Ch 1 Intro A&P TERMS Vet Tech A&P1
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Adjacent
Next to, adjoining, or close to.
Caudal
Pertaining to the tail end of the body or denoting a position more toward the tail or rear of the body than some other reference point (body part).
Cranial
Pertaining to the cranium or head end of the body, or denoting a position more toward the head end of the body than some other reference point (body part).
Cephalic
pertaining to the head
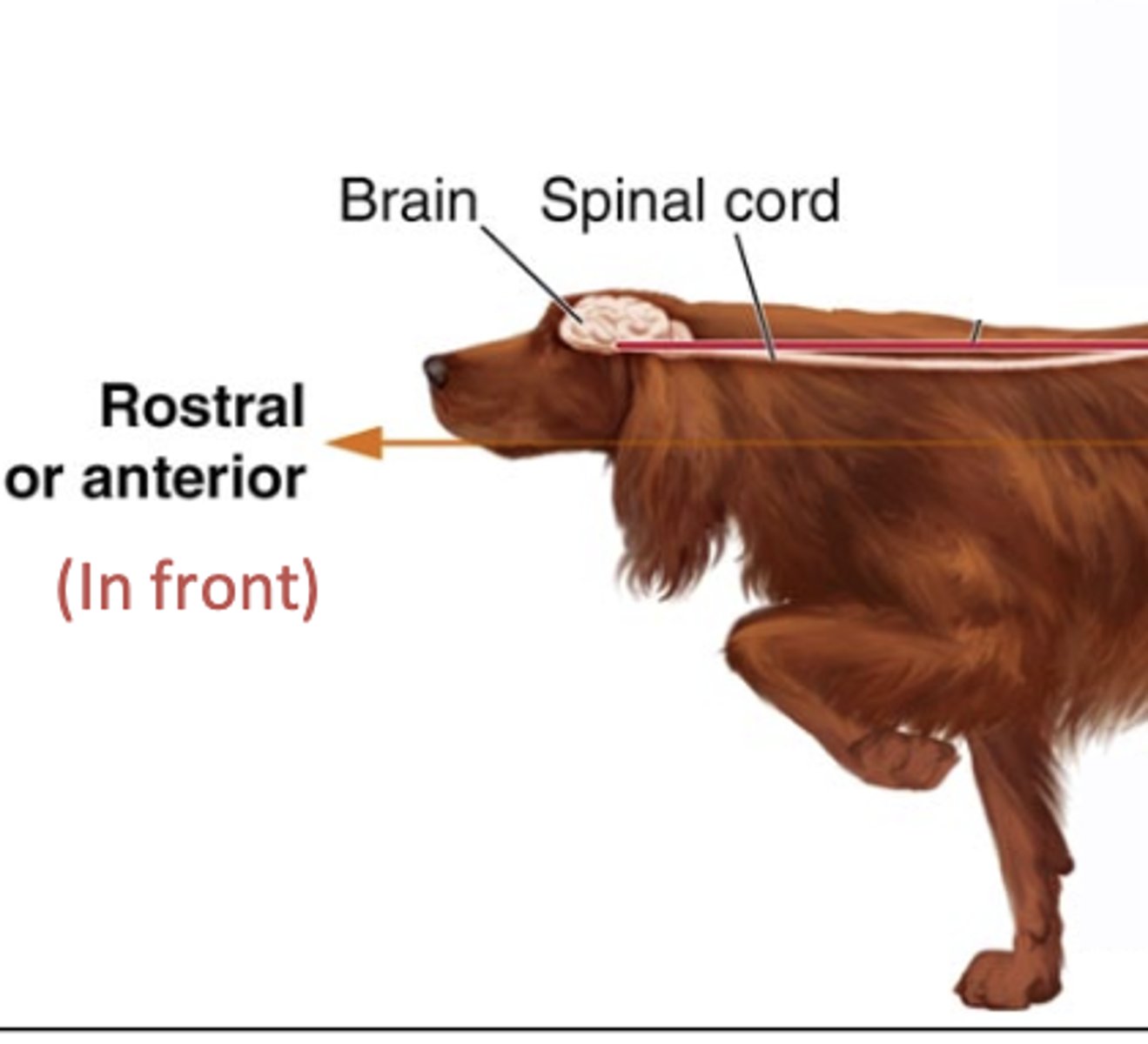
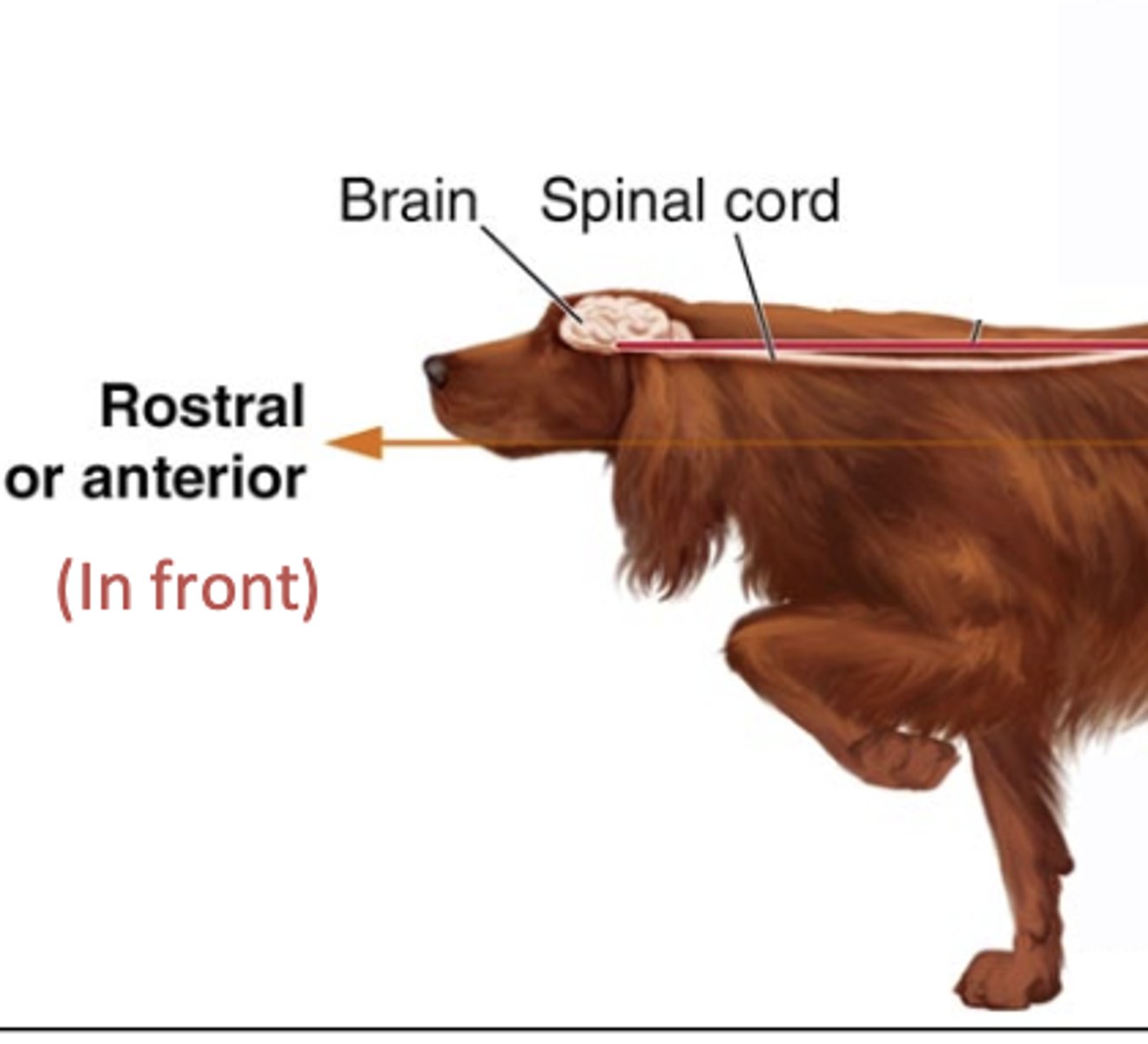
Rostral
Pertaining to the nose end of the head or toward the nose.
Dorsal
Pertaining to the back area
Ventral
Pertaining to the belly or underside of a quadruped or denoting a position more toward the belly (downward)
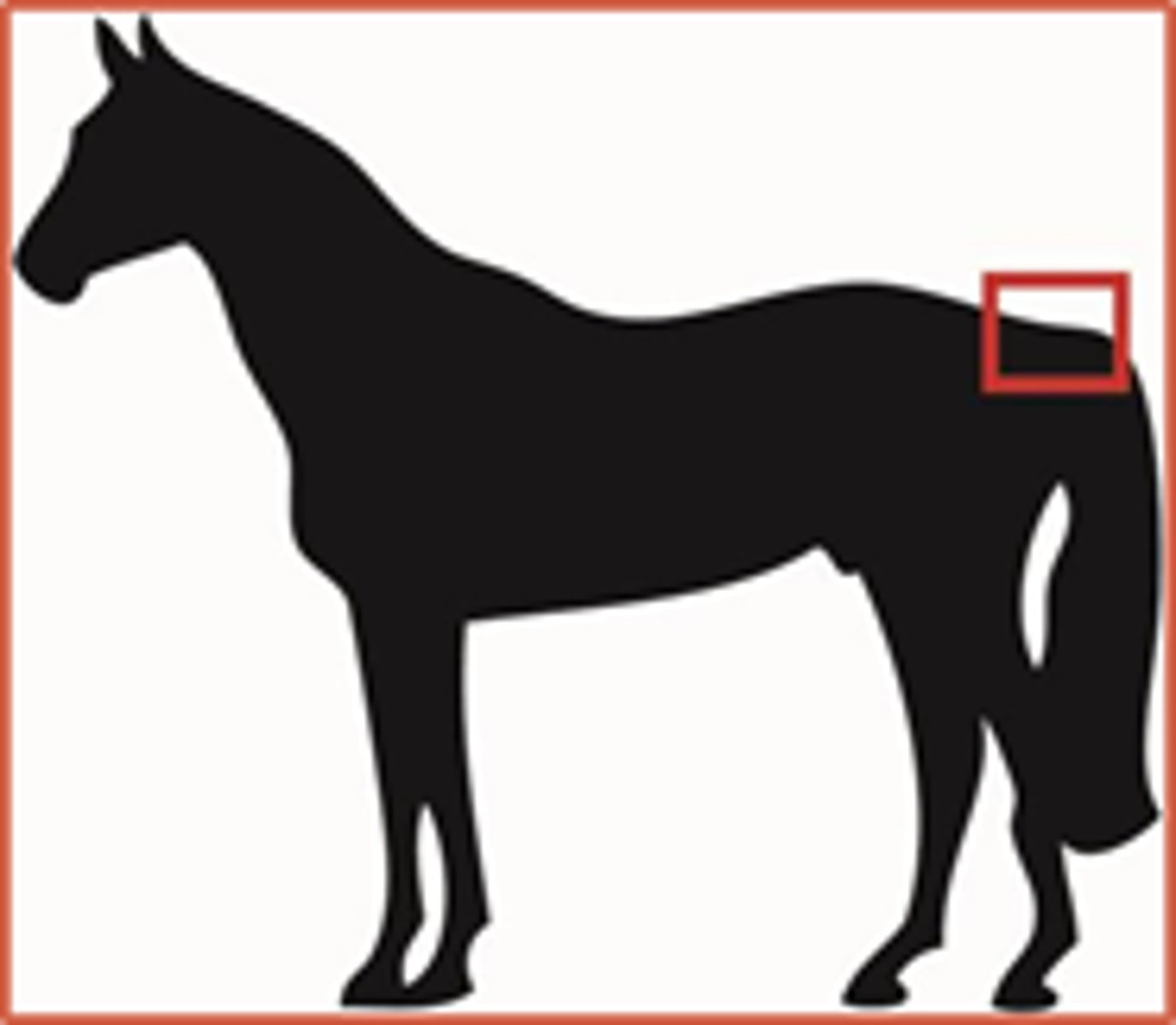
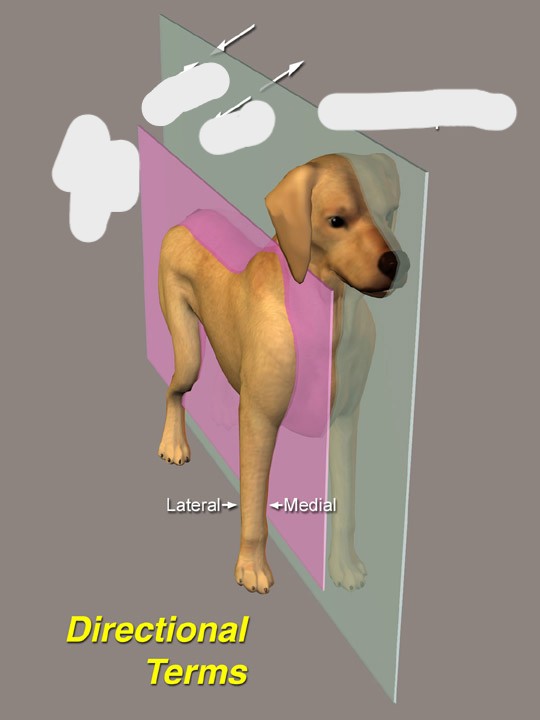
Lateral
Toward the side, away from the median plane, or pertaining to the side of the body.
Medial
toward the middle (midline)
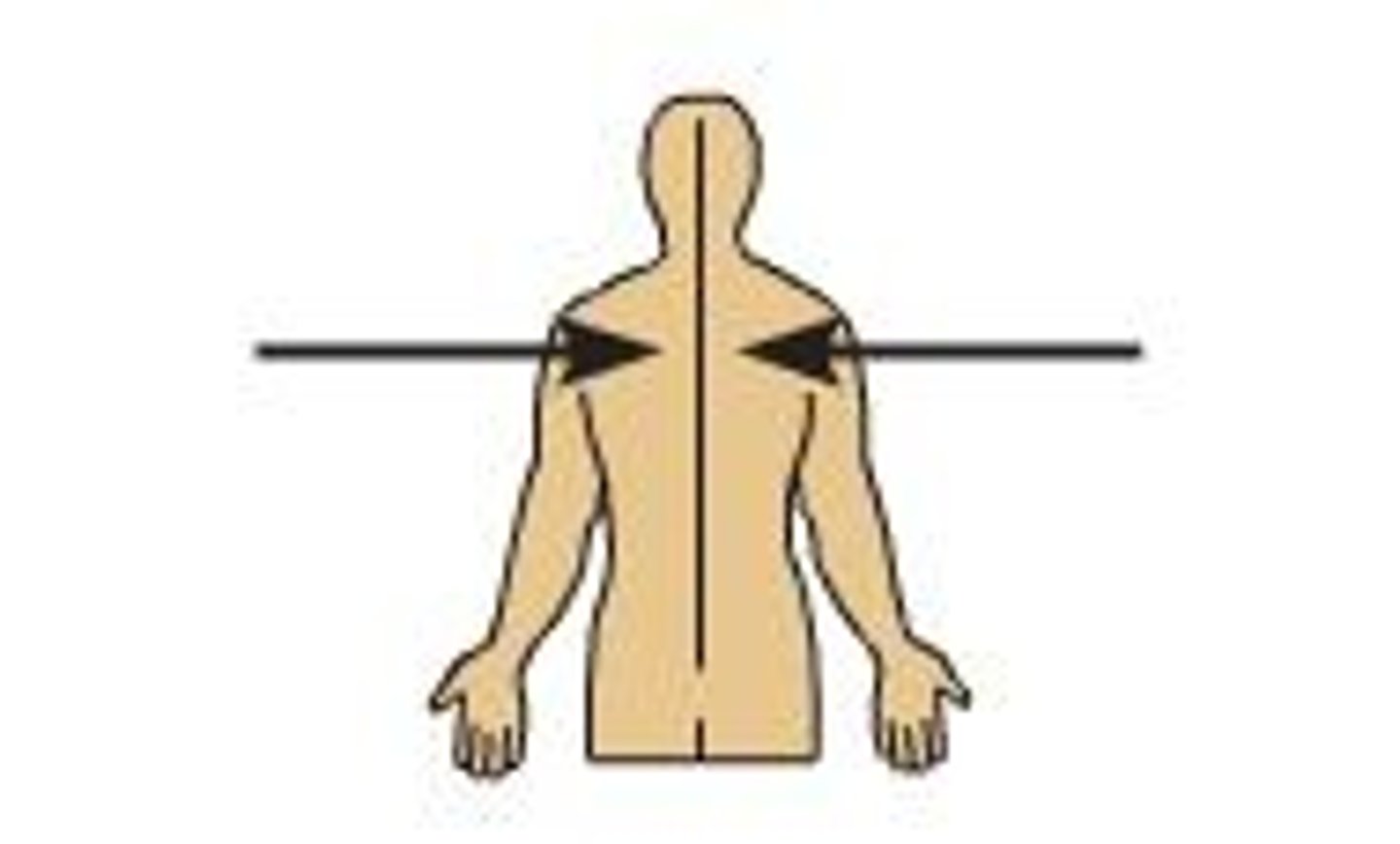
Oblique
At an angle or pertaining to an angle.
Superficial
Near the surface; not deep.
Deep
Situated far beneath the surface; not superficial.
Peripheral
Situated near the outer areas or surface of the body
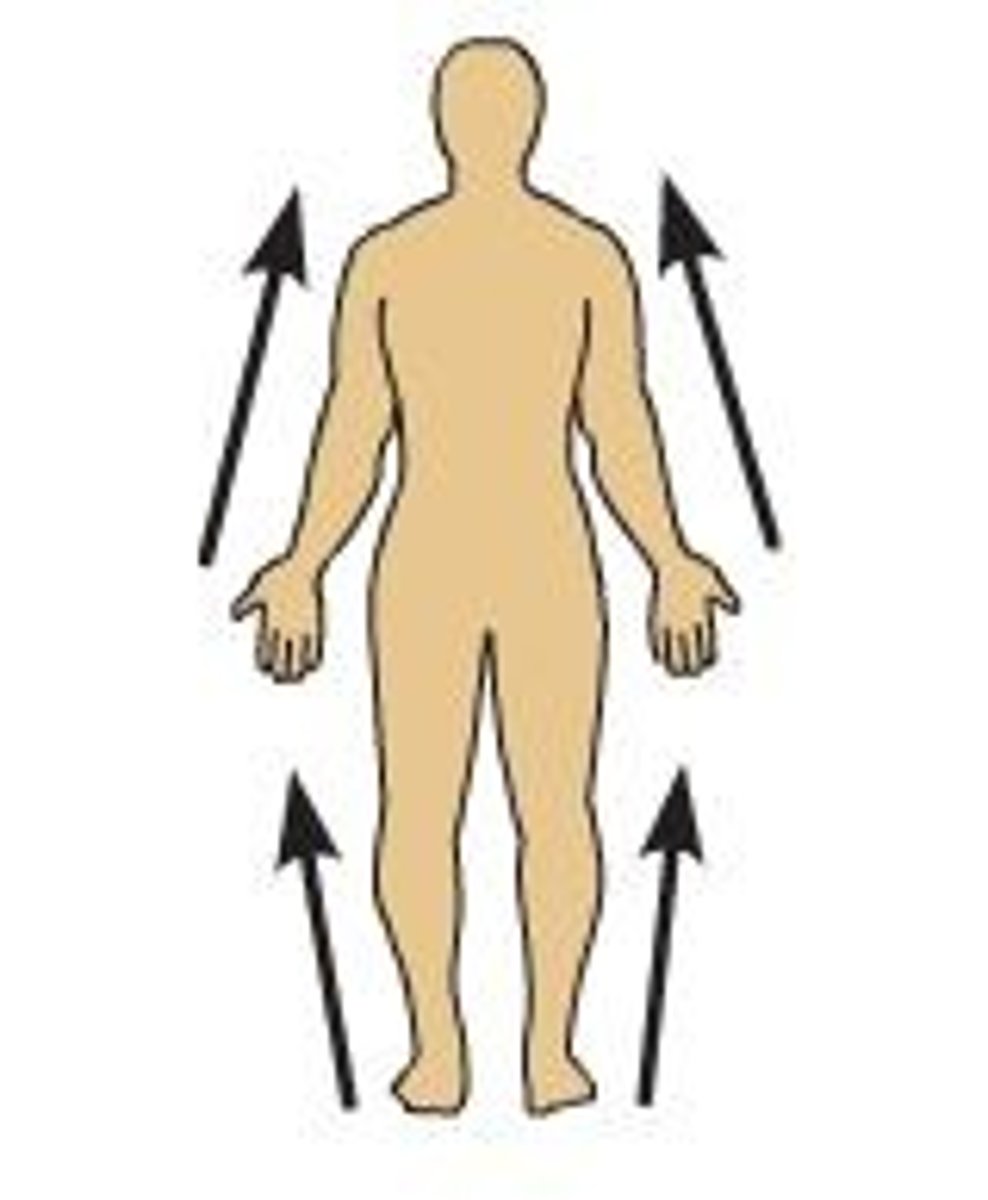
Proximal
nearest the point of attachment at the trunk (where arm attaches at shoulder, leg at hip)
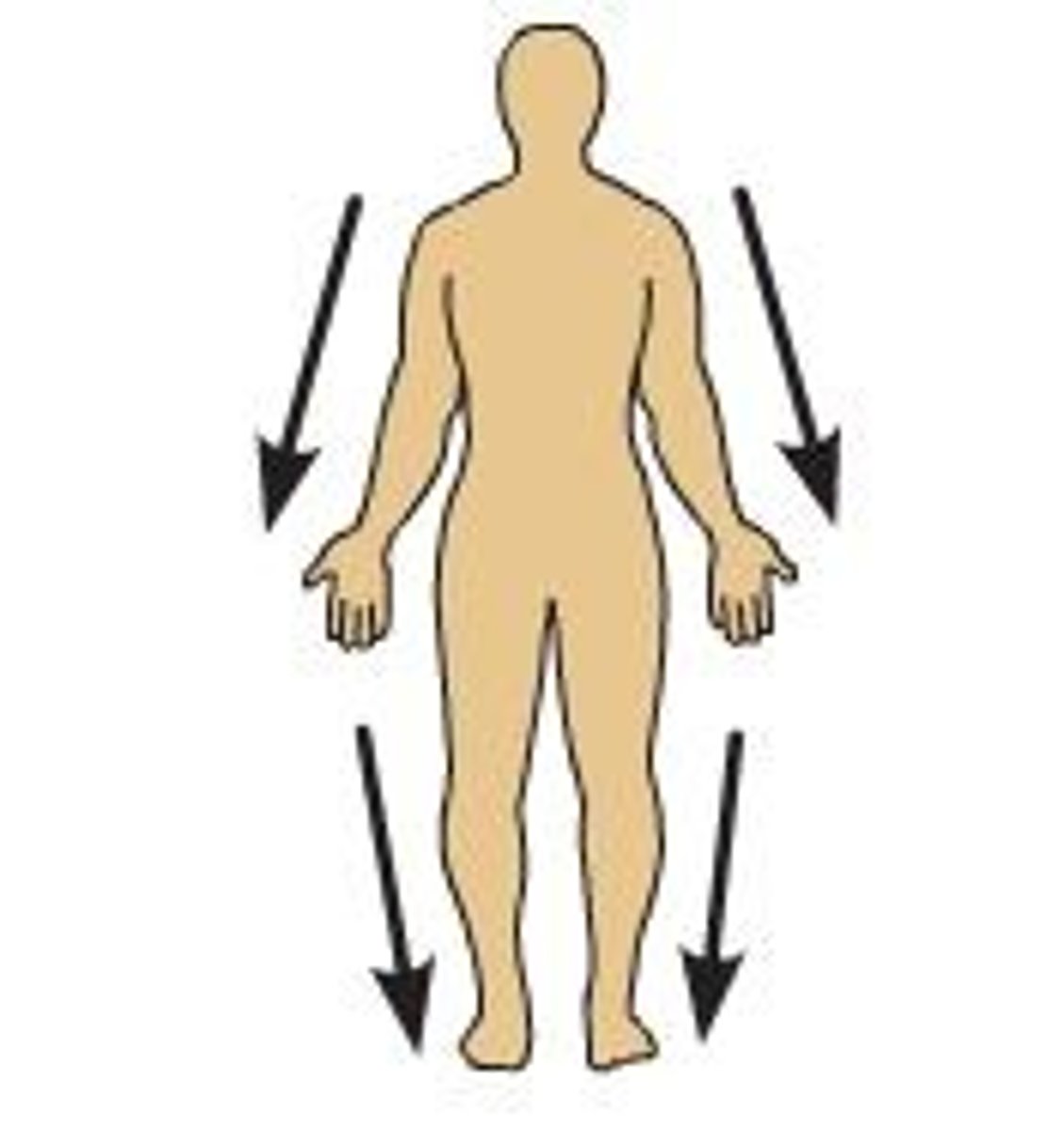
Distal
Farthest from the center of the body relative to another body part, or a location on a body part relative to another closer location.
