Respiratory anatomy, breathing and heart sounds
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
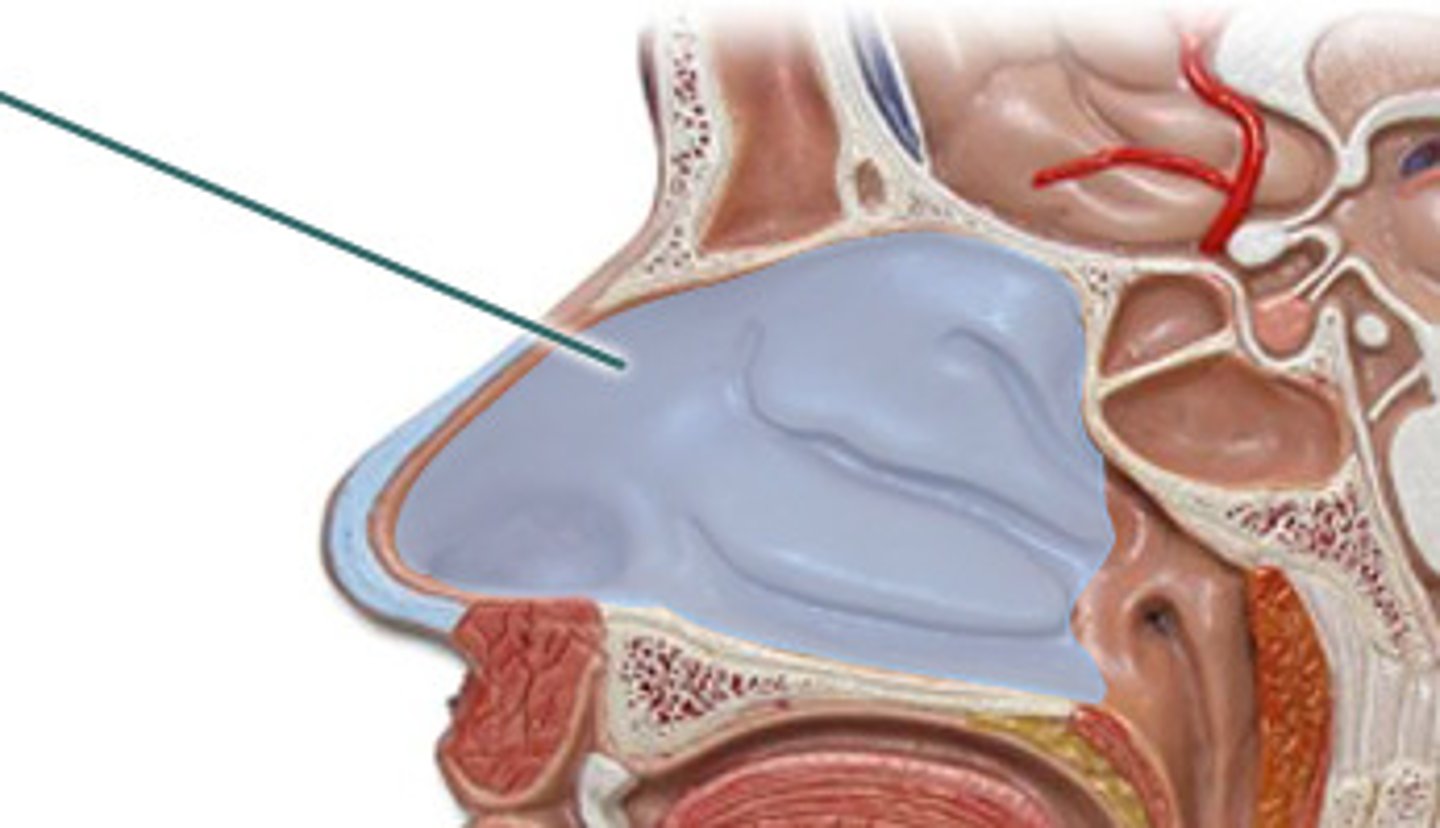
nasal cavity
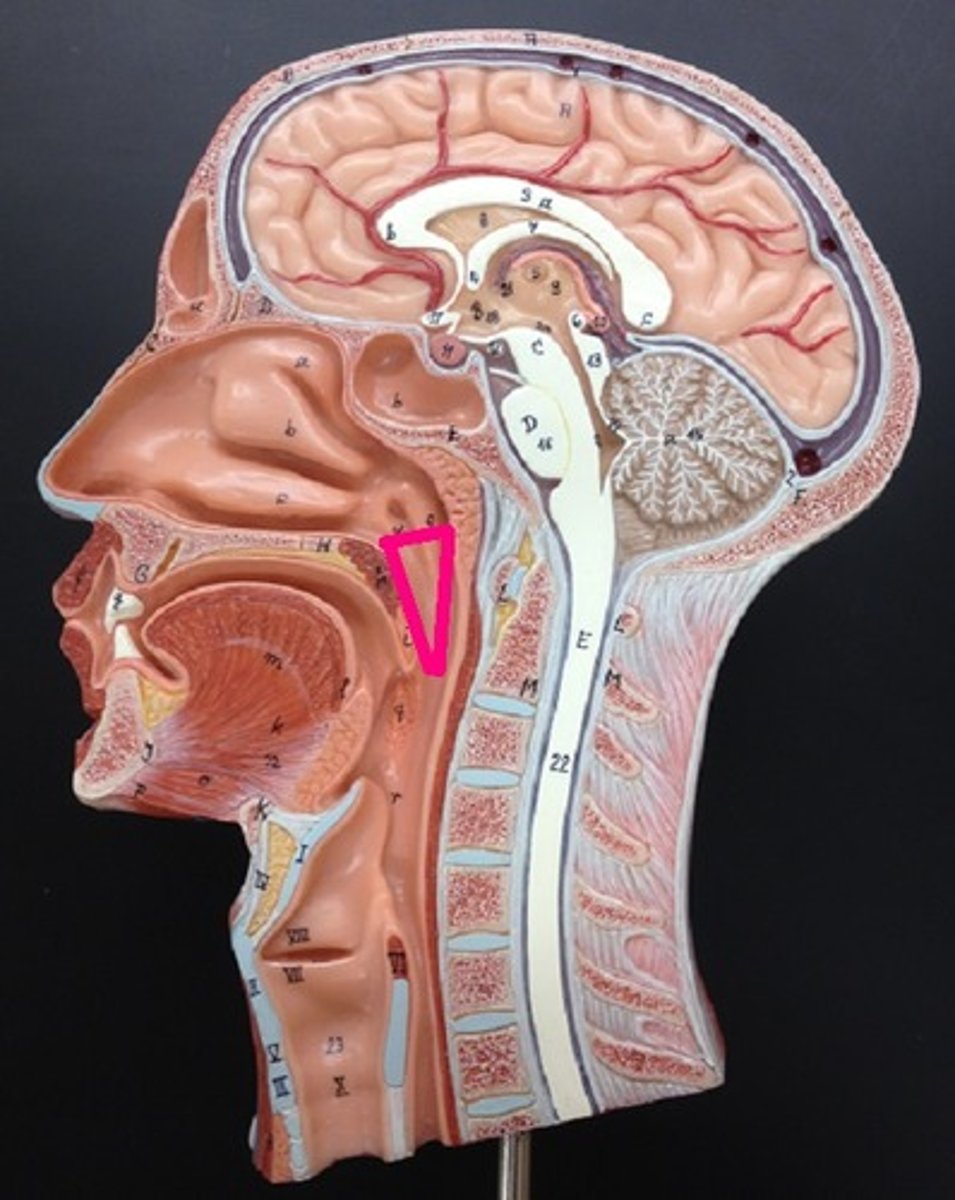
oropharynx
between nasopharynx and laryngopharynx
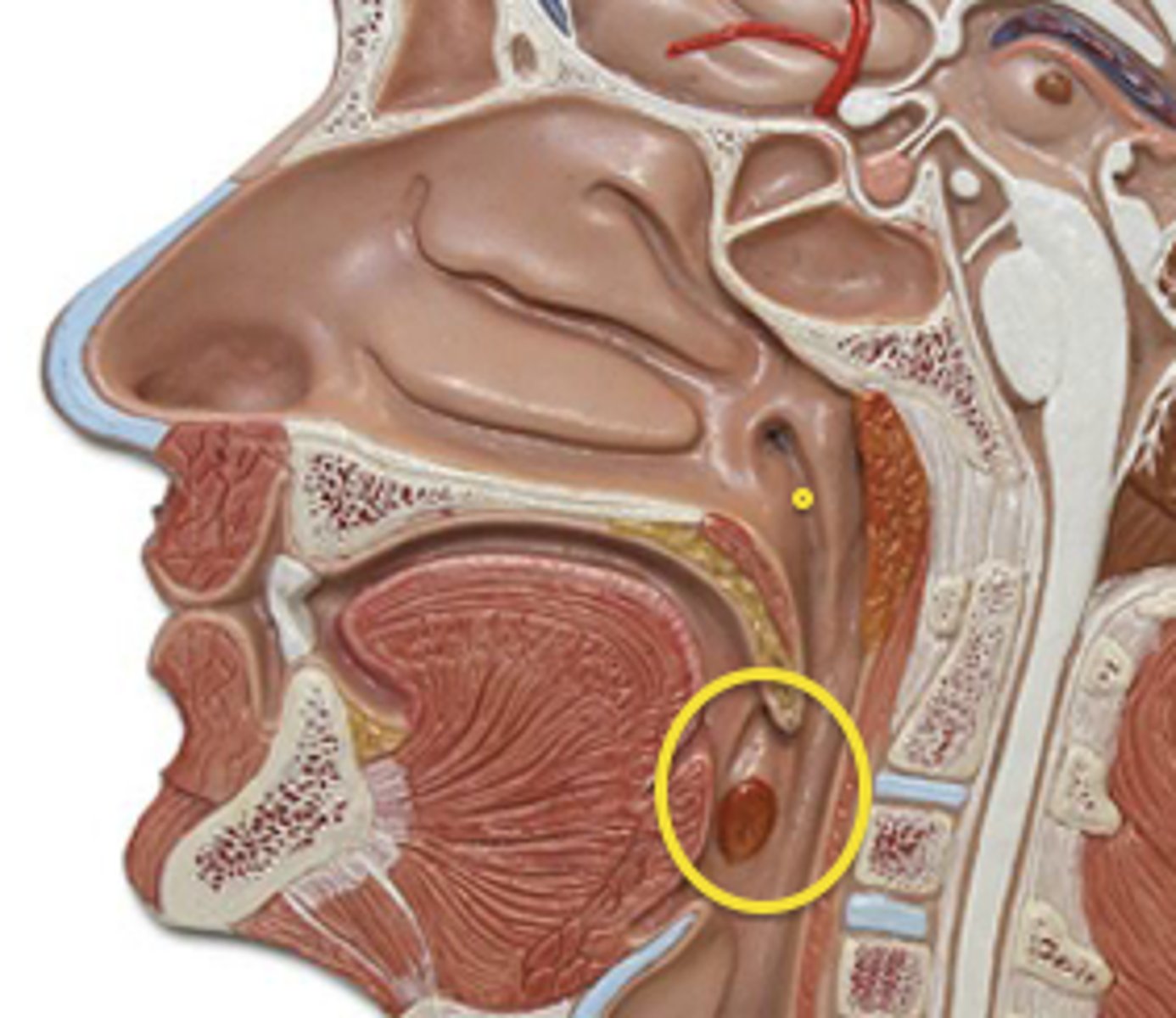
nasopharynx
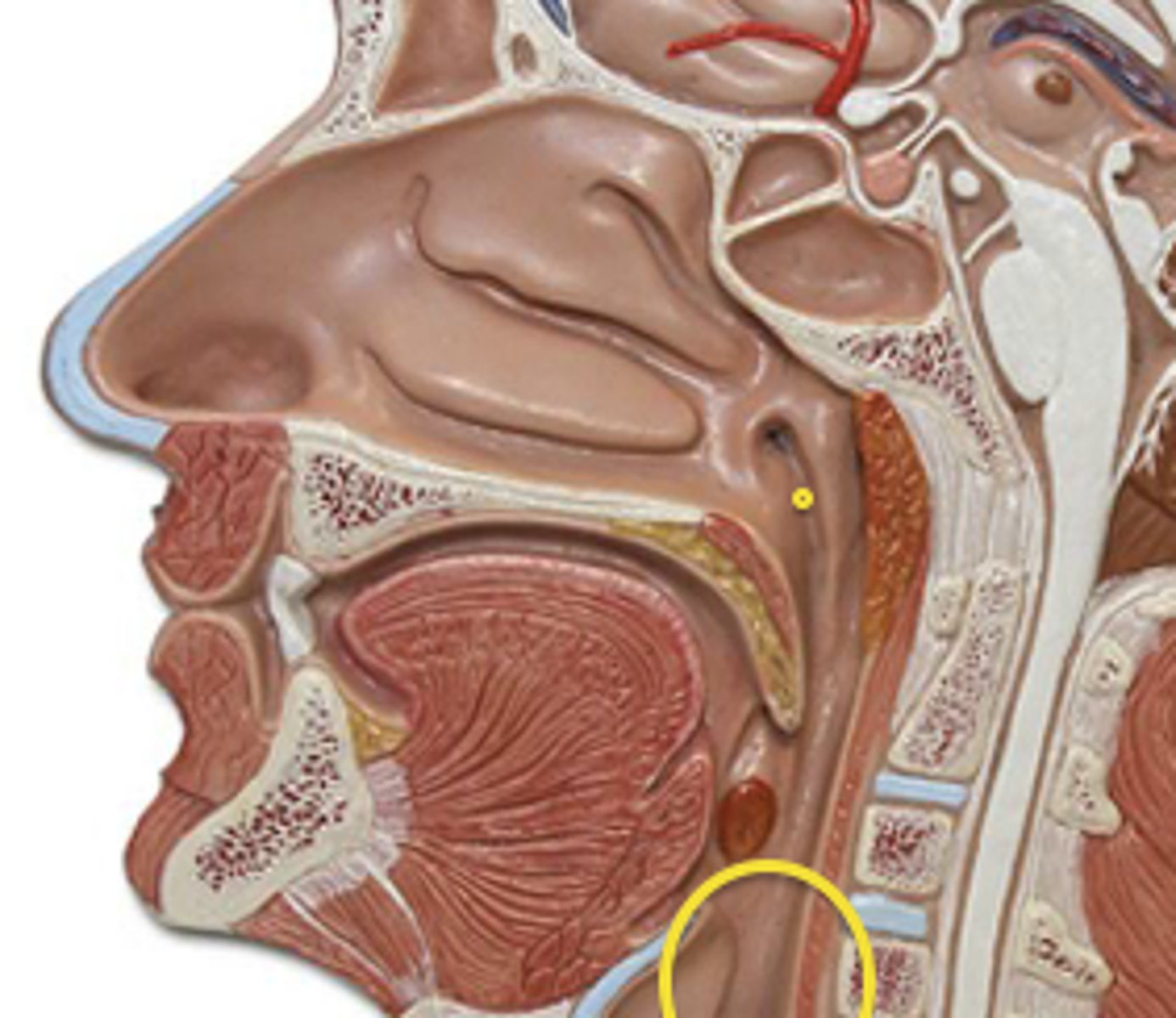
laryngopharynx
larynx
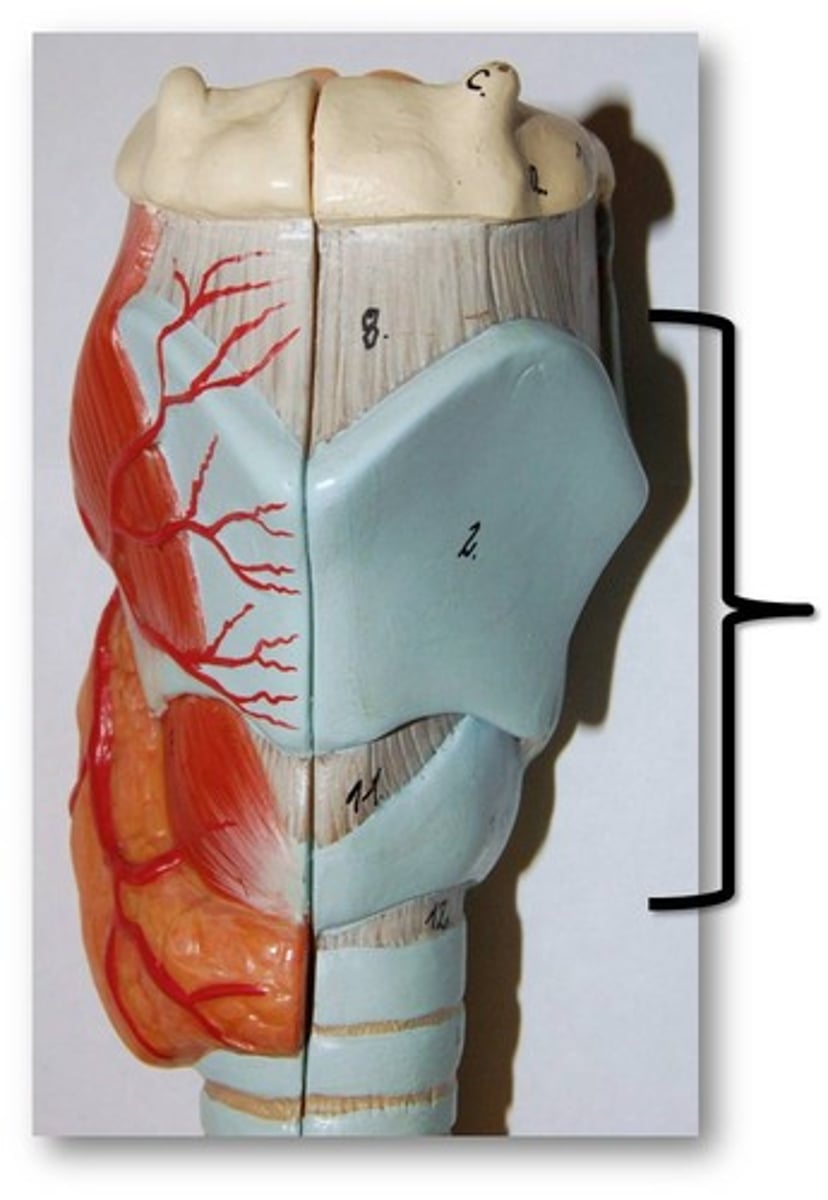
primary (main) bronchi
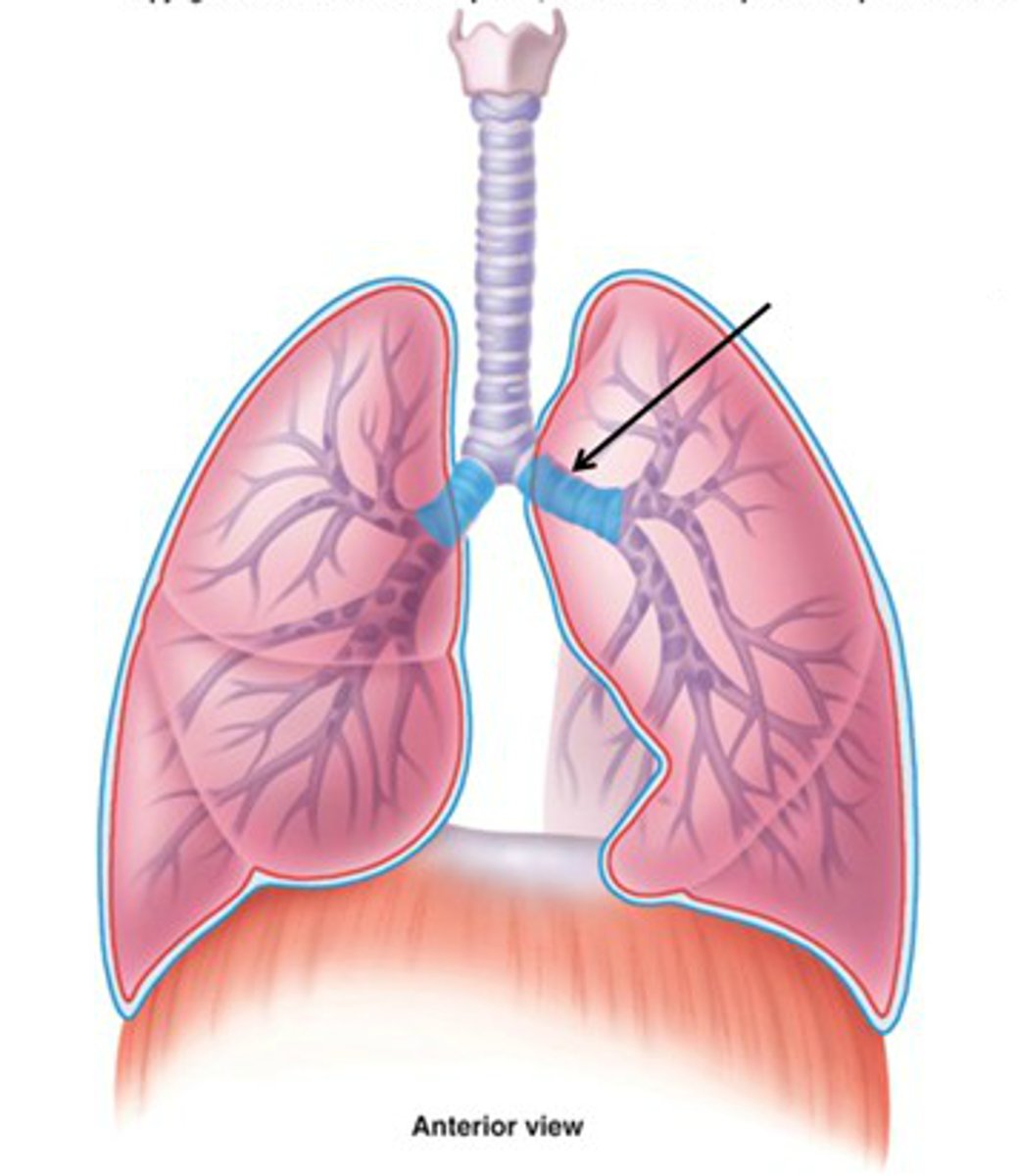
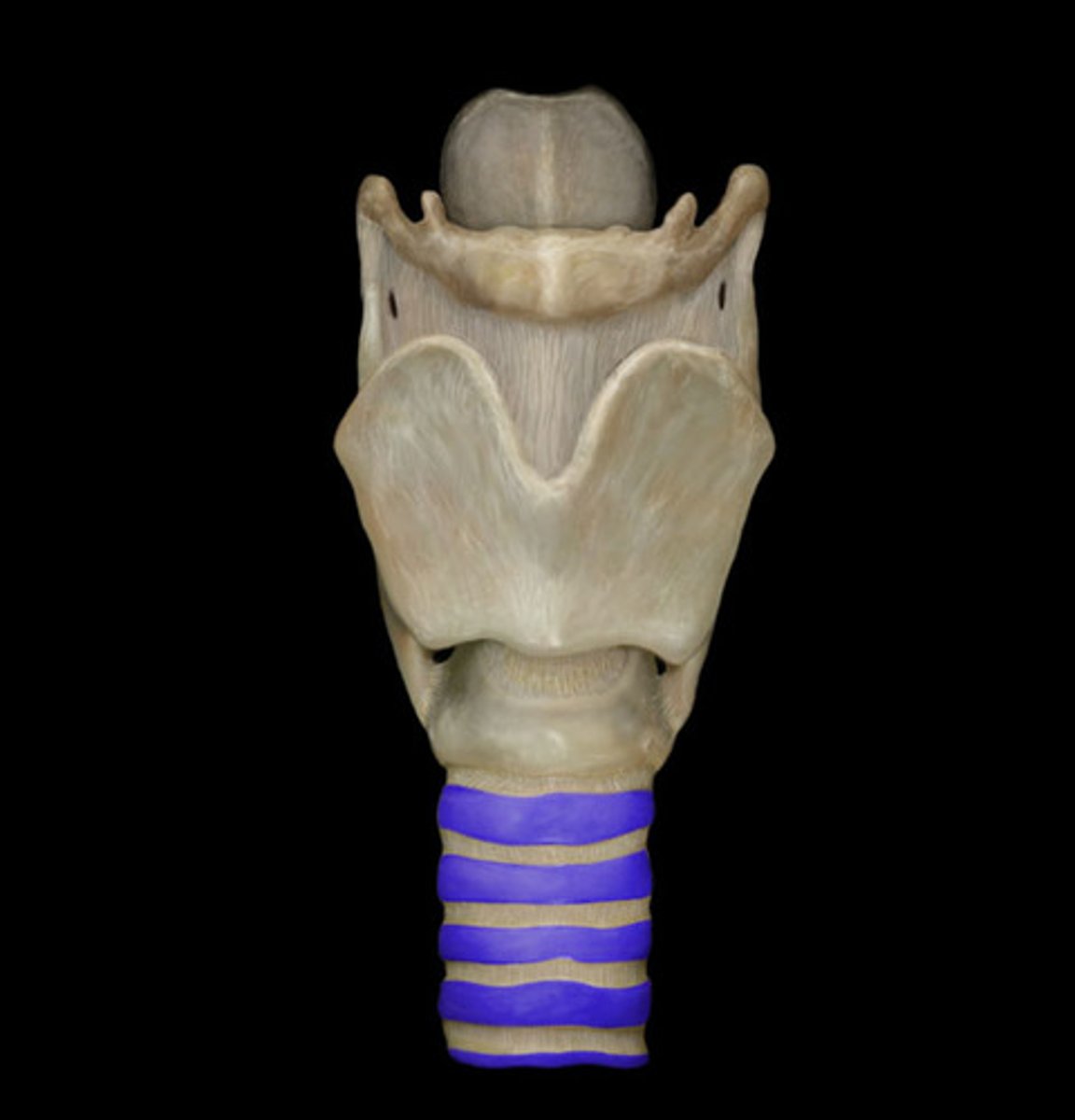
trachea
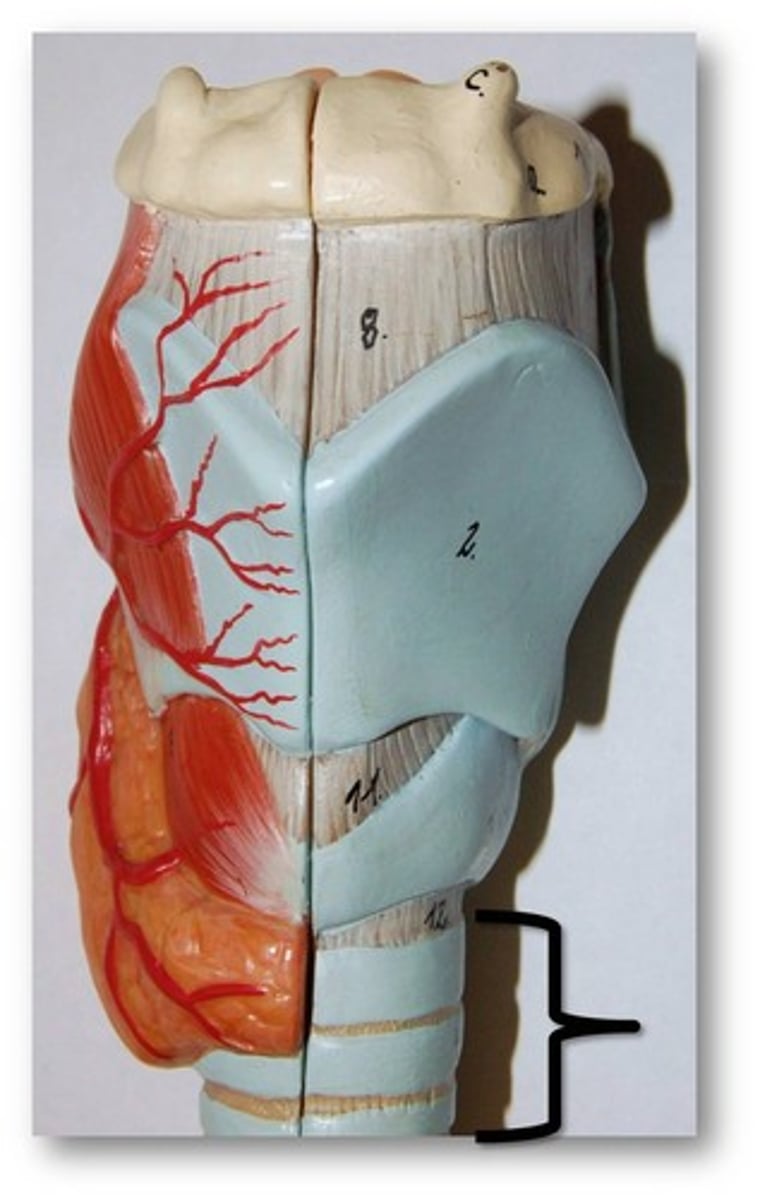
function of the nasal cavity
