14: troubleshooting after start up
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
shell
portion of an OS that relates to the user and to applications. The Windows shell provides tools such as File Explorer and the Windows desktop and is made
up of subsystems that operate in user mode
kernel
responsible for interacting with hardware
The kernel has two main components
HAL (hardware abstraction layer) – the layer closest to hardware
Executive services interface – a group of services that operate in kernel mode
between the user mode subsystems and the HAL
registry
store hardware and software configuration
information, user preferences, and application settings
process
a program that is running under the authority of the shell, together with the system
resources assigned to it
thread
When a process makes a request for resources to the Win32 subsystem. ometimes a process is called an instance
multithreading
A process with more than one thread
You are having difficulty uninstalling freeware a user accidentally installed while surfing the web.
You look online and see the software is designed to work in an x86-based version of Windows.
In which folder should you expect to find the program files for the software?
a. C:\Windows
b. C:\Program Files (x86)
c. C:\Program Files
d. It depends on the version of Windows installed
Answer: d. It depends on the version of Windows installed.
• An x86-based app is a 32-bit app. If Windows is 32-bit, the app is installed in the
C:\Program Files folder. If Windows is 64-bit, the app is installed in the C:\Program Files
(x86) folder
tools to conveniently access and manage other Windows tools
Control Panel, Administrative Tools or Windows Tools, Computer Management (compmgmt.msc), Microsoft Management Console (MMC, mmc.exe),
tools to observe Windows, Windows user, network, application, and hardware activities as tracked and logged by Windows
Event Viewer (eventvwr.msc), Resource Monitor (resmon.exe), Performance Monitor (perfmon.msc),
Solve Windows, application, networking, and Windows user problems with these tools
Task Manager (taskmgr.exe), Services console (services.msc), System Configuration (msconfig.exe), Registry Editor (regedit.exe)
Solve Windows problems using these tools
System File Checker (sfc.exe), Windows Updates, System Restore (rstrui.exe)
Solve application errors or crashes with these tools and techniques
Programs and Features (appwiz.cpl), secondary logon, Digital signature, Task Scheduler (taskschd.msc),
Manage and solve problems with hardware using these tools
Device Manager (devmgmt.msc), chkdsk
Event Viewer logs
might give clues about hardware or network failure, OS error messages, a
device or service that has failed to start, or general protection faults
Resource Monitor
view in real time how the CPU, hard drive, network, and memory are being used. Can find out why a system may be sluggish due to hogging resources
Performance Monitor (perfmon.msc)
tracks how resources are used in real time, and it can save
collected data in logs for future use
If the %Disk Time is more than 80% and the Avg. Disk Queue Length is more than two, you can conclude that
the hard drive is working hard and processes are slowed down waiting on the
drive
Task Manager
end a process causing trouble and to enable or disable programs that
launch at Windows startup
Here are two ways to open Task Manager:
− Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
− Right-click the Start menu and click Task Manager
Services console (services.msc)
permanently adjust when services run in the
background to support Windows and applications
Task Scheduler (taskschd.msc)
in the Administrative Tools/Windows Tools group of Control Panel is used to schedule a program to run at startup or some other time in the future
System File Checker (SFC) command
to repair the Windows 10/11 system. scans for and replaces corrupted or missing Windows system files, which include device drivers for many hardware devices
System Configuration (msconfig.exe)
in the Administrative Tools/Windows Tools group to control Windows startup, including temporarily disabling programs from launching at startup.
