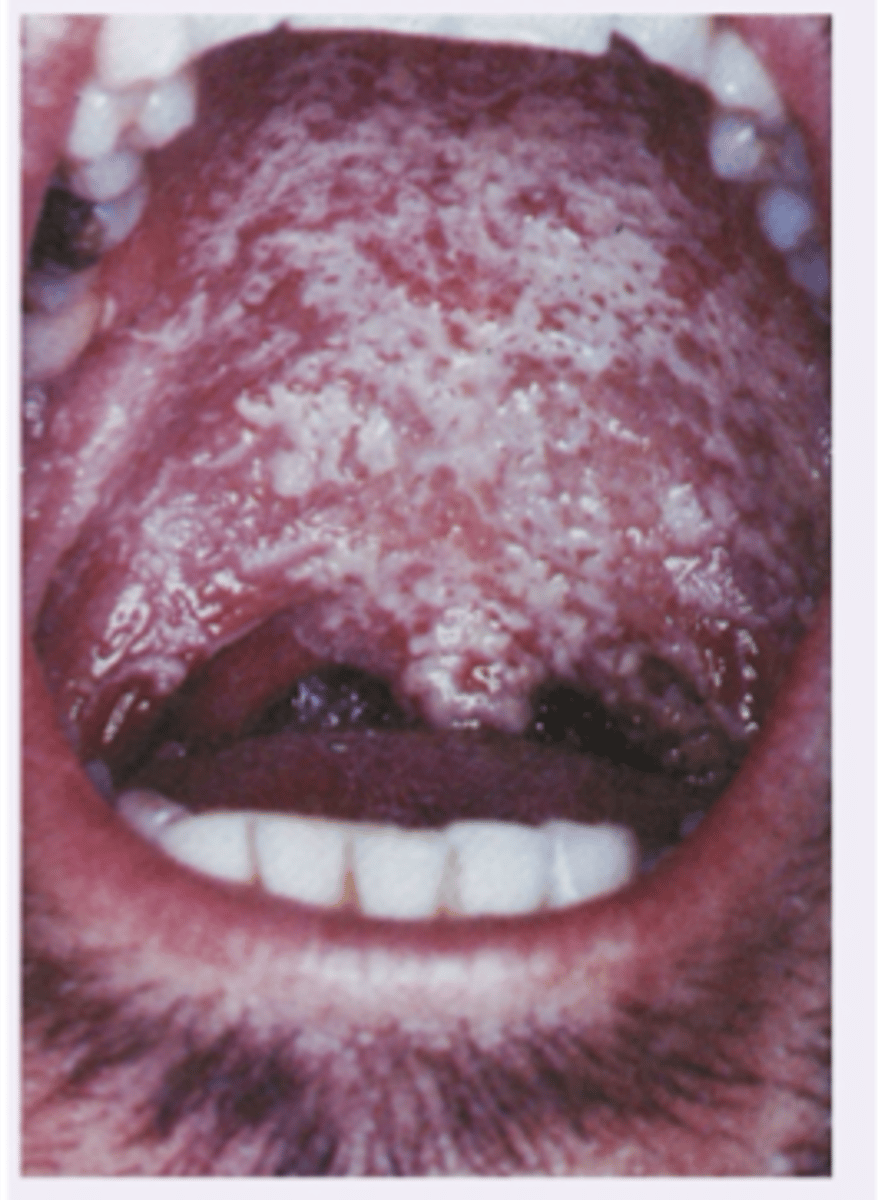
Kaposi sarcoma in AIDS
This is a low grade vascular tumor associated with AIDS
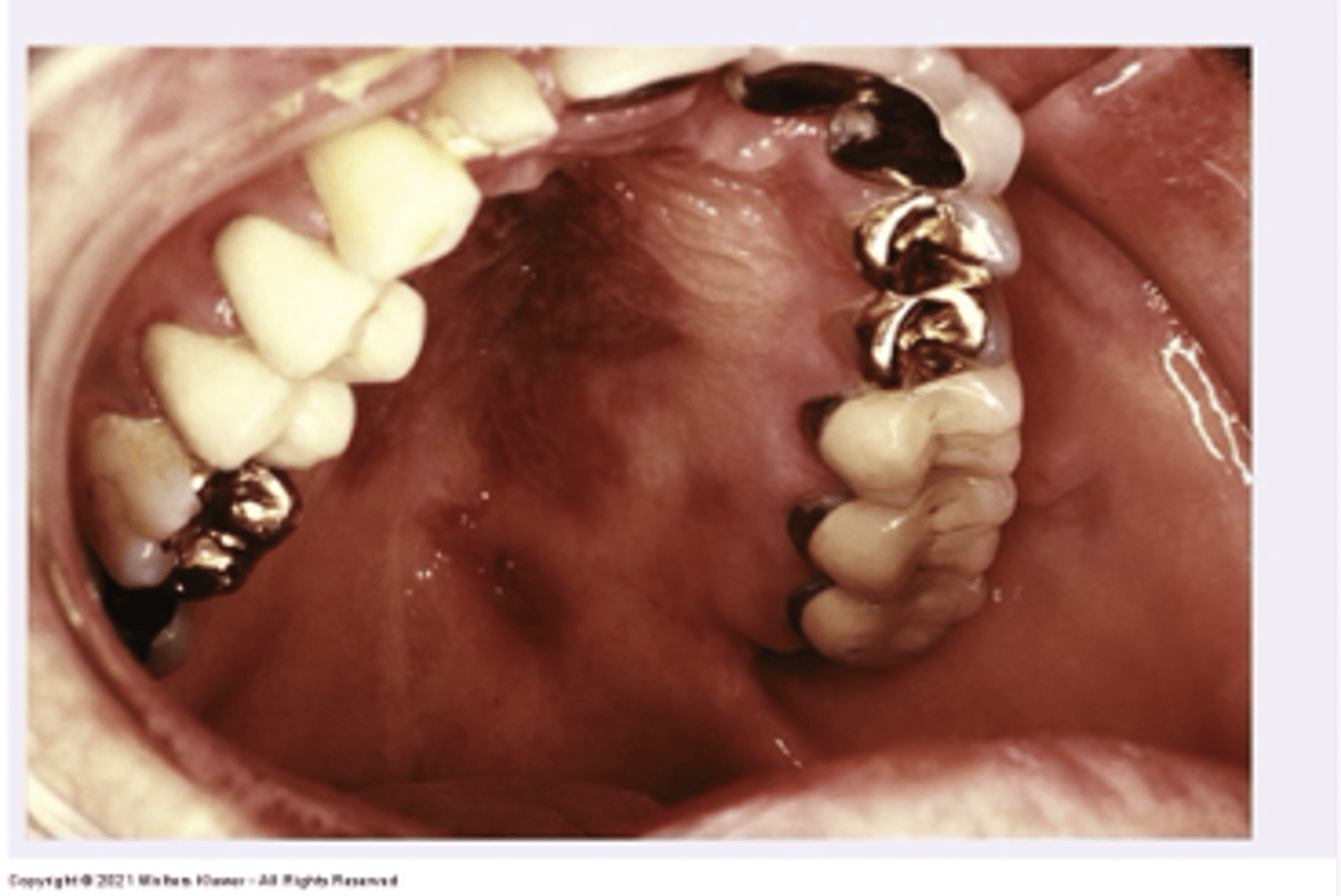
Acute bacterial pharyngitis
- Infection of tonsils or posterior pharynx by microorganisms (Group A Beta hemolytic strep Neisseria)
- Symptoms: Sore throat, dysphagia, fever, malaise, decreased appetite
- Tonsil crypt filled with exudate, lymph node enlargement
- Antibiotics
- Culture to ID pathogen
Acute bacterial pharyngitis treatment?
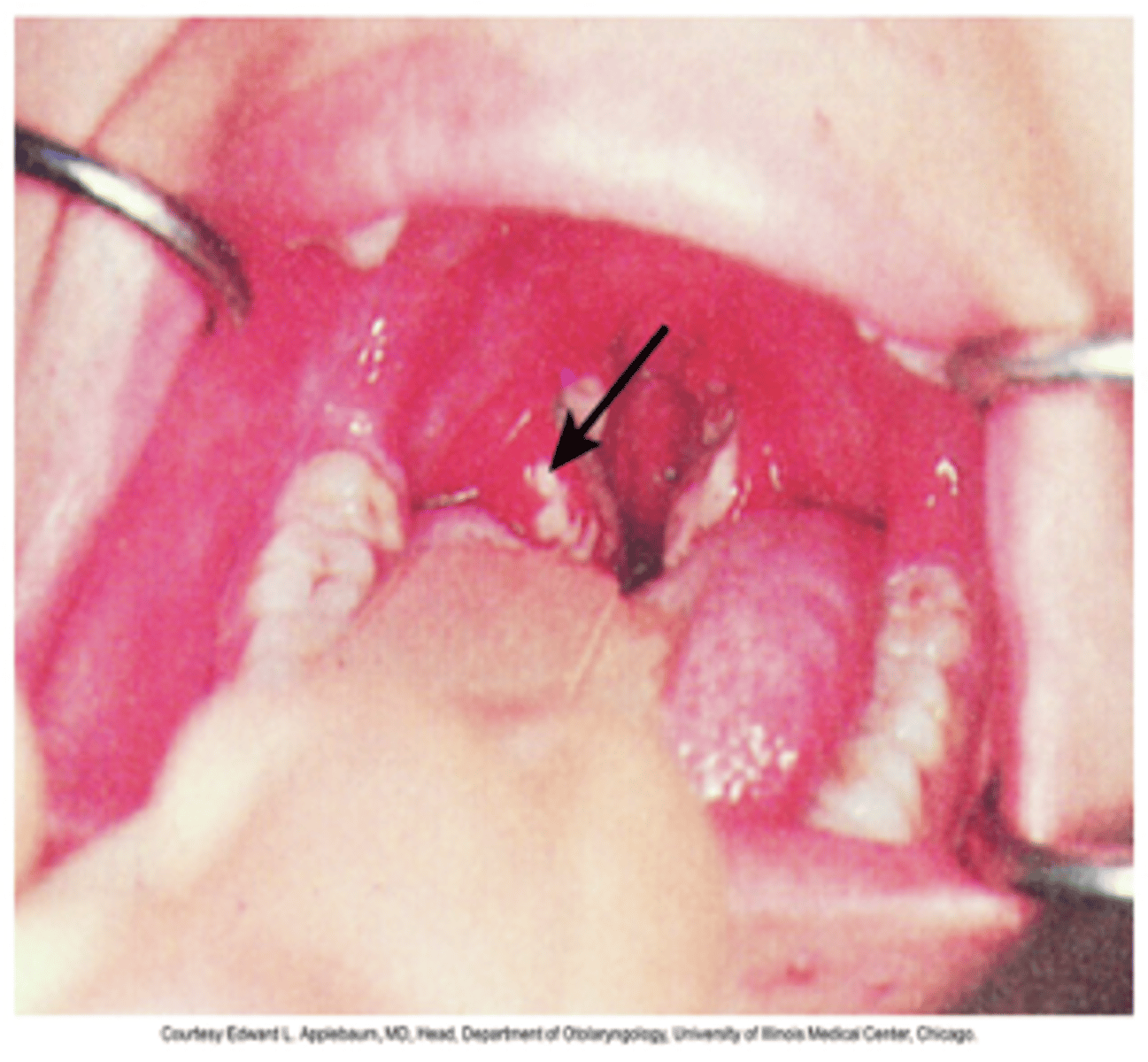
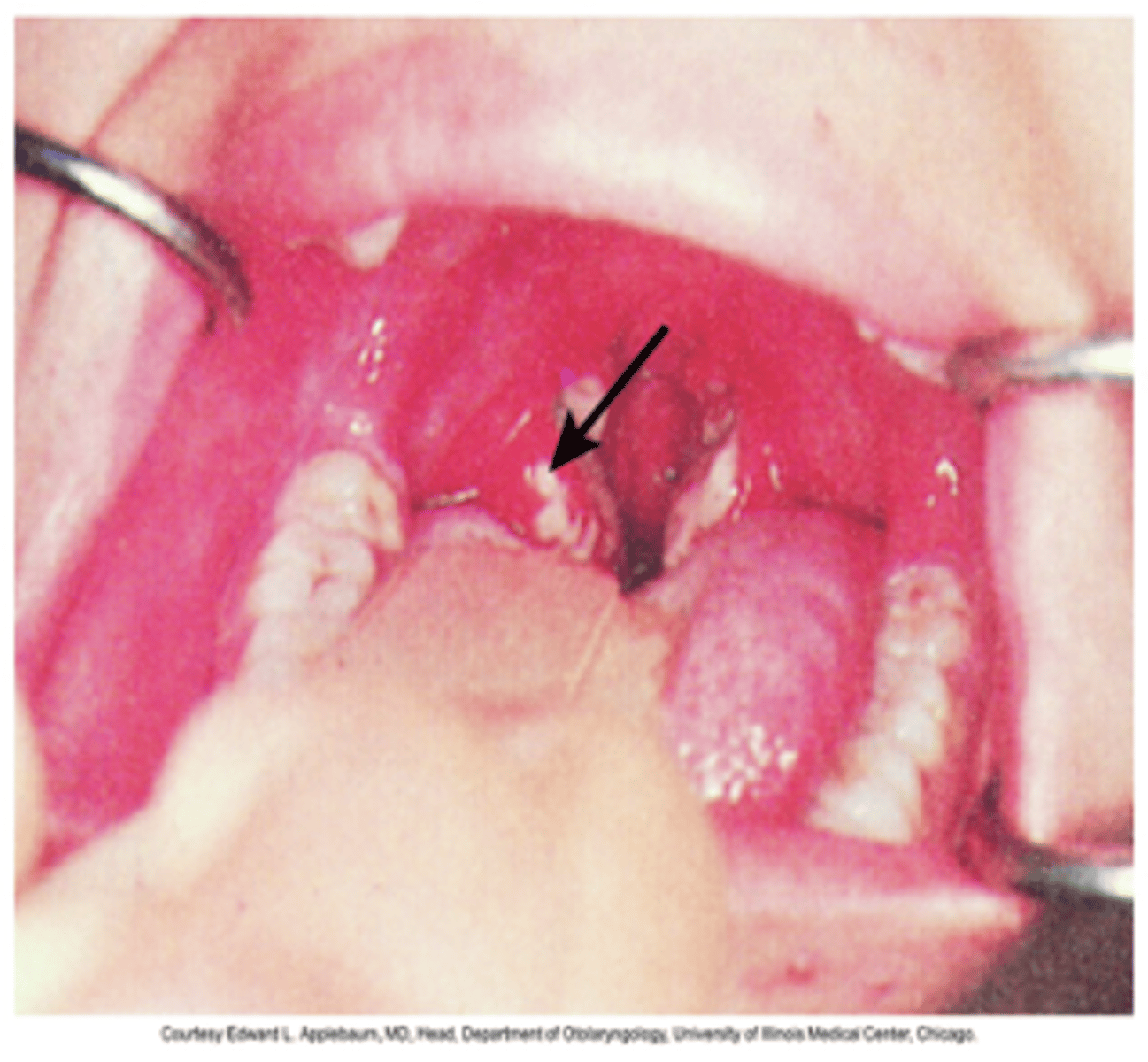
Peritonsillar abscess
- Deep infection in the space between the palatine capsule and pharyngeal muscles
- Complication of adenotonsilitis or blockage of salivary glands
- Polymicrobial common A beta-hemolytic strep
- Subjective: severe sore throat, dysphagia, drooling, fever, malaise
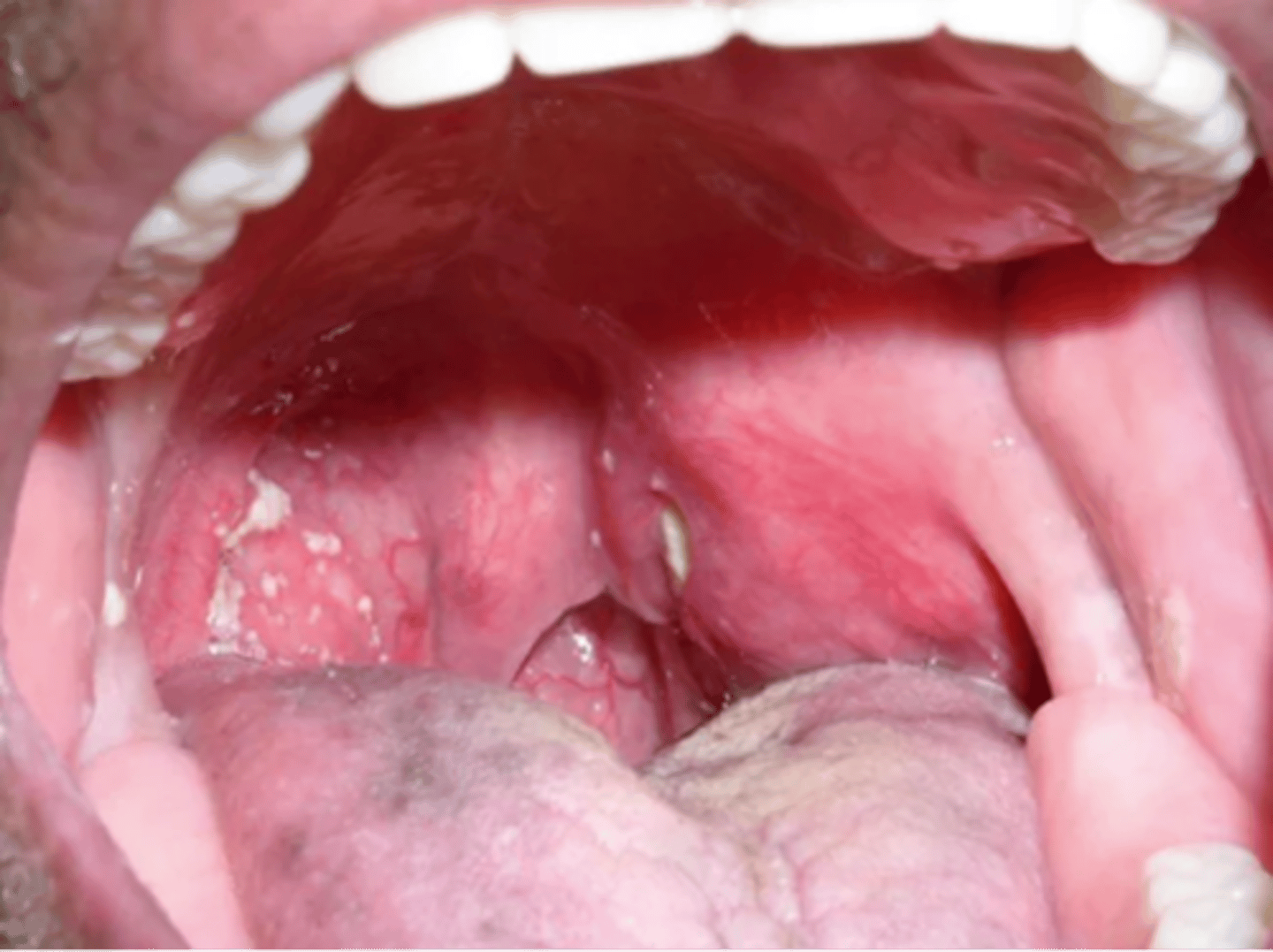
- Antibiotics
- Culture to ID
Peritonsillar abscess treatment
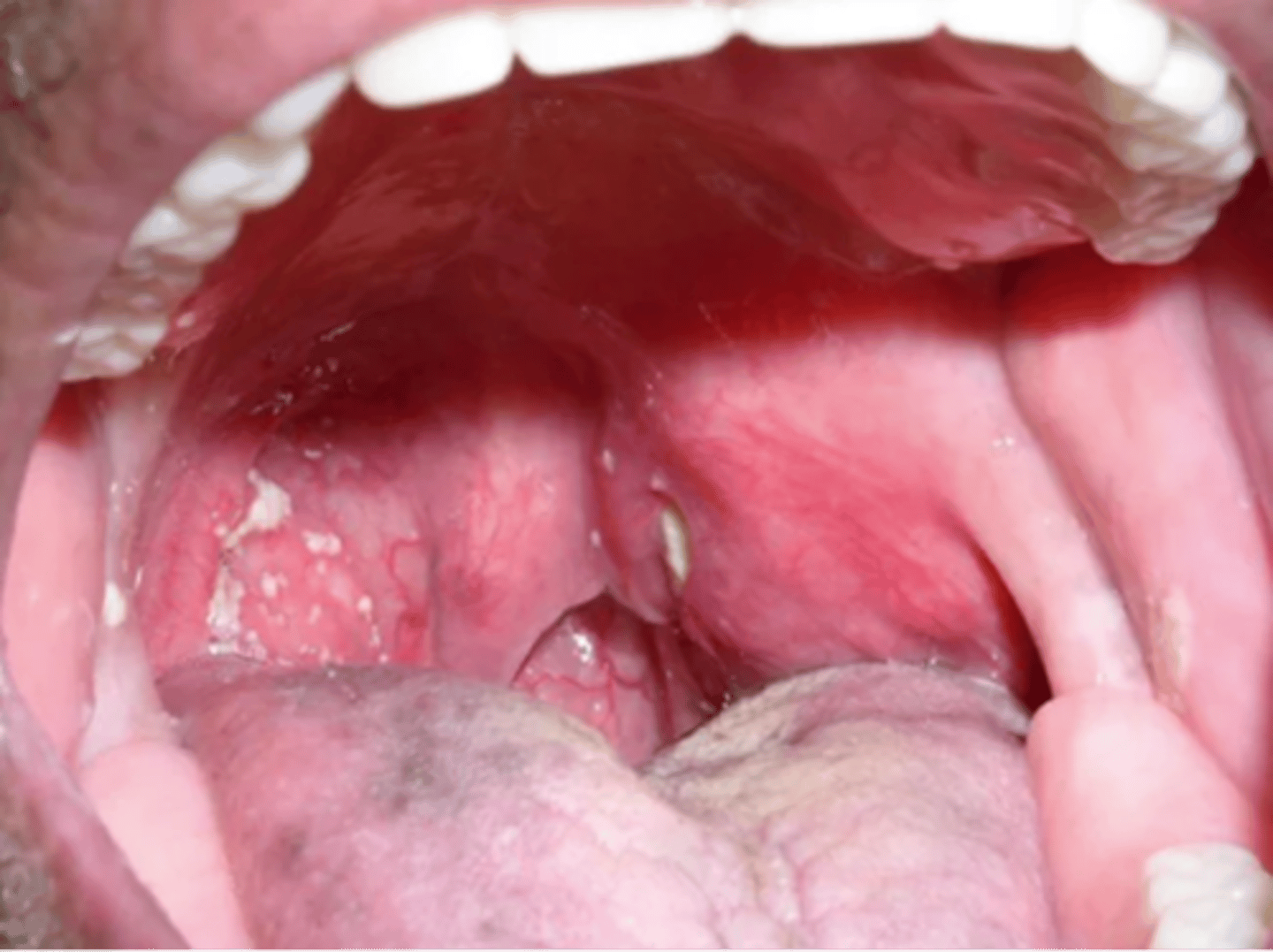
