Neural Substrates Final Exam
1/175
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
176 Terms
holism
the school of thought that espouses that the brain works as an integrative whole
plasticity property of the brain
1. the brain can reorganize itself following damage
2. the ability to reorganize is greater at younger ages
3. the brain never stops changing itself
synaptic pruning occurs
postnatally only
synaptogenesis occurs
pre- and postnatally and continues throughout life
experience dependent
neural connections that are made in response to unique/individual experiences
a possible reason for the cause of autism
inappropriate development of neural circuitry
glial cells
cells that help the neurons migrate as they disperse from the neural tube
teens rely more on feelings and impulses than logic and planning because their frontal lobes are not fully mature due to:
the axons in the frontal lobes are not fully myelinated until the mid 20s
what do the vocal folds do when you breathe?
abduction
synaptic pruning
the process in which extra connections between neurons are eleminated
what changes to the aging brain result in normal loss of memory, attention, learning and language skills?
1. cortical thinning
2. decrease in neurotransmitter levels
3. loss of plasticity
ectoderm
the embryonic layer which will later form the nervous system
the jerky uncontrolled movements of infants and toddlers are due too
initial separate systems of sensory, motor, cognition, and emotion
the bending of your knee is an example of what kind of muscle action?
flexion
knowledge of neuroanatomy and neurphysiology is important for you because:
1. it allows you to communicate with neurologists
2. helps you to predict what problems a patient with a neurological disorder will have
3. it allows you to choose appropriate tests and treatments
the neuron doctrine
established that each neuron is a separate cell
tracts
large numbers of axons that course together in the CNS
nerves
large numbers of axons that course together in the PNS
terminal boutons
contain the neurotransmitters
function of myelin
1. insulation of nerve fibers
2. protection of nerve fibers
3. prevention of electrical energy loss during action potential conduction
neurons are similar to other cells in the body except
