Chapter 17 - Lab
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Forms pathways between the diencephalon, cerebrum, and cerebellum
What is the function of the brain Stem?
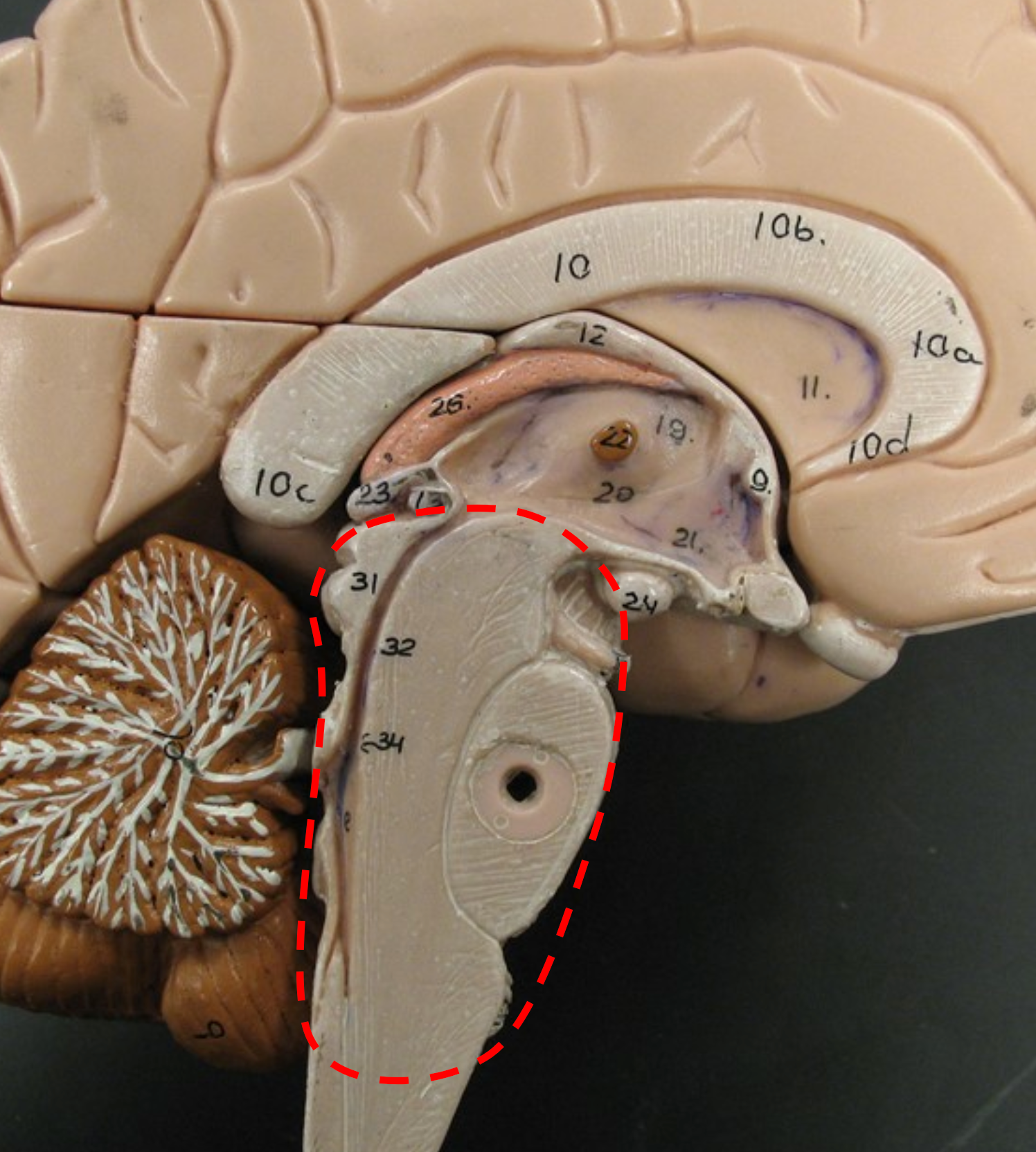
Midbrain
The superior portion of the brain stem, mainly composed of tracts of myelinated axons.
Tectum
The dorsal surface of the midbrain.
Corpora quadrigemina
Four lumps on the tectum of the midbrain.
Superior colliculi
The two superior lumps on the tectum that house reflex centers for head and eye movement.
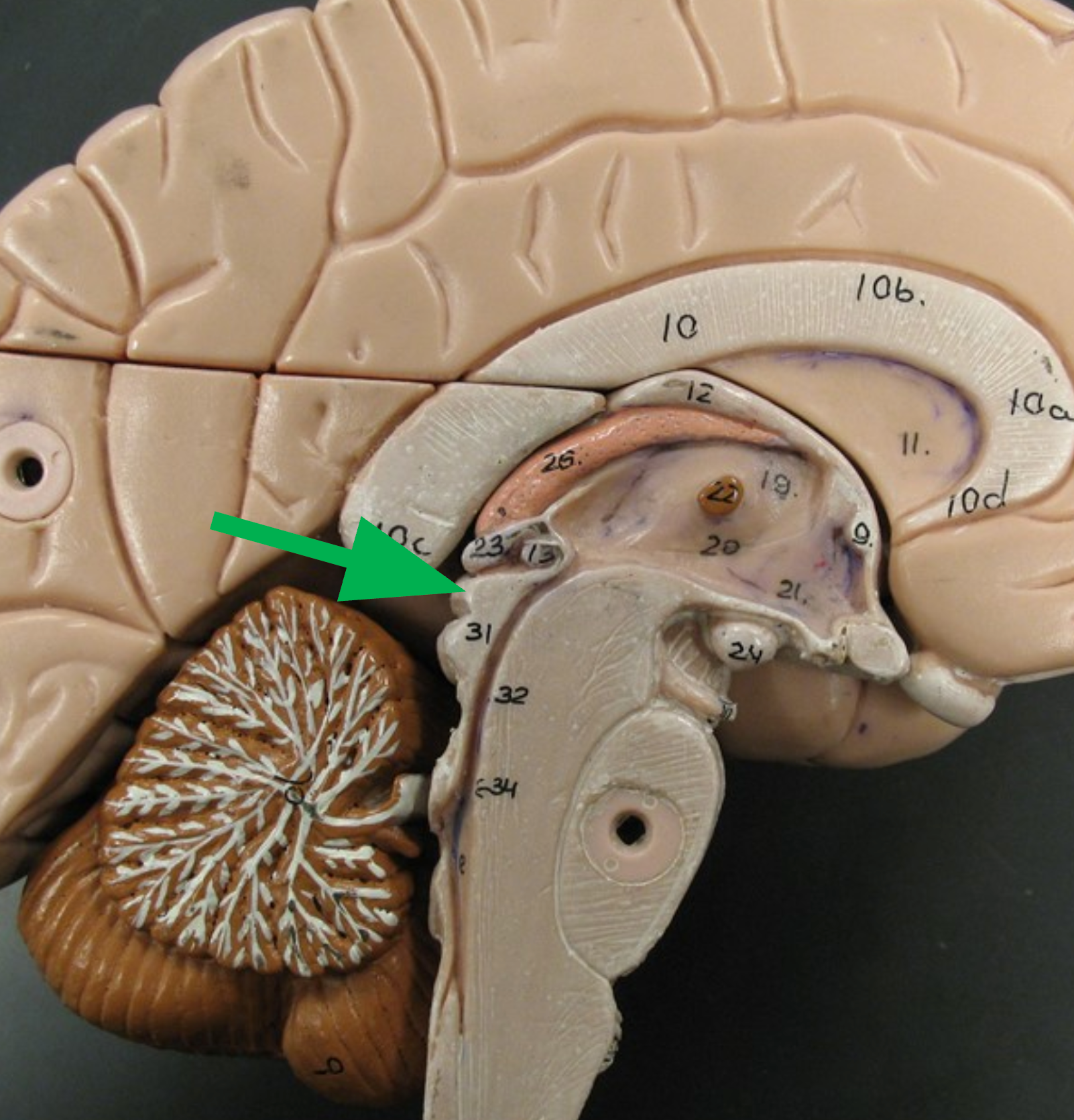
Inferior colliculi
The two inferior lumps on the tectum that house reflex centers responding to startling sounds.