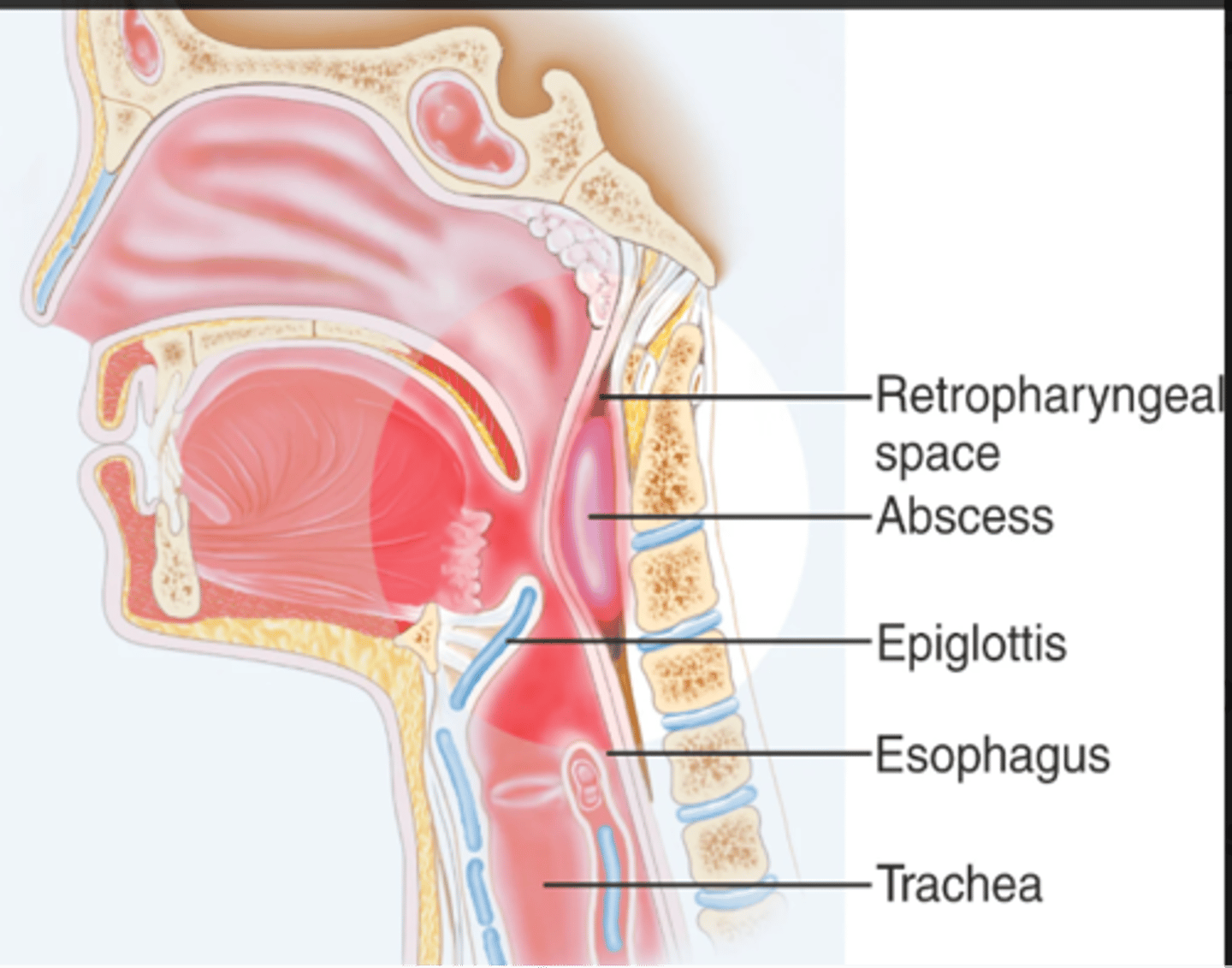
Retropharyngeal abscess
- A life-threatening deep neck space infection that has the potential to occlude the airway
- More common in boys, highest incidence is children under 5
- Strep A, Staph aureus
- Predisposing factors tonsillitis, pharyngitis, dental infection
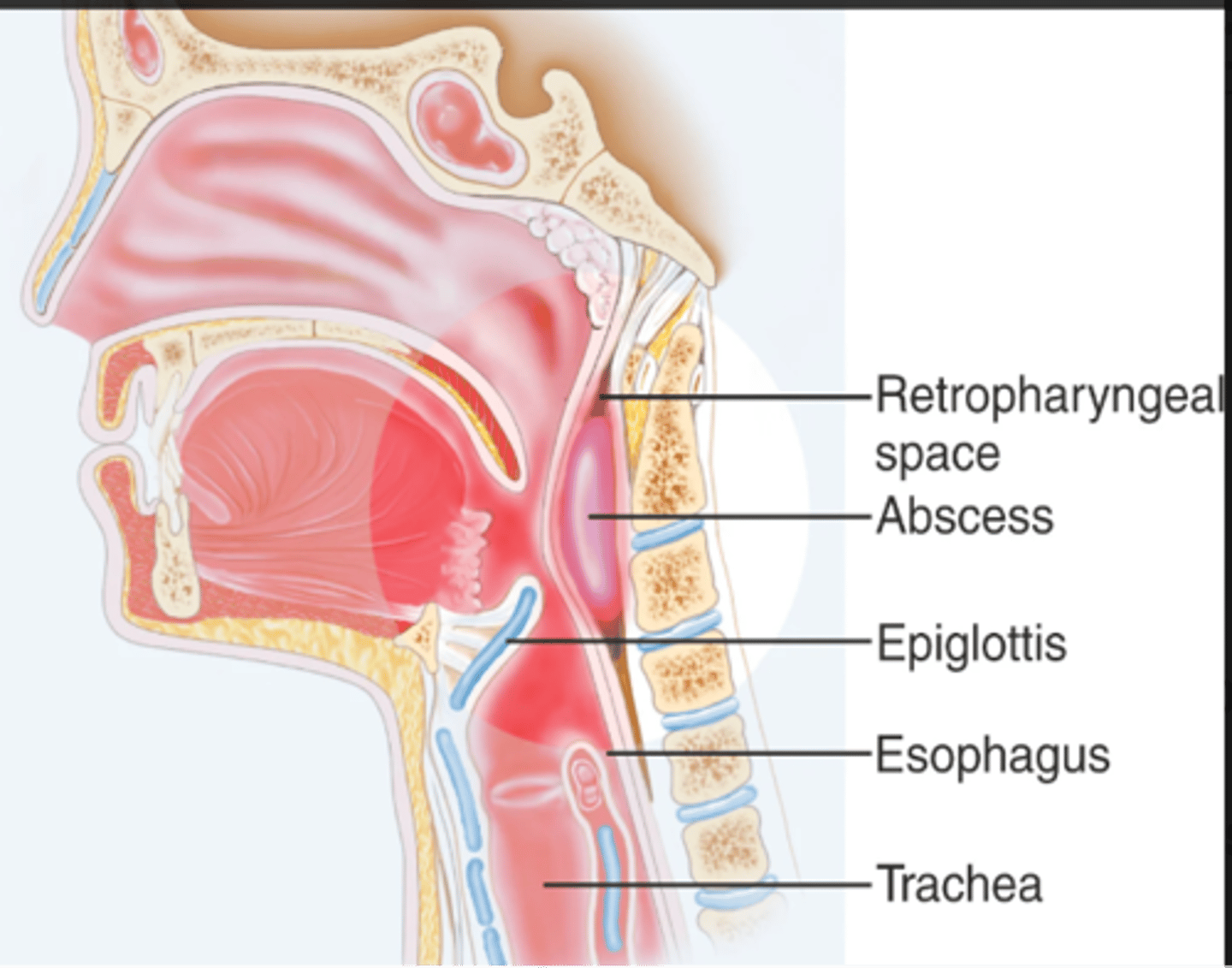
- Acute illness
- High fever
- Malaise
- Anorexia
- Respiratory distress
Retropharyngeal abscess symptoms
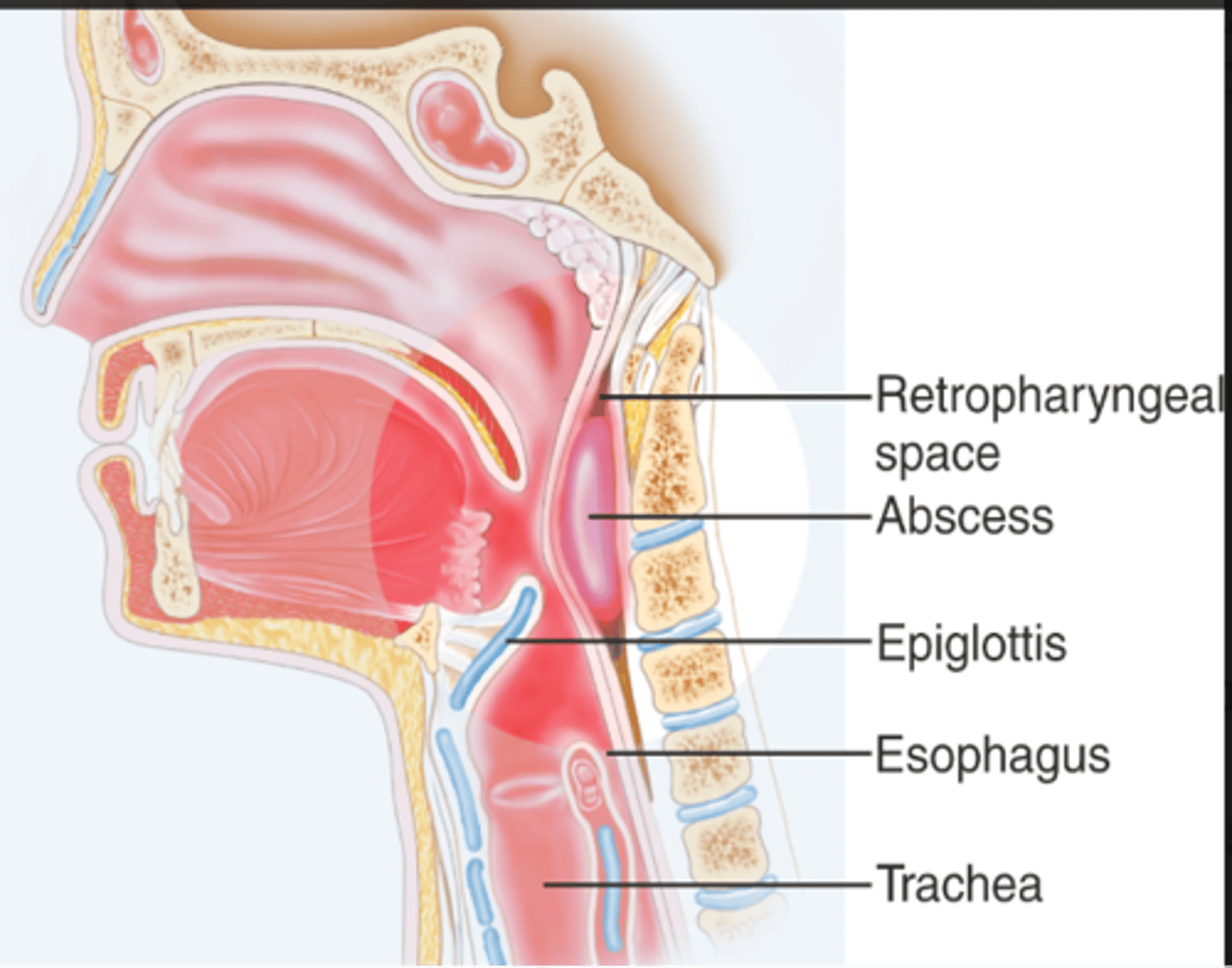
- Antibiotics
- Maintain airway
Retropharyngeal abscess treatment?
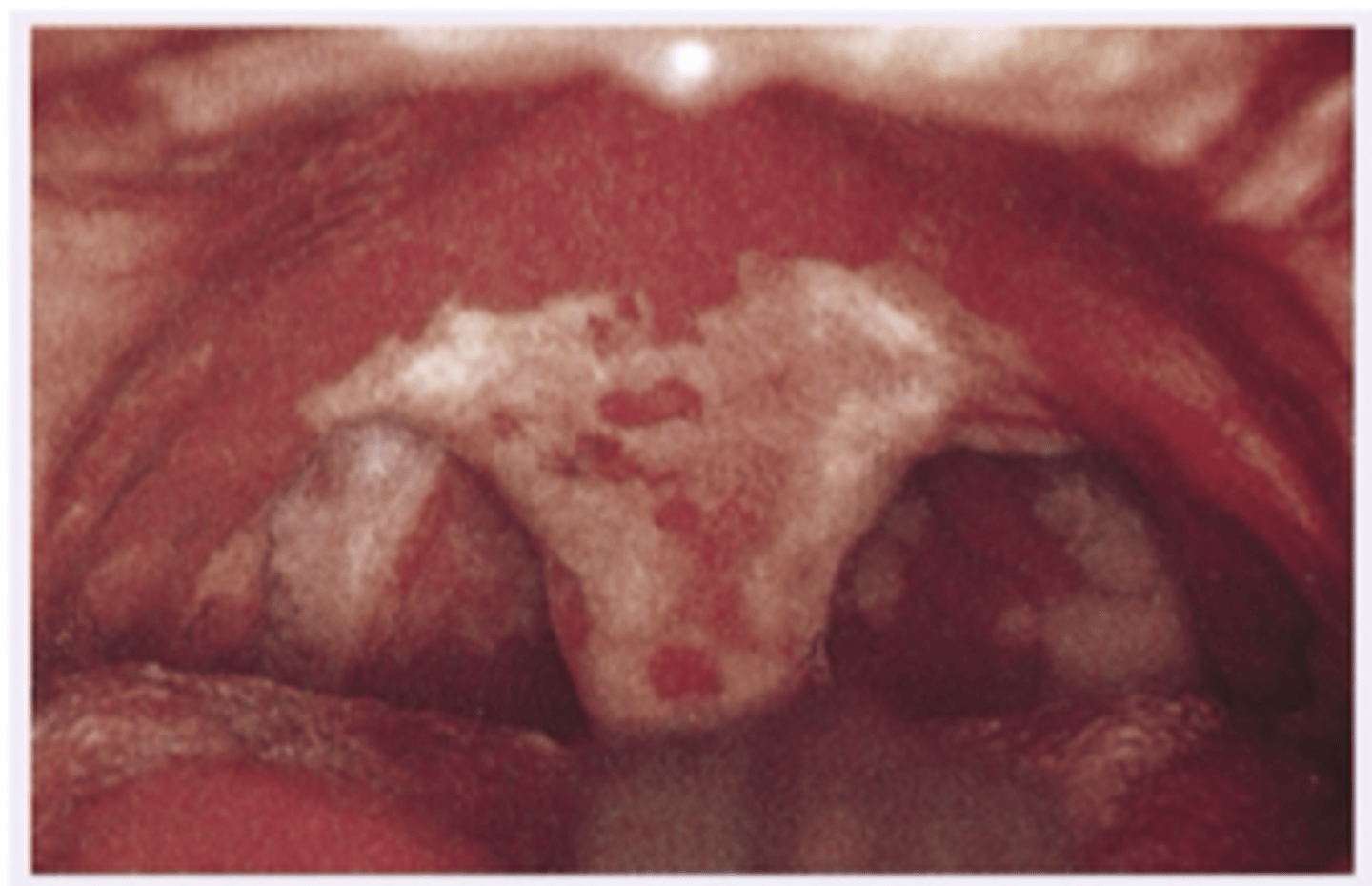
Diphtheria
This patient is a 10 year old unvaccinated amish child with sore red throat, there is a gray red exudate as shown in the photo. The airway may become obstructed, so this is a life threatening bacterial infection. What is the diagnosis?
- Rubeola
- Kaposi's Sarcoma
- Diphtheria
- Thrush
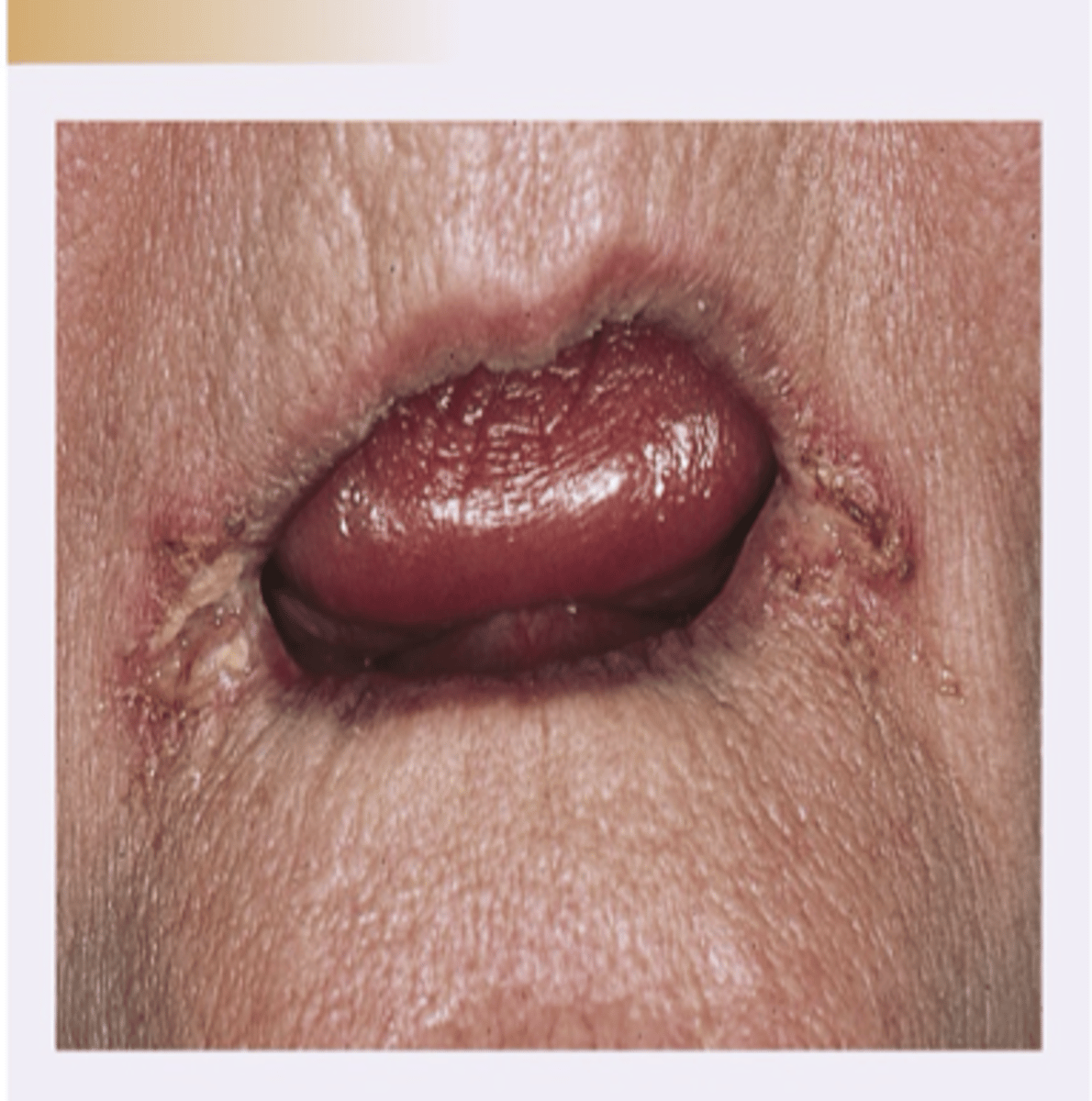
Angular Cheilitis - with candida at angles of mouth
Diagnosis?
