public health and injuries, aging, and bone health
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
2020 leading causes of death
unintentional injuries
leading cause of death 15-24 and 25-34 yo
unintentional injuries, homicide, suicide
biggest causes of injury deaths
unintentional poisoning
unintentional fall
unintentional motor vehicle traffic
suicide firearm
homicide fire arm suicide suffocation
overdose deaths
major contributor to unintentional poisoning deaths
more male deaths than female
Other causes of poisoning deaths
• Carbon monoxide
• Pesticides
• Adults: legal drugs taken in error or at the wrong dose, e.g., acetaminophen
• Child accidental overdose, e.g., iron-containing vitamins
Carbon monoxide
Fuel-burning products in a poorly ventilated area (generators, heating systems, charcoal grills, etc.)
Pesticides
usually unintentional exposure (occurs especially children under 6 yrs and adults > 20 yrs) – especially rat poisons
Alcohol-Related Deaths
highest among 55-64 yo in females and males
more deaths among male than females
Non-Fatal Injuries
2021: Unintentional falls dominate as the overall cause of nonfatal emergency department visits
followed falls, struck by/against, motor vehicle occupant
Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) can be caused by
Bump or blow to head
Penetrating injury (e.g., gunshot)
affects how the brain works
Common causes of TBIs
• Falls (approx. half of TBI-related hospitalizations)
• Firearm-related injuries
• Motor vehicle crashes
• Assaults including domestic violence
chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive brain disease caused by repeated head trauma, often seen in athletes and military personnel. Symptoms, which include mood disorders, cognitive decline, and dementia, emerge years after injuries and worsen over time. CTE is diagnosed only post-mortem by detecting tau protein buildup, which damages brain cells.
Originally identified in boxers as "pugilistic dementia" in 1928, CTE gained attention in the 2000s when Dr. Bennet Omalu diagnosed former NFL player Mike Webster. Subsequent studies, including a 2017 study by Dr. Ann McKee, found CTE in 110 out of 111 former NFL players. Research links early exposure to tackle football (before age 12) with an increased risk of cognitive and behavioral issues later in life.
Despite safety reforms in football, such as rule changes and concussion protocols, the NFL and other organizations have been criticized for downplaying CTE's risks. Efforts to ban youth tackle football under age 12 have faced legislative hurdles. Ongoing research seeks to develop a living diagnosis for CTE, which could lead to early detection and treatment.
Work-related deaths
most from transportation incidents
equal incidents of falls slips and trips, violence and other injuries by persons or animals, exposure to harmful substances/environments, contact with objects and equipment
least are fire and explosions
injuries/illnesses by event or exposure
most form exposure to harmful substances or environments
equal incidents of overexertion and bodily reaction, falls slips and trips, and contact with objects and equipment
least from violence and other injuries but persons or animals and transportation incidents
Osteoporosis
skeletal disorder
Diminished bone strength
Increased risk of fracture
Osteoporosis is characterized by
decrease in bone mass and density
• enlarged spaces within bone that produce fragility
Diminished bone strength
• Quality
• Density
• Increased risk of fracture
Wrist • Spine • Hip
treatment for Osteoporosis
remodeling
resorption
remodeling
bone removal and replacement
resorption
removing bone thats damages or needed for minerals
minerals like calcium are essential to
cell function and are taken from bones as needed
prevalence of Osteoporosis
more among older adults
