Chapter 12: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
spinal cord
the major communication link between the brain and the PNS inferior to the head
it integrates incoming info and produces responses through reflex mechanisms
consists of peripheral white matter and central gray matter
has 31 pairs of spinal nerves
composed of 4 segments
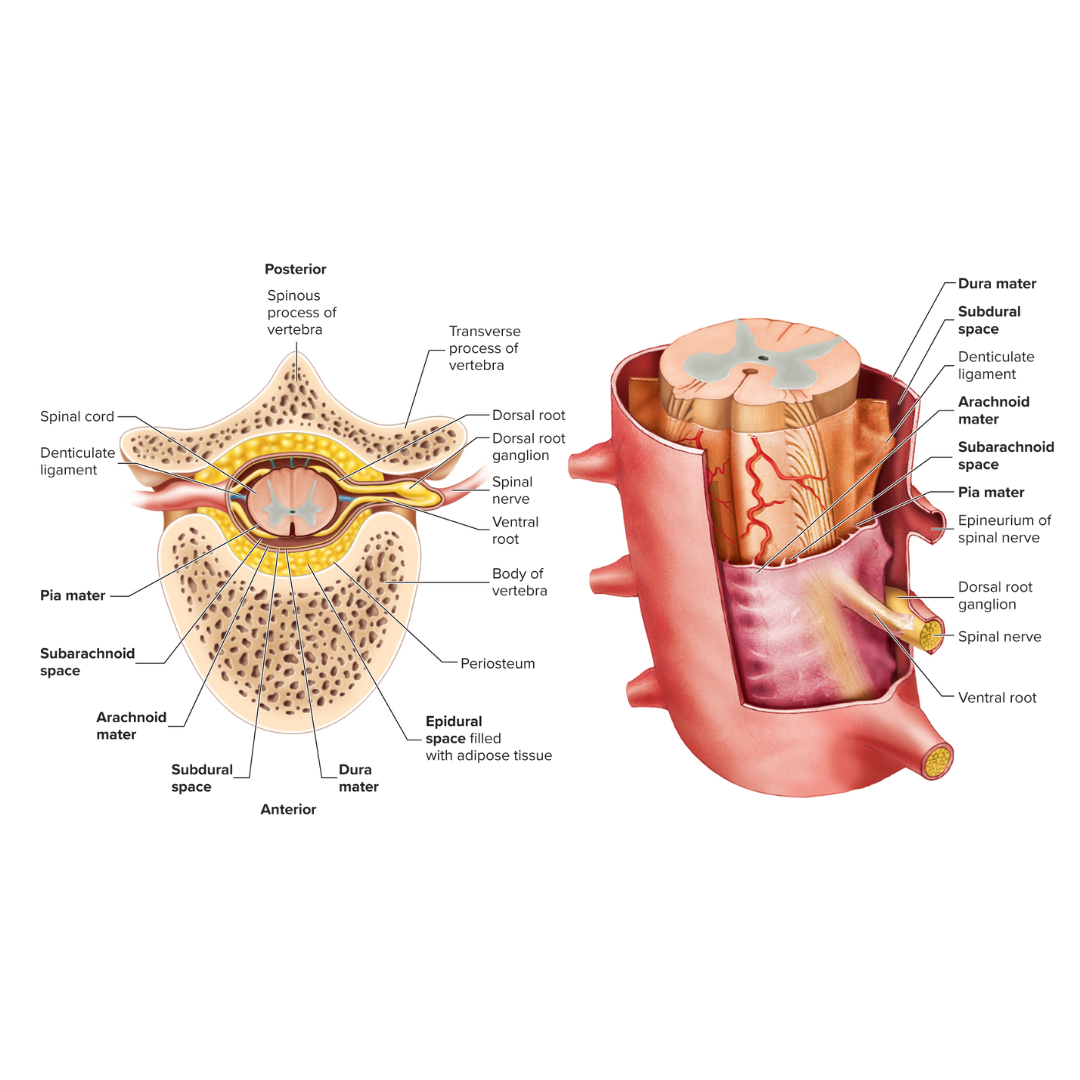
meninges
12.1: Spinal Cord
connective tissue membrane surrounding the brain
epidural space
12.1: Spinal Cord
the space between the bone and the dura mater
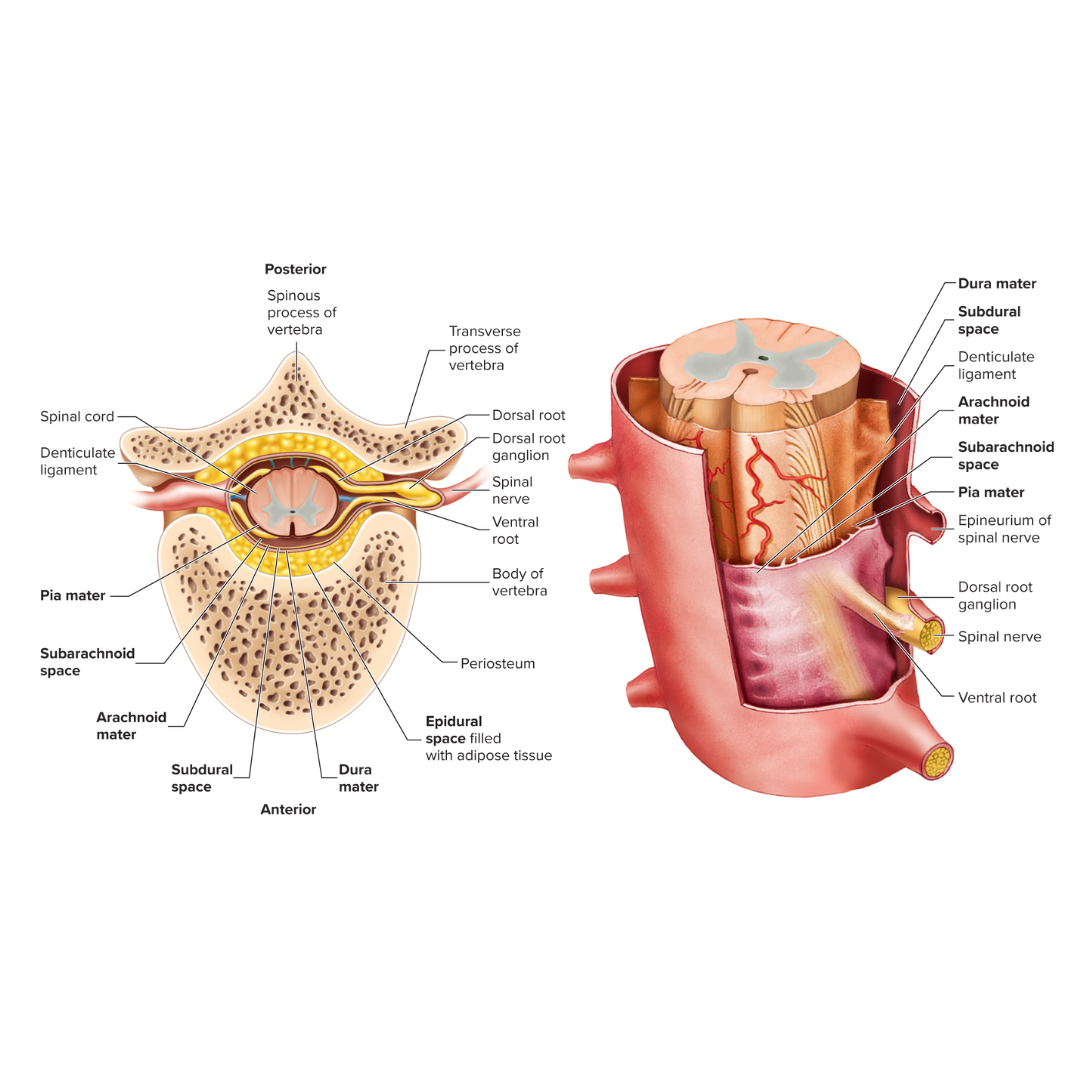
dura mater
12.1: Spinal Cord
A tough, fibrous membrane that forms the outer covering of the brain and spinal cord
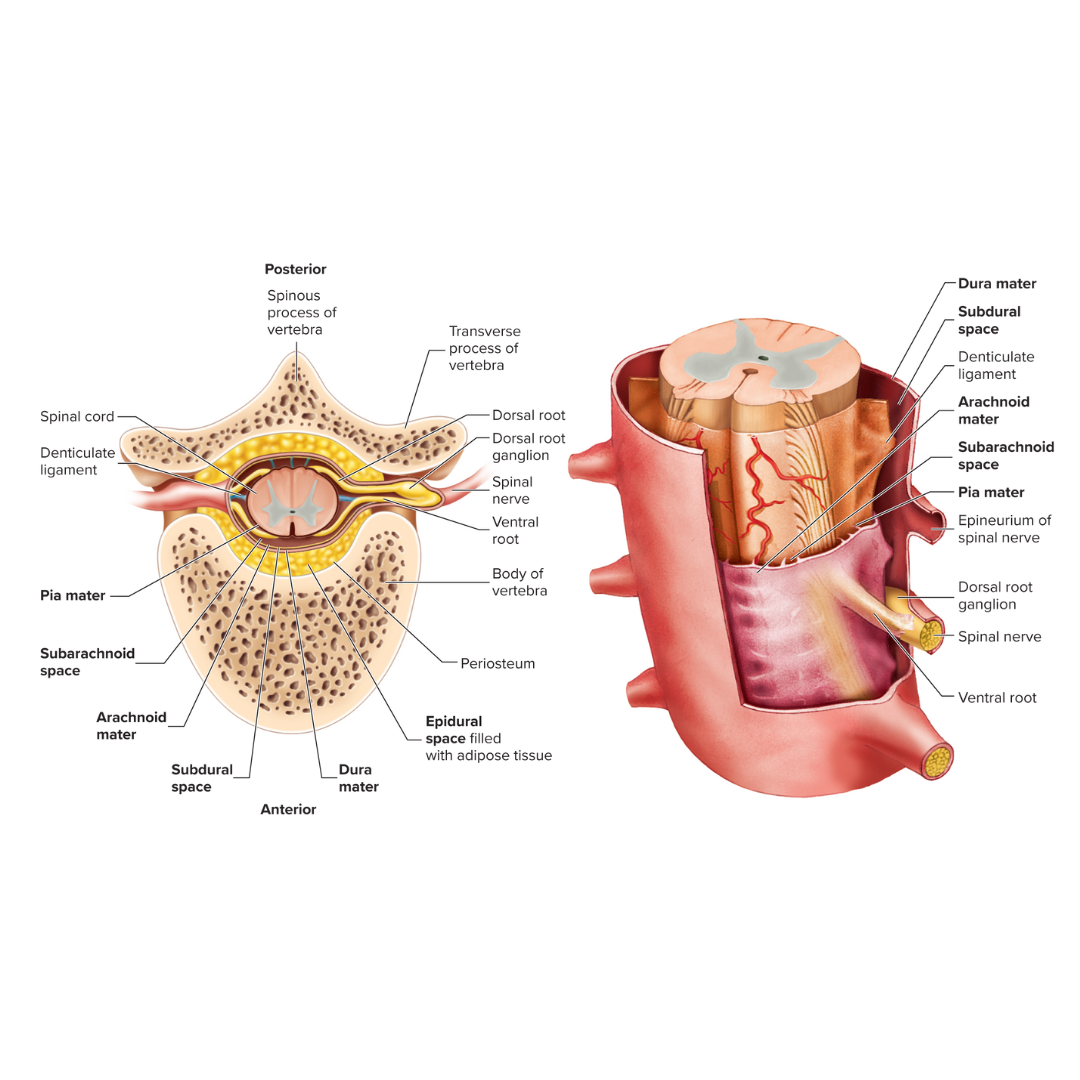
subdural space
12.1: Spinal Cord
the space between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater