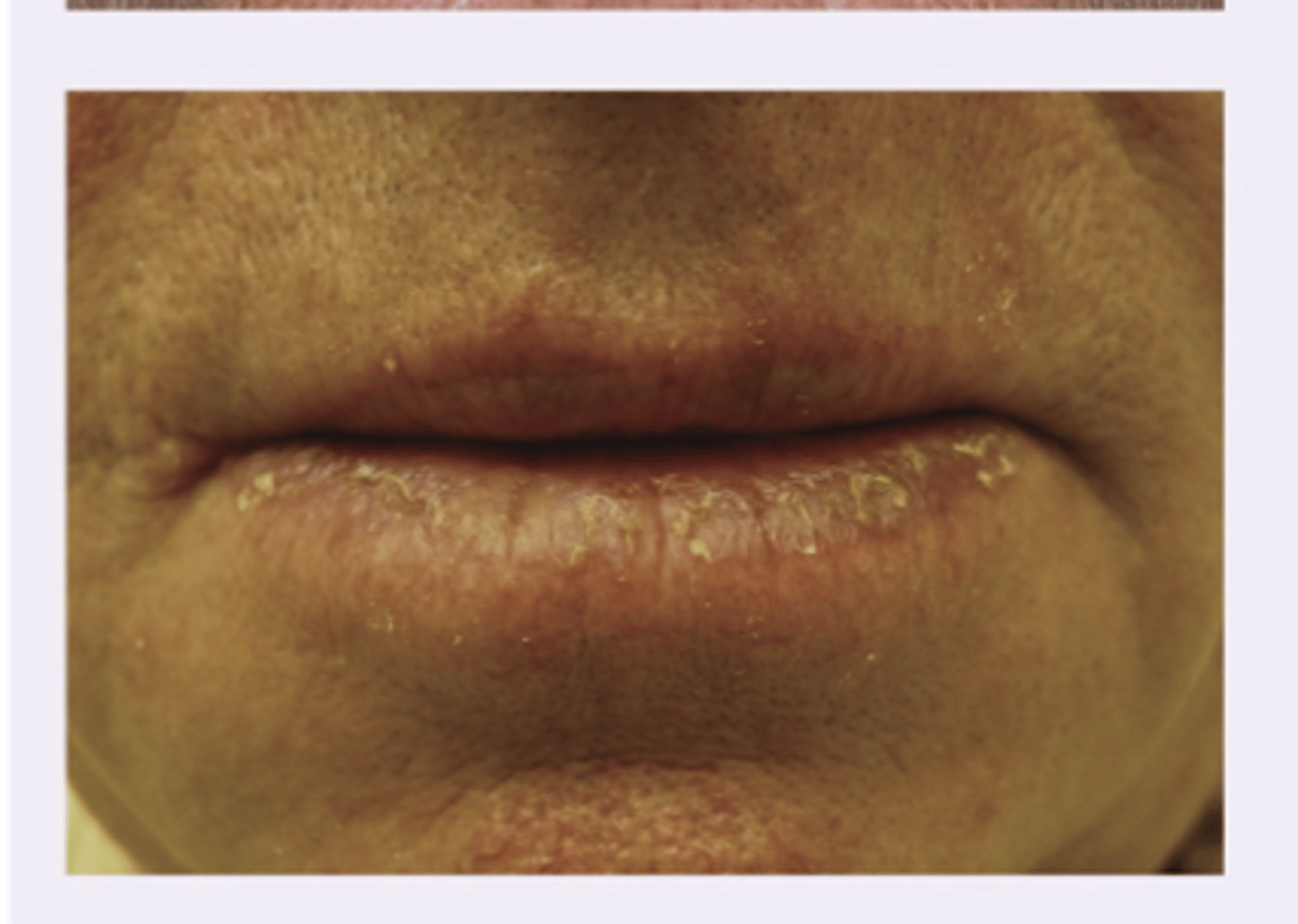
Actinic Cheilitis - precancerous sun exposure
Diagnosis?
Herpes Simplex - new vesicular and older yellow brown lesions
Diagnosis?
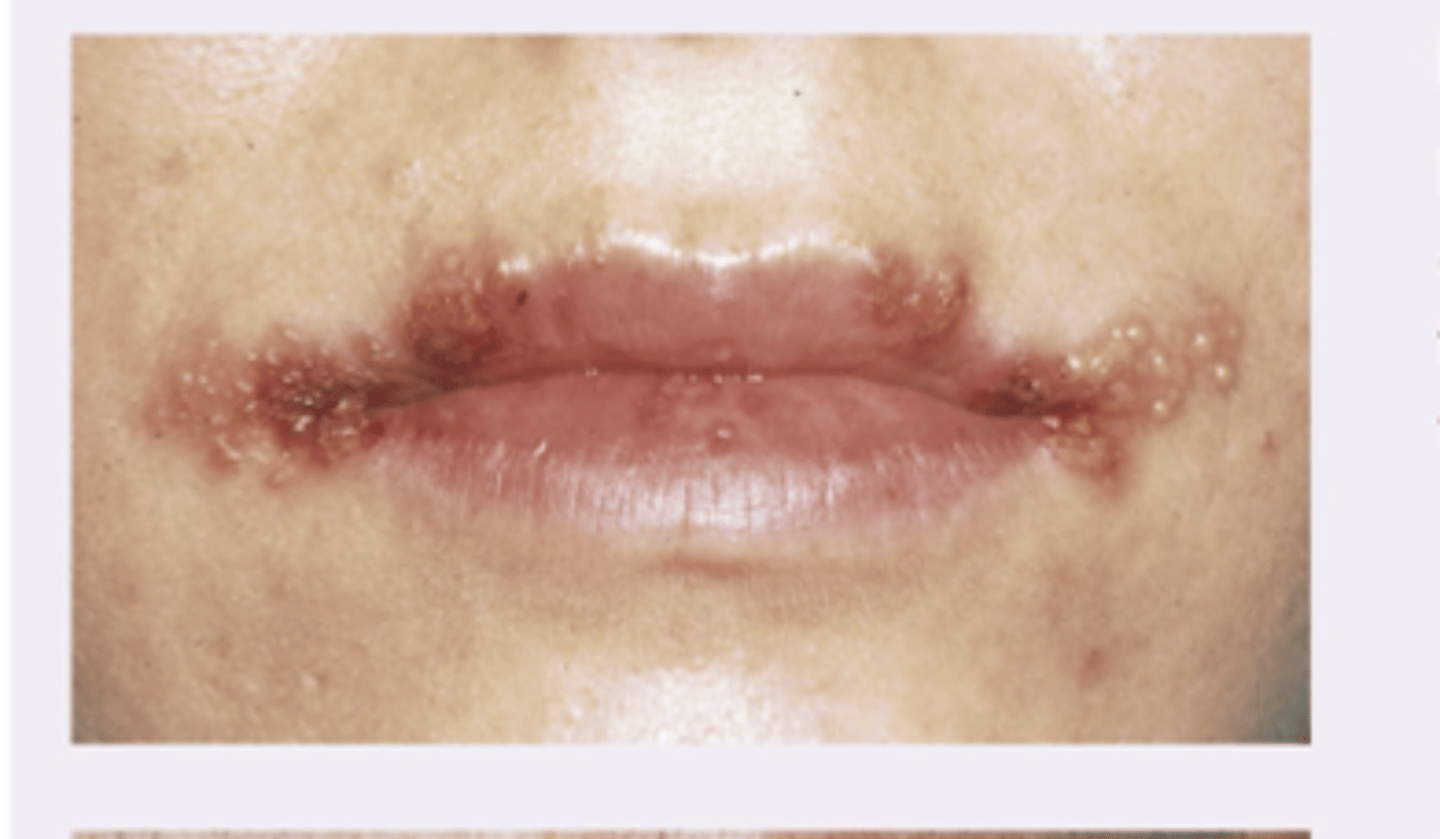
Angioedema - allergic and NSAID. Self limiting unless in the larynx, tongue, upper airways (life threatening)
Diagnosis?
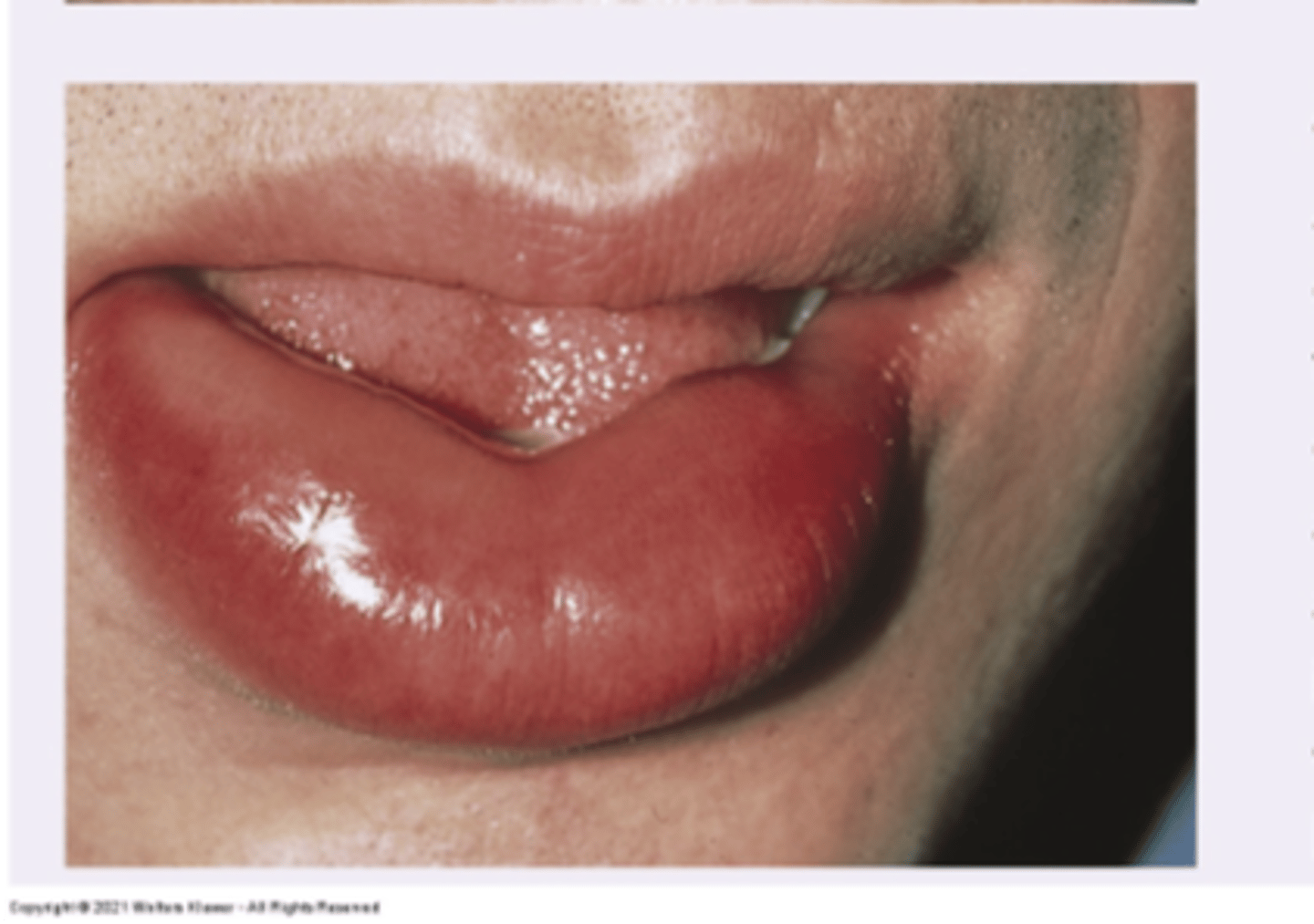
Telangiectasia
Diagnosis?
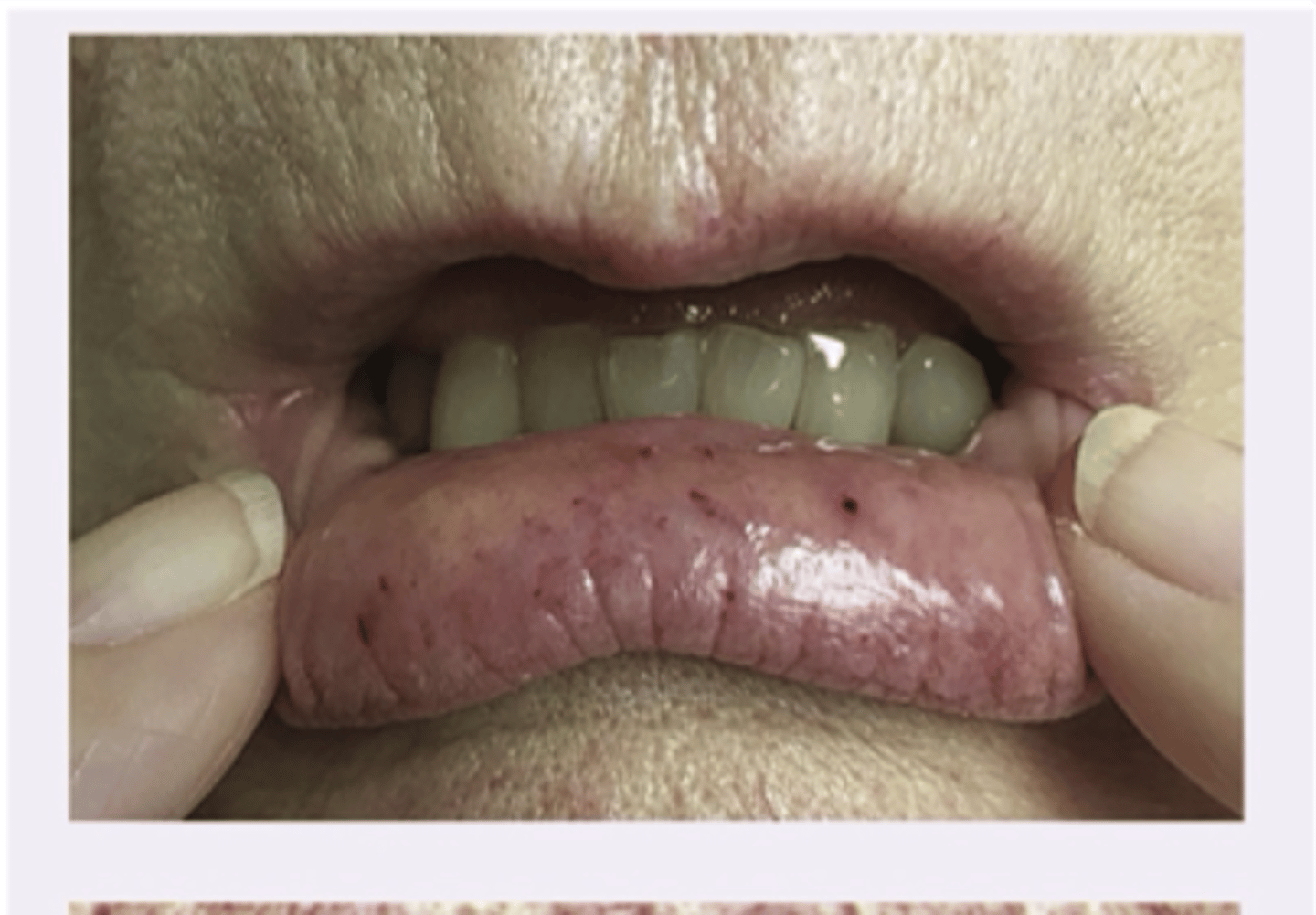
Peutz-Jehers Syndrome
Diagnosis?
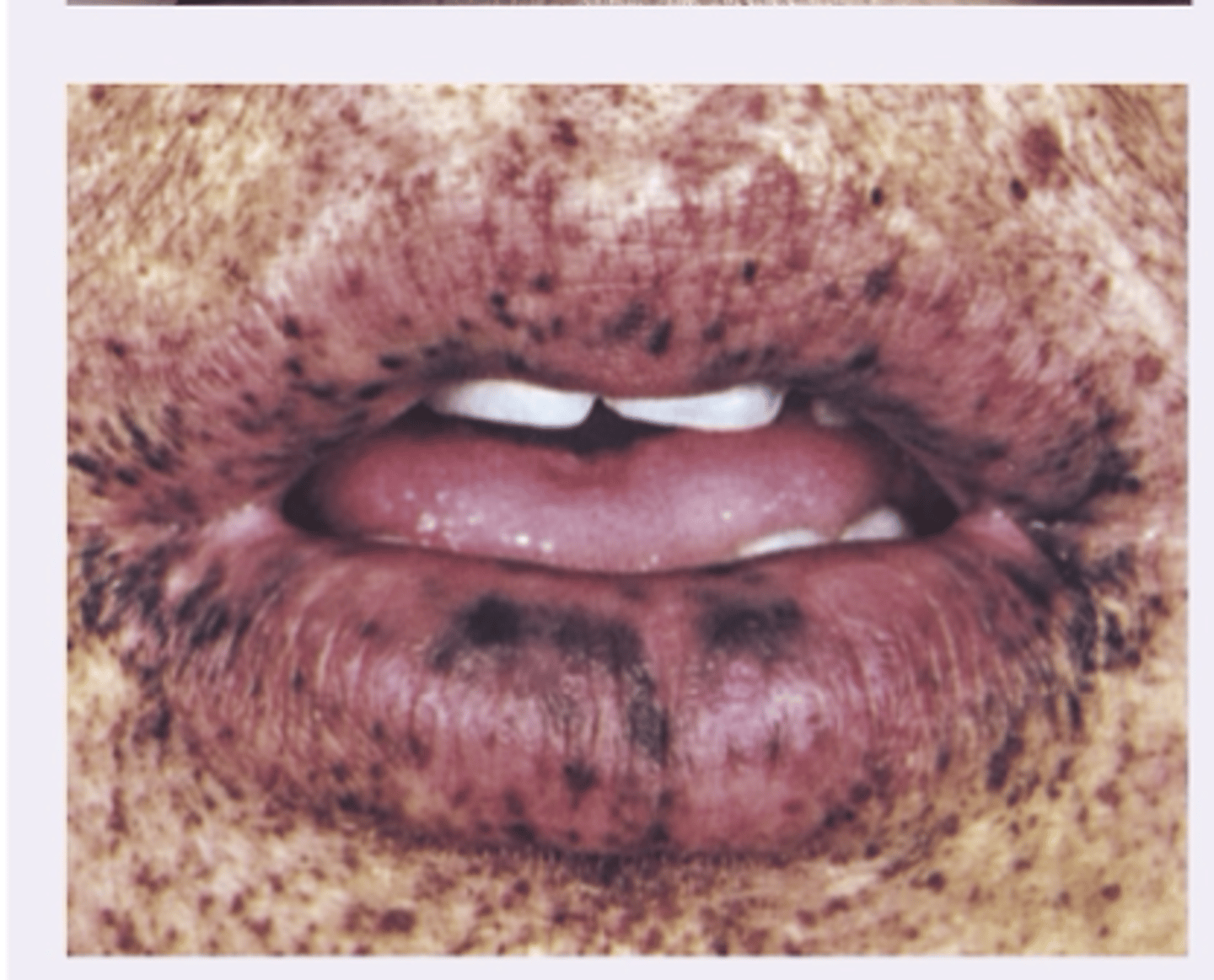
Primary Syphilis
Diagnosis?
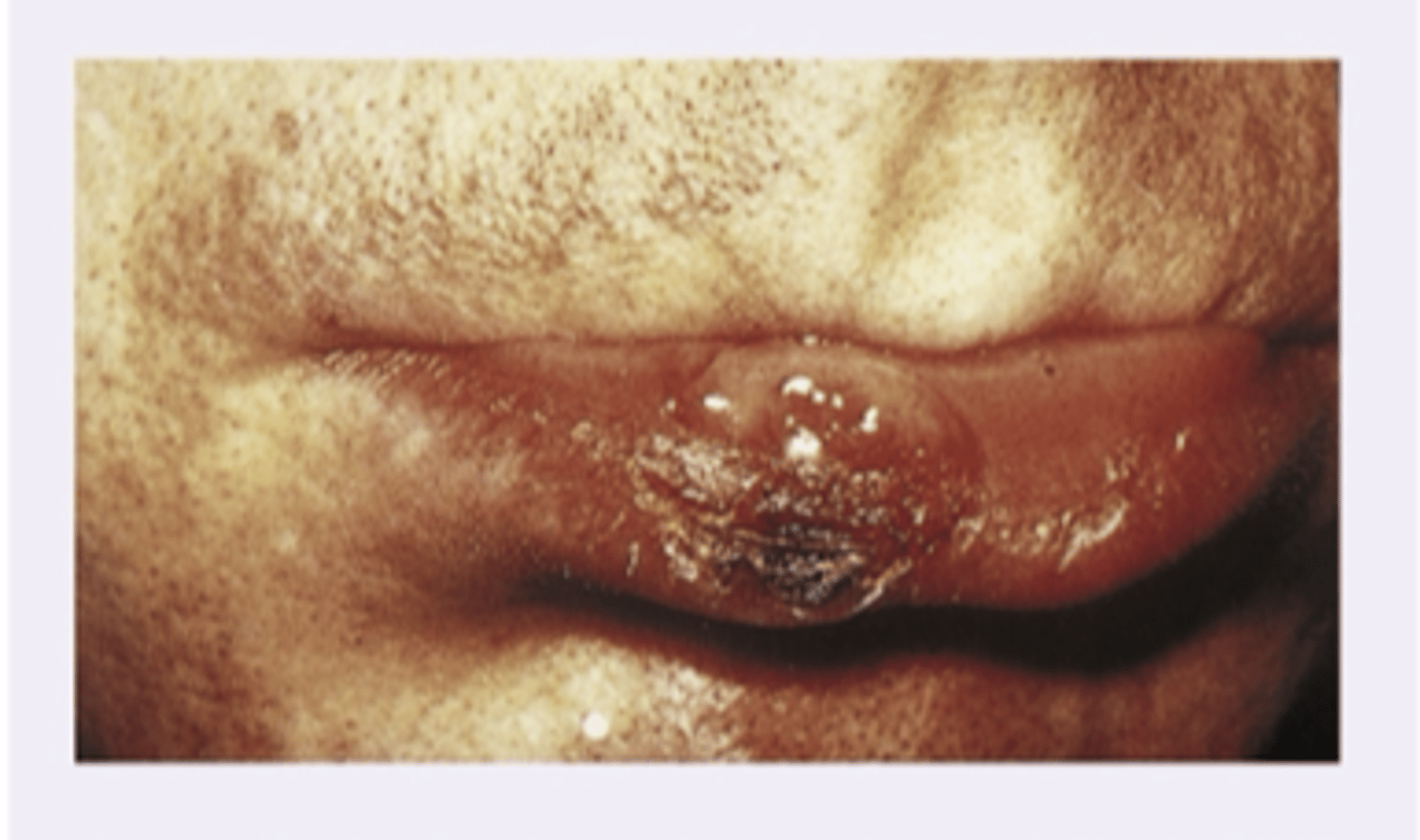
Carcinoma of the lip
Diagnosis?