filter large particles by hairs within nose
- air encounters the nasal conchae which generates turbulence in the air flow and causes it to swirl around causing particles to MATTER or stick to moist mucous membranes
- air gets humidified
function of the nasopharynx
connecting your nose to your respiratory system
function of oropharynx
between nasopharynx and laryngopharynx
function of laryngopharynx
between oropharynx and larynx
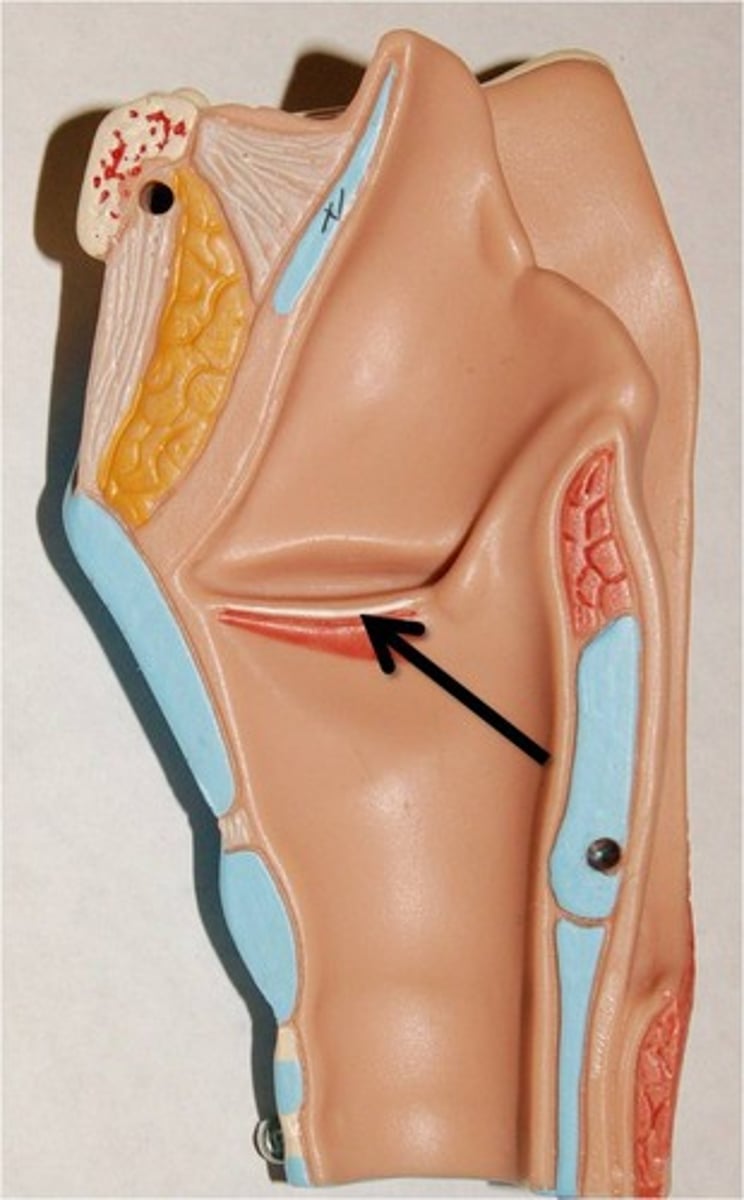
what the larynx
voice box
what is the function of the trachea
large tube structure that transmits air to the primary bronchi
