Hematology & Body Fluids Lab Practical - Study Guide
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Hematocrit
Male: 42 - 52%
Female: 36-46%
Hemoglobin
Male 14.0 - 17.4 g/dL
Female: 12.0-16.0 g/dL
RBC Count
4.5 - 5.5 × 10^6 uL / 10^12 L
WBC Count
4.5 - 11.0 × 10³ uL / 10^9 L
What are the RBC indices and their significance?
MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume):
avg vol. of RBC → diagnose types of anemia.
MCH (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin):
avg amt of HgB in a single RBC; indicates oxygen-carrying capacity.
MCHC (Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration):
conc. of HgB in RBCs → identify types of anemia.
RDW (Red Cell Distribution Width):
Measures the variation in size of RBCs → cause of anemia.
MCV Value for Adults
80 - 100 fL
MCH Value for Adults
28 - 34 pg
MCHC Value for Adults
32 - 36%
RDW Value for Adults
12.0 - 14.6%
WBC Differential Values
PMS: 40-80%
Bands: 0-5%
Lymphs: 25-35%
Monos: 2-10%
Eos: 0-5%
Basos: 0-1%
Absolute Values for WBC Diff
PMN’s/Bands: 1.8 - 7.0 × 10^9 / L
Lymphs: 1.0 - 4.0 × 10^9 / L
Monos/Eos/Basos: 0.2 - 1.0 × 10^9 L
Plt Count
150,000 - 450,000 uL or 150 - 450 10^6 L
Spun Hematocrit (manual method)
34-50%
Reticulocyte Count
0.5 - 2.0%
Rule of 3 for RBC indices calculations
Hgb x 3 = HCT
RBC x 3 = Hgb
RBC x 9 = Hct
What is the principle of the reticulocyte count procedure?
immature RBCs with RNA and organelles that can be stained with vital dyes, forming a filamentous network. They appear polychromatophilic on Wright’s stain (Methylene Blue Reagent) and assess bone marrow erythropoietic activity.
Reticulocyte Count Procedure
2 drops of methylene blue + 2 drops of well-mixed blood
Mix & incubate for 15 mins
2 smears + Air Dry
100x until 500+ total cells counted for each slide
(Divide sum of reticulocytes by total number of RBCs)100
Results should be within 10% of each other
Reticulocyte Count Formula
% Retics = (# of retics x 100)/1000 RBCs
Platelet Clumps Procedure
Check specimen for clot
Make peripheral smear and stain
Under 50x objective lens, check for plt clumps, fibrin strands, satellitosis → WBC estimate
100x objective to perform a plt estimate
Plt. estimate should be ±20% from the analyzer result
Platelet Clumps Significance
Source of interference → causes falsely low plt count
incubate at 37C for 15-30 min
Vortex aliquot of sample (only 2 min to not activate plts → cause clumps)
Draw another EDTA & blue top tube if too many clumps
Corrected WBC Count (due to nRBC)
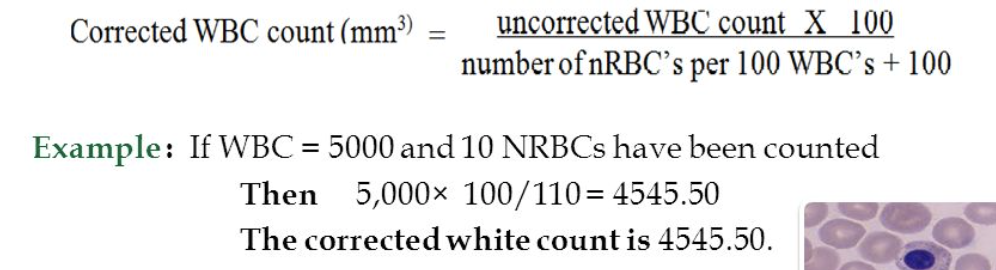
Correct any total WBC count per mm3 that has greater than 5* nRBCs/100 WBCs counted.
