Urinary System Pathology
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
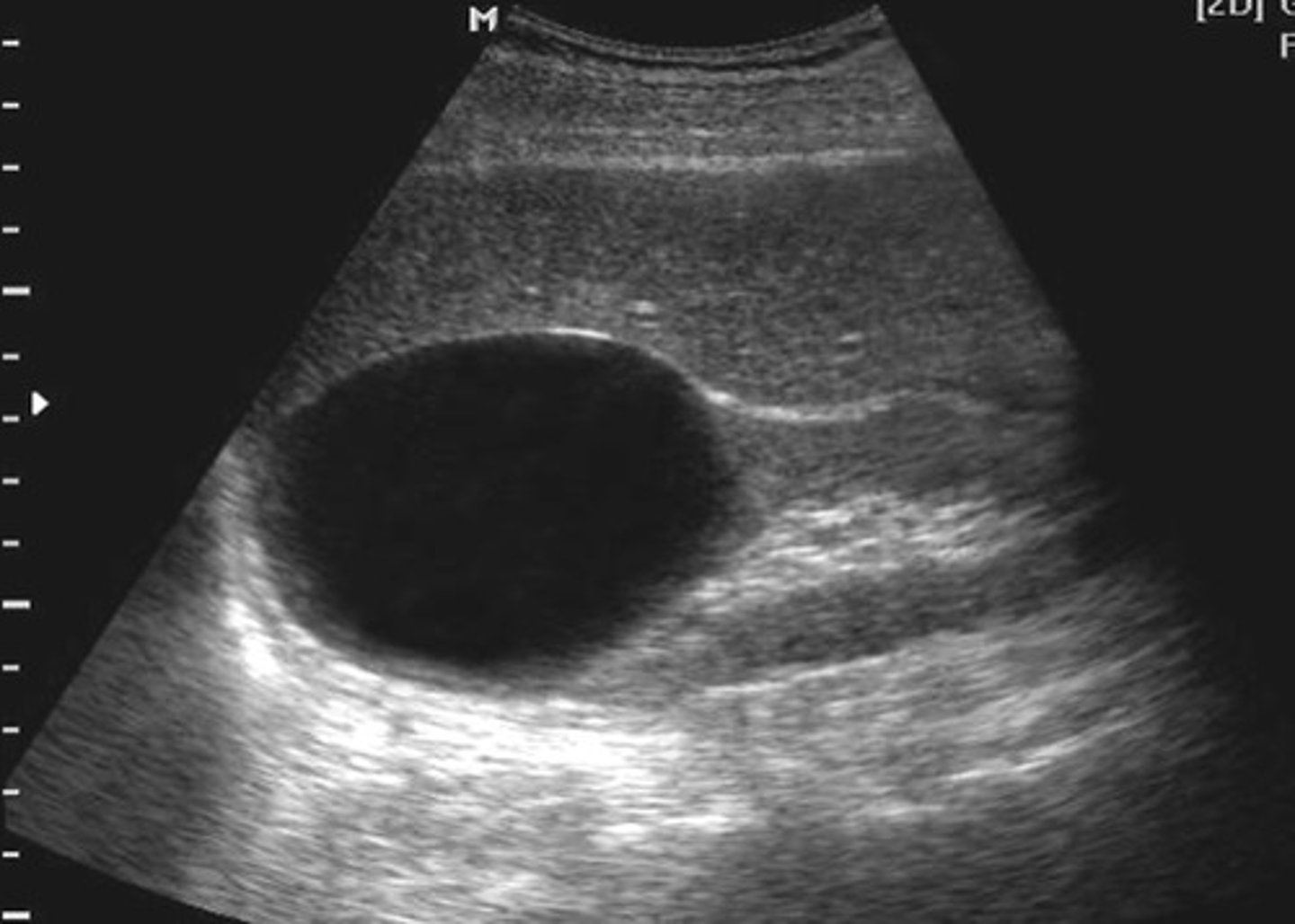
With simple renal cysts, ___ is unknown
etiology
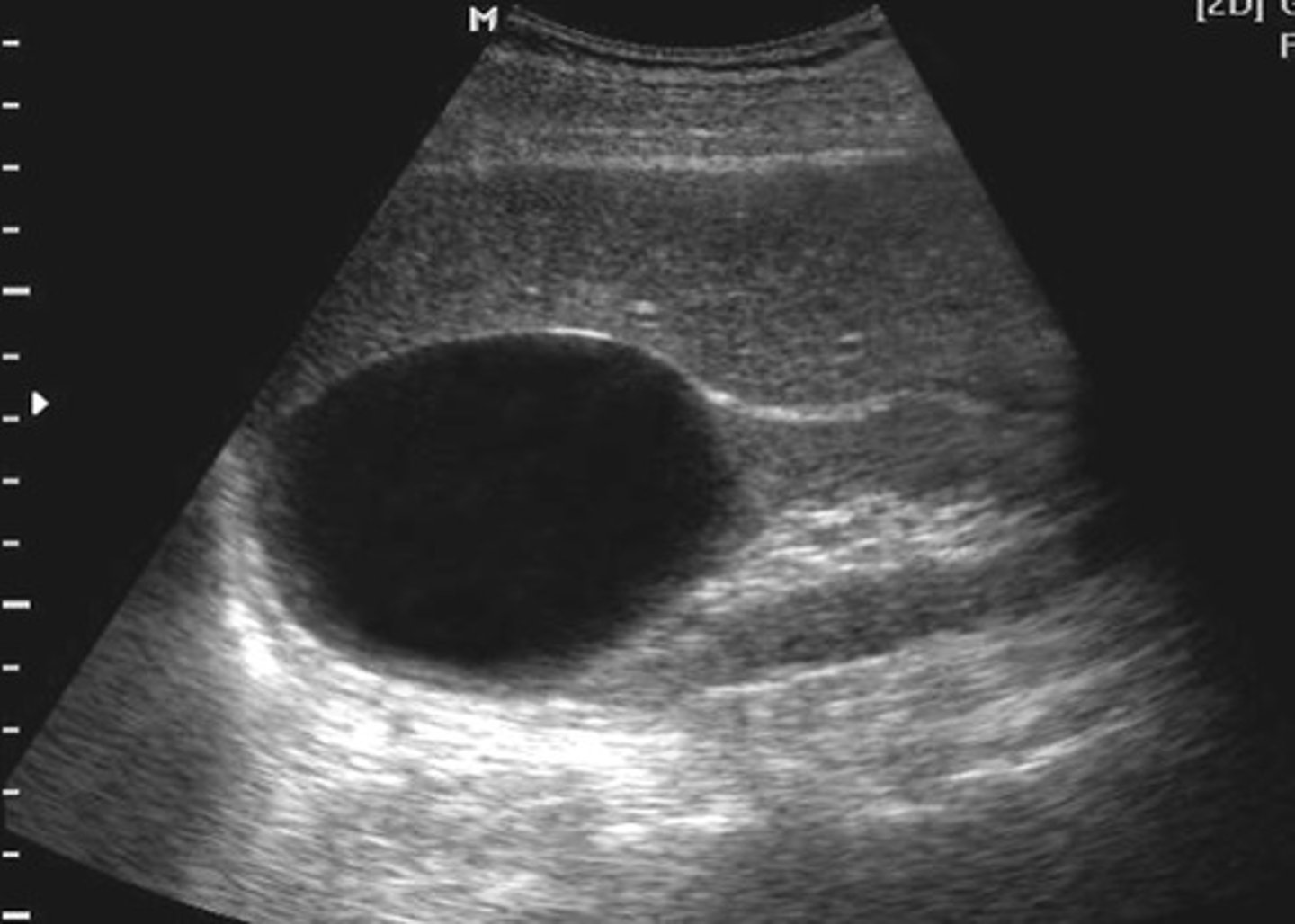
Simple renal cysts are common in
adults greater than 50
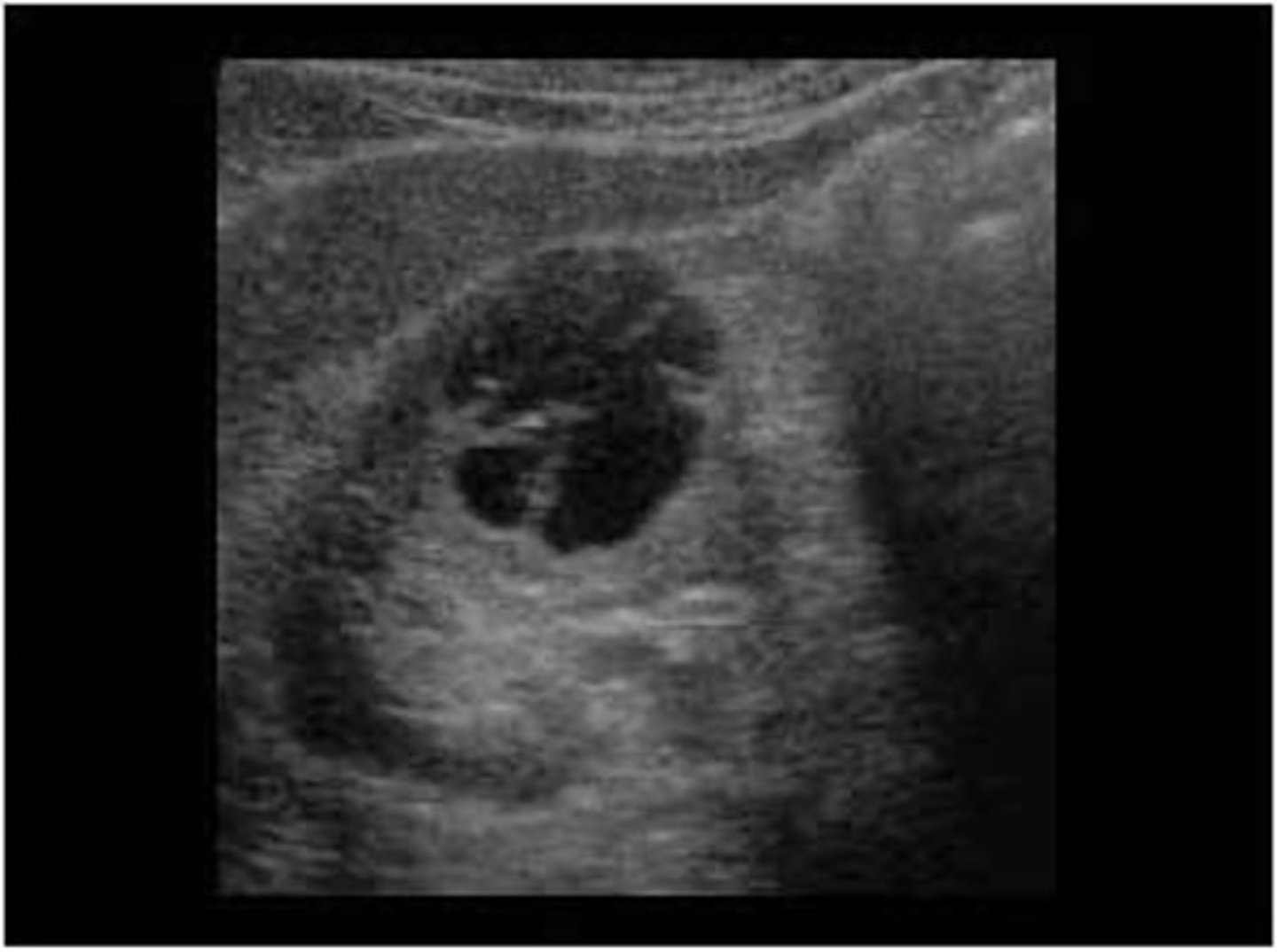
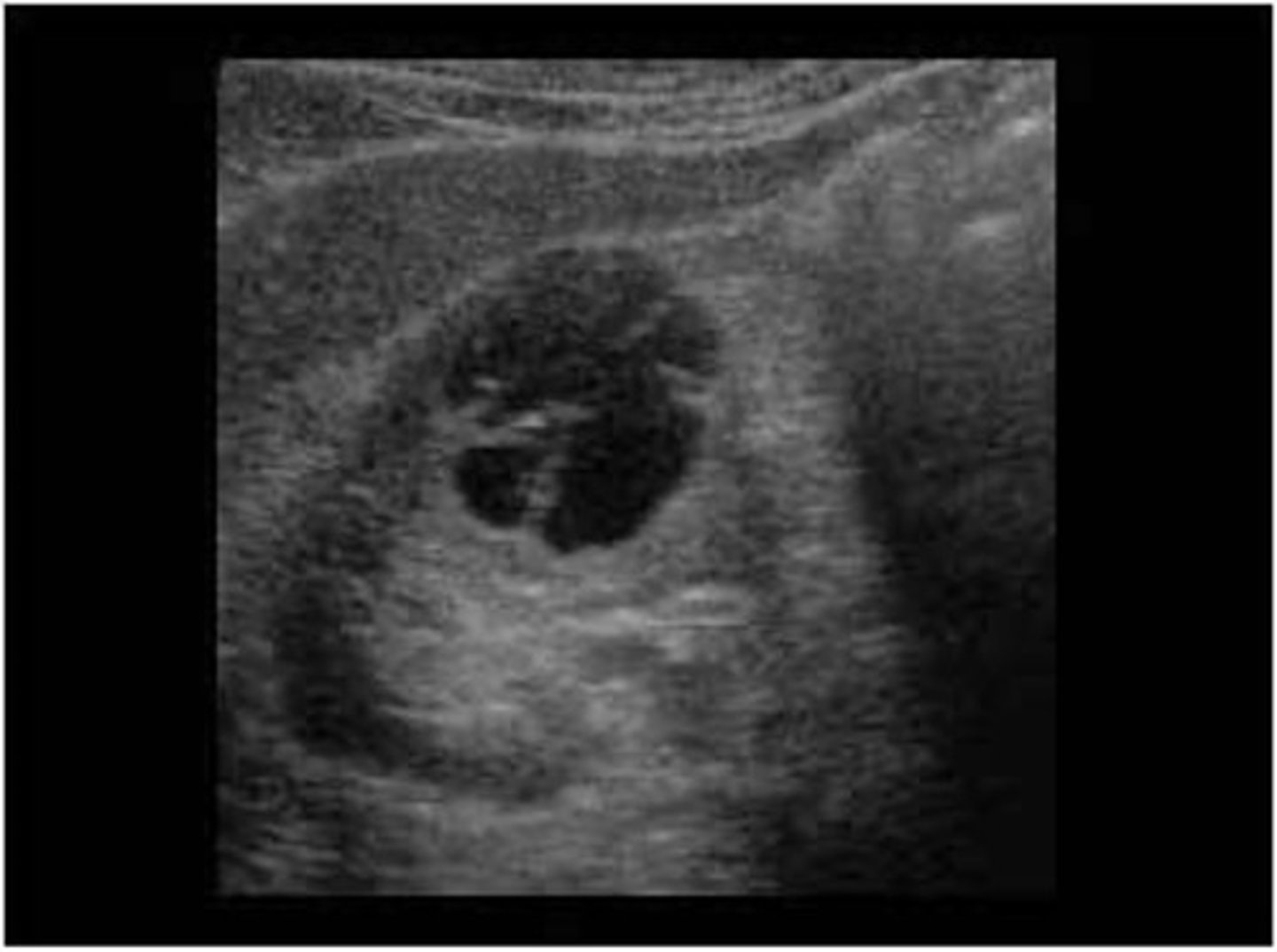
