A&P 1 Final Exam Flash Cards
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Autonomic Nervous system
Function: Involuntary nervous system, Transmits signals from CNS to: Cardiac Muscles, smooth muscles, glands, Homeostatic Maintenance
Sympathetic Nervous system
Function: responsible for "fight-or-flight"
Location: thoracolumbar region of spinal cord,
Preganglionic neurons found from T1-L2 or L3
Effectors: smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands, adipose tissue, Liver, blood vessels, pupils, hair follicles
parasympathetic nervous system
Function: rest and digestion
location: Craniosacral division (cranial nerves: oculomotor, facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus. Sacral: spinal nerves S2-S4
Effectors: eyes, salivary glands, heart, lungs, digestive system, bladder, reproductive organs
Preganglionic Sympathetic Fiber
transmit impulses from the spinal cord to the sympathetic ganglia. relatively short and myelinated and are close to the vertebral column
Preganglionic Parasympathetic Fibers
Long fibers, extend from CNS almost to target organs. Brainstem and Sacral region of the spinal cord. Preganglionic fibers have few branches
sympathetic ganglia and chains
Location: paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia. runs down the spine and contains ganglia connected by the nerve fibers
Parasympathetic ganglia and chains
Location: closer to the target organ they innervate
postganglionic fibers
sympathetic: long
parasympathetic: short
Acetylcholine
Released by Cholinergic fibers. released by all ANS preganglionic axons, all PSNS postganglionic axon at effector synapse, and SNS postganglionic axons at sweat glands
Norepinephrine
Adrenergic fibers, released on most SNS postganglionic axons (exception: SNS postganglionic axons secrete ACh at sweat glands)
Adrenergic fibers
nerve fibers that secrete norepinephrine.
receptors: Alpha and Beta
cholinergic fibers
fibers that release ACh
receptors: Nicotinic receptors and Muscarinic receptors
Autonomic Tone
the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity
Vasomotor tone
a moderate state of vasoconstriction in a blood vessel that sets the resting level of systemic vascular resistance
Parasympathetic tone
slows the heart, dictates normal activity levels of the digestive and urinary systems
Cooperative effects
two divisions act on different effectors to produce a unified overall effect
Antagonist effects
one hormone opposes the action of another
Hypertension
abnormally high blood pressure
Raynaud's disease
exaggerated vasoconstriction in fingers and toes
autonomic dyreflexia
uncontrolled activation of ANS neurons in quadriplegics and those with a spinal injury, blood pressure skyrockets
Endocrine system
Consists of glands that control many of the body's activities by producing hormones.
Calcium Hormone Homeostasis (Parathyroid Hormone)
Hormone that regulates calcium levels in the blood and is a key component of calcium homeostasis. Increases reabsorption in the kidneys and blocks phosphate reabsorption from the tubules
Antidieuretic Hormone (ADH)
Increases water reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to concentrated urine and increased blood volume.
Aldosterone
Promotes sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidneys, influencing blood volume and blood pressure
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide)
hormone produced by the heart that helps regulate blood pressure and is important to the body's response to heart failure
lipid soluable hormones
-steroid and thyroid hormones
-act on intracellular receptors that directly activate genes
-can enter cell
water soluble hormones
(all amino acid-based hormones except thyroid hormone)
Act on plasma membrane receptors
Act via G protein second messengers
Cannot enter cell
Hyposecretion diseases
Hypothyroidism- slowed metabolism, weight gain, depression, cold intolerance, dry skin
Addison's disease- weakness, fatigue, weight loss, low blood pressure, darkening of the skin, salt craving (adrenal hormone)
Diabetes Mellitus- high blood sugar, frequent urination, excessive thirst, weight loss, decreases TH production (insulin hormone)
Hypopituitarism- growth retardation in children, reduced sex hormone production, and decreased TH production (pituitary hormone)
Diabetes Insipidus- excessive thirst and urination due to inability to concentrate urine
pituitary dwarfism- short stature, low blood sugar
Kallmann syndrome- testicular atrophy, anosmia (hypogonadism in males)
Hypersecretions diseases
Hyperthyroidism- increased metabolic rate, weight loss, anxiety, palpitations, and heat intolerance (Thyroid hormone). Grave's disease, an autoimmune disorder is most common cause
Cushing's syndrome- weight gain, buffalo hump, moon face, high blood pressure, and increased susceptibility to infections (cortisol excess)
Acromegaly- enlargement of hands, feet, and facial features, along with other growth abnormalities (growth hormone)
Hyperparathyroidism- high calcium levels in blood, leading to bone loss, kidney stones, and muscle weakness (parathyroid hormone)
Hyperaldosteronism- high blood pressure, low potassium levels, muscle weakness (aldosterone excess)
SIADH- syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion, retention of fluid, headache, disorientation
Pituitary gigantism- before puberty, excessive growth, increased blood sugar, and enormous internal organs
Hyperprolactinemia- females: amenorrhea, galactorrhea, anovulation, hirsutism, osteopenia. males: hypogonadism, erectile dysfunction, impaired libido, oligospermia, diminished ejaculate, testicular atrophy
Oxytocin
A hormone released by the posterior pituitary that stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and milk ejection during breastfeeding.