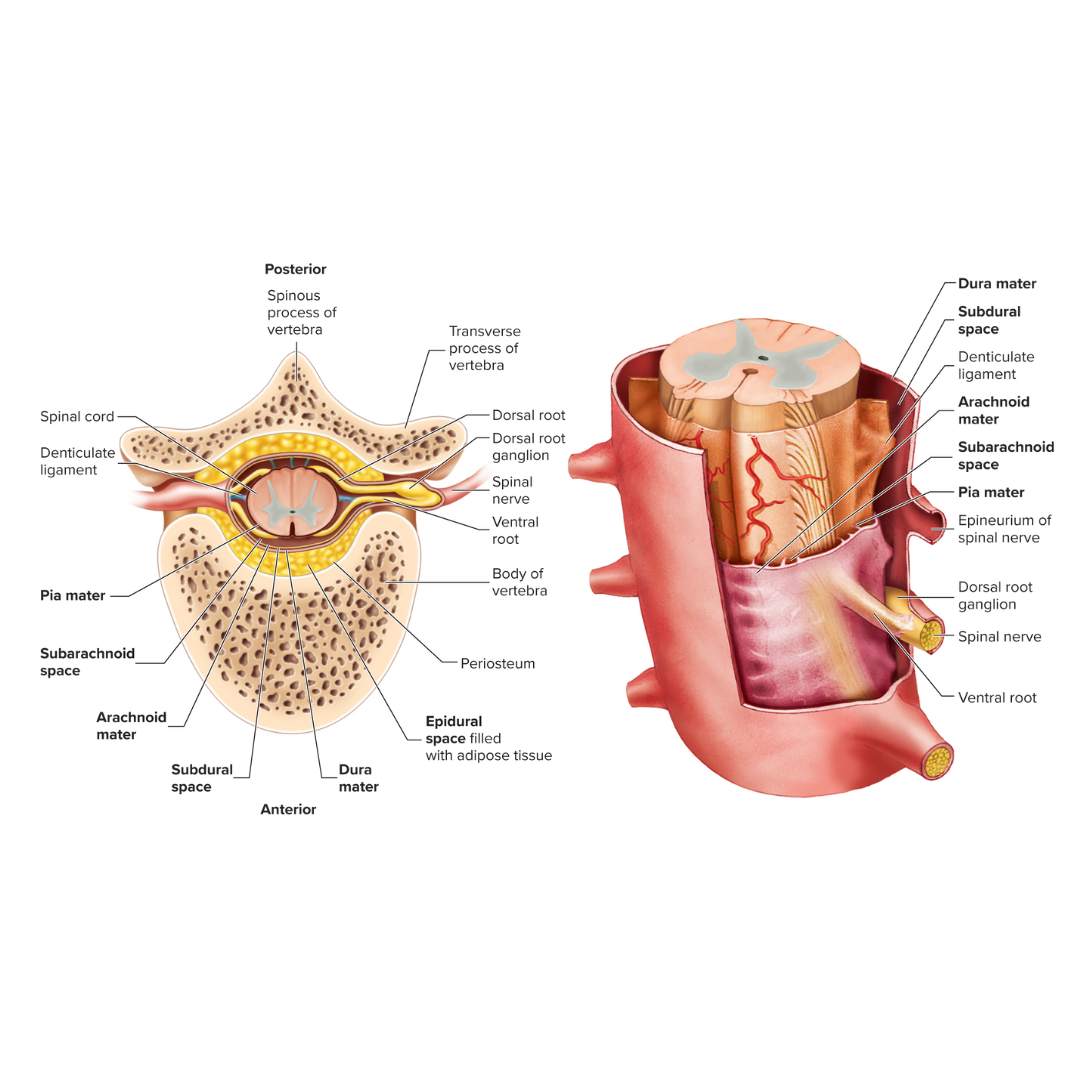
arachnoid mater
12.1: Spinal Cord
Thin, cobweb-appearing meningeal layer surrounding the brain; the middle of the three layers.
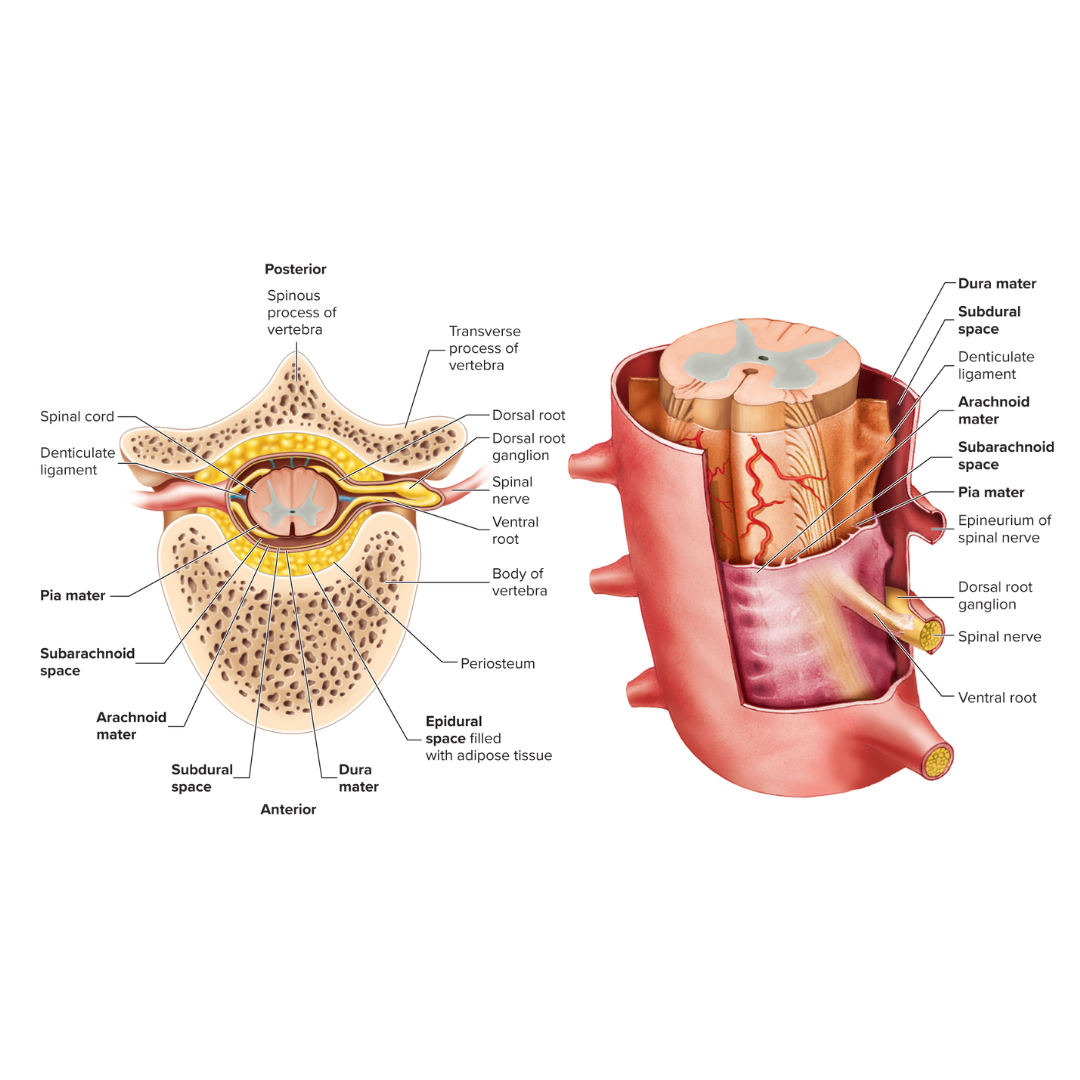
subarachnoid space
12.1: Spinal Cord
the space between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater
place where cerebrospinal fluid is found around the spinal cord
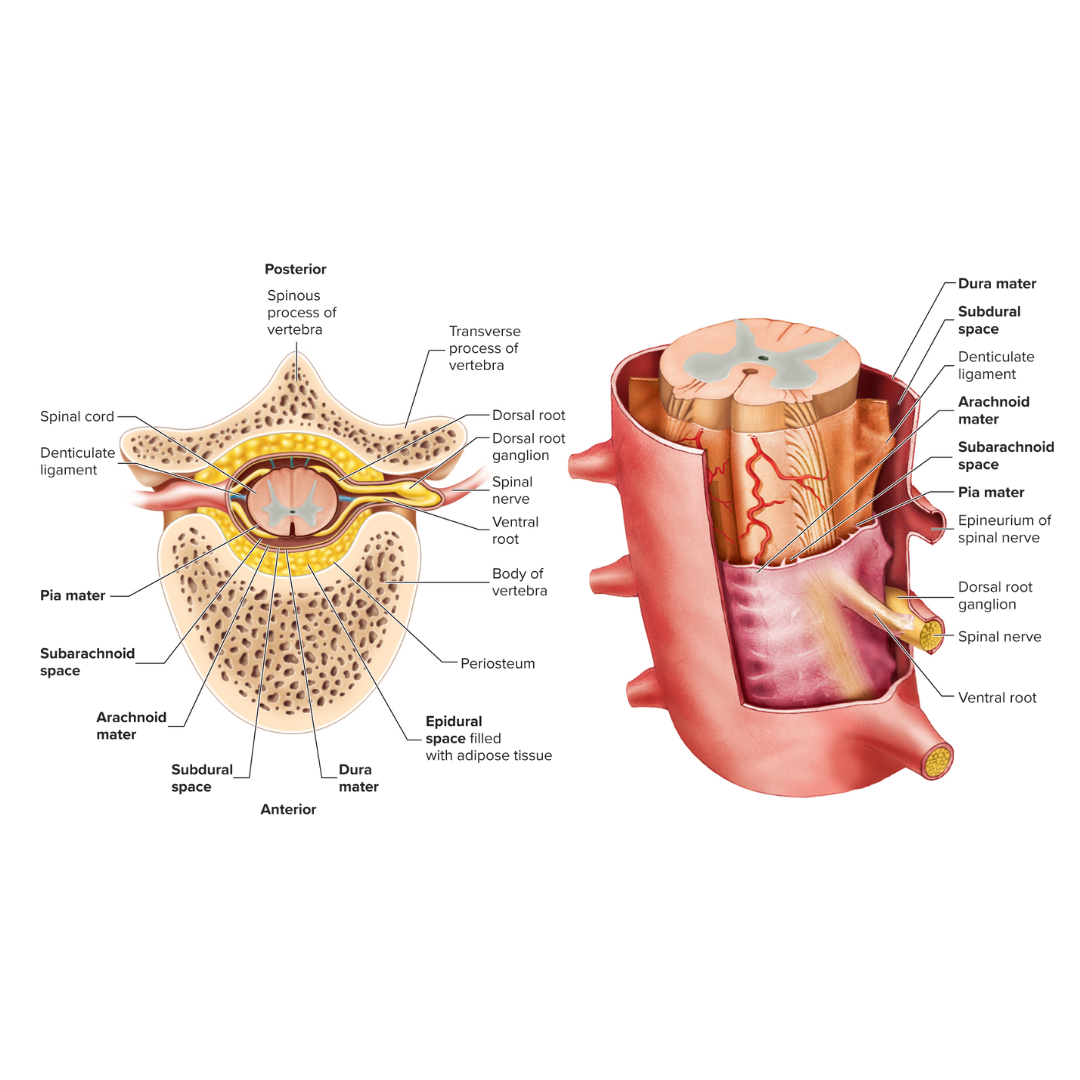
pia mater
12.1: Spinal Cord
Delicate membrane forming the inner covering of the brain and spinal cord.
ventral root
12.1: Spinal Cord
Motor (efferent) root of a spinal nerve
conveys motor output away from the spinal cord
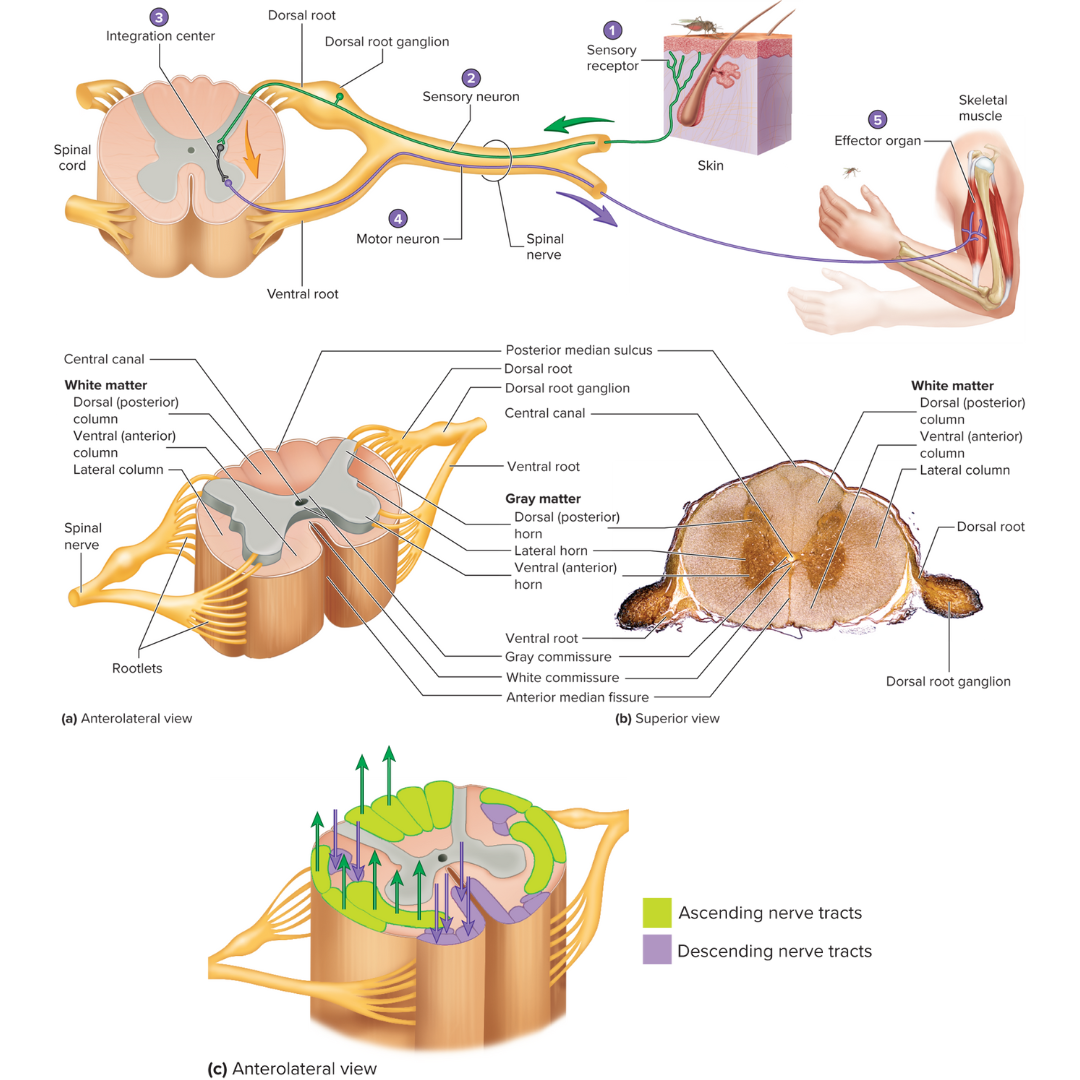
dorsal root
12.1: Spinal Cord
Sensory (afferent) root of a spinal nerve
conveys sensory input into the spinal cord
has a ganglion
