Social Cognition: Knowing the Self
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
lateral regions of pre-frontal cortex
dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) - involved in working memory
ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (vlPFC)
medial regions of prefrontal cortex
orbitofrontal cortex (deals with value assessment)
ventromedial pre frontal cortex (vmPFC) - also involved in value assessment in different ways
regions involved in self-referential processing
dlPFC
vmPFC
posterior cingulate cortex
medial and lateral parietal cortex
regions involved in subhective feelings
orbitofrontal cortex
anterior cingualte cortex
insula
development in regions
there is different rates of development in different regions
prefrontal cortex vs striatum development
striatum develops first - adolescents
then prefrontal develops - adults
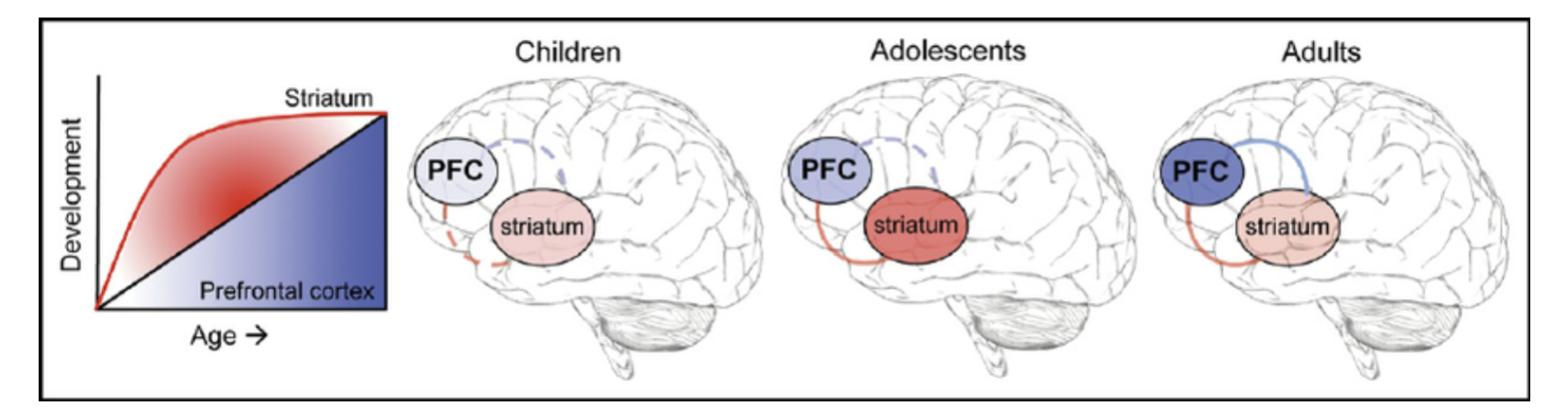
Some psychologists attribute the risky behavior of adolescents to a mismatch between development of the prefrontal cortex and development of the limbic system. This is based on the fact that one of these two brain regions develops before the other. Which region develops first?
A. The prefrontal cortex
B. The limbic system
C. They develop at the same time
D. The cerebellum
B
when does the PFC develop?
continues to develop throughout teenage years and doesn’t fully develop until age of 25
what events affect the PFC and developing brain regions?
adverse social events and adverse events(such as limiting social interaction) such as chronic stress are more likely to affect PFC and developing brain areas
how can adverse events affect the PFC and developing areas?
affects on social interaction, density of spines affected
how does stress affect us?