A complex cyst is normally the result of ___ or ___
hemorrhage; infection
A parapelvic cyst arises in the renal ___
hilum / sinus
Parapelvic cysts are usually ___
asymptomatic
What are symptoms of parapelvic cysts, if any?
- pain
- hypertension
- obstruction
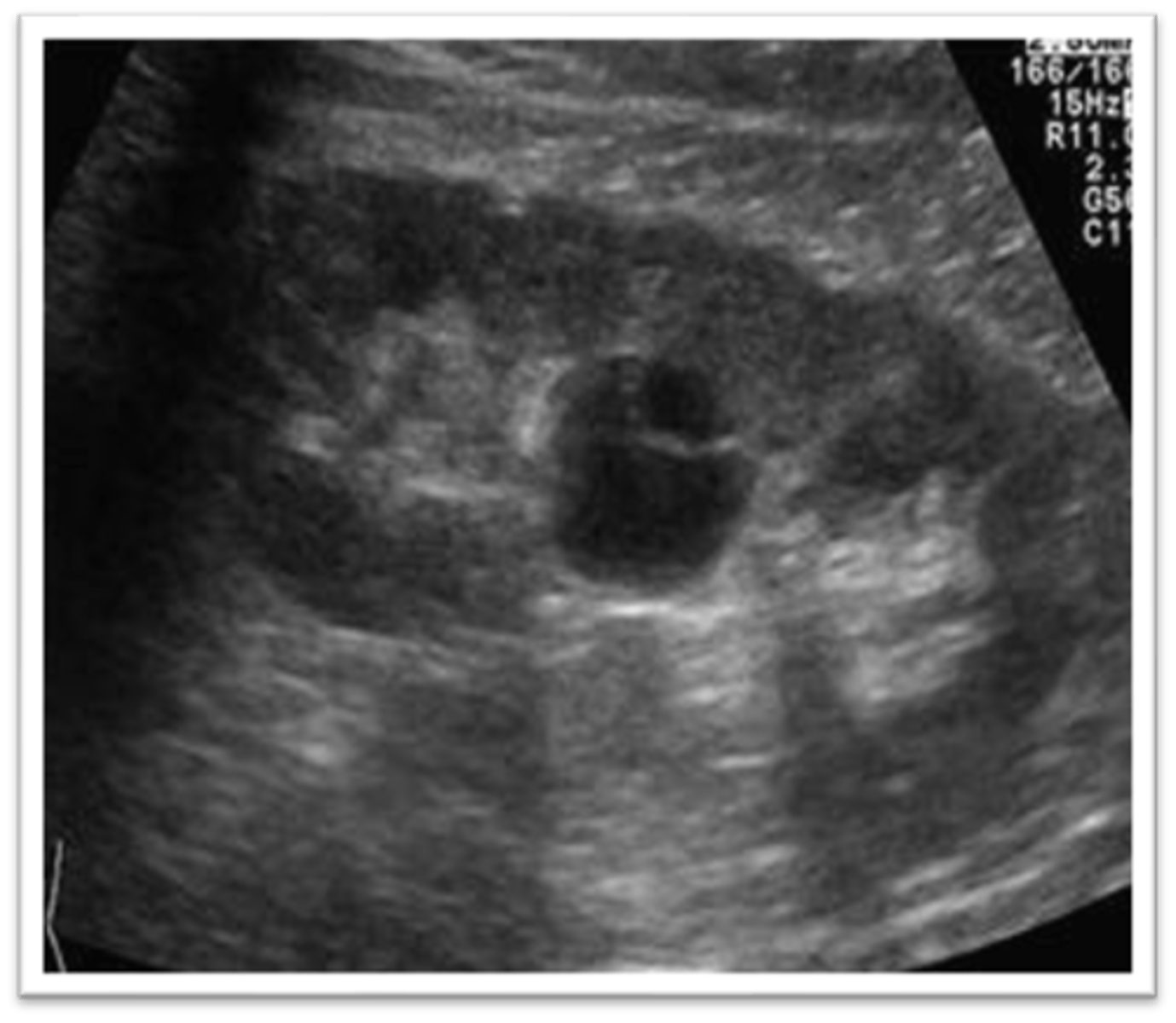
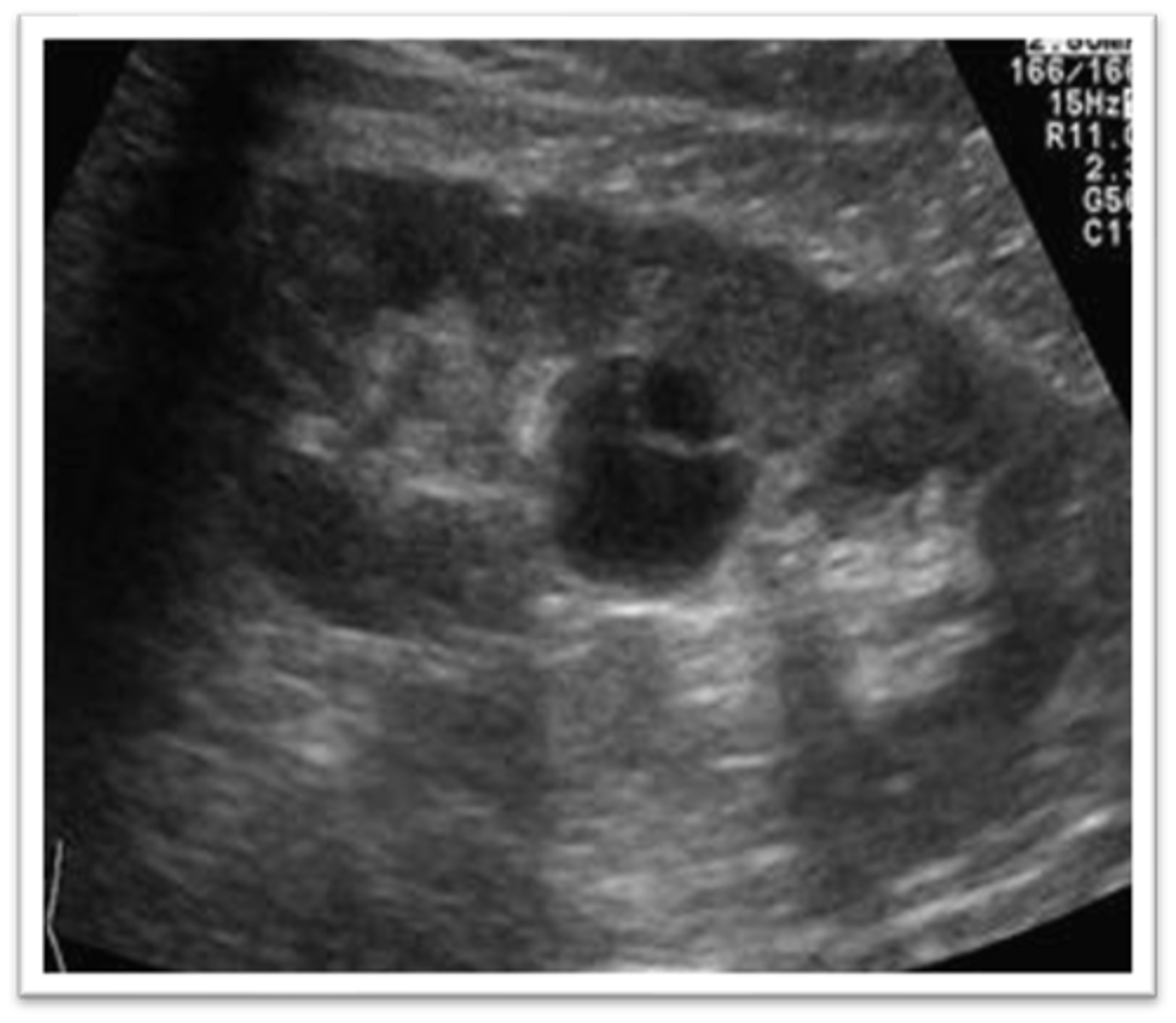
What are sonographic findings of a parapelvic cyst?