Platelet Estimate Calculation and Ranges
Decreased: 4-9 plt/field
Normal/Adequate: 10 – 30 plt/field.
Increased: 31-45 plt:
determine the avg number of platelets per field using 5 – 10 different fields (100x) and multiply this result by 15,000.
Serous Fluids Lining Cells are called?
Mesothelial Cells
CSF Lining Cells
Choroid - Lining of Choroid Plexus
Ependymal - Lining of Ventricles of neural
Spindle - Arachnoid Membrane Lining
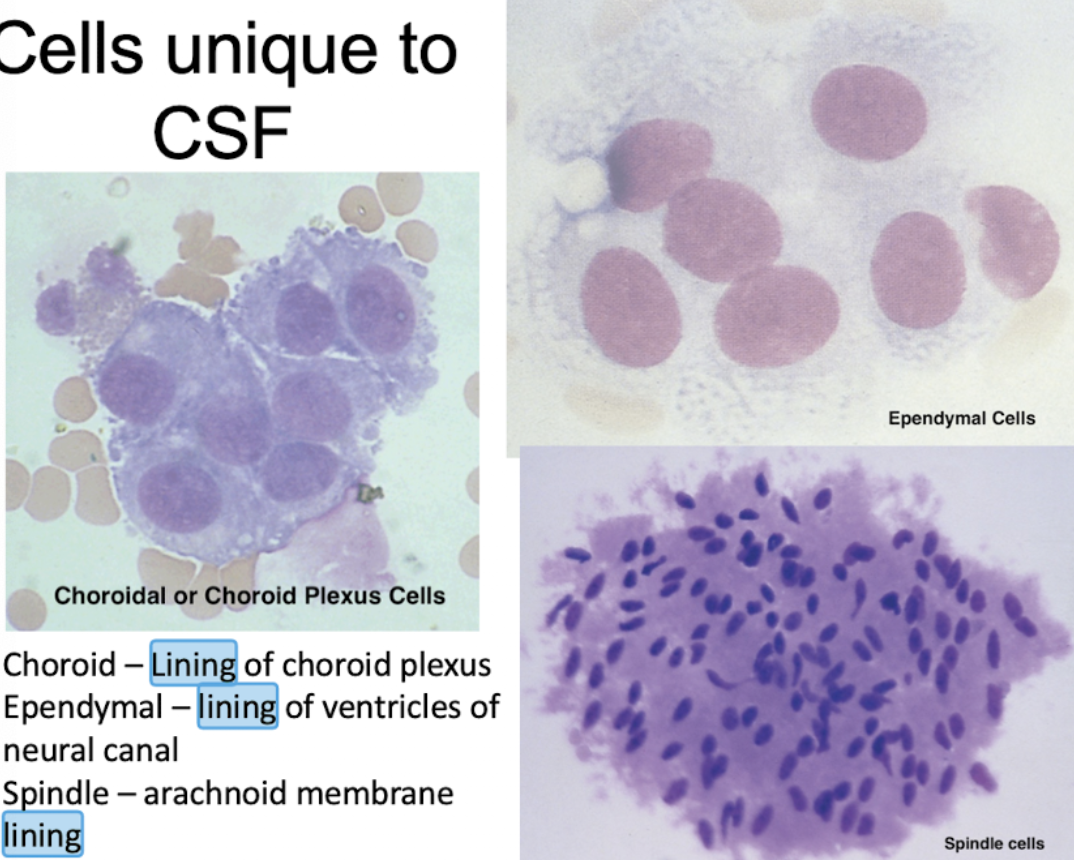
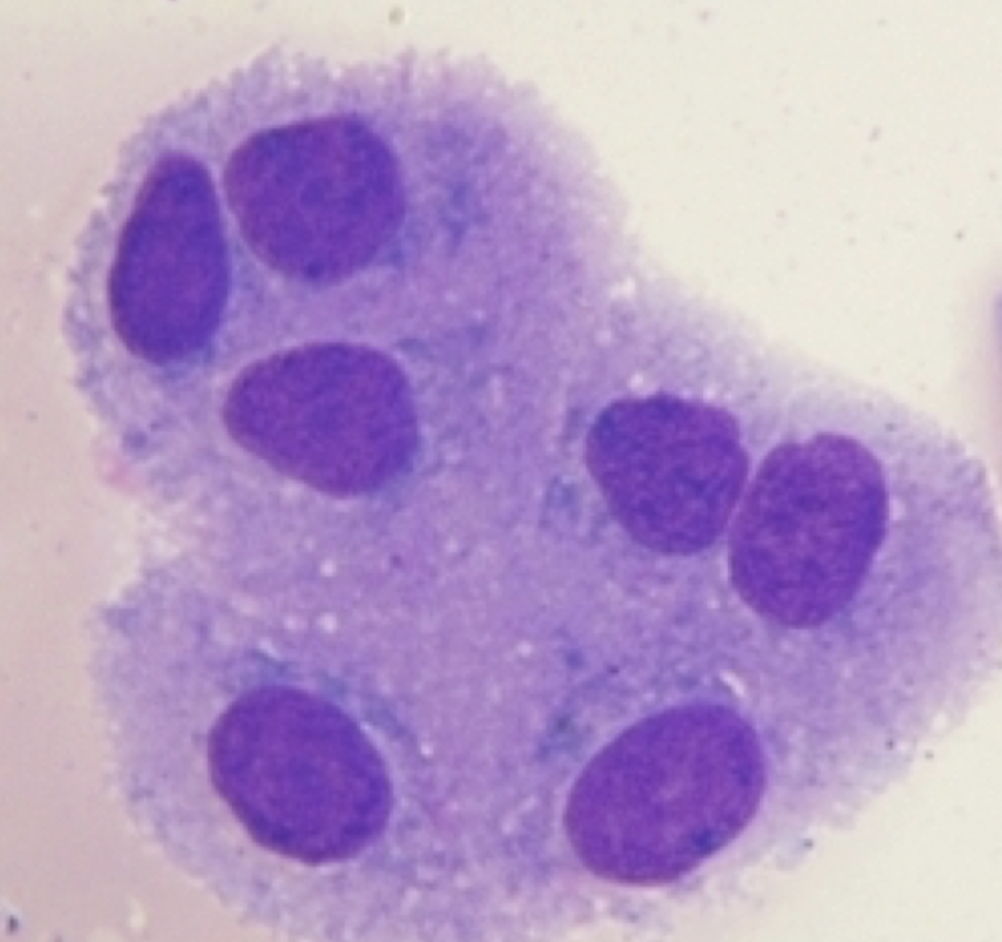