thyroid cartilage (anterior)
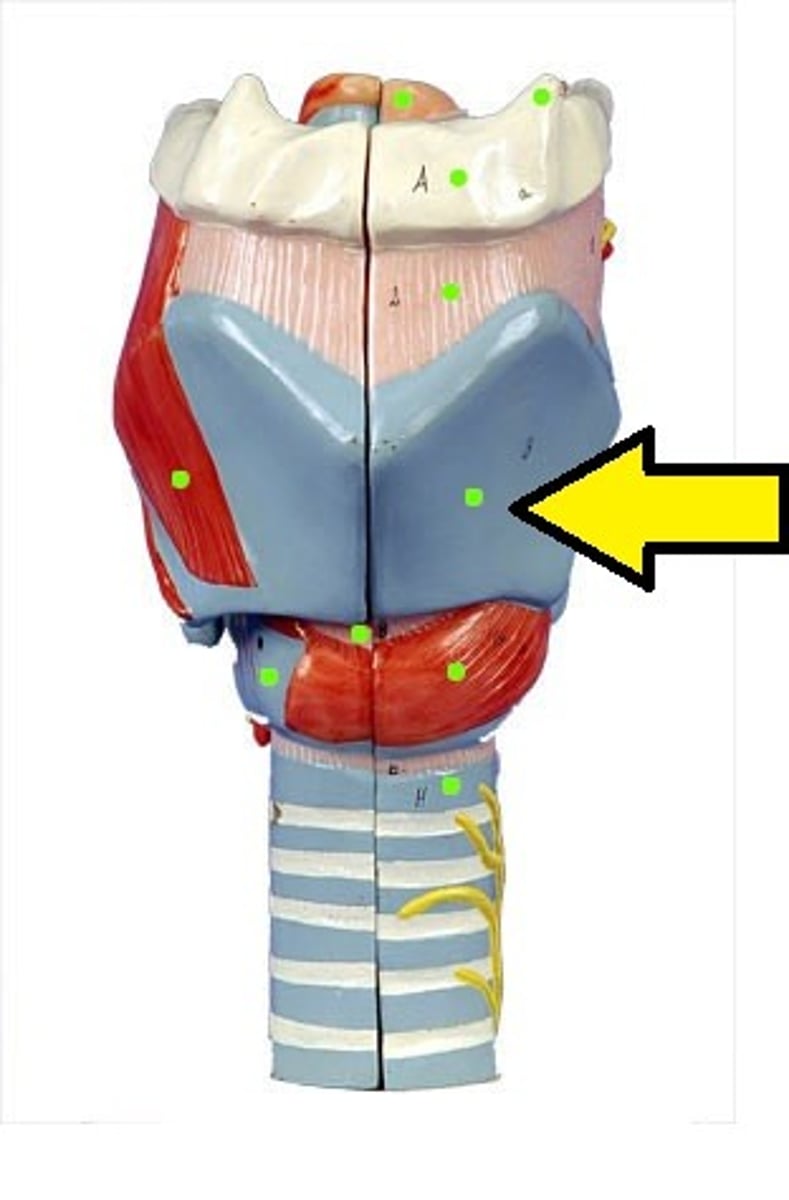
thyroid cartilage (posterior)
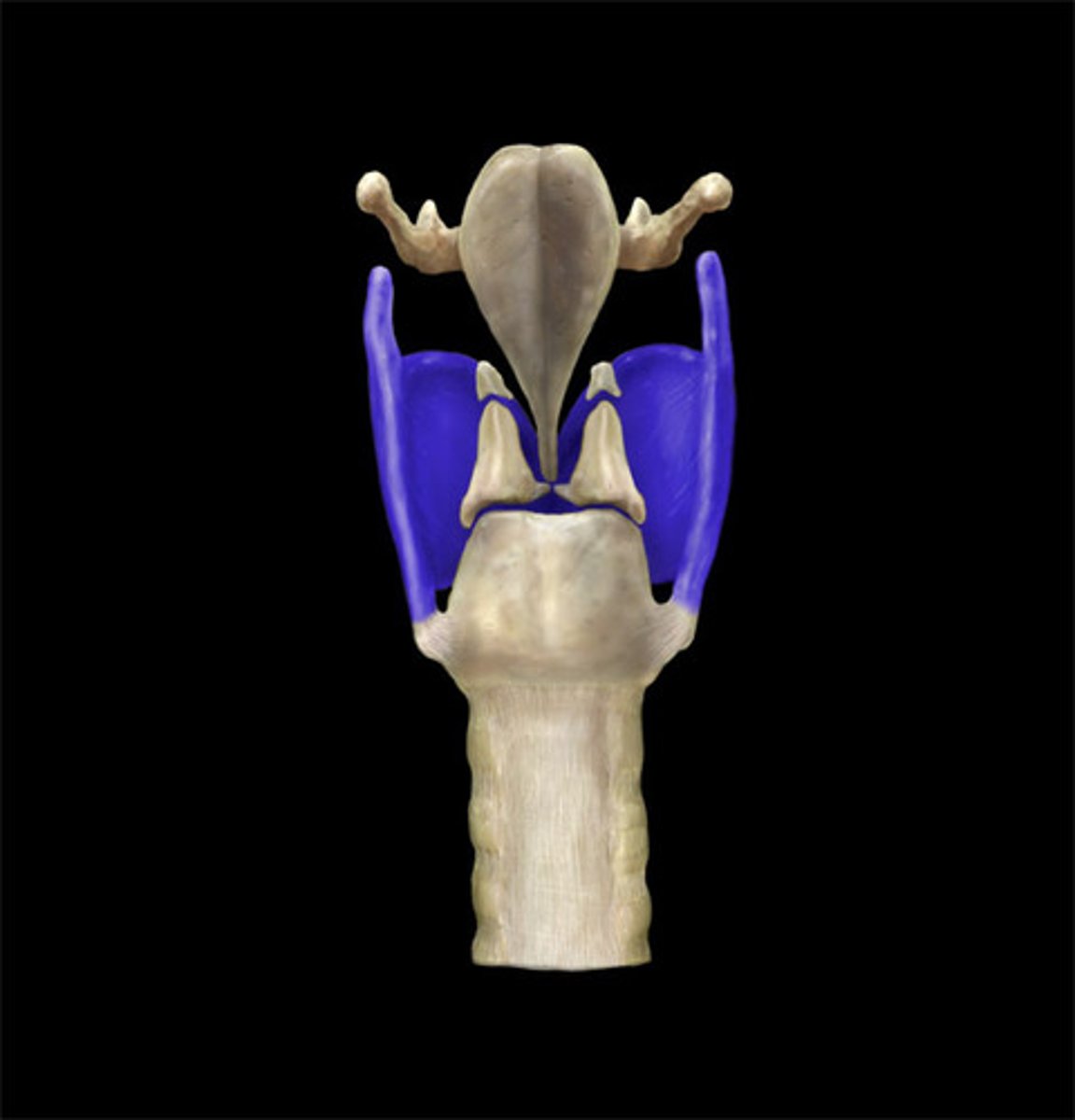
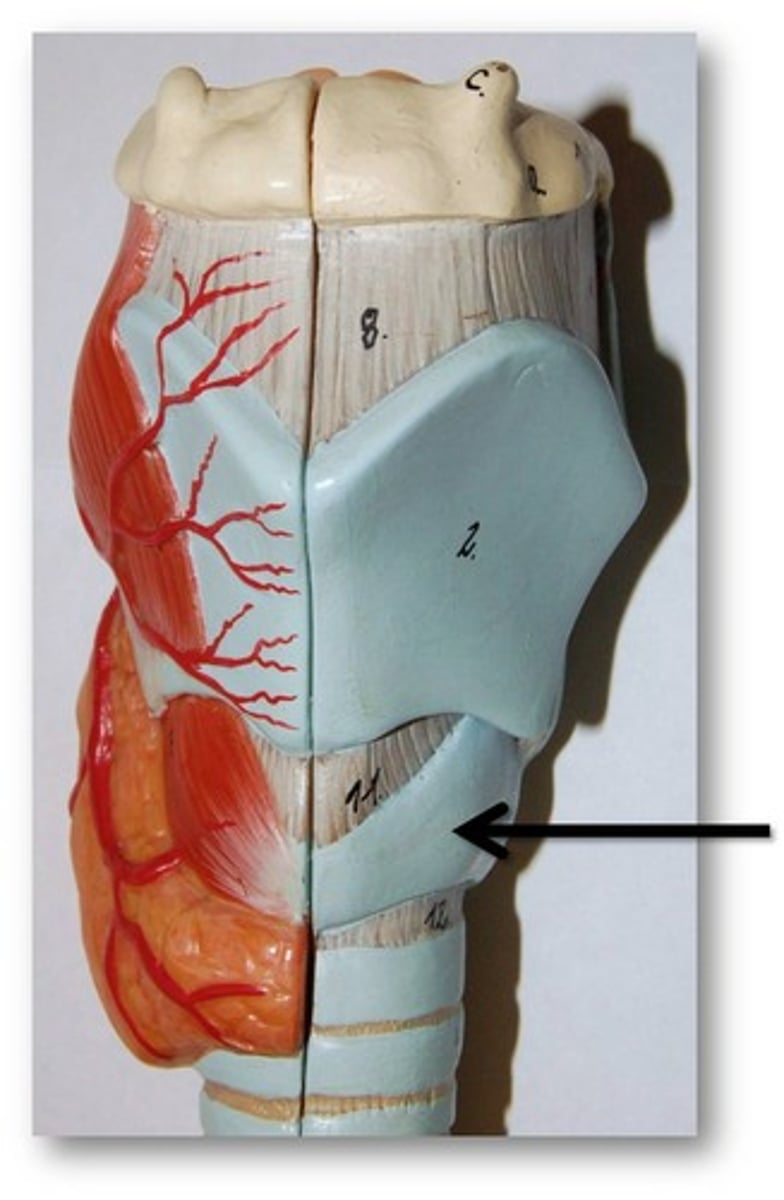
cricoid cartilage
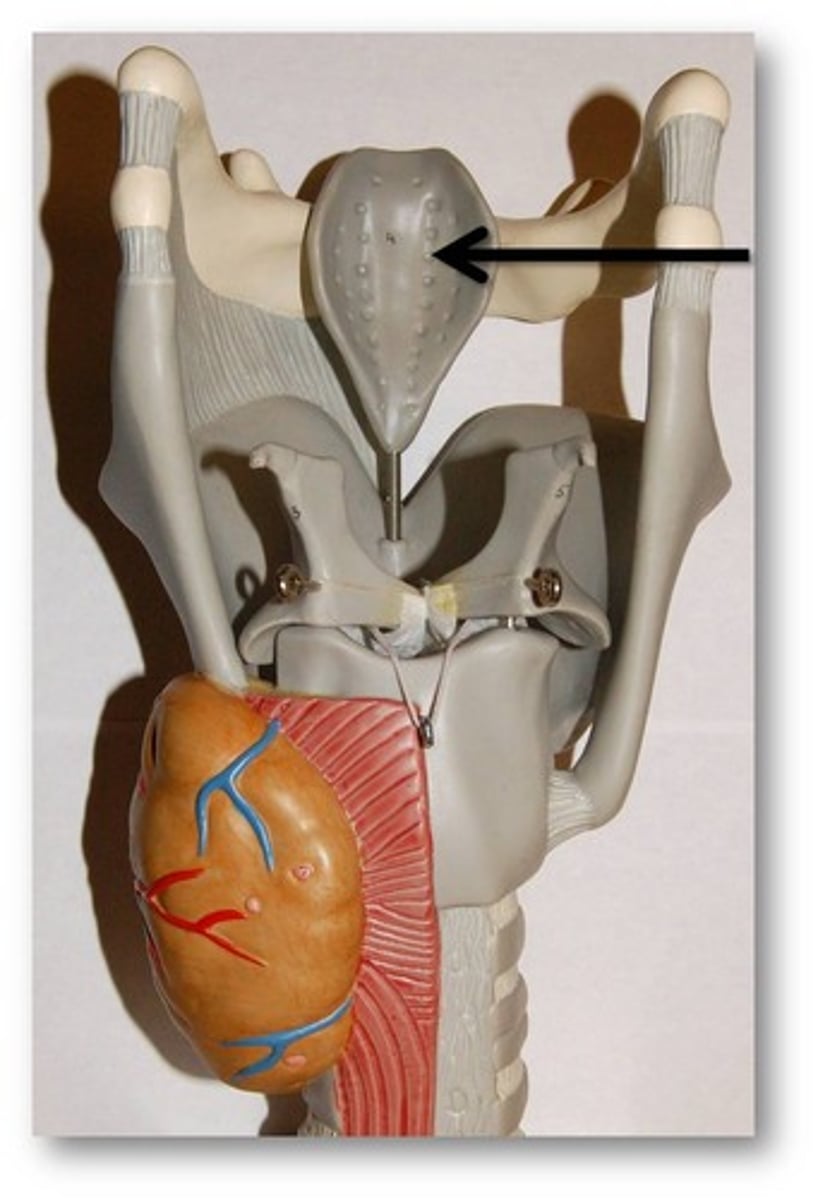
epiglottis
vestibular folds
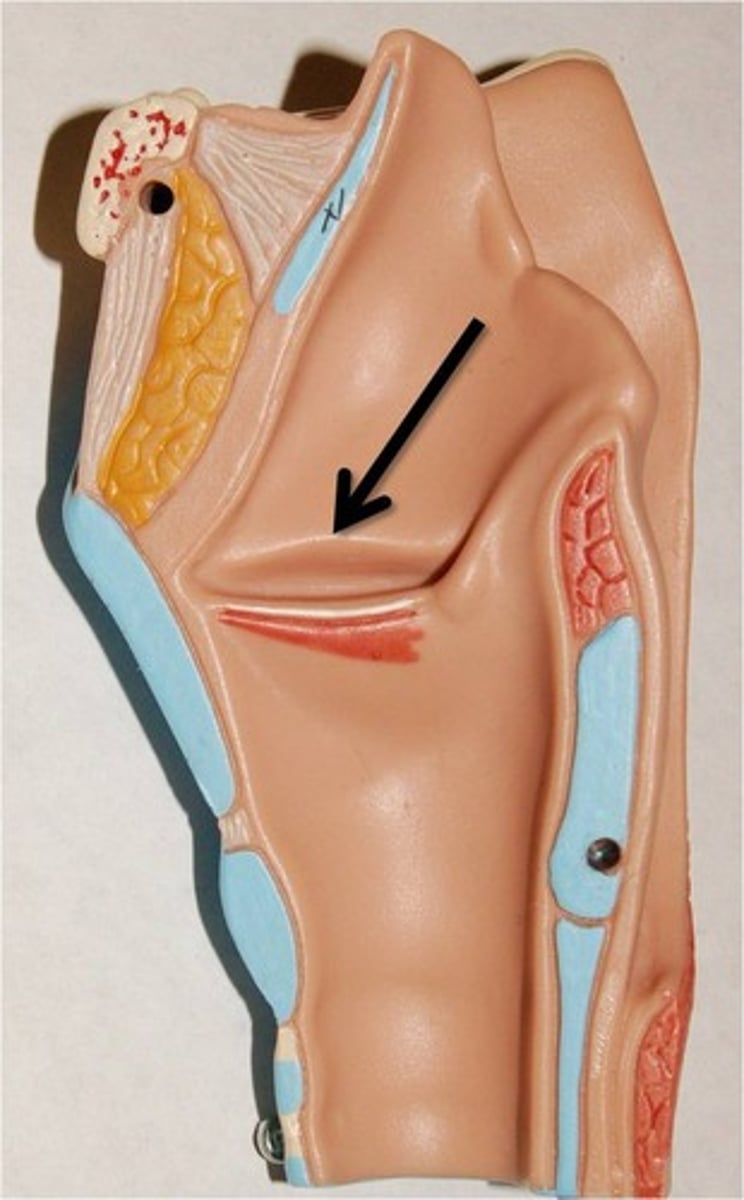
vocal cords
tracheal cartilage
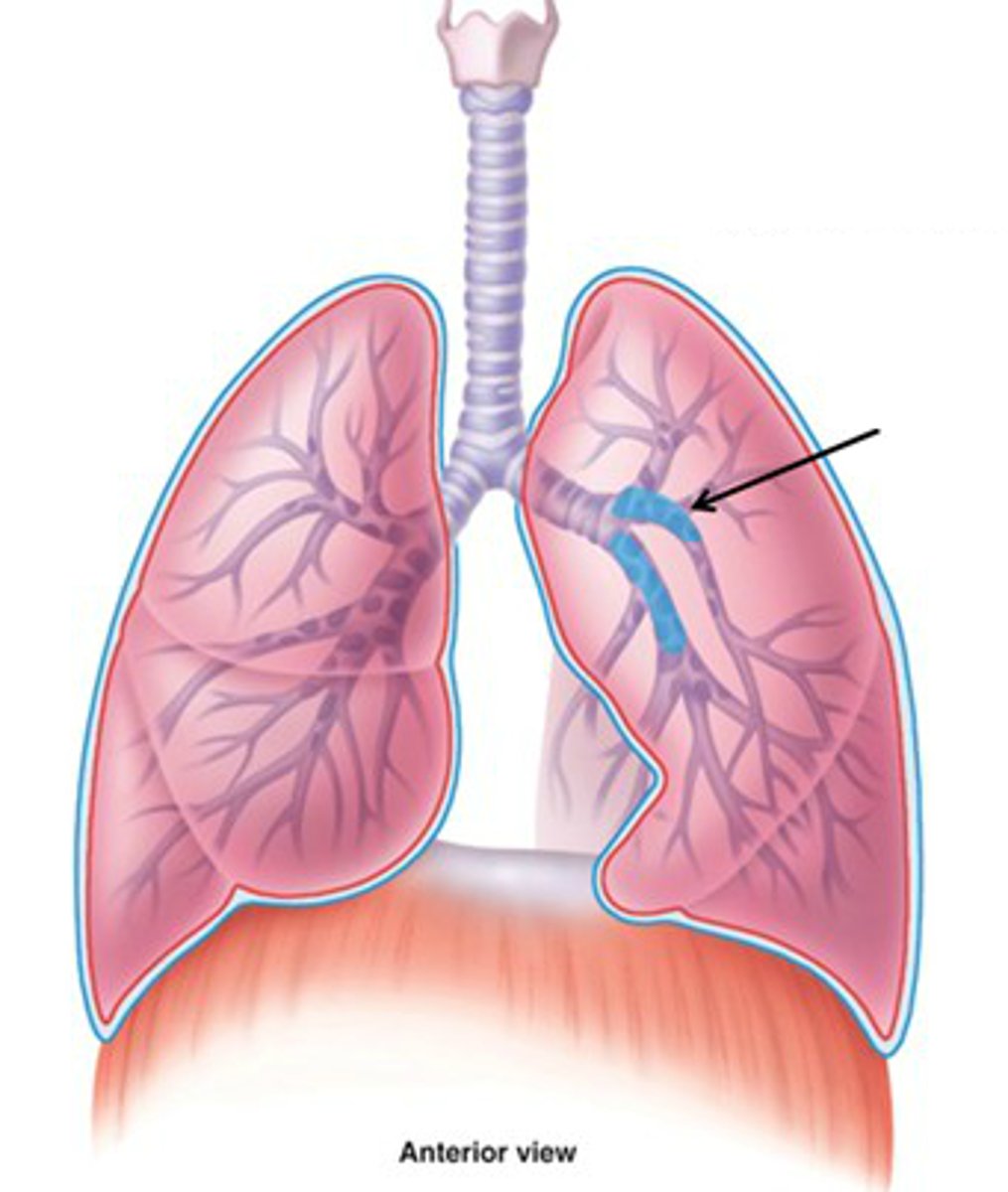
secondary (lobar) bronchi
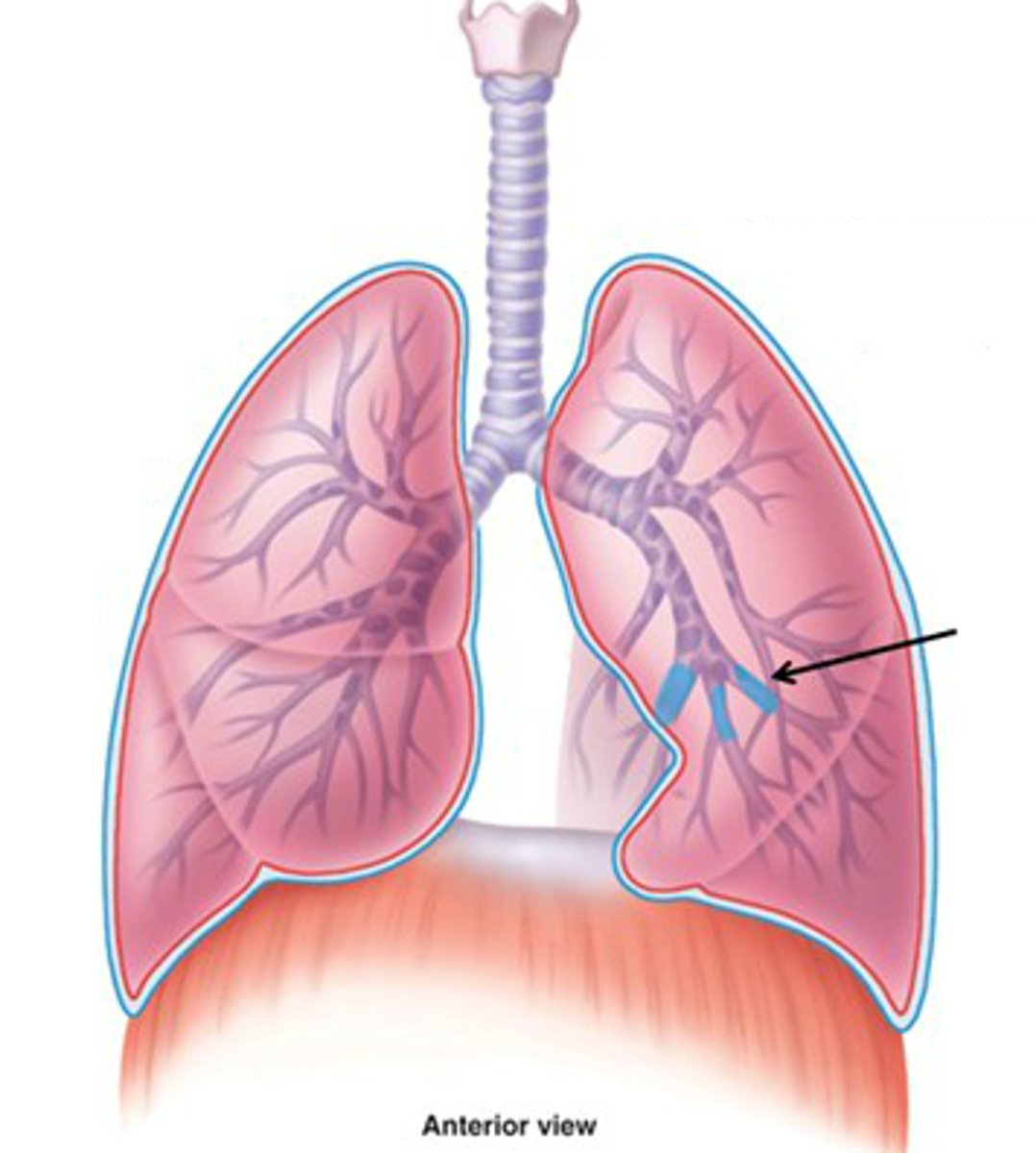
tertiary (segmental) bronchi
terminal bronchiole
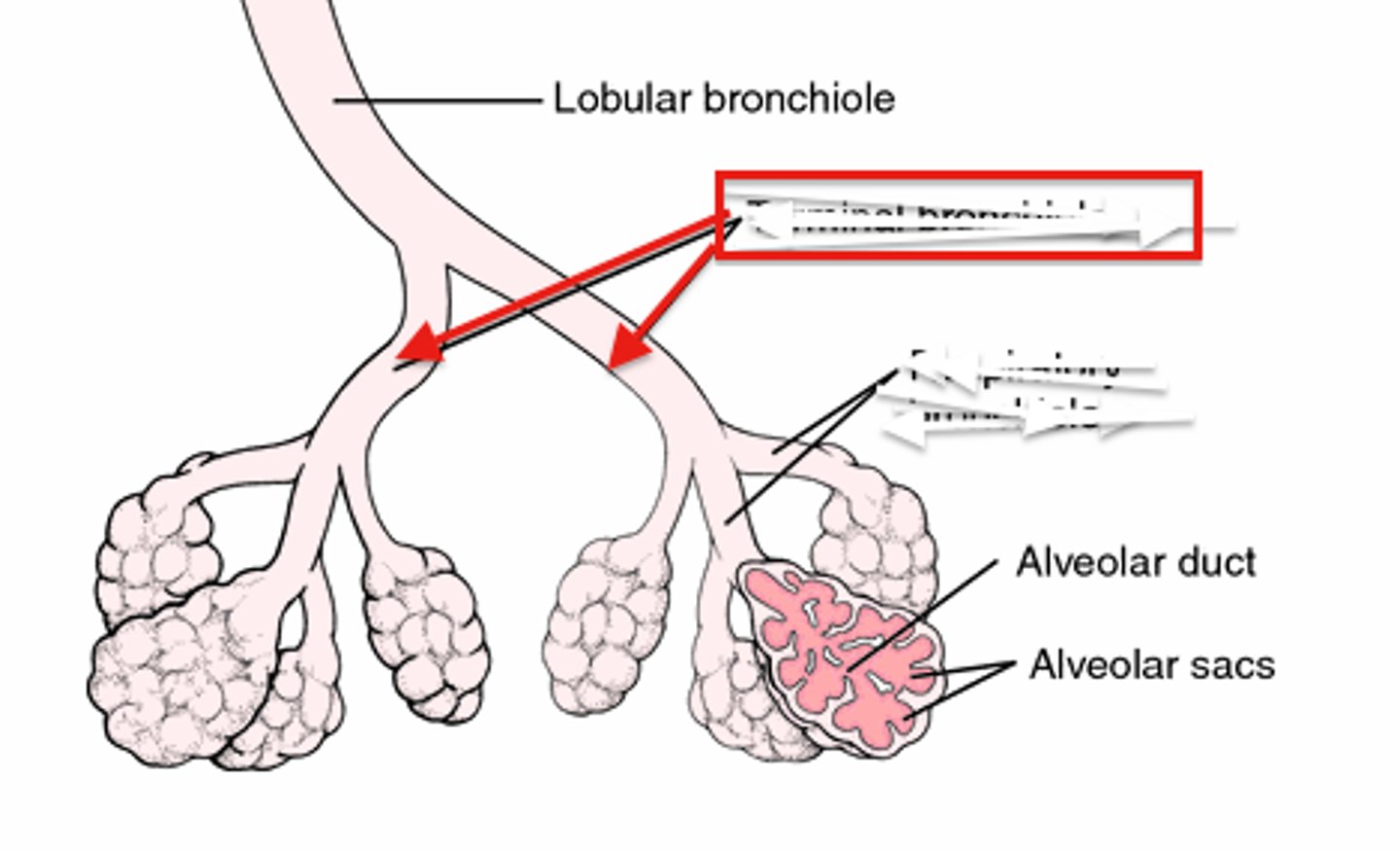
respiratory bronchioles