- no septations
- irregular borders
What is autosomal dominant genetic disorder that affects multiple areas of the body?
Von Hippel-Lindau disease
Patients with Von Hippel-Lindau disease have a high incidence of ___ and bilateral ___
renal cysts; RCC
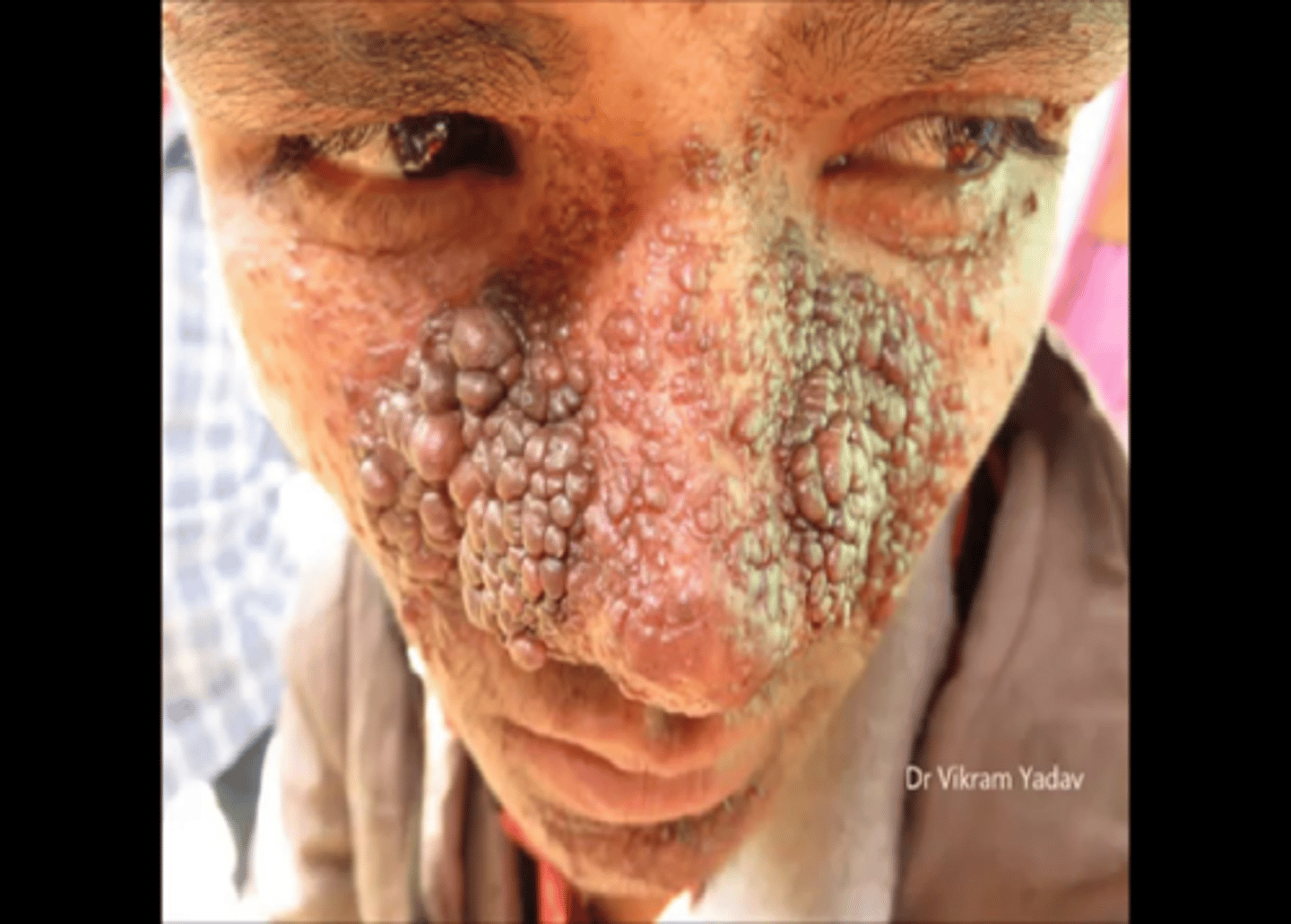
What is an autosomal dominant disorder causing benign tumors to grow on multiple organs?
tubular sclerosis
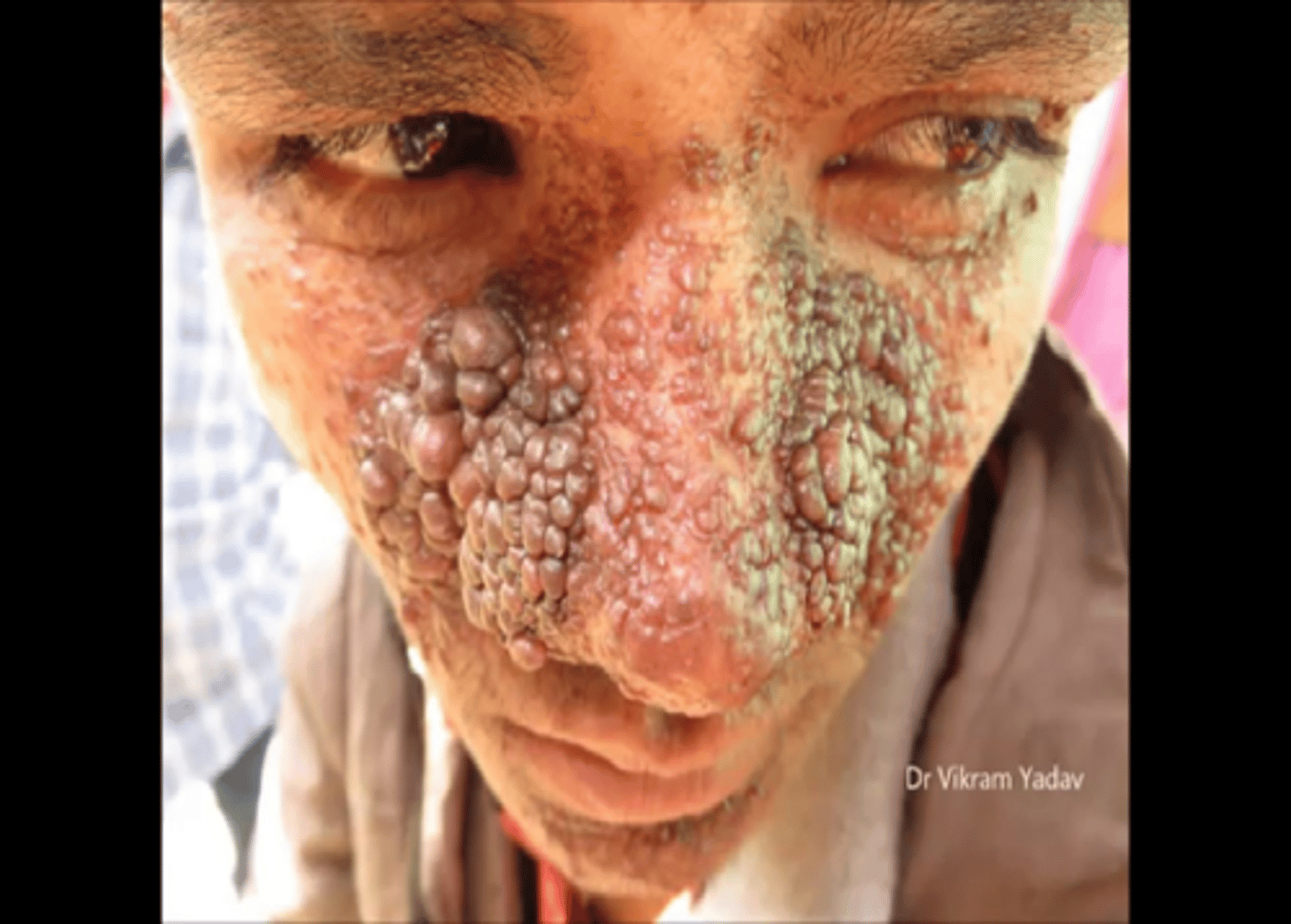
Tubular sclerosis causes ___, ___, and ___
seizures; mental deficiency; adenoma sebaceum
Tubular sclerosis is seen with renal ___ and ___
cysts; angiomyolipomas
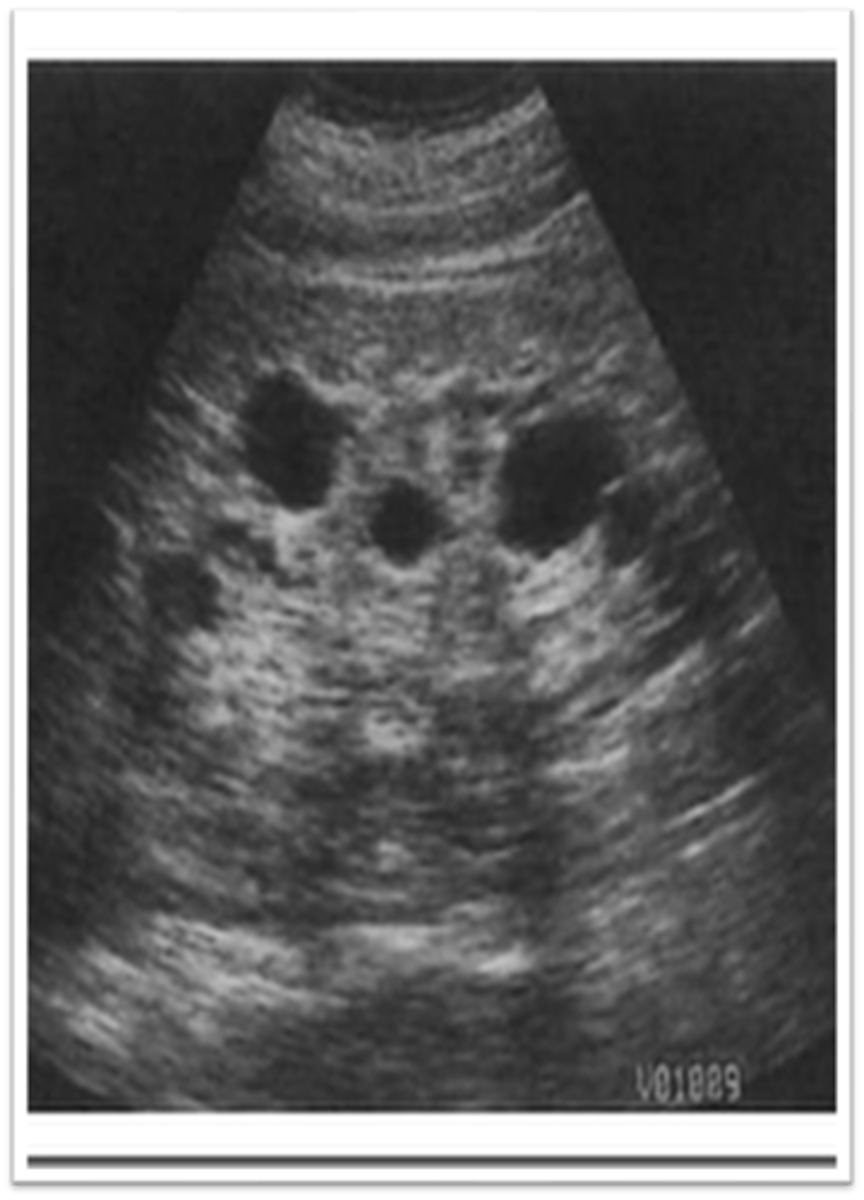
What is ACKD?