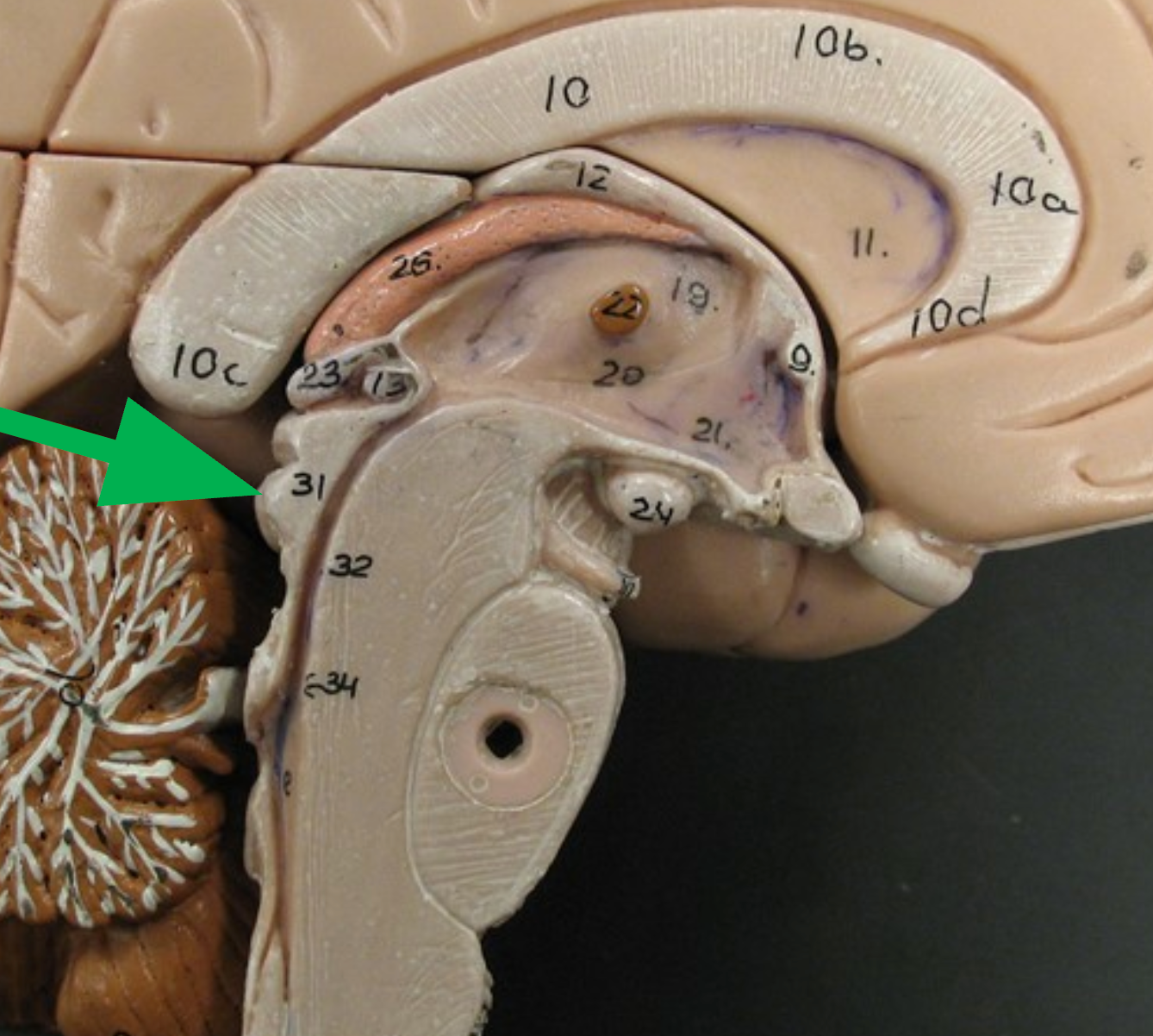
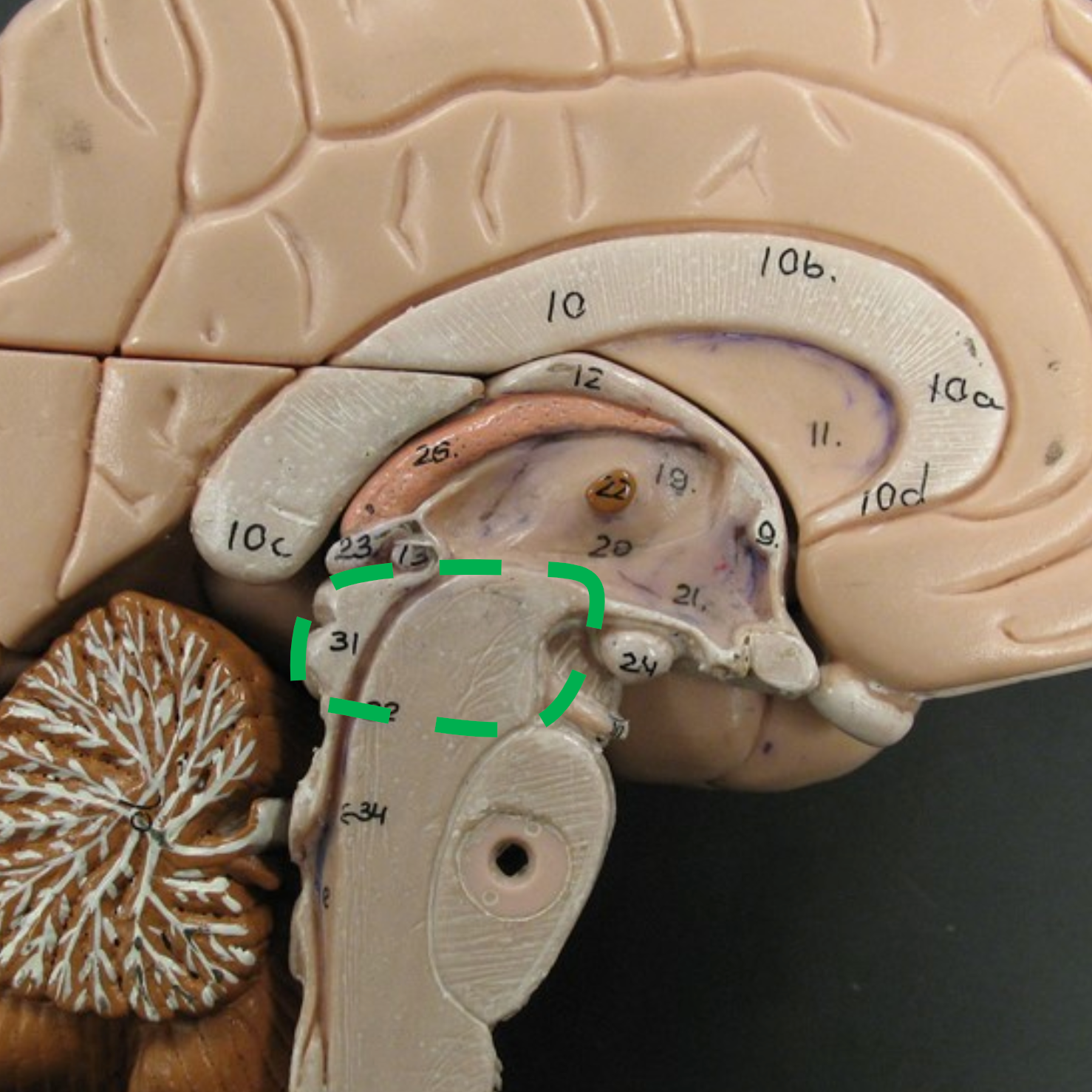
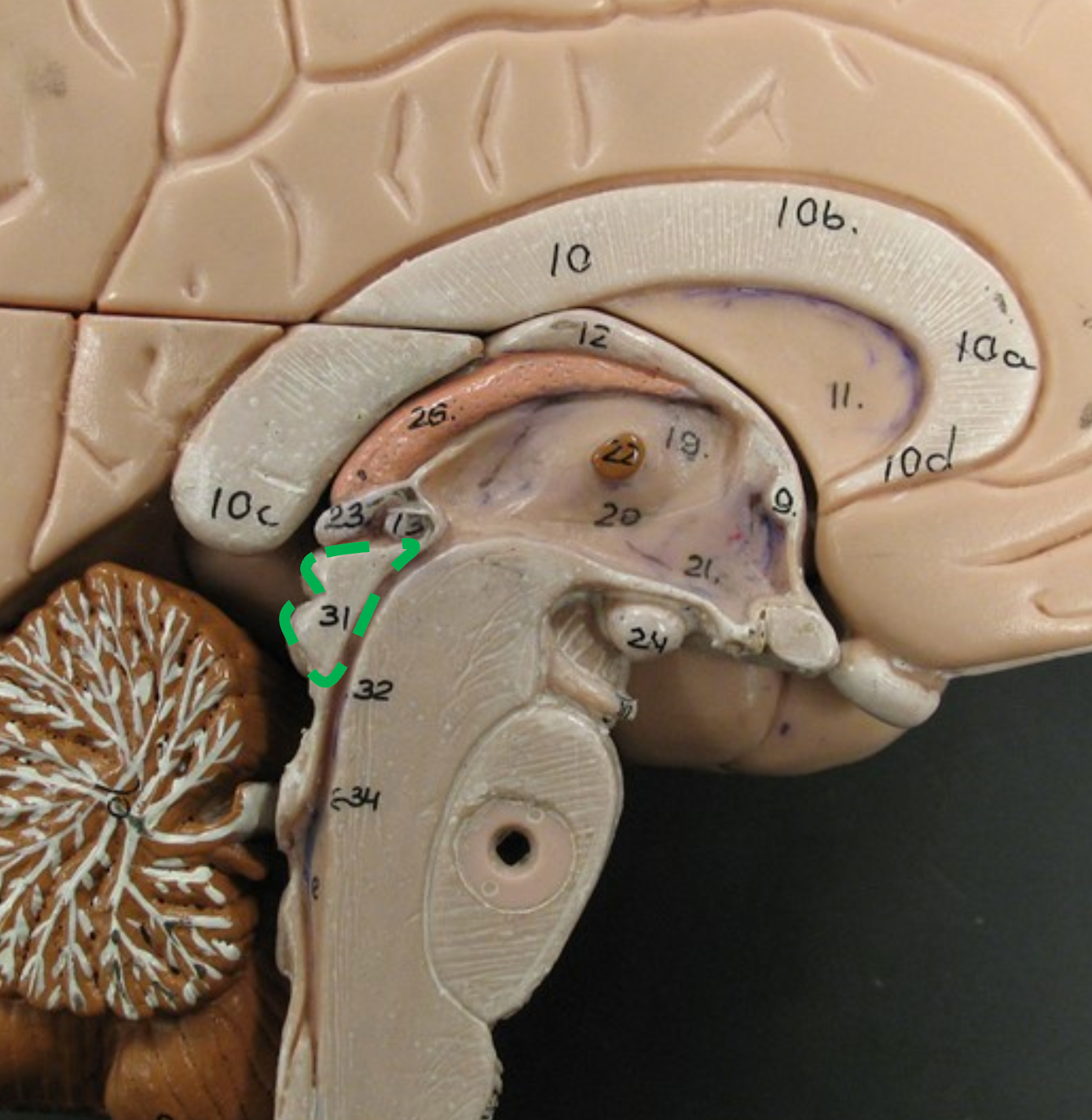