Superior
Above. Up.
Inferior
Below, underneath.
Palmar
The caudal surface of the front leg from the carpus to the phalanges. This includes the bottom surface of the front foot.
Plantar
The caudal surface of the hind leg from the hock to the phalanges. This includes the bottom surface of the hind foot.
Prone
To lie face down, in ventral recumbency.

Recumbent
Lying down.
Dorsal Recumbency
Lying on its back, face up.
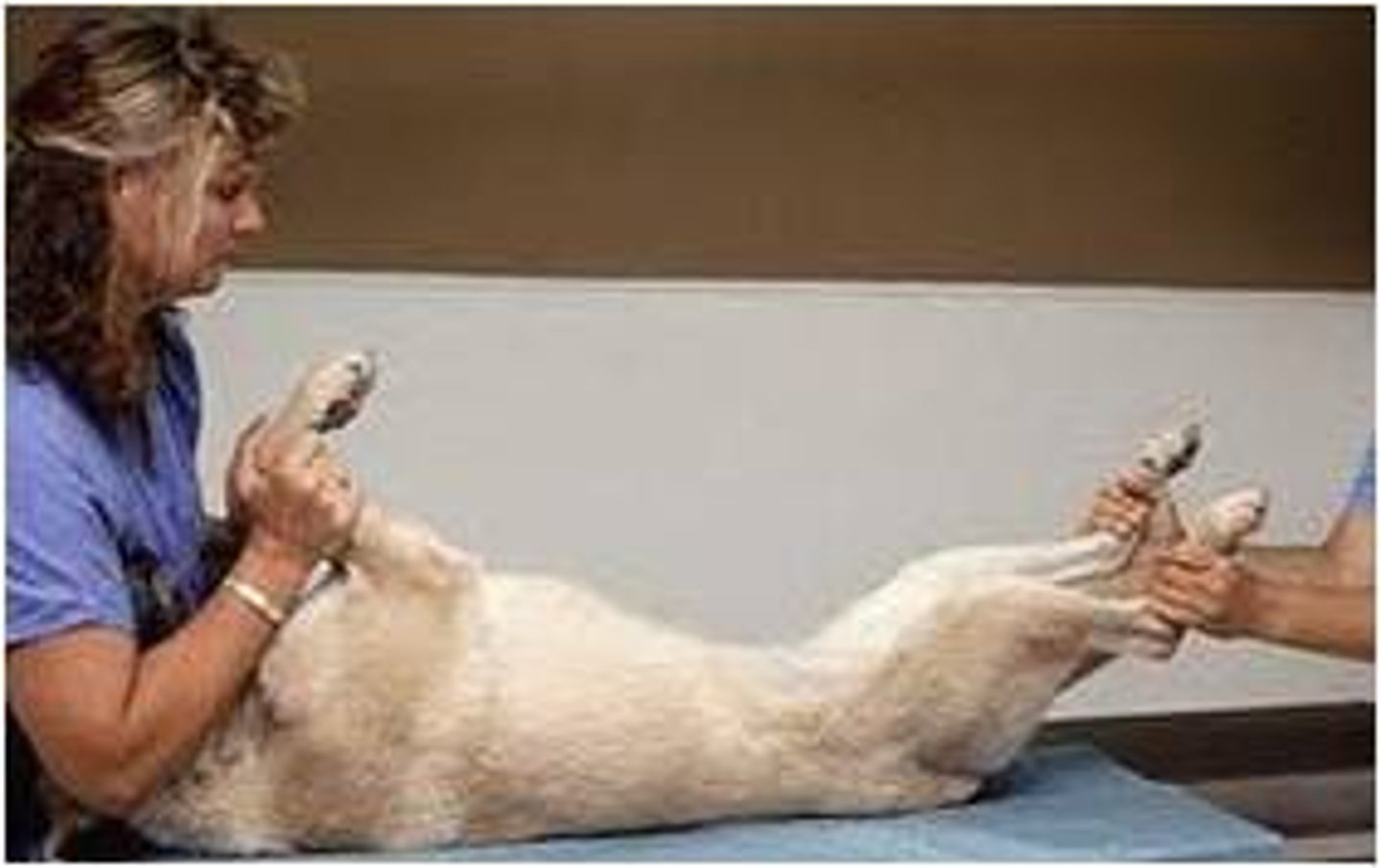

Ventral Recumbency
Lying on it's ventral surface, or belly.
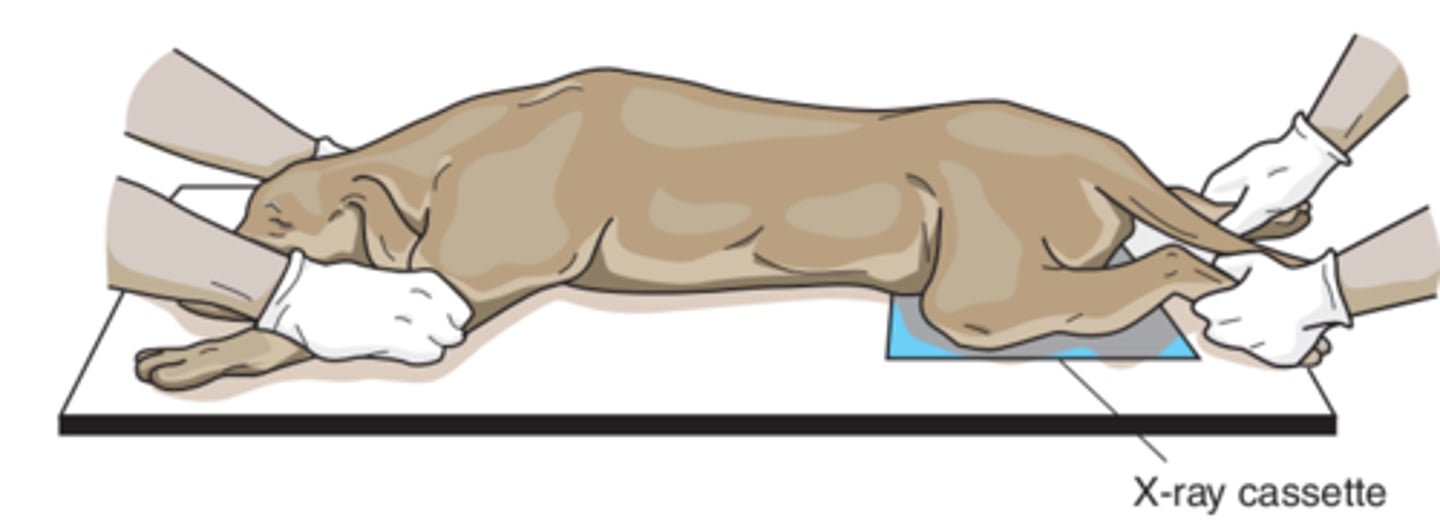
Lateral Recumbency
Lying on it's side.
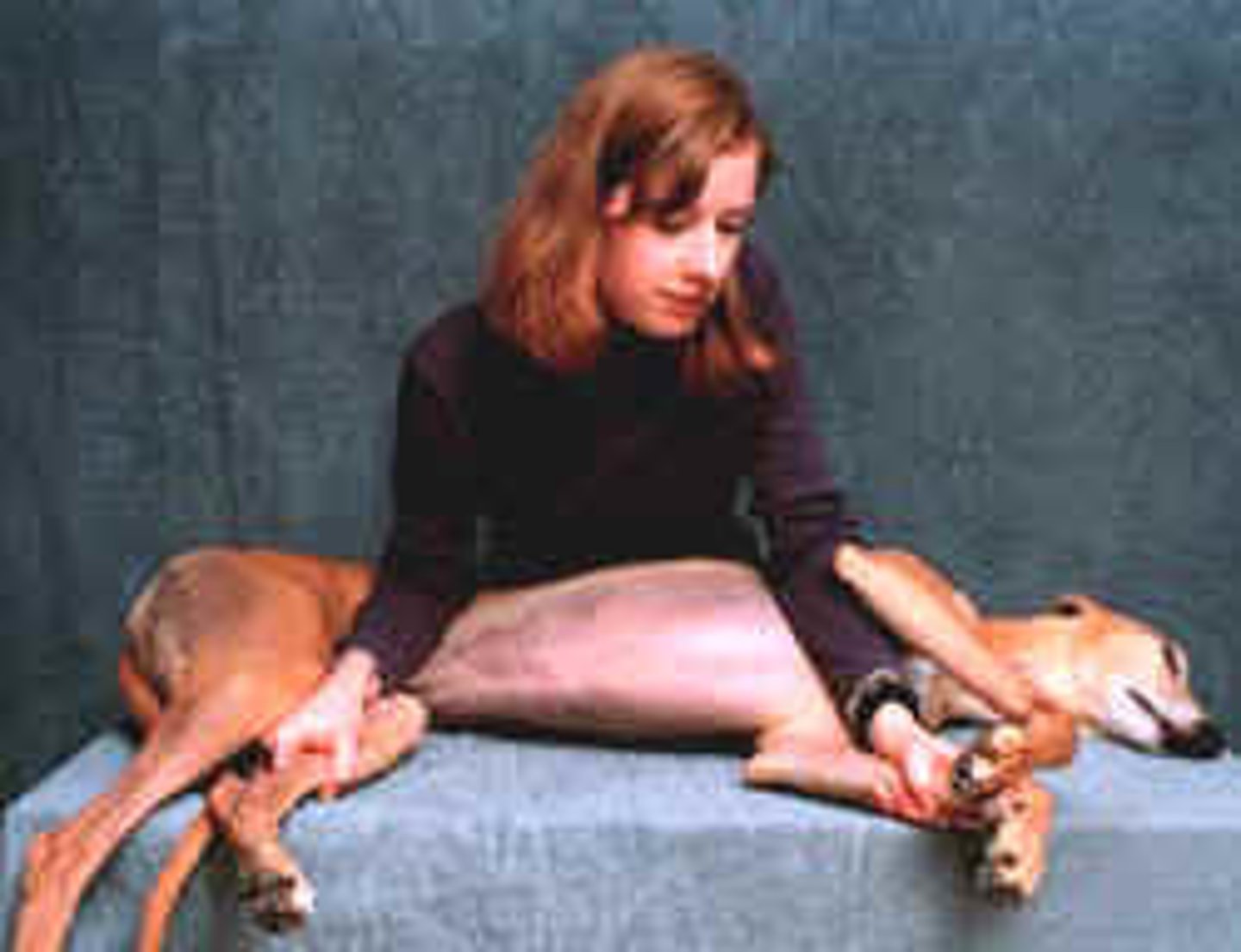

Supine
To lie face up, in dorsal recumbency.
Abdominal
Pertaining to the abdomen.
Antebrachium
The distal area of the front legs of an animal, below the elbow joint.
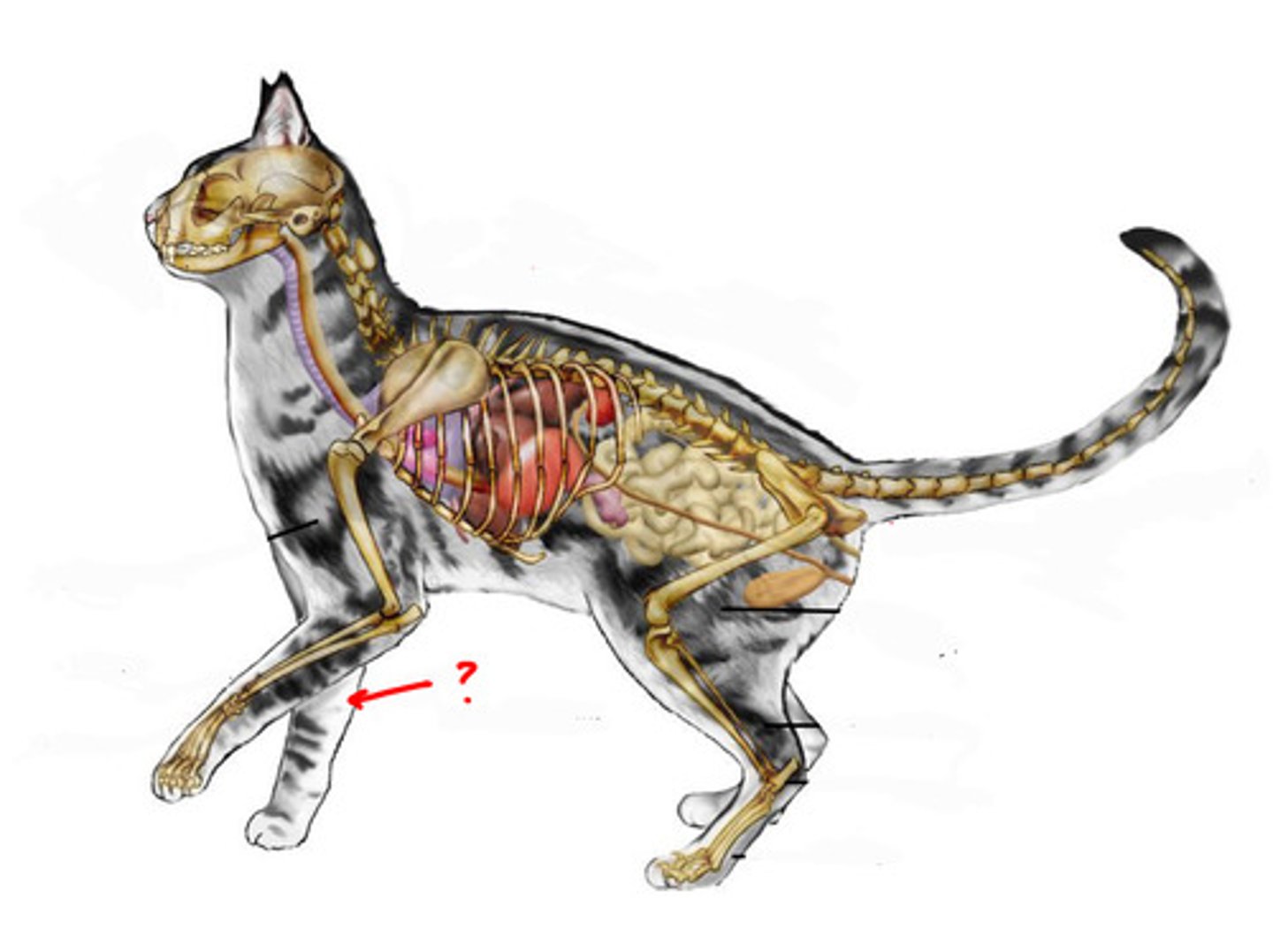
Appendicular
Related to the limbs and their attachments to the trunk (axis) of the body. Legs/tail=appendages (blue skeleton)
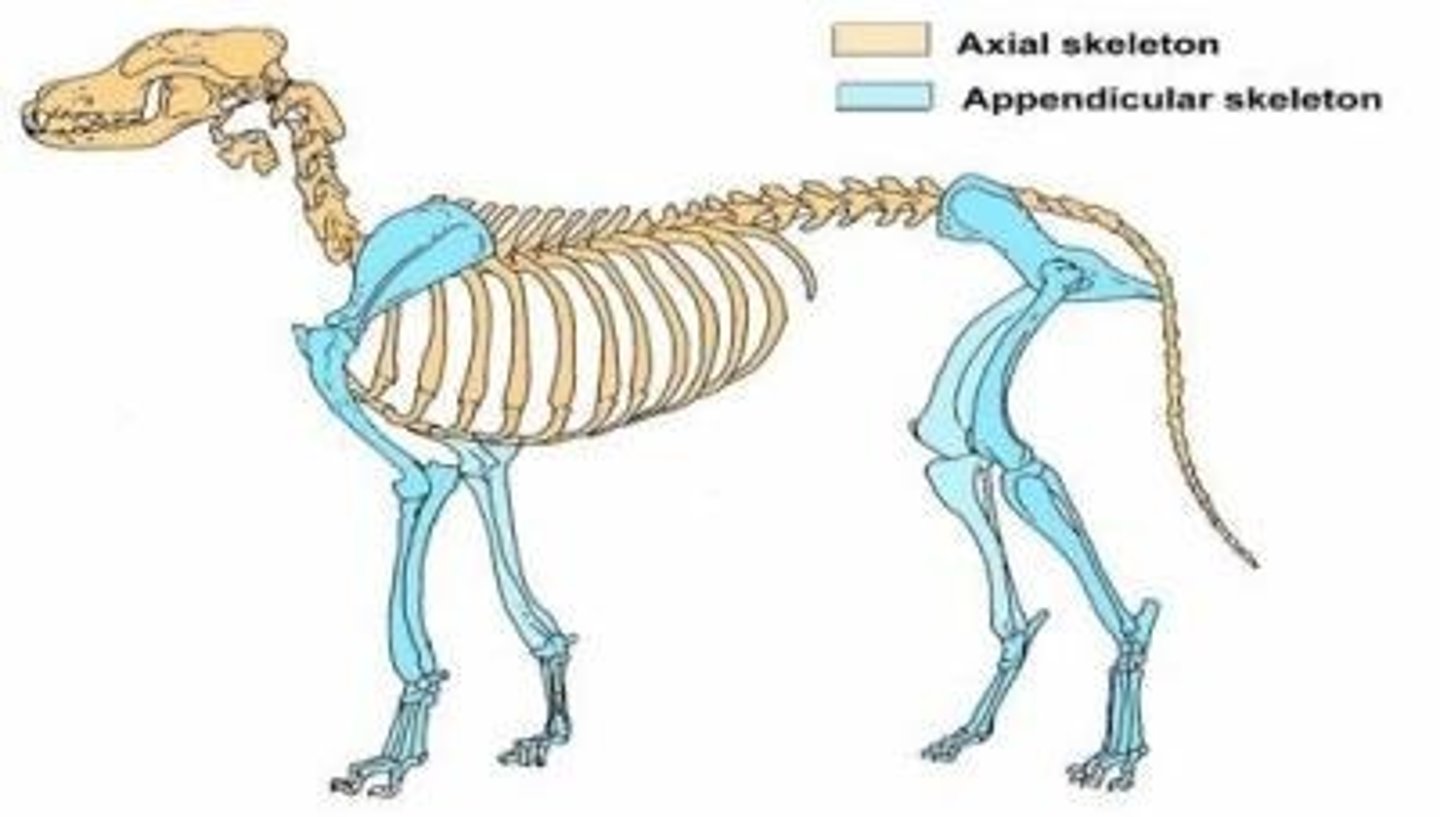
Axial
Related to the head, neck, and trunk or torso, the axis of the body. (Tan skeleton)
Axillary
Armpit area, where the front leg meets the torso.
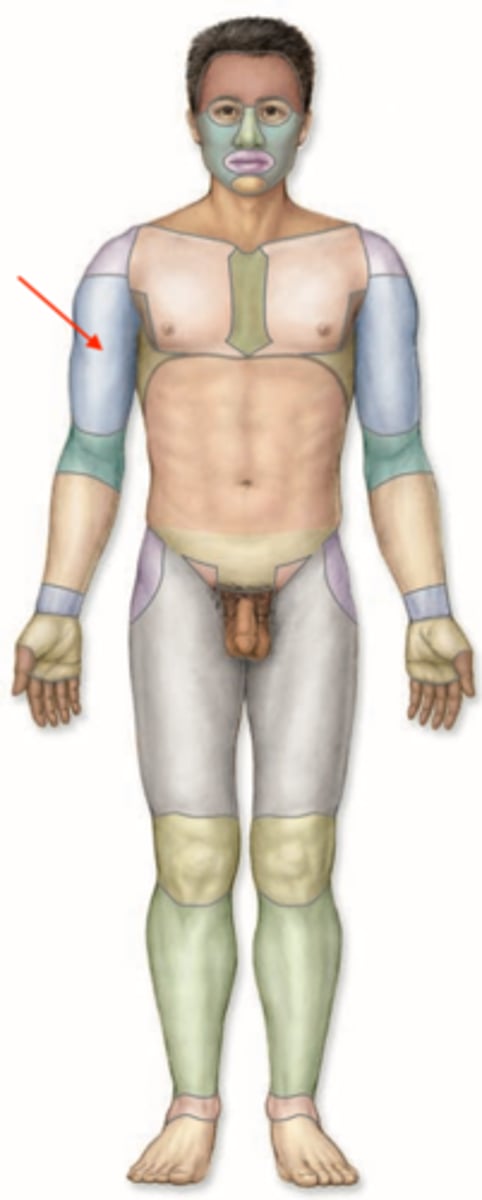
Brachial
The proximal area of the front legs of an animal, above the elbow joint.
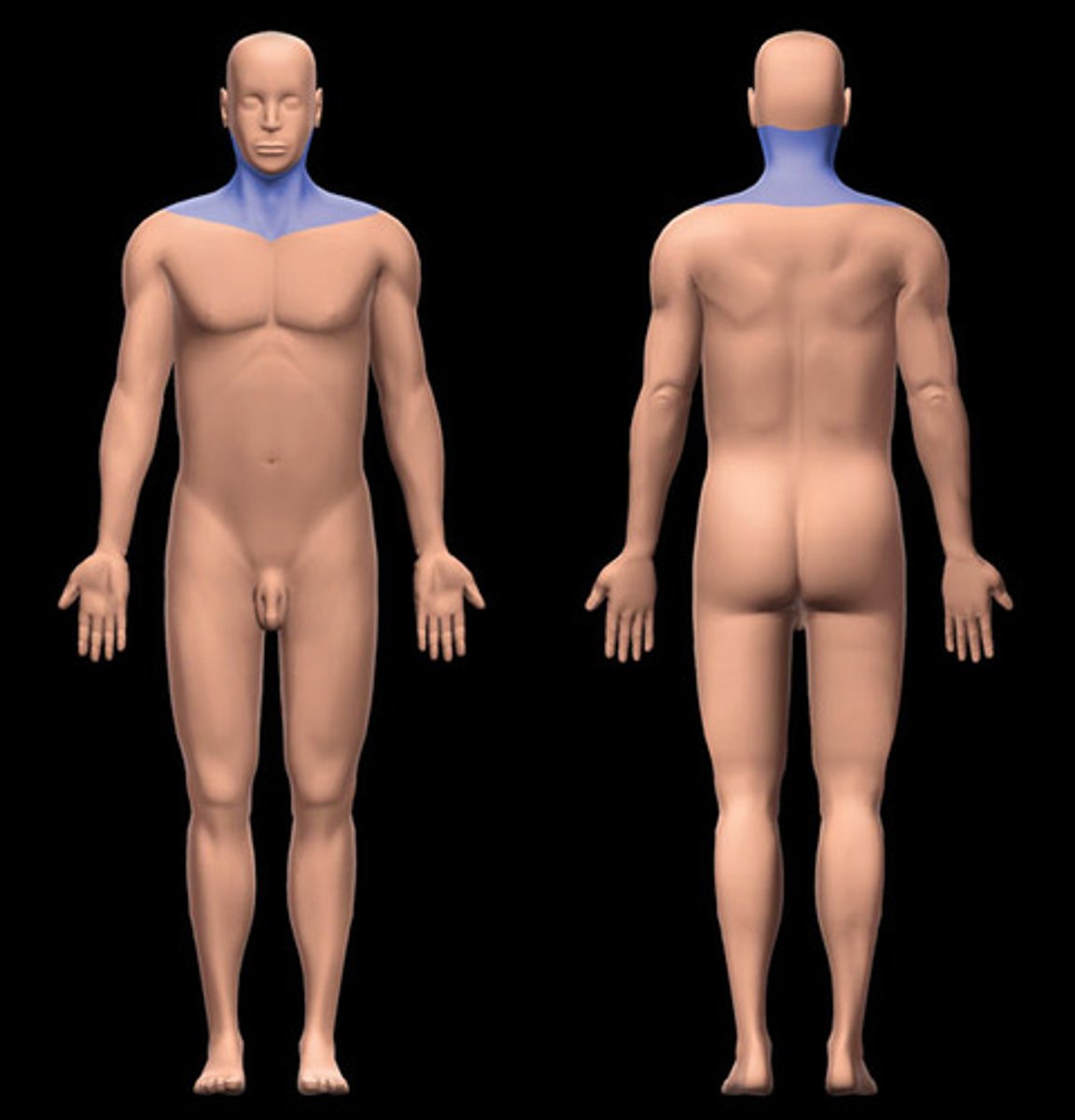
Cervical
1. The neck area. 2. The cervix in the female's reproductive system.
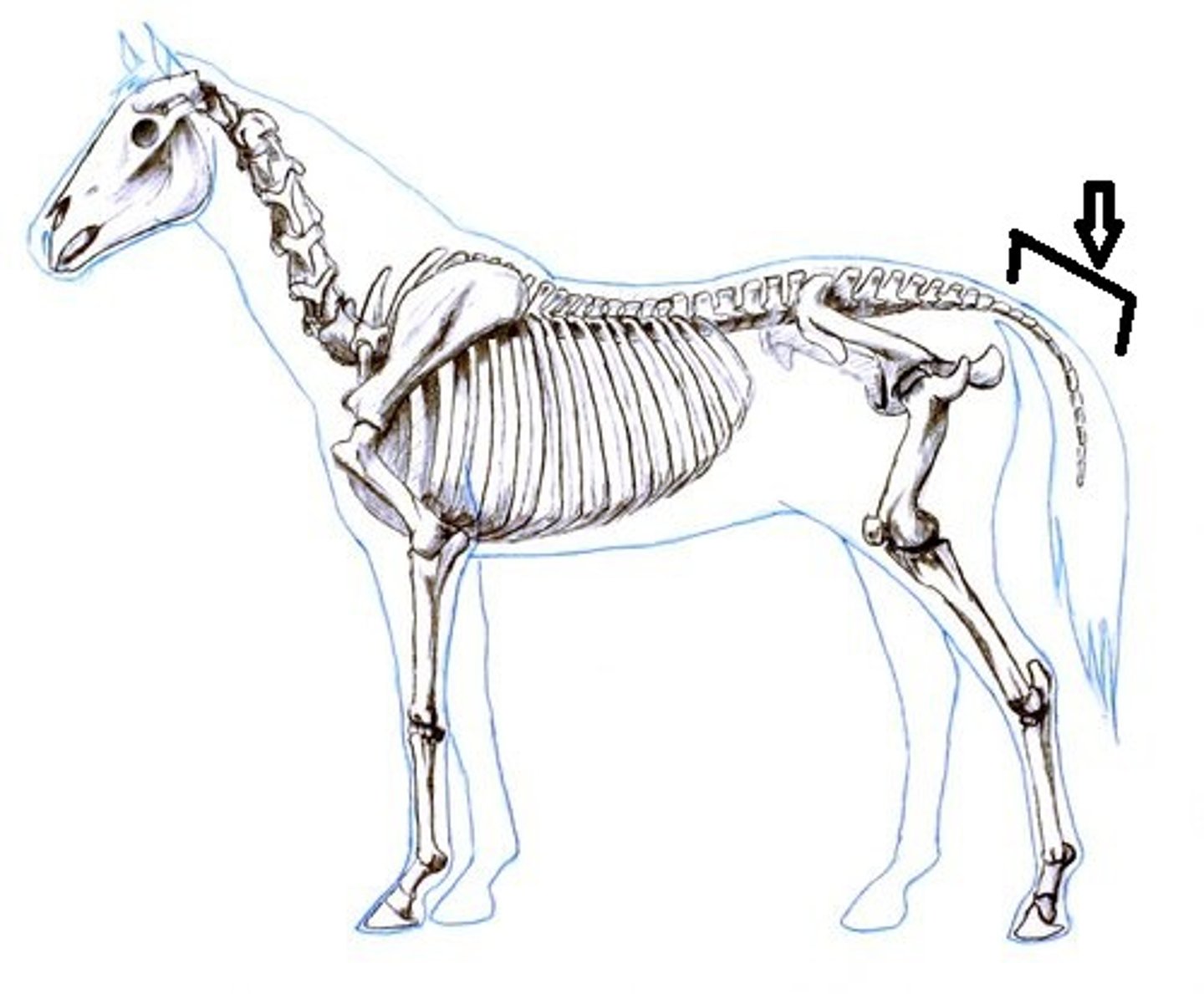
Coccygeal
Pertaining to the tail or vertebrae of the tail.