acquired cystic kidney disease
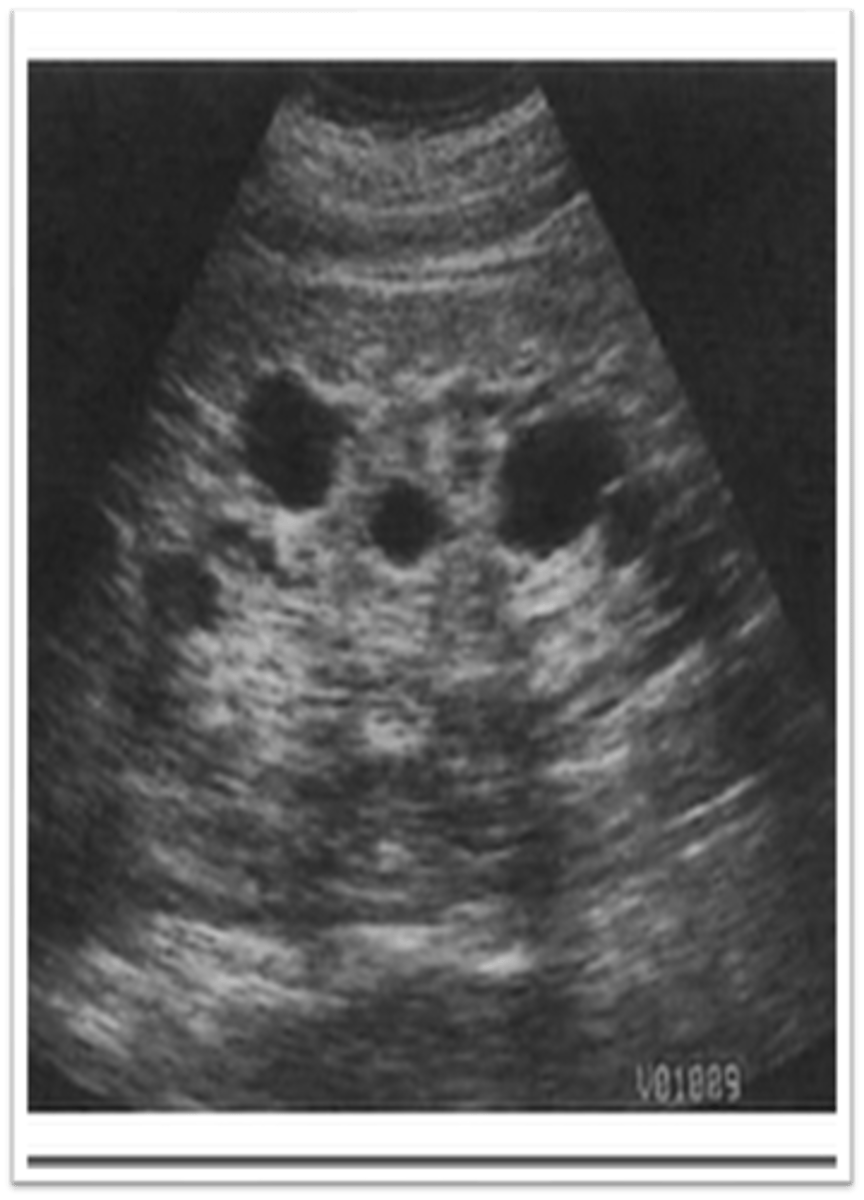
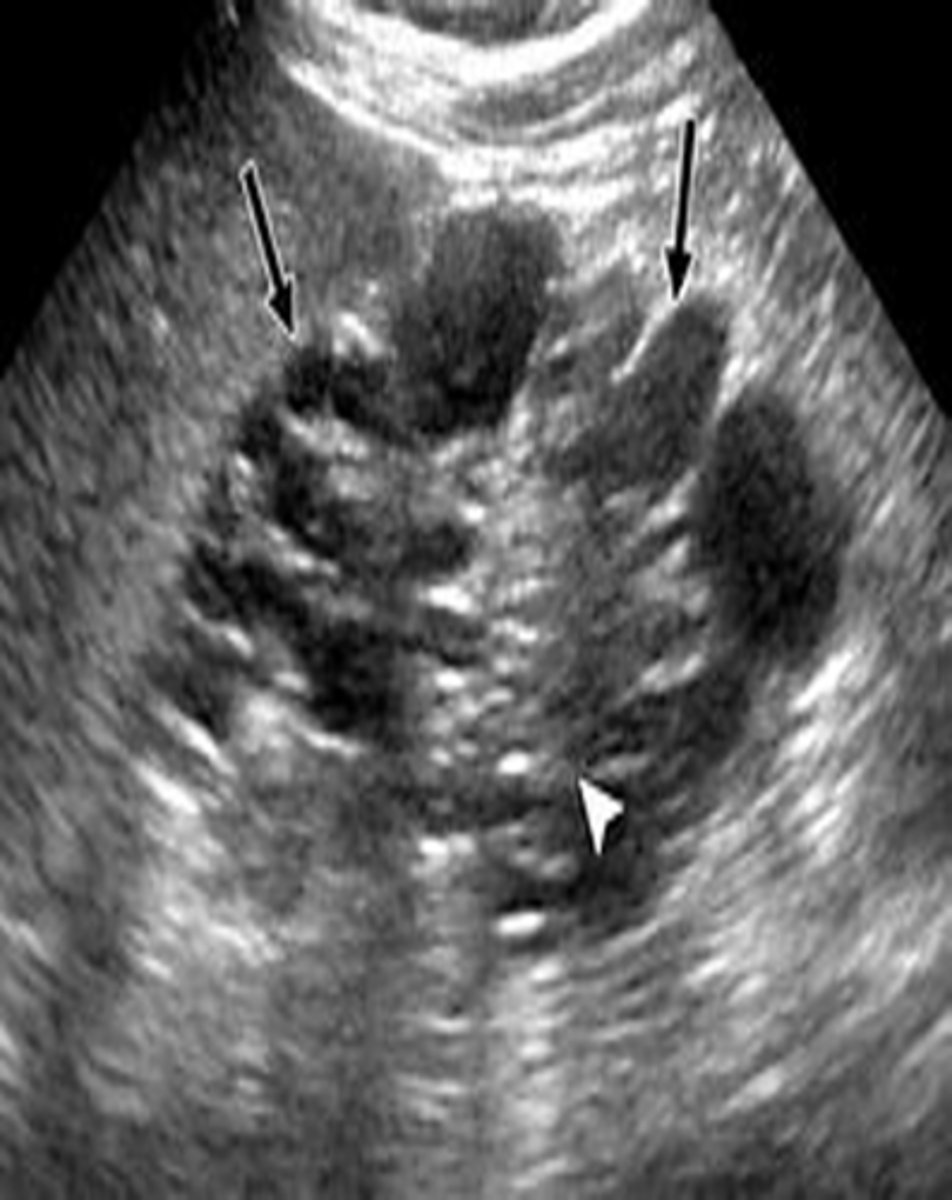
ACKD is found in patients in renal failure and on ___
dialysis
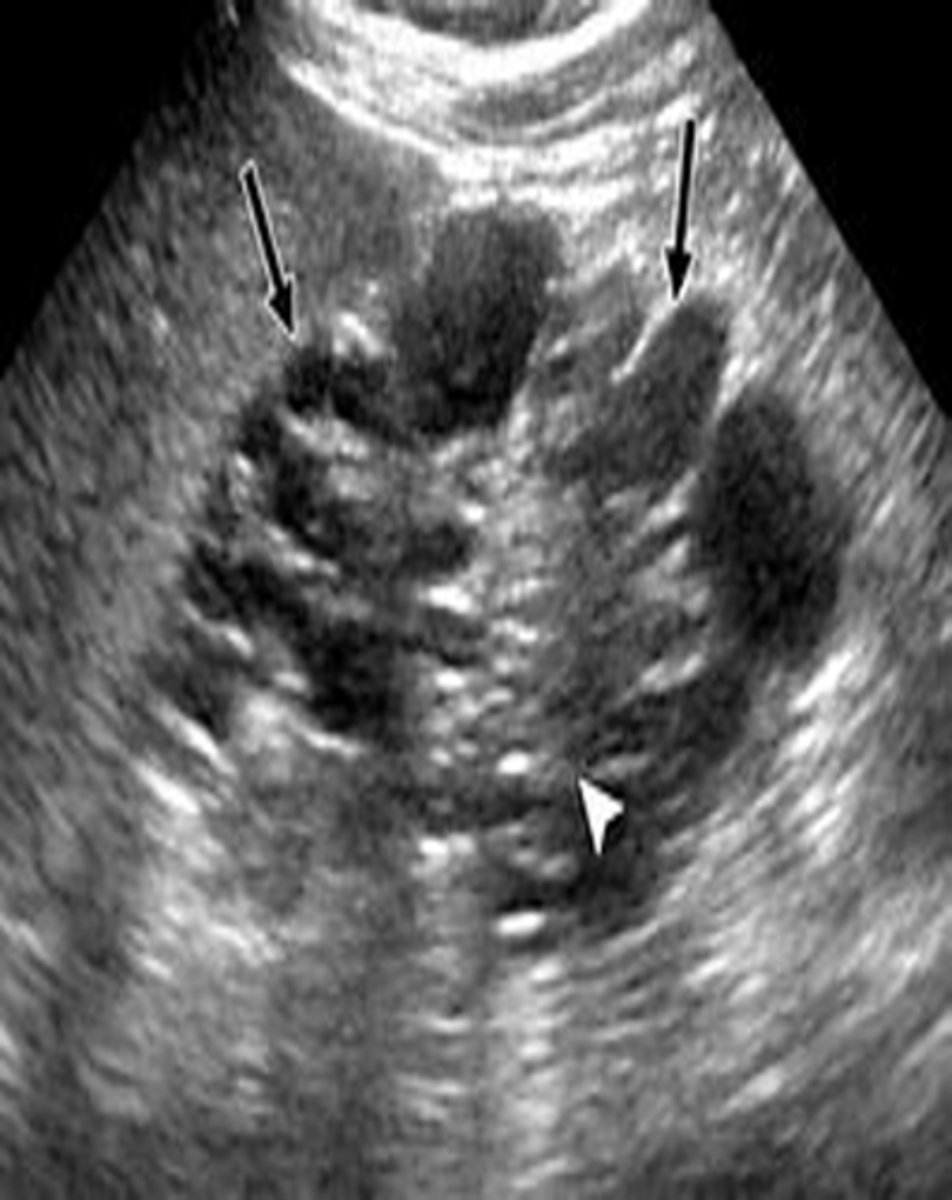
Dialysis increases incidence of ___, ___, and ___
cysts; adenomas; renal carcinoma
What is seen in up to 7% of patients with ACKD?