Safe boot,
goes beyond a clean boot by eliminating third-party software and also reducing startup to only the Windows minimum configuration necessary to start the OS
System Restore
restore the system to a point just before the problem started
Registry Editor (regedit.exe)
used to manually change the Windows registry
Items in the registry are called
key, which are assigned values
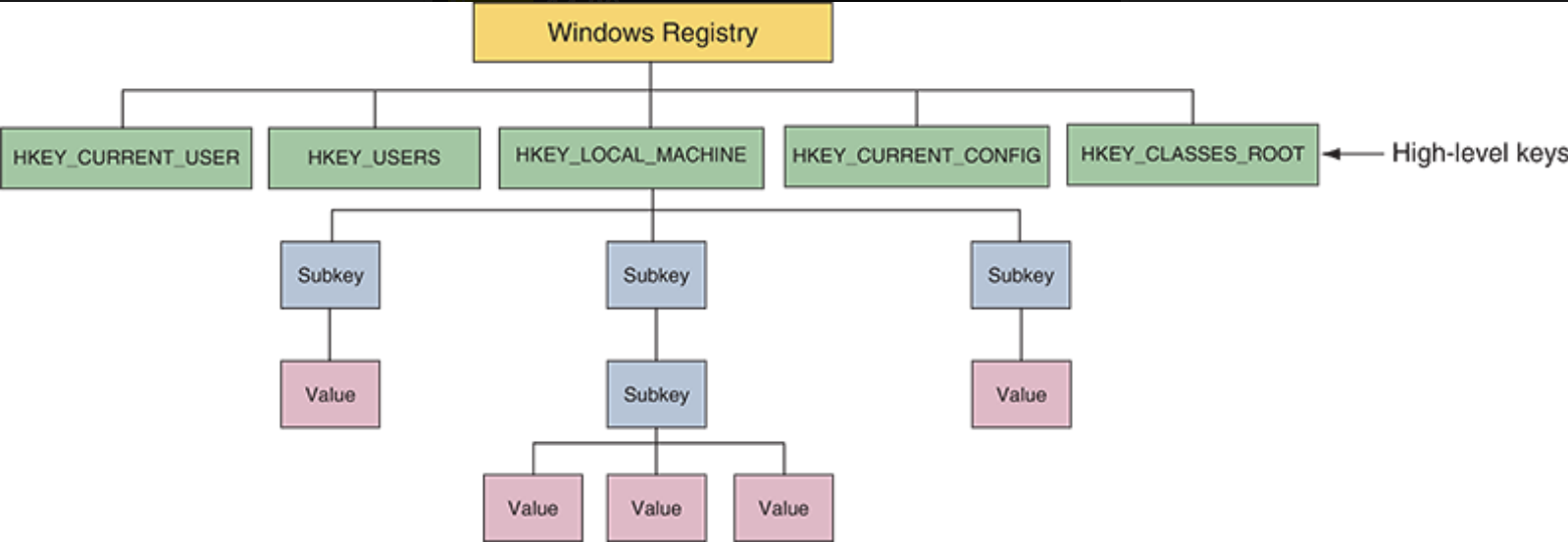
Registry
registry is a database designed with a treelike structure (called a hierarchical database)
− It contains configuration information for Windows, users, software applications, and installed
hardware devices
After the registry is built it is then organized into five high-level keys
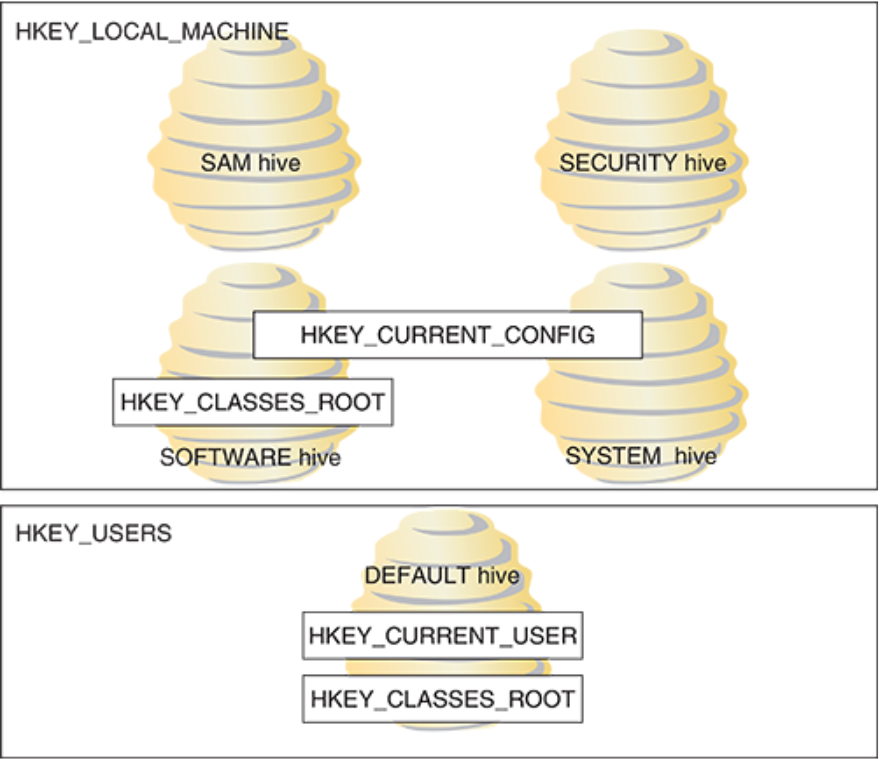
Five files used to build the registry are called ____ and include
hives:
SAM (Security Accounts Manager), SECURITY, SOFTWARE, SYSTEM, and DEFAULT
hives
the five high-level keys and functions
− HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE (HKLM) contains hardware, software, and security data
− HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG (HKCC) is used to identify each hardware device
− HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT (HKCR) is used to determine which application opens
− HKEY_USERS (HKU) contains data about all users
− HKEY_CURRENT_USER (HKCU) contains data about the current user
Ways to back up the registry (3)
− Use System Protection to create a restore point
− Back up a single registry key just before editing the key
− Make an extra copy of the C:\Windows\System32\config folder
What to do if services not starting
Use Task Manager and the Services console, uninstall and reinstall an app or service, and do a final reboot
what to do if USB controller resource warnings
Use Device Manager, adjust settings in Power Options, and update the chipset drivers on the motherboard.
What to do if time drift
On a Windows domain, use the Windows Time Service (W32Time) or third-party software for time accuracy
What to do if Low memory warning