Cranium
the part of the skull that encases the brain.
Crural
Pertaining to the lower rear legs of an animal.
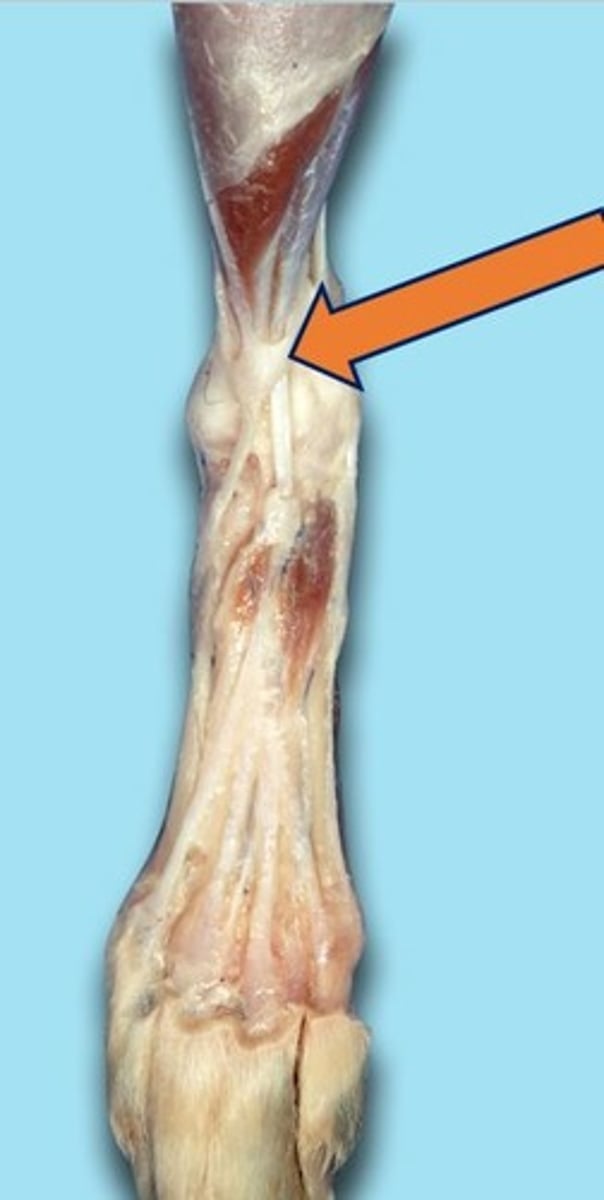
Digital
Area of the toes or toe bones (the phalanges) are located.
Frontal
The forehead, above the eyes, where the frontal bone and frontal sinuses are located.
Inguinal
pertaining to the groin where the thigh attaches to the hip
Lumbar
Pertaining to the lumbar vertebrae (the part of the backbone in the lower back
Mammary
Pertaining to the mammary glands (the milk-producing glands).
Nasal
Pertaining to the nose.
Oral
Pertaining to the mouth.

Orbital
Pertaining to the bony eye socket (the orbit).
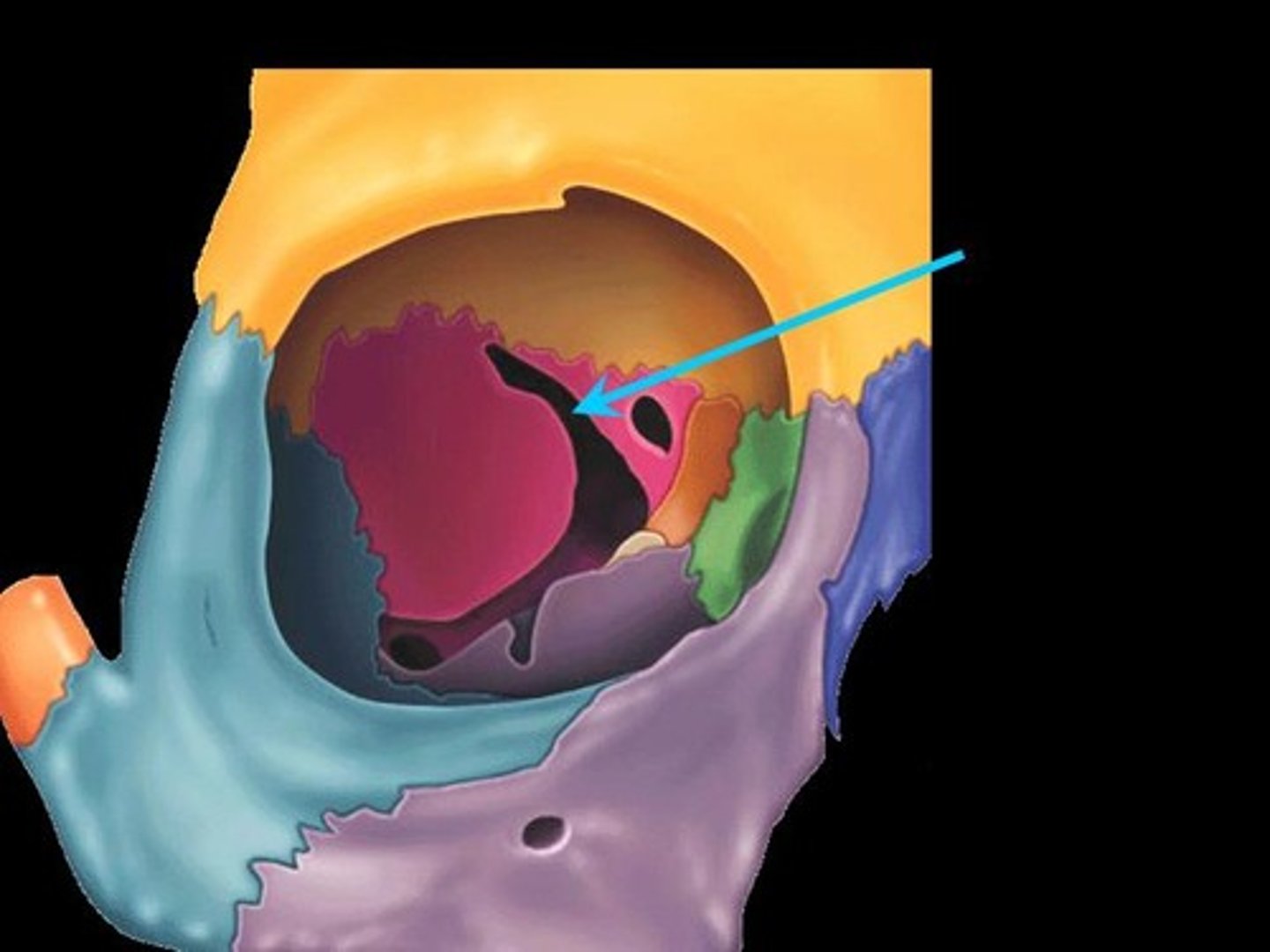
Patellar
Pertaining to the patella or knee cap.
Pelvic
Pertaining to the pelvis or hip bones (which are made up of four bones of each side of the pelvis: the ilium, ischi
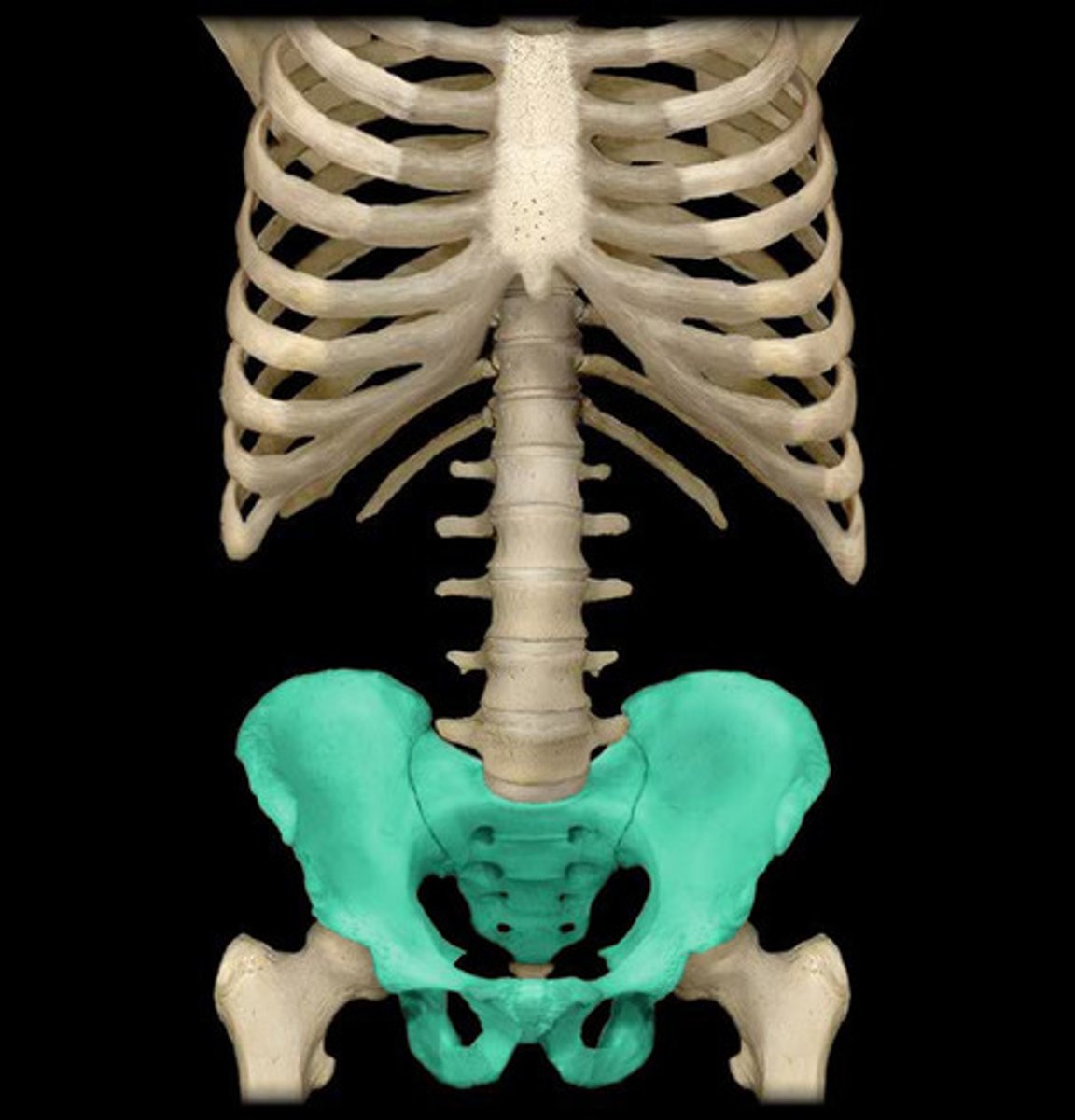
Perineal
Pertaining to the area between the anus and the genitals.
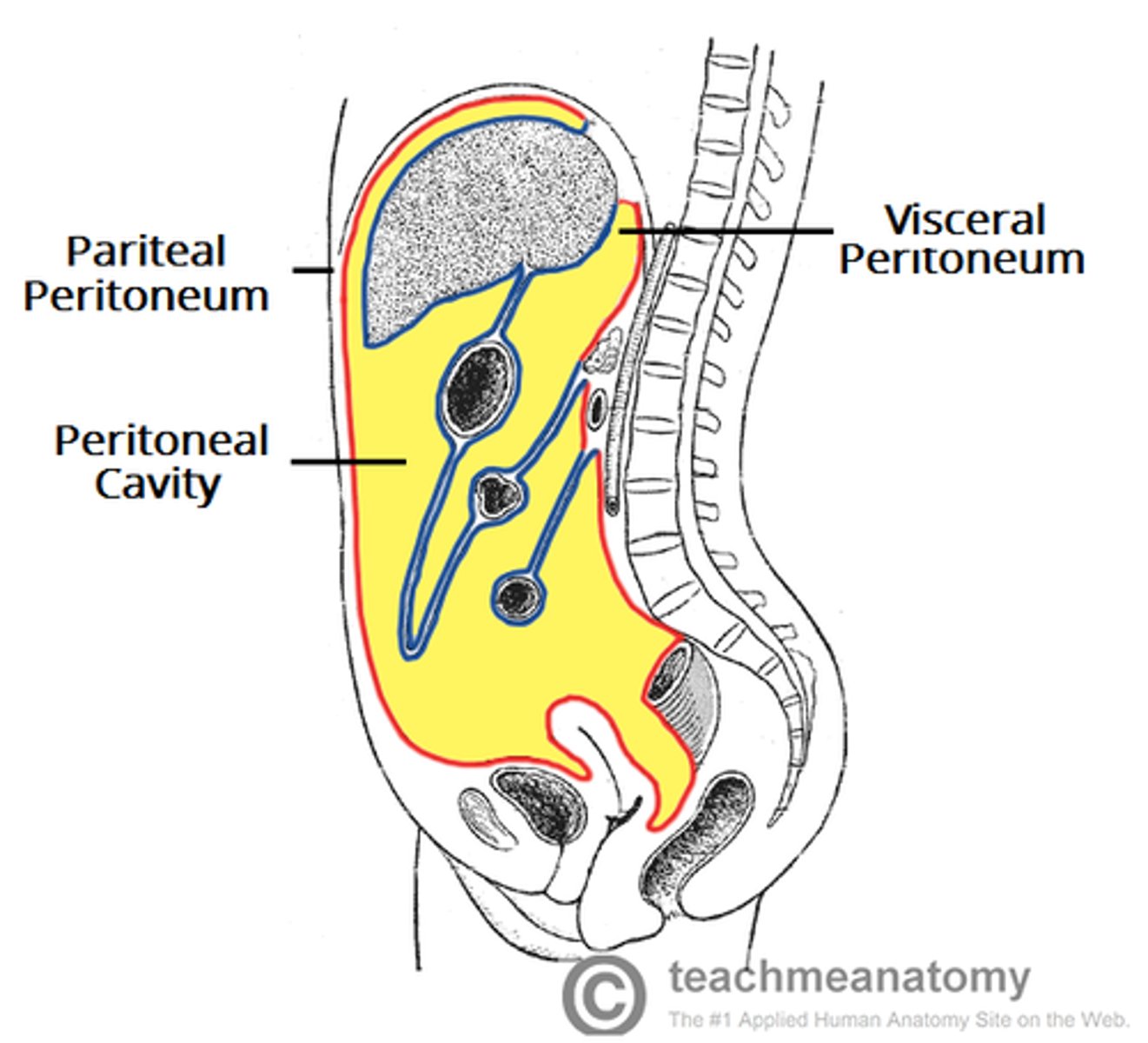
Peritoneal
Pertaining to the cavity inside the abdomen and the membrane that lines this cavity.
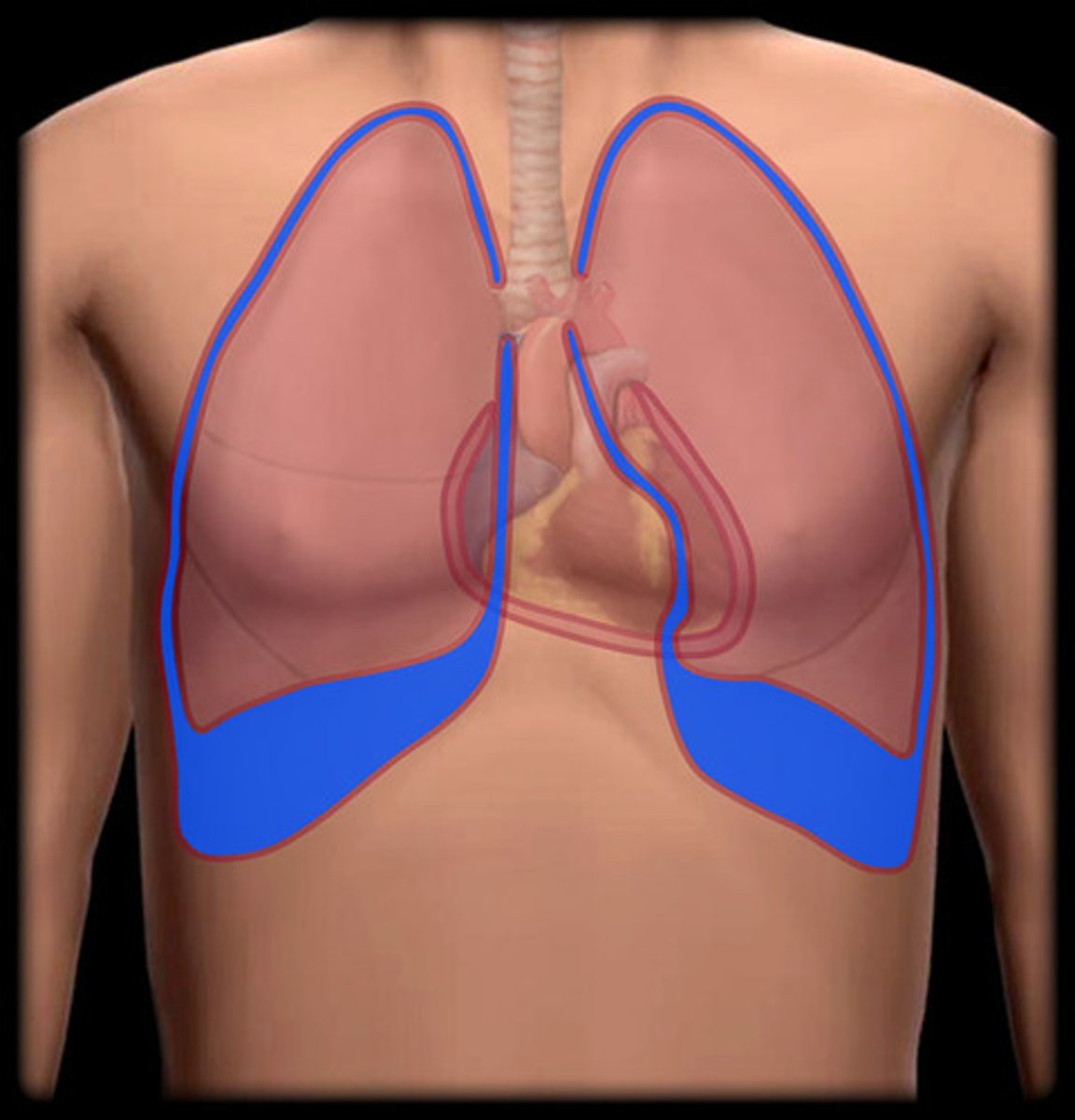
Pleural
Pertaining to the cavity inside the chest and the membranes that line this cavity.
Popliteal
Pertaining to the caudal area or back of the true knee, the stifle joint, where the popliteal lymph node is located.
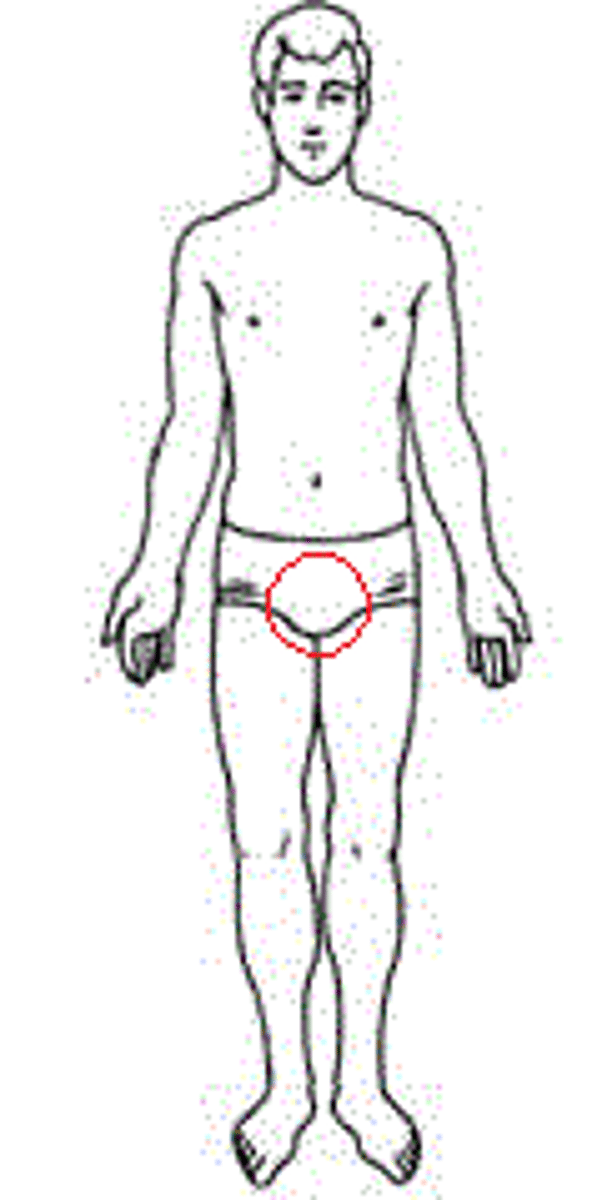
Pubic
Pertaining to the area located between the animals's rear legs where genitals are found
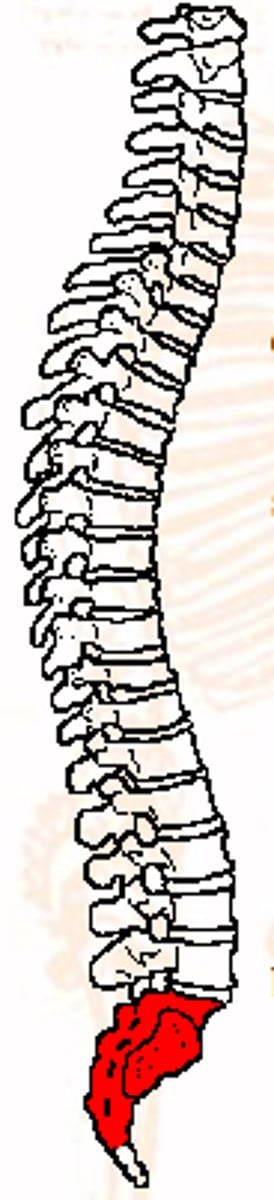
Sacral
Pertaining to the sacrum, the fused vertebrae by which the pelvis is attached to the backbone.