- adenomas
- oncocytomas
- RCC
Polycystic kidney disease has two forms: the infantile/juvenile autosomal ___ form and the adult autosomal ___ form
recessive; dominant
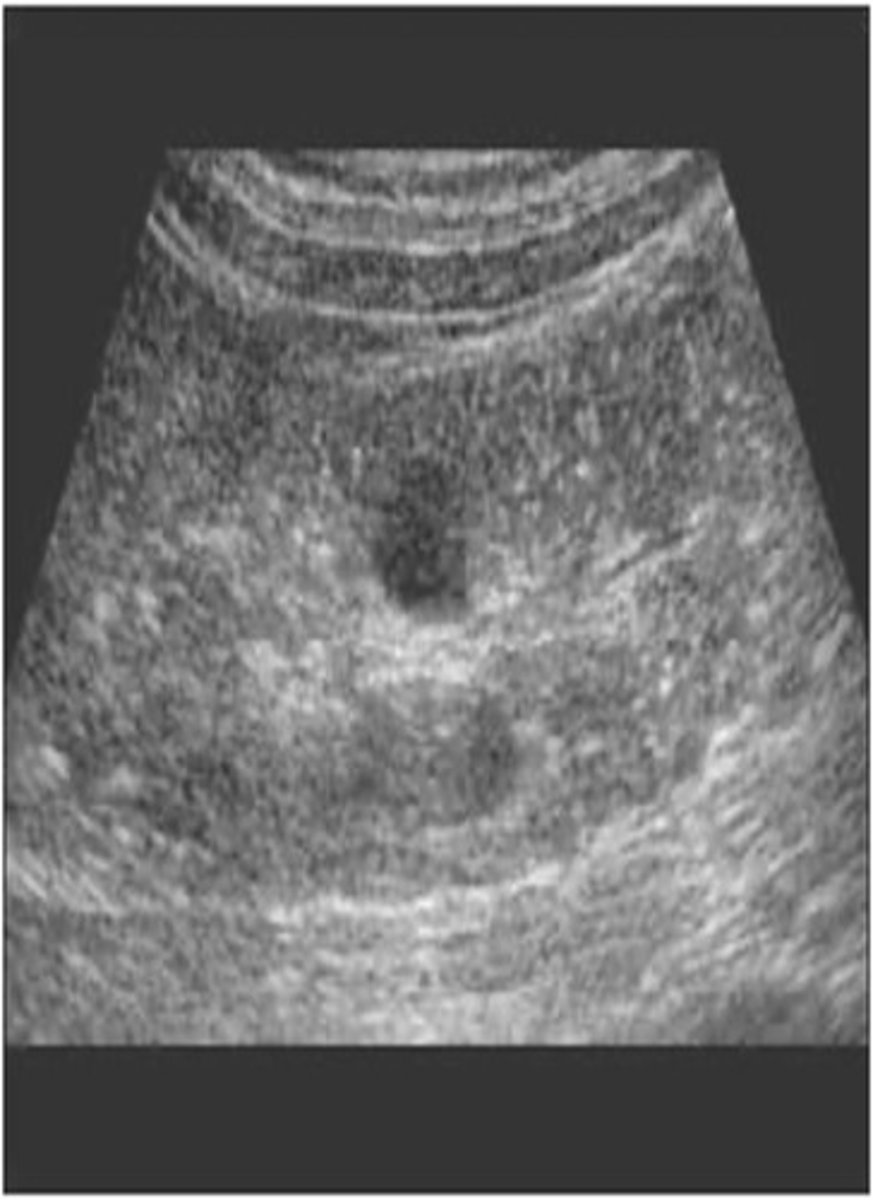
With infantile polycystic kidney disease, ___, ___ kidneys are seen in utero causing renal ___ and fetal ___
enlarged; echogenic; failure; demise
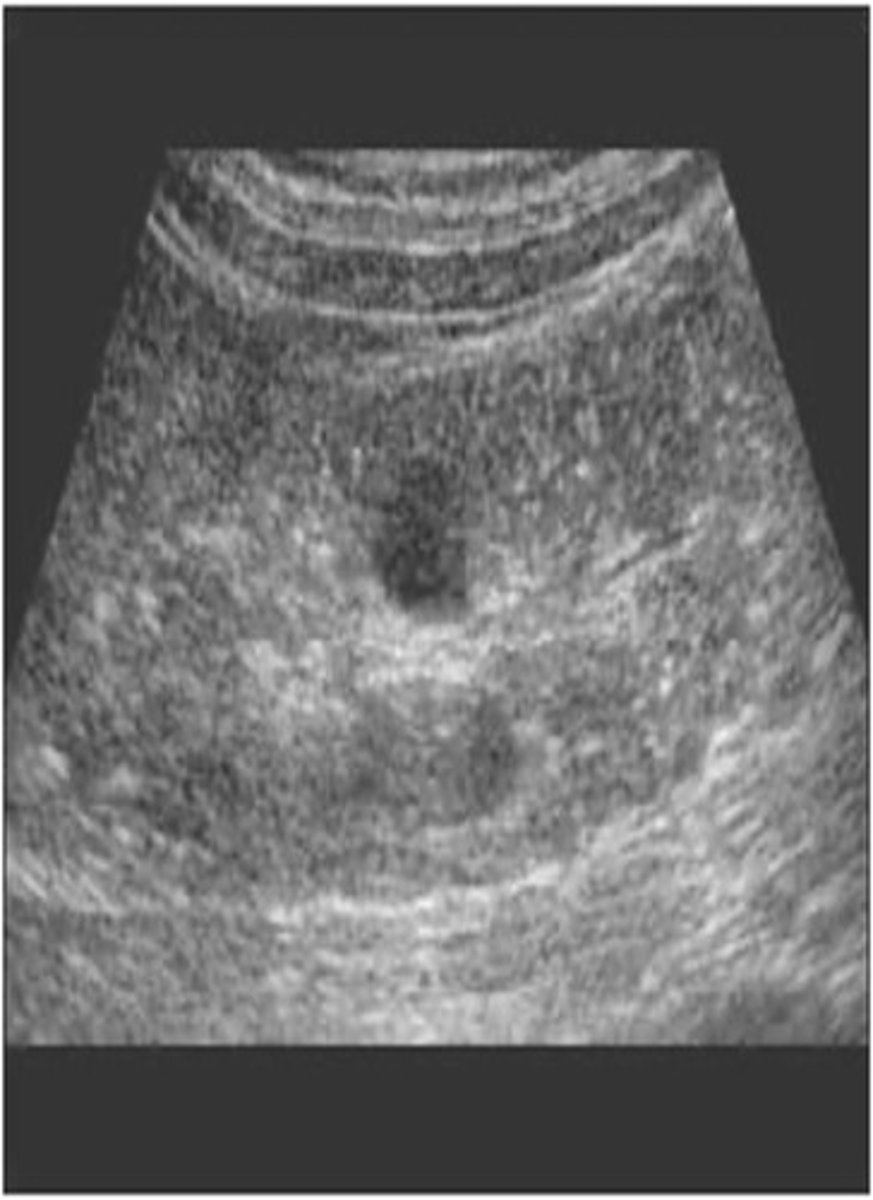
What form of polycystic renal disease is associated with microscopic renal cysts?
infantile
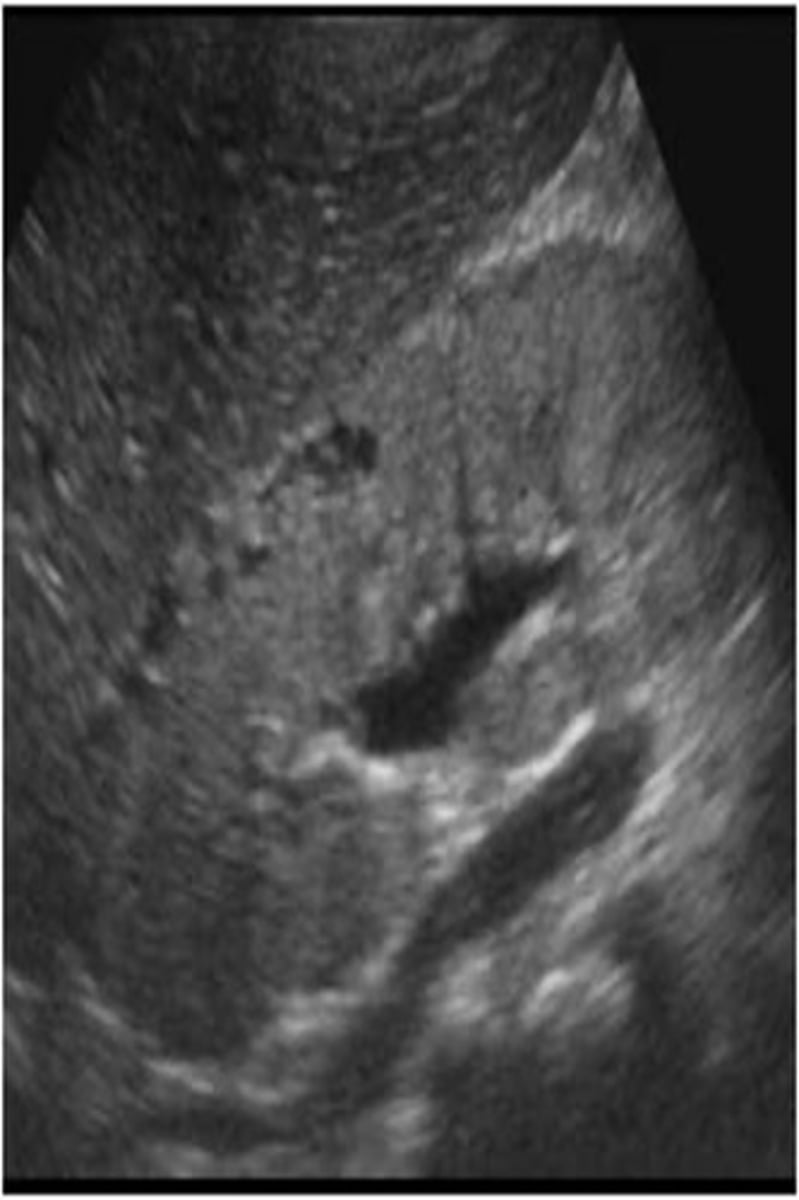
What form of polycystic renal disease is associated with hypertension, renal insufficiency, hepatic cysts, Caroli disease, bile duct proliferation, periportal fibrosis, portal varices, and nephromegaly?