Use Task Manager, eliminate or repair an app with a memory leak, update the chipset drivers on the motherboard, and upgrade memory
what to do if Sluggish performance
Use Task Manager, Resource Monitor, and Windows updates. Uninstall or disable unneeded apps, startup programs, and scheduled tasks. Try a clean boot. Upgrade hardware.
what to do if System instability
Use Event Viewer and Windows Update, repair or reinstall an app or service, and use Windows Memory Diagnostic, chkdsk, System File Checker, and Device Manager. Try a clean boot, Safe Mode, and System Restore. Repair Windows with a Windows 10/11 upgrade.
Application errors and crashes
Use Task Manager, taskkill, and uninstall and reinstall the app. Try a secondary logon and verify the app’s digital signature. To eliminate conflicts with other apps, perform a clean boot, and then run the app.
Steps to Solve Any Computer Problem (6)
Step 1. Identify the problem
• Step 2. Establish your theory of probably cause
• Step 3. Test your theory
• Step 4. Fix the problem
• Step 5. Verify that the problem is fixed
• Step 6. Implement preventative measures and document your findings
When trying to improve performance of a slow system, you notice in Task Manager that the
superfetch service is using a high percentage of CPU time. What is your best next step?
a. Disable superfetch to improve performance.
b. Update Windows to improve superfetch performance.
c. Superfetch is an essential Windows process and should not be disabled. Move on to other
solutions to improve performance.
d. Ask the user if they use the superfetch service. If they don’t, uninstall it.
a. Disable superfetch to improve performance.
• This Windows service cannot be uninstalled. It is supposed to improve performance but
can actually degrade performance on some systems. If it is hogging CPU time, it should
be disabled. This question includes information not in the module and is designed to help
you learn to use the web to research a problem. A good search string is “what is
Windows superfetch.