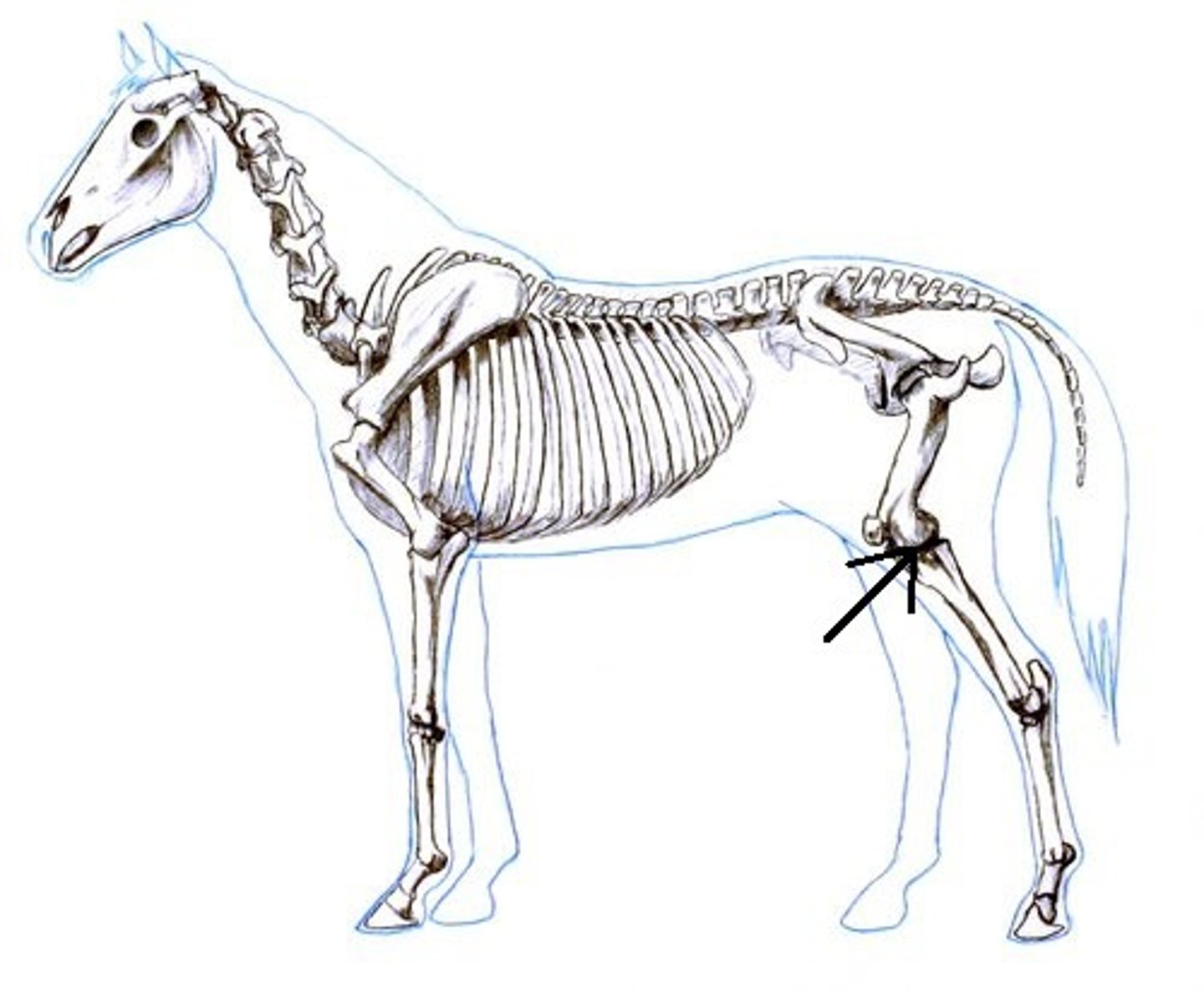
Scapular
Pertaining to the scapula or the shoulder blade area.
Sternal
Pertaining to the region of the sternum, or breastbone.
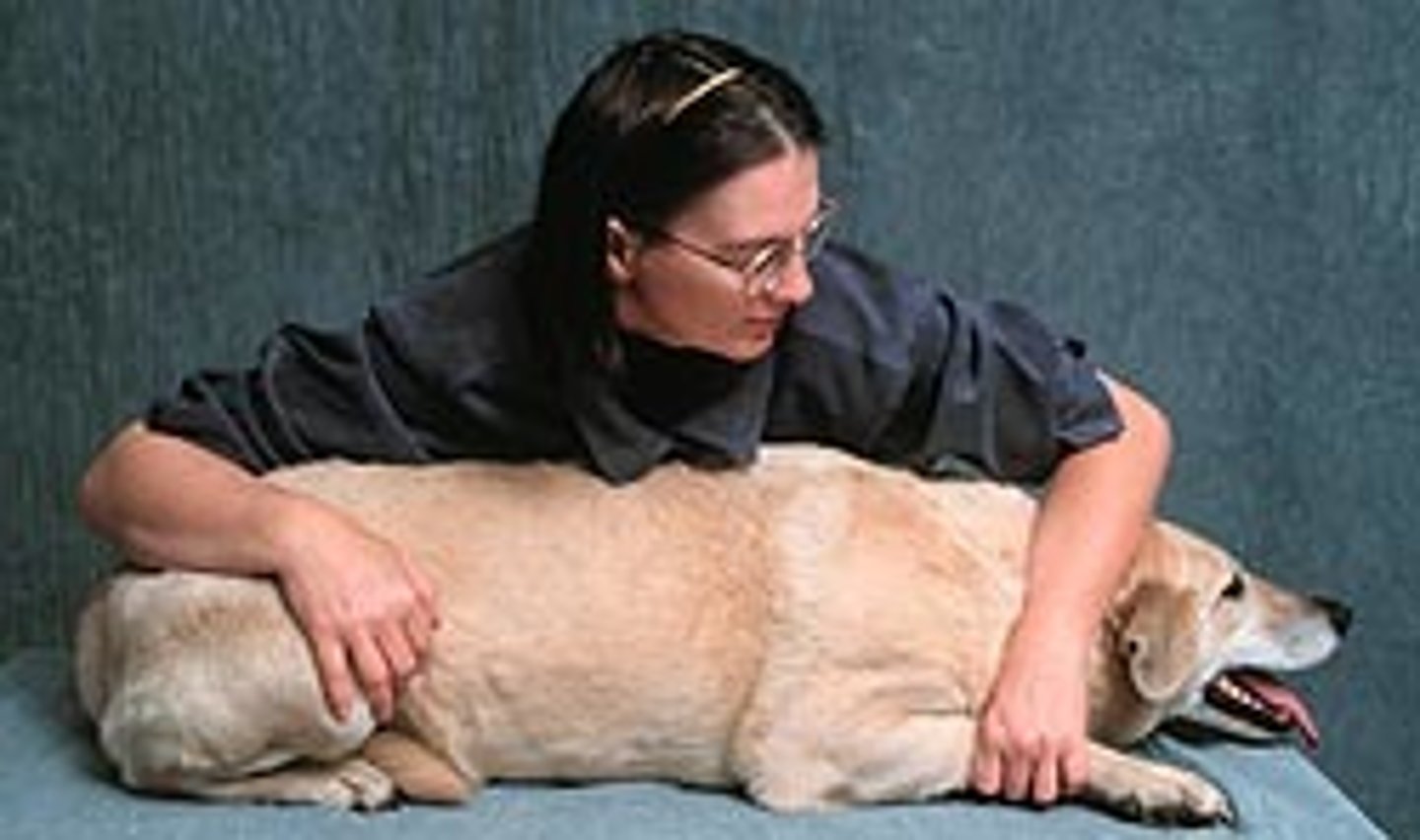

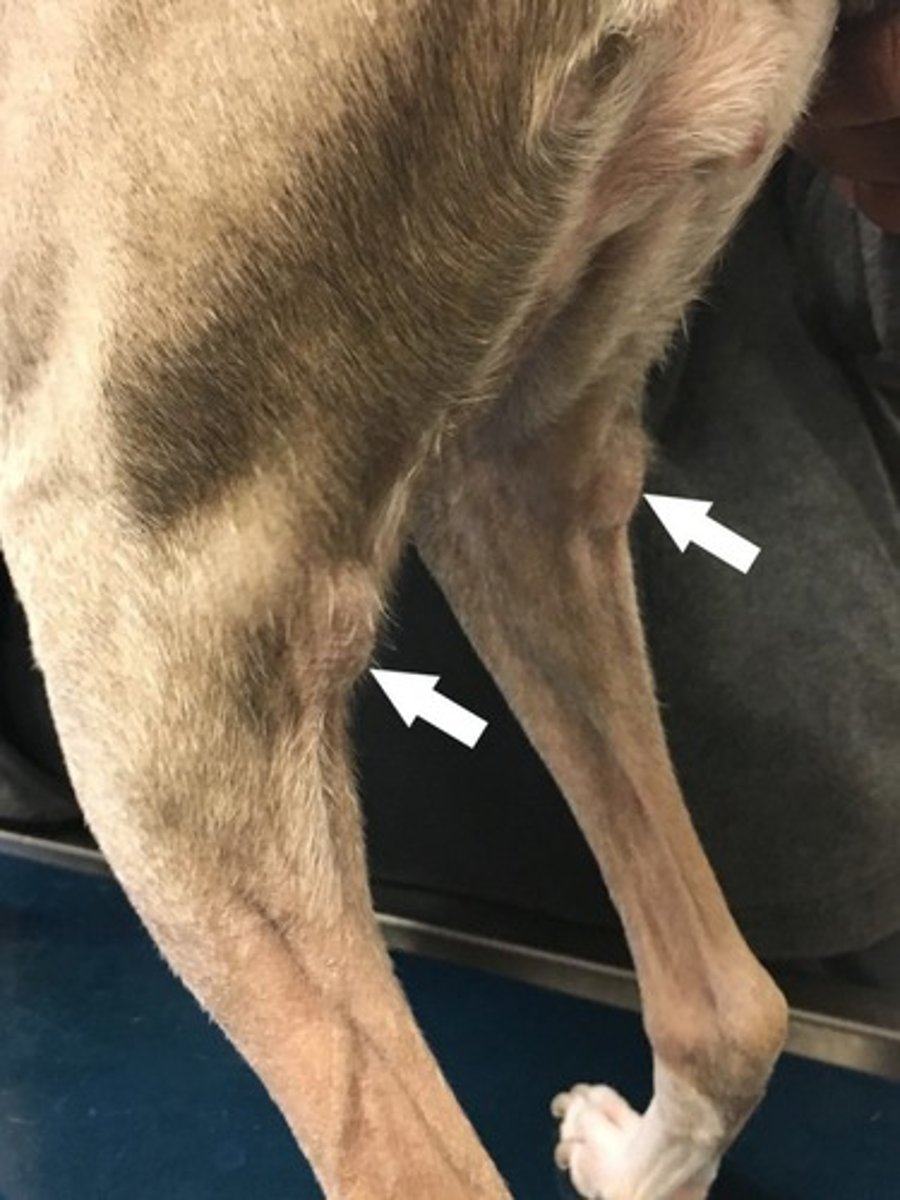
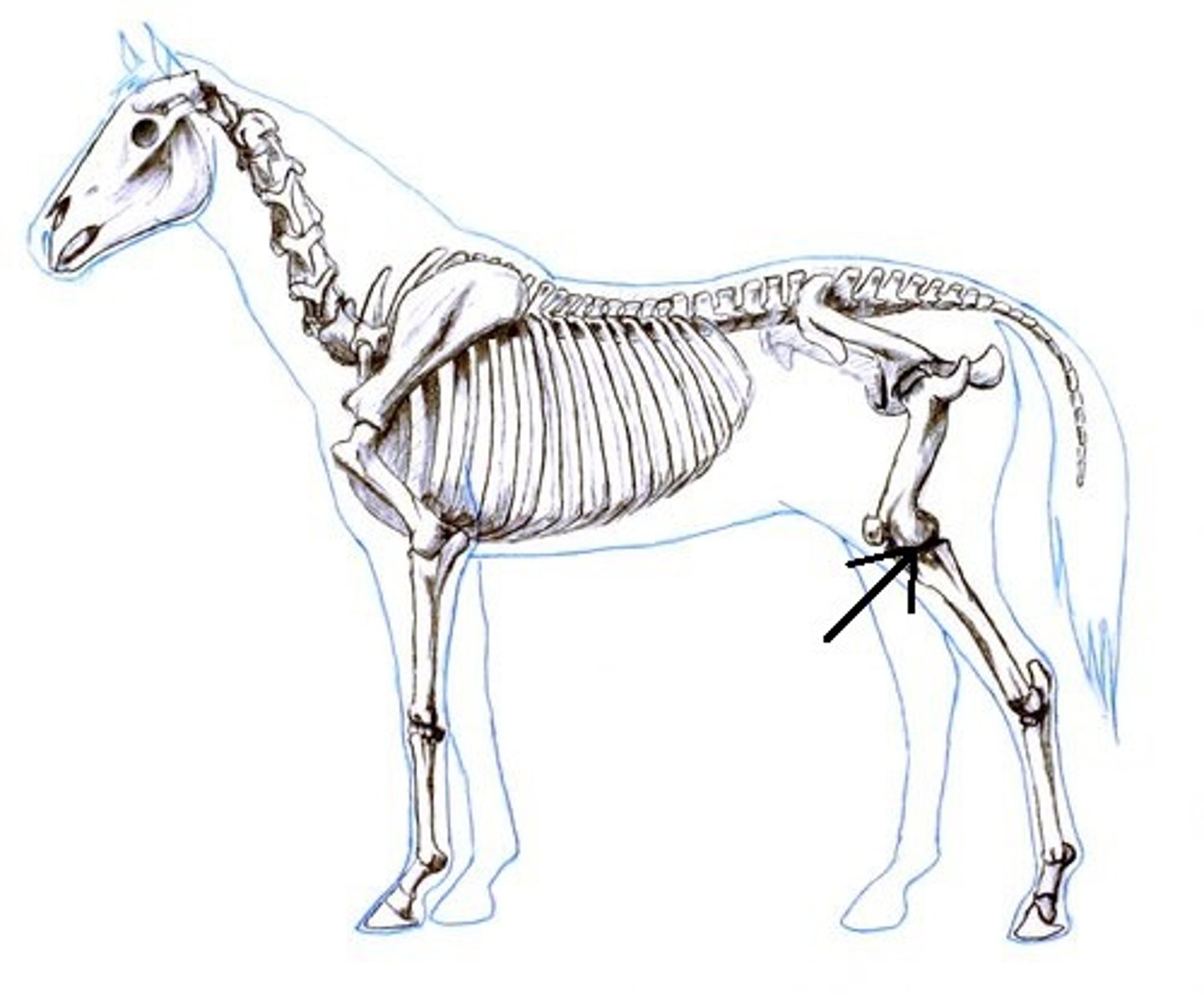
Stifle
the true knee, the femorotibial joint.
Thoracic
pertaining to the thorax or chest
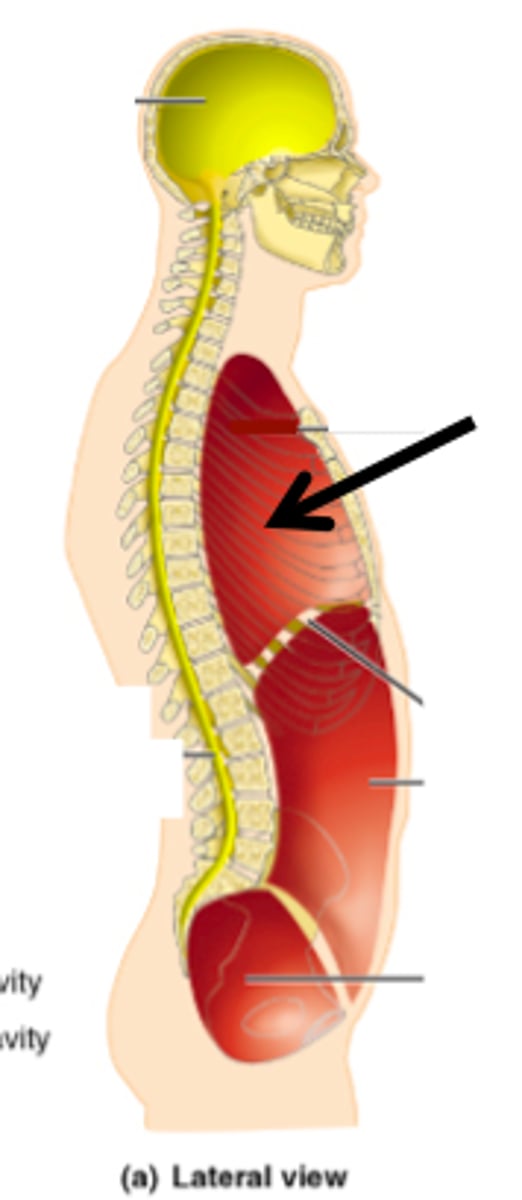
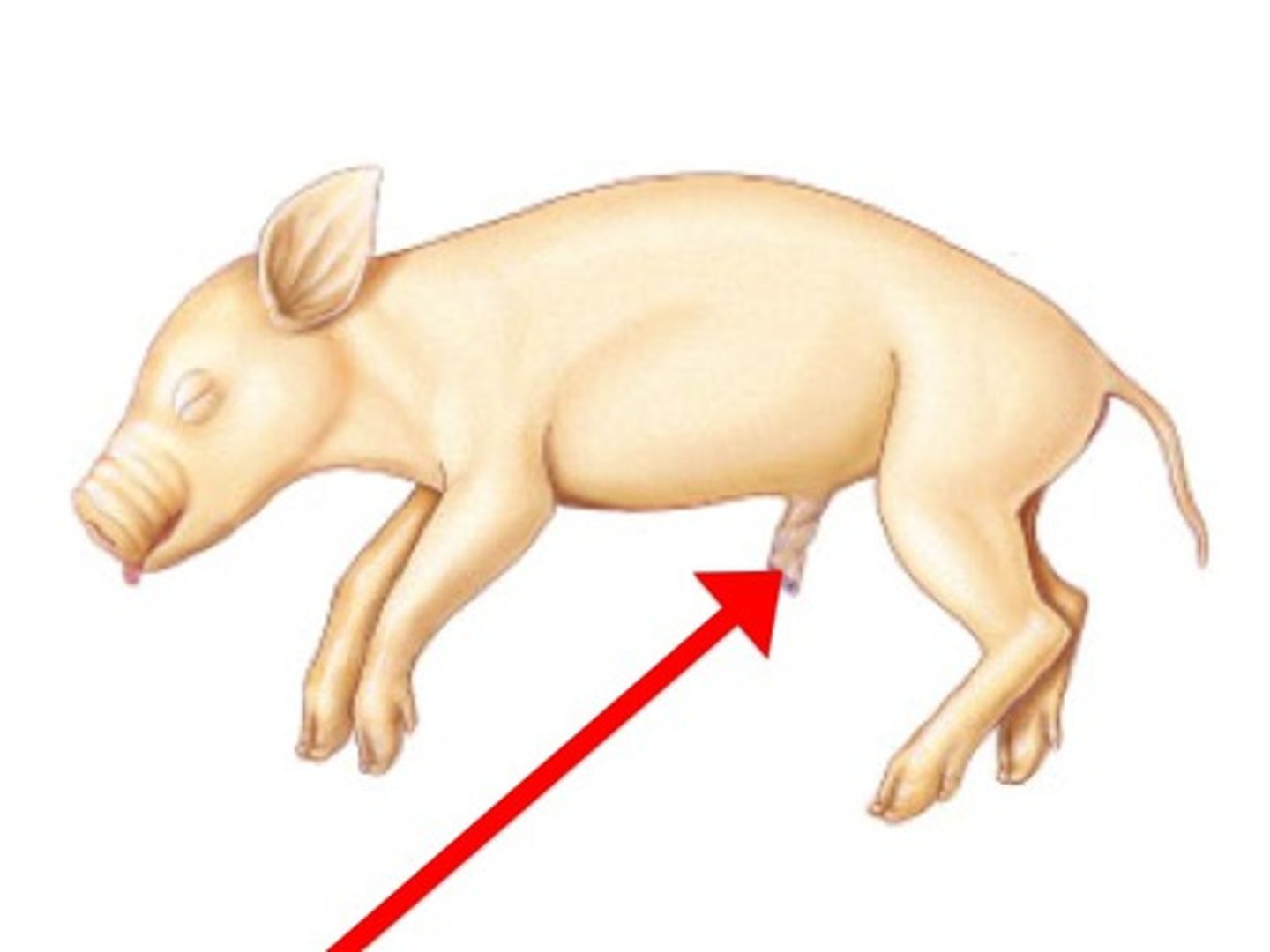
Umbilical
Pertaining to the umbilicus or navel (bellybutton).
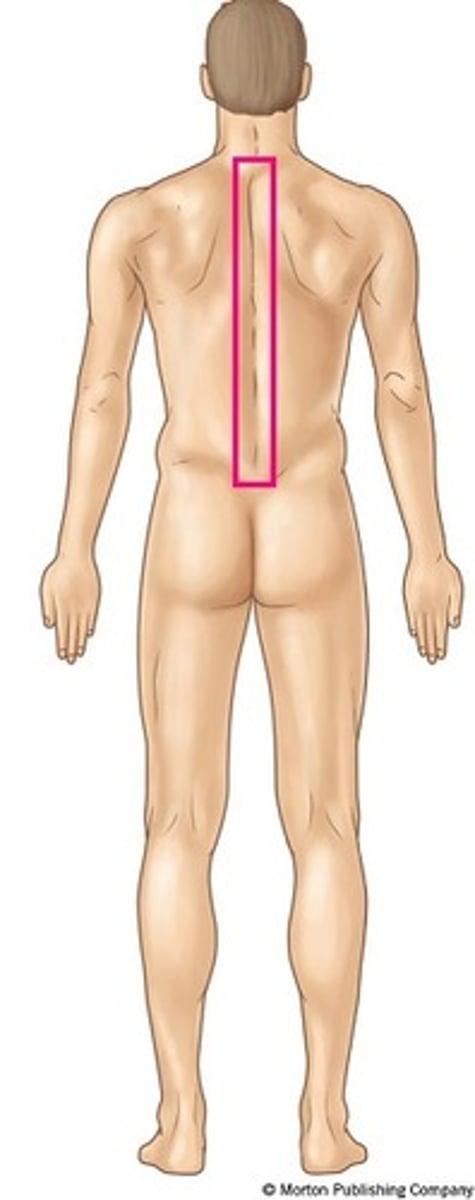
Vertebral
Pertaining to the vertebrae or spinal column.
Buccal
Surface of the tooth that is next to the cheek.