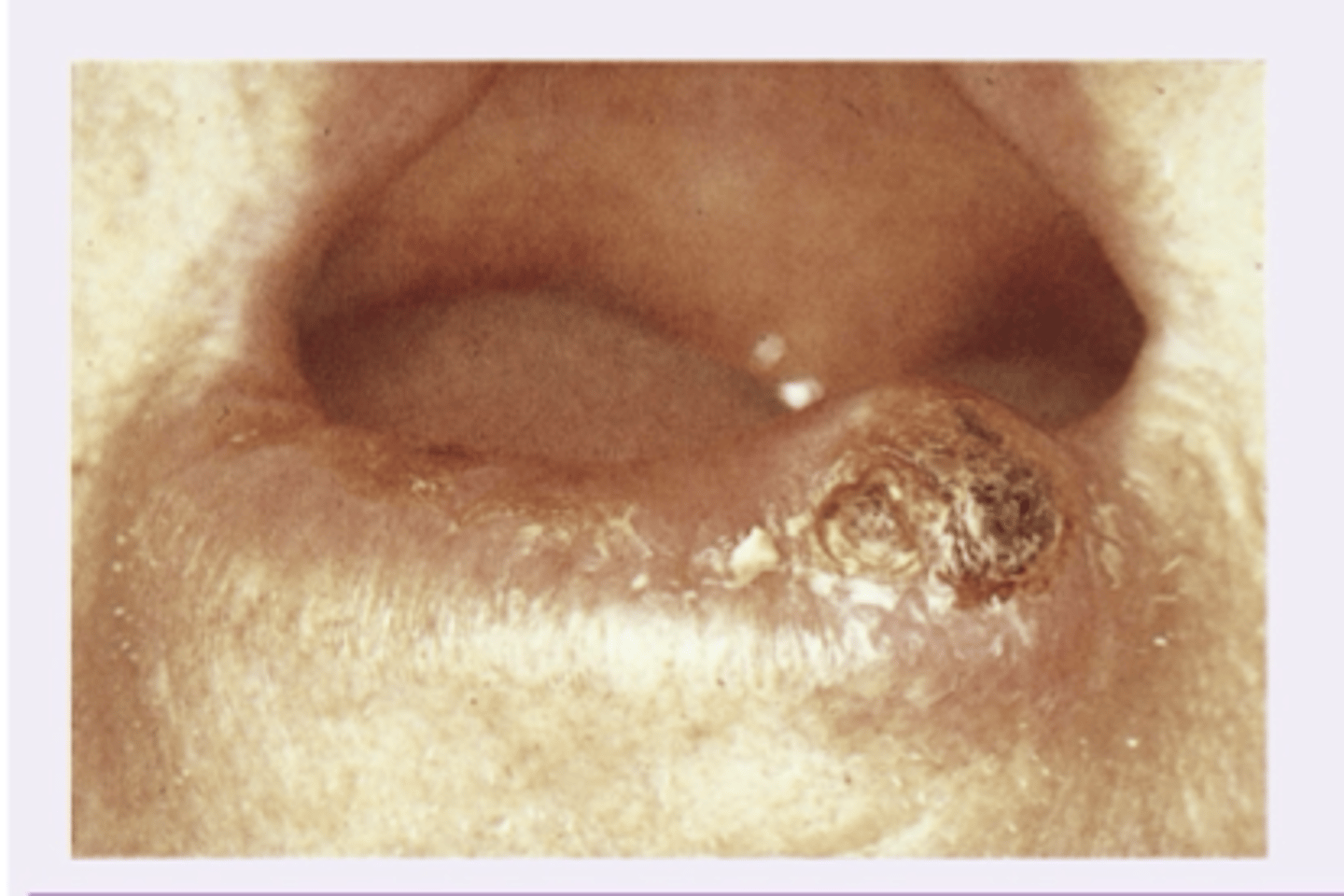
Candidiasis
This patient has been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease and has been on antibiotics of a severe tooth infection recently prior to the onset of this white accumulation on the oral pharynx. It can be scraped off but returns quickly. What is the diagnosis of the oral pharynx?
- Acute bacterial pharyngitis
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Candidiasis
- Peritonsillar abscess
Vertigo
Which condition results in a false sense of motion, as though the surroundings are moving, there is an acute onset of the room spinning with imbalance and ataxia, and nystagmus.
- Vertigo
- Presyncope
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Panic Disorder
- CN XII lesion
- Asymmetric protrusion suggests a lesion of CN XII (tongue points toward the side of the lesion)
Diagnosis?
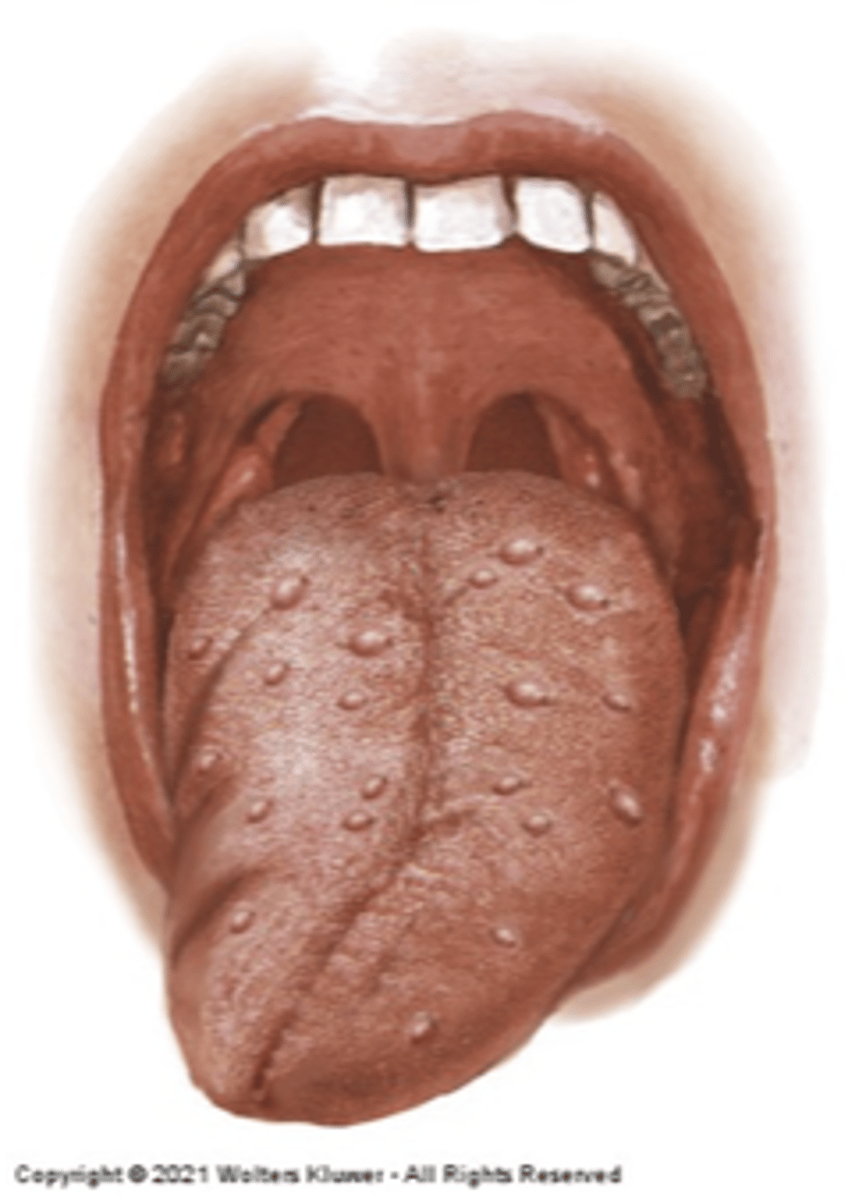
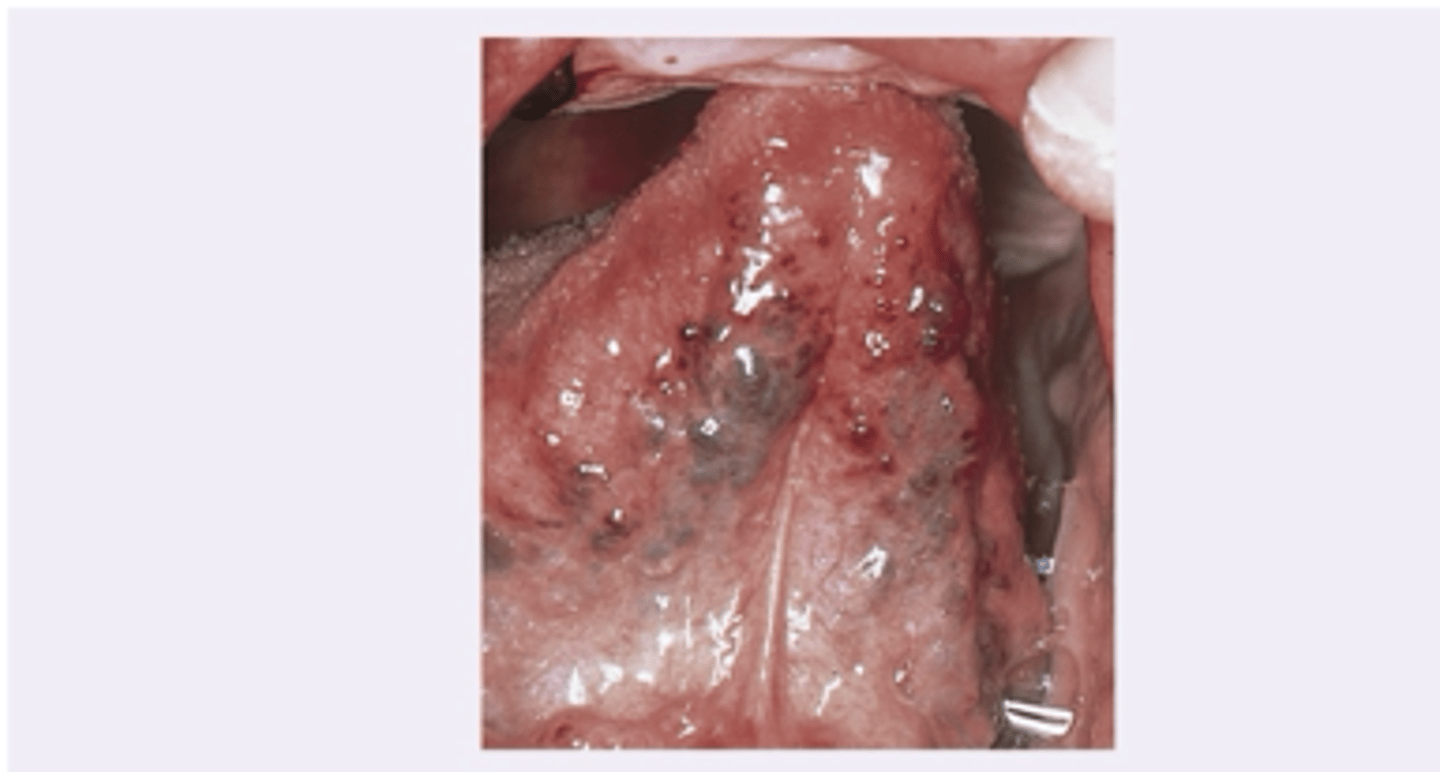
Varicose veins
Diagnosis?
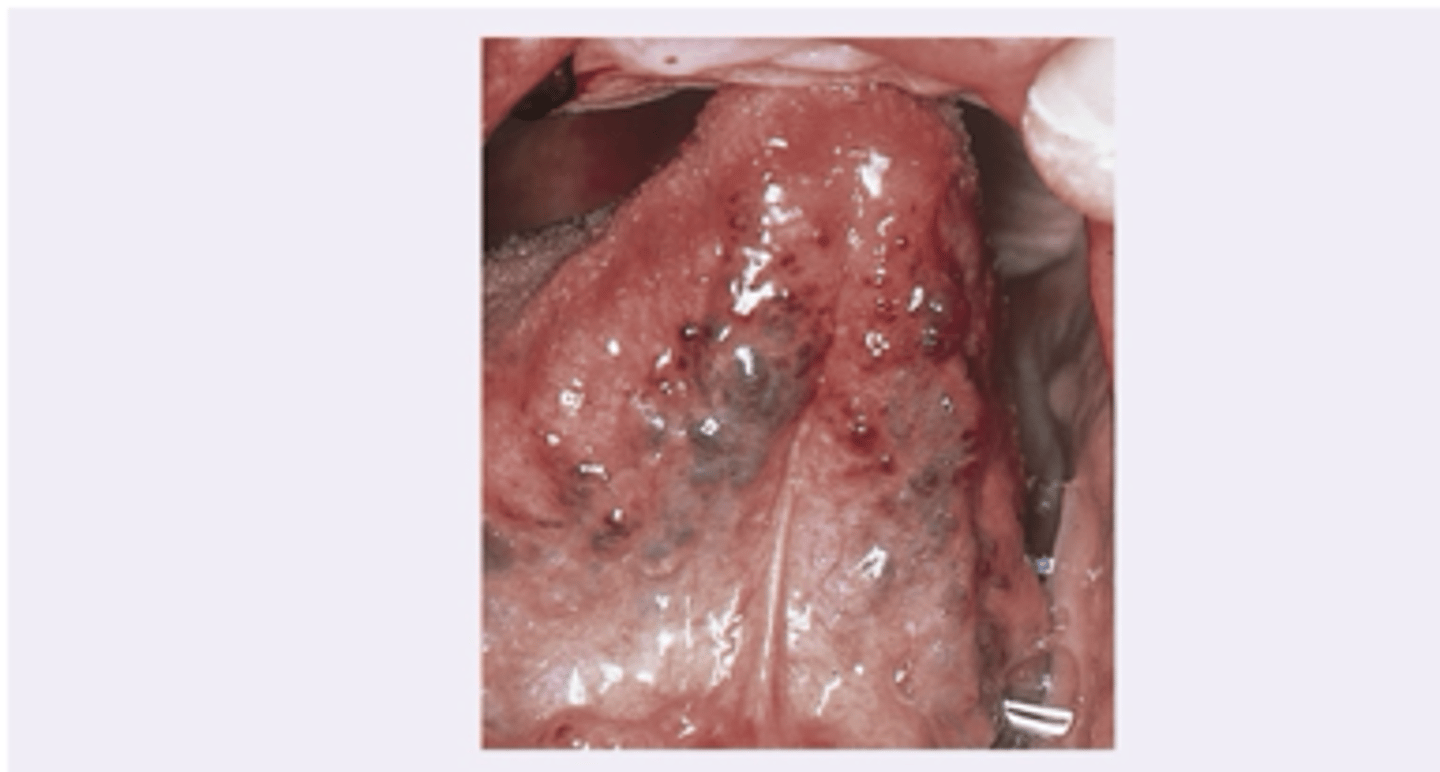
None
Varicose veins clinical significance
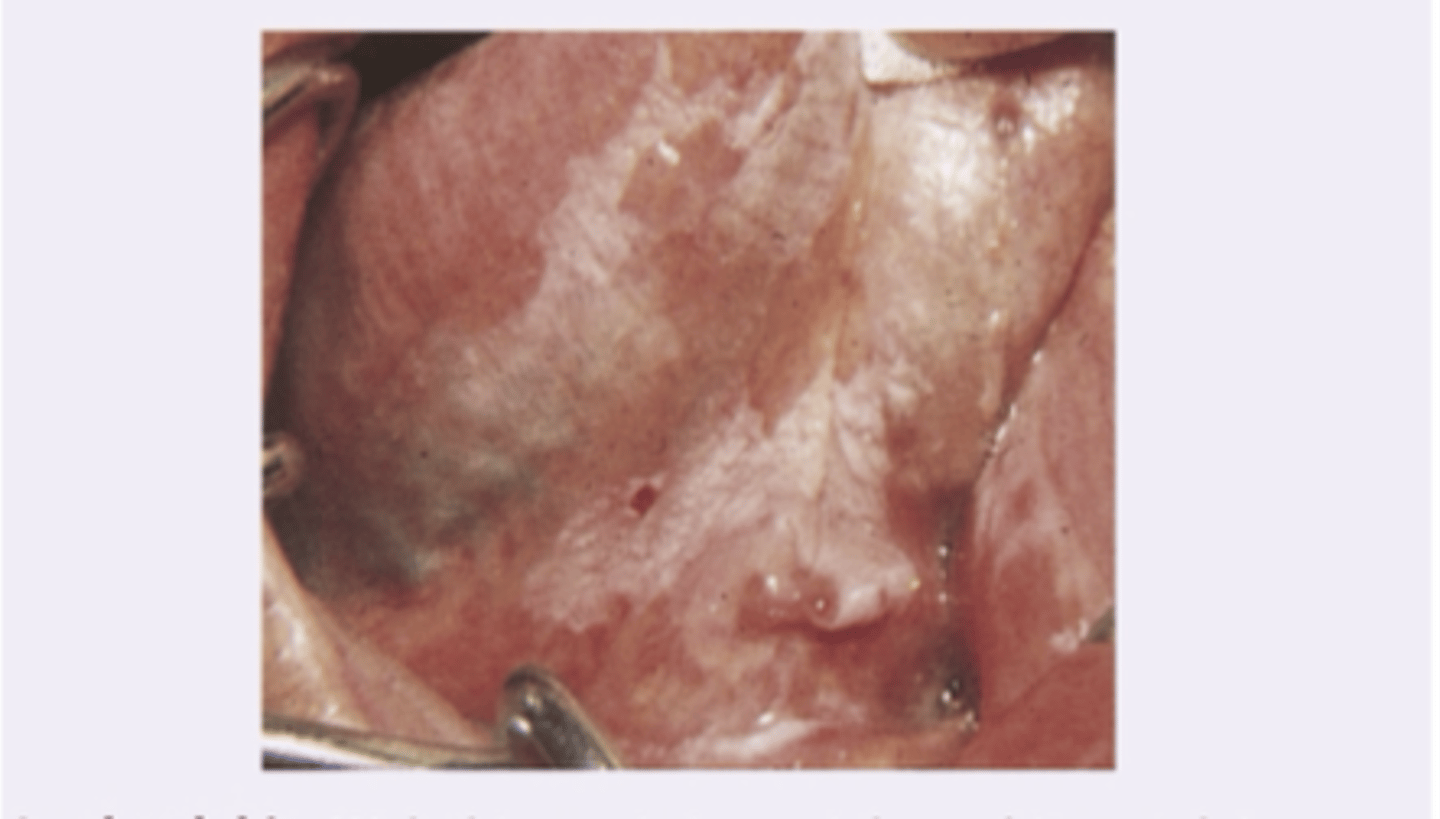
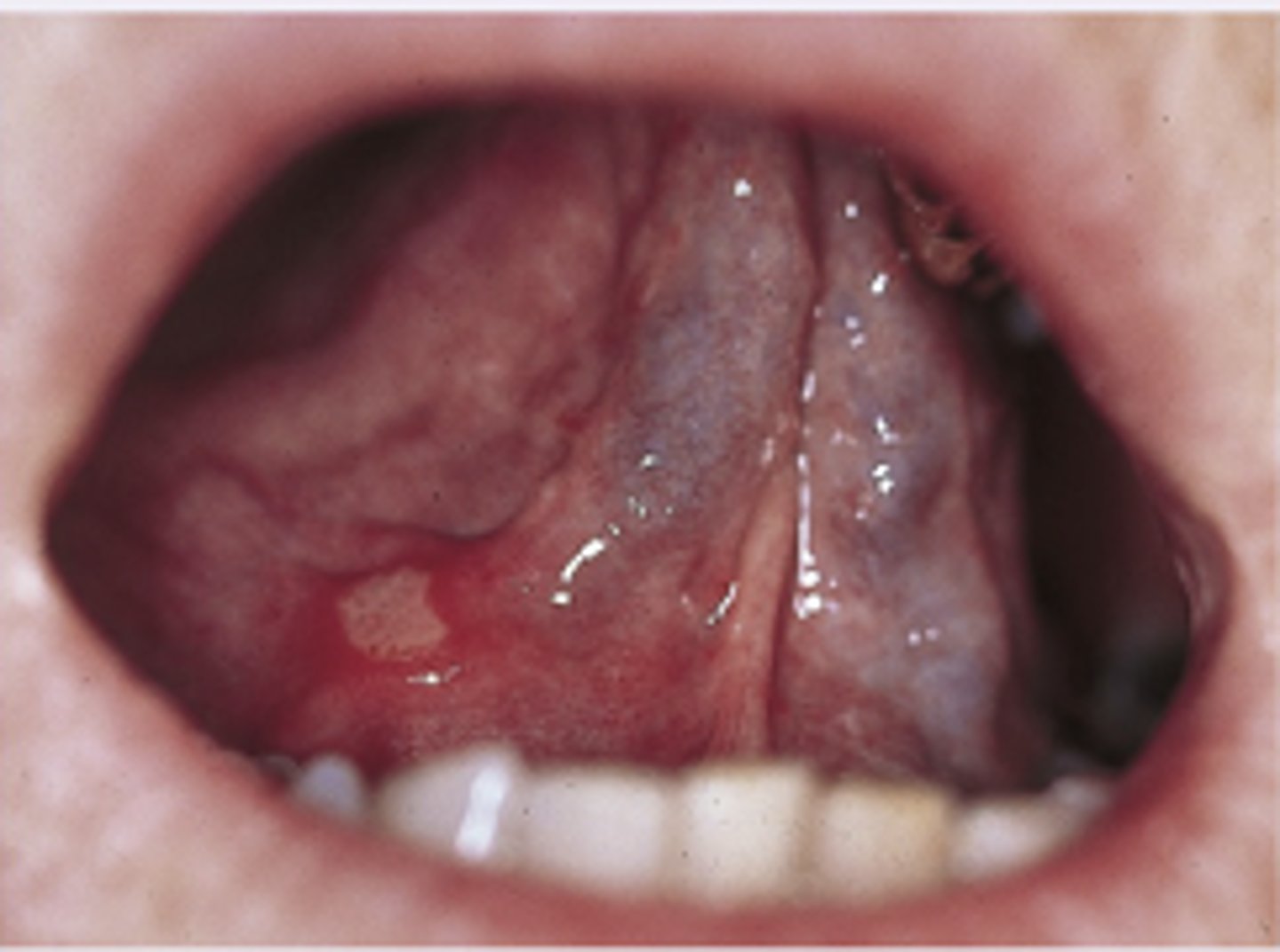
Leukoplakia
Diagnosis?