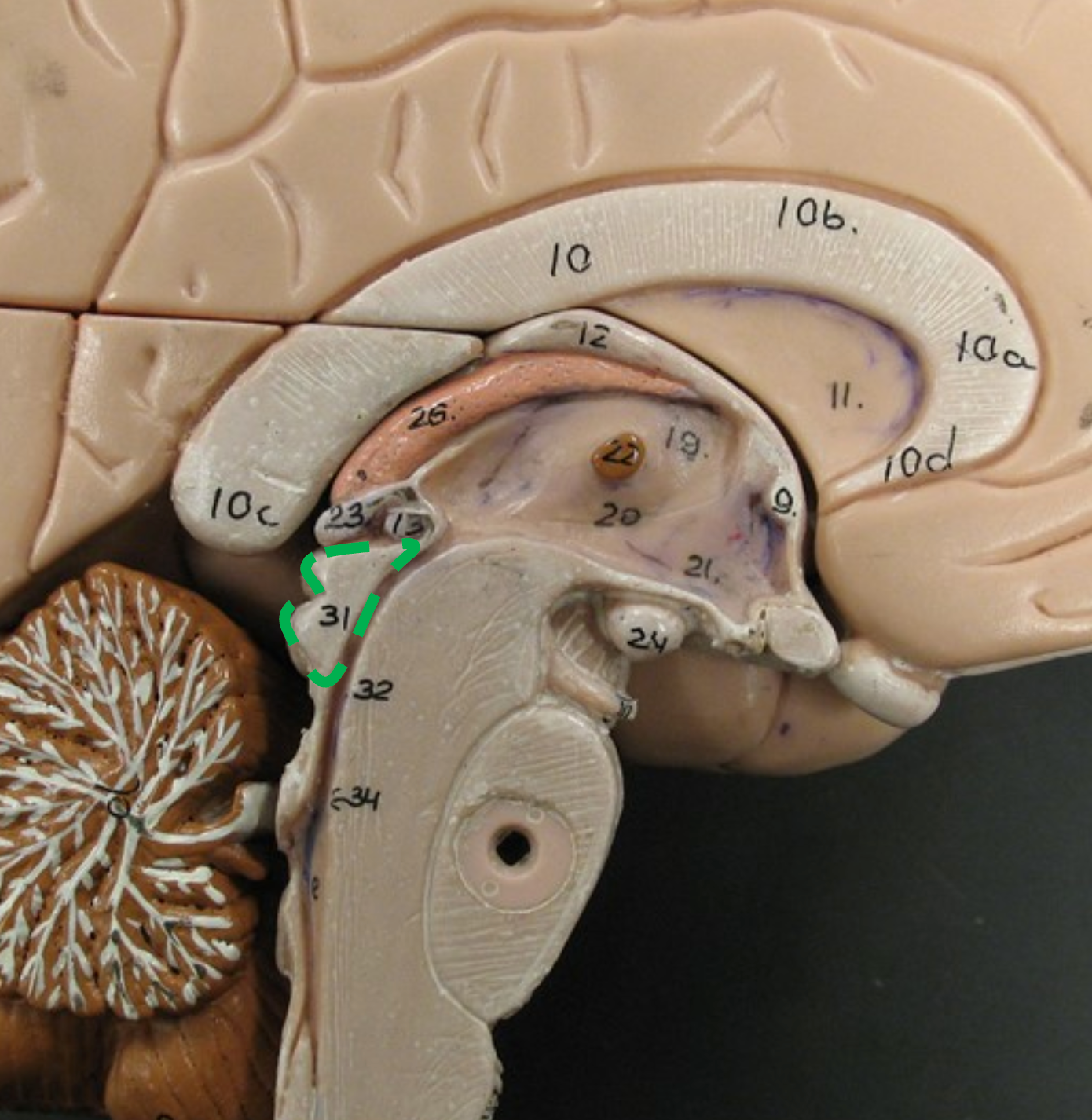
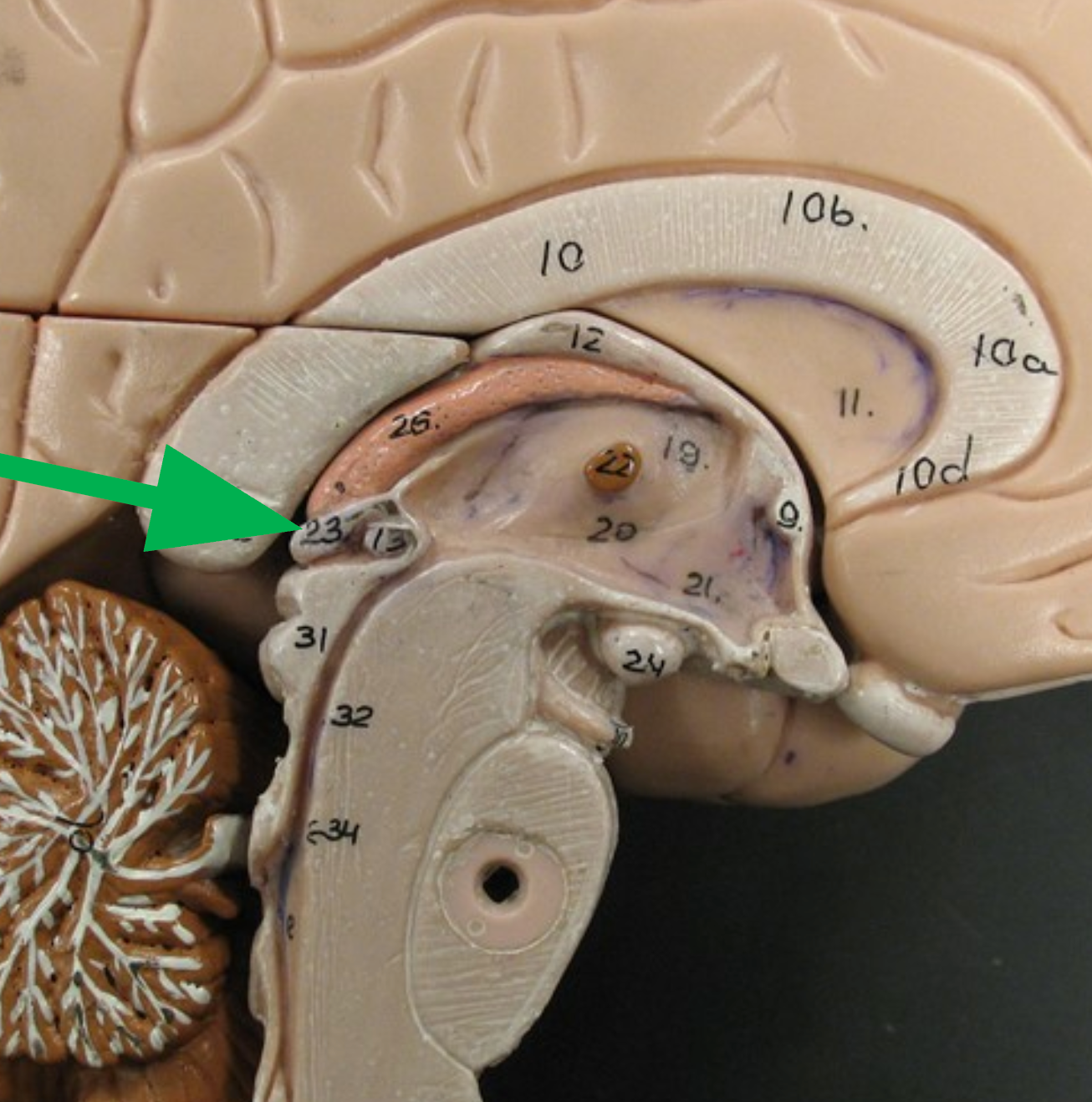
Pons
The central portion of the brain stem.