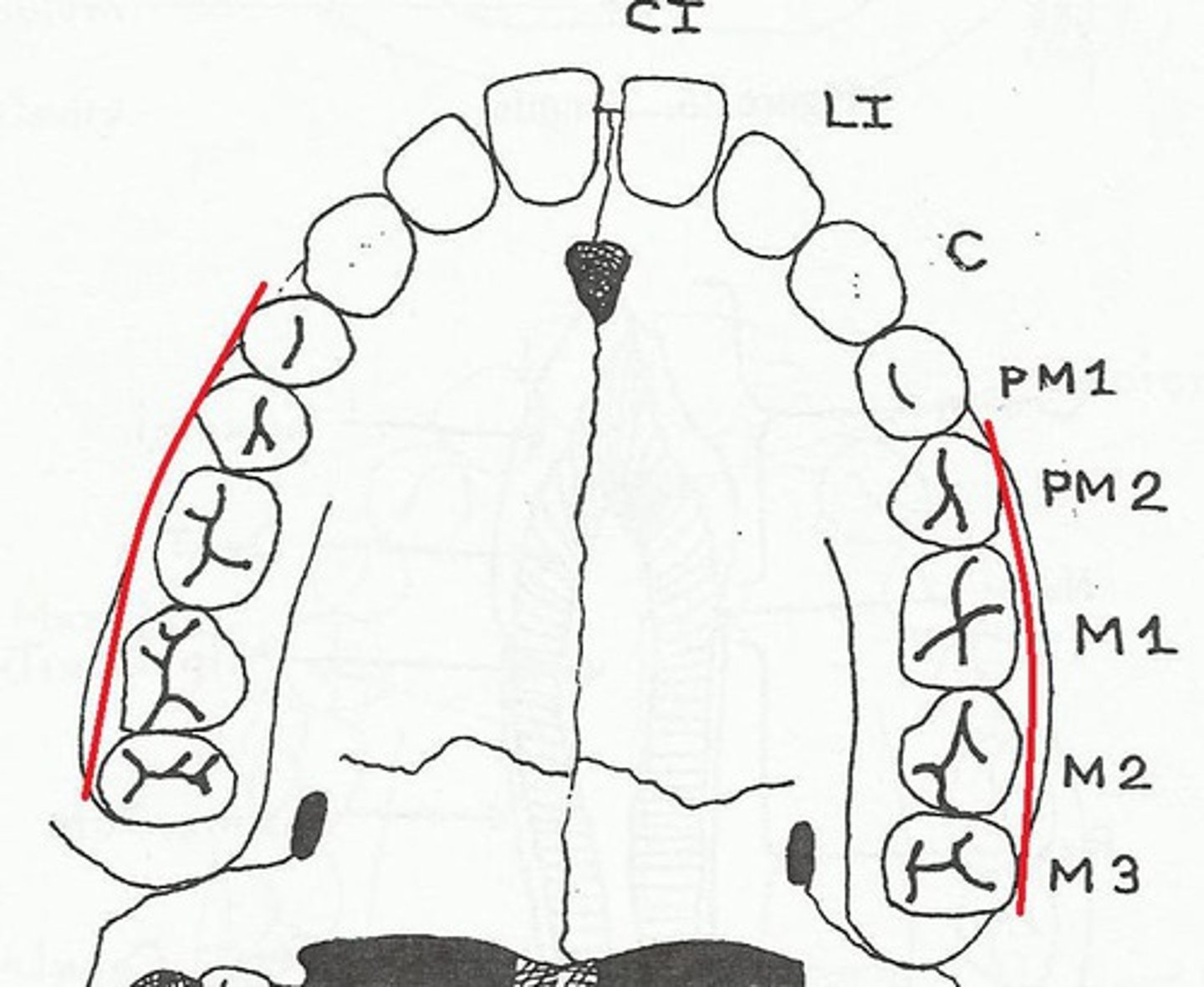
Contact of teeth
Surface of the tooth that is adjacent to the next tooth.
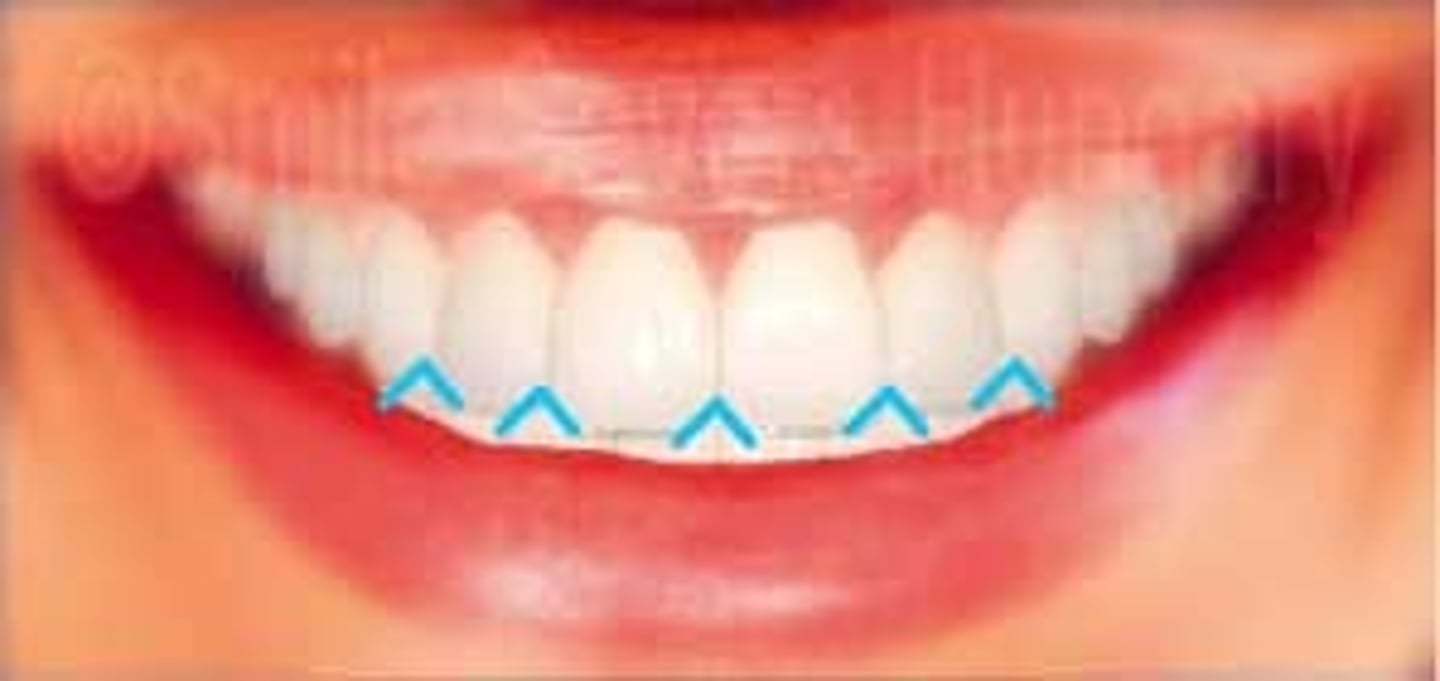
Labial
Surface of the incisor teeth that is next to the lips.
Palatal
Surface of the upper teeth that is next to the hard palate.
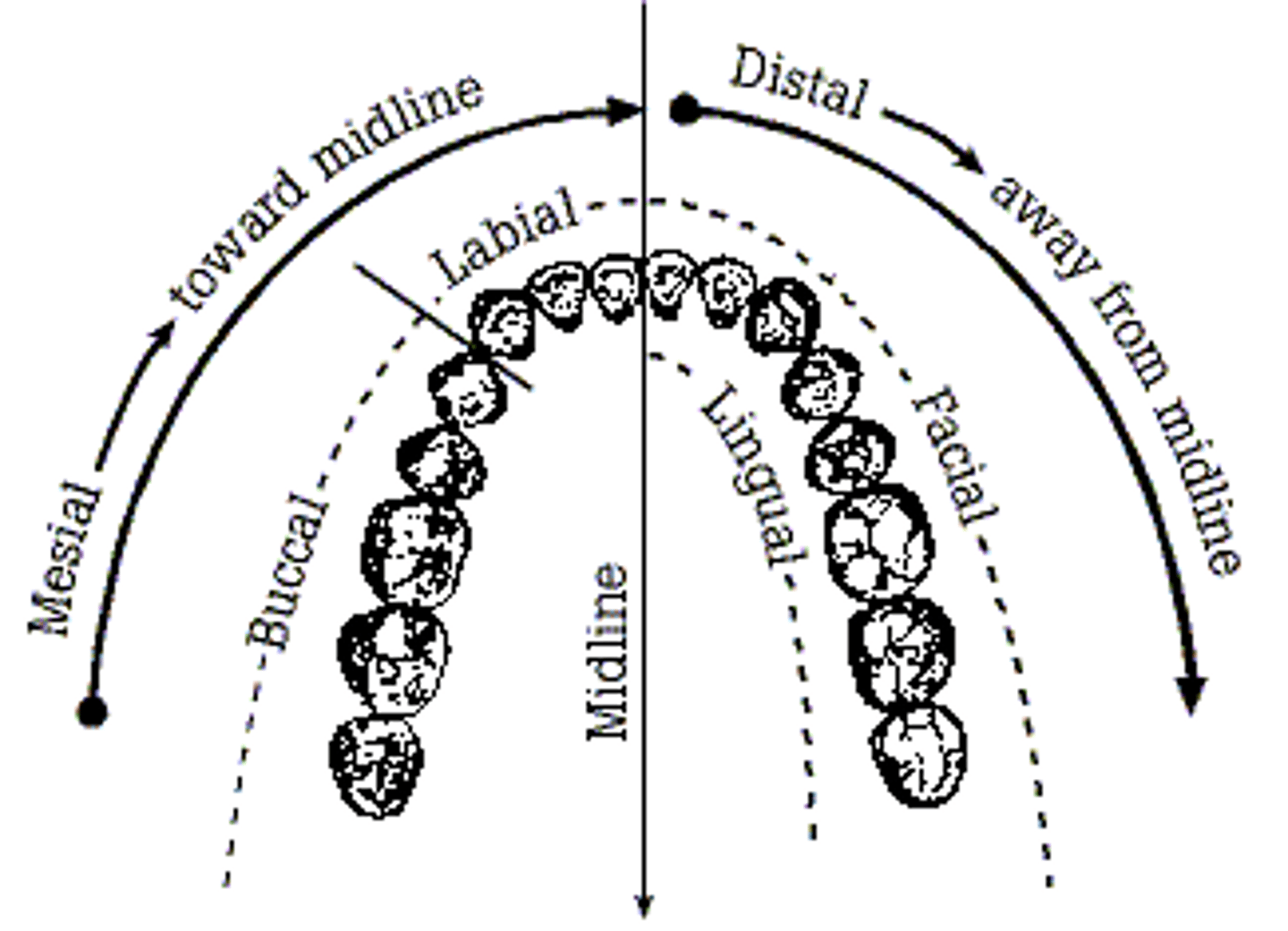
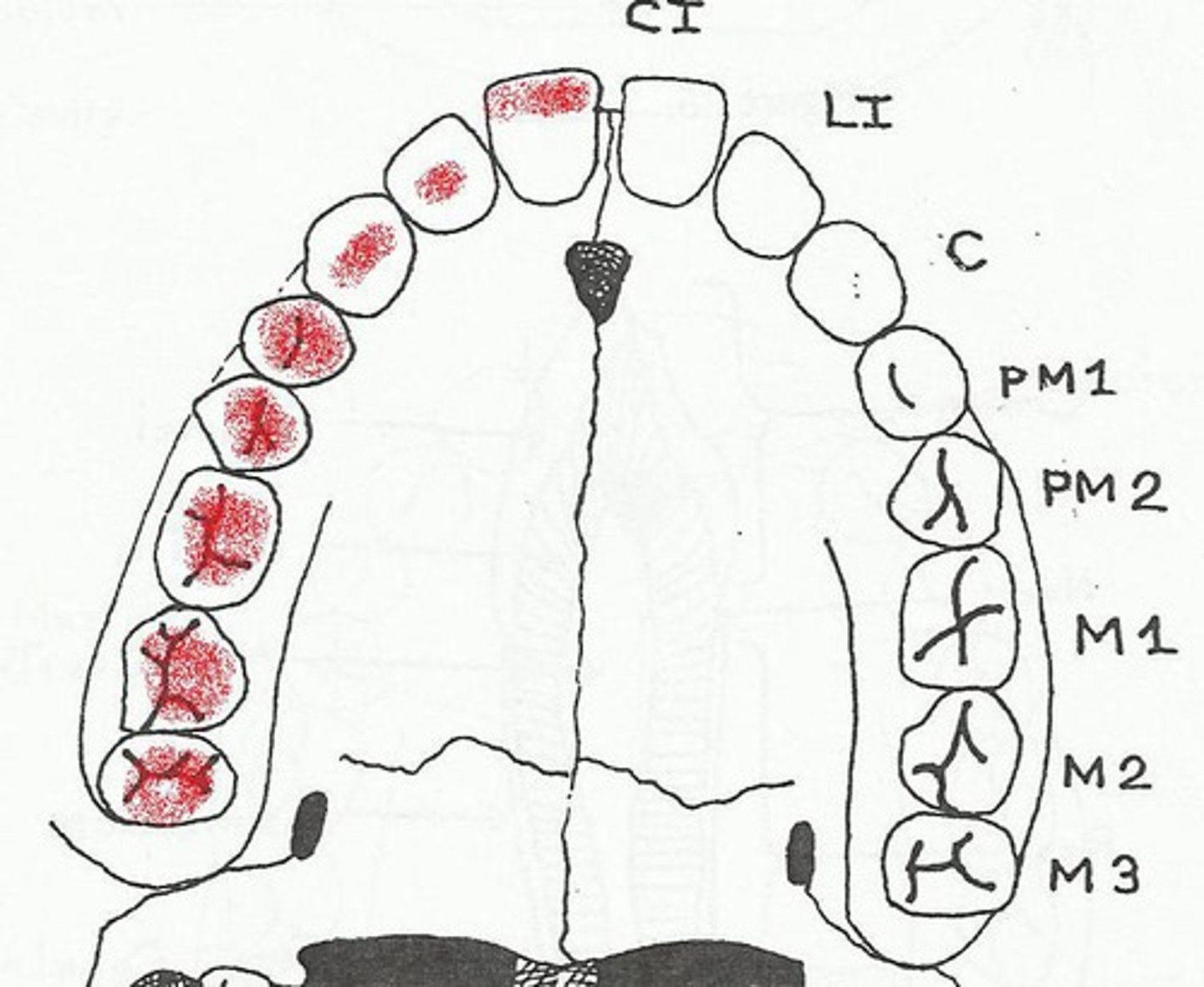
Distal (teeth position)
Surfaces of the incisor teeth that are away from the middle or median plane of the mouth (the lateral surfaces), and the caudal surfaces of the canine, premolar, and molar teeth.
Lingual
Surface of the lower teeth that is next to the tongue.
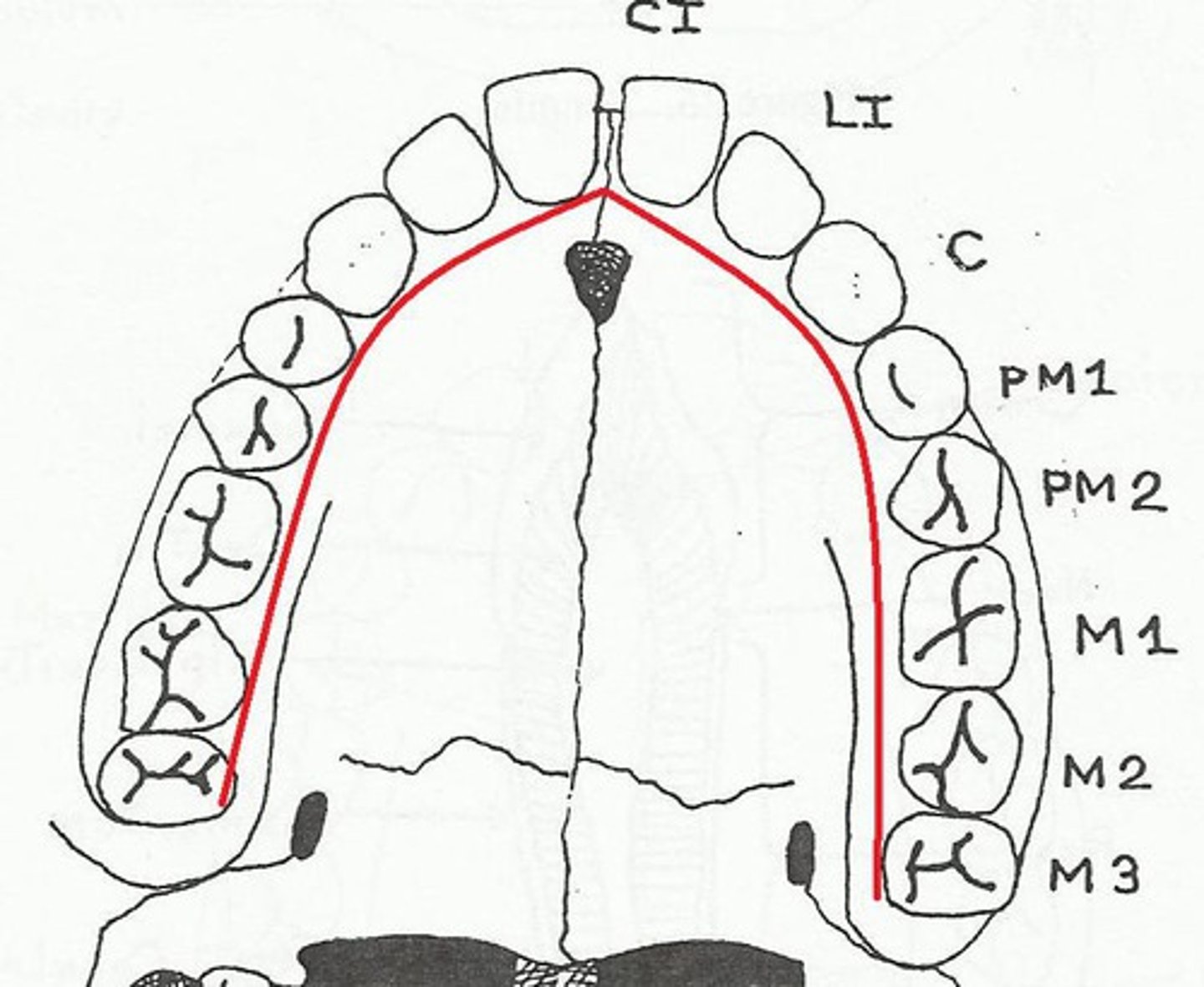
Mesial
Surfaces of the incisor teeth that are toward the middle or median plane of the mouth (the medial surfaces), and the rostral surface of the canine, premolar, and molar teeth.
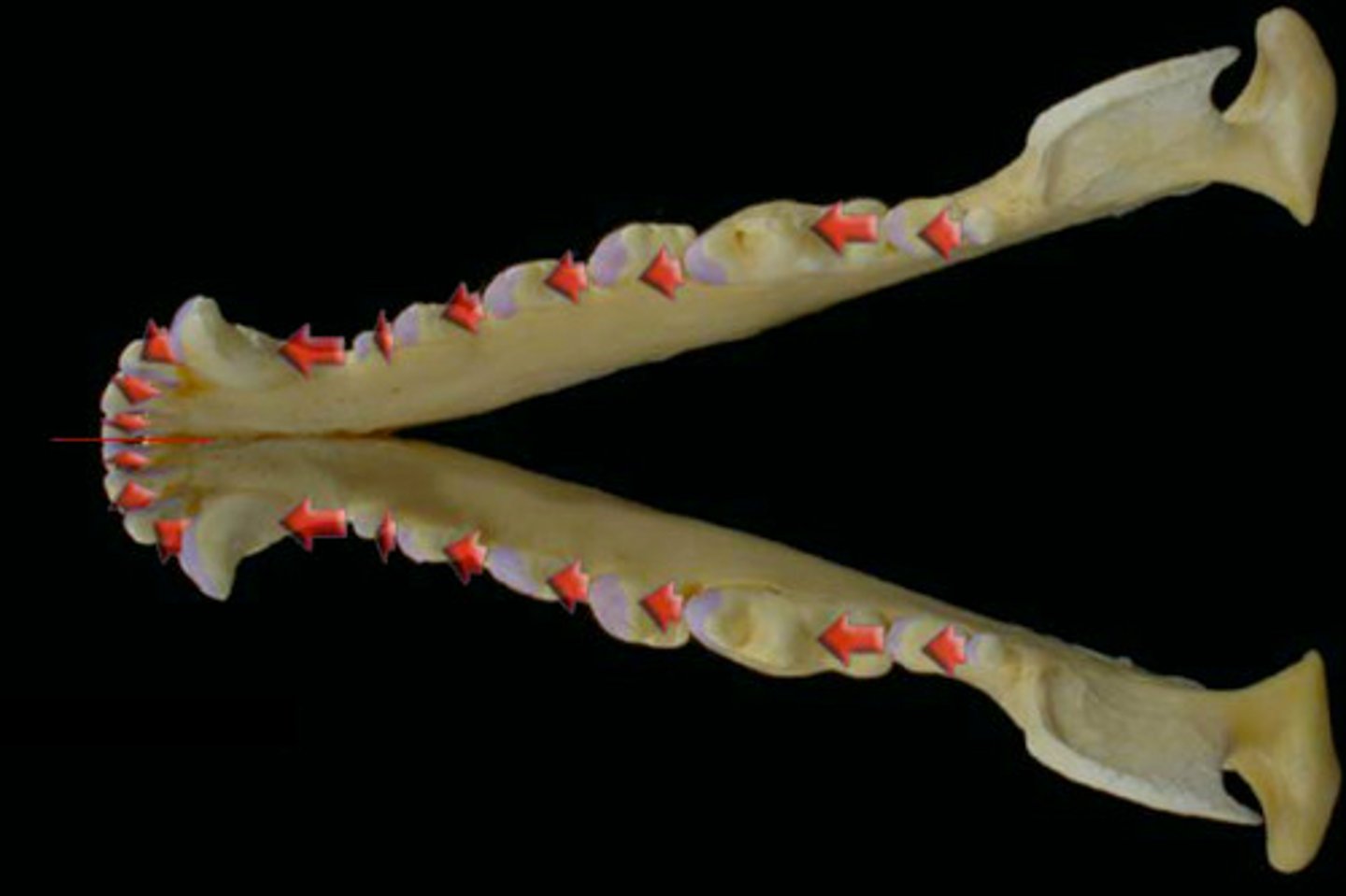
Occlusal
Surface of the tooth that makes contact with the opposing tooth. It is the chewing or biting surface.
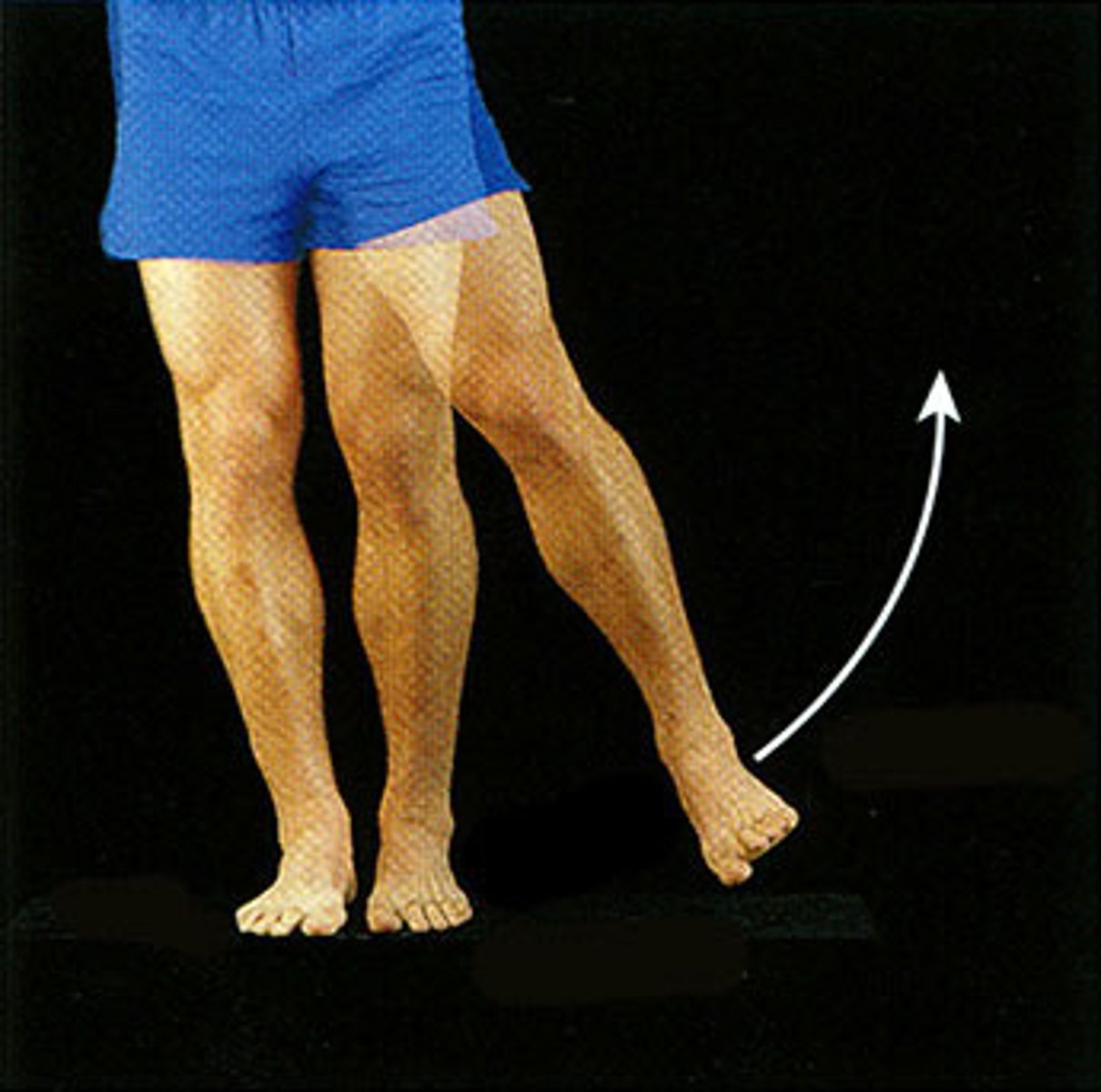
Abduction
Movement of a limb away from the median line or middle of the body.