juvenile
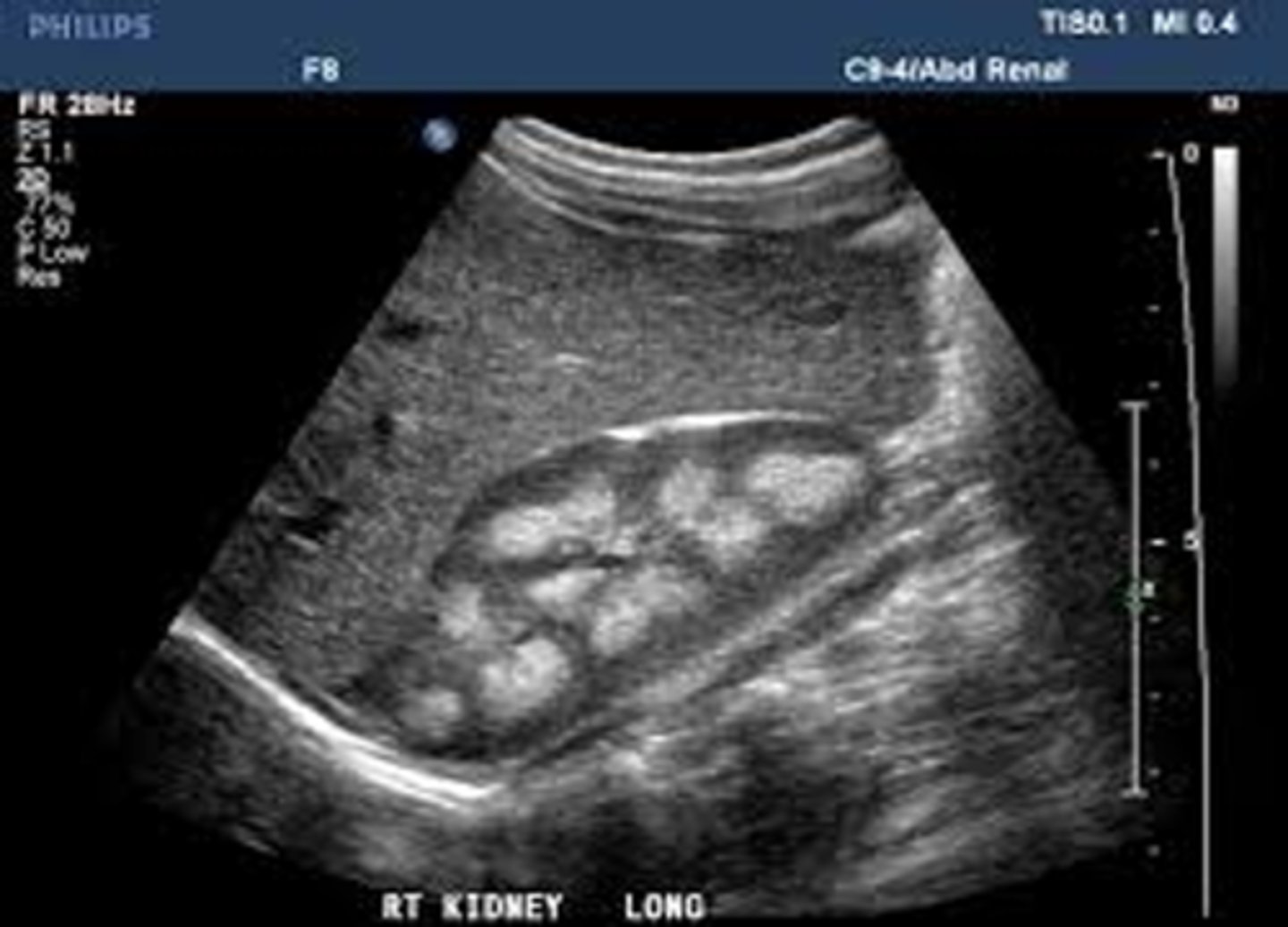
What form of polycystic renal disease is bilateral and associated with enlarged kidneys, spontaneous bleeding, and kidney tissue completely replaced by cysts?
adult (ADPKD)
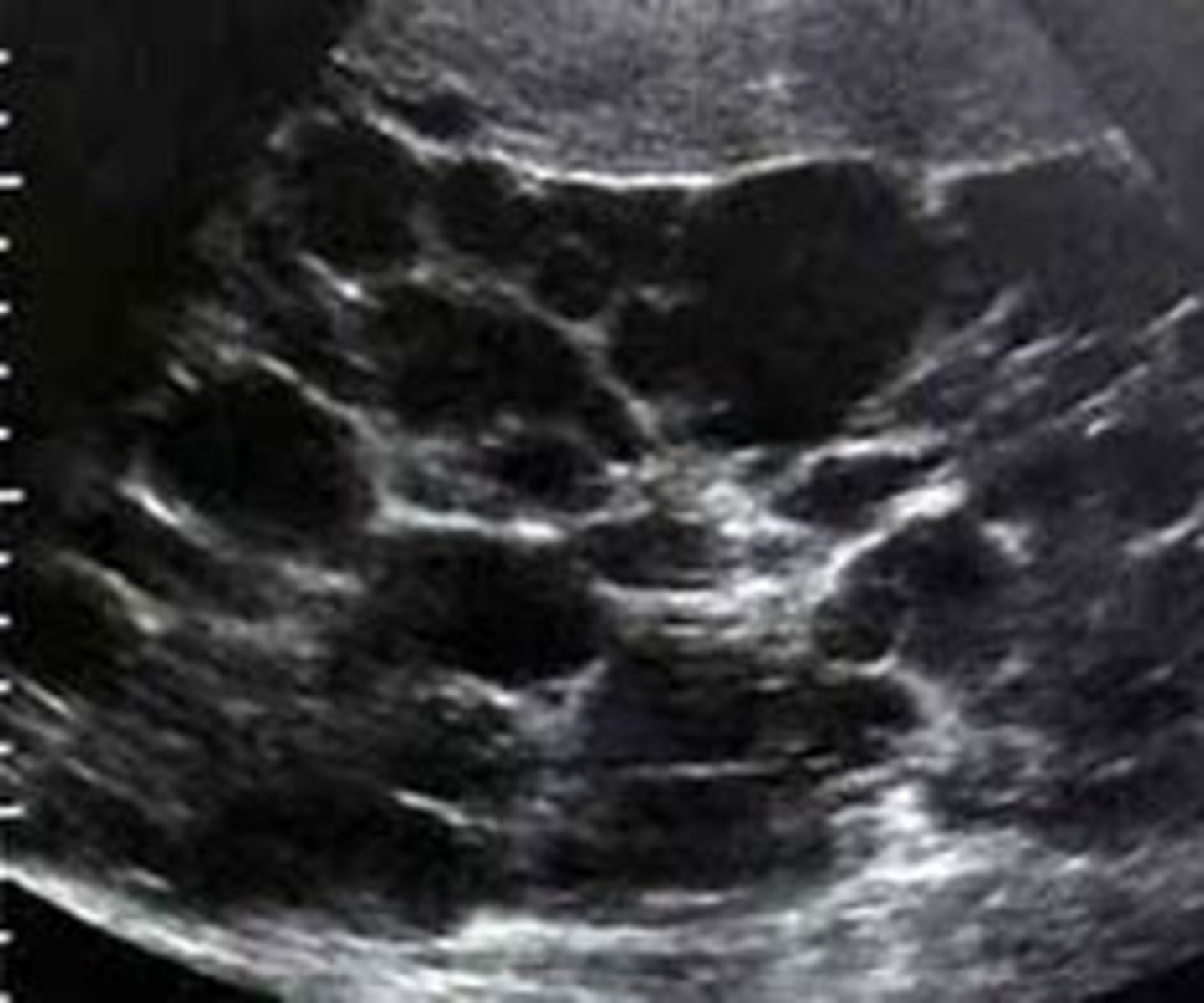
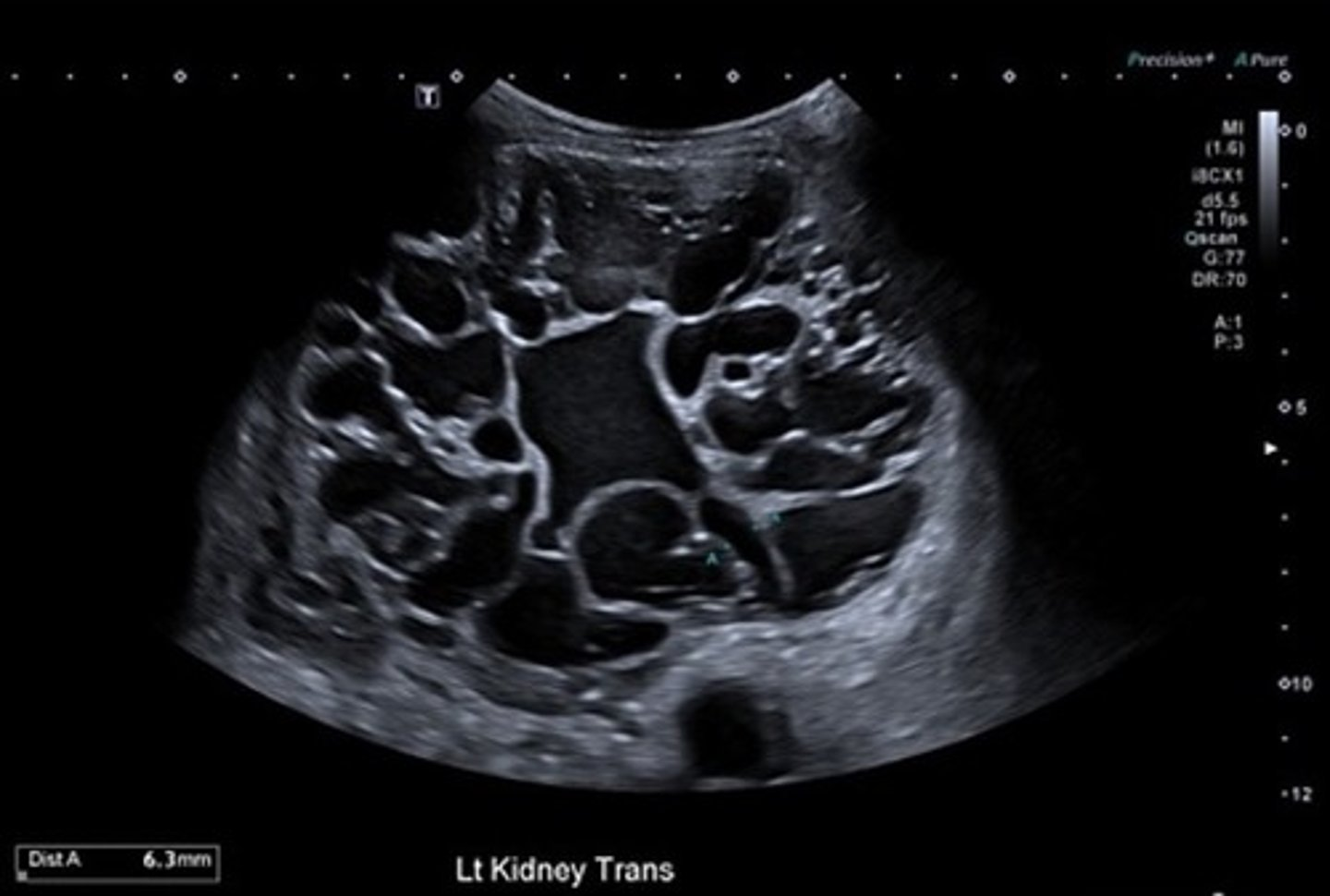
What are sonographic findings of polycystic kidney disease?