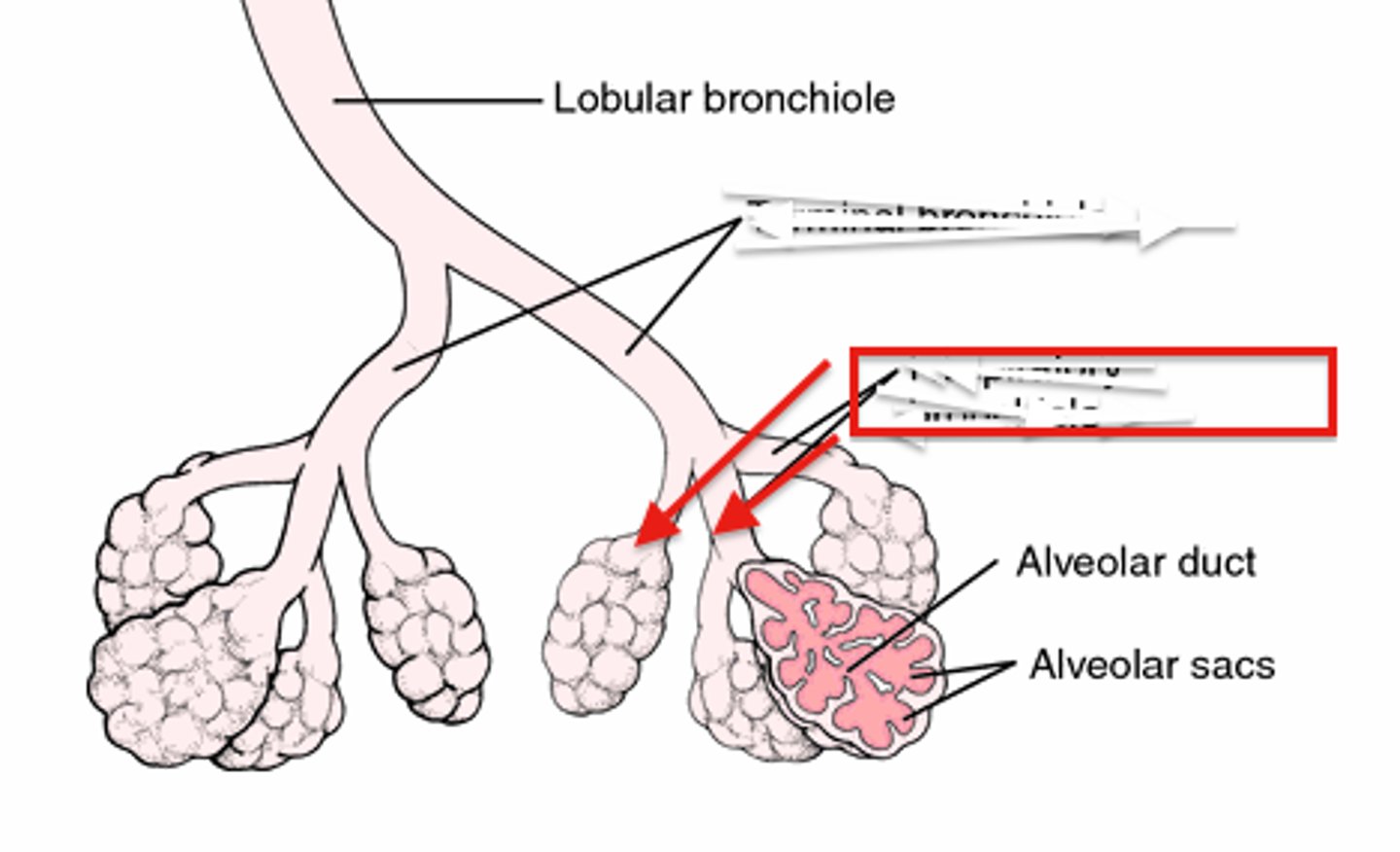
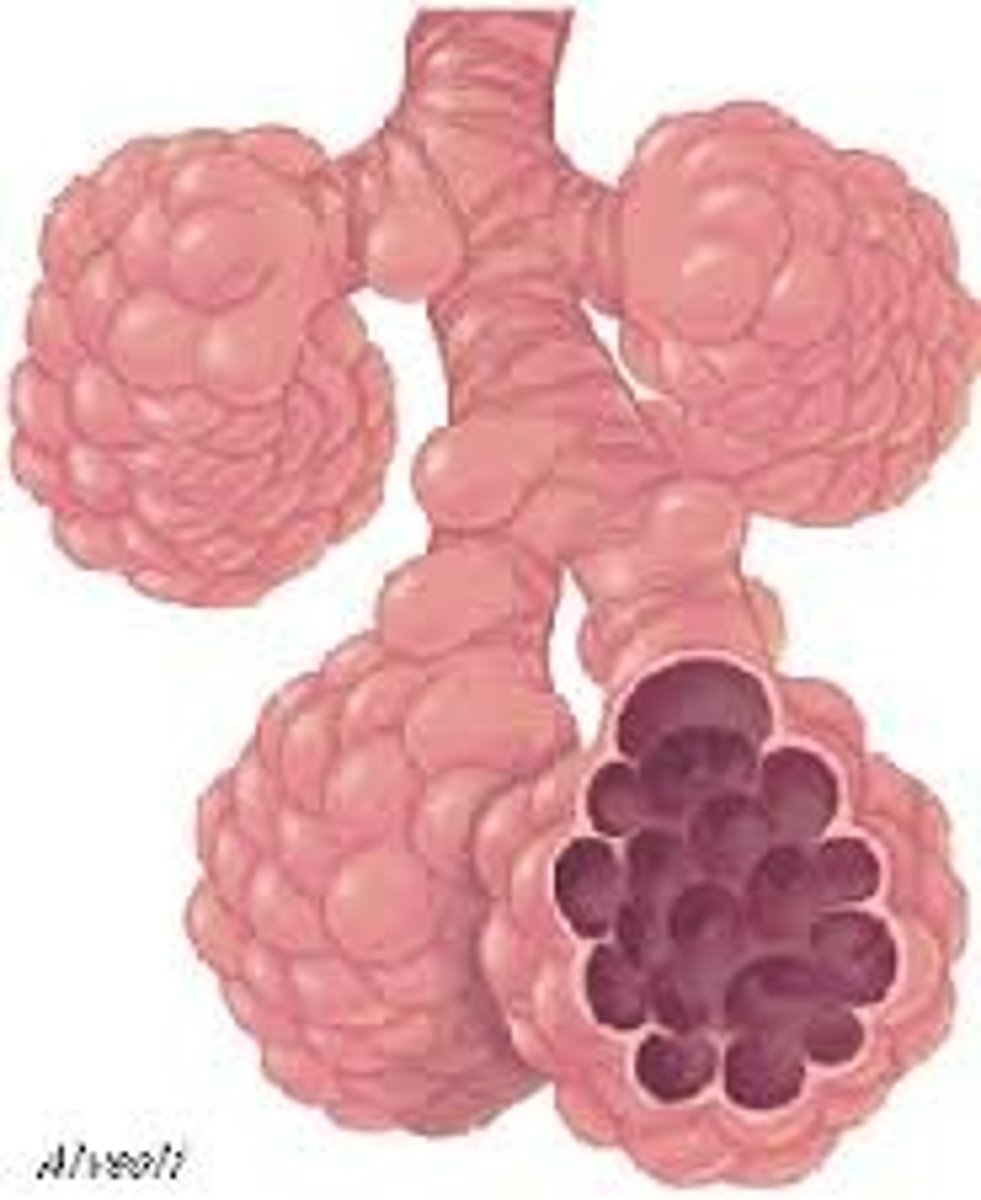
alveolar sac
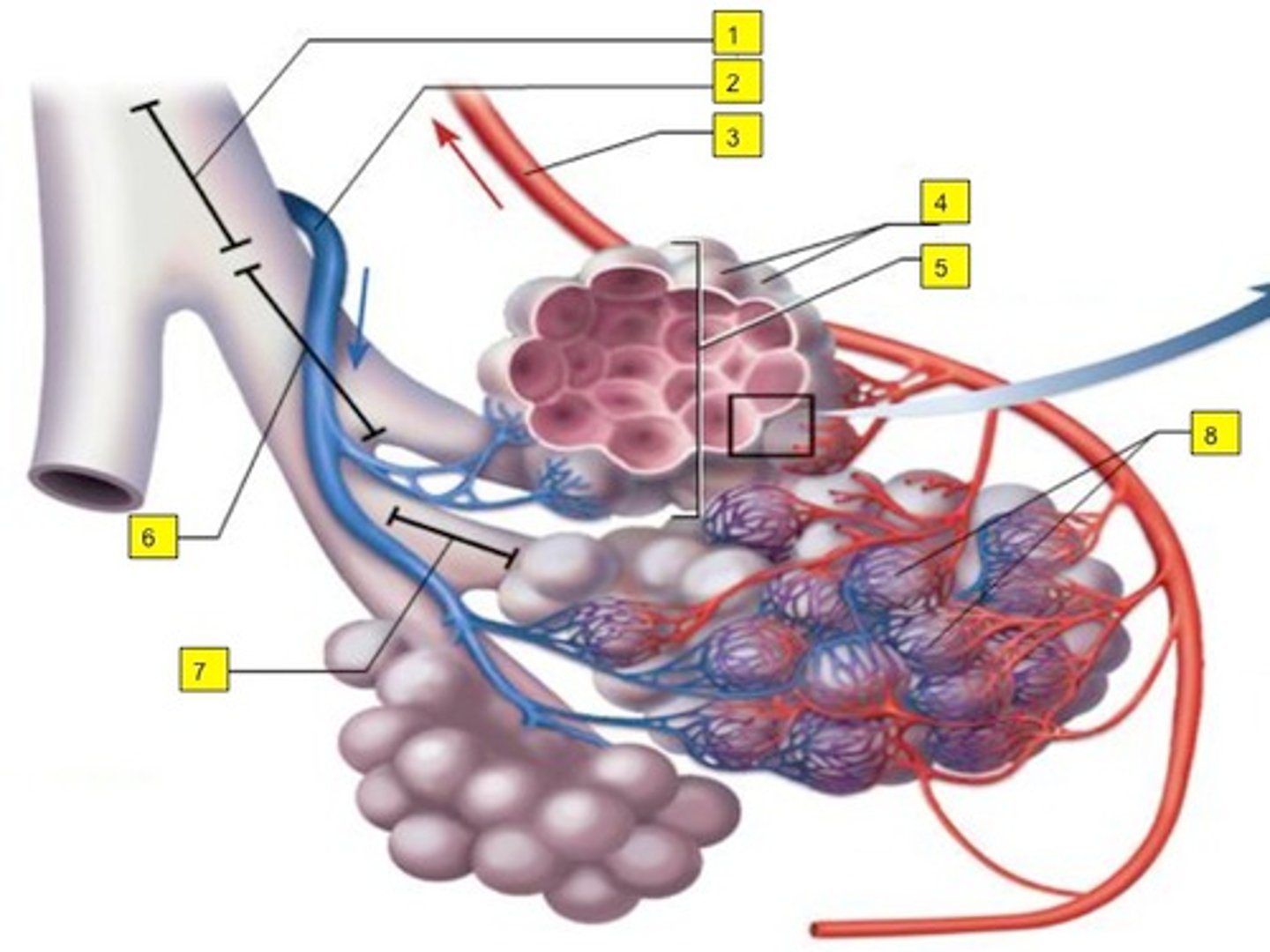
alveoli
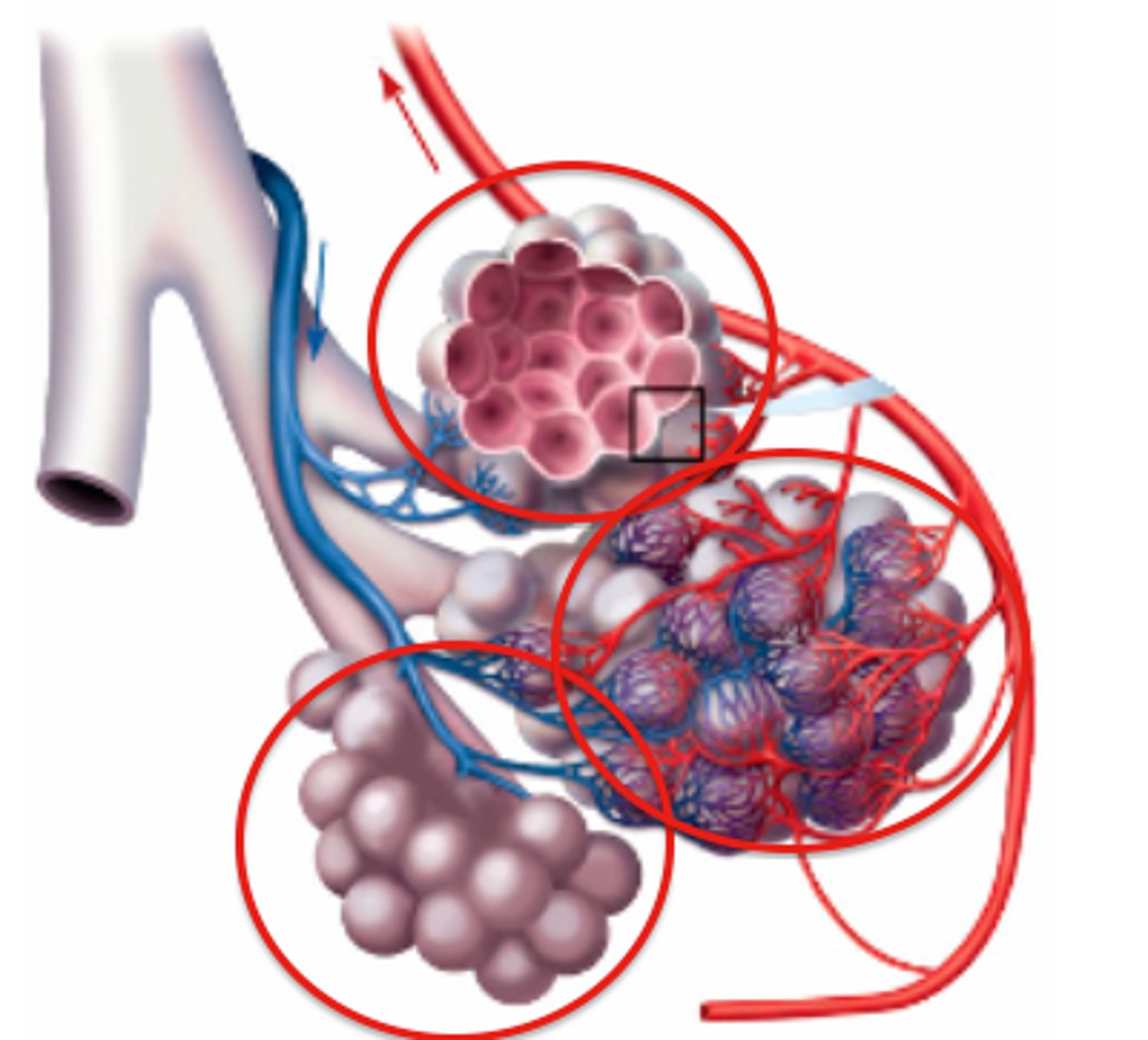
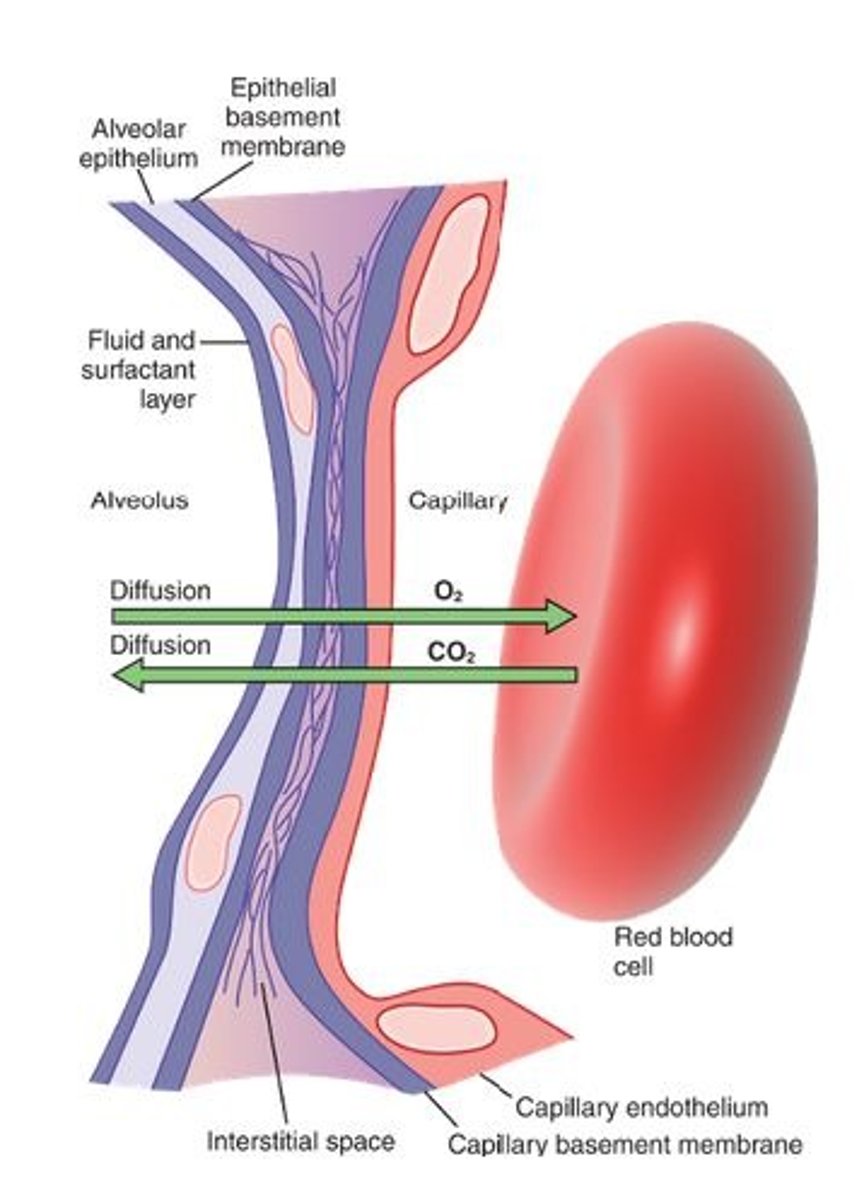
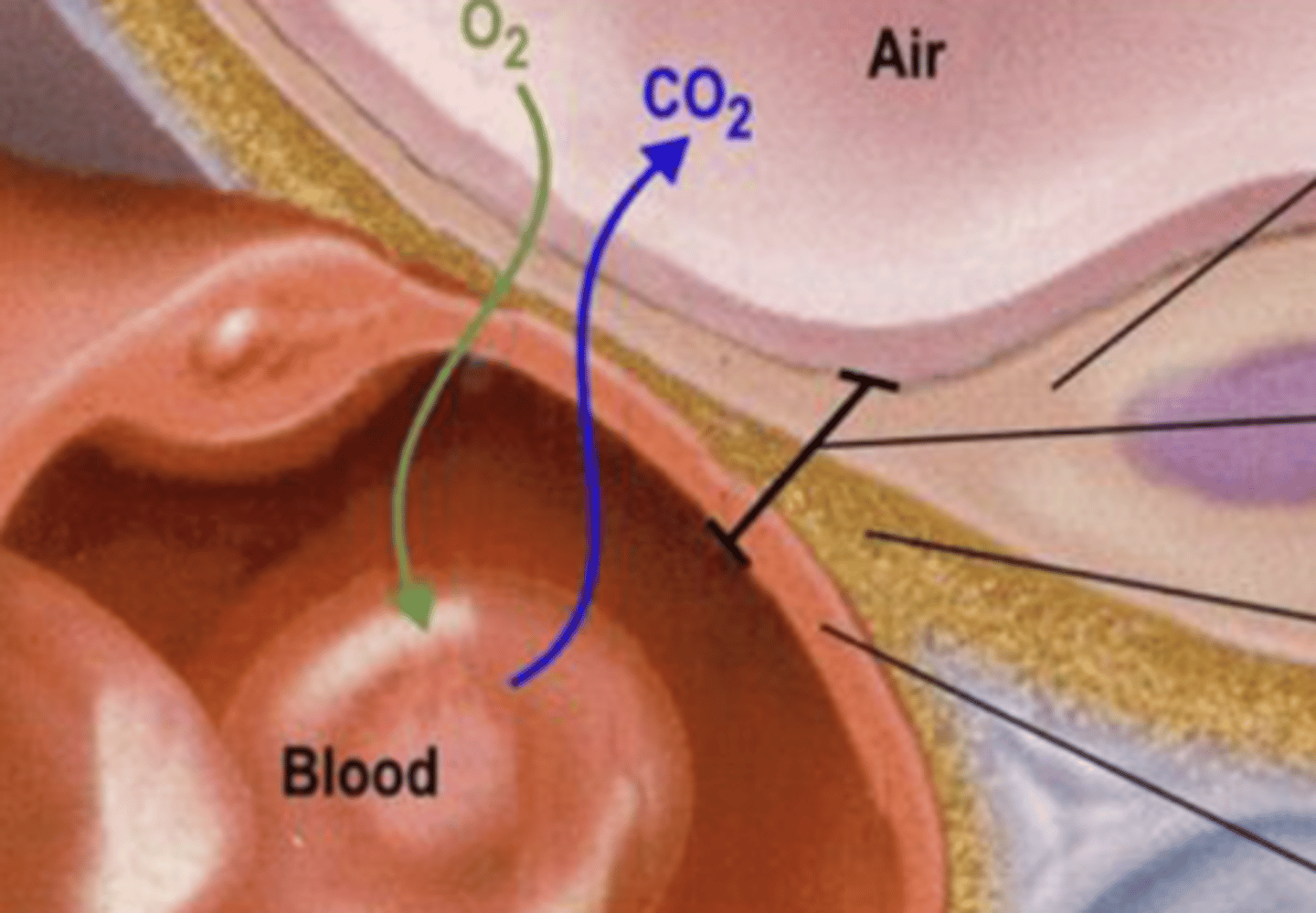
respiratory membrane
composed of 3 layers
- squamous alveolar cell, squamous endothelial cell of capillary, and basement membrane
squamous alveolar cell of respiratory membrane (pink)
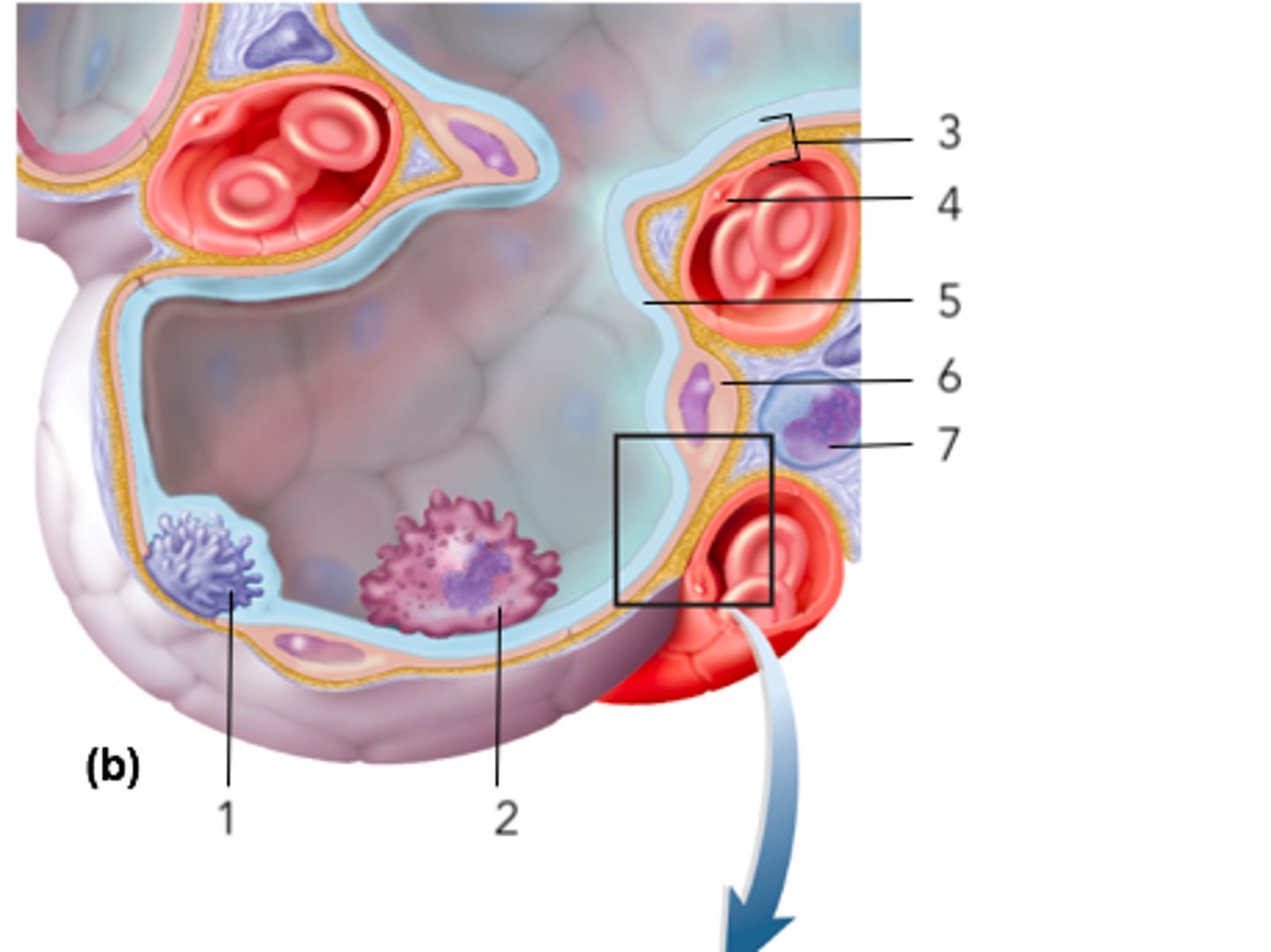
squamous endothelial cell of respiratory membrane
where RBC are
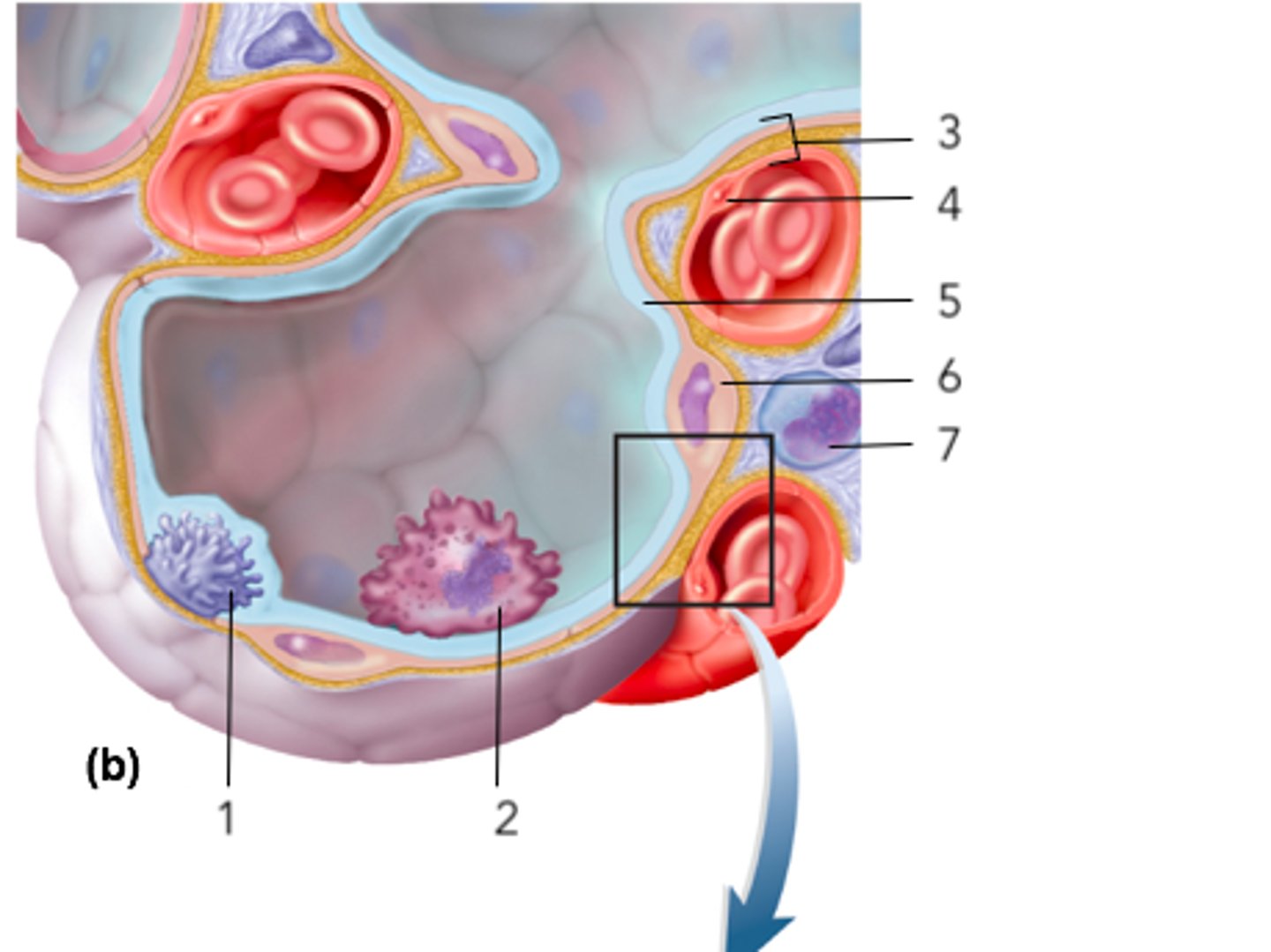