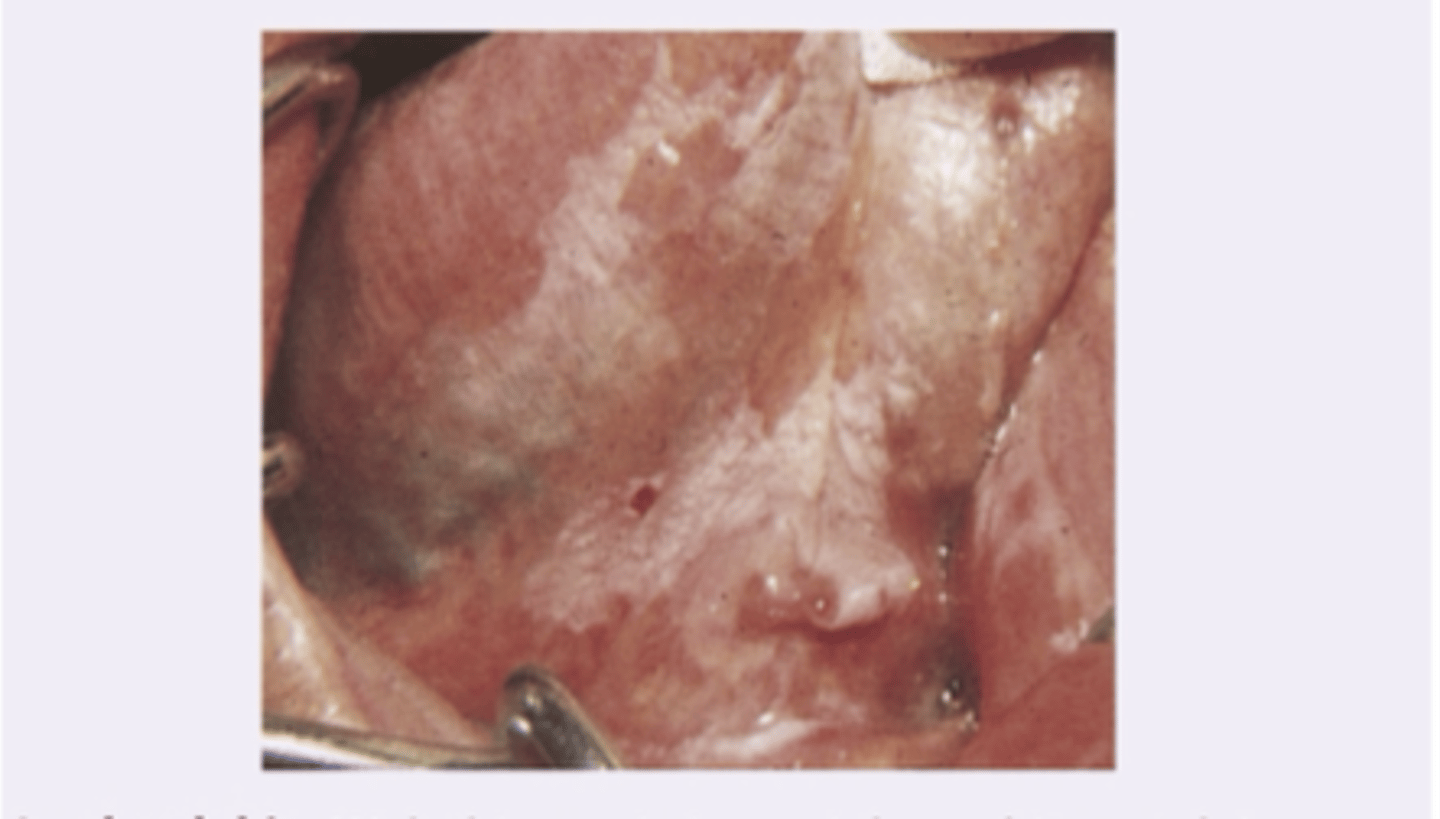
Raises the possibility of squamous cell carcinoma
Leukoplakia clinical significance
Carcinoma of the floor of the mouth
Diagnosis?
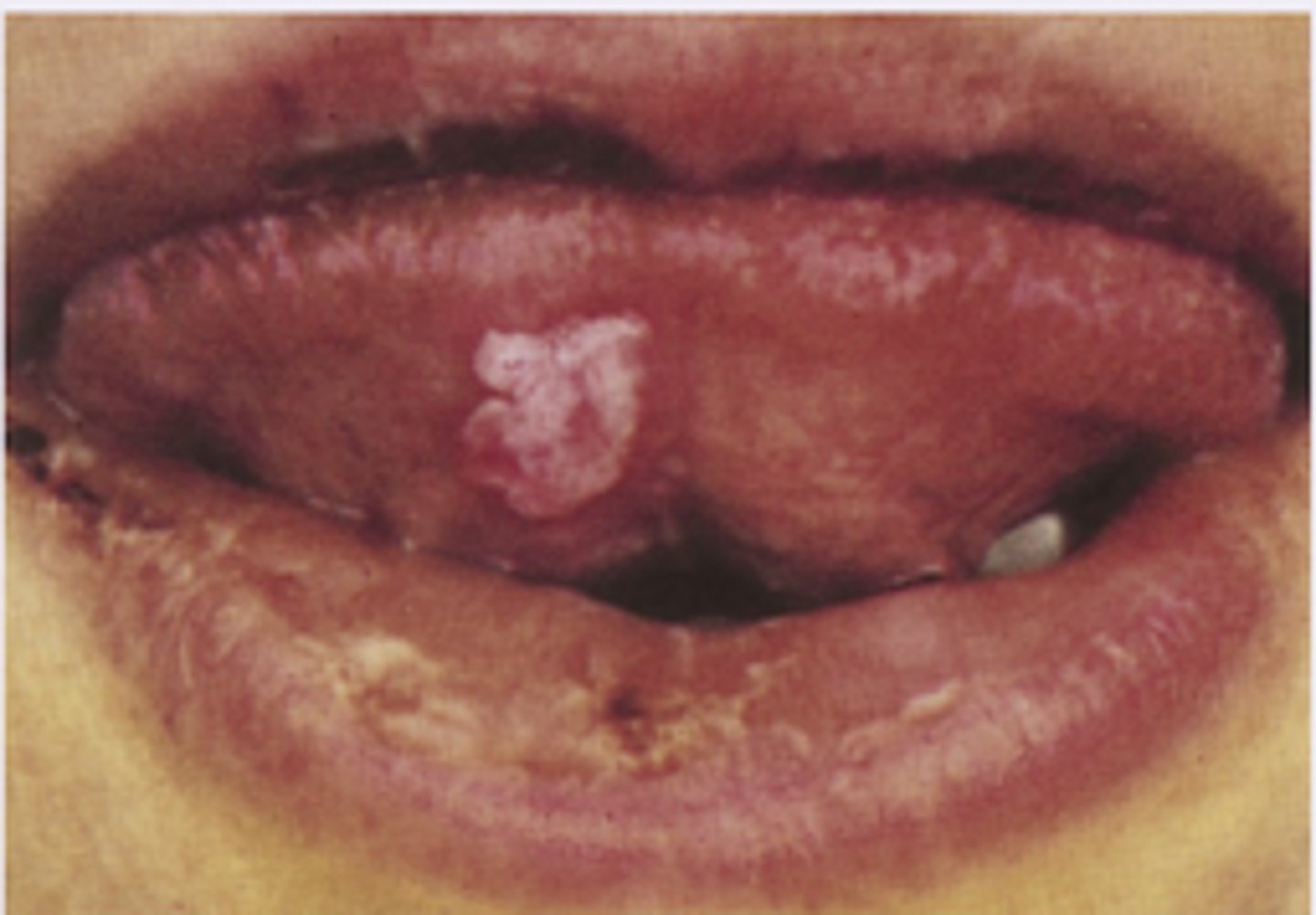
Canker sore
Diagnosis?
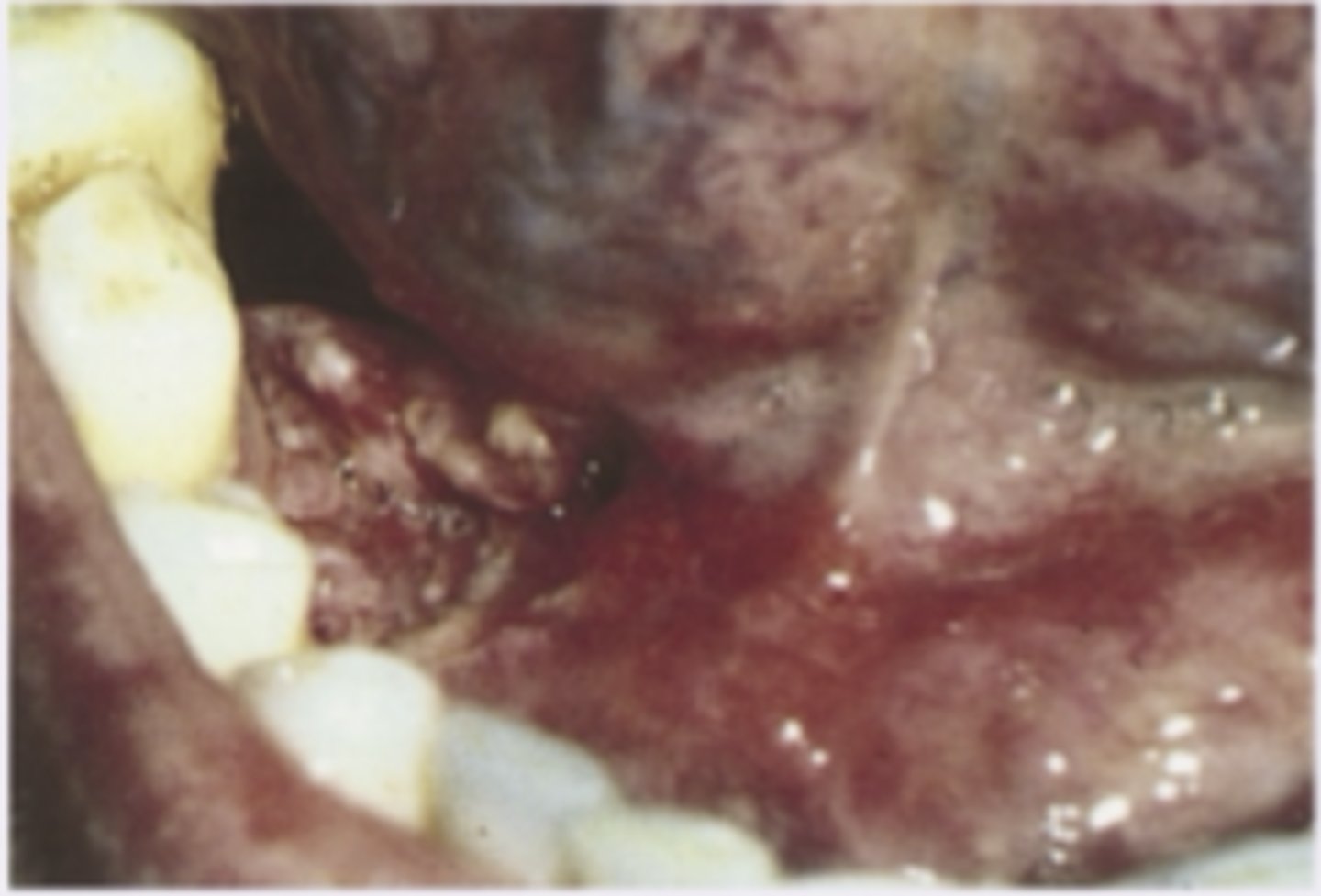
Mucous patch of syphilis
Diagnosis?
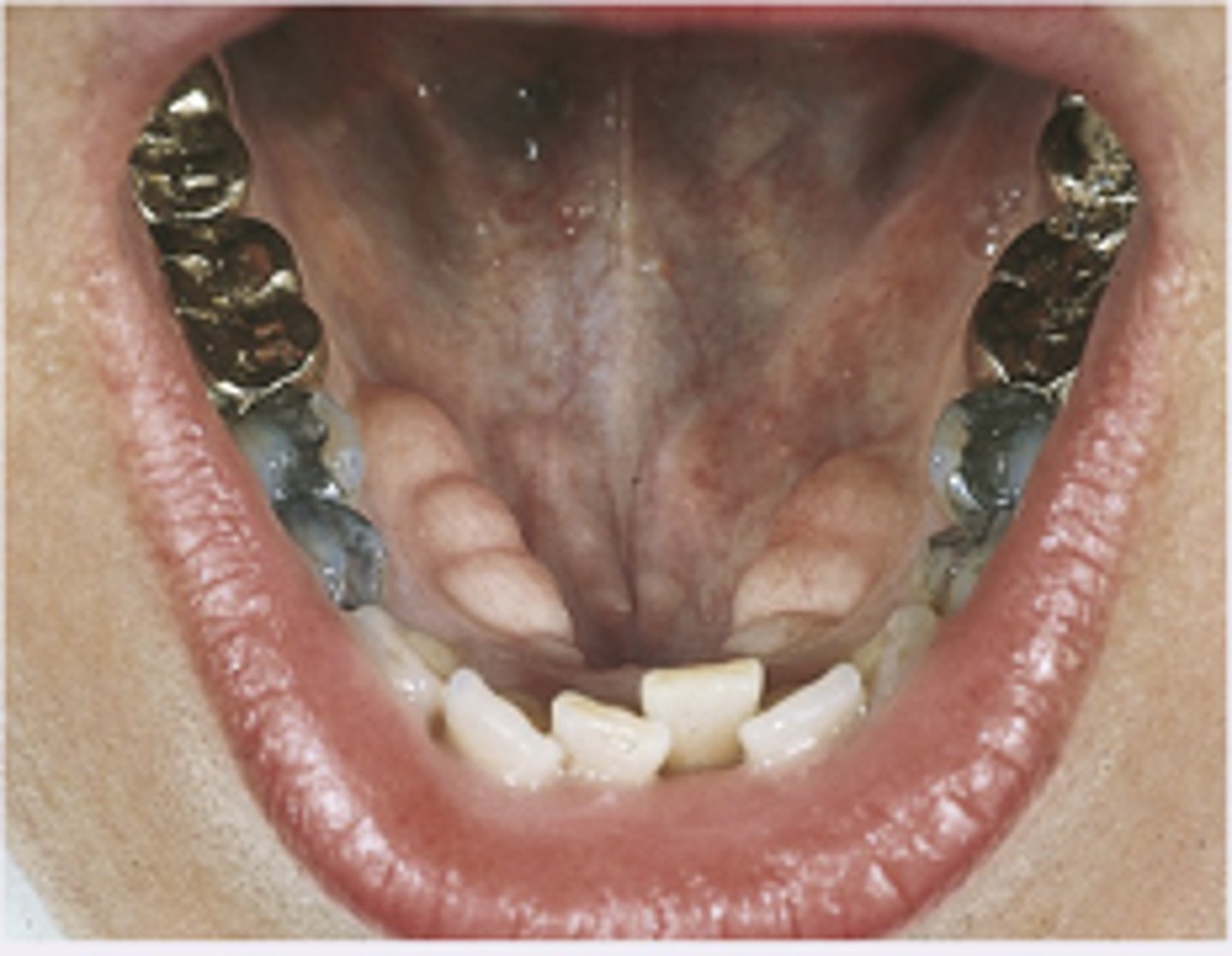
Tori Mandibularis
Diagnosis?
Geographic tongue: benign
Diagnosis?