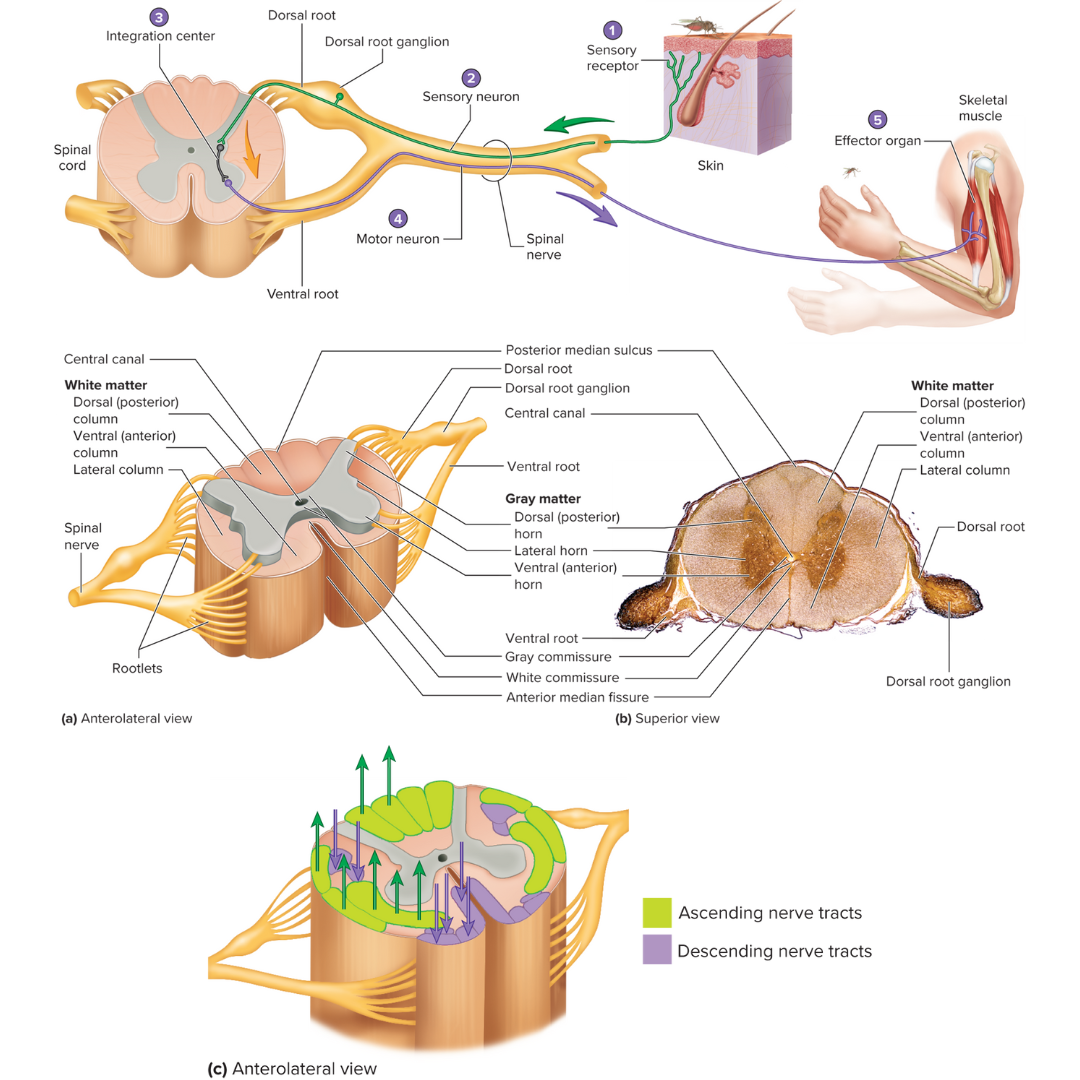
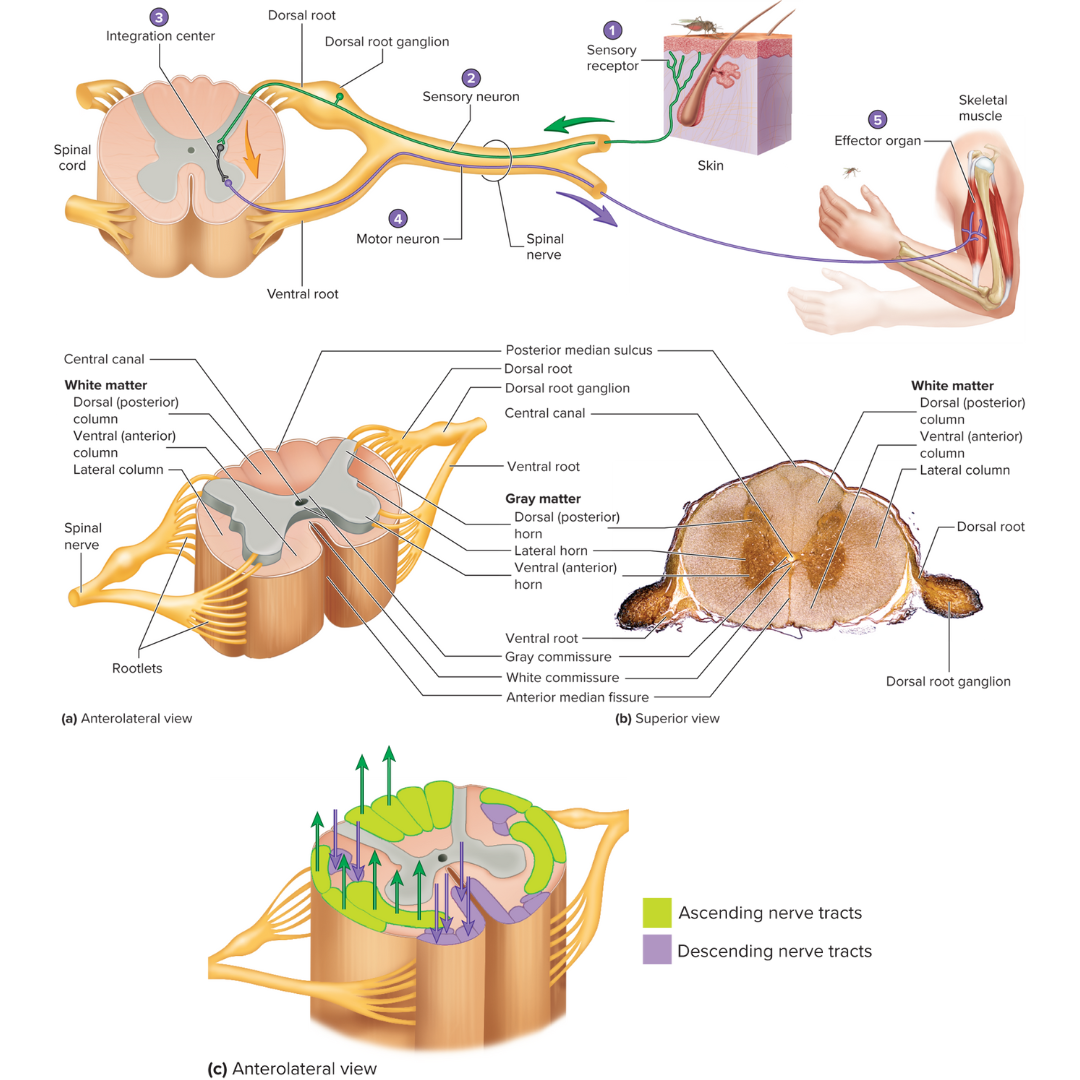
white matter
12.1: Spinal Cord
organized into columns, which are subdivided into nerve tracts, or fascicles, which carry action potentials to and from the brain
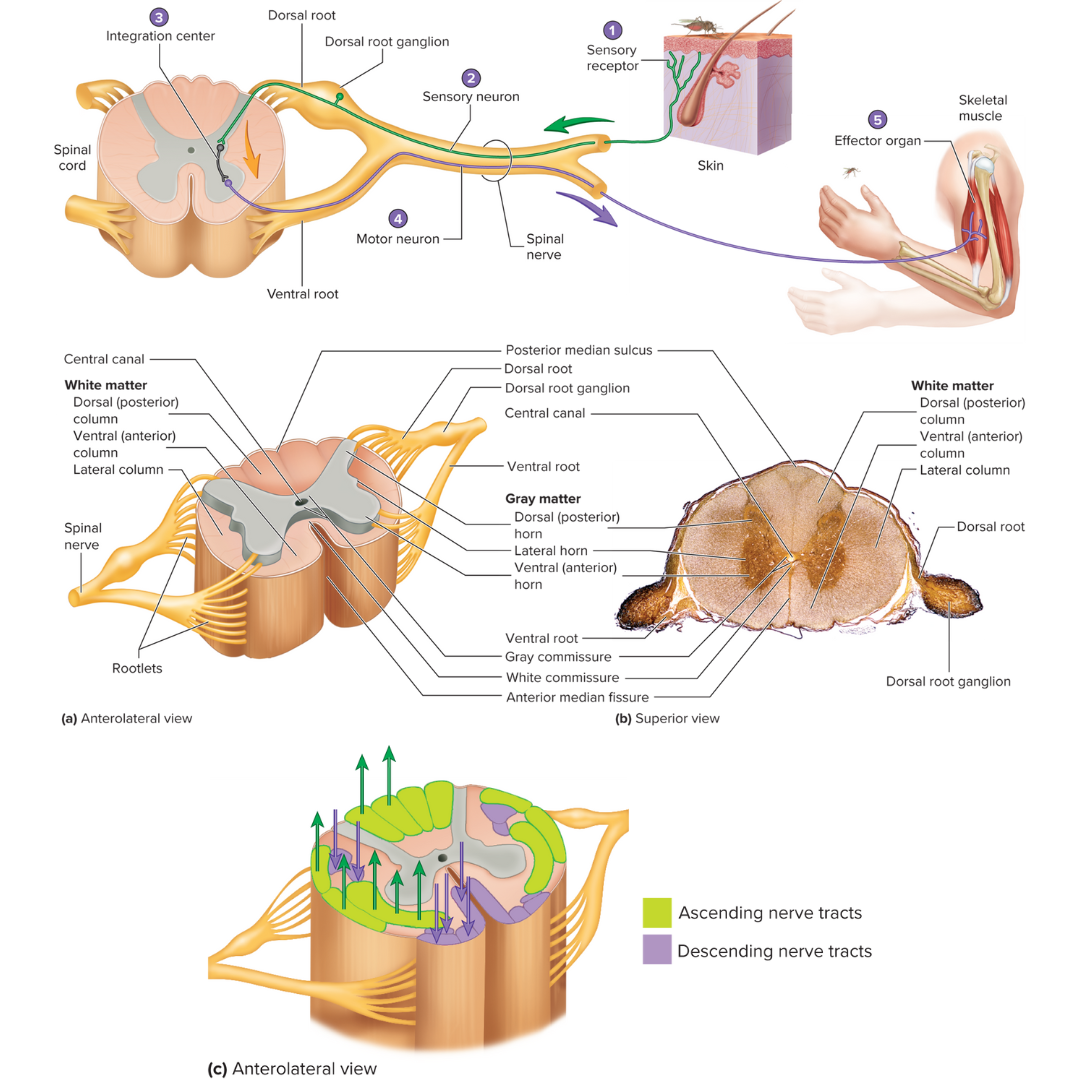
gray matter
12.1: Spinal Cord
divided into horns
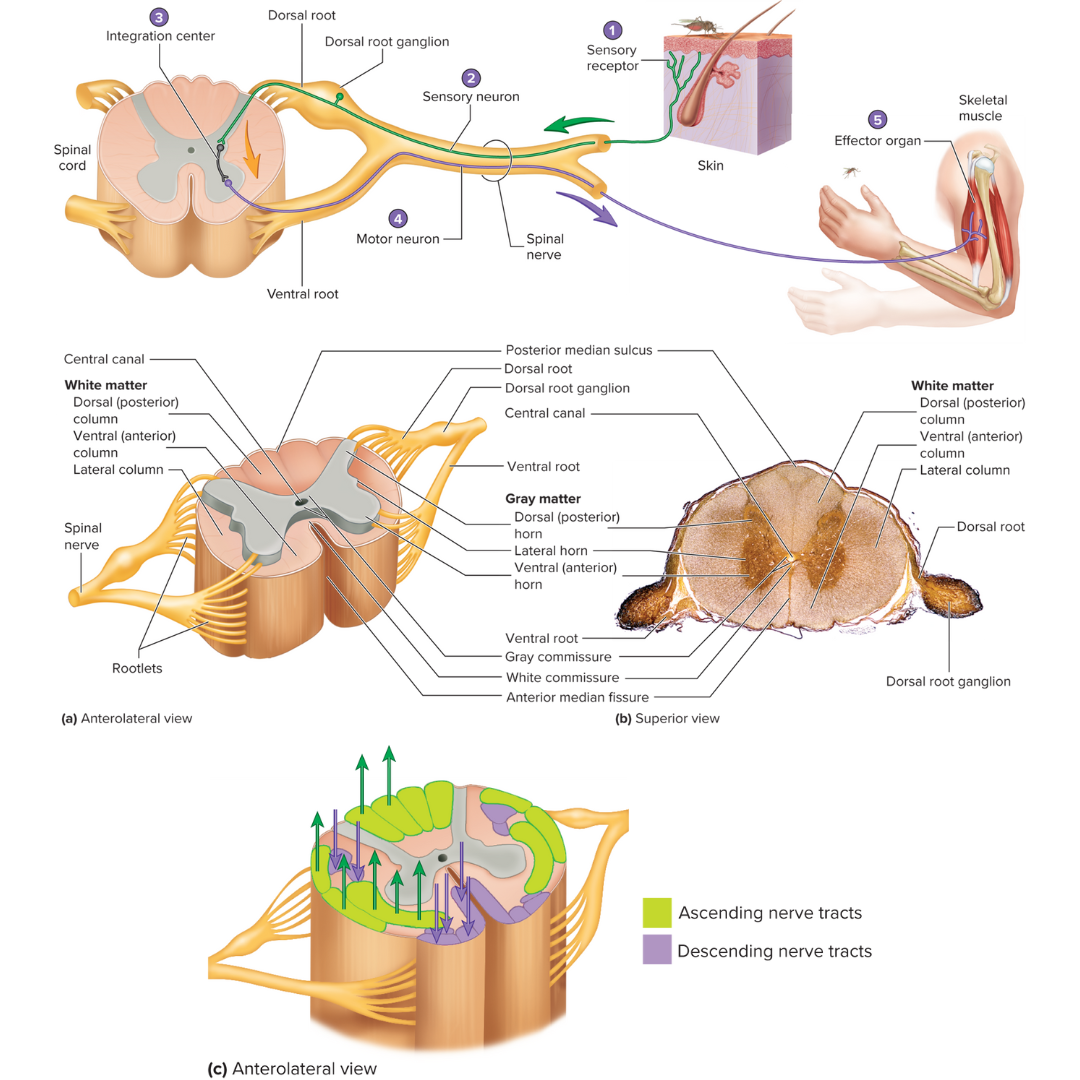
dorsal horns
12.1: Spinal Cord
contain sensory axons that synapse with interneurons
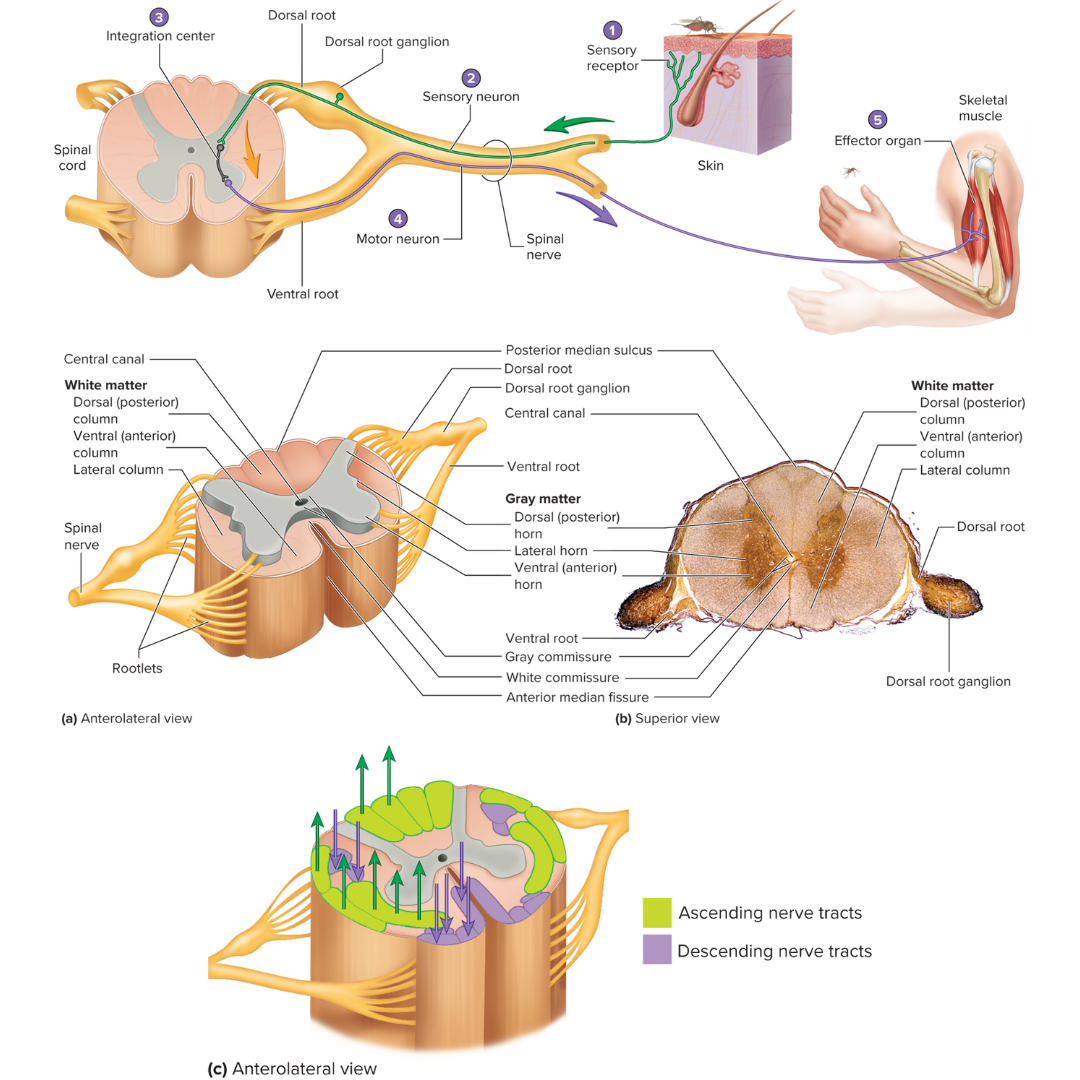
ventral horns
12.1: Spinal Cord
contain the neuron cell bodies of somatic motor neurons
lateral horns
12.1: Spinal Cord
contain the neuron cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons
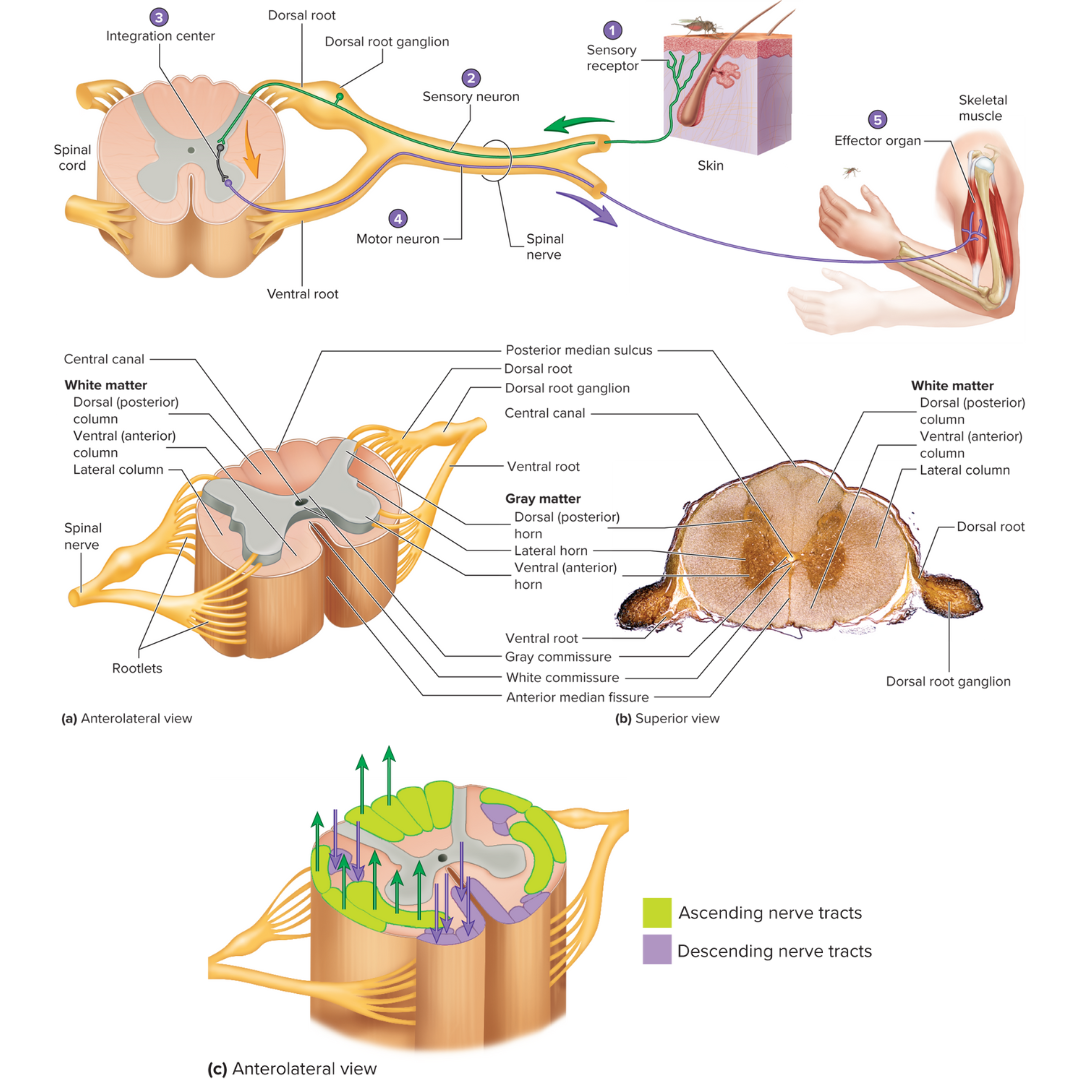
gray and white commissures
12.1: Spinal Cord
connect each half of the spinal cord