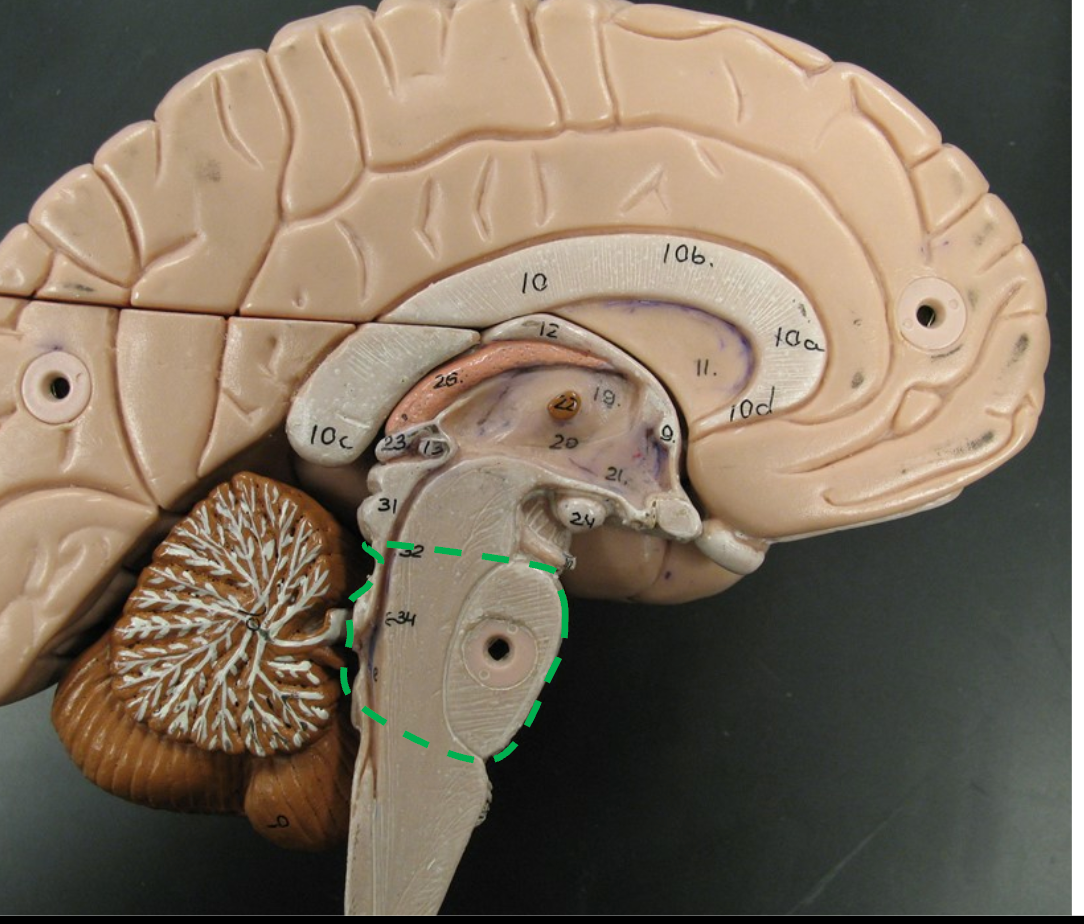
Nuclei
Clusters of neuron bodies involved in maintaining the rhythm of breathing.
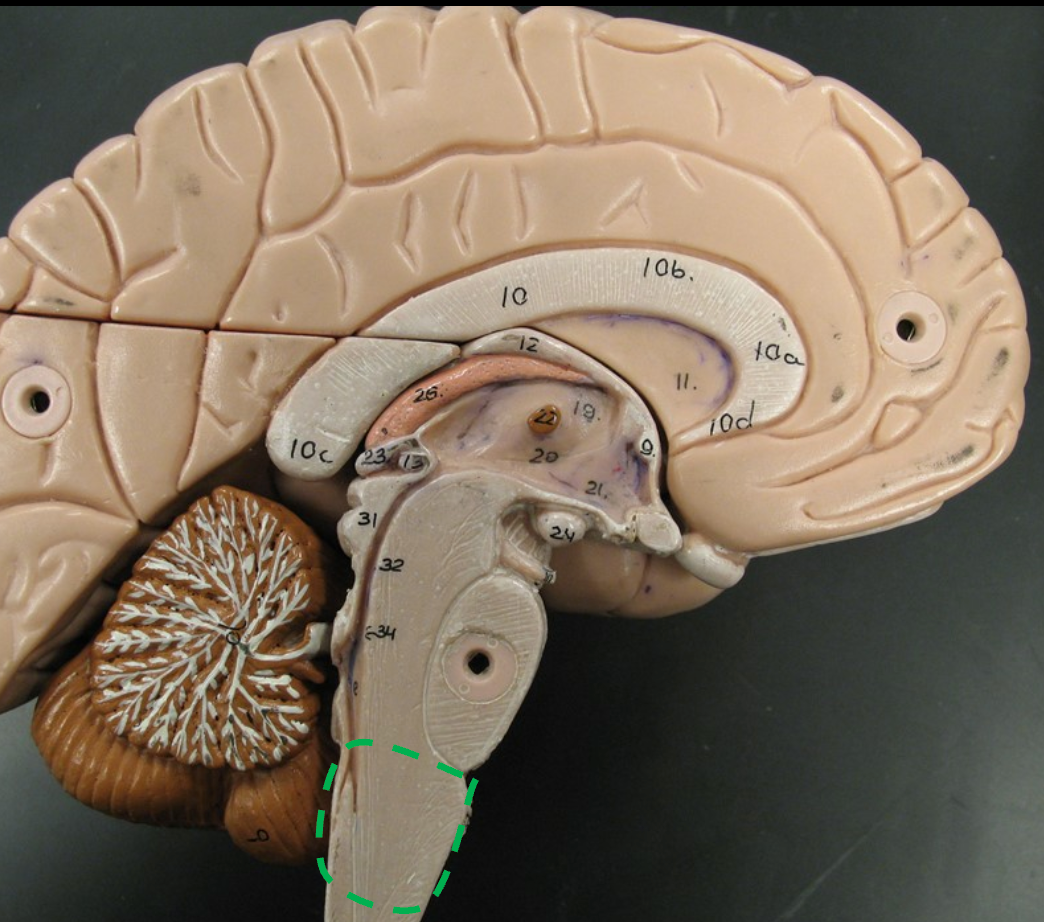
Medulla Oblongata
The most inferior part of the brain stem, connected directly to the spinal cord, controlling heartbeat and breathing.