Choroid Plexus Cell
Synovial Lining Cell
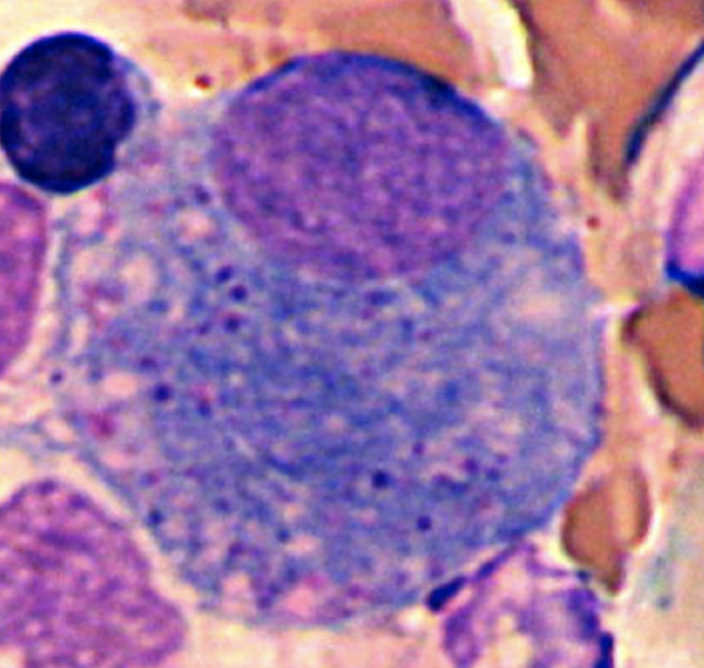
Synoviocytes
Eccentric nucleus
“Fried Egg” appearance
Possible debris inside cytoplasm
Serous Fluid Lining Cell
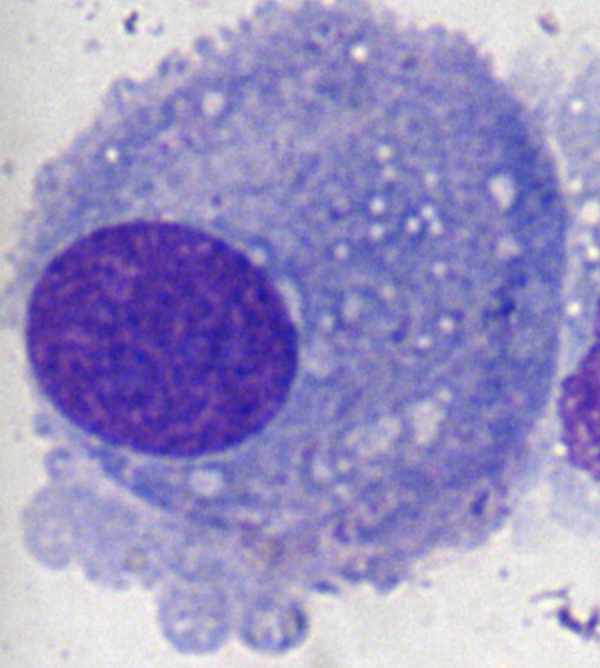
Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BAL) Lining Cell
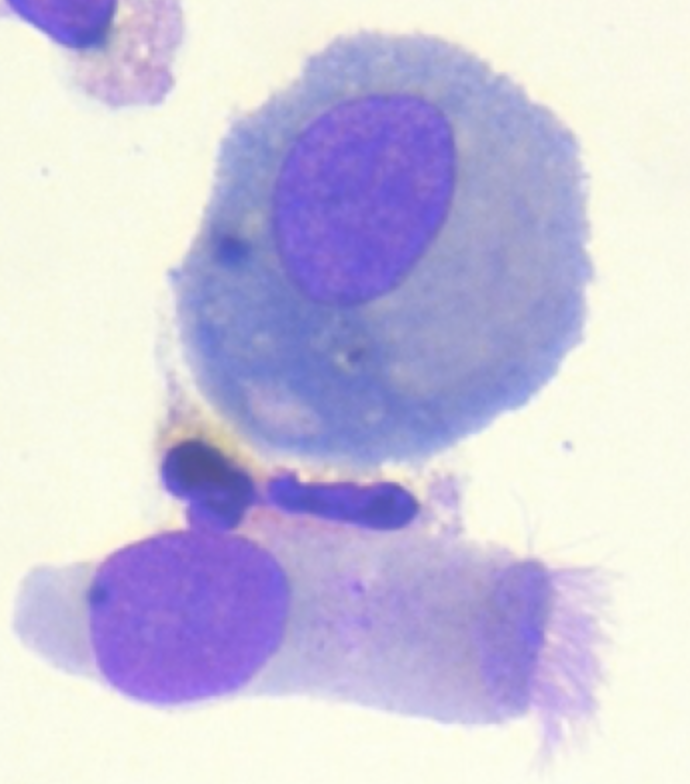
Macrophage and Ciliated Cell
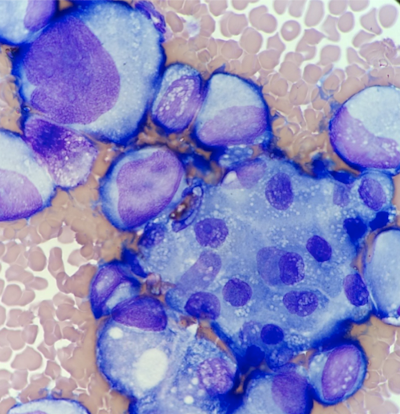
Malignant Cells
Very large, basophilic cells
Irregular shaped nuclei and nucleoli