basement membrane of squamous endothelial cell of respiratory membrane
capillary network on alveolar sac
great (type II) alveolar cells
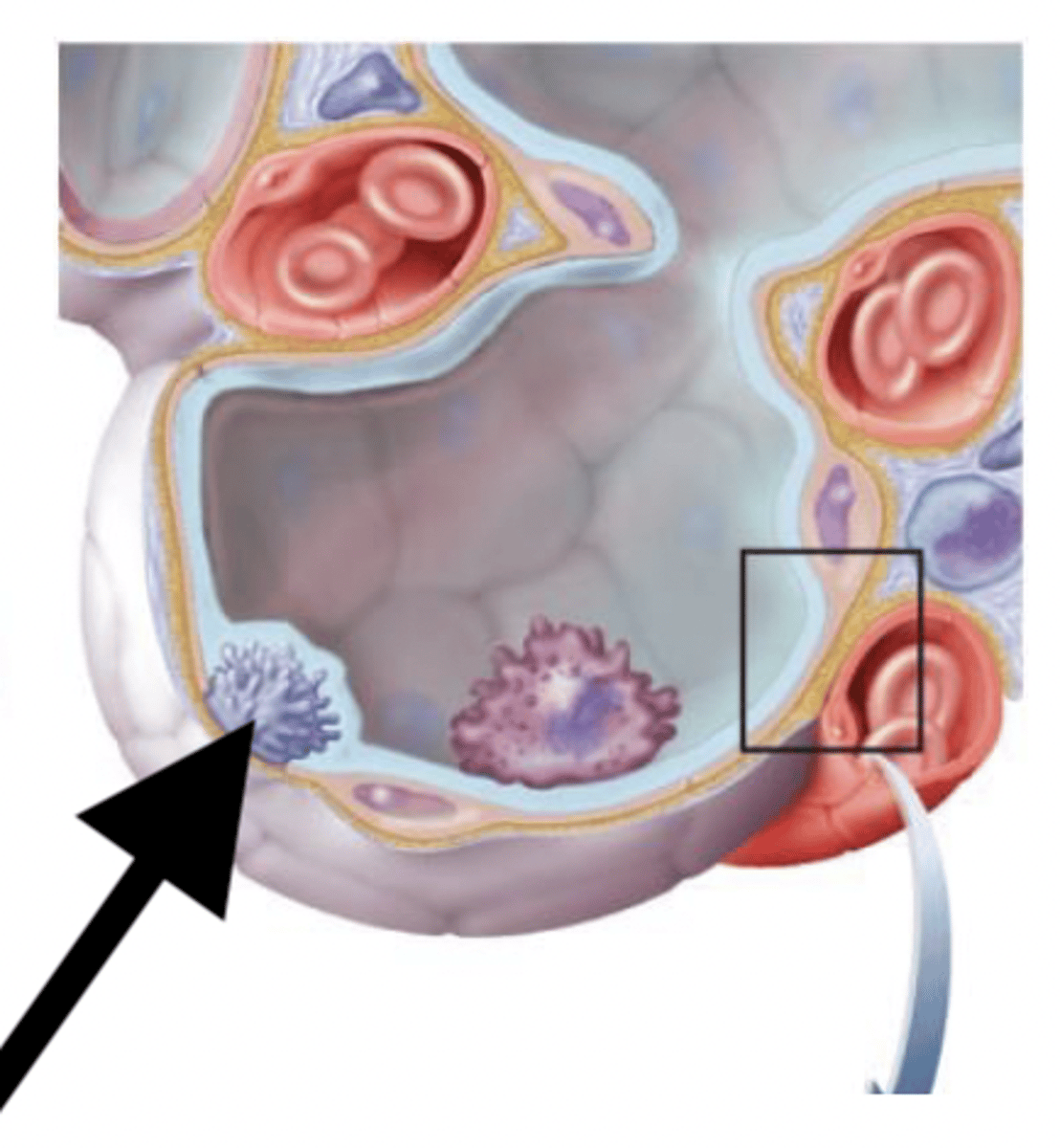
alveolar macrophages
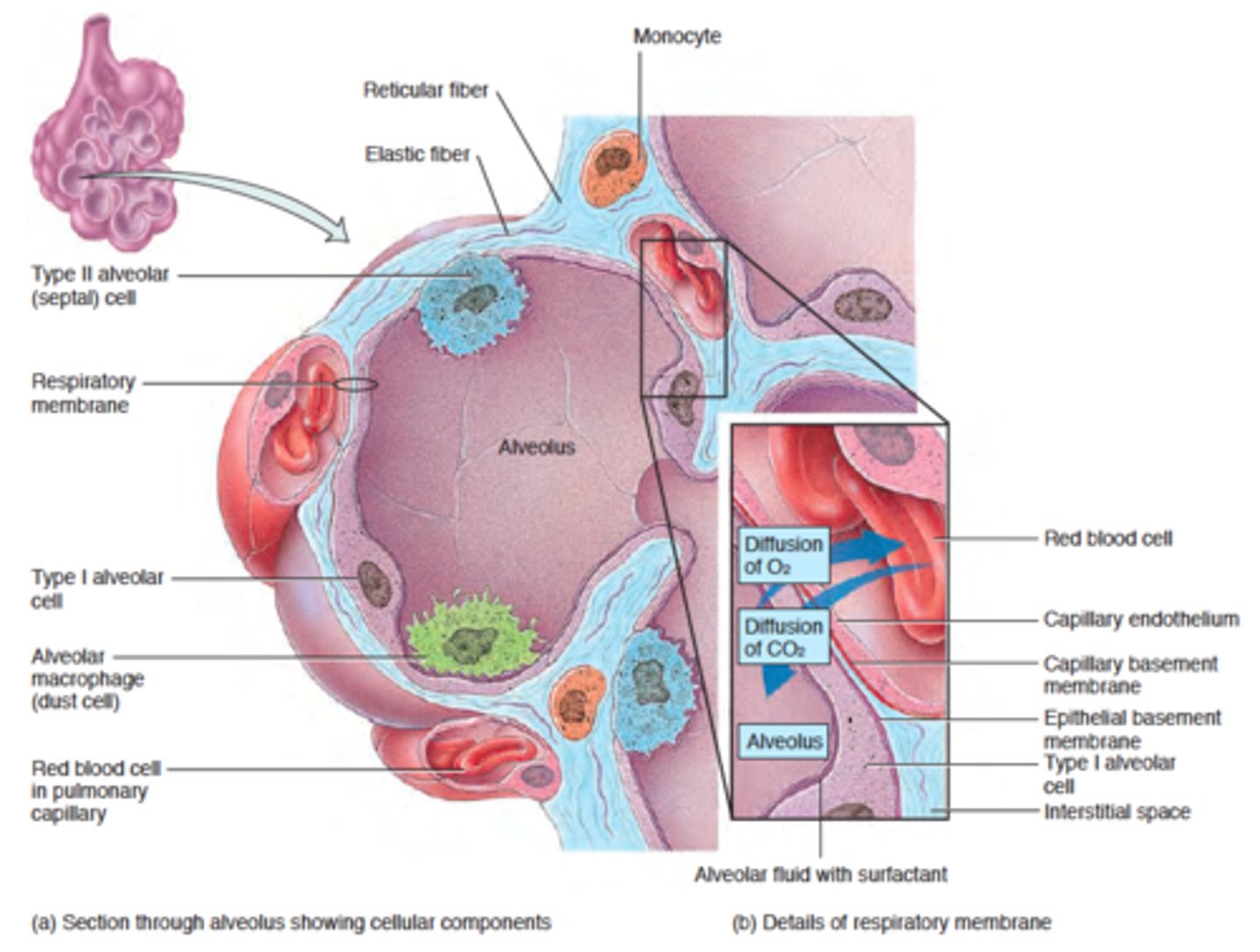
squamous (type I) alveolar epithelial cells
function of squamous cells
gas exchange
function of great cells
pulmonary surfactant-->sticking and collapse=hard to breath
function of alveolar macrophages
clear debris
left lung superior lobe
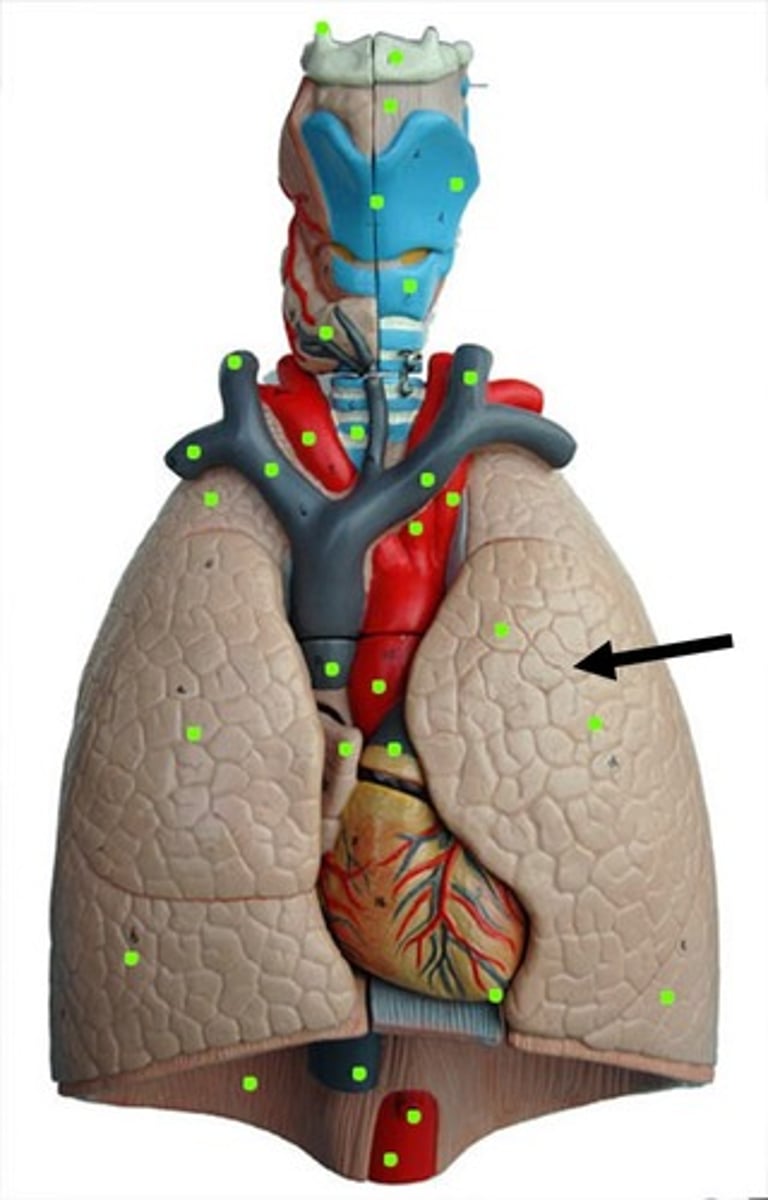
left lung inferior lobe
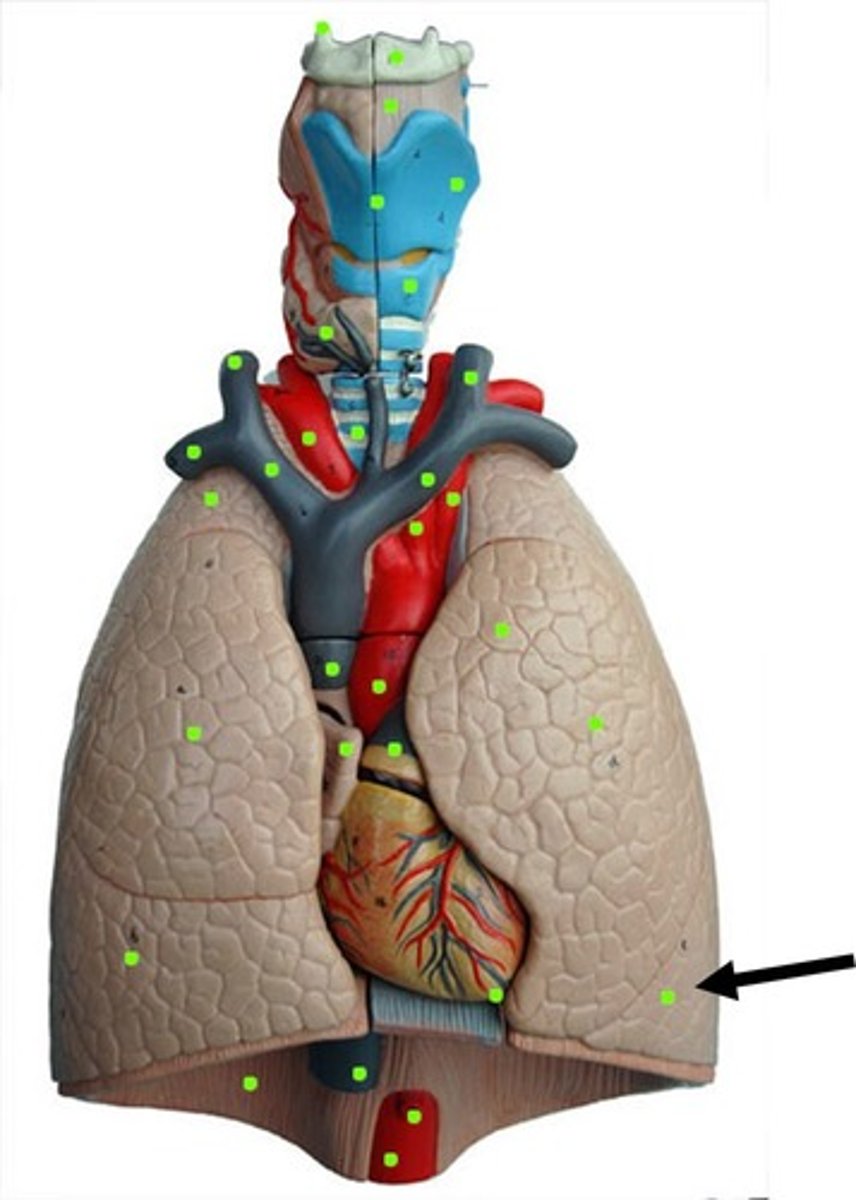