Cerebral aqueduct
The canal that passes through the midbrain, connecting the third and fourth ventricles.
Cerebrospinal fluid
What flows through the cerebral aqueduct?
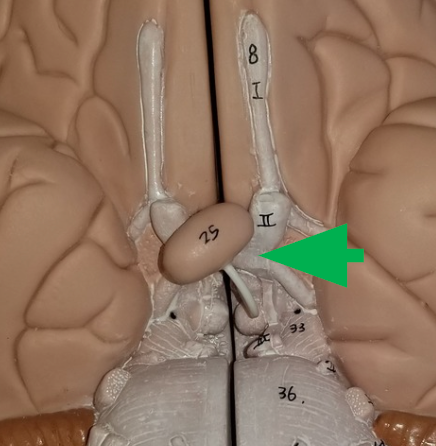
Pineal Gland
produces melatonin, a hormone involvedin sleep cycles
Fourth ventricle
Receives CSF from the 3rd ventricle (via the cerebral aqueduct) and allows it to move inferiorly into the central canal of the spinal cord as well as laterally and posteriorly into the subarachnoid space.
It exerts control over heart rate and breathing
A blow to the back of the head that damages the medulla oblongata may be fatal. Why?
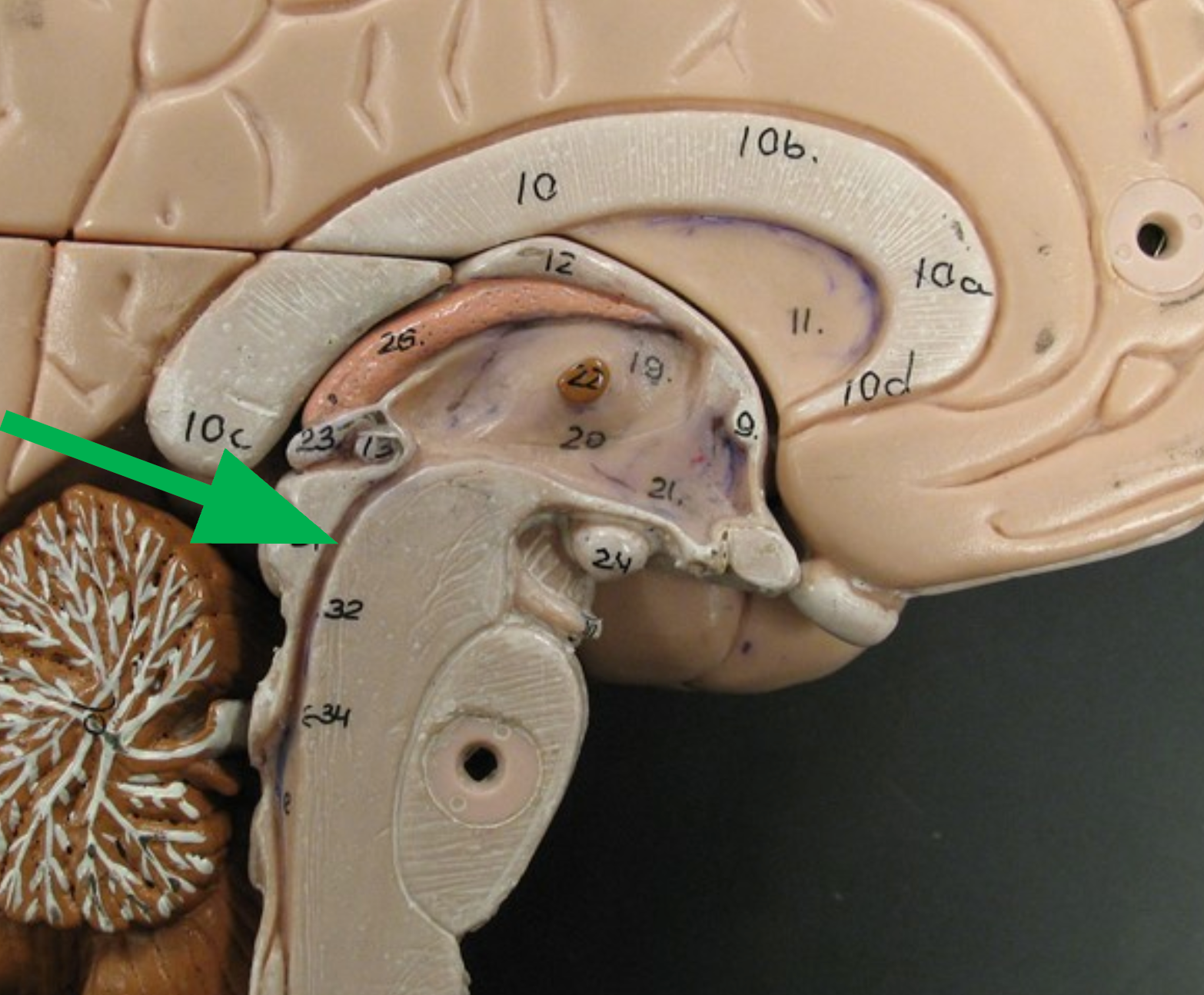
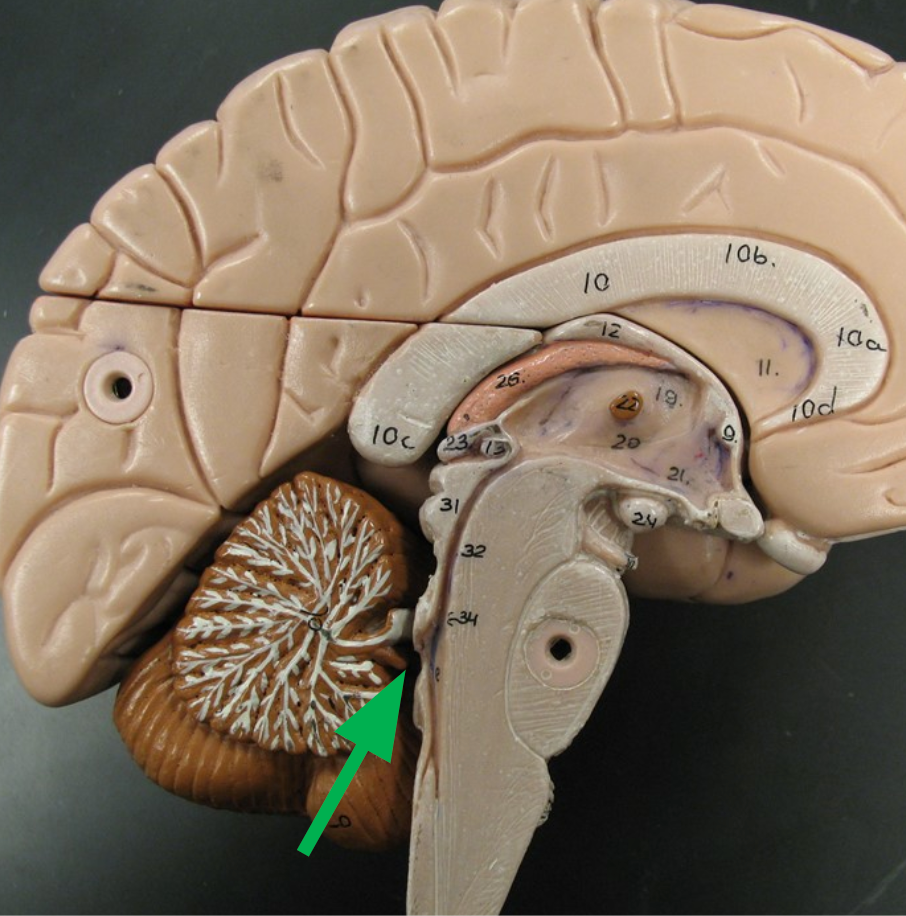
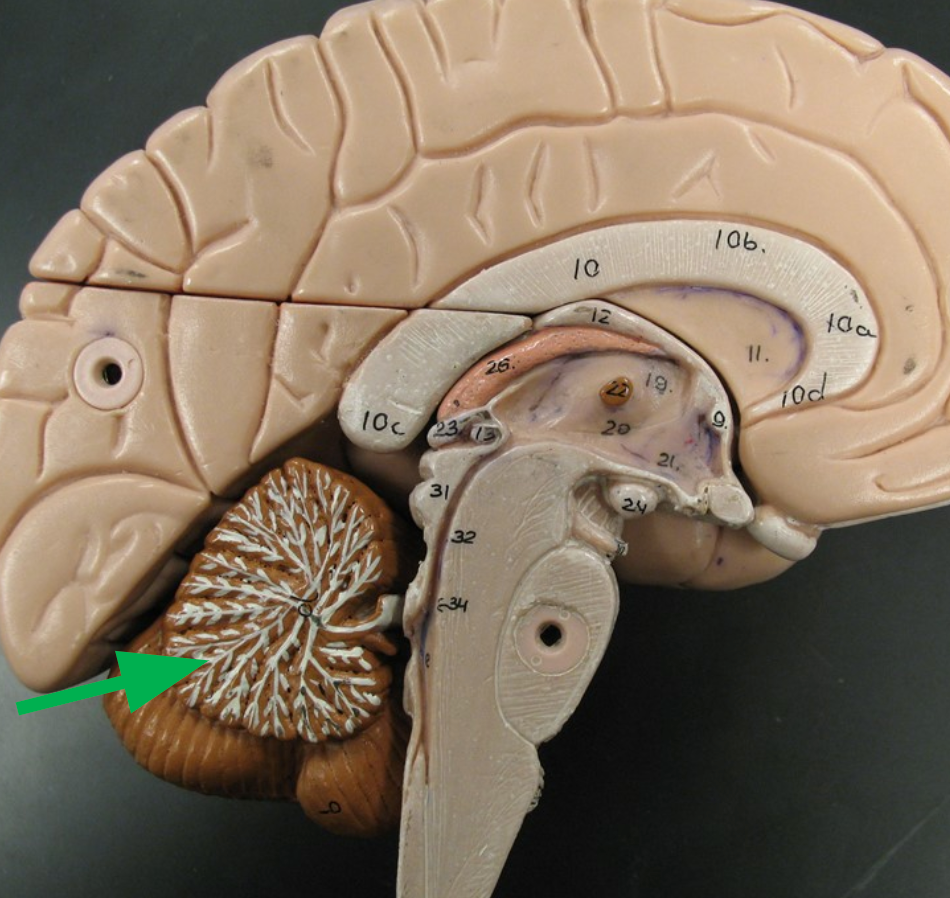
Cerebellum
Region of the brain that unconsciously coordinates movements of the body.
Transverse fissure
A deep groove that separates the cerebellum from the cerebrum.
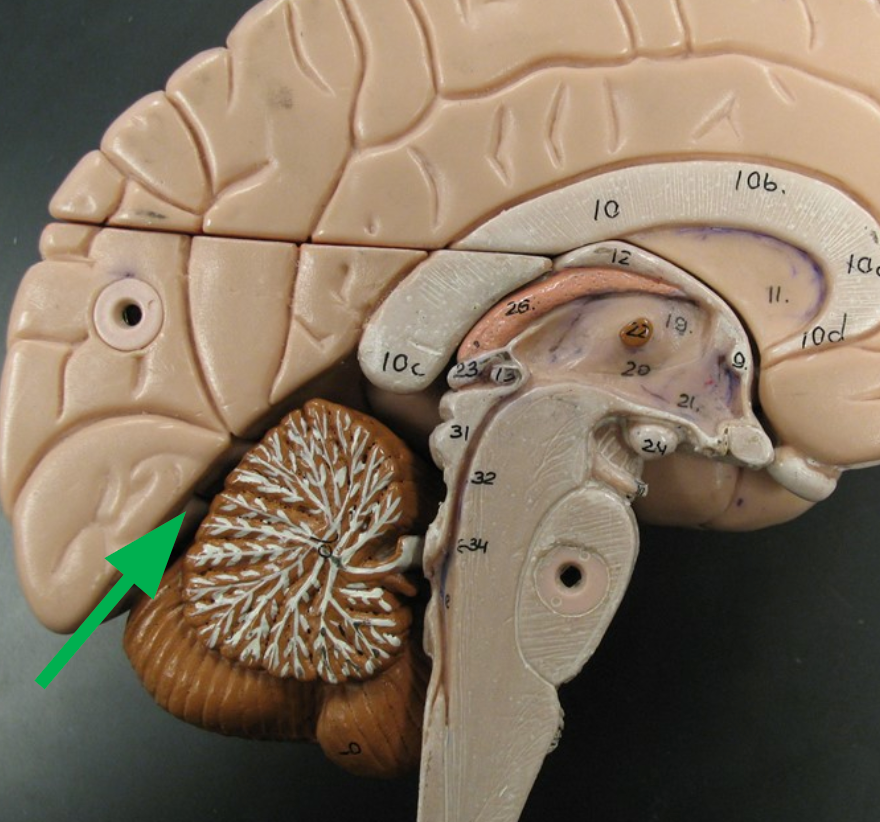
Vermis
The midsection of the cerebellum
Cerebellar Hemisphere
The sides of the cerebellum
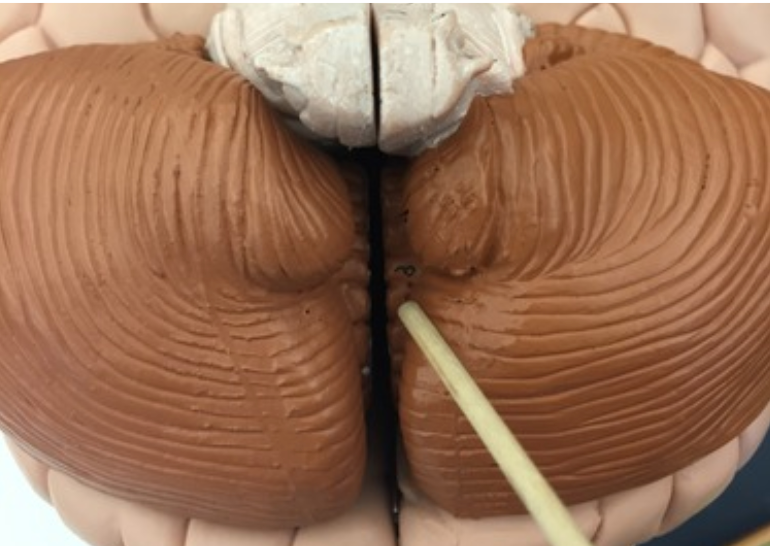
Folia
Folds on the surface of each cerebellar hemisphere, separated by shallow sulci.