Uneven staining in the cytoplasm
Various nuclear size and shape
Vacuoles over the nucleus
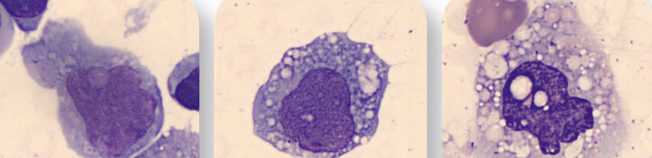
Signet ring vs. LE cell
Signet cells = Large Vacuole, nucleus flattens to one side → many: possible malignancy
LE cell (Lupus erythematosus) = ingested WBC within vacuole (pink blob) → autoimmune disease

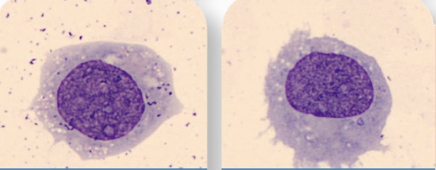
Macrophage in Body Fluid
Monocyte in Body Fluids
Manual Platelet Count Procedure
40x = Within each of the small 25 squares, count cells touching the top & left-hand borders. If the border has 3 parallel lines, use the middle line as the border.
Count both sides of the hemocytometer. The difference should be 10% or less. Take the avg of the count from both sides.
plt count X 1000 = plt/μL
plt normal range: 150,000 – 450,000/μL or 150 – 450 X 10^9/L
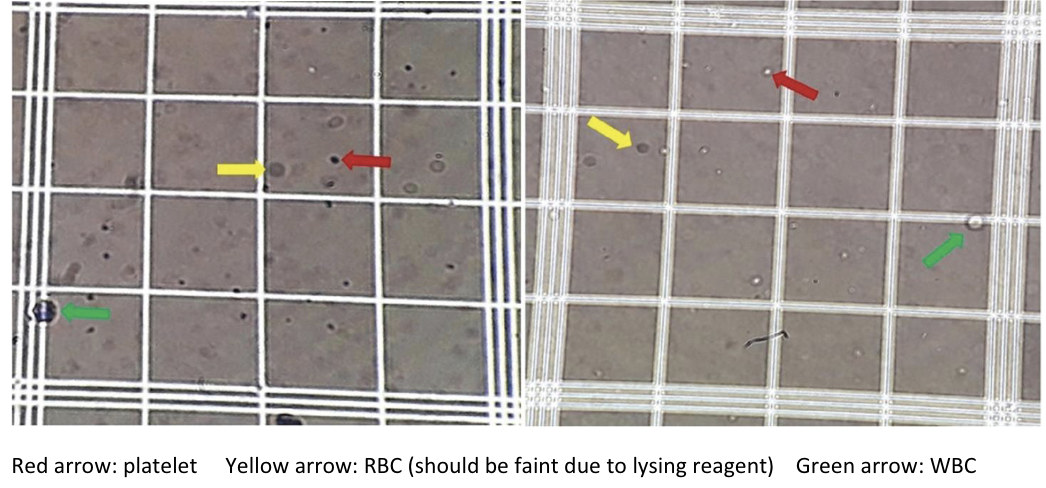

Waiting times for plt count
5 mins for cell lysis to complete
Place the hemocytometer into the humidity chamber (petri dish) and allow the cells to settle for 5-10 mins