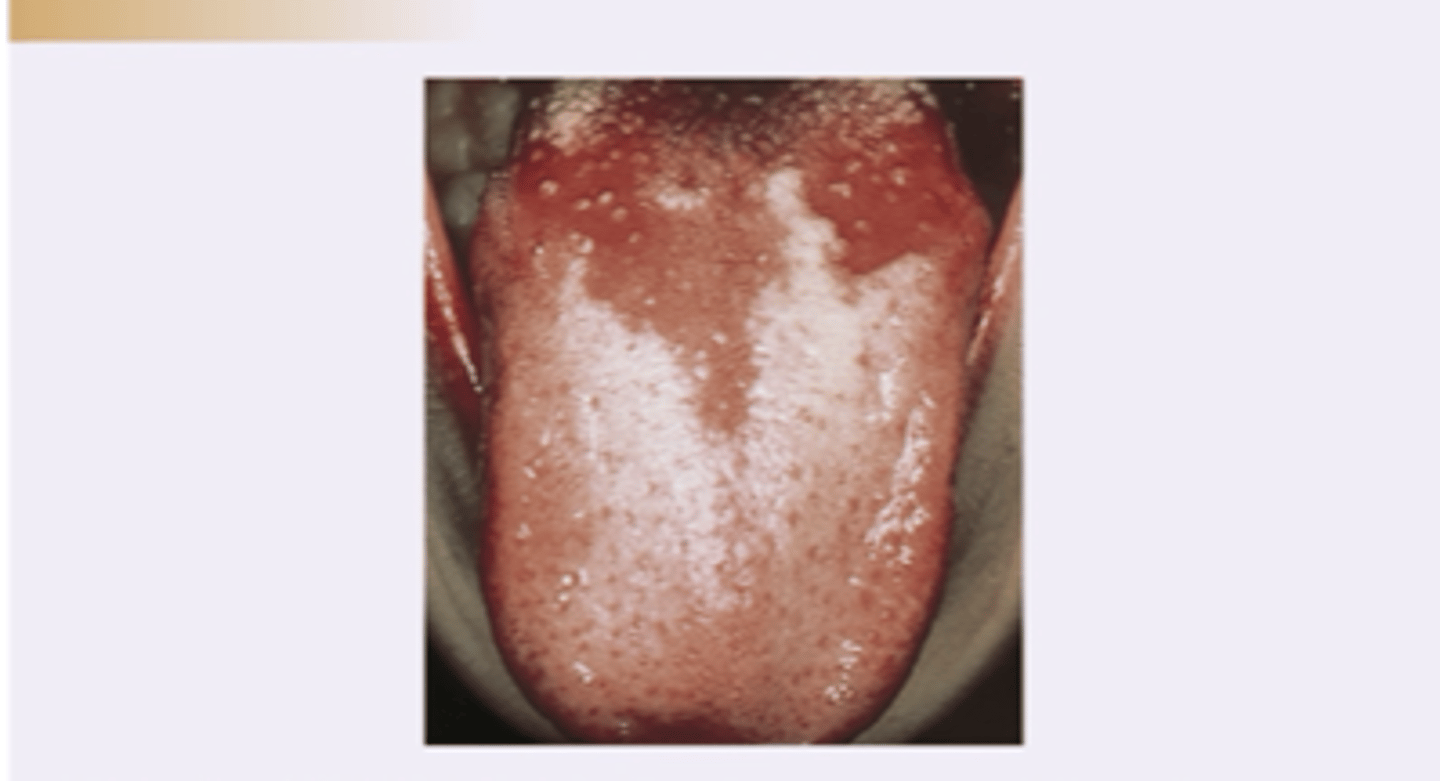
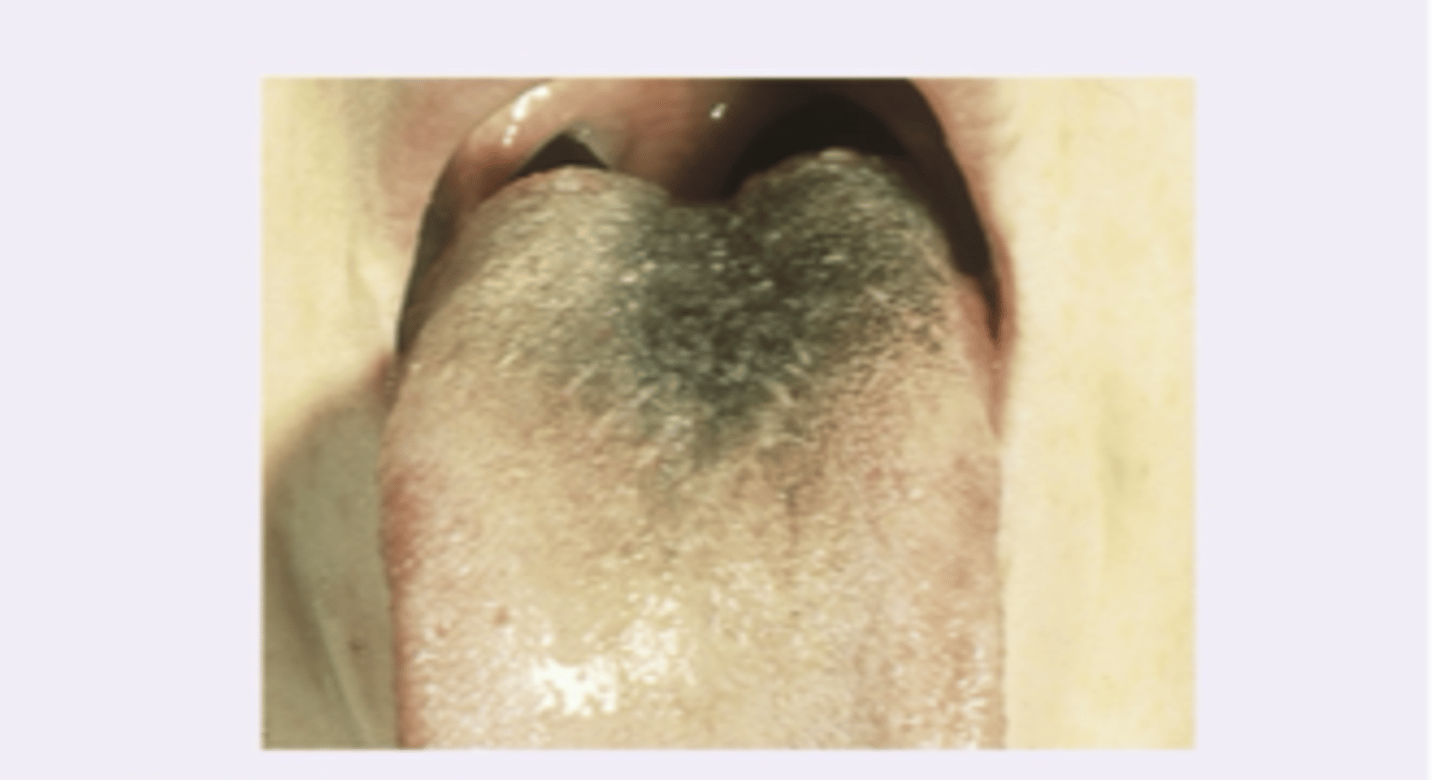
Black hairy tongue
Diagnosis?
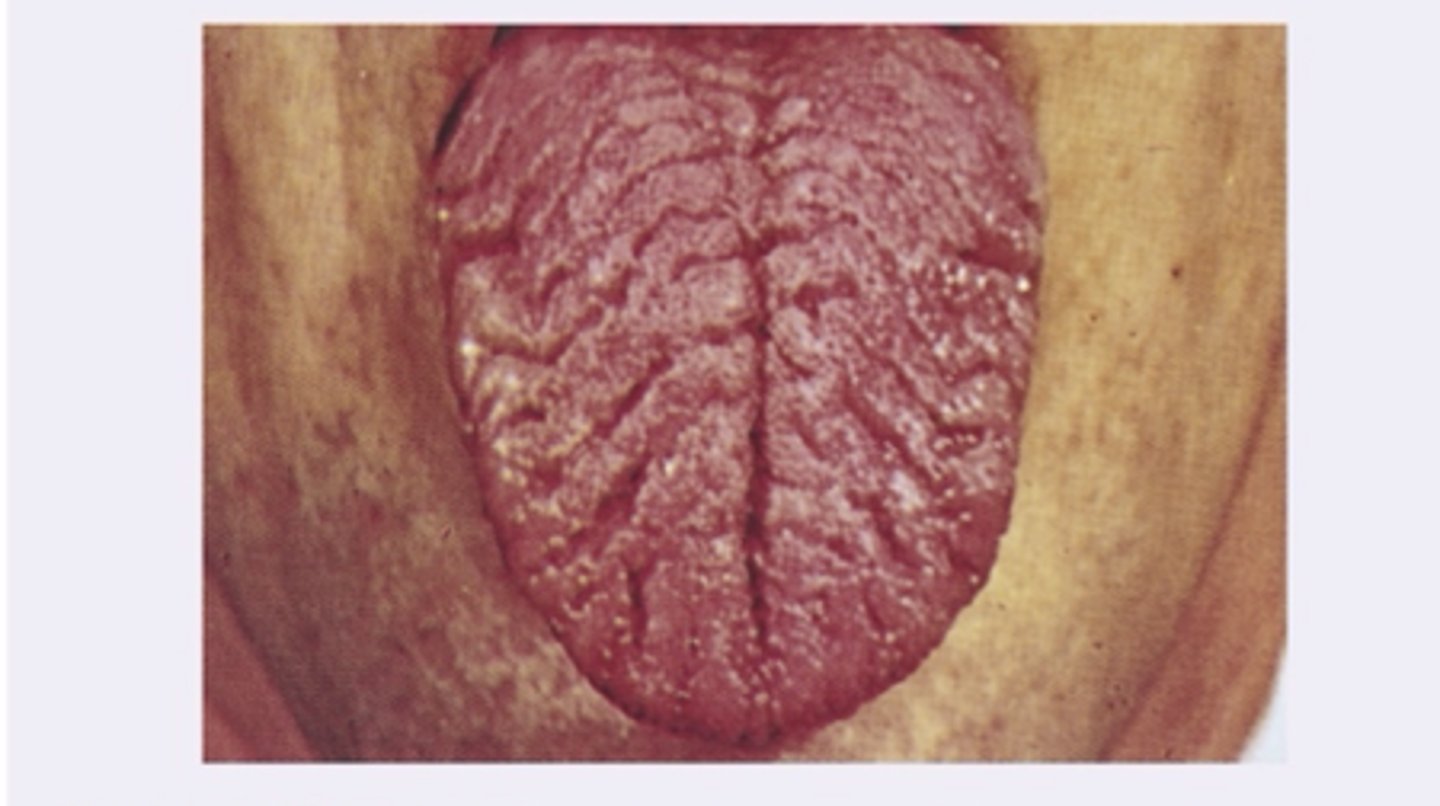
Fissured tongue
Diagnosis?
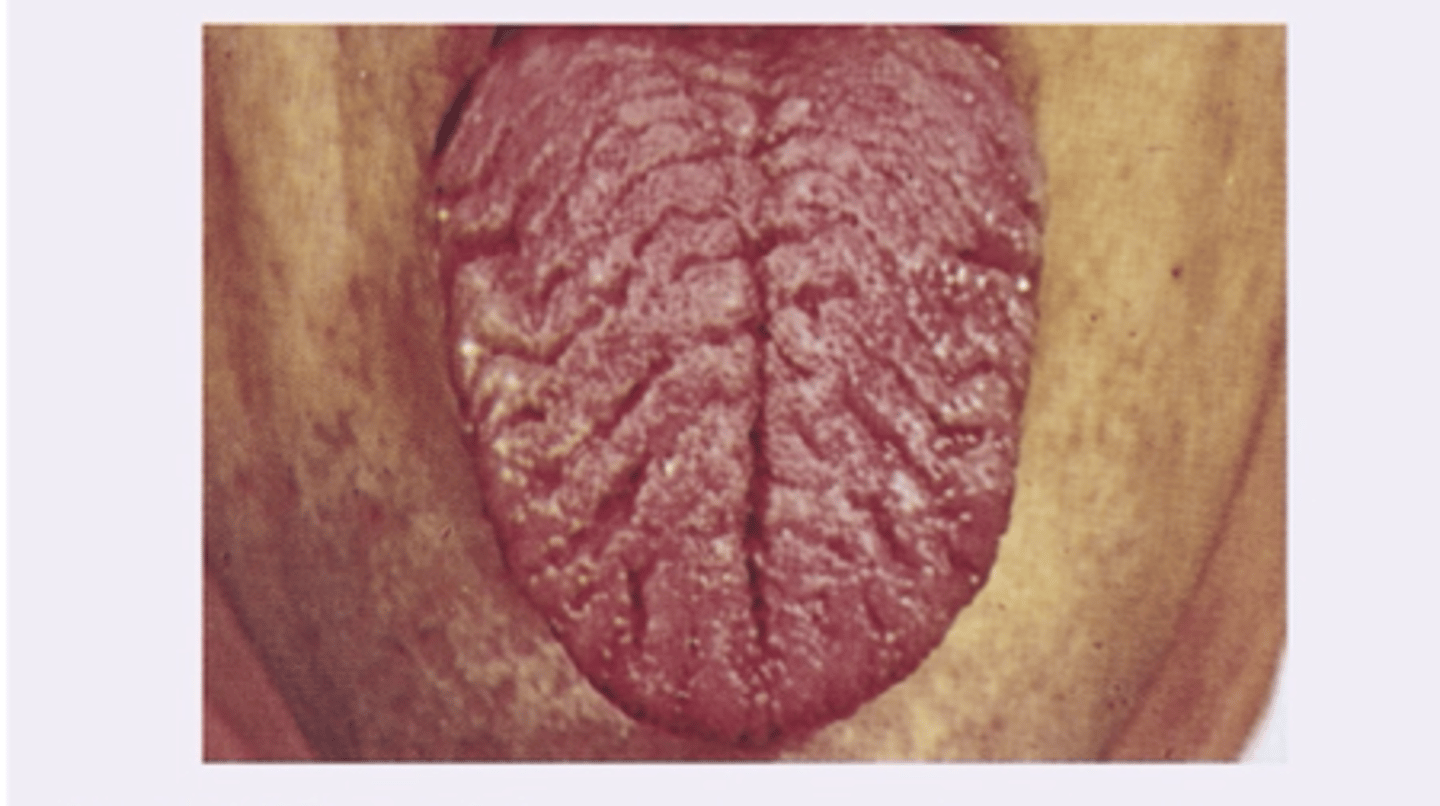
Geriatric
Fissured tongue is common in _____ patients
Smooth glossitis
Diagnosis?
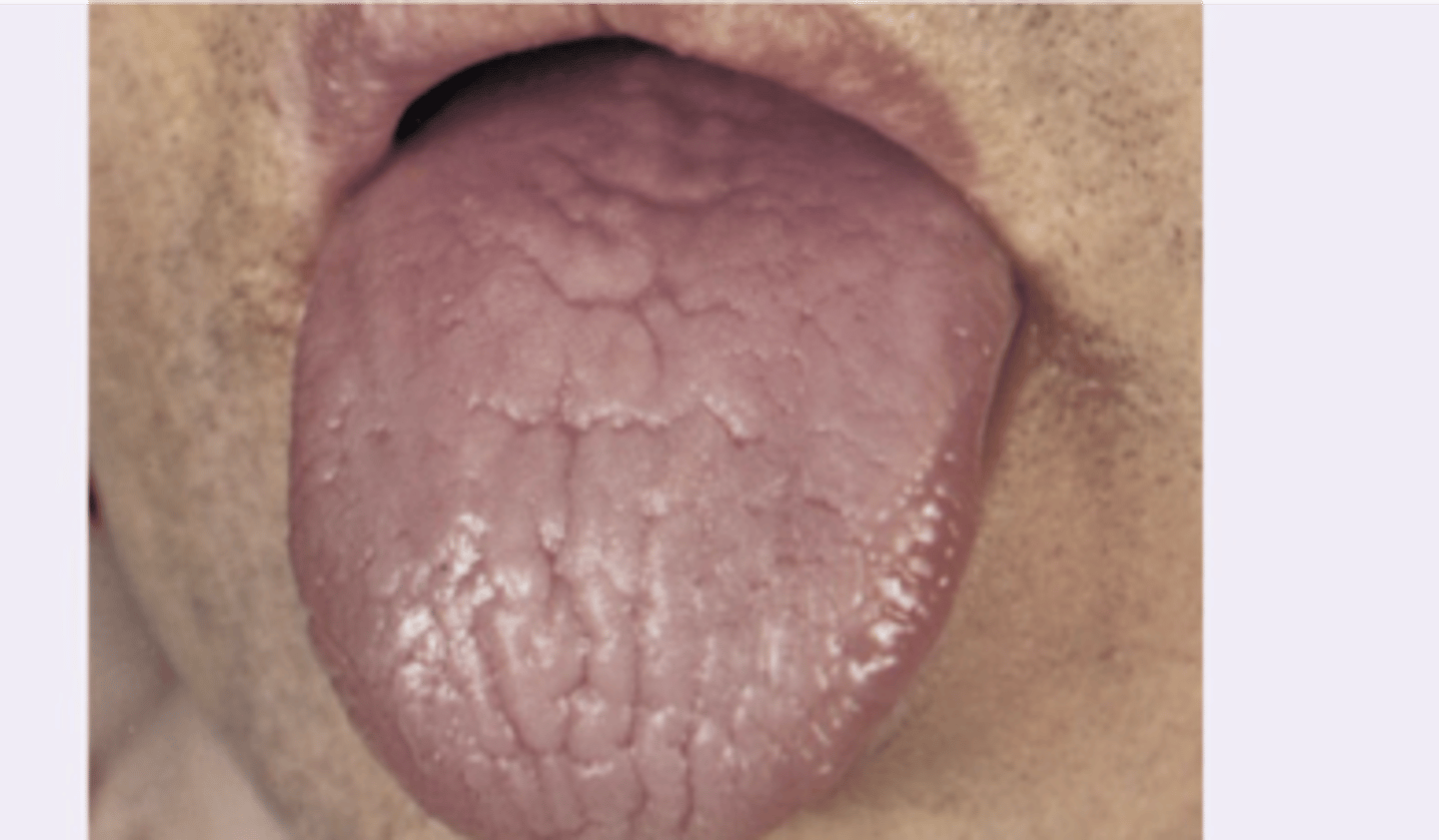
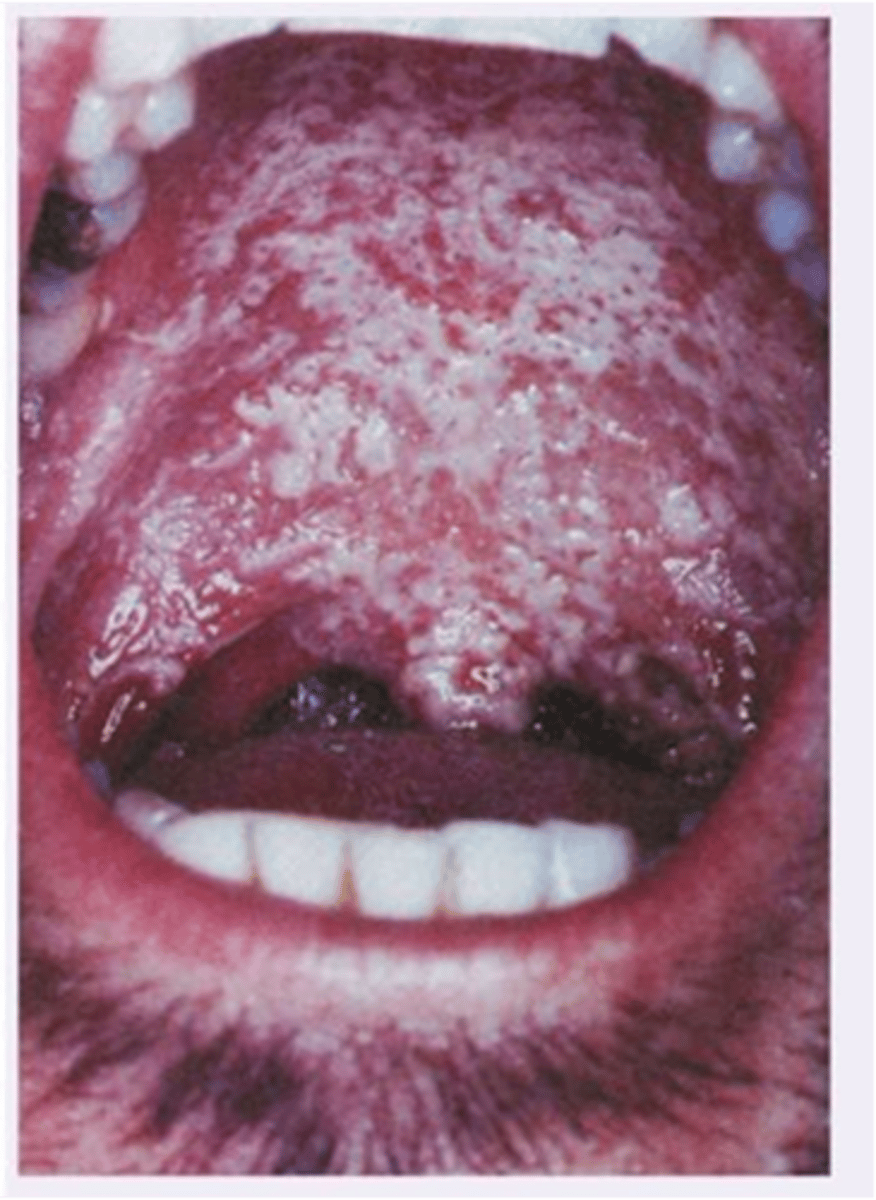
Hairy leukoplakia
Diagnosis?
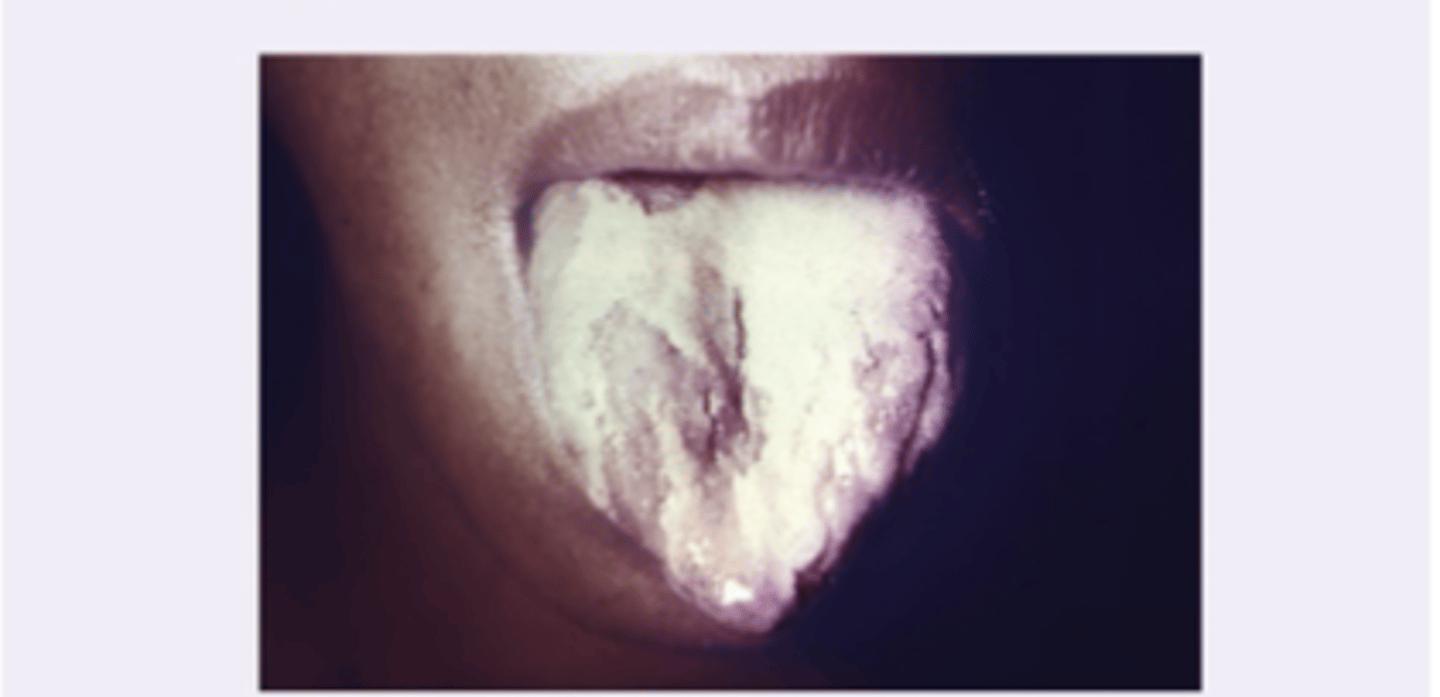
Oral cancer
- Cancer involving the oral cavity or related structures
Diagnosis?