- diffusely enlarged kidneys
- multiple cysts of varying size
- loss of shape
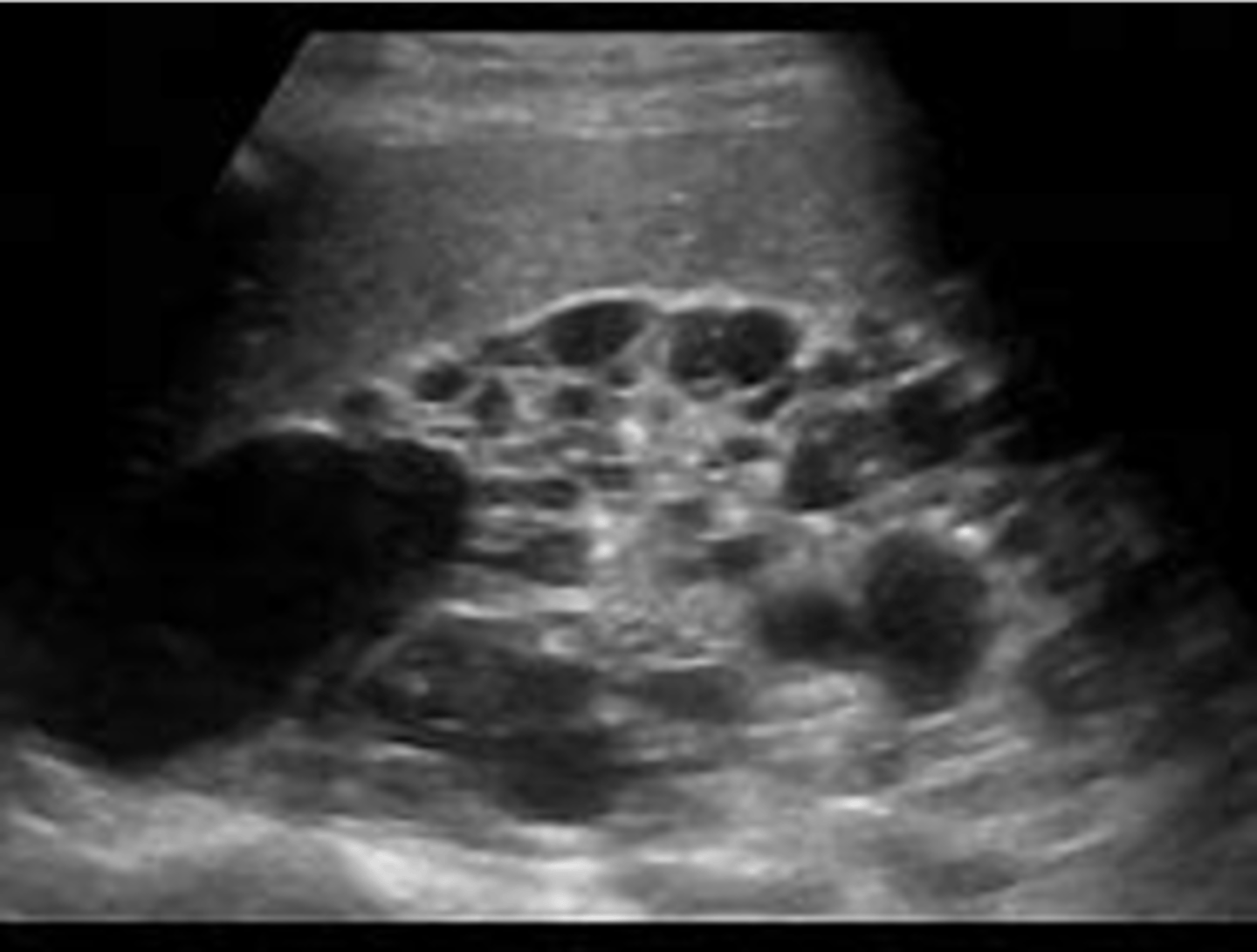
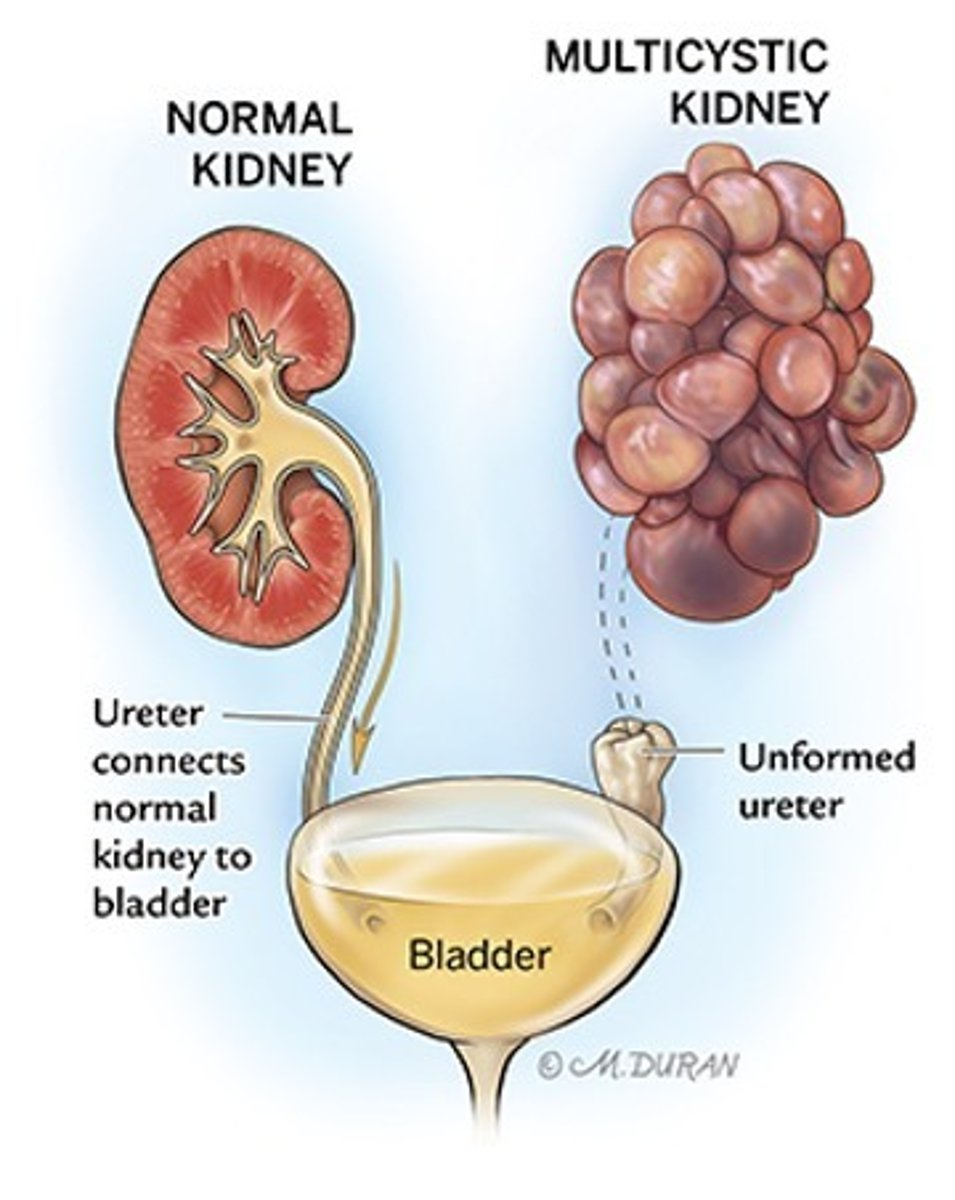
What is the most common form of cystic disease in neonates?
multicystic dysplastic kidney disease (MCDK)
Is MCDK hereditary?