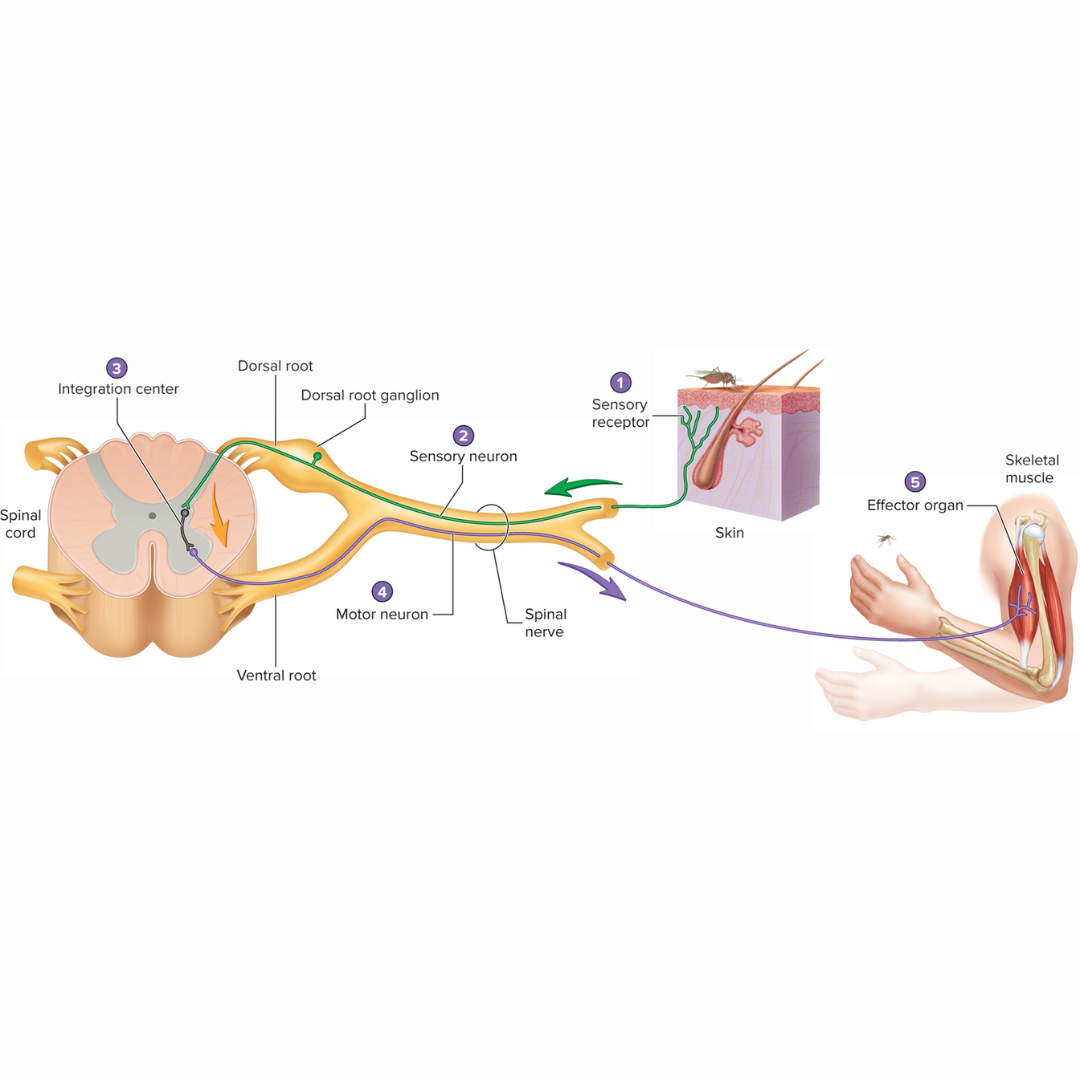
reflex arc
12.2: Reflexes
a neutral pathway that controls a reflex
basic functional unit of the nervous system that is capable of receiving a stimulus and producing a response
has five components:
1 - sensory receptor, 2 - sensory neuron, 3 - an integration center, 4 - motor neuron, 5 - effector organ
somatic reflexes
12.2: Reflexes
if an effector is skeletal muscle, then the reflex is considered…
autonomic reflexes
12.2: Reflexes
if an effector is smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, or a gland, then the reflex is considered…
cranial reflexes
12.2: Reflexes
If the integration center's location is in the brain, then the reflex is considered…
spinal reflexes
12.2: Reflexes
If the integration center's location is in the spinal cord, then the reflex is considered…