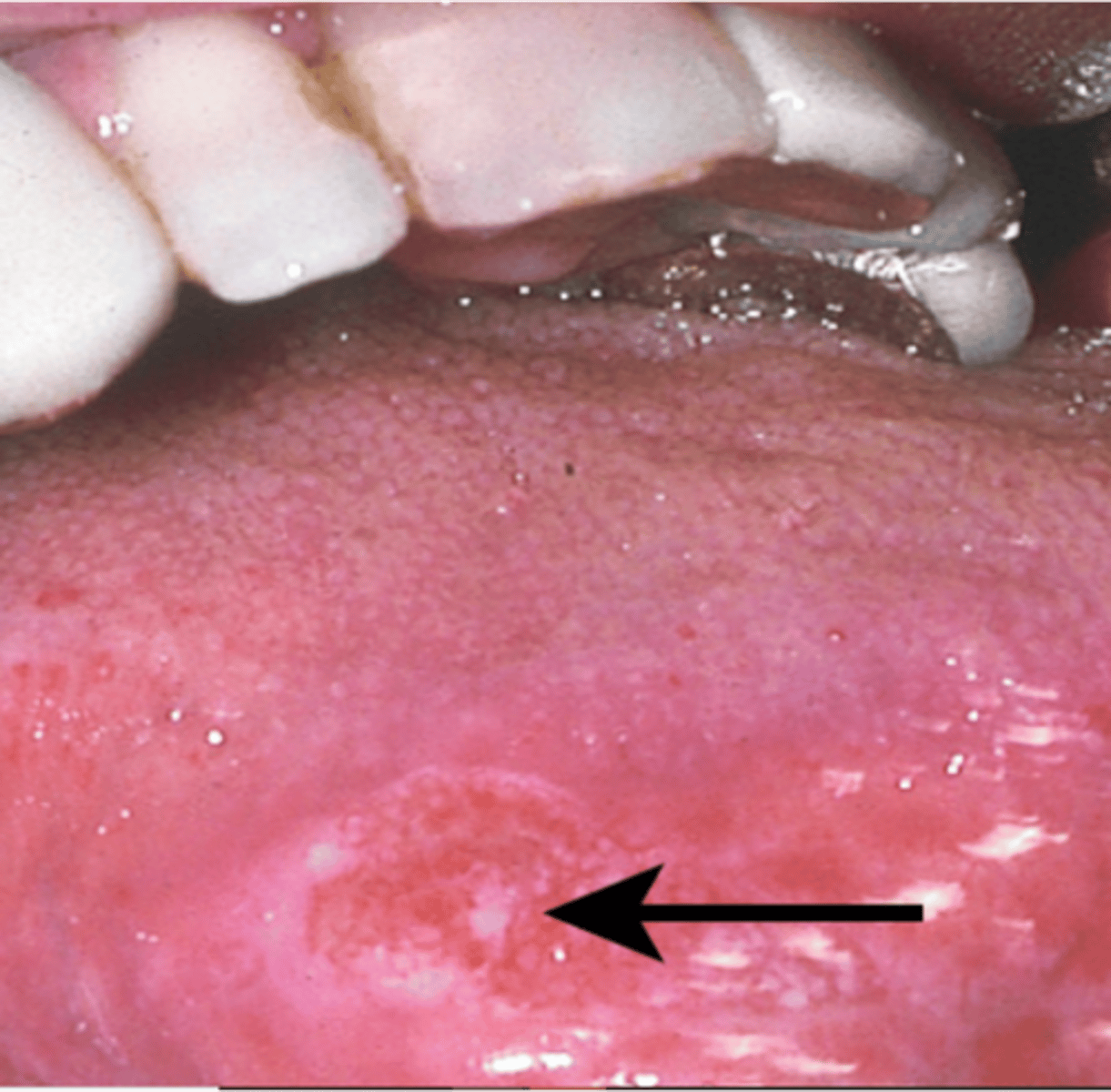
Referral to oncology/EENT
Oral cancer recommendations?
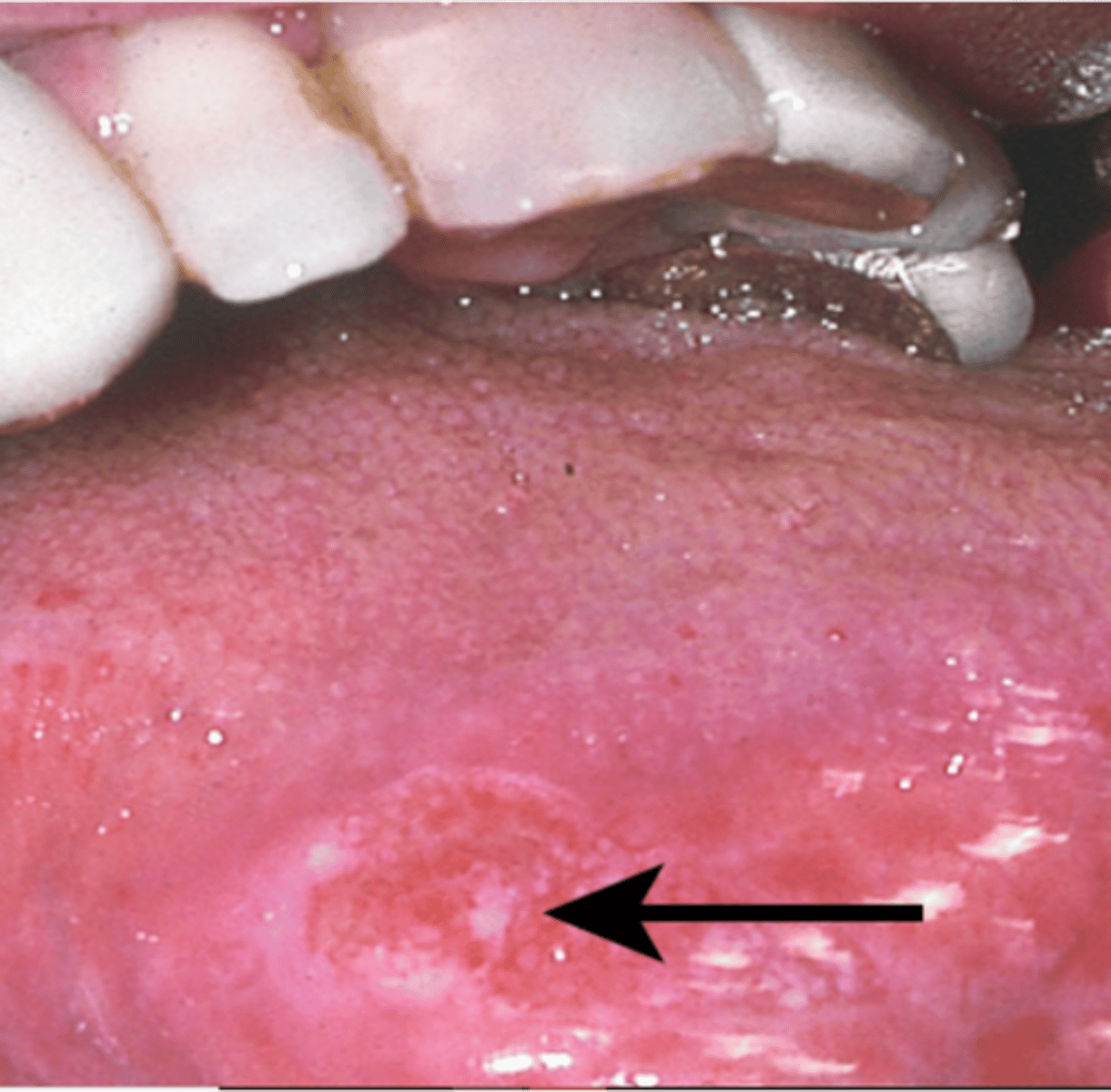
Squamous cell
_____ is the most common form of oral cancer
Basal layer, oral mucosa
Oral cancer originates in the _____ or _____
Periodontitis disease
- Chronic infection of the gums, bones, and other tissues that support and surround the teeth
- Plaque builds up
- Gums swell
- Bone loss
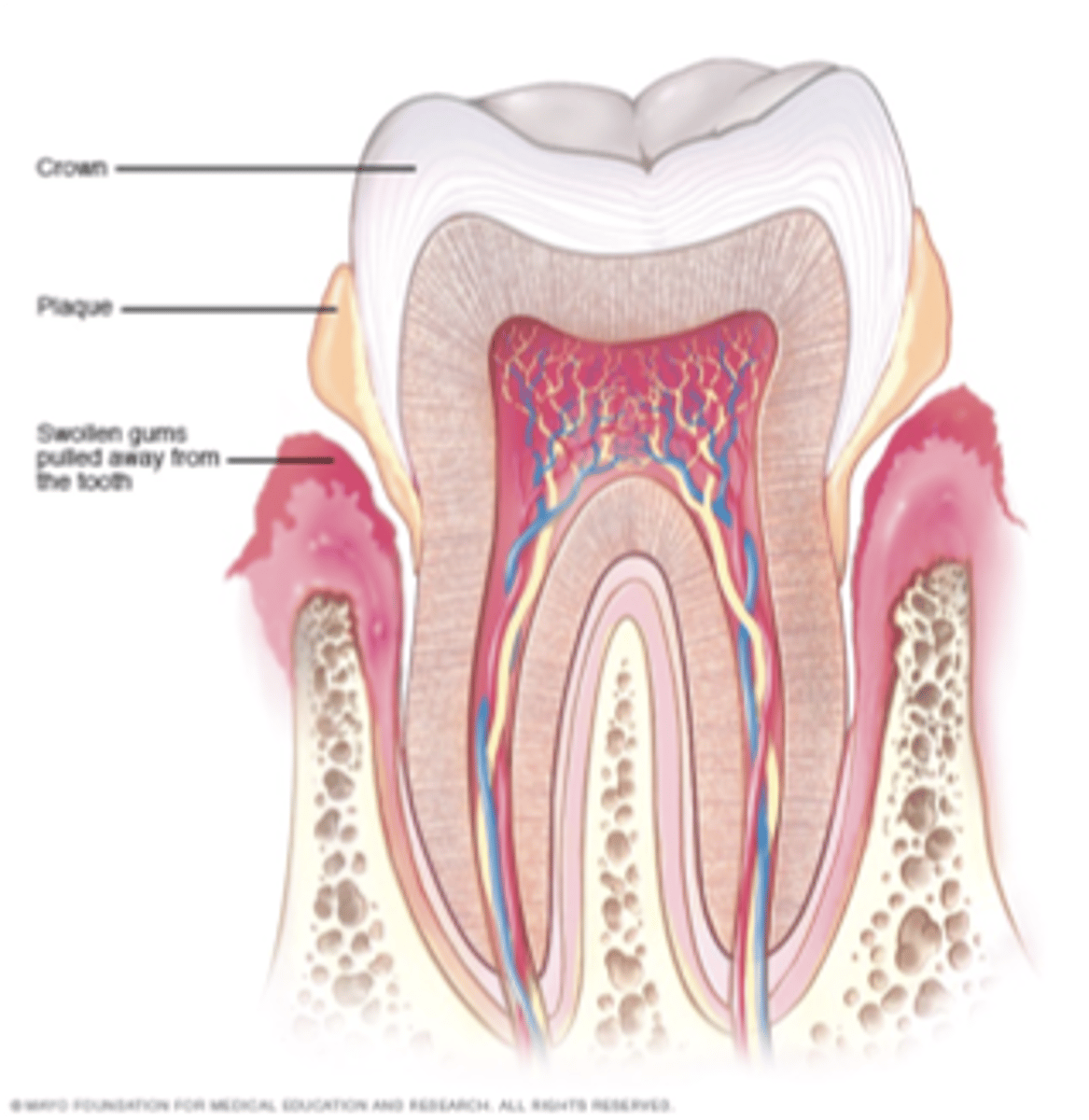
- Bleeding gums
- Swollen puffy gums
Periodontitis disease signs
Dental appointment
Periodontitis disease treatment
- Attrition of teeth
- Recession of gums
Diagnosis?
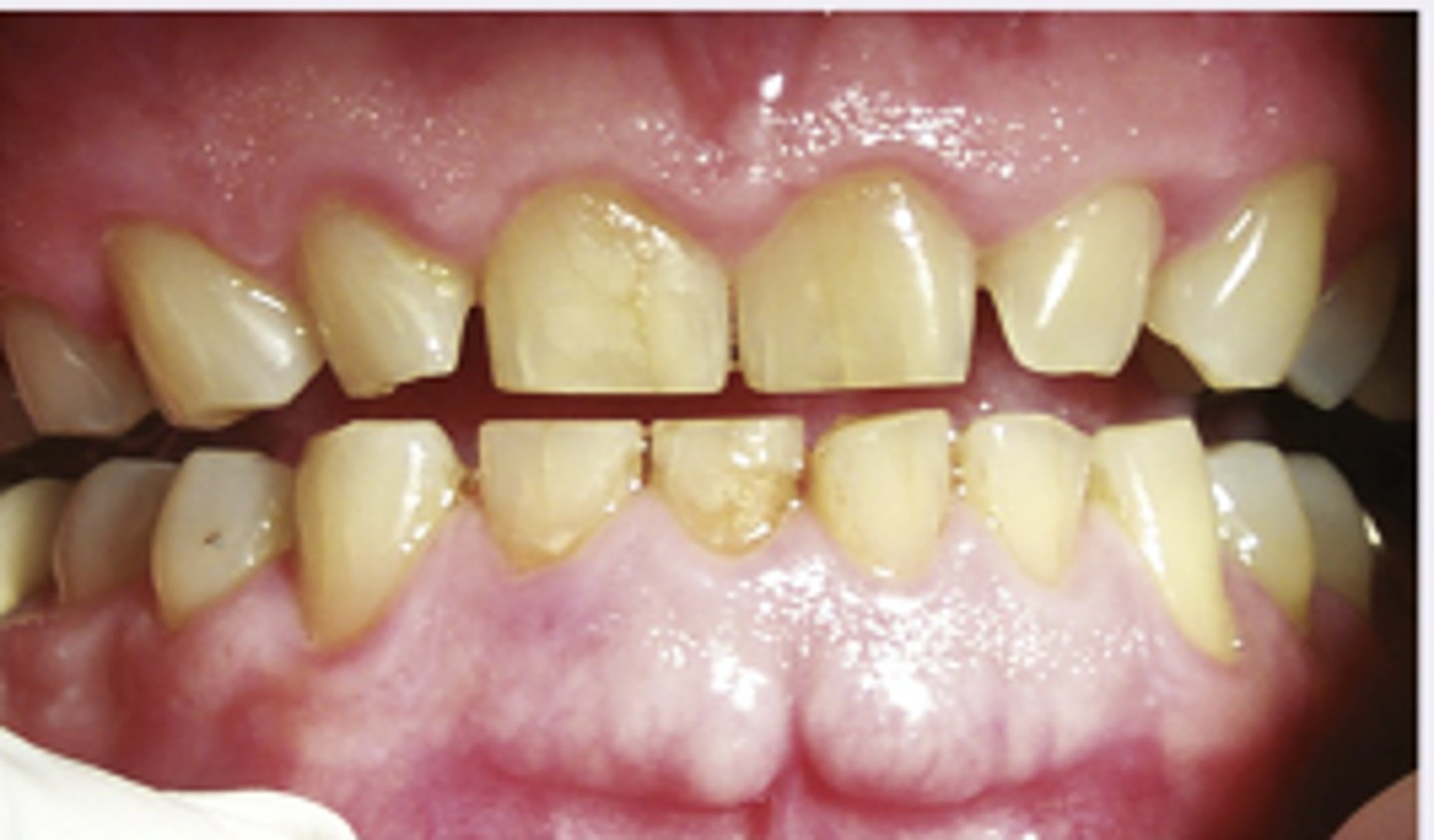
Erosion of teeth
Diagnosis?
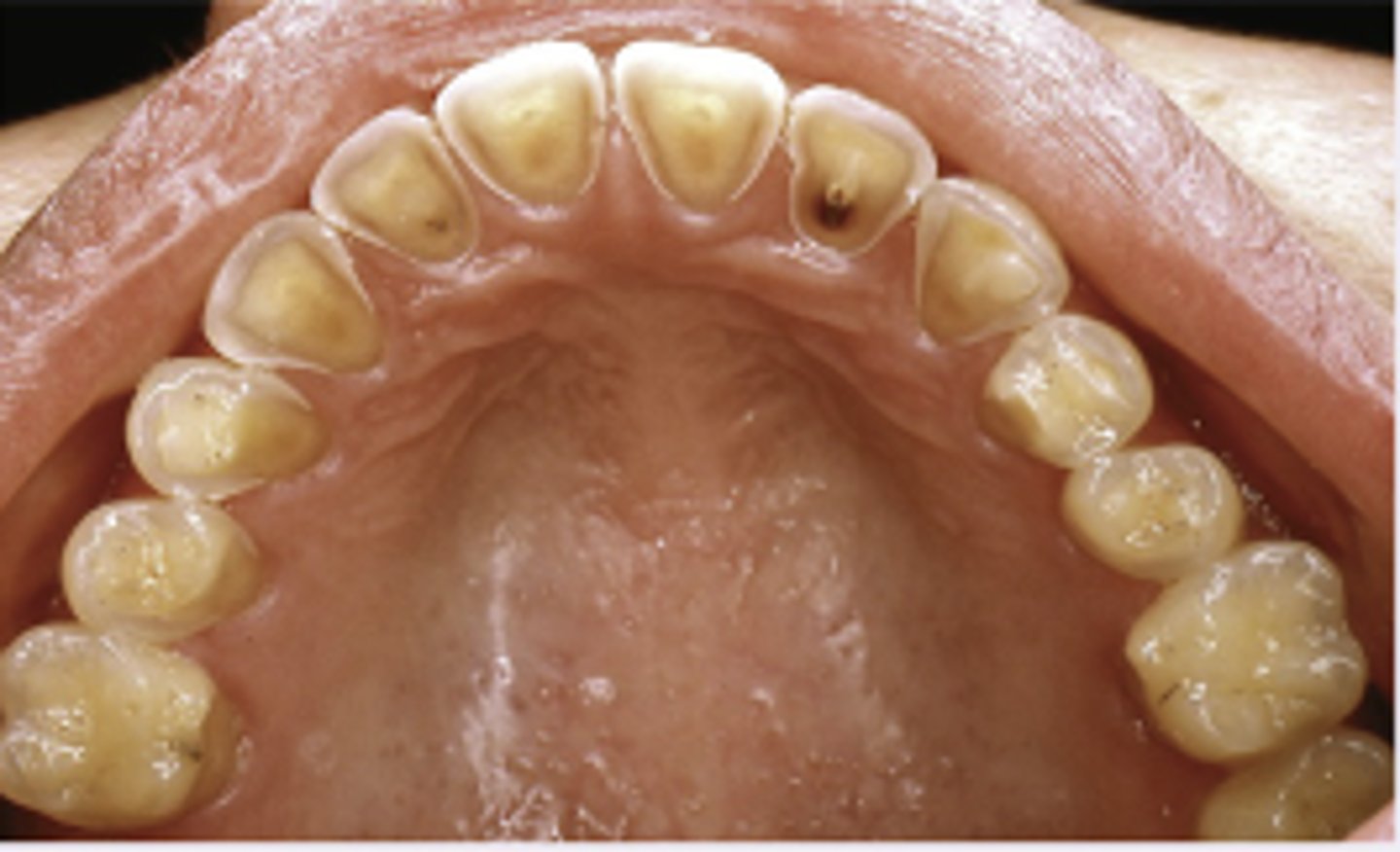
Abrasion of teeth with notching
Diagnosis?