neurons produce a chemical substance released at the synapse
williams syndrome
neurodevelopmental disorder where language skills are not affected
neuronal differences found in the brains of at least 50% of autistic children
1. amygdala is larger
2. fusiform gyrus has altered neurons and neuronal connections
3. the cerebral cortex has altered neurons and neuronal connections
ventral/inferior
synonyms when referring to the brain
the heart is _ to my right arm
contralateral
if you sleep on your stomach you are sleeping in which position?
pronate
walking requires which types of leg movements?
flexion and extension
activity barrier
a medical model of health would describe a disability where the social model of health would describe and activity barrier
fMRI
is the neurimaging technique with the best spatial resolution
prior to modern neuroimaging techniques doctors would do what to establish a lesion site responsible for a behavior deficit?
perform a brain dissection after death to determine the site of lesion
efferent communication
top-down, descending communication through neural pathways from brain to body
phinneas gage legacy
1. survived an accident where a large iron rod was driven completely through his head
2. influenced a 19th century discussion about the mind and brain, particularly the debate on cerebral localizaation
3. was perhaps the first case to suggest the brain's role in determining personality
proximal
point nearest to the limb's attachment
ipsilateral
on the same side
distal
point farthest from the limb's attachment
peripheral
toward the outer surface
ventral
toward the stomach
holoprosencephaly
failure of brain cleavage
microcenphaly
interruption in neural proliferation
hydrocephalus
excess cerebrospinal fluid
anencephaly
neural tube defect
lissencephaly
neuronal migration defect
santiago ramon y cajal
neurons do not actually touch each other
franz josef gall
created phrenology
camillo golgi
developed staining method that allowed seeing whole neurons
karl wernicke
theorized that understanding speech was localized to a specific place in the left hemisphere
paul broca
theorized that speech production was localized to a specific place in the left hemisphere
ependymal glial cells
creates CSF (cerebrospinal fluid)
oliogodendrocyte glial cells
creates myelin in the CNS