stretch reflex
12.2: Reflexes
the simplest reflex
a reflex contraction of muscles in response to stretching of that same muscle
sensory receptor: muscle spindle
withdrawal reflex
12.2: Reflexes
also known as a flexor reflex
the function is to remove a limb or another body part from a painful stimulus
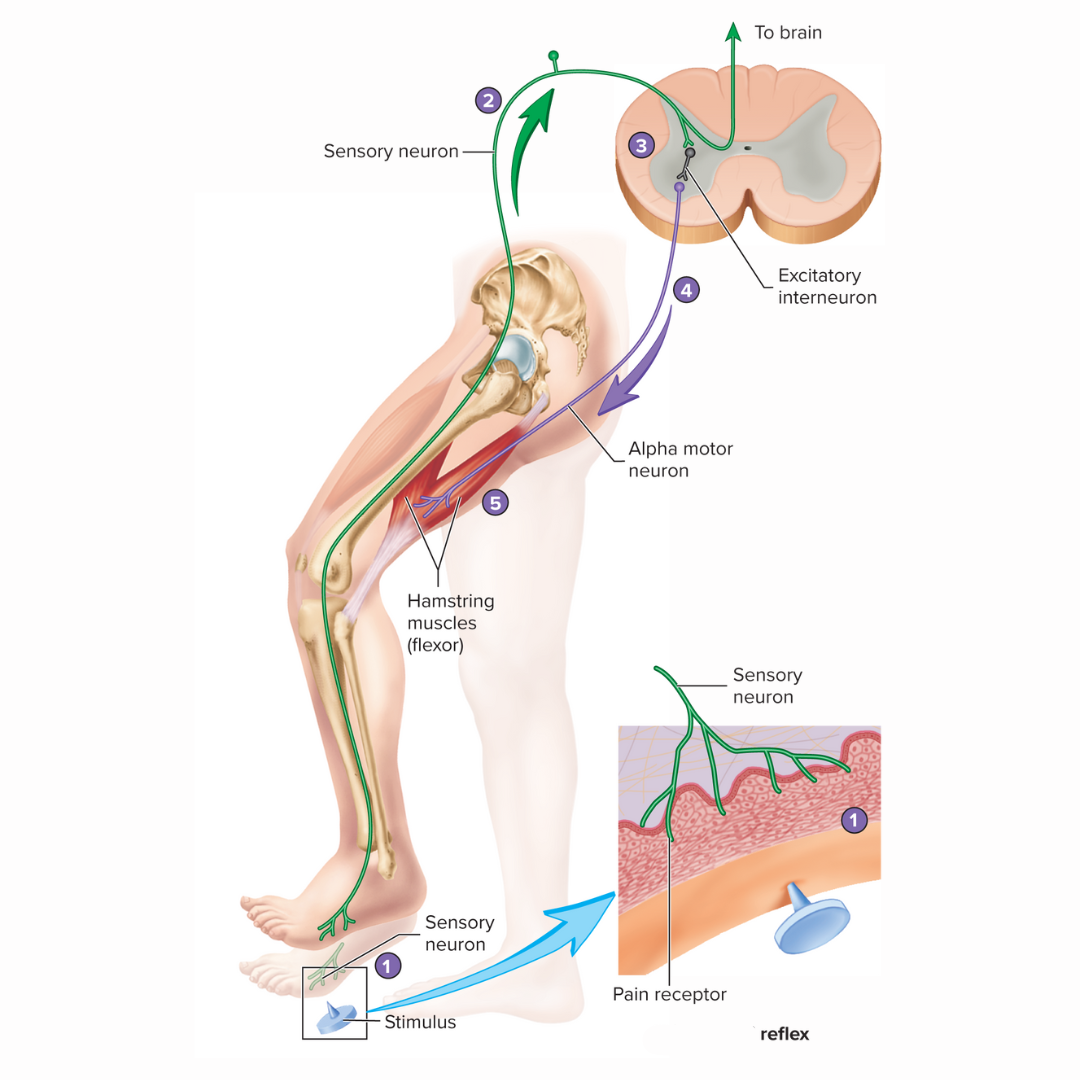
crossed extensor reflex
12.2: Reflexes
occurs on the opposite side of the body from the stimulus
when the withdrawal reflex occurs in one limb, the [term] causes the opposite response to occur in the other limb
![<p><strong>12.2: Reflexes</strong></p><ul><li><p>occurs on the opposite side of the body from the stimulus</p></li><li><p>when the withdrawal reflex occurs in one limb, the [term] causes the opposite response to occur in the other limb </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b95e2776-bace-470d-9bfa-4f4ca798fde6.png)
