Valvular Regurgitation - General
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Primary regurgitation
– problem with the valve leaflets, e.g., rheumatic, age related, inflammation, congenital, therapy.
• Functional or secondary –
– The valve morphology is normal but there is a problem with supporting structures, e.g., ischemic heart disease and papillary muscle dysfunction and annular dilation.
Chronic regurgitation
results in chamber dilation with normal pressures
Acute regurgitation
results in normal chamber size with a sudden increase in pressure
Chronic mitral regurgitation will eventually lead to
o pulmonary hypertension and heart failure Increased afterload over time will lead to left ventricular hypertrophy
Regurgitation leads to
volume overload.
Left Ventricular Volume Overload
dilated left ventricle and hyperdynamic function
Right Ventricular Volume Overload
dilated right ventricle and paradoxical septal motion
Stenosis leads to
pressure overload.
Spectral Doppler waveform density –
the more severe results in a more prominent or dense spectral Doppler waveform.
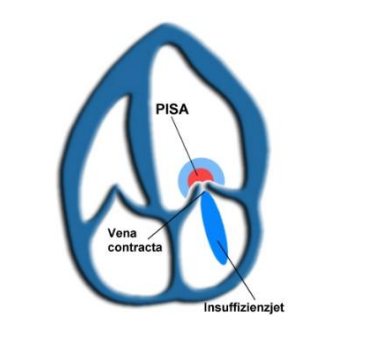
• Flow convergence or PISA
– the flow velocity before the valve – small or none with mild regurgitation and more prominent when more significant regurgitation is present.
• Jet –
jet area and length, central or eccentric.
• Vena Contracta –
– the narrowest part of the jet at the valve leaflet tips.
know dis