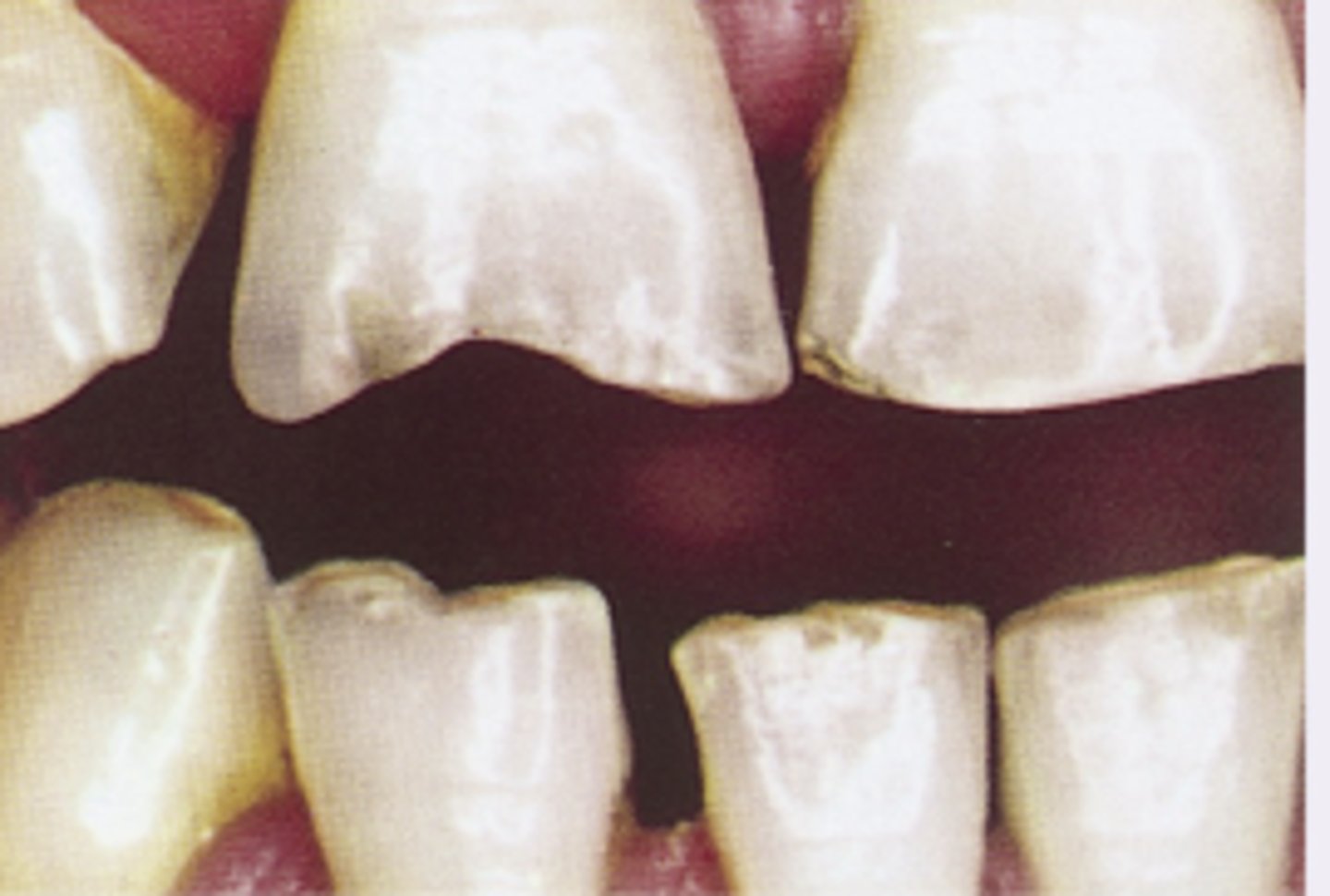
Hutchinson teeth in congenital syphilis
Diagnosis?
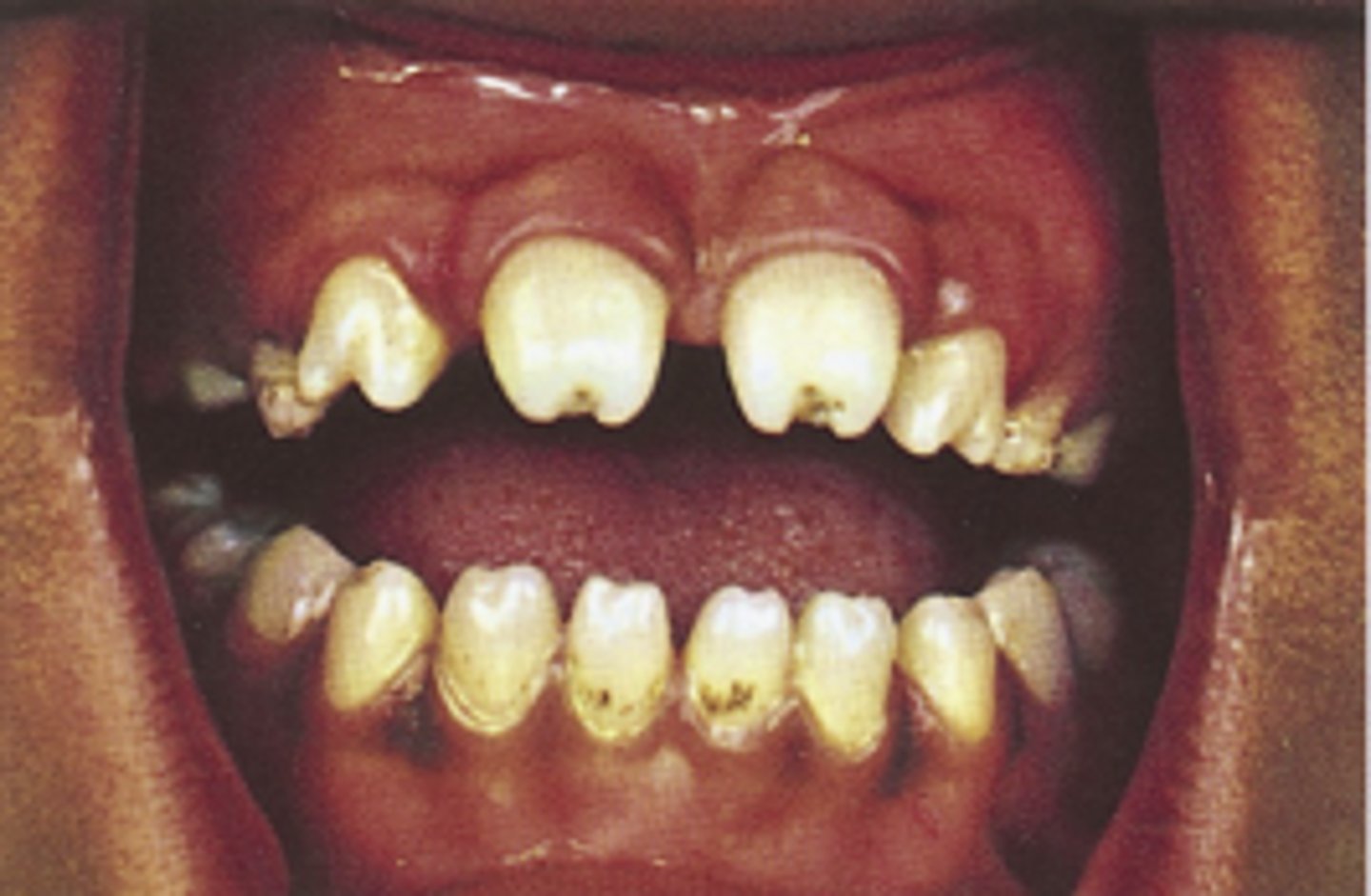
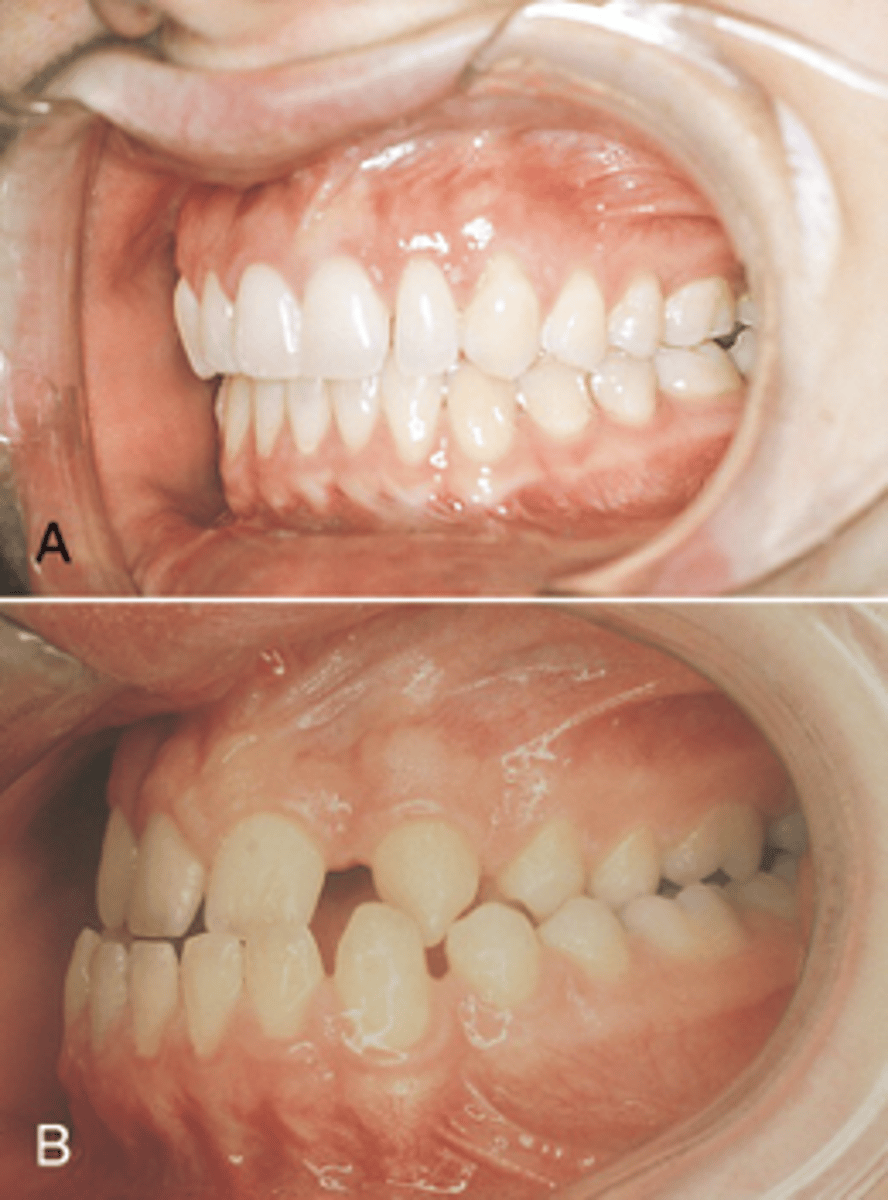
Malocclusion
- Rotated teeth molars aligned
- Lower molars are distally positioned
- Lower molars medially positioned
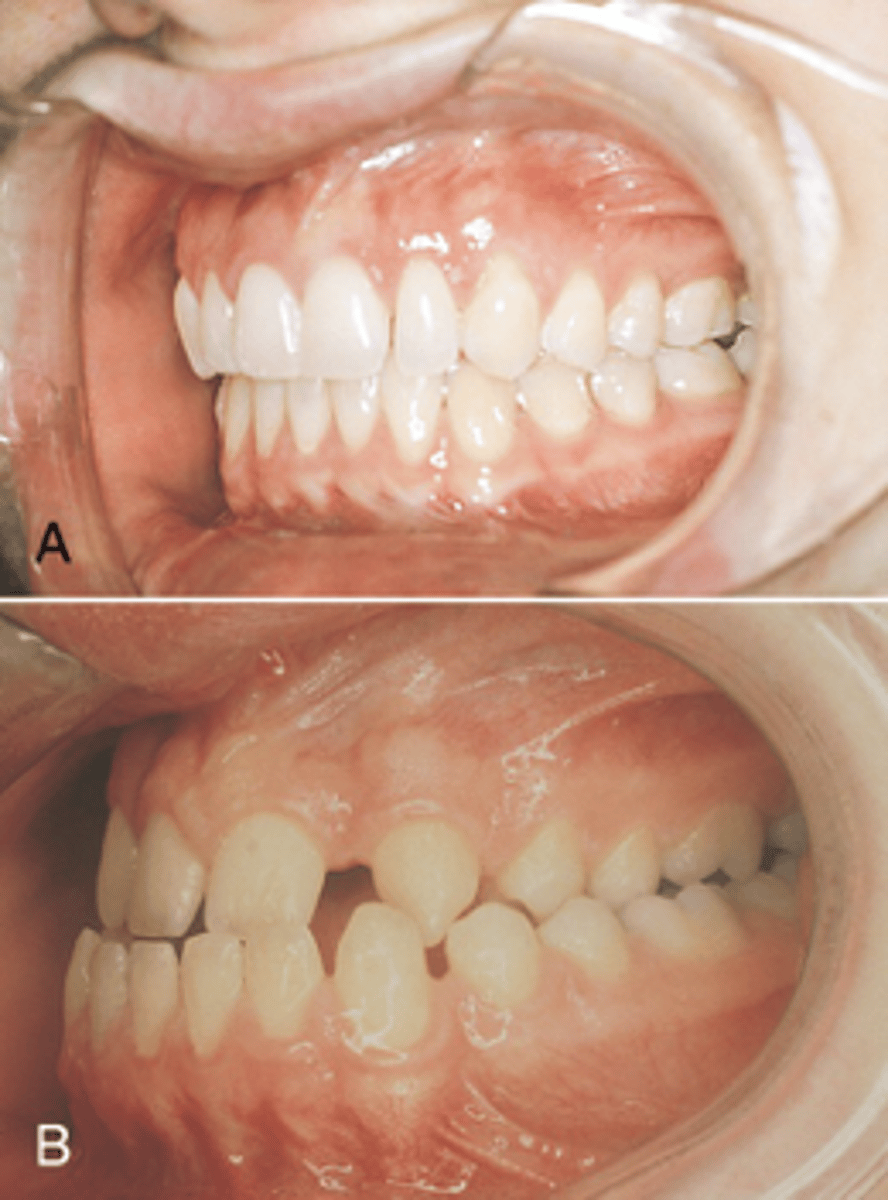
Orthodontics
Malocclusion treatment
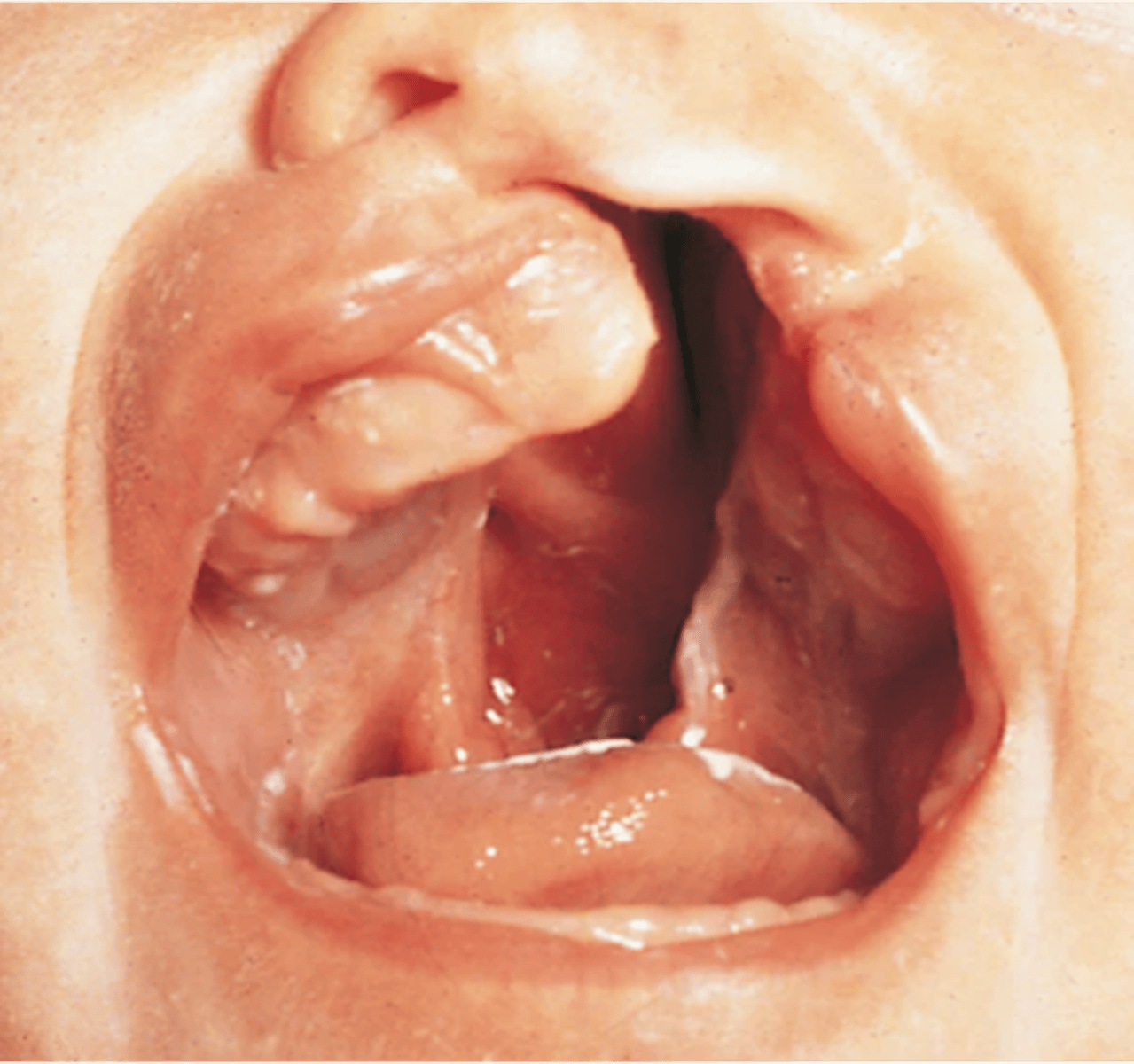
Cleft palate and lip
- Failure of the palate to close prior to 12th week
- 1/1000 births incidence
- Seen in genetic conditions
- Mothers use of alcohol, anticonvulsants
- Diabetes, folate deficiency, smoking
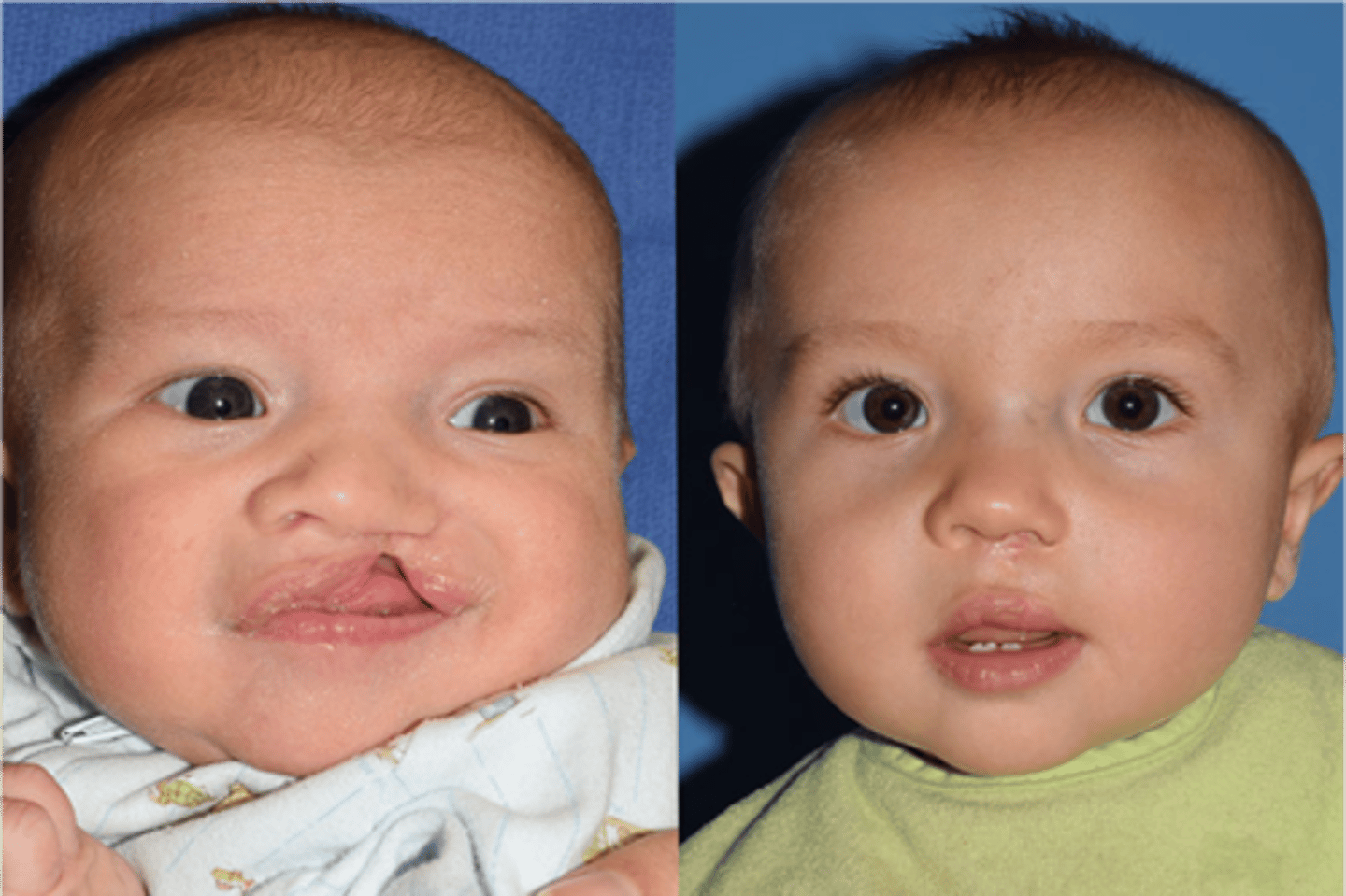
Cranio facial surgery
Cleft palate and lip treatment
Labyrinthitis
Which condition below has a hearing loss as part of the clinical presentation?
- Vertigo from BPPV
- Labyrinthitis
- Vestibular neuritis
- All have hearing loss