connective tissue of nerves
12.2: Spinal Nerves
the endoneurium, the perineurium, and the epineurium
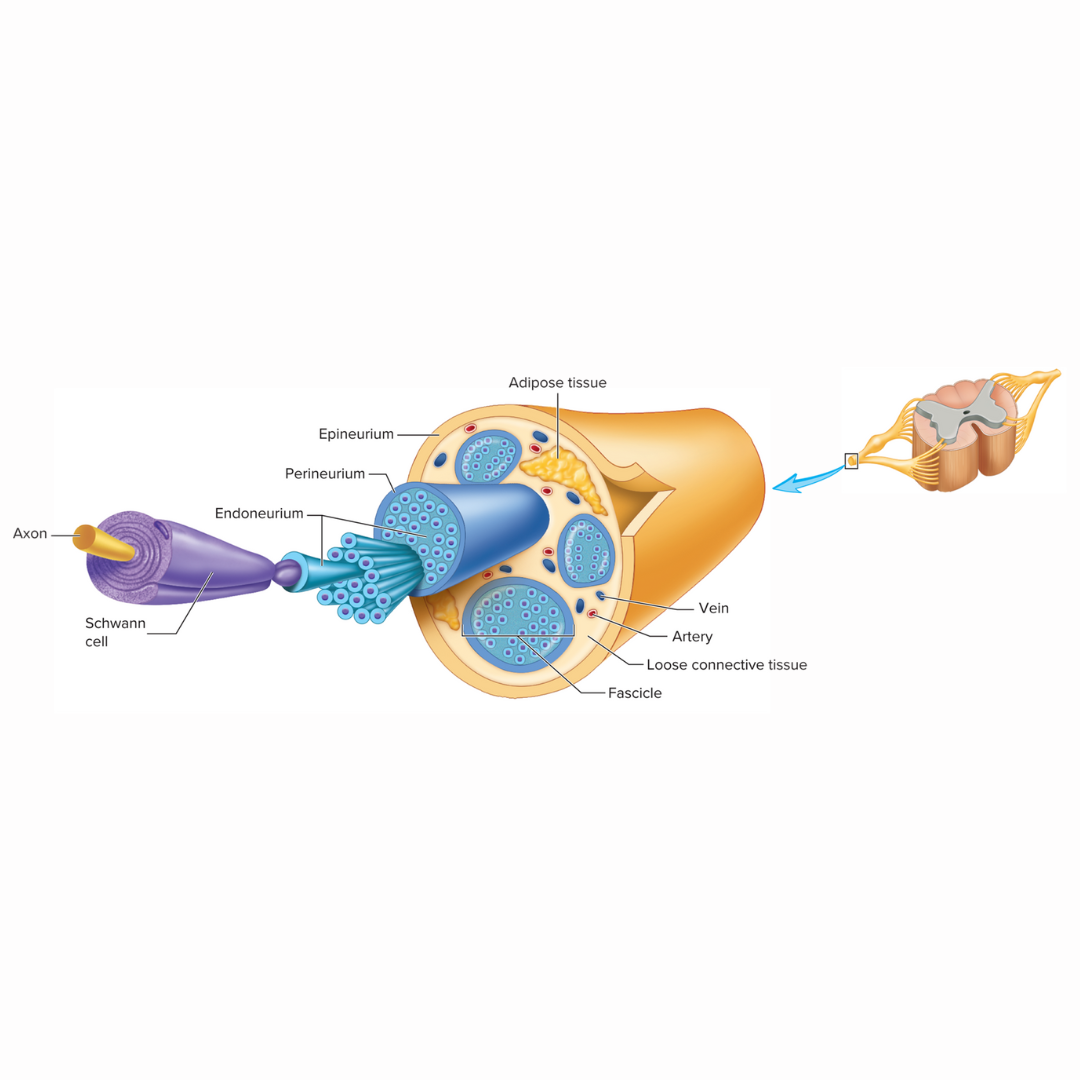
endoneurium
12.2: Spinal Nerves
the delicate connective tissue layer that surround each axon, or nerve fiber, and its Schwann cell sheath (this is not myelin)
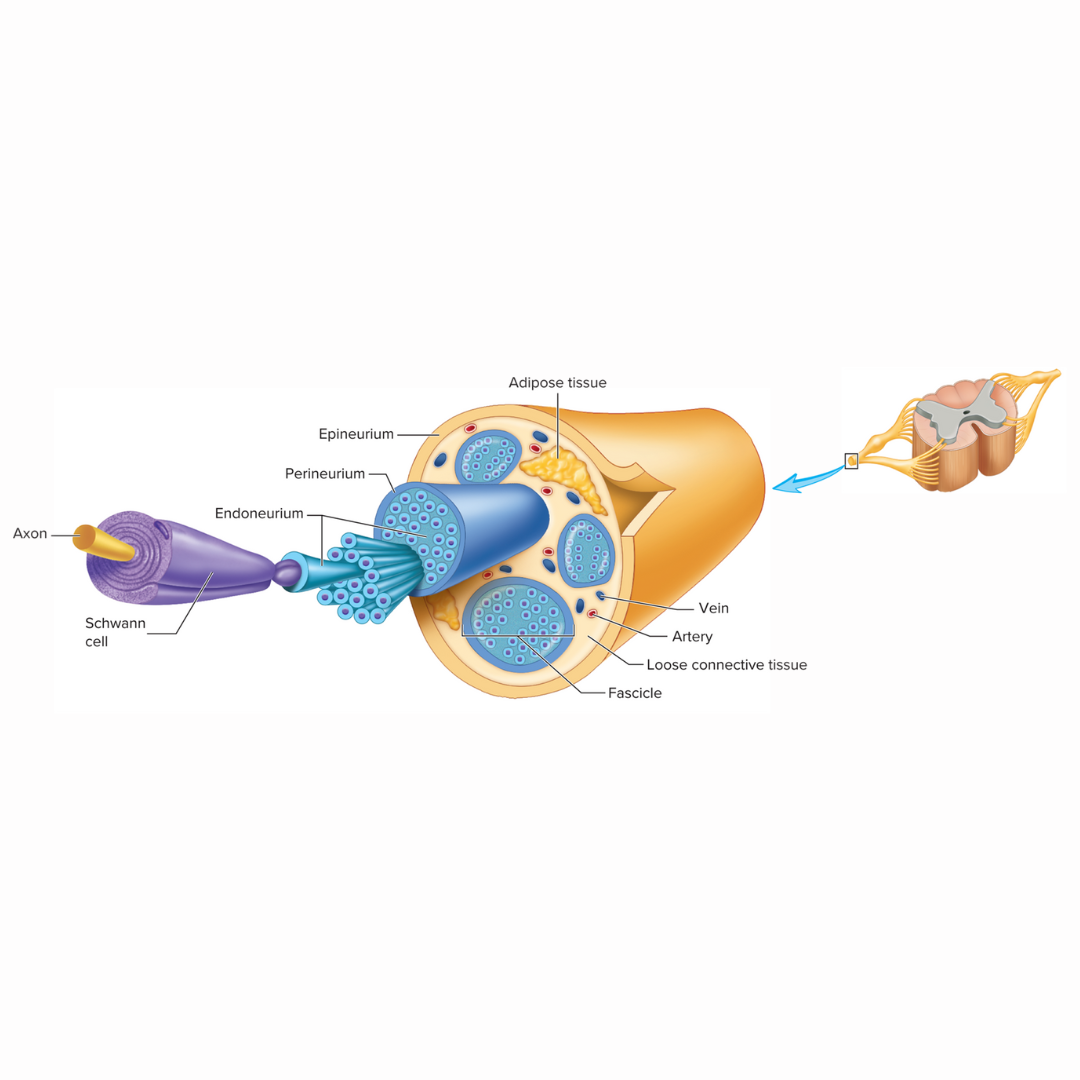
perineurium
12.2: Spinal Nerves
the heavier connective tissue layer that surrounds groups of axons to form nerve fascicles
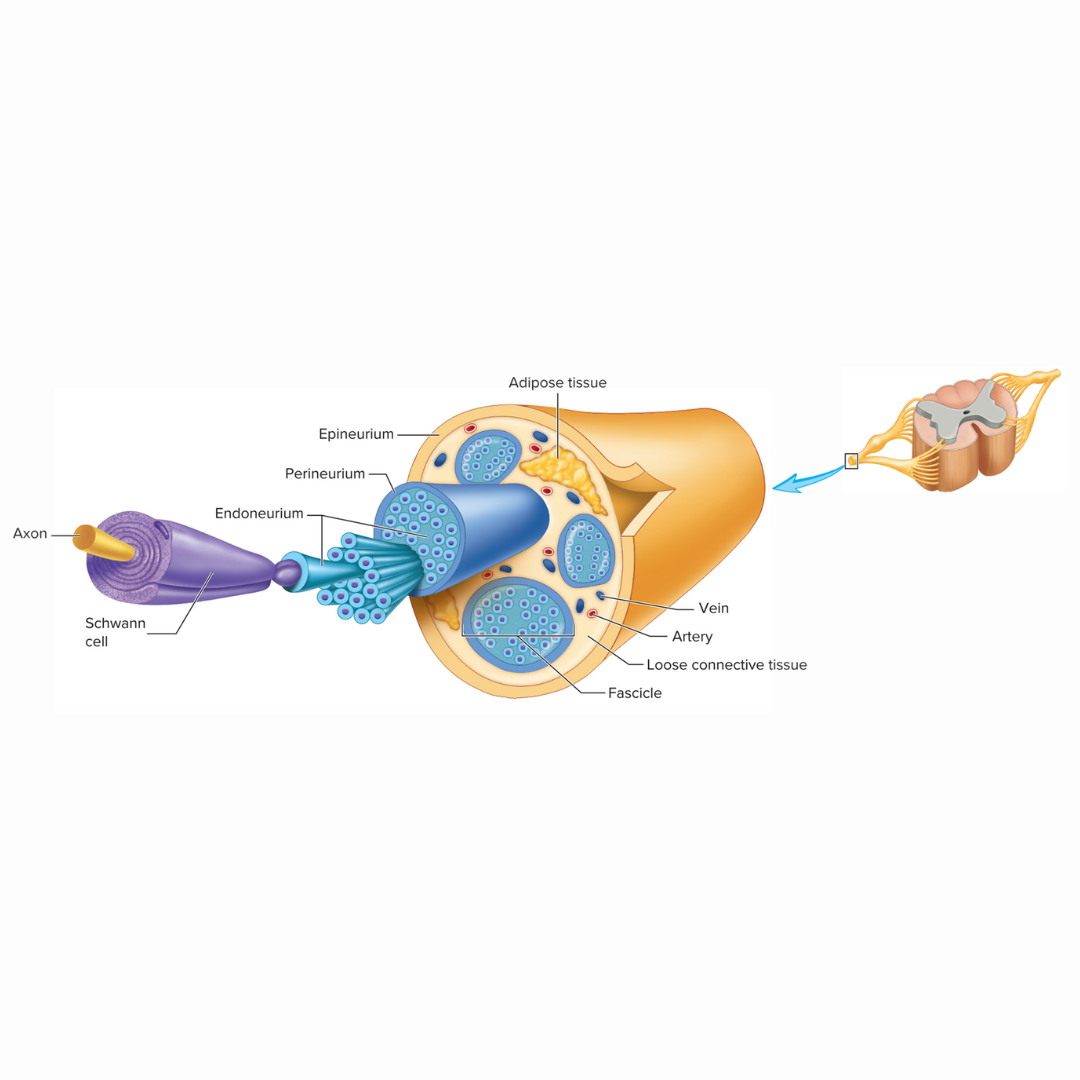
epineurium
12.2: Spinal Nerves
the third layer of dense connective tissue that binds the nerve fascicles together to form a nerve. This tissue us continuous with the dura mater surrounding the CNS
dermatome
12.3: Spinal Nerves
an area of skin supplied with sensory innervation by a pair of spinal nerves