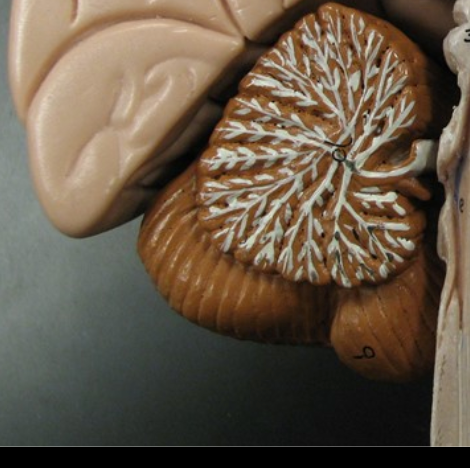
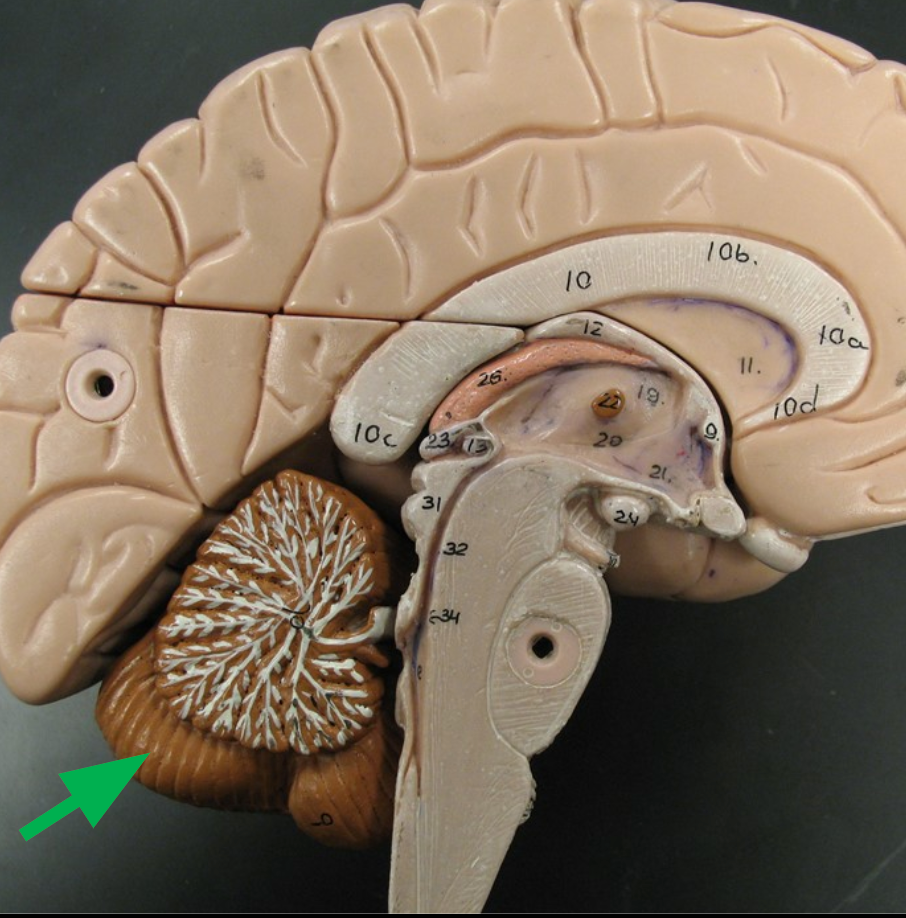
Arbor Vitae
Branches of white matter in the cerebellum resembling a tree.
Nerve
bundle of axons located outside of the CNS
12 pairs
How many nerves are attached directly to the brain?
Cranial nerves
Nerves that carry sensory information to and from the brain, with 12 pairs attached directly to it.
The olfactory and the optic nerves
Which two nerves attach to the brain stem?
Olfactory nerve
Cranial nerve that provides the sense of smell.
Optic nerve
Cranial nerve that provides vision.
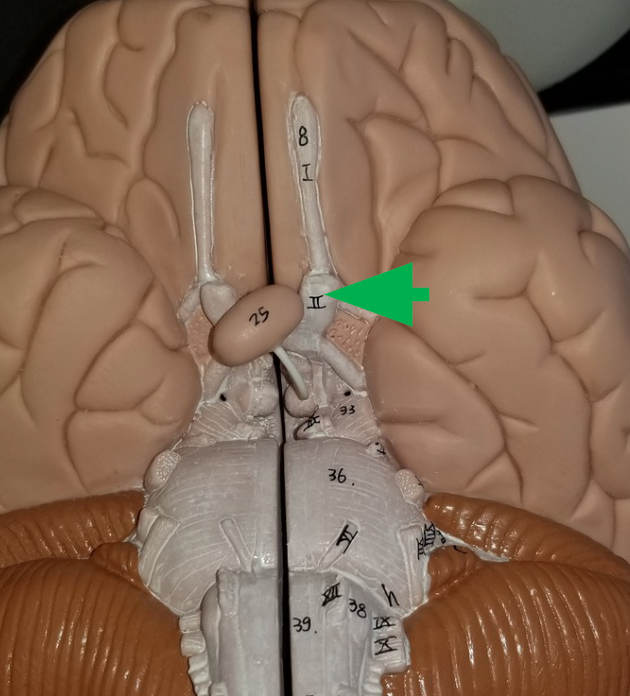
Oculomotor nerve
Cranial nerve responsible for opening and moving the eyes and adjusting pupil width.
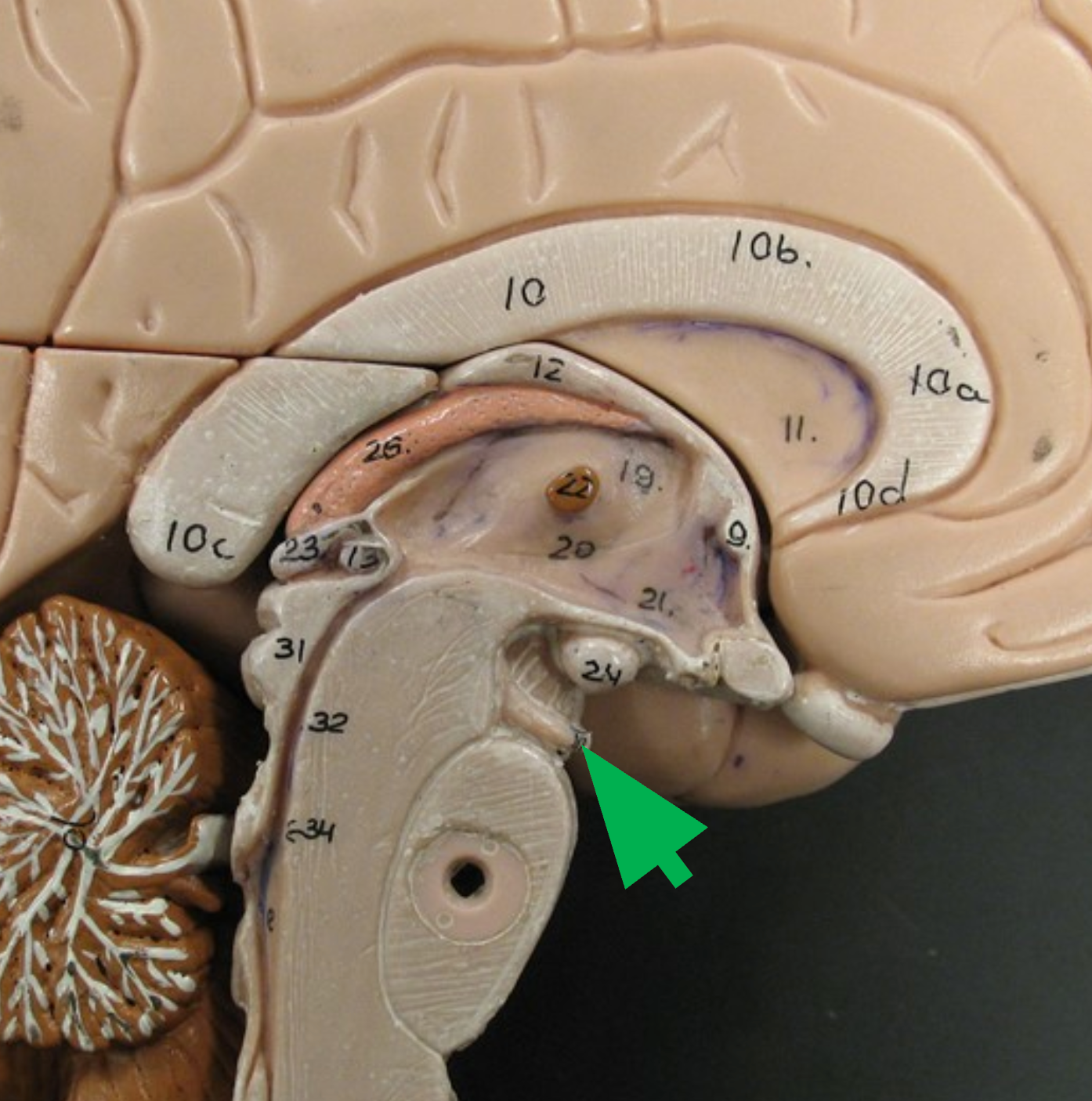
Trochlear Nerve
Looking down and moving eyes towards or away from nose
Trigeminal Nerve
Carries sensory information from face and motor commands to chewing muscles
Abducens nerve
moving eyes left and right
Facial nerve
controls facial muscles to make facial expression and provide sense of taste
Vestibulocochlear nerve
provides sense of hearing
Glossopharyngeal nerve
taste sensations, control muscles for swallowing, bp regulation, saliva production
Vagus nerve
regulates automatic bodily processes
Accessory nerve
controls shoulder and neck movement
Hypoglossal nerve
controls tongue movement
carry commands from the brain to motor neurons in the spinal cord. Ascending tracts through the dorsal portion carry sensory information to the brain. Contains nuclei associated with exerting control over the heartbeat, and nuclei that work with the pons to control breathing.