Up-regulation
Increase number of receptors, increases sensitivity to hormone, sometimes occurs when blood hormone levels are LOW
Down-regulation
decreased number of receptors, decreased hormone sensitivity, sometimes occurs when blood levels of hormone are HIGH
Humoral stimuli
changing blood levels of ions and nutrients directly stimulate secretion of hormones
Neural stimuli
nerve fibers stimulate hormone release
Hormonal stimuli
Hormones stimulate other endocrine organs to release their hormones
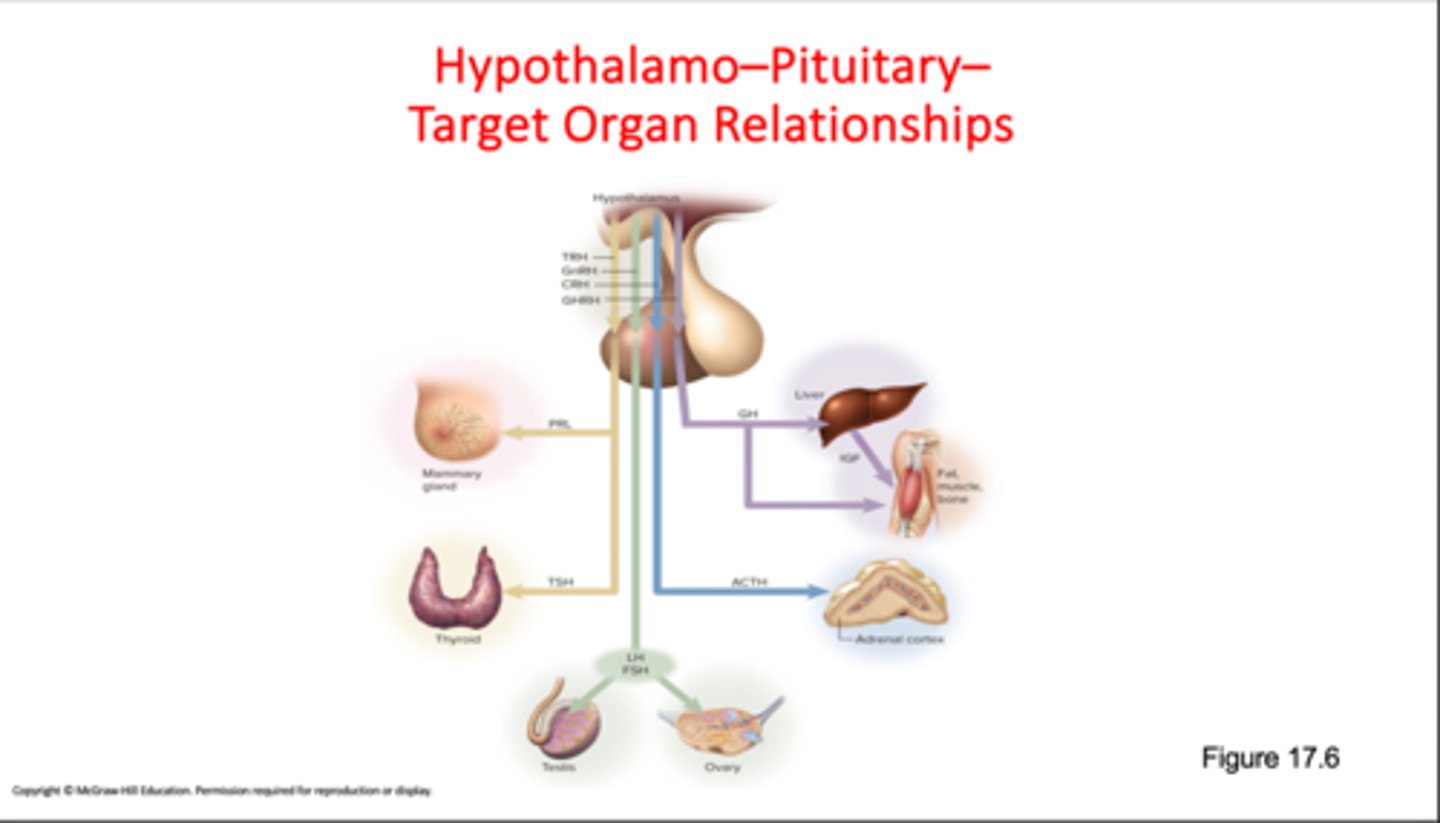
Hypophyseal portal system
blood travels from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary. Drain primary plexus and transport to secondary plexus
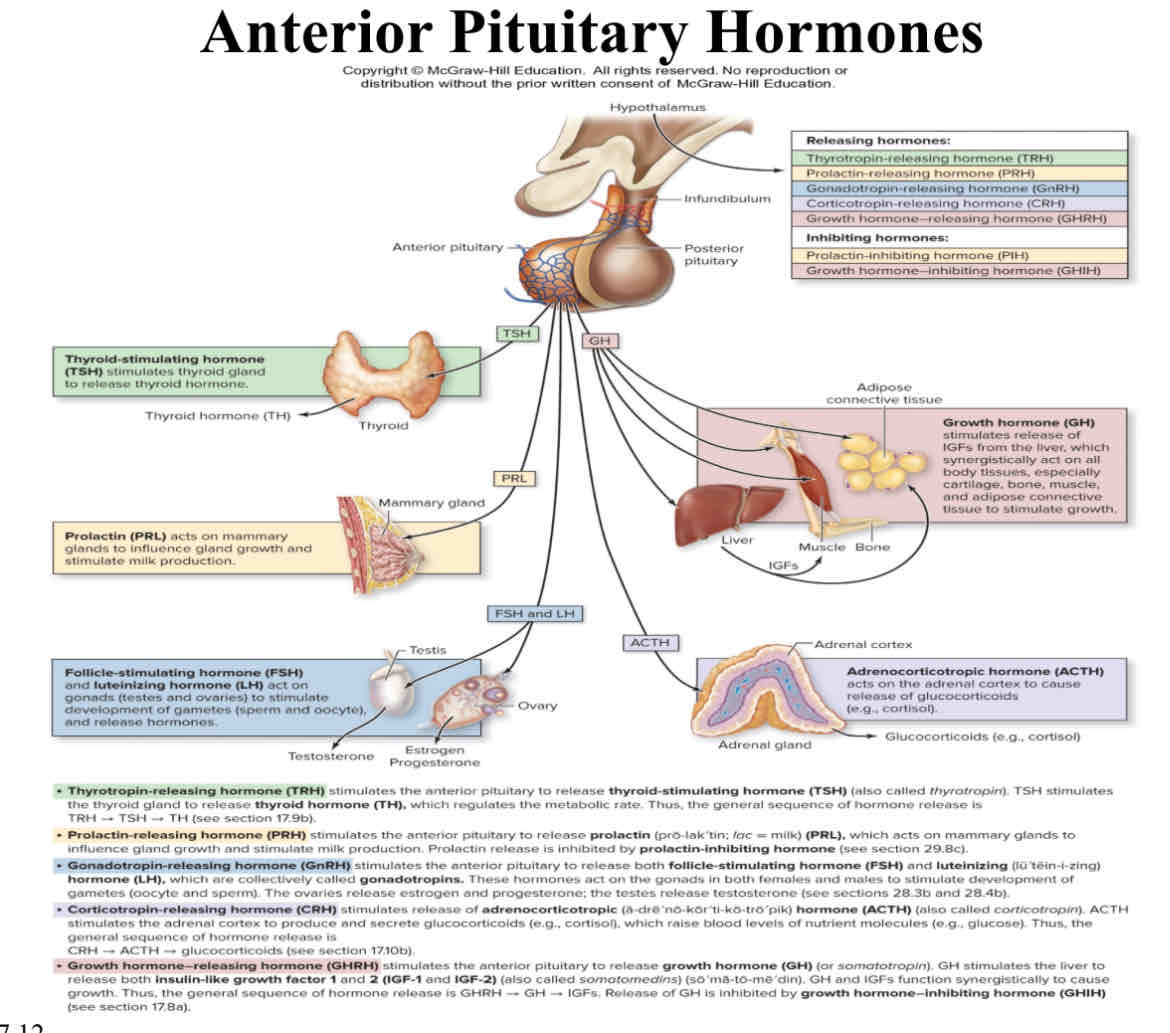
Endocrine Diagram
Hypothalamo-pituitary target organs relationship
Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
ANS diagram