more among women
Osteoporosis risk factors include:
Physical inactivity
• Excess alcohol consumption
• Tobacco use
Gender (women more vulnerable)
• Age
• Race (greatest if white or Asian)
• Family history
• Small body frame size (less bone mass to draw on during aging)
• Sex hormones, e.g., drop in estrogen during menopause
• Low calcium intake
• Eating disorders
• Gastrointestinal surgery, e.g., for weight loss (limits surface area for nutrient absorption)
• Certain medications
Prevention & treatment for osteoporosis
• Healthy balanced diet including calcium and vitamin D
• Exercise
• Weight bearing
• Resistance training
• No smoking
• Low alcohol intake
• Check medication side effects
• Limit caffeine to < 2 cups/day
Arthritis
• Includes > 100 diseases & conditions that affect joints, tissues surrounding joints, & other connective tissue
• Major cause of disability & chronic pain
• Typically involves pain, stiffness around joint(s)
• Major cause of limitations to usual activities
Arthritis prevalence
• US adults aged ≥18 years (2019-2021): 21.2% reported diagnosed arthritis
• 88.3% of US adults with arthritis were ≥45 years
• More common among women than men
Osteoarthritis
• Affects > 30 million US adults
• Also called degenerative joint disease or “wear and tear” arthritis
• Degeneration of cartilage from bone rubbing tgt
• Leads to bone degeneration
• Gradual
Osteoarthritis Symptoms
pain
inflammation
stiffening
decreased range of motion
swelling
Osteoarthritis risk factors
• Age (>40)
• Gender (female)
• Obesity
• Trauma
• Joint injury/overuse
• Infection
• Poor alignment
• Occupation & repetitive motions
• Genetics
joint friendly activities
low risk of injury
walking
biking
swimming
water aerobics
muscle strengthening with resistance bands
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune disease
• Mainly attacks joints, usually many joints at once
• Causes inflammation of the synovial membrane (joint lining)
• Can affect other organs, e.g., lungs, heart, eyes
Symptoms Rheumatoid Arthritis
pain
inflammation
redness
fatigue
stiffness
same symptoms on both sides of body
weight loss
Rheumatoid arthritis risk factors
Any age; likelihood increases with age
• Female
• Smoking
• Obesity
• Genetic
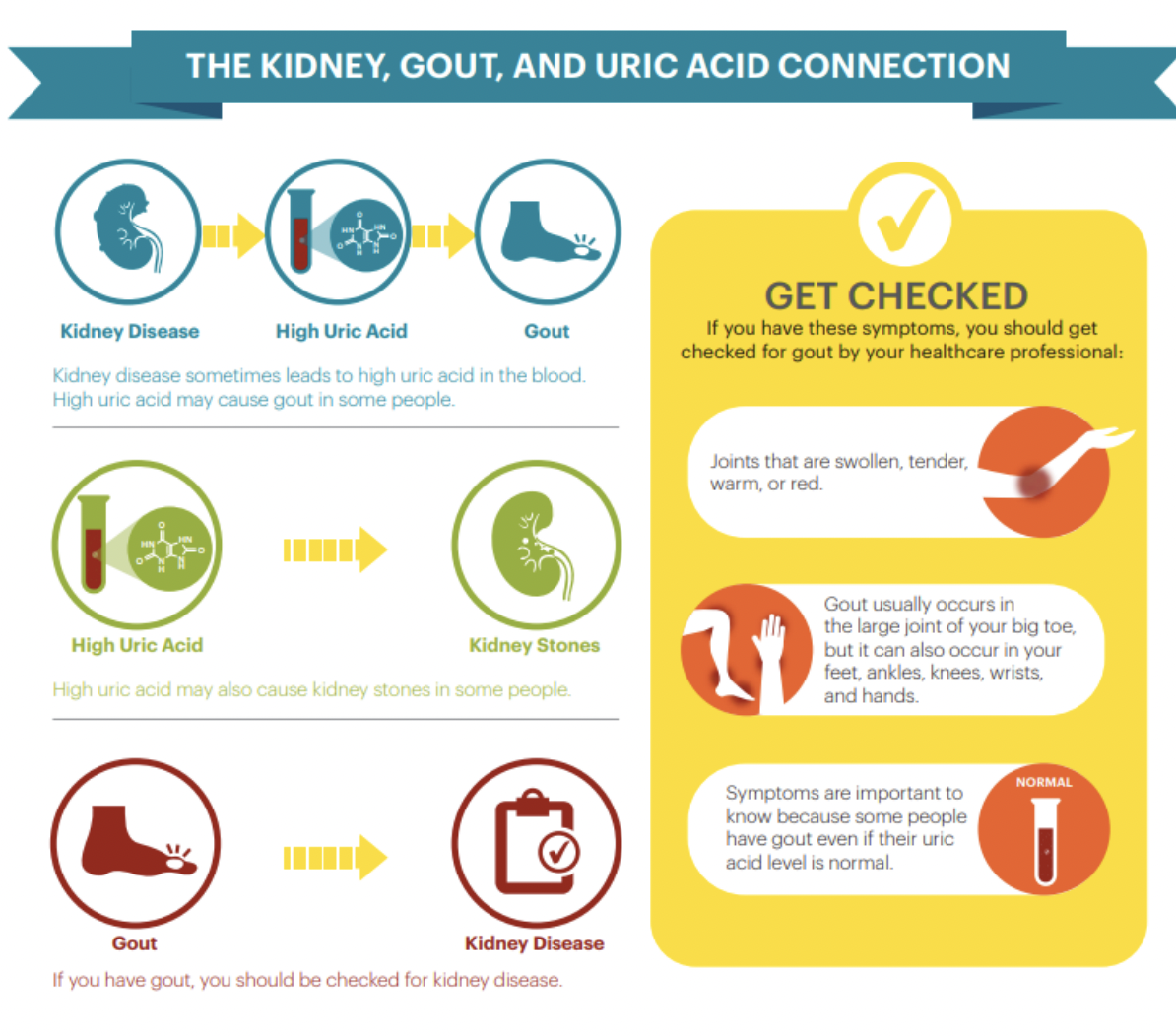
Gout
• Common type of inflammatory arthritis
• Usually affects one joint at a time
• Bouts of flares (symptoms are present) and remission (no symptoms)
• Deposition of uric acid crystals in tissues and fluids
• Recurring acute flares can lead to gouty arthritis (type of arthritis that worsens over time)
Symptoms Gout
acute flares:
• Red, hot swollen joints
• Extreme pain
Gout risk factors
• Male
• Obesity
• Medications including diuretics
• Alcohol
• Certain health conditions, e.g., hypertension, diabetes, poor kidney function, insulin resistance
• Diet high in fructose (type of sugar) & purines (e.g., in red meat, alcohol)
Arthritis pain
Severe joint pain adults
• Higher in women
• Highest among non-Hispanic blacks (50.9%), then Hispanics & Native Americans/Alaska Natives (42.0%), Asians (27.7%), and non-Hispanic whites (27.4%)
• More common in adults with arthritis who also have other chronic conditions
severe joint pain definition
when an individual rates his or her pain as a 7 or higher out of 10
persistent pain definition
when an individual reports having pain of any severisty on most or all days in the past 3 months
Fibromyalgia
Condition causing pain all over body, sleep problems, fatigue
• Symmetrical tender points (pressure is painful)
Symptoms Fibromyalgia
Pain, stiffness
• Fatigue
• Depression & anxiety
• Sleep problems
• Difficult with thinking, memory & concentration
• Headaches
• Digestive problems
• Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
Risk factors Fibromyalgia
Age
• Preexisting lupus or rheumatoid arthritis (RA)