Adduction
Movement of a limb toward the median line or middle of the body.
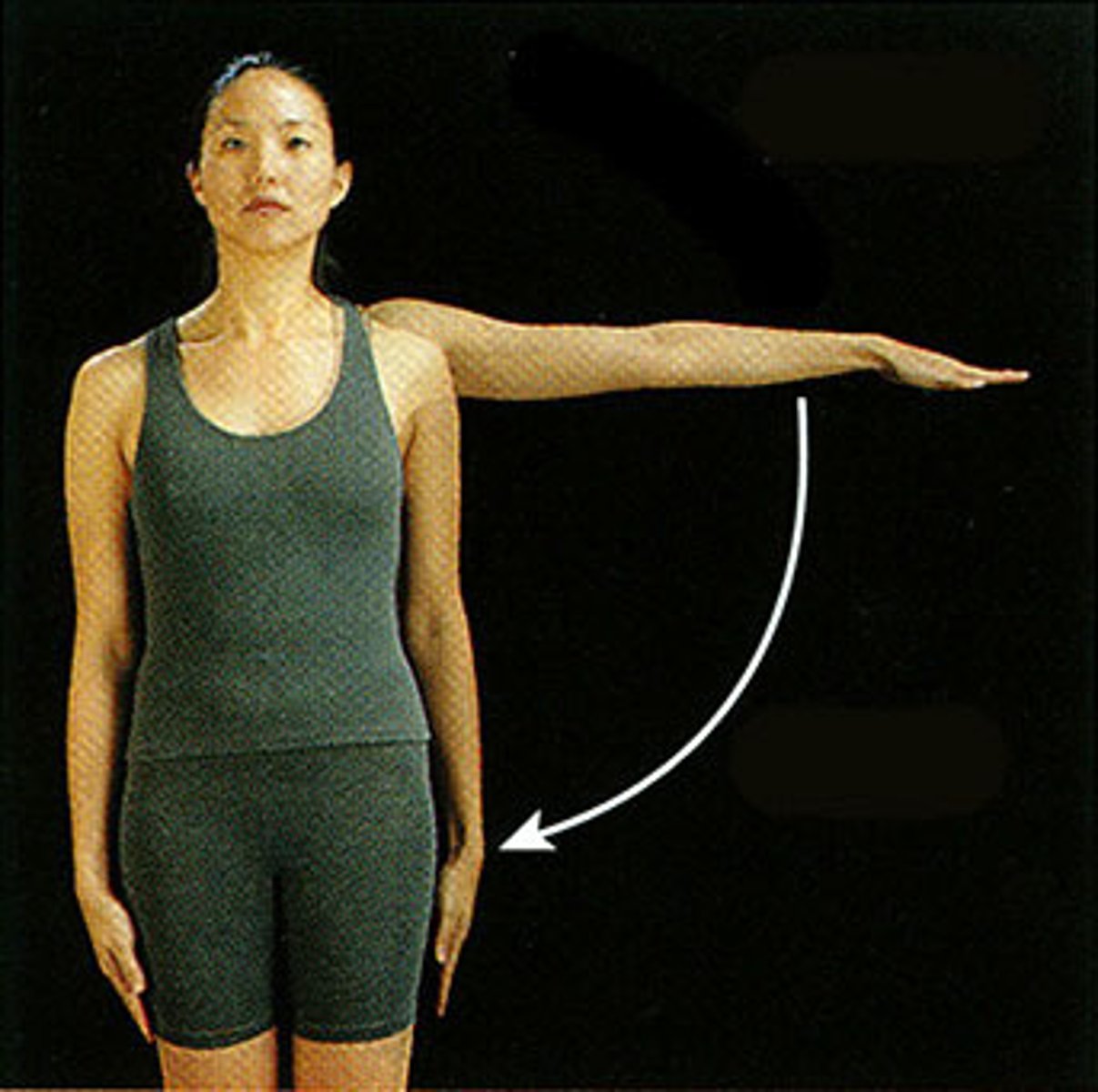

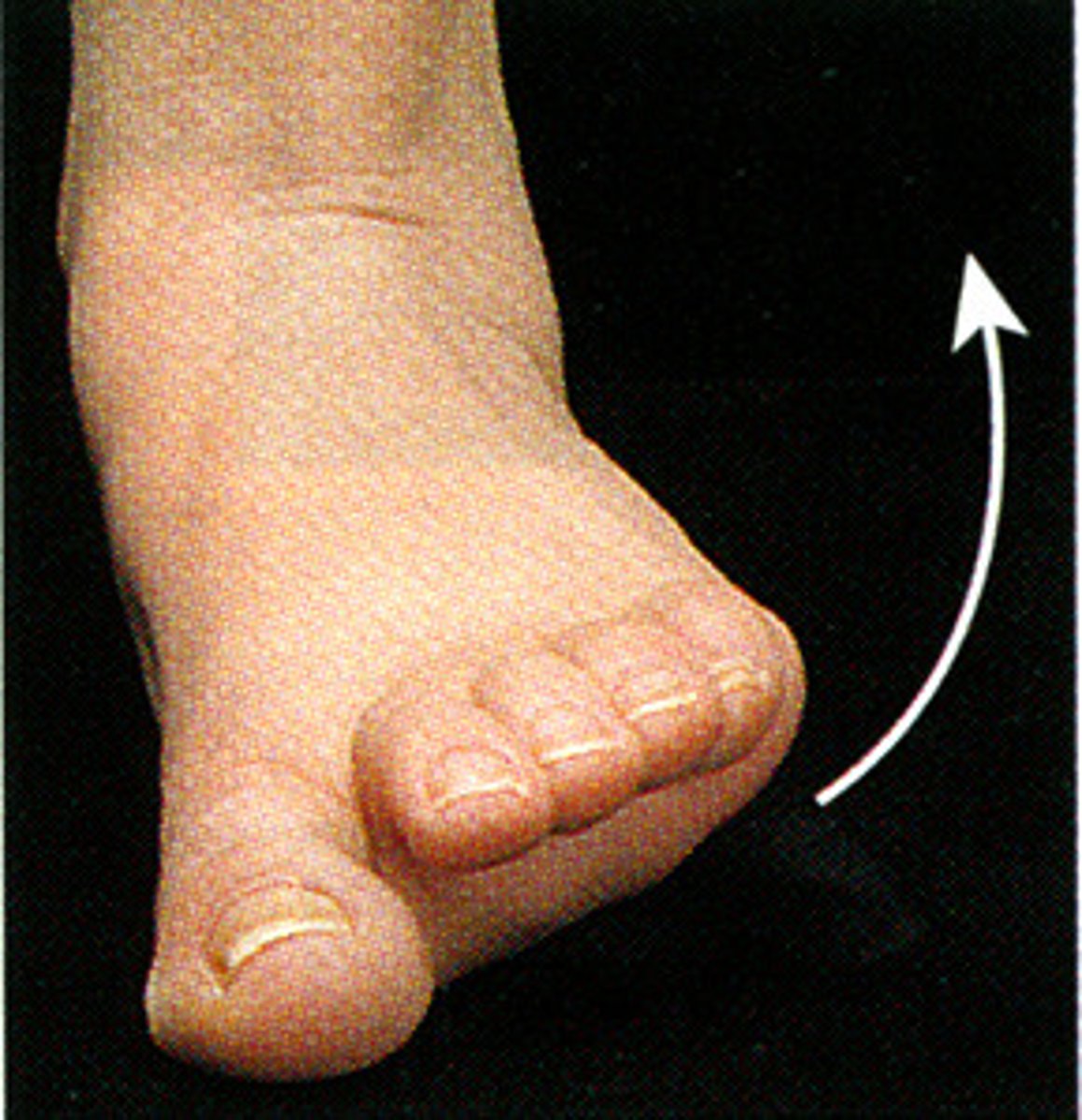
Eversion
Turning outward or inside out.
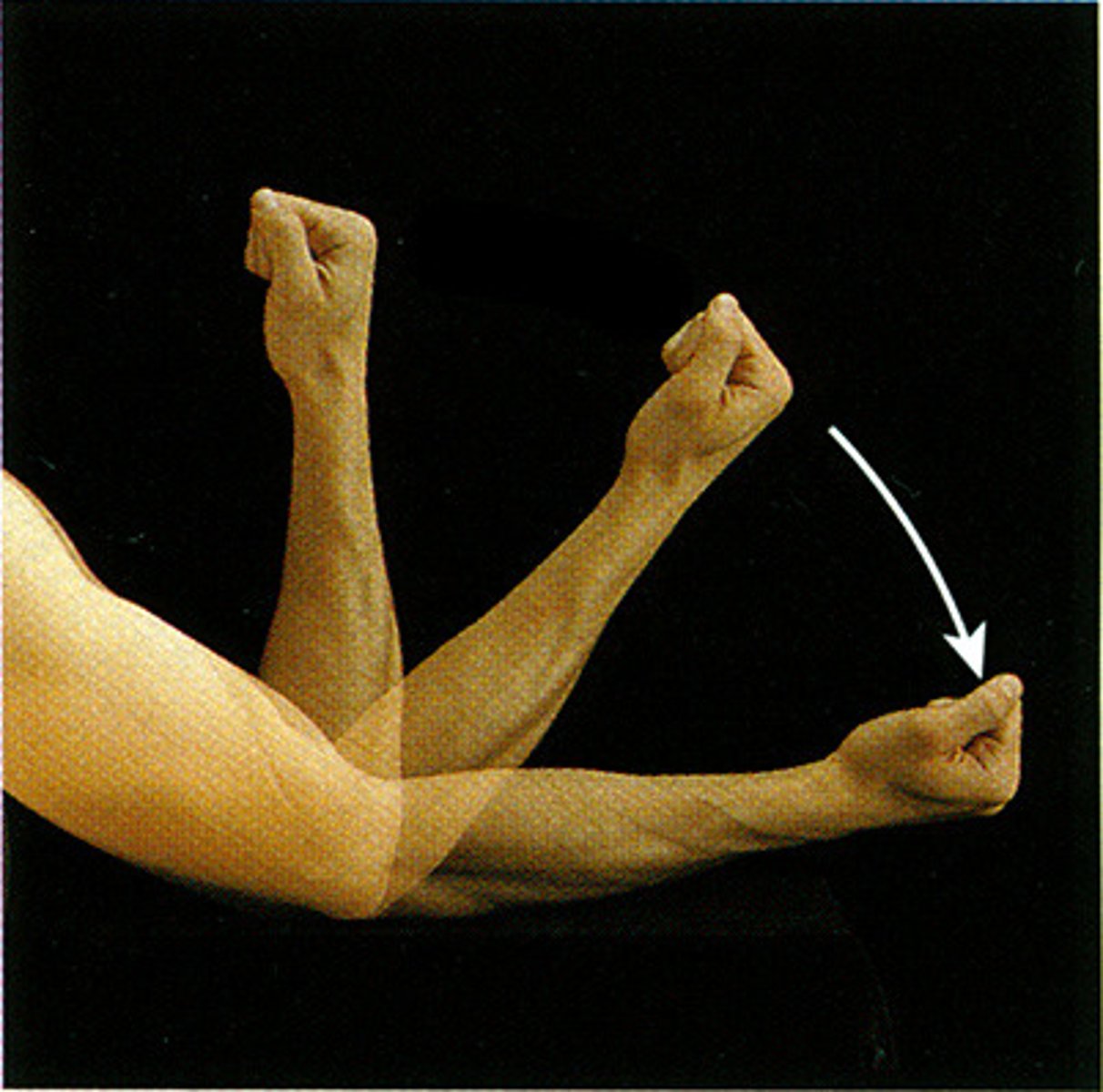
Extension
Straightening, or the act of straightening, as with a joint.
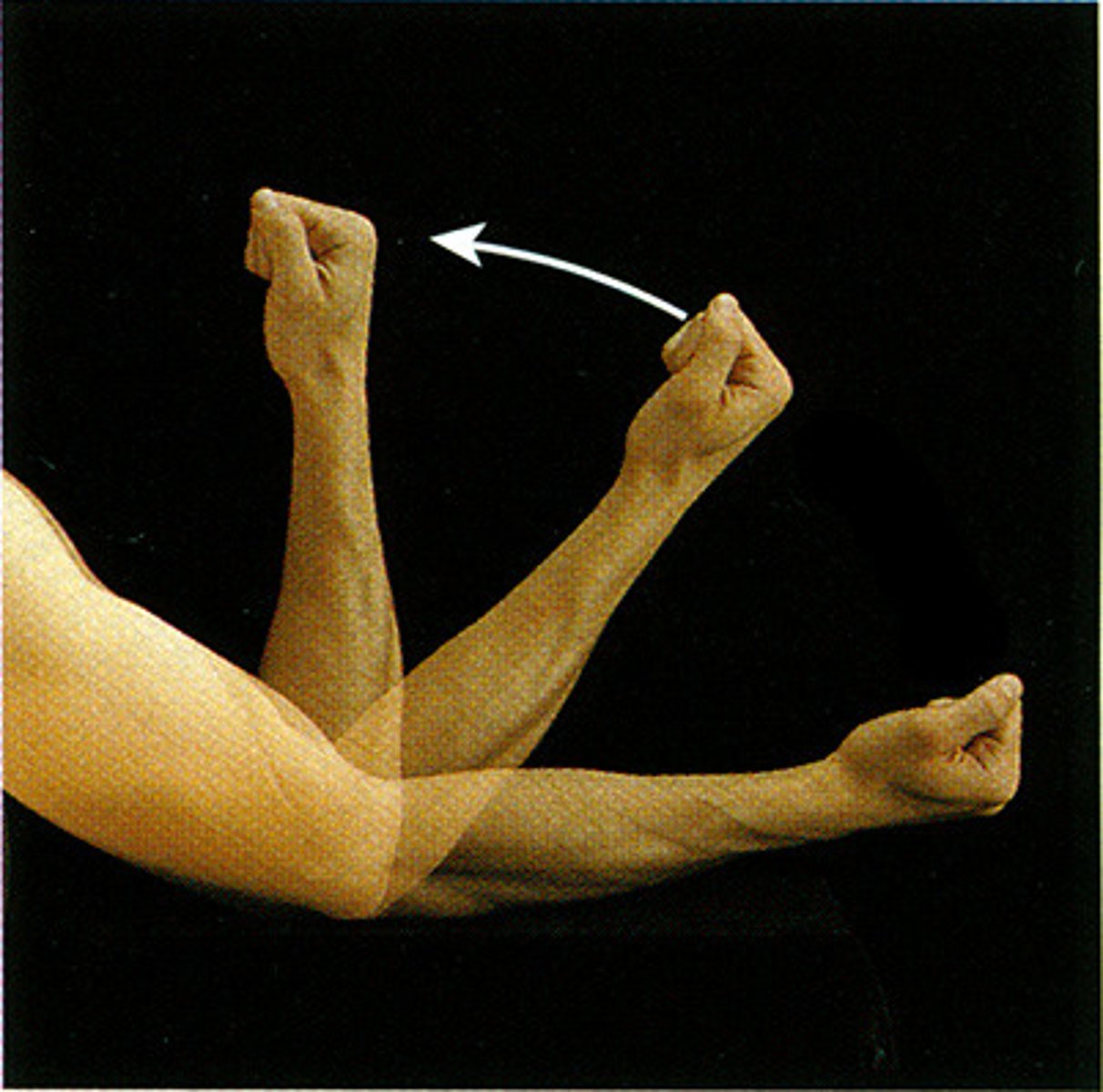
Flexion
Bending or the act of bending, as with a joint.
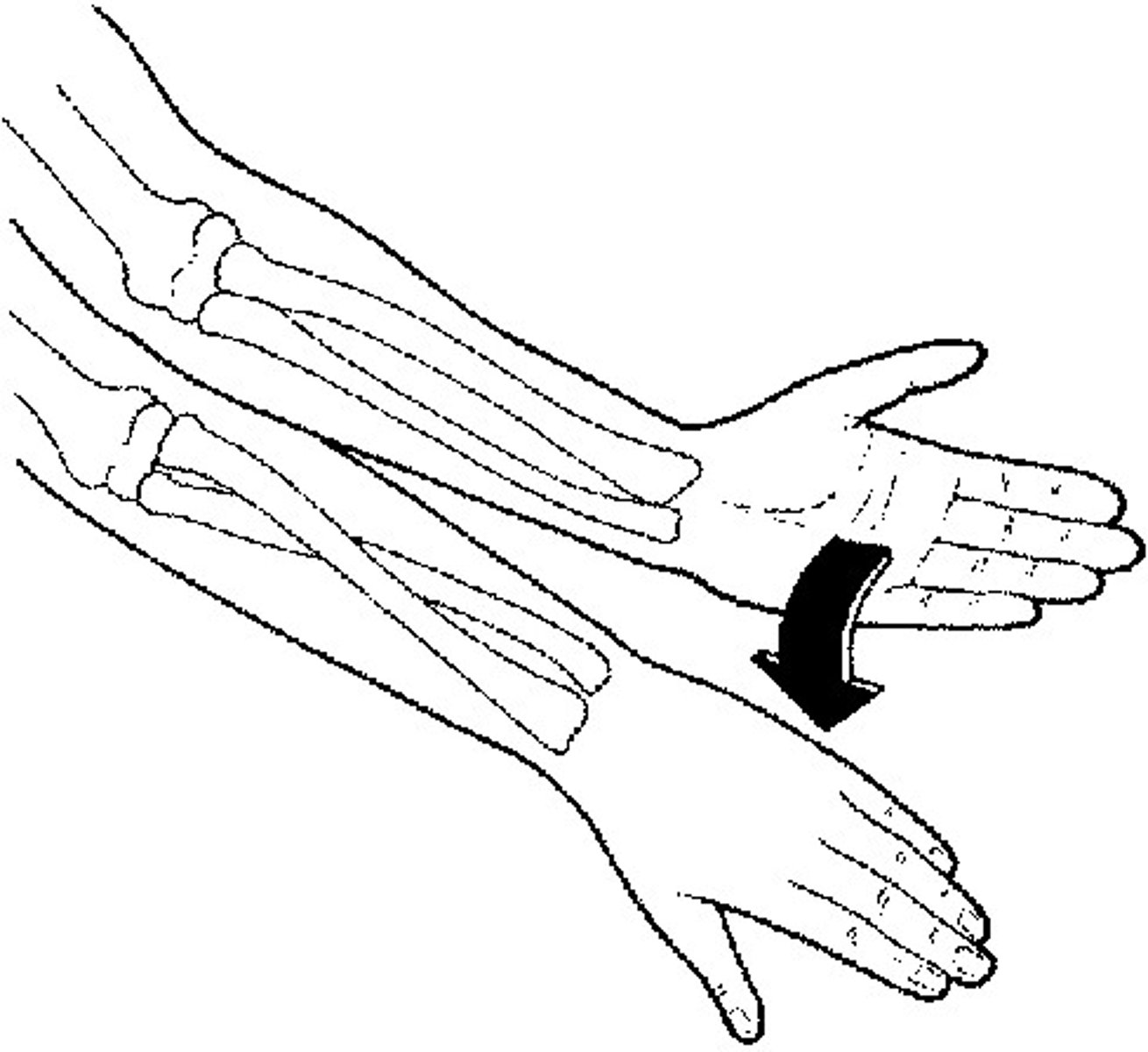
Pronation
The act of turning the body or arm (leg) so the ventral aspect of the body or the palm is down.
Rotation
turning about an axis.
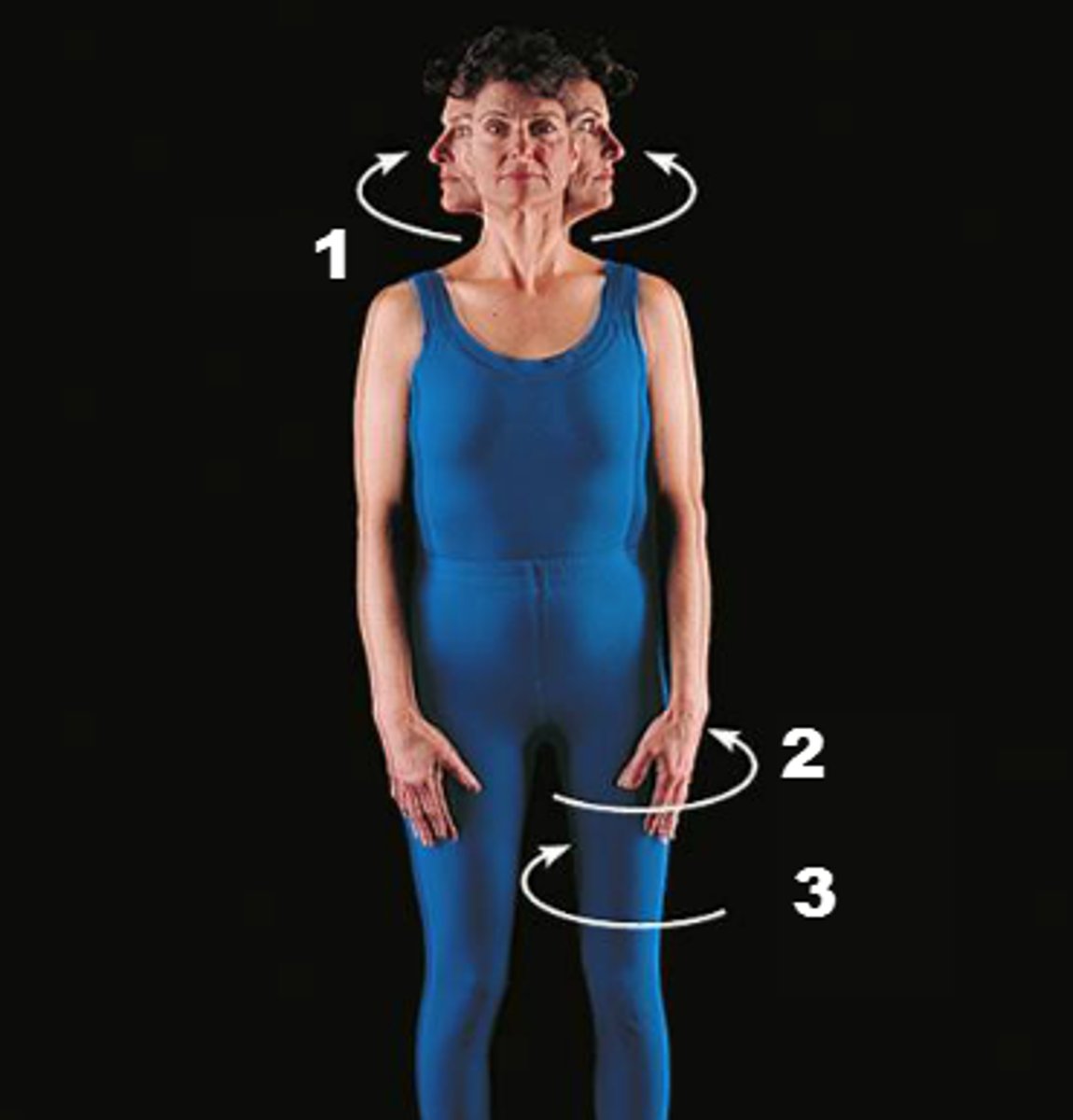
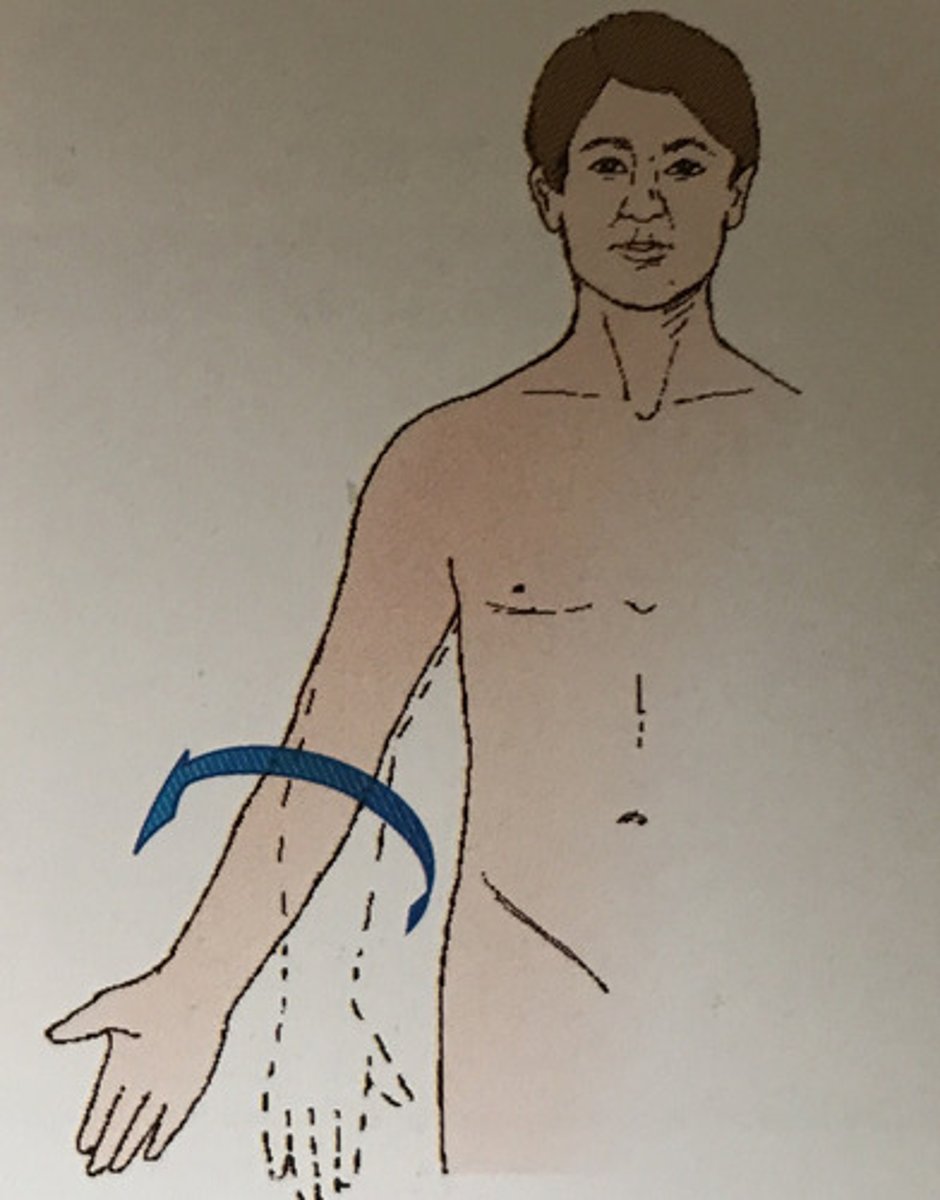
Supination
The act of turning the body or arm (leg) so the ventral aspect (palm) is up.
