Topic 12 - Surface Water and Ground Water
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what are some examples of surface water resources?
lakes, glaciers, oceans, ice and snow, wetlands
what is infiltration?
the water soaks into the ground, this is the major way that ground water is refilled
what is runoff?
the water flows across the surface, the water doesn’t soak in
what is earths largest lake?
Caspian Sea
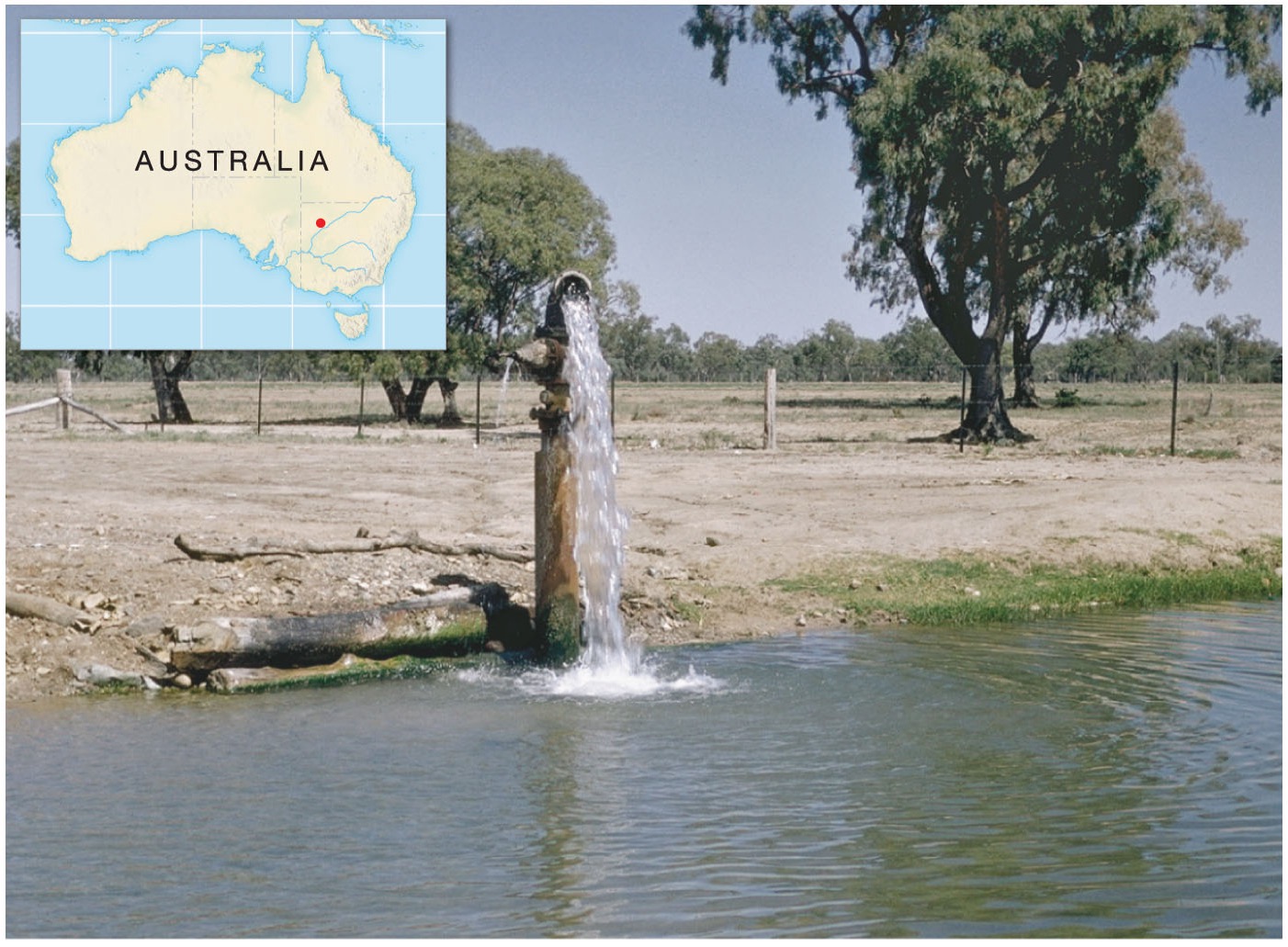
Why do we use groundwater?
We turn to groundwater because much of the surface freshwater supply is inaccessible to us
what do we use groundwater for?
hydroelectric power, drinking water, irrigation, industrial needs
what happens if ground water is overused?
it causes ground water mining
what is ground water mining?
describes the extraction of ground water at a rate faster than it can be recharged
what are the negative effects of groundwater mining?
land will subside (sink down/collapse), rivers and streams nearby can dry up, saltwater can intrude (flow up into the dry river beds), need to dig the wells deeper
where to go in times of water shortages?