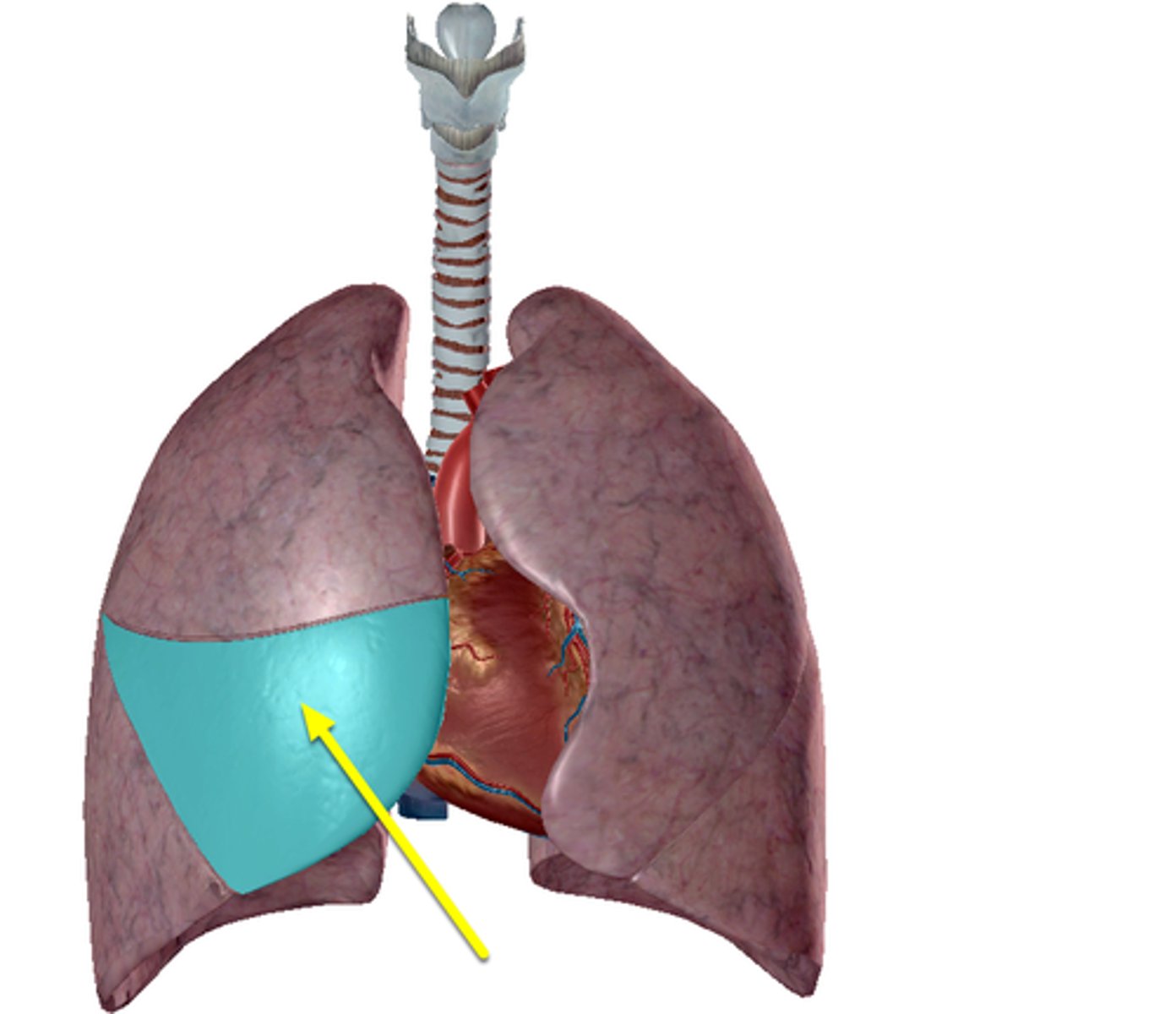
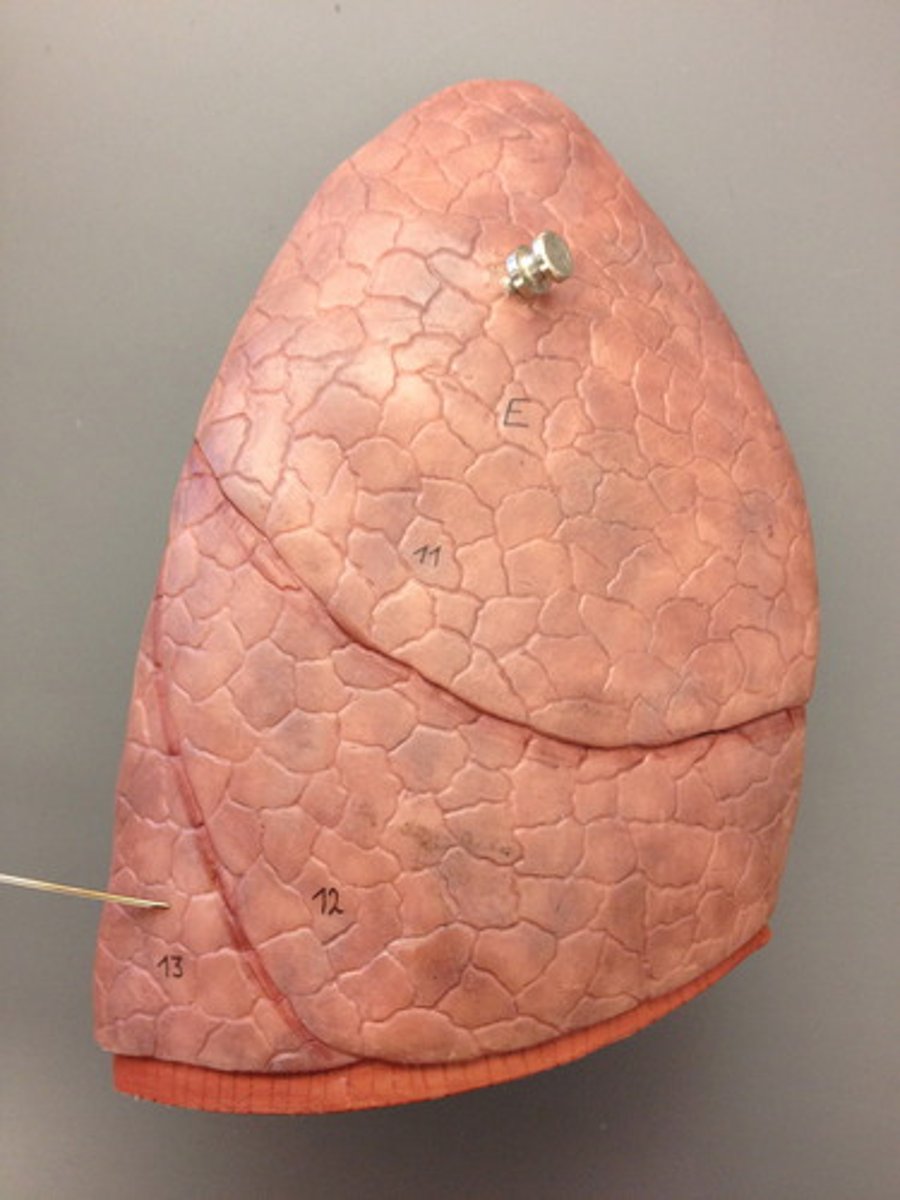
right lung superior lobe
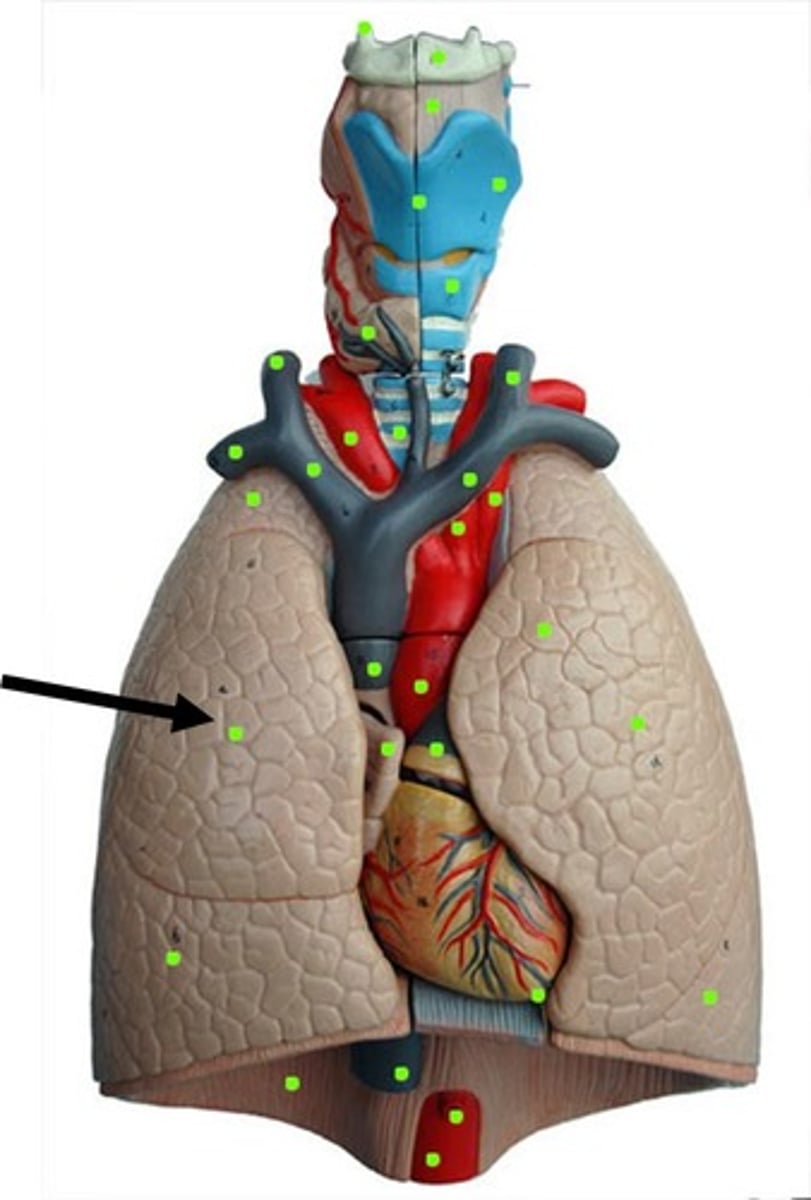
right lung middle lobe
right lung inferior lobe
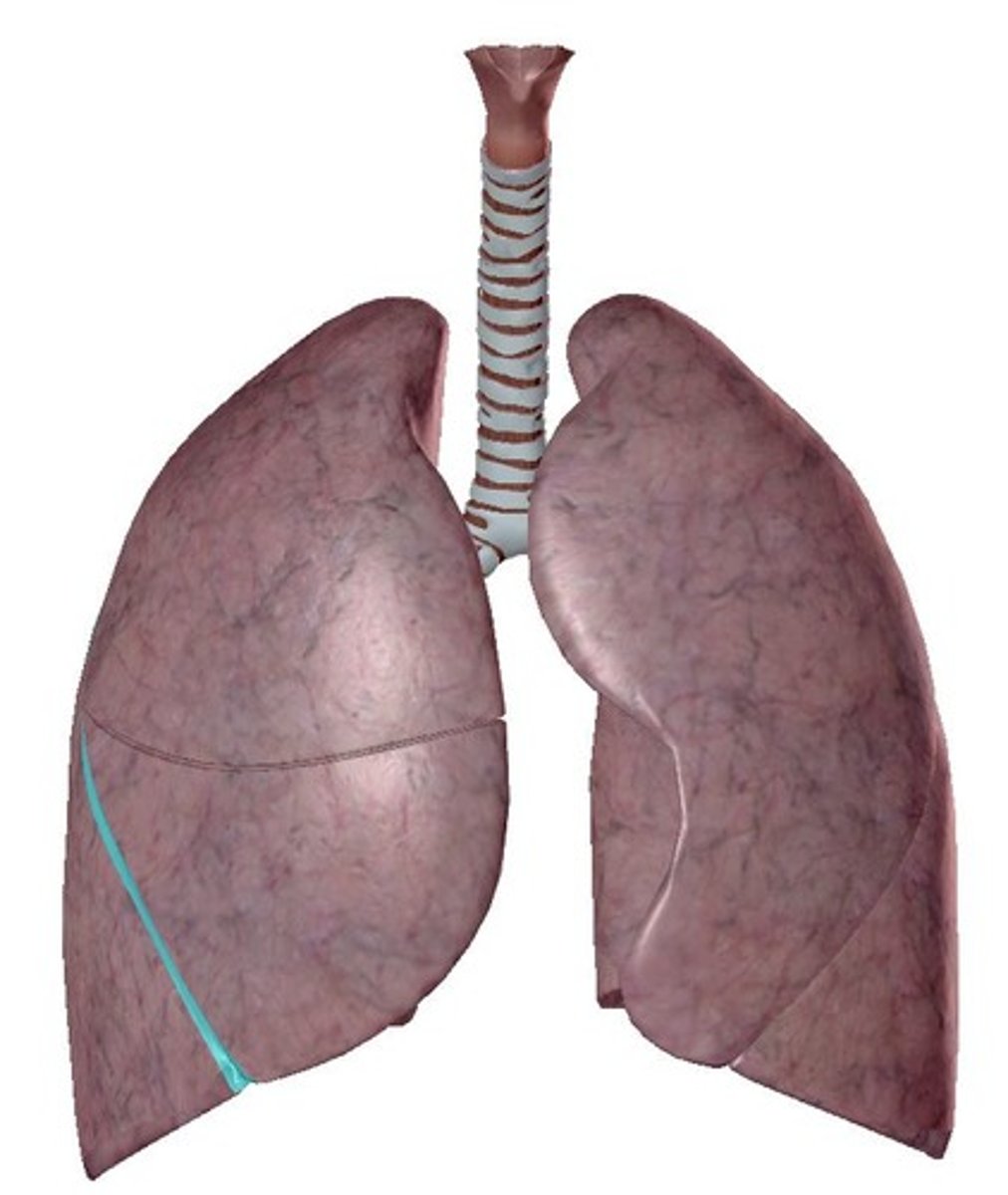
left lung oblique fissure
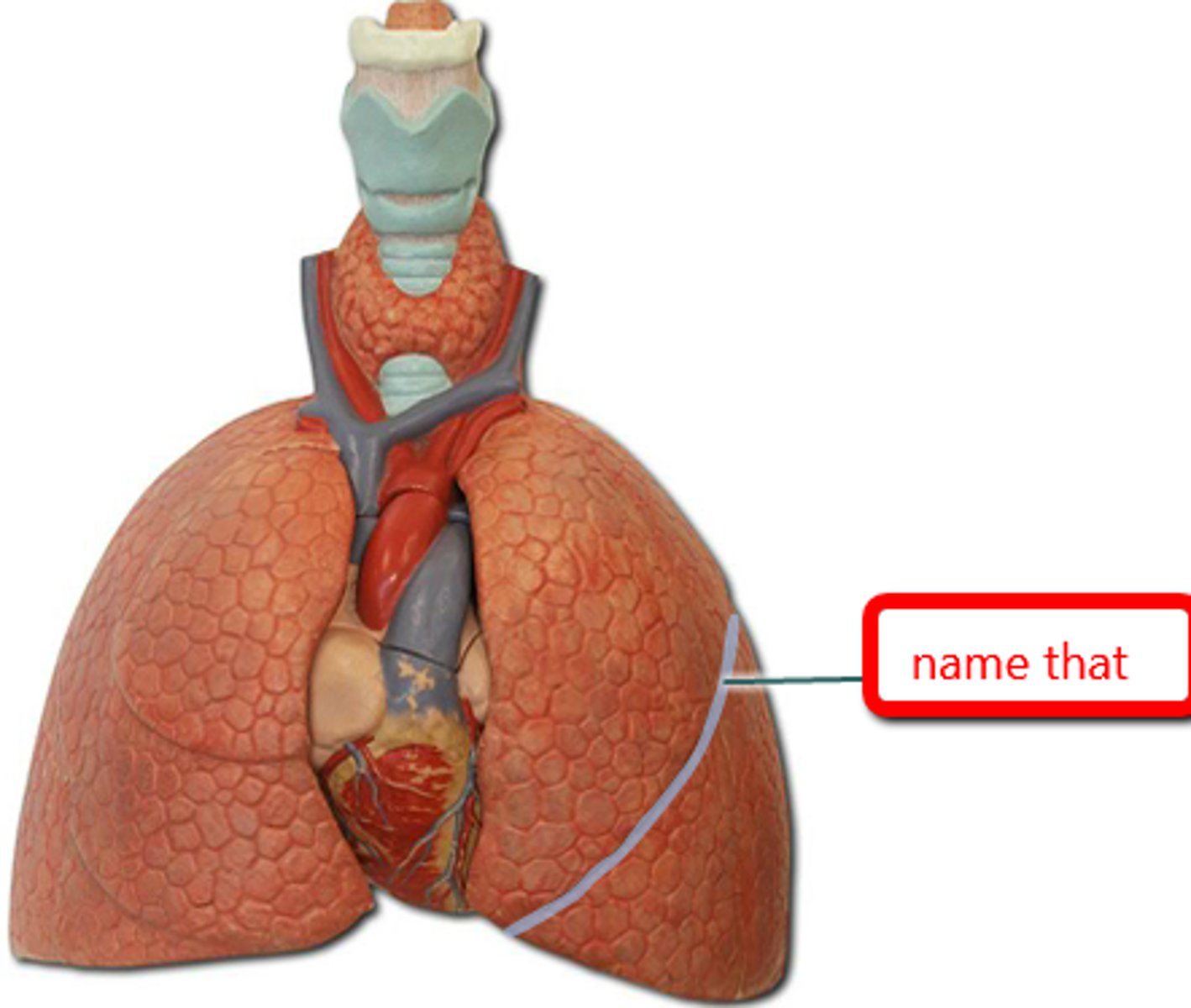
right lung oblique fissure
diaphragmatic surface of diaphragm
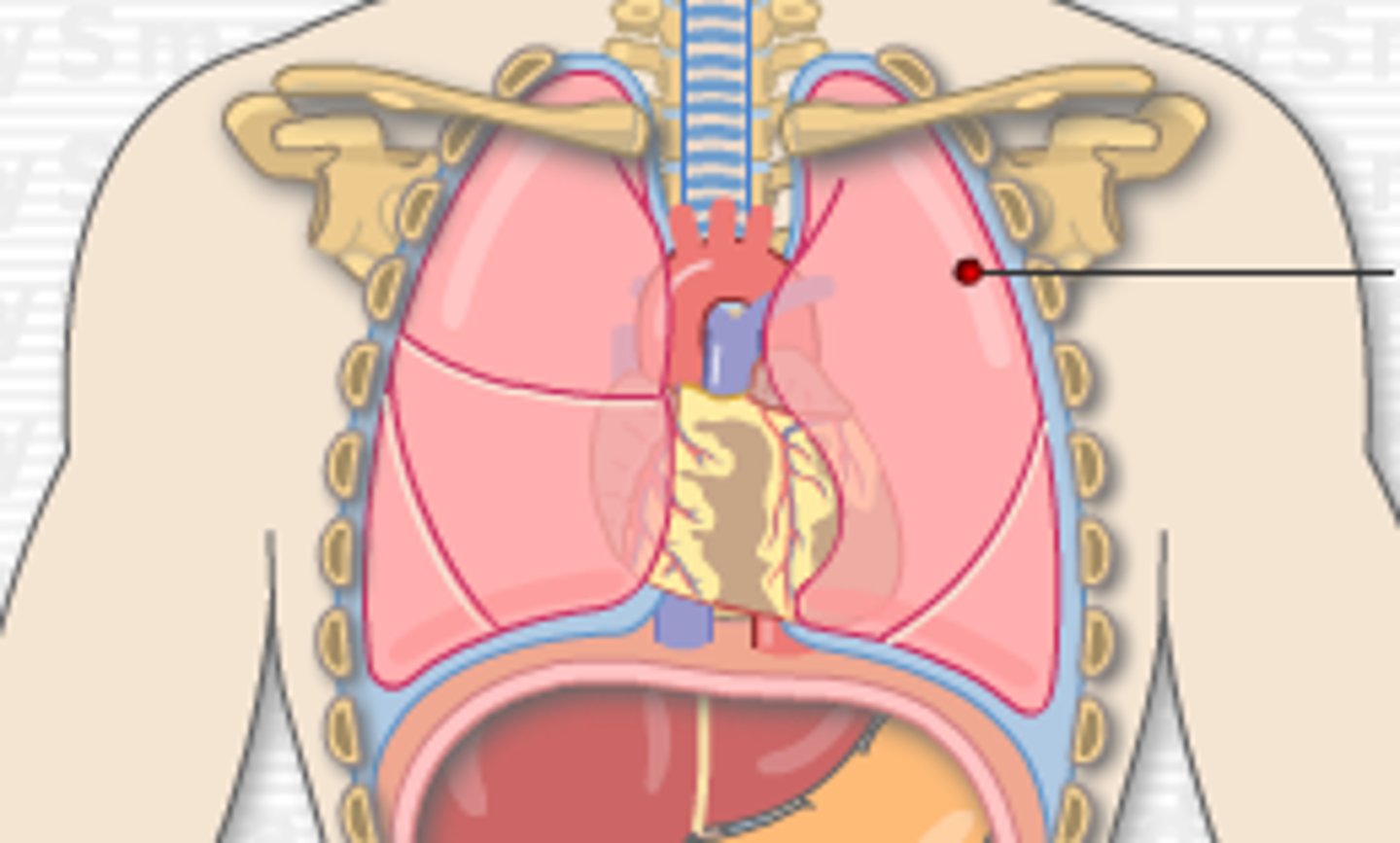
costal surface of lungs
faces rib cage
mediastinal surface
faces heart
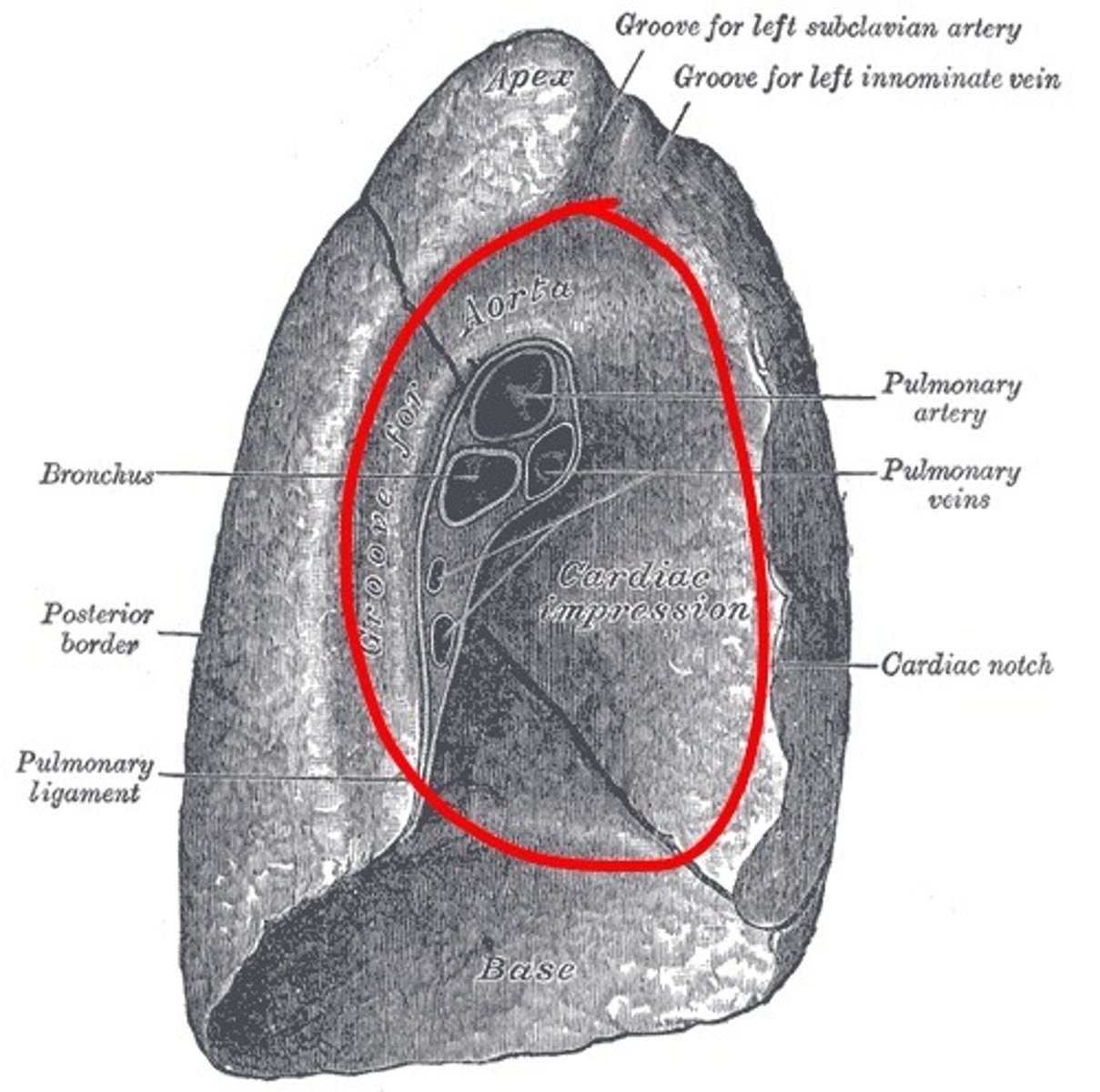
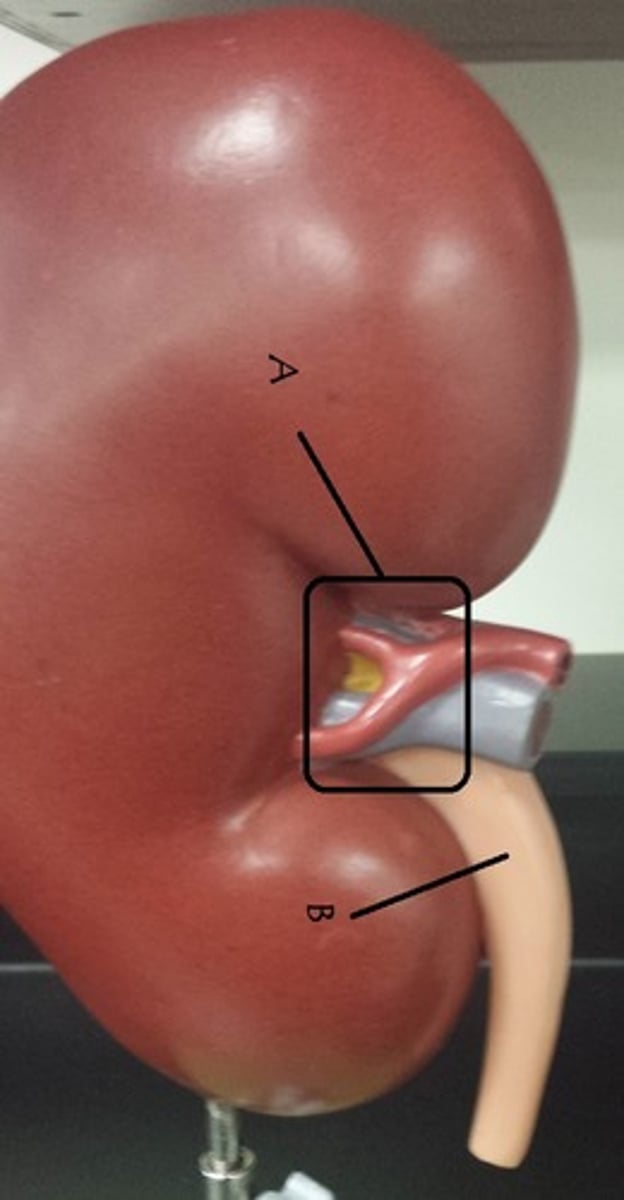
hilum