central nervous system is vulnerable to stress throughout life, even into adulthood
perceptions of isolation correlated with:
higher morbidity and mortality rates
increased vascular resistance
higher blood pressure
fragmented sleep
sedentary lifestyles
decreased immunity
decreased impulse control
healthy social interactions and what area is responsible
healthy social interactions are important
prefrontal cortex is important for social cognition
The case of Phineas Cage
a metal rod went up his skull and damaged large regions of prefrontal cortex
it had a lot of changes to his temperament and cognition
before people described him as respectable and after the described him as more impulsive, harder to get along with
shows importance of prefrontal cortex for social cognition
disorders affecting social cognition
anti-social personality disorder (ASPD)
schizophrenia and Autism Sppectrum Disorder (SD)
anti-social personality disorder (ASPD)
aware of social norms, but may disregard them
may lack empathy
low impulse control, increased aggression
may not care for the welfare of others, deceitful
schizophrenia and Autism Spectrum Disorder (SD)
both are heterogenous disorders that lie on a spectrum
deficits in social perception (perceiving cues from eye gaze, body language, facial expressions)
difficulties understanding the mental states of others
ASD - find social interactions rewarding its just how they interact that is different
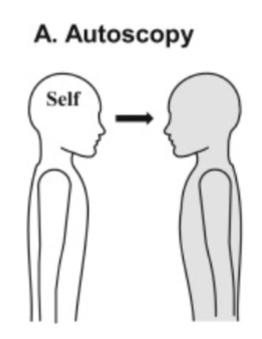
autoscopic phenomena
person seems to be awake yet sees their body and the world from a location outside the body:
three types
autoscopic
out of body
heautoscopy
autoscopic
not residing in your body
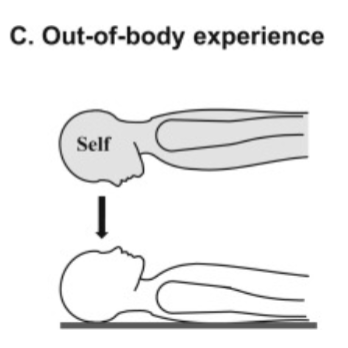
out of body
inhabiting another body (usually hovering above) - you perceive yourself as looking down @ your physical body
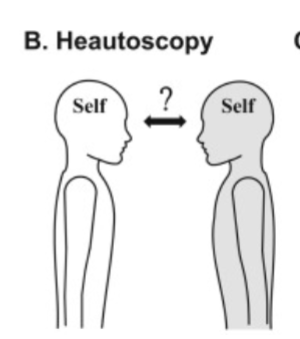
heautoscopy
see your own body and a view of the world from that location - inhibiting another space; in that horizontal plane
what part of your brain is activated with an out of body experinece?
right temporoparietal cortex
what part of your brain is activated with an autoscopic hallucination?
right parietooccipital cortex; right temporo-occipital cortex
what part of your brain is activated with a heautoscopy?
left temporoparietal cortex
What area of the brain is most involved in body ownership?
A. mPFC
B. OFC
C. ACC
D. Temporoparietal cortex
D
temporoparietal junction
involved in self-processing and integrating multisensory body related information
xenomelia
another phenomenon with body ownership
rare condition in which able-bodied individuals report experiencing a lifelong desire for the amputation of one or several of their limbs because they feel the limb does not belong to their body
this limb is usually on the left side (right hemisphere of the brain tend to be affected)
affects superior parietal lobule where somatosensory, visual, and vestibular converge, critical for sensorimotor integration
self-reference effect
more likely to recall information if you can relate it to the self
what area is involved in the self-reference effect
medial PFC
less inhibition and increased activation in the medial PFC when relating words to the self
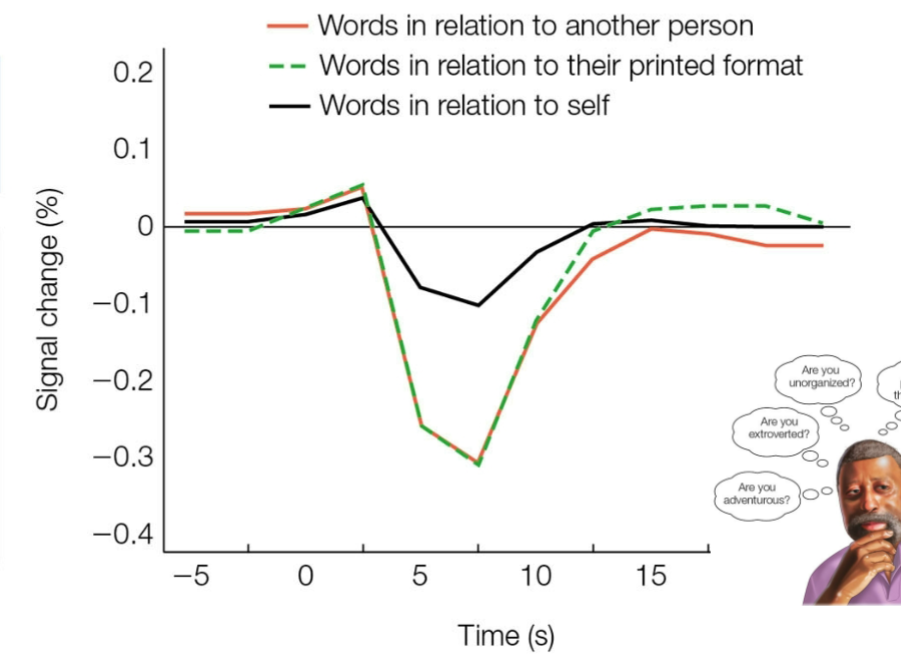
are self-descriptive personality traits based on recent episodic memories?