Ground water offices are the best resource
what is the zone of aeration?
the pore spaces are filled with air
what is the zone of saturation?
the pore spaces are filled with water
what is a water table?
the line separating the two zones (aeration and saturation)
how does the shape of the water table reflect the surface topography?
it follows the curves of the land, high under hills and lower in the valleys
when the water table is at the surface what forms?
swamps
when the water table is above the surface what forms?
lakes
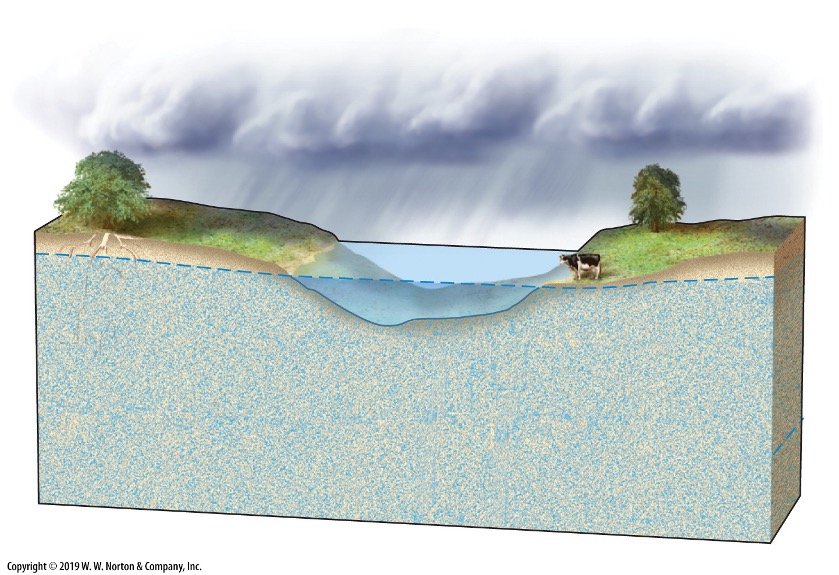
what is the position of the water table for a lake?
water table intersects land and is closed in on all sides, the water forms a lake
what is the position of the water table for a stream?
water table intersects land on one side only
what is the position of the water table for a spring?
forms when the water table comes out at the boundary between an impermeable layer of rock and a permeable layer
how is water able to flow through rock and soil layers?
There must be spaces between the grains to allow this happen, or there must be cracks in the rock itself
what is porous?
the material has holes throughout
what is permeable?
the holes in the material are connected
what does “high porosity but low permeability” mean?
lots of tiny holes, water does not flow freely
what does “High porosity and high permeability”?
lots of tiny holes, water flows freely ex: sandstone
How does GW move?
gravity
How do you get GW out of the ground?
you dig a well
what are the requirements for a good well?
it must be deep enough to hit the dry season water table and the rock material the well is drilled into must be porous and permeable
what is an aquifer?
a rock body that holds and carries water - usually a large sandstone formation
what is the name of the famous U.S aquifer?
Ogallalla
why is the ogallalla aquifer famous?
covers across 8 states, scientists think accumulation started about 30,000 years ago (glacial era)
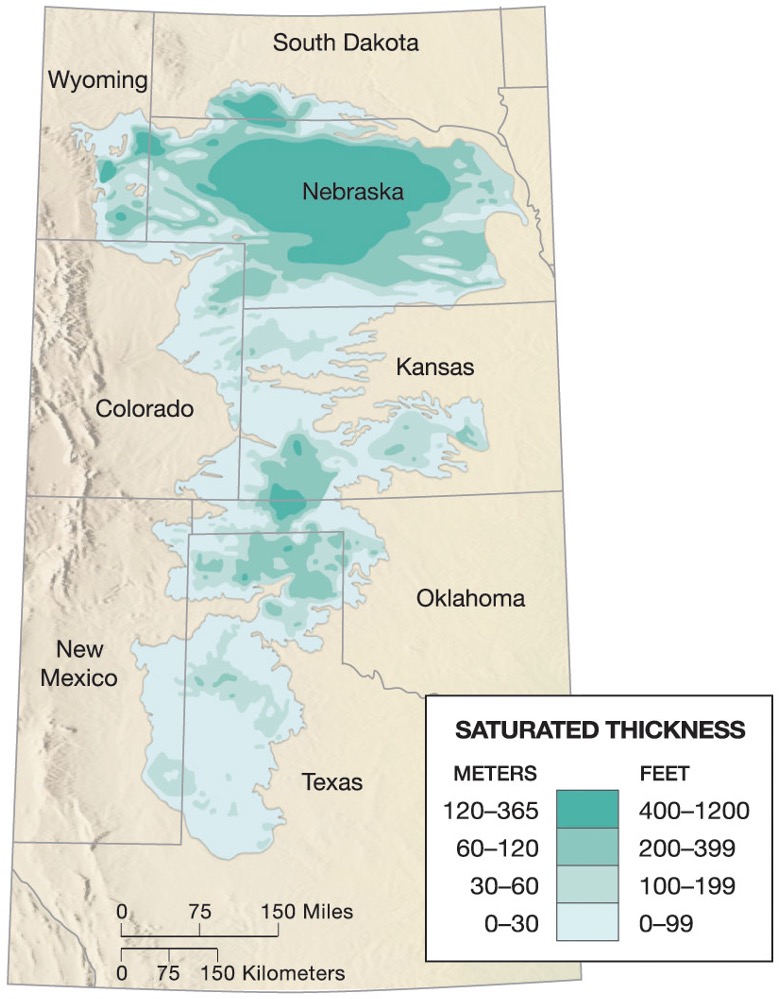
what is the ogallala aquifer initiative?
aims to reduce aquifer water use, improve water quality and enhance the economic viability of croplands and rangelands
what is an aquiclude?
rock body that carries water very slowly or not at all
what is an artesian well(wonderful thing when you are really thirsty)?
the groundwater doesn't need to be pumped out, the water is under great pressure and the pressure pushes the water up and out