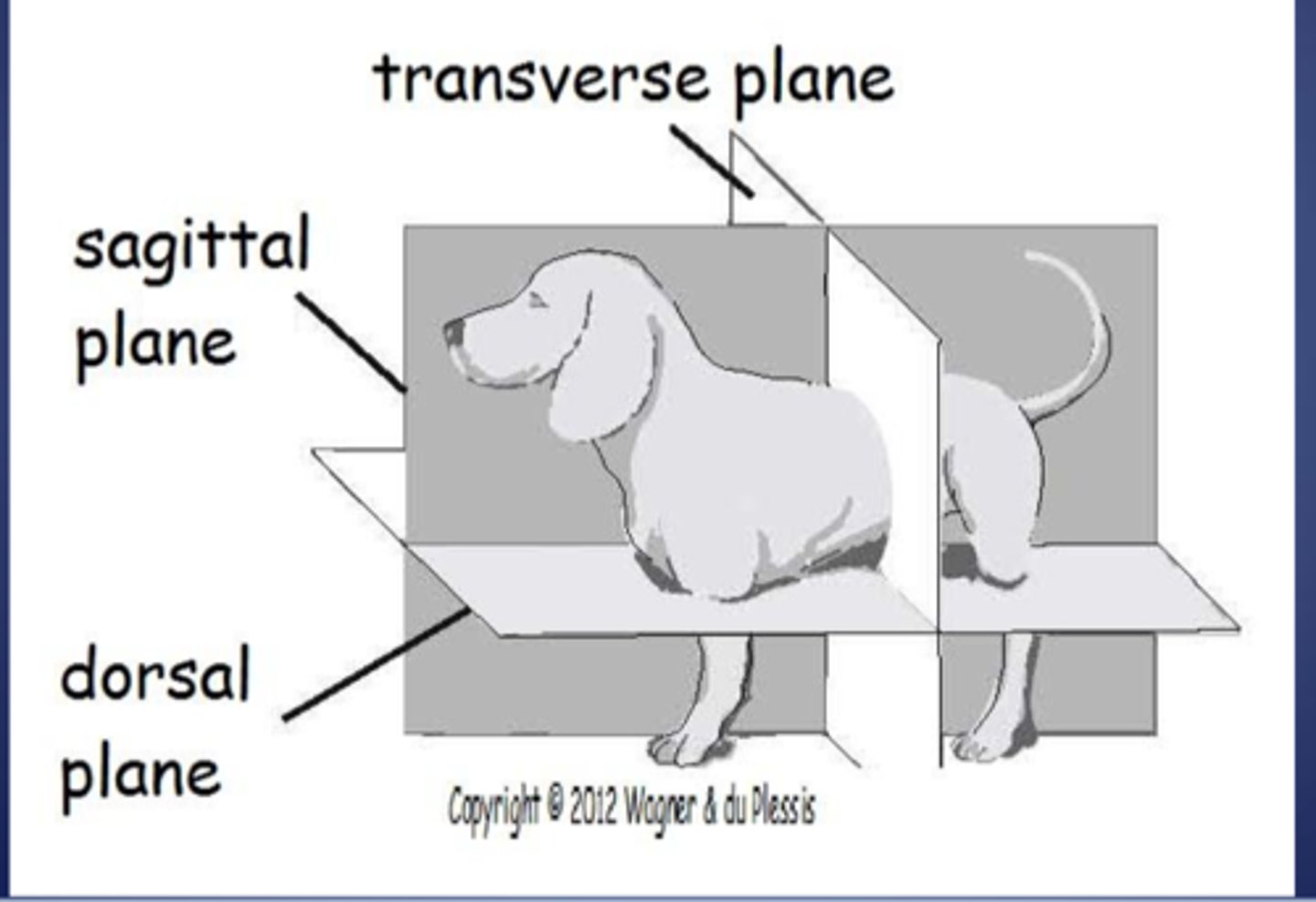
Dorsal Plane
Divides the body dorsally and ventrally, not necessarily in equal divisions.
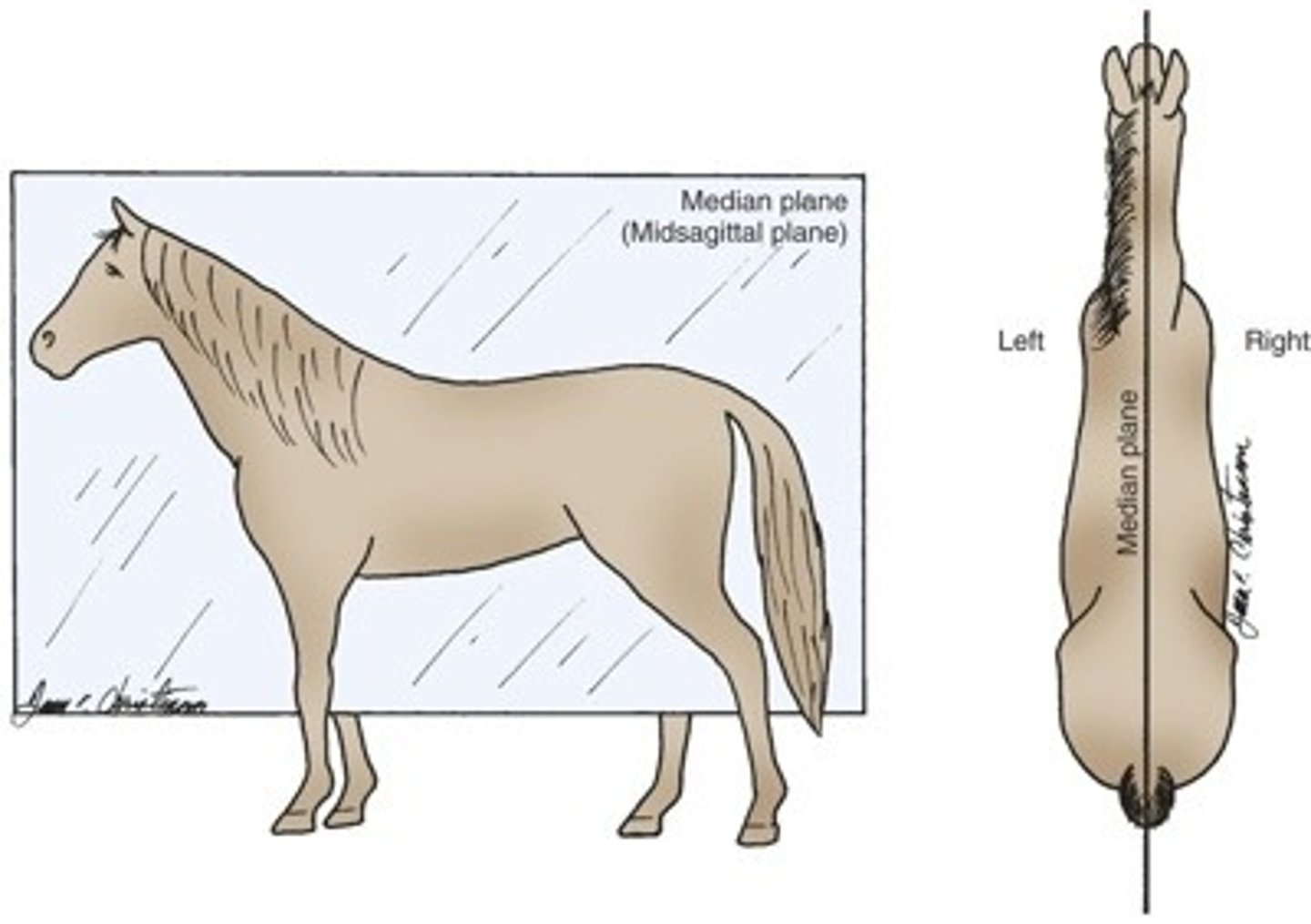
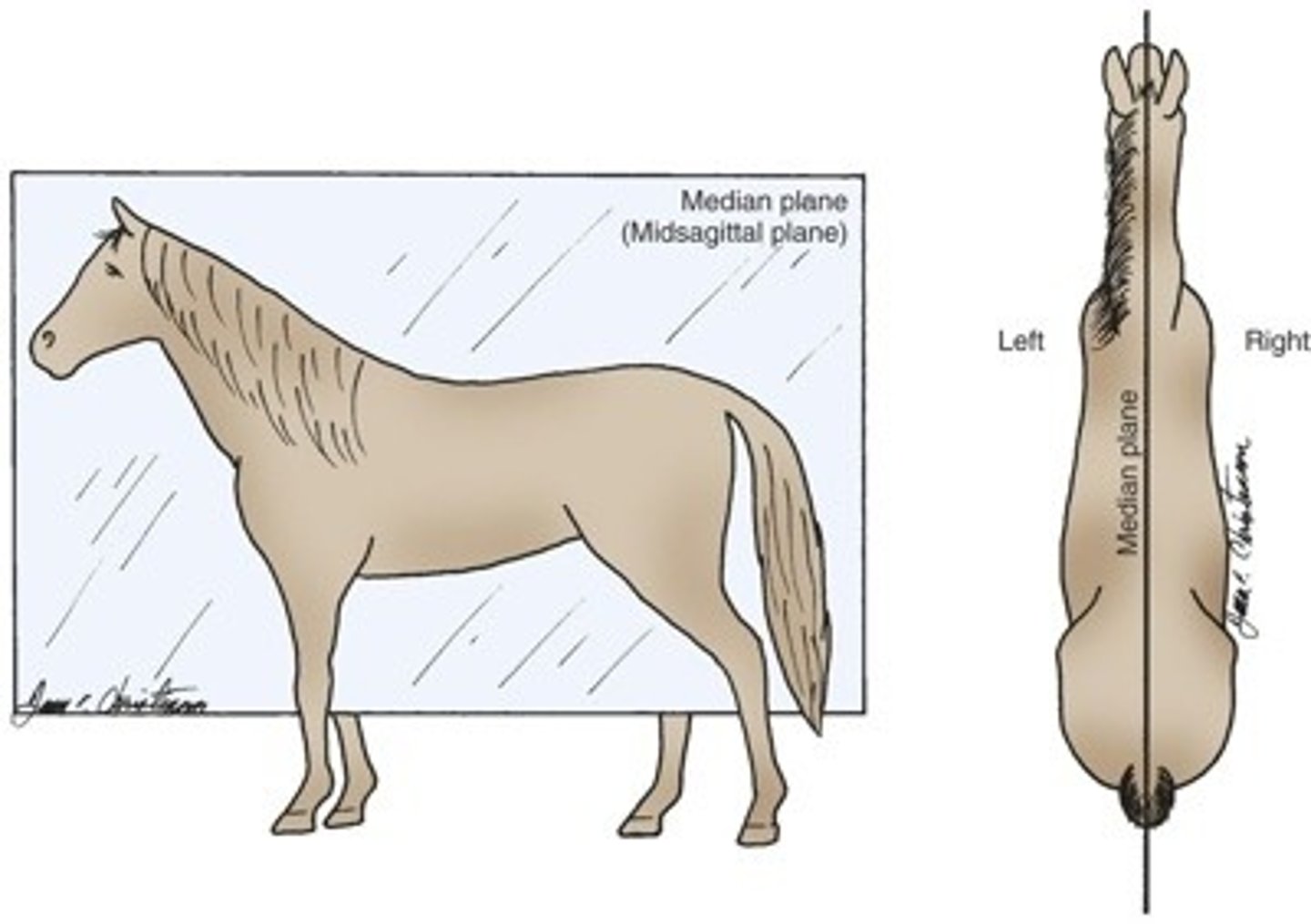
Median Plane
Divides the body into left and right halves, equally.
Paramedian Plane
Parallel to the median plane and also divides the body into left and right parts, but not equally.
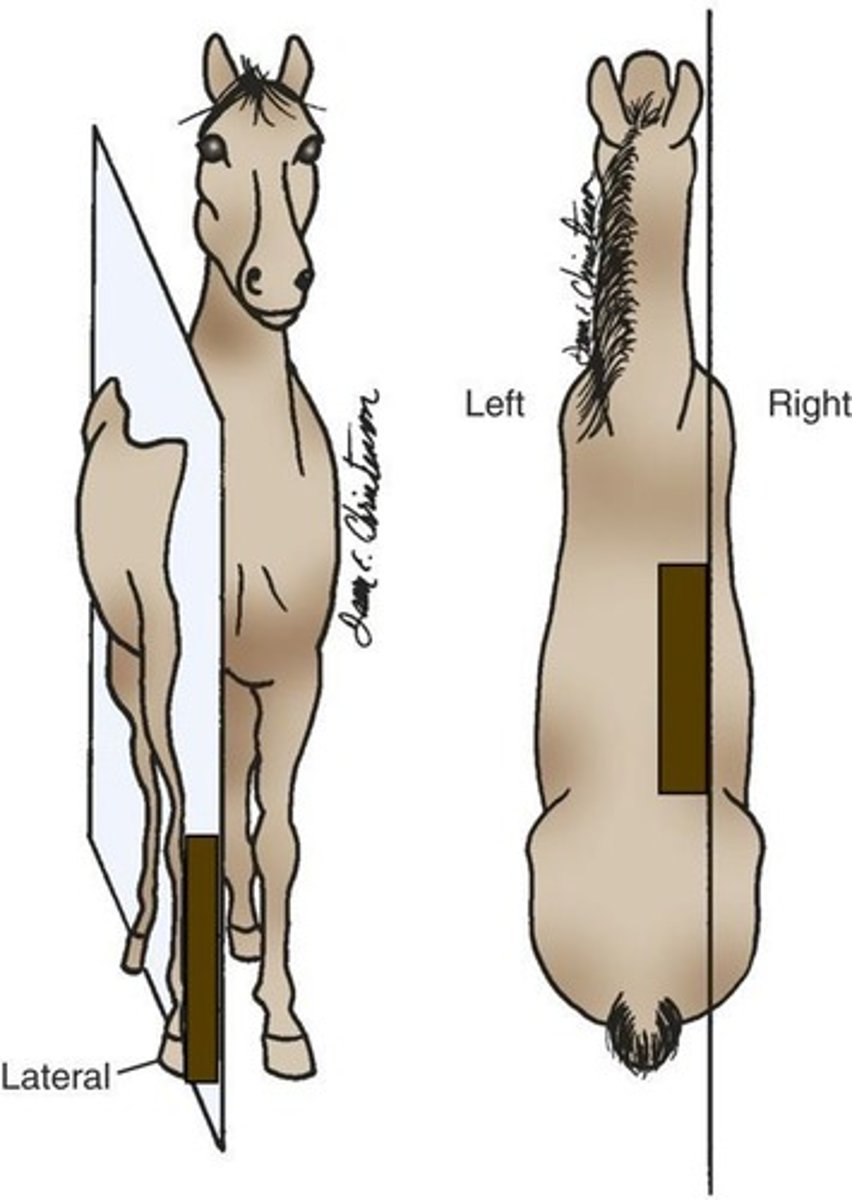
Sagittal Plane
Parallel to the median plane and also divides the body into left and right parts, but not necessarily equal.
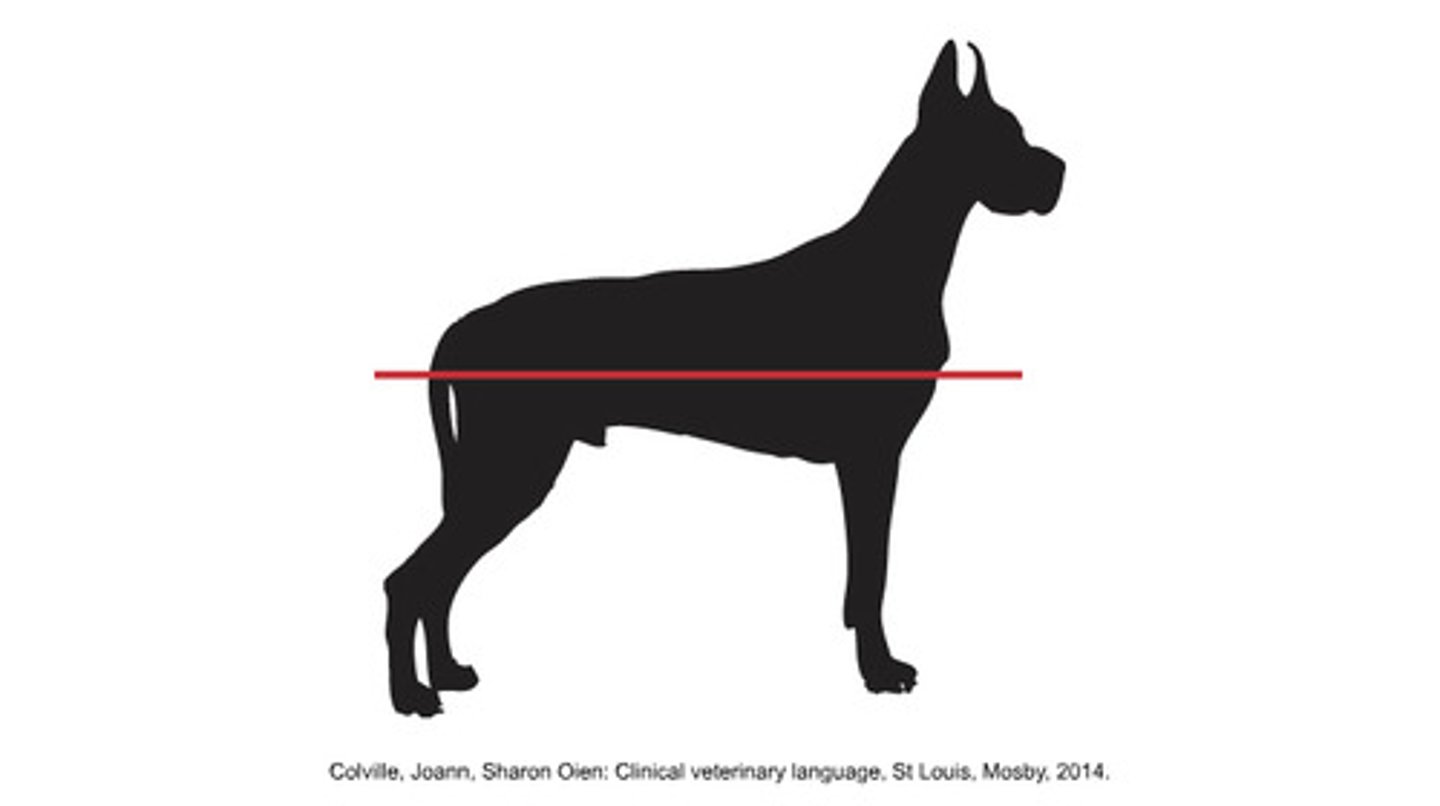
Transverse Plane
Divides the body cranially and caudally, not necessarily in equal divisions.
Microscopic Anatomy
structures too small to be seen with the naked eye
macroscopic anatomy
study of large body structures visible to the naked eye
Homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment (Ex: shiver when its cold to warm up body)

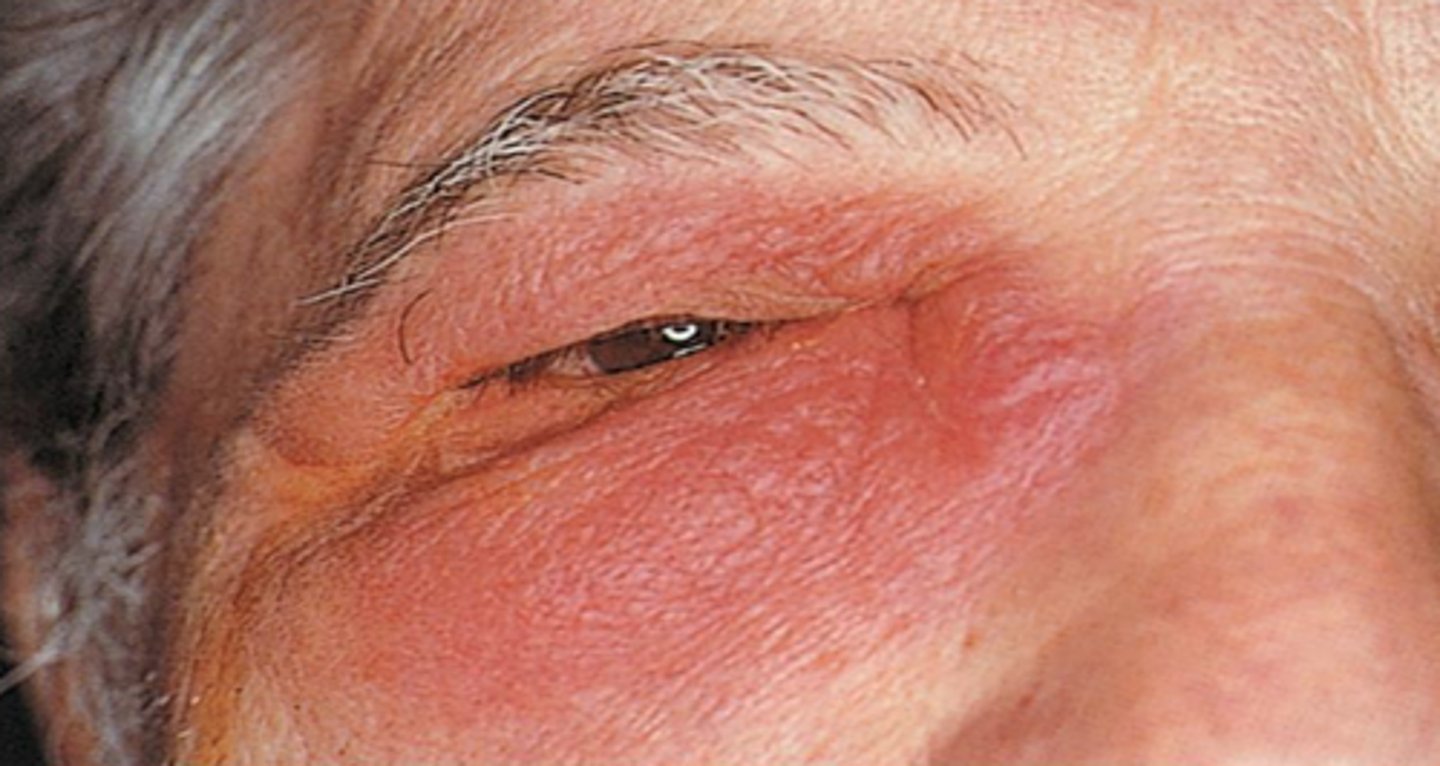
inflammation
Injured or infected area becomes red, swollen, hot, and painful.
internal
inside
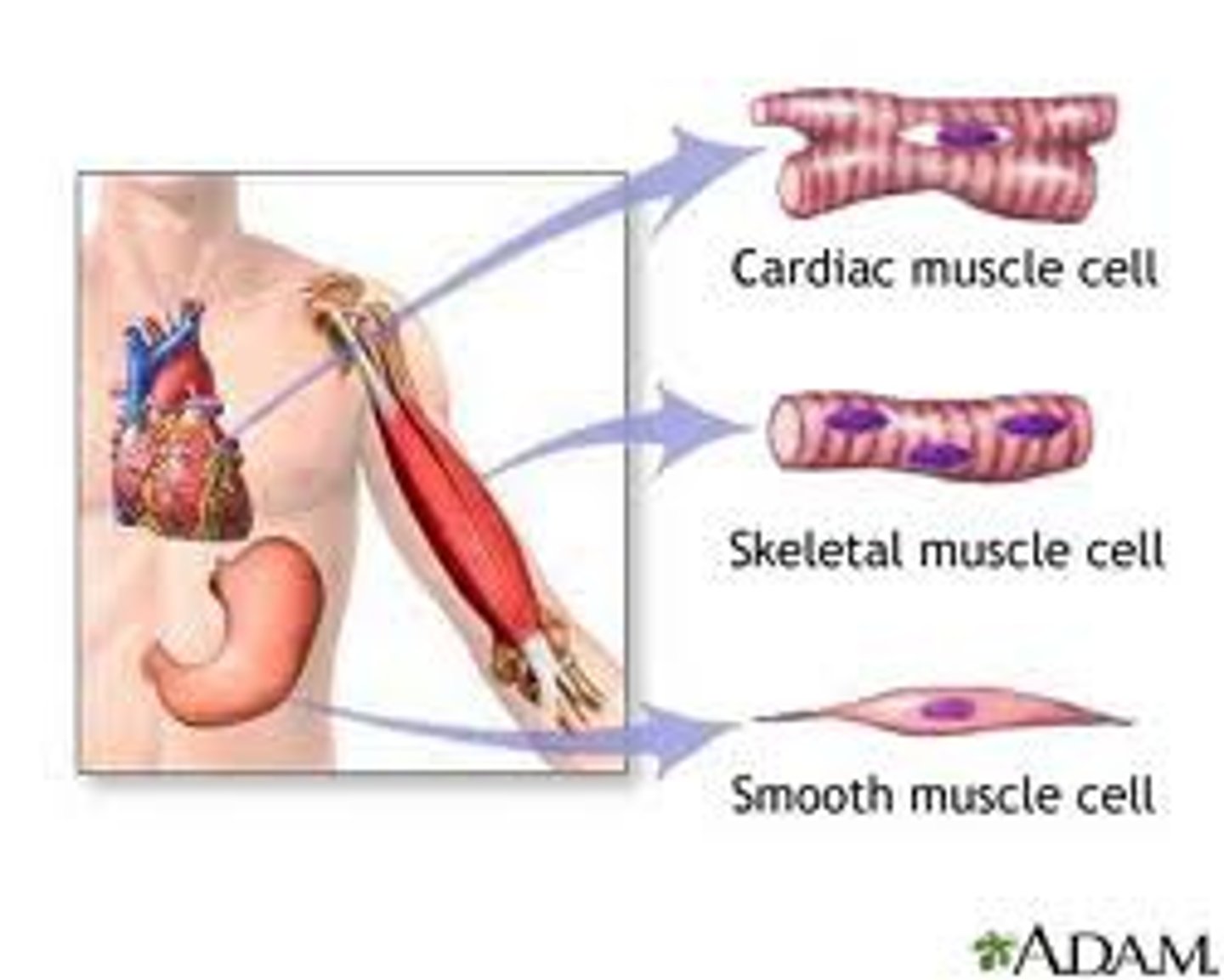
muscle tissue
A tissue that contracts or shortens, making body parts move.
nervous tissue
Tissue that senses stimuli and transmits signals.