satellite glial cells
protection to sensory nerve cell bodies
atstrocyte glial cells
forms the blood-brain barrier
microglia glial cells
phagoycytosis and forms scar tissue
schwann glial cells
creates myelin in PNS
order neurodevelopmental events
1. dorsal induction
2. ventral induction
3. neural proliferation
4. neuronal migration
5. cortical organization
6. myelination
coronal section of the brain
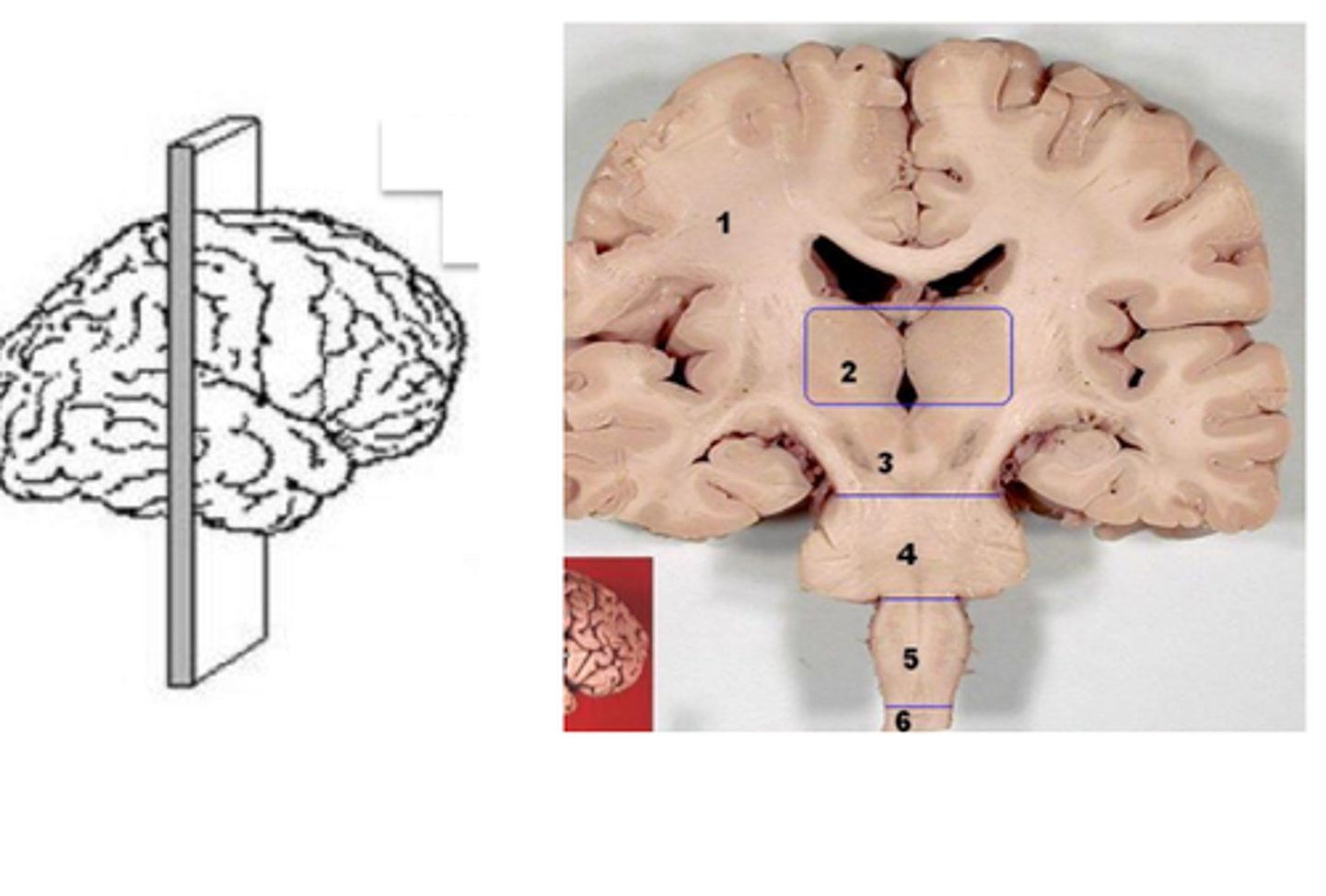
horizontal section of the brain
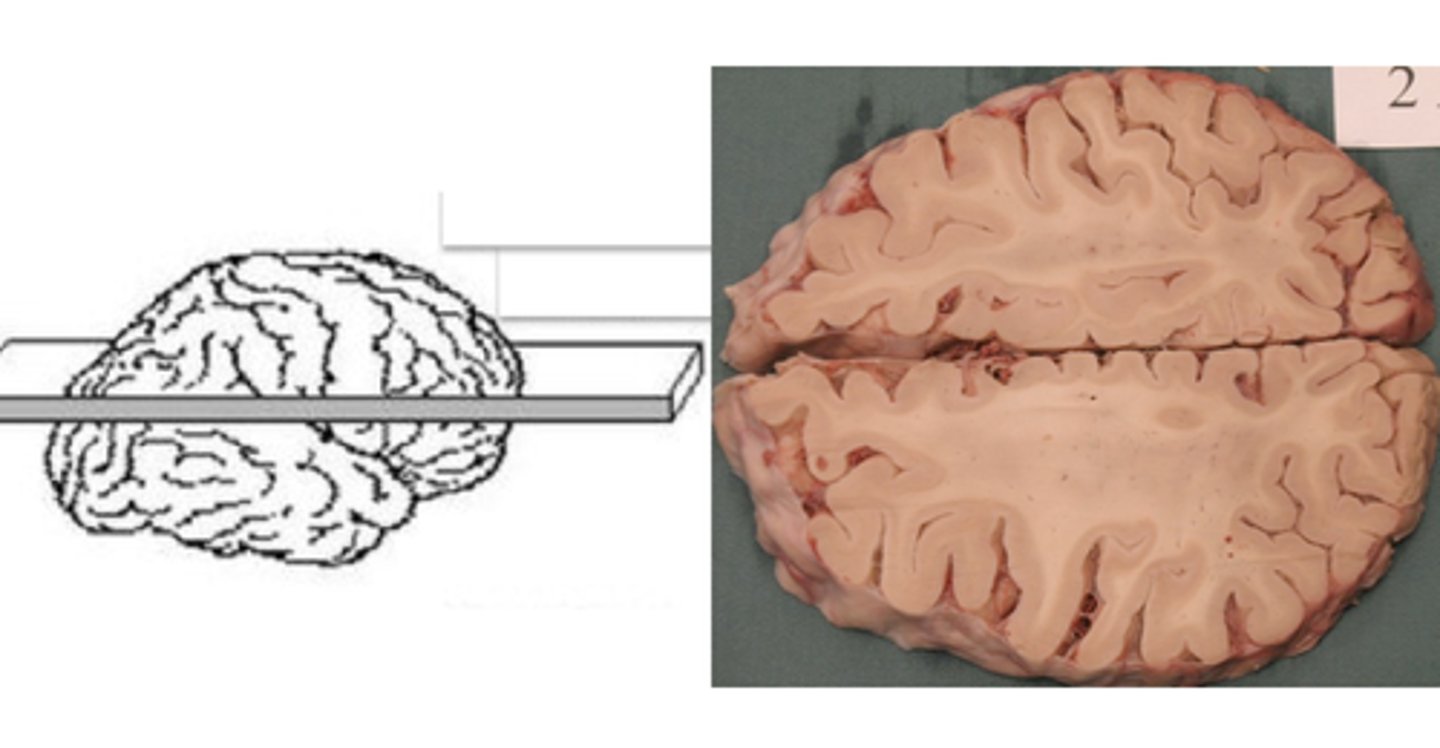
sagittal section of the brain
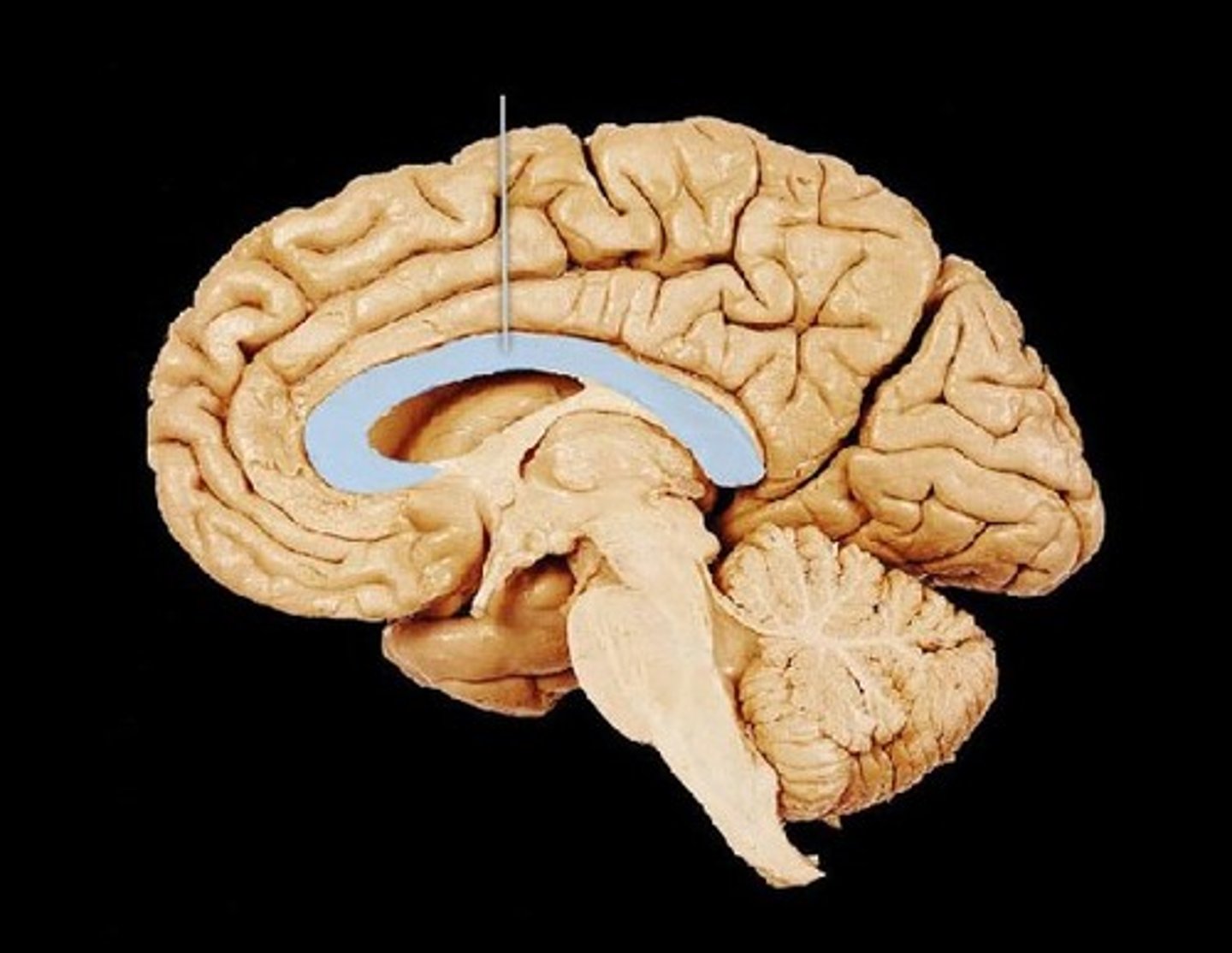
middle cerebral artery vascular problem may result in
speech/language deficit
salience matters principle of neuroplasticity
the importance of training experience - a rewarding and functional therapy task is most likely to induce brain plasticity
damage to the thalamus can cause the following
altered sensory perception, anomia, altered thresholds for pain (DOES NOT cause paralysis)
arteriovenous malformations (AVM)
disorder involving dilated arteries and veins
functions of the thalamus
1. channeling projections of sensation information (pain, taste, temperature, audition, and vision) to specific cortical areas
2. regulation of associational cortex as well as cortically mediated cognitive functions
3. integration of sensorimotor information before the projection to the primary and premotor cortices
(DOES NOT include regulating autonomic functions)
CNS - 1 glial cell can myelinate
many neurons
PNS - 1 glial cell can myelinate
one neuron
transcortical motor aphasia
non-fluent aphasia with intact auditory comprehension and repetition
acetylcholine
the only neurotransmitter that is active at the neuromuscular junction
transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
1. considered silent stroke because they often have no outward symptoms
2. typically, individuals are unaware they are having a TIA
3. cause brain damage
damage to the anterior cerebral artery
results in paresis of leg, reduced reasoning, and impaired planning
repetition and intensity matter
principle brain plasticity sometimes referred to as dose frequency
astroglia
"glue that holds neurons in place"
function circle of willis
supply blood to the hemisphere contralateral to the damaged hemisphere
corticospinal tract