no they do not rely on episodic memories; it relies more on semantic knowledge involving medial PFC
experiment showing how self destructive personality traits are not based on recent
had participants answer questions based on three conditions
self-judgement (are you generous?)
autobiographical (give an example of when you were stubborn?) → episodic memory
definition (what does lazy mean?) → semantic knowledge
2 weeks later they had to perform this same task with half old traits and hald new traits
Prediction: if self-descriptions rely on searching episodic memory, then participants should answer faster when asked about a personality characteristic they had recently thought about in relation to themselves.
Result: No difference in timing between the two groups.
what do you think about “at rest”? and what has high activity
think about topics related to self-referential processing
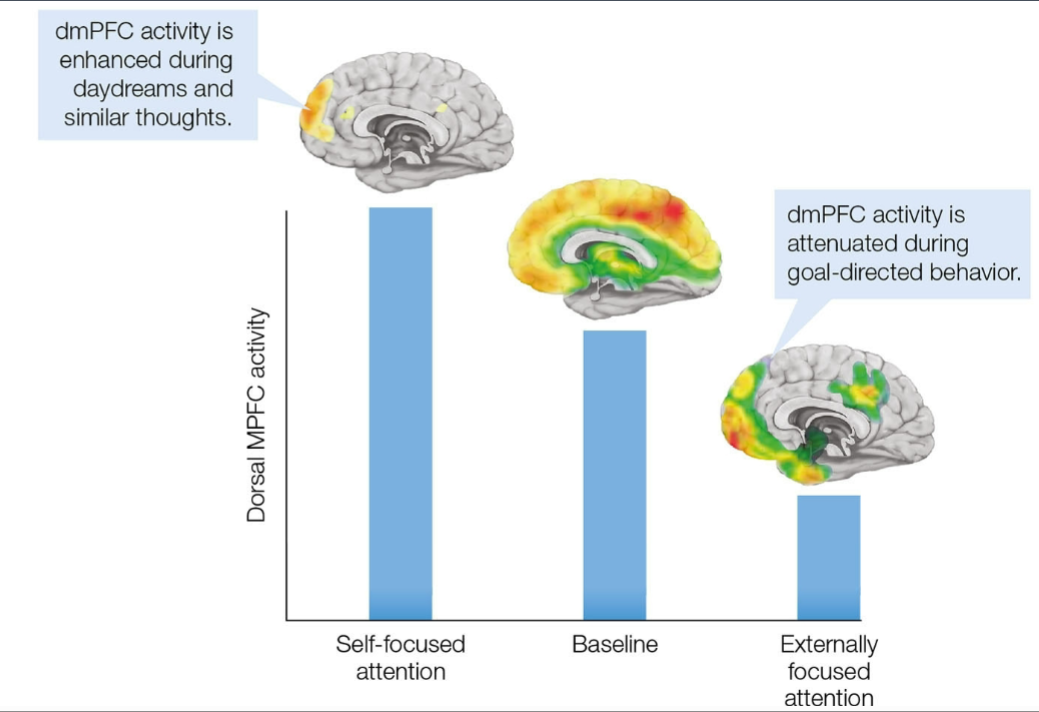
mPFC has higher activity when “at rest or not performing a specific cognitive task
default mode network - resting state network
default more network: sentinel hypothesis
the default mode network is there to ensure we always have some idea what is going on around us
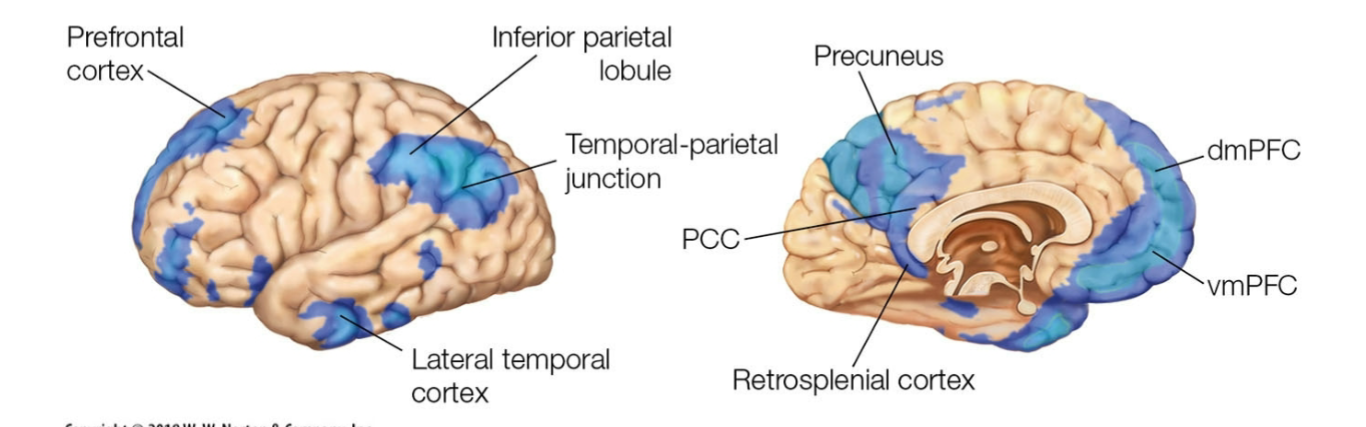
default mode network define (activation) and regions
most active when inwardly focused (focused on internal stuff rather than external)
ex. daydreaming
connected to memory system
default mode network activation during self-focused attention vs externally focused attention
default mode network: social cognition
also active during social cognition(huge overlap) as involves self-referential or internally generated thought.
areas of left angular gyrus, precuneus and ventral anterior cingulate cortex also has this overlap