What function does the Medulla Oblongata serve?
Causes problems moving the eyeballs.
What would happen if cranial nerve damage occurs to the oculomotor nerve?
Problem with vision
What problem would a person have if his optic nerves were damaged?
Vagus nerves
Which pair of cranial nerves innervates various structures in the ventral body cavity?
The heart, lungs, and stomach
What parts of the body do vagus nerves connect to the brain?
Olfactory nerves
extend from the nasal cavity to the anterior portion of the brain
Olfactory bulbs
carries sensory information about smell
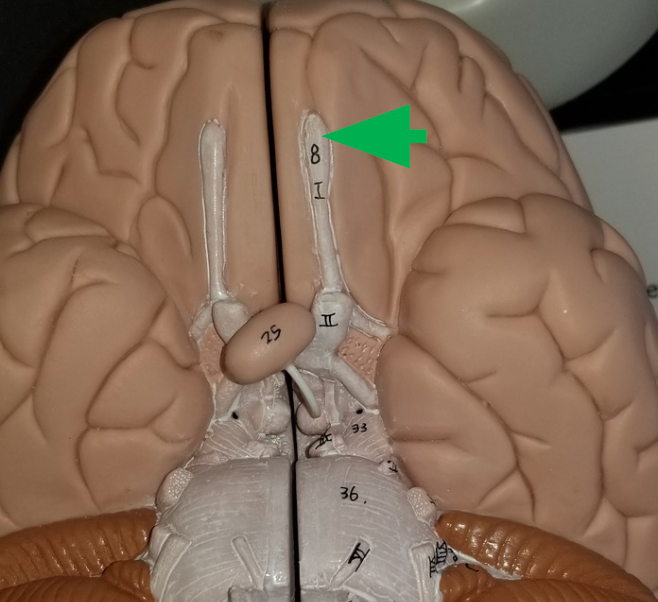
Olfactory tract
carry sensory information about smell
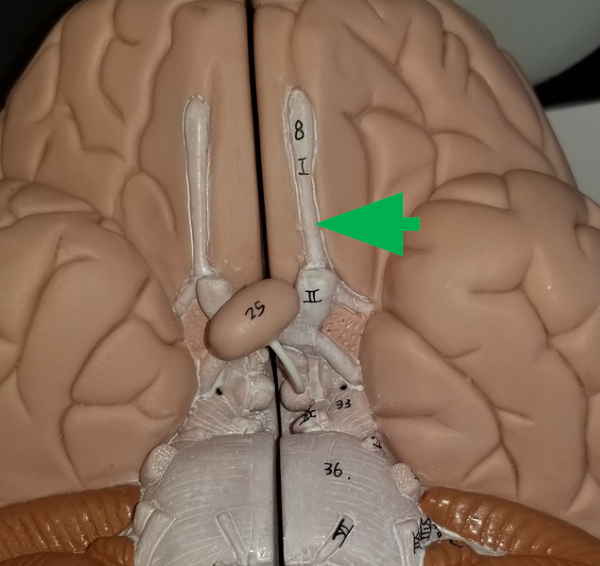
Optic nerves
carries visual sensory information
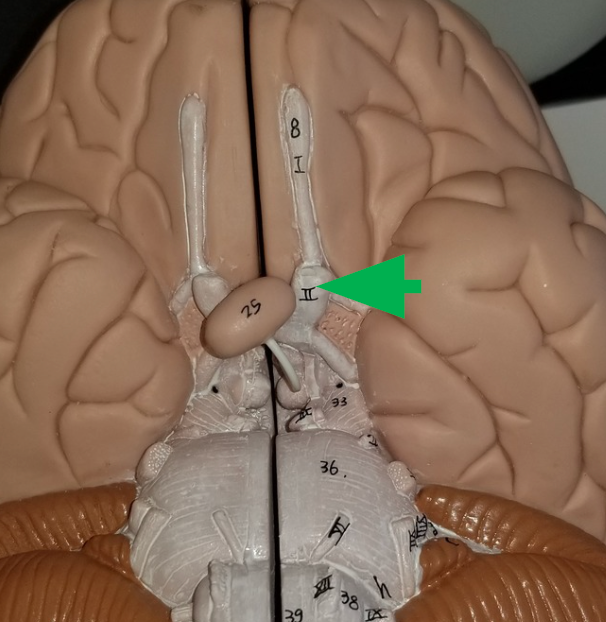
Optic chiasm
The pair of optic nerves
Optic tracts
Where axons travel through the brain paired together after the optic chiasm.
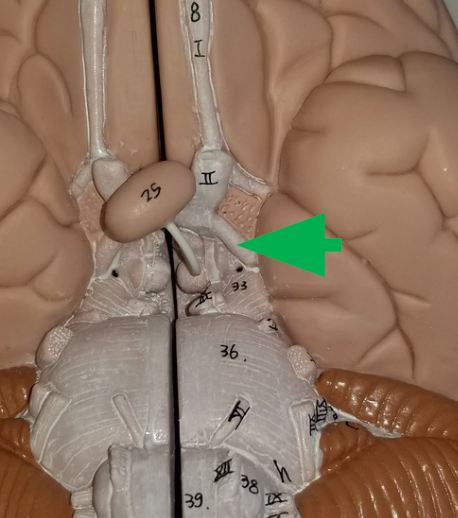
Oculomotor nerves
between the mammillary bodies and the pons, carry motor commands for movement of the eyeballs
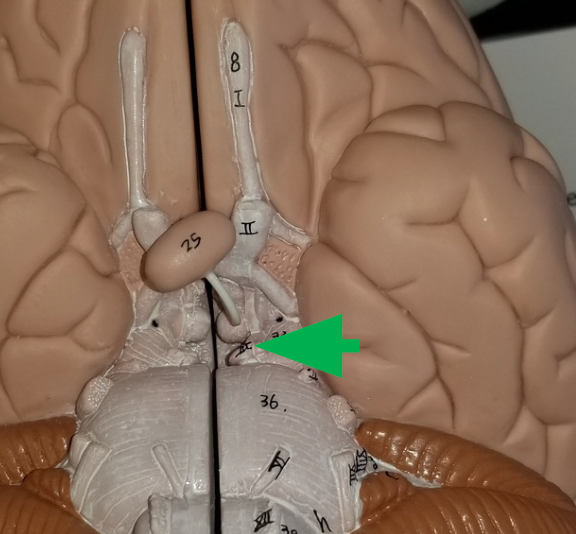
Trigeminal nerves
extend from the sides of pons, receive sensory information from parts of the face, mouth, and tongue, and send motor commands to muscles involved in chewing.
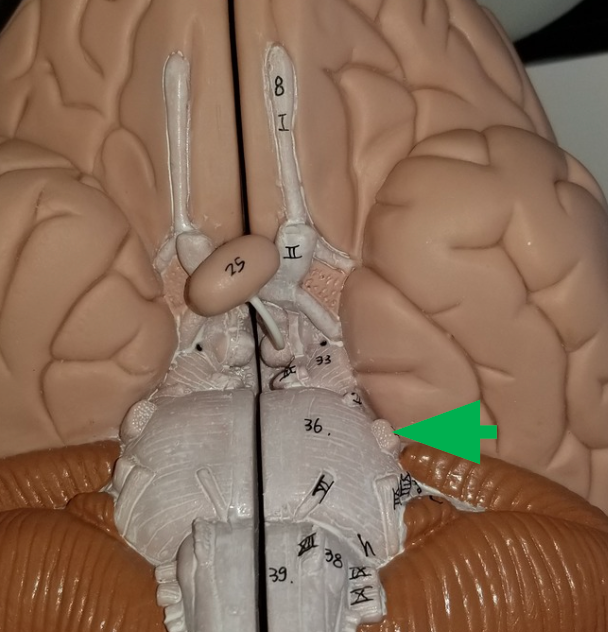
A tract is found in the CNS, while a nerve is found in the PNS.
What is the main difference between a tract and a nerve?
Regulates automatic bodily processes such as heart rate and digestion.
What is the function of the Vagus nerve?
There are multiple olfactory nerves attached to each side of the brain. The other cranial nerves are paired.
How does the structure of olfactory nerves differ from the other cranial nerves?