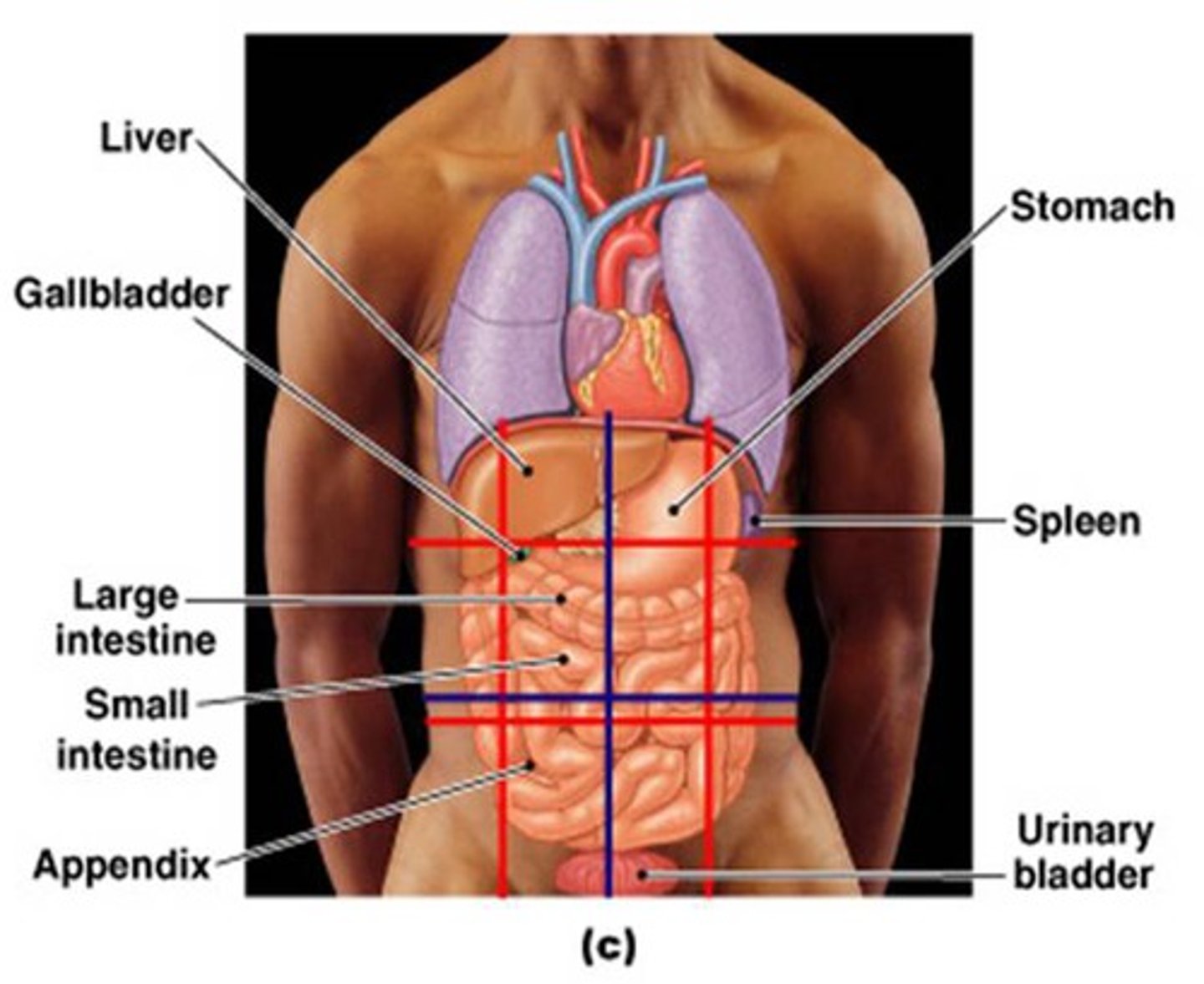
Organs
Tissues that work together to perform a specific function
Parietal
pertaining to the wall of a cavity, covered in a membrane
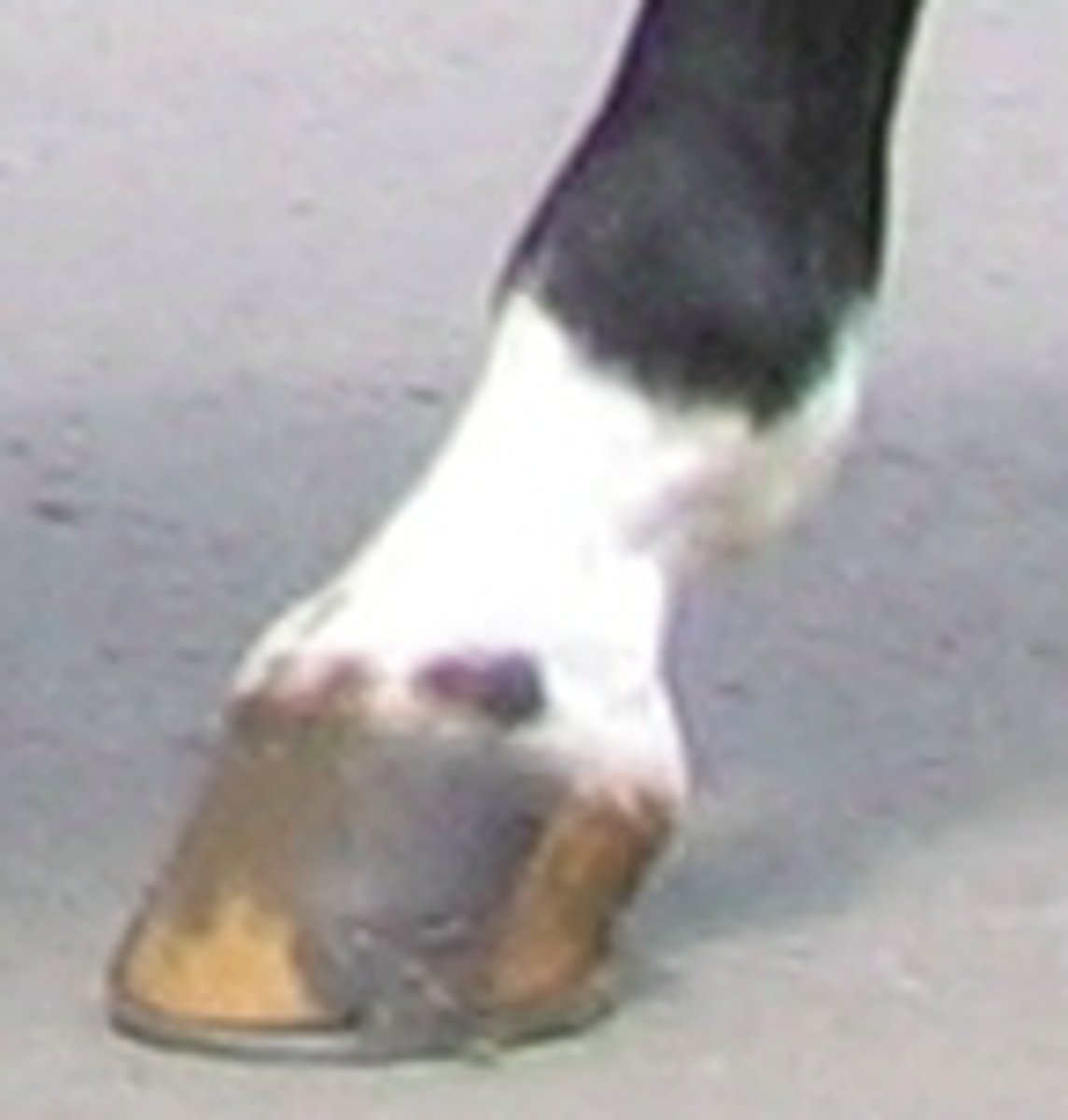
Pastern
area of the limb between the fetlock and hoof

Physiology
How the body functions

pleura
double-layered membrane surrounding each lung
poll
nuchal crest (top of head)

Posterior
toward the back
rostral
toward the nose or mouth
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
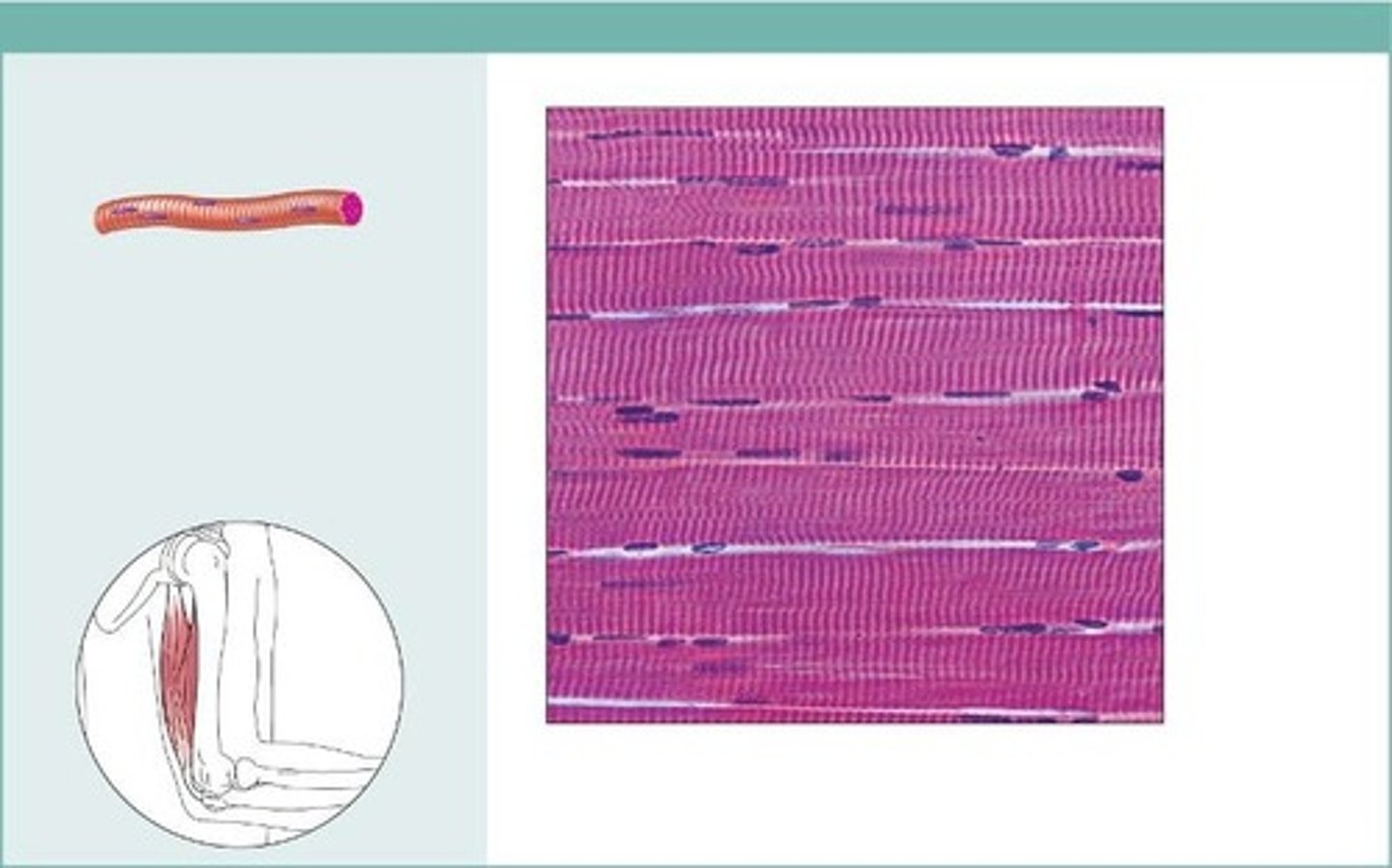
skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the ske leandprovides the force that moves the bones.
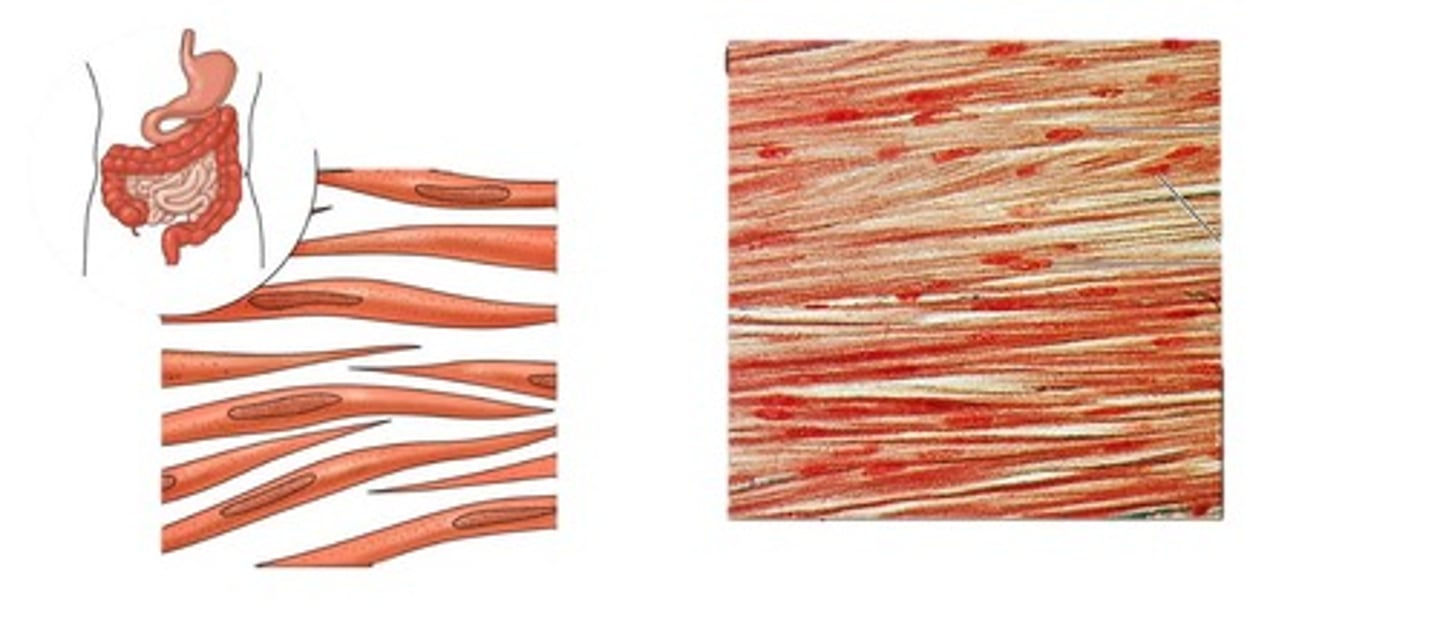
smooth muscle
involuntary muscle found in internal organs
spinal canal
the canal formed by the vertebrae that protects the spinal cord
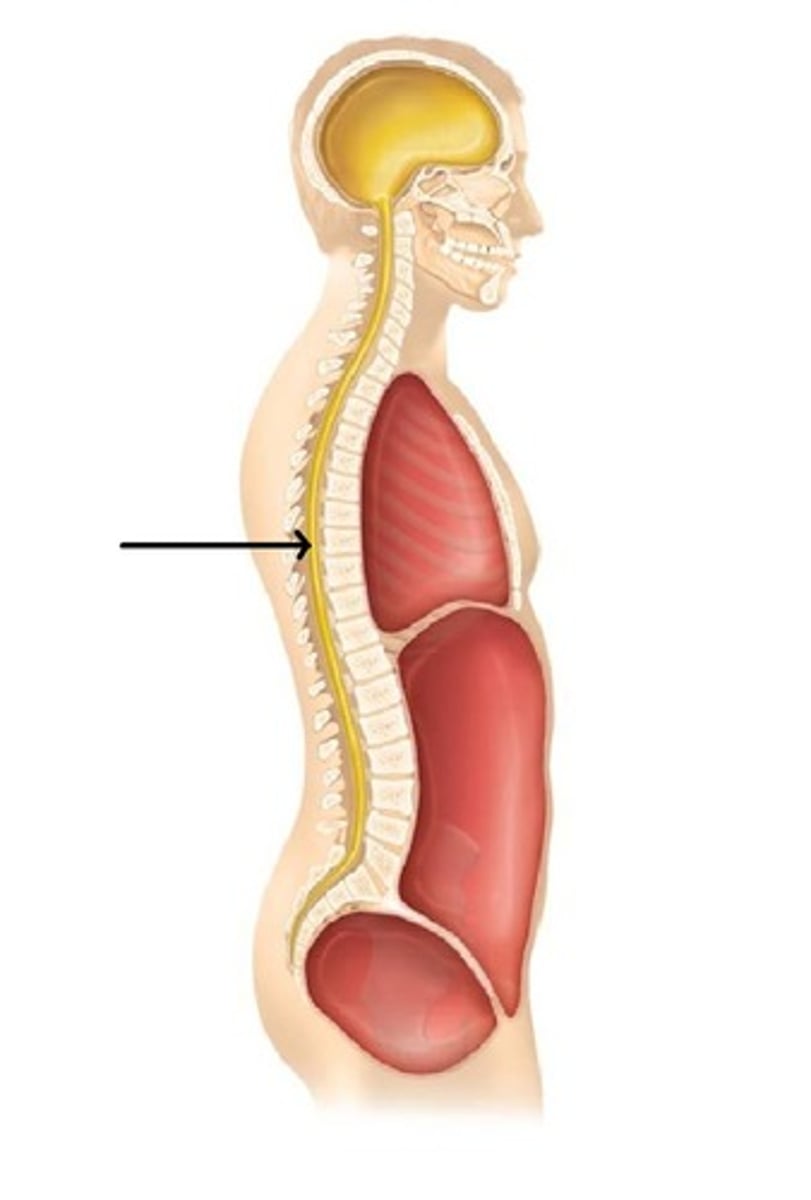
stifle
knee
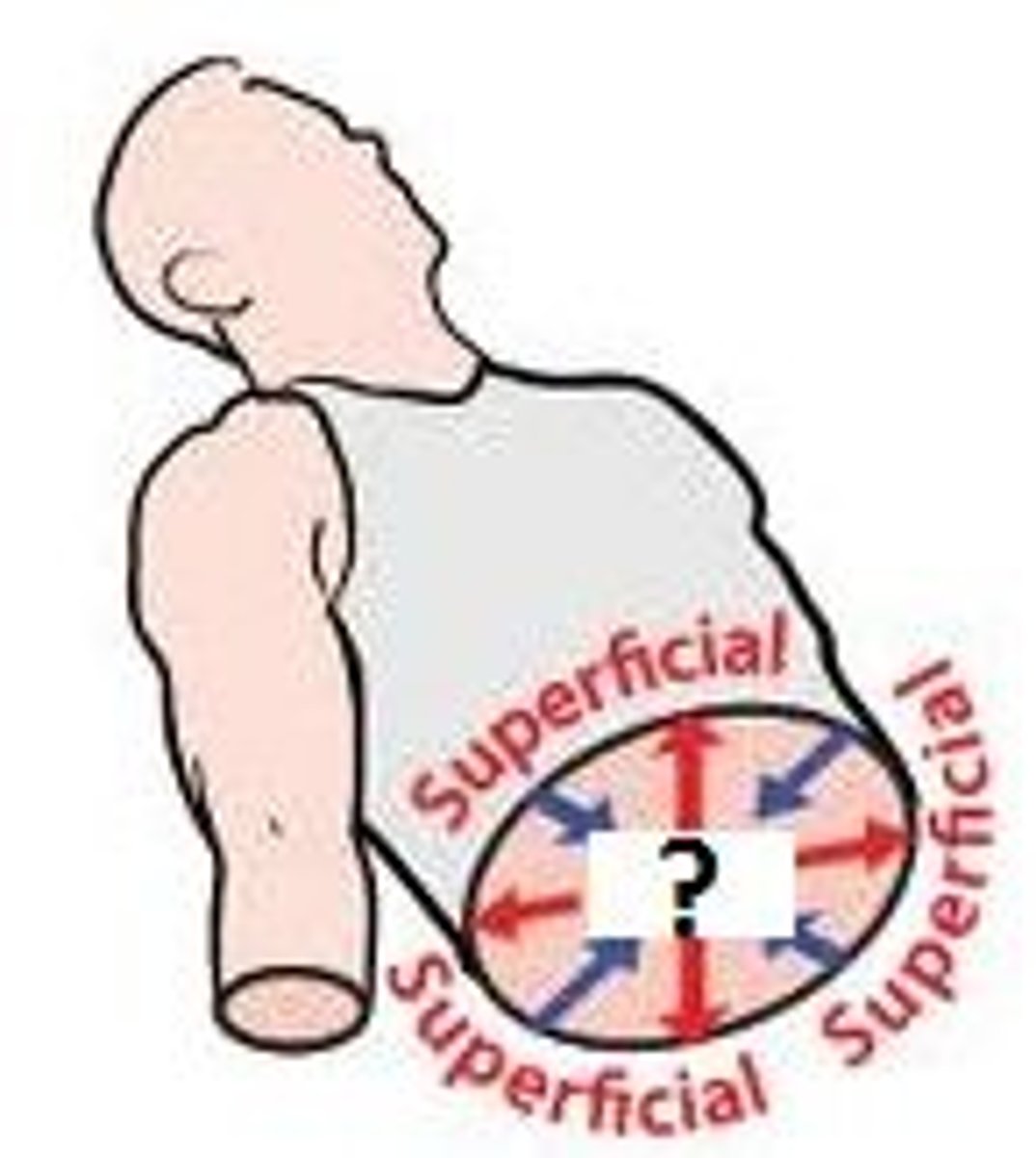
superficial
near the surface (red)
Tailhead
base of tail