slit opening on the mediastinal surface of each lung that receives main bronchus, pulmonary vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves
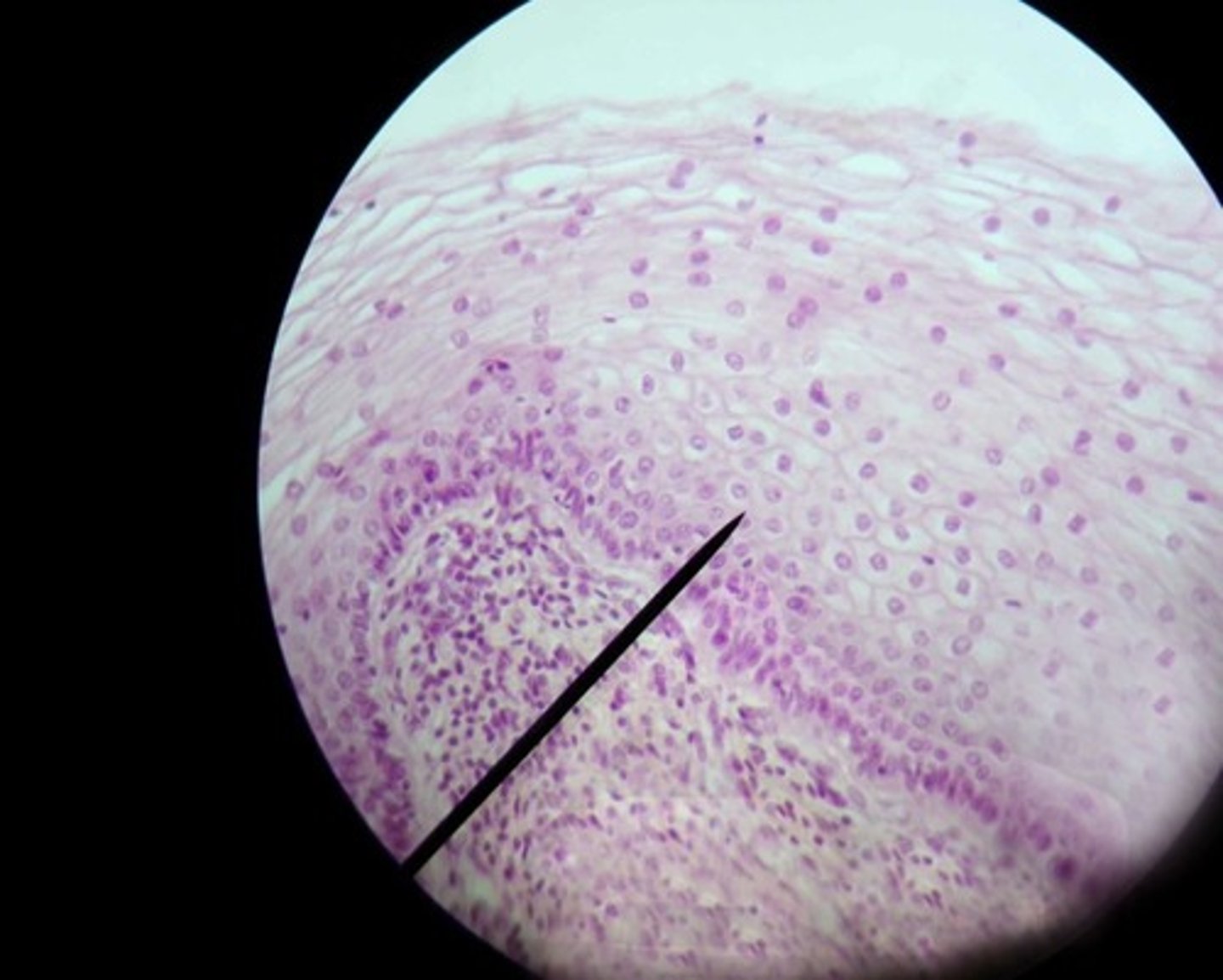
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
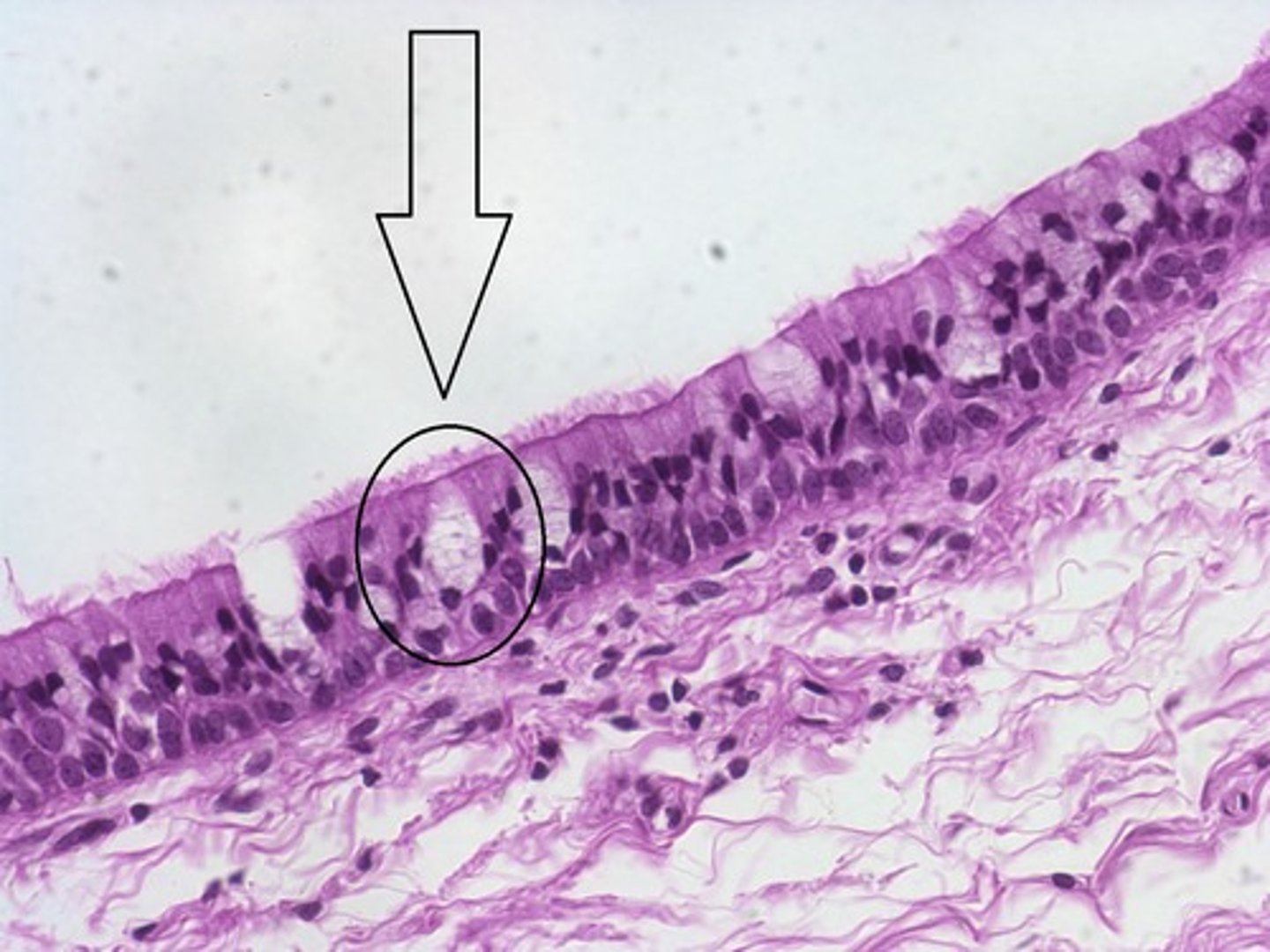
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
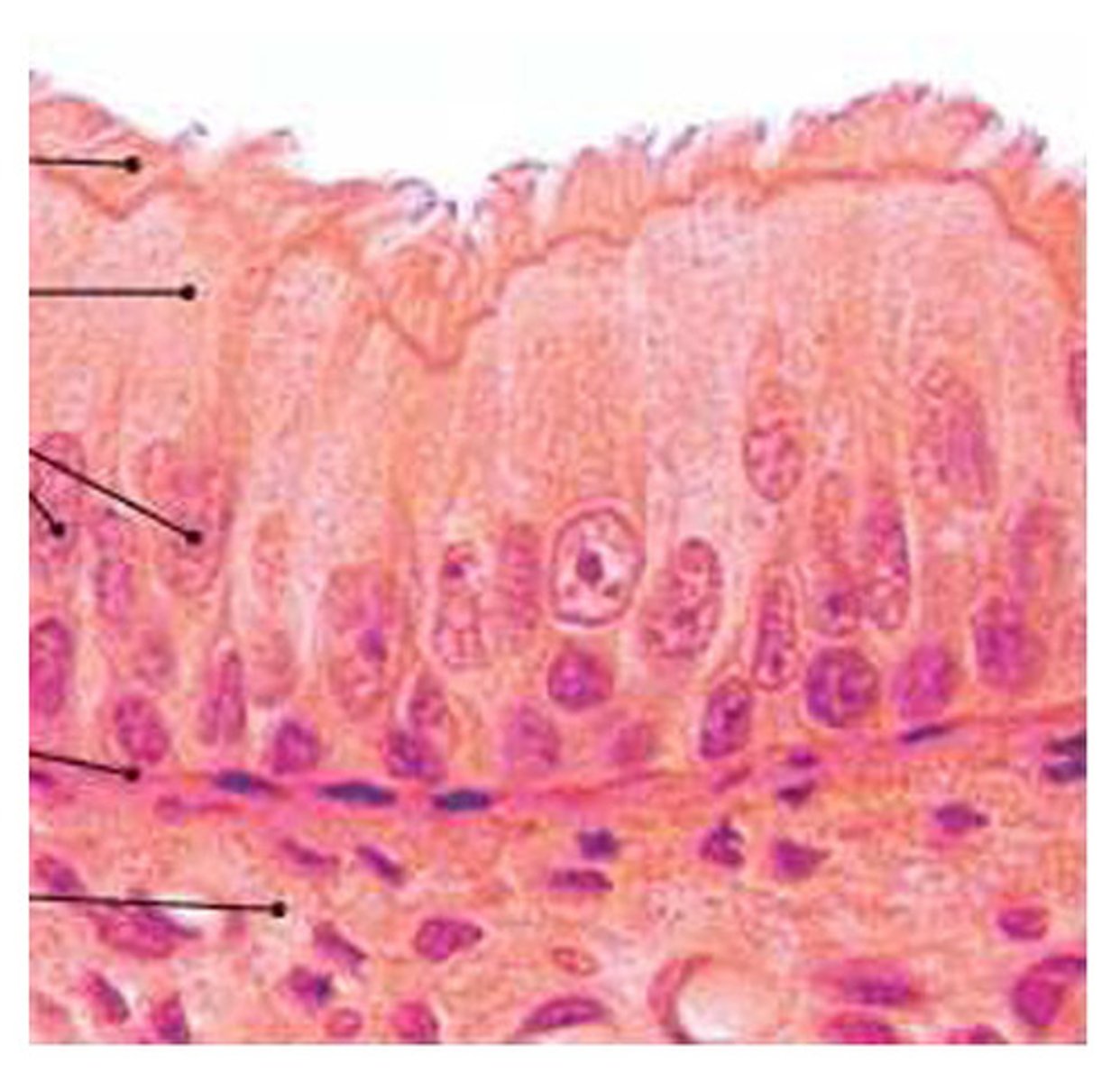
cilia
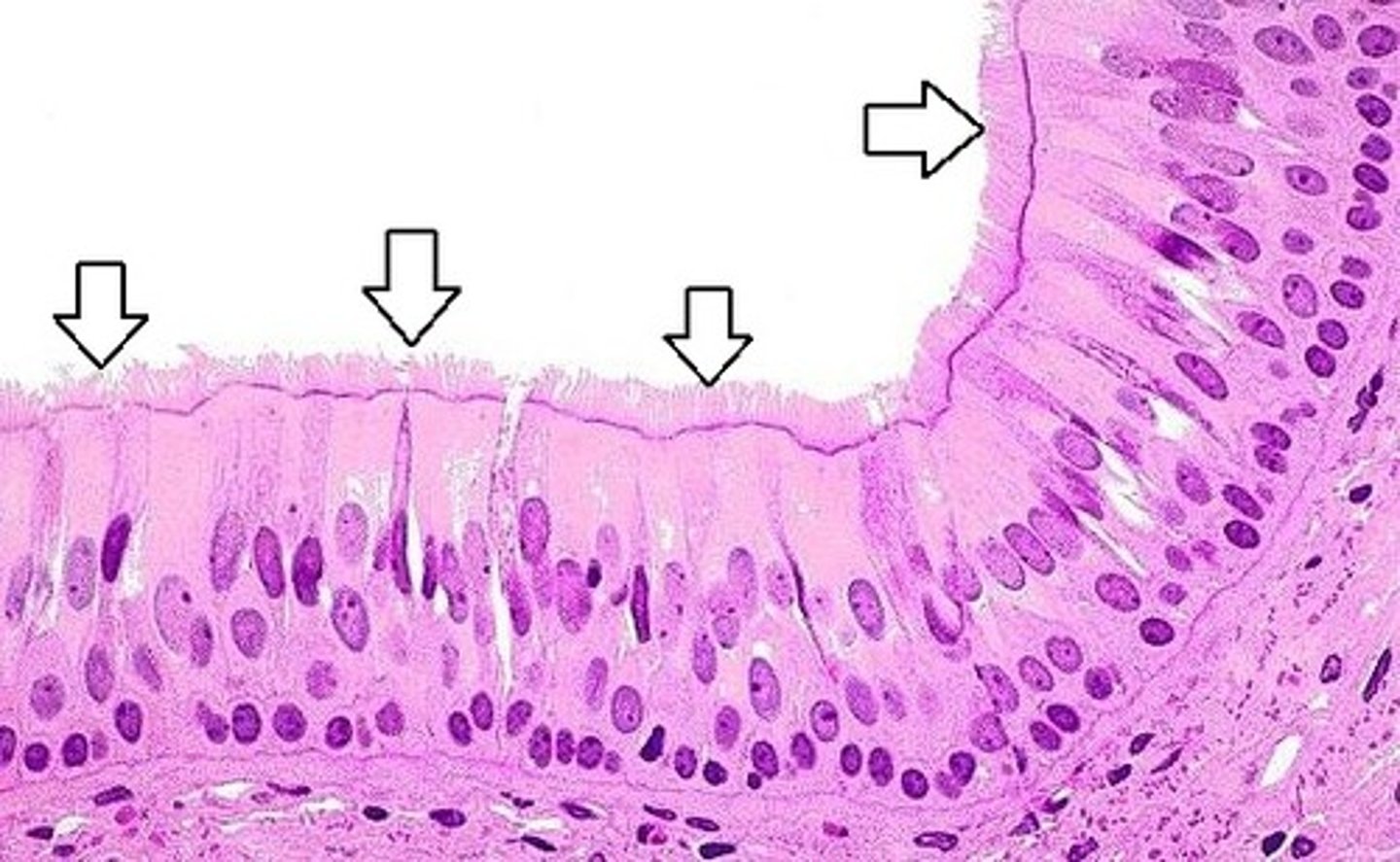
goblet cells
Compare heart rate and pulse rate upon inspiration and expiration
1st cycle of inspiration: finger pulse demonstrates that inspiration increases sympathetic drive to increase HR in response to increases venous return
cycle of expiration: whereas expiration is associated with less venous return and a decreased HR
2nd cycle of inspiration: results repeated to increase HR
what are wheezes?
the movement of air through the bronchi can become turbulent in places with restrictions, causing sounds like wheezing (asthma and bronchitis)
what are rales/crackles?
when air flow in alveoli and small bronchioles must bubble up through mucous of edema during exhalation (accumulation of fluid in small airways=pneumonia or left side heart failure)