When people engage in social cognition, their mPFC responses are often:
1.Much stronger than when they are resting
2.Not very different from when they are resting
3.Much less activated than when they are resting
4.None of the above
2
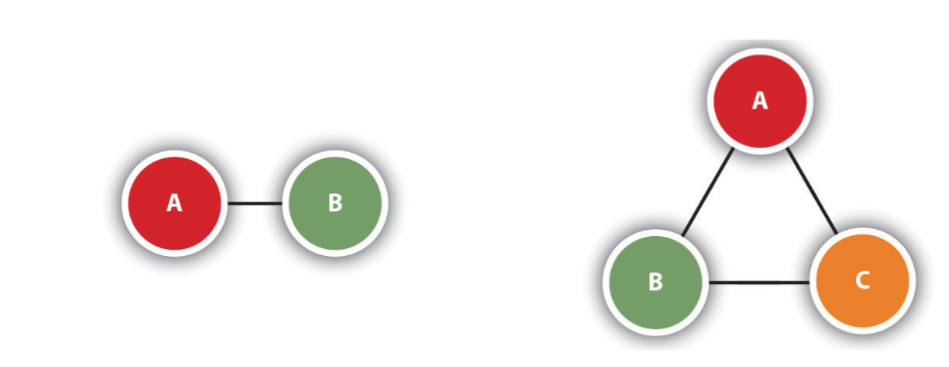
social geometry involves:
dyads - groups of two
triads - groups of three (need to know your relationship with others as well as their relationship with each other)
what areas are social interaction related to?
connected to areas of emotional processing, dopaminergic pathways to make more appropriate decisions in specific social contexts
A woman (Nour) gave a vase to her friend (Elena) as a gift. Several years later Nour is
visiting Elena and accidentally breaks the vase. Elena says “Don’t worry about it, I got
that vase as a gift and never liked it much anyway” What do you think is the most likely
scenario?
A. Elena is trying to insult Nour’s choice in vases
B. Elena is trying to make Elena feel better about breaking the vase
C. Elena no longer wants to be friends with Nour
D. Nour broke the vase intentionally
B → if you are taking context into account
However if you didn;t take context into account you may say A
OFC importance for social cognition?
important for knowing when to use social rules and taking context into account
what is vmPFC important for? and what happens with lesions
important for social-decision making
important for value based decision in general
when you have a lesion → you can learn a stimulus initially but have difficulty with encounters that involve reversal learning (when the value of the stimuli changes)
vmPFC vs OFC
vmPFC seems to base social decisions more on internal factors such as emotional value;