each to the spinal nerves except C1 has a specific cutaneous sensory distribution
rami
12.3: Spinal Nerves
major branches of a spinal nerve
there are dorsal and ventral [term] in each spinal nerve
plexuses
12.3: Spinal Nerves
an intermingling of nerves, much like hair in a braid
formed by the ventral rami of different spinal nerves joining together
cervical plexus
12.3: Spinal Nerves
spinal nerves C1-C4
supplies some muscles and the skin of the neck and shoulder
the phrenic nerves innervate the diaphragm
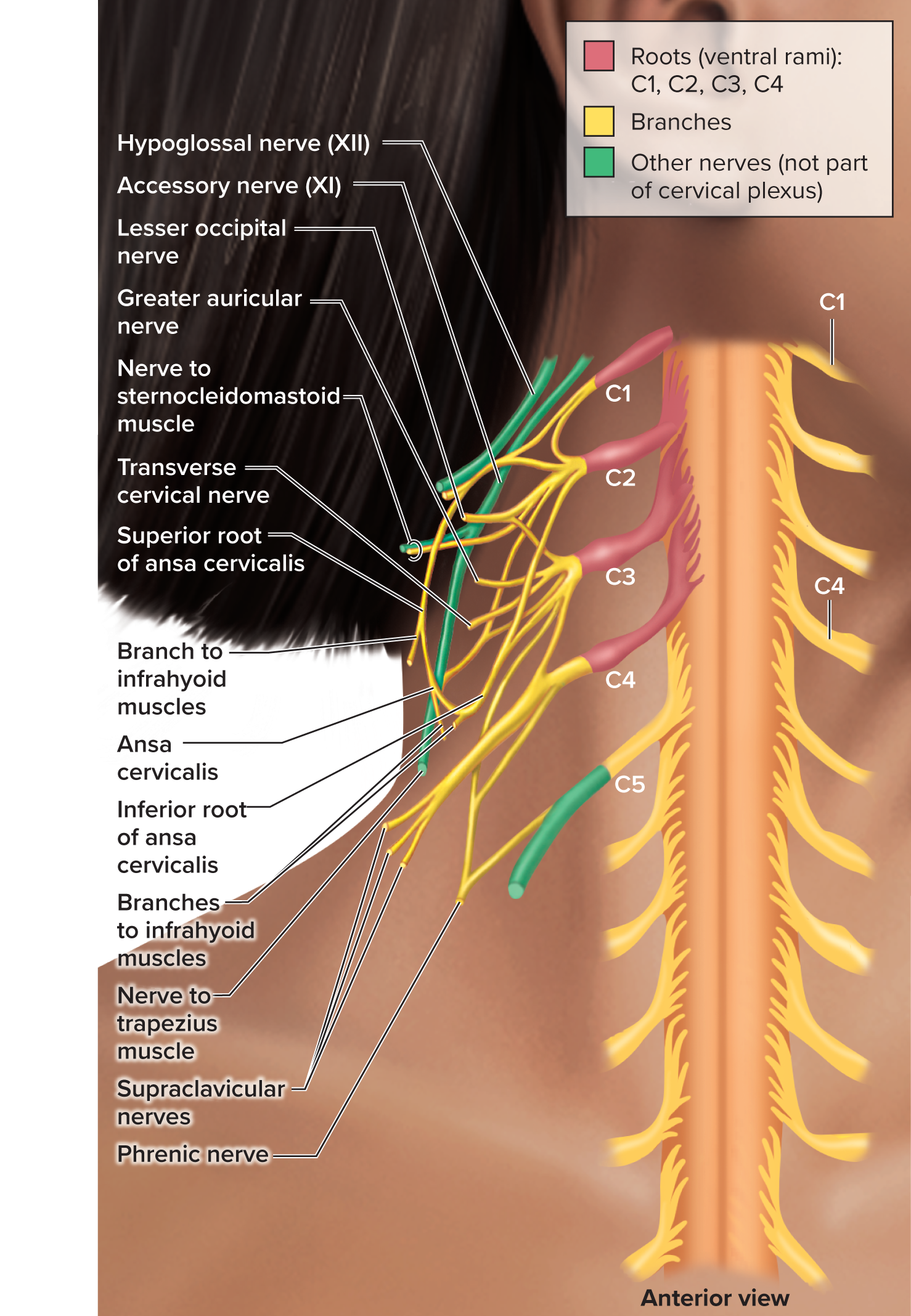
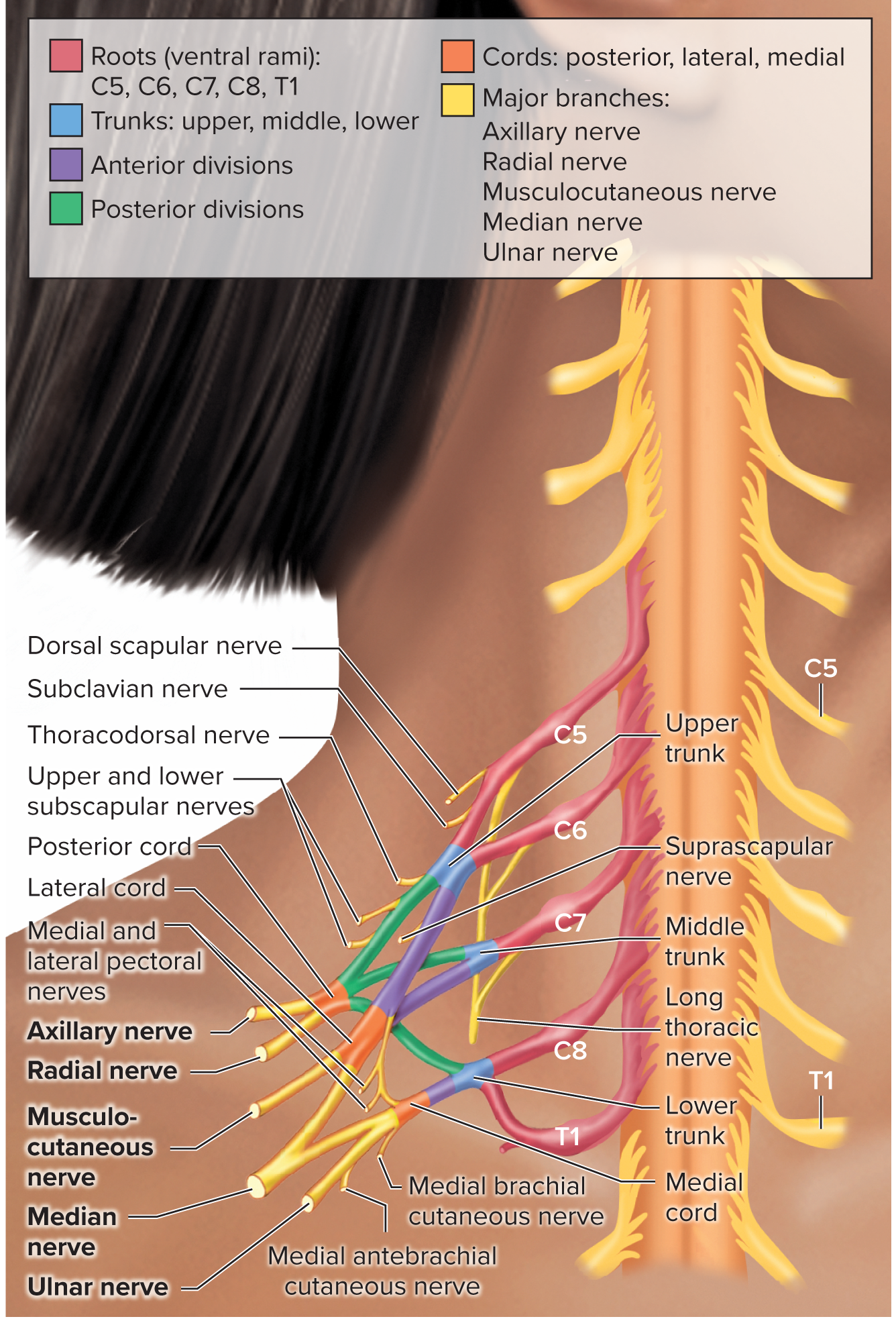
brachial plexus
12.3: Spinal Nerves
spinal nerves C5-T1
supplies the upper limb
includes the axillary, radial, musculocutaneous, ulnar, and median nerves
lumbosacral plexus
12.3: Spinal Nerves
spinal nerves L1-S4
four major nerves exit the [term] and enter the lower limb: the obturator, the femoral, the tibial, and the common fibular
other [term part] nerves supply the lower back, hip, and lower abdomen
![<p><strong>12.3: Spinal Nerves</strong></p><ul><li><p>spinal nerves L1-S4</p></li><li><p>four major nerves exit the [term] and enter the lower limb: the obturator, the femoral, the tibial, and the common fibular</p></li><li><p>other [term part] nerves supply the lower back, hip, and lower abdomen</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b852838d-ae0c-47dd-a9c1-72e3d77d2122.png)
coccygeal plexus
12.3: Spinal Nerves
small plexus
spinal nerve S5 and the coccygeal nerve (Co)
supplies the motor innervation to muscles of the pelvic floor
supplies the sensory cutaneous innervation to the skin over the coccyx