contains the upper motor neurons for the spinal motor neurons
corticobulbar tract
contains the upper motor neurons for the cranial nerves
the corticobulbar tract innervates
oral facial muscles on both sides for the most part
if you are having hearing loss and balance issues which cranial nerve may be the problem?
CN VIII: vestibulocochlear
you wake up and smell coffee, which cranial nerve is responsible?
CN I: olfactory
damage to the right upper motor neuron that controls cranial nerve VII: facial will cause
lower facial droop on the left side
left spinal sensory neurons recieve input from
ipsilateral
how could you asses if cranial nerve XI: spinal accessory is function properly?
have the patient shrug their shoulders and turn their head
the muscles to make a pouty face are innervated by which cranial nerve?
CN VII: Facial
spinal-cerebellar pathway
tells the cerebellum what movement is happening
the cerebellum influences movement
ipsilaterally
the tremor in parkinson's disease
is worse at rest
when the left upper motor neuron synapses with cranial nerve V: trigeminal which masseter muscles will be activated?
both left and right
lateral corticospinal motor tract
carries information for contralateral body movement
which cranial nerve receives the pain sensation on the tip of your tongue?
CN V: trigeminal (mandibular portion)
subcortical nuclei consist of
cell bodies of neuron
apraxia of speech
refers to the loss of ability to voluntarily execute the movements of speech
meninges
consists of three layers that surround the brain and spinal cord
Amuotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS
degeneration of motor neurons
myasthenia gravis
reduces number of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors at neuromuscular joint
parkinson's disease
loss of dopaminergic producing neuron
alzheimer's disease
widespread neuronal degeneration
multiple sclerosis
demyelination of axons
blink reflex
controlled by CN V (trigeminal) and CN VII (facial)
pupillary light reflex
CN II (optic) CN III (oculomotor)
gag reflex
CN IX (lossopharyngeal) and CN X (vagus)
association fibers
connect gyri within the same hemisphere
projection fibers
ascending and descending fibers connecting cortex with brainstem and spinal cord
commisssural fibers
connect gyri in opposite hemispheres