no, nonhereditary
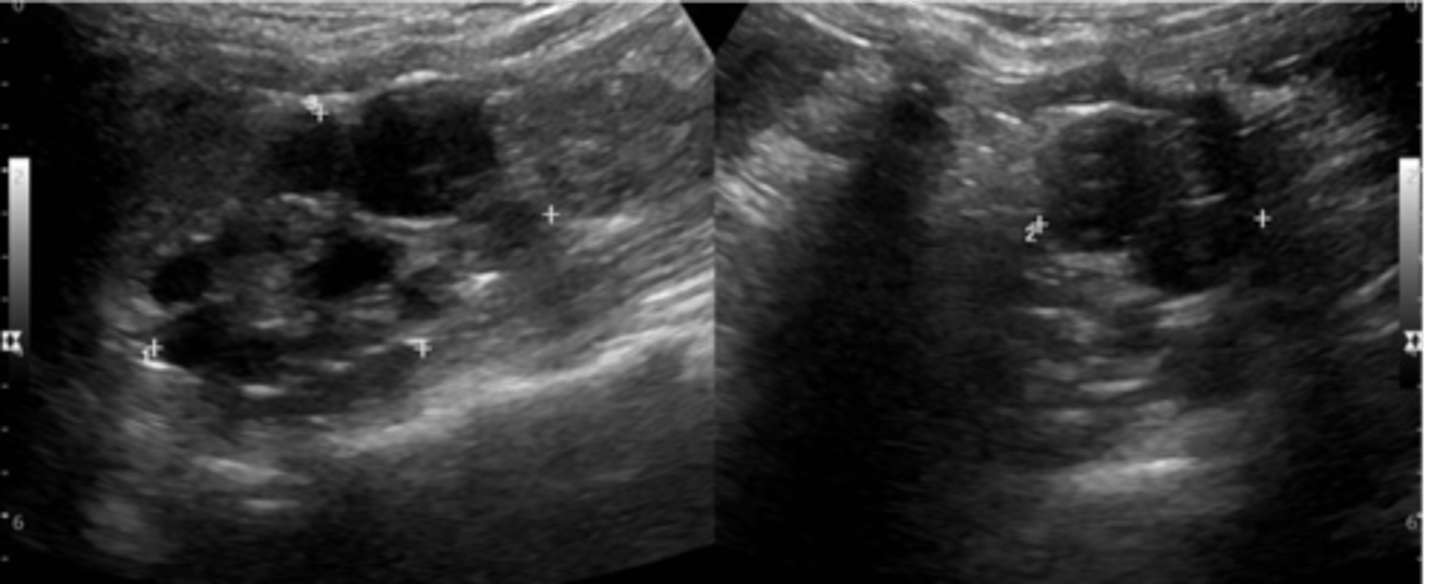
MCDK appears as multiple ___ cysts of varying sizes with no ___ seen
non-communicating; parenchyma
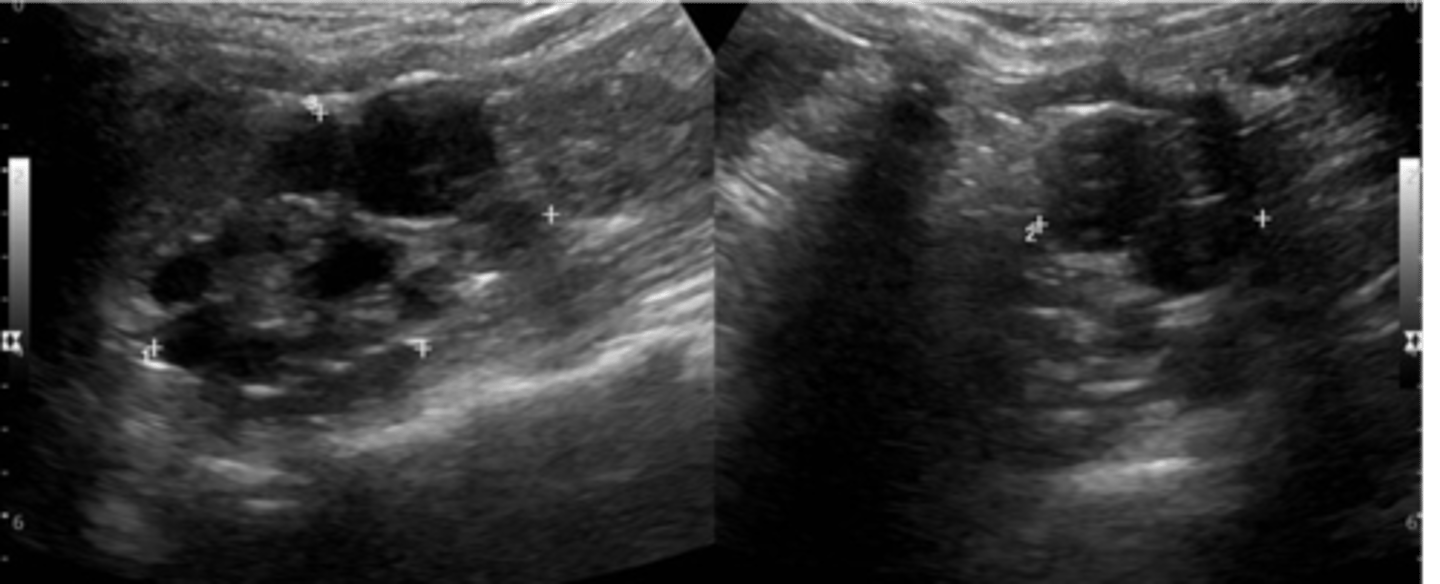
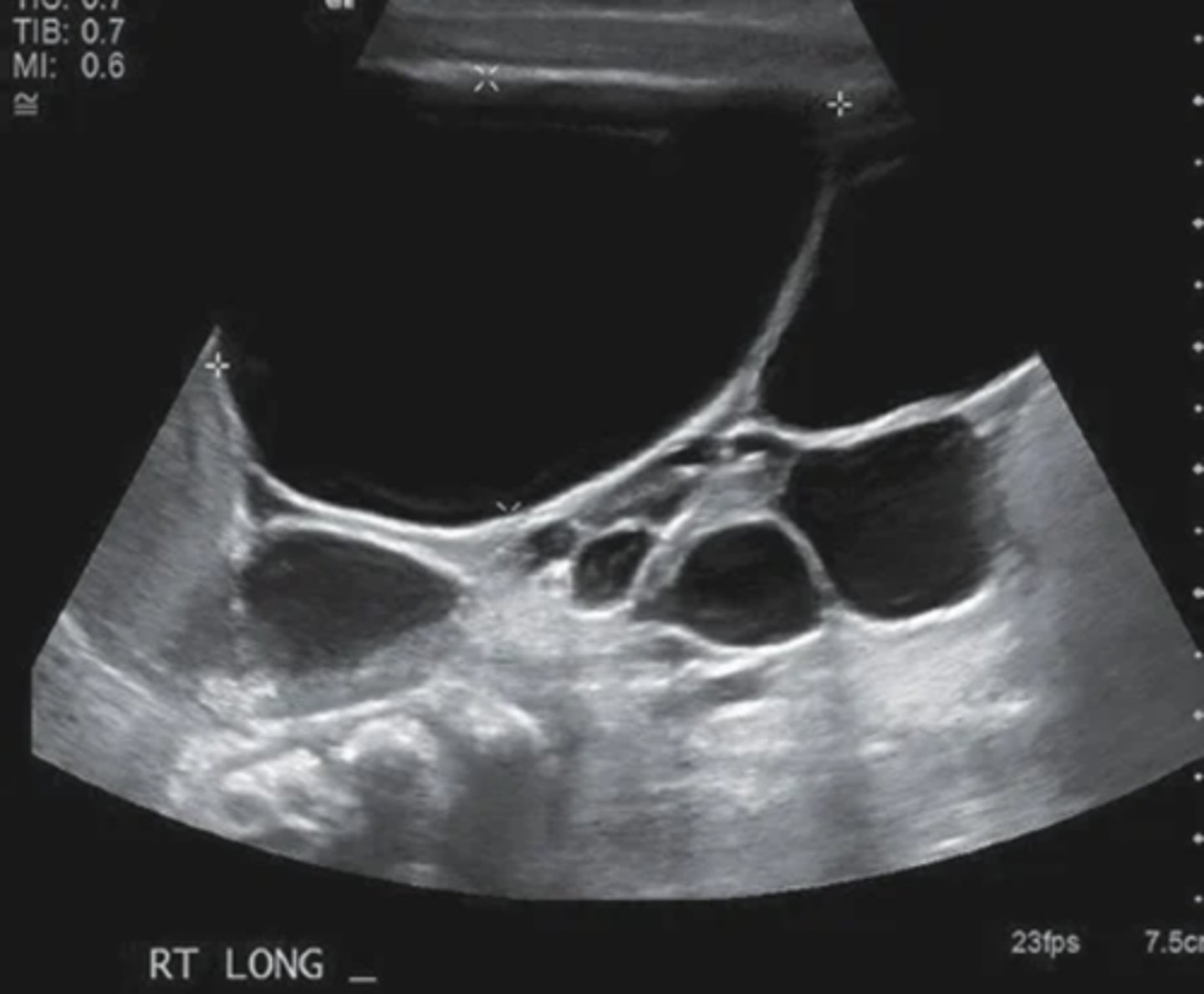
MCDK is associated with:
- ureteral atresia
- contralateral UPJ
- nonfunctioning kidney
- absent renal artery
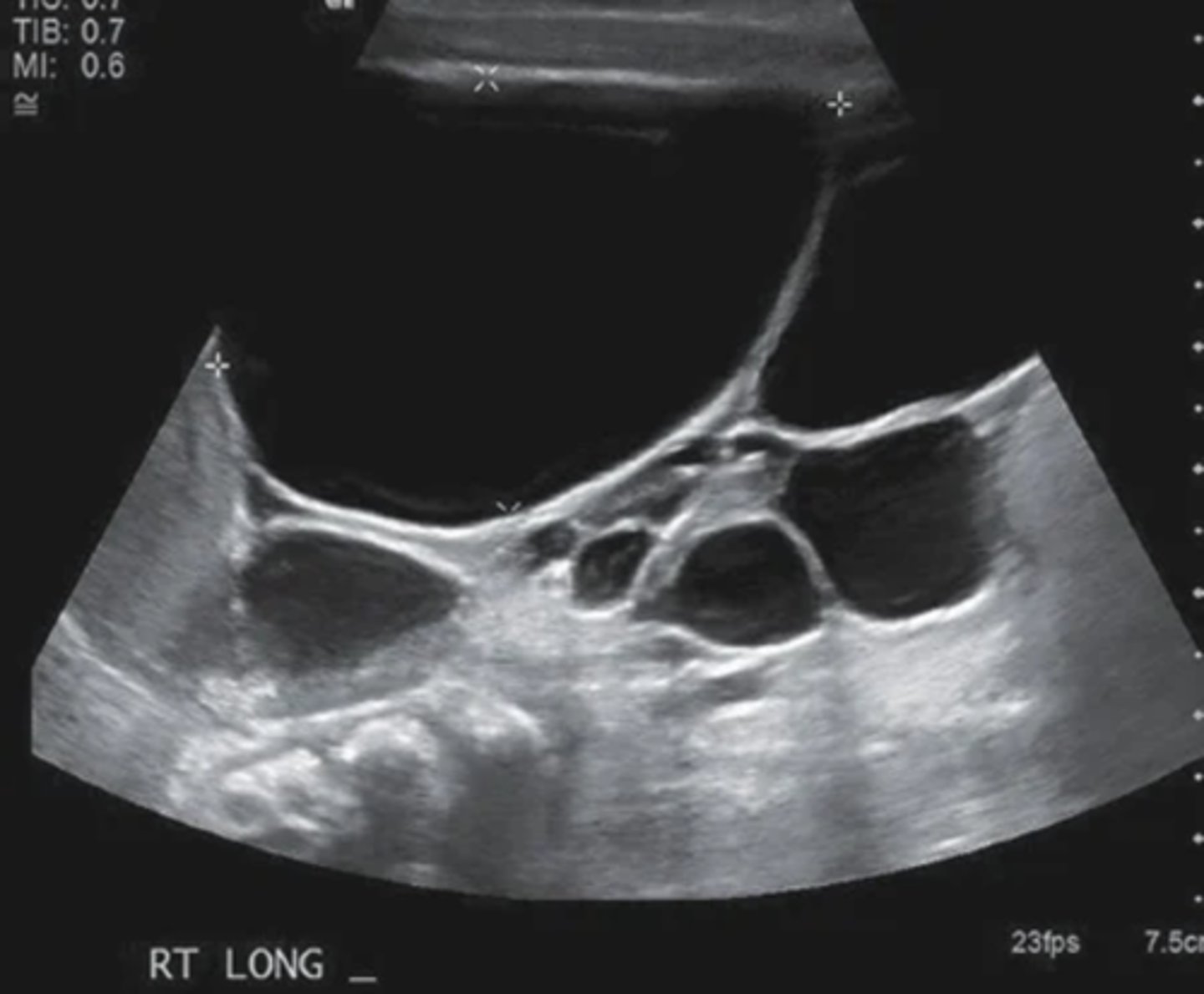
___ MCDK is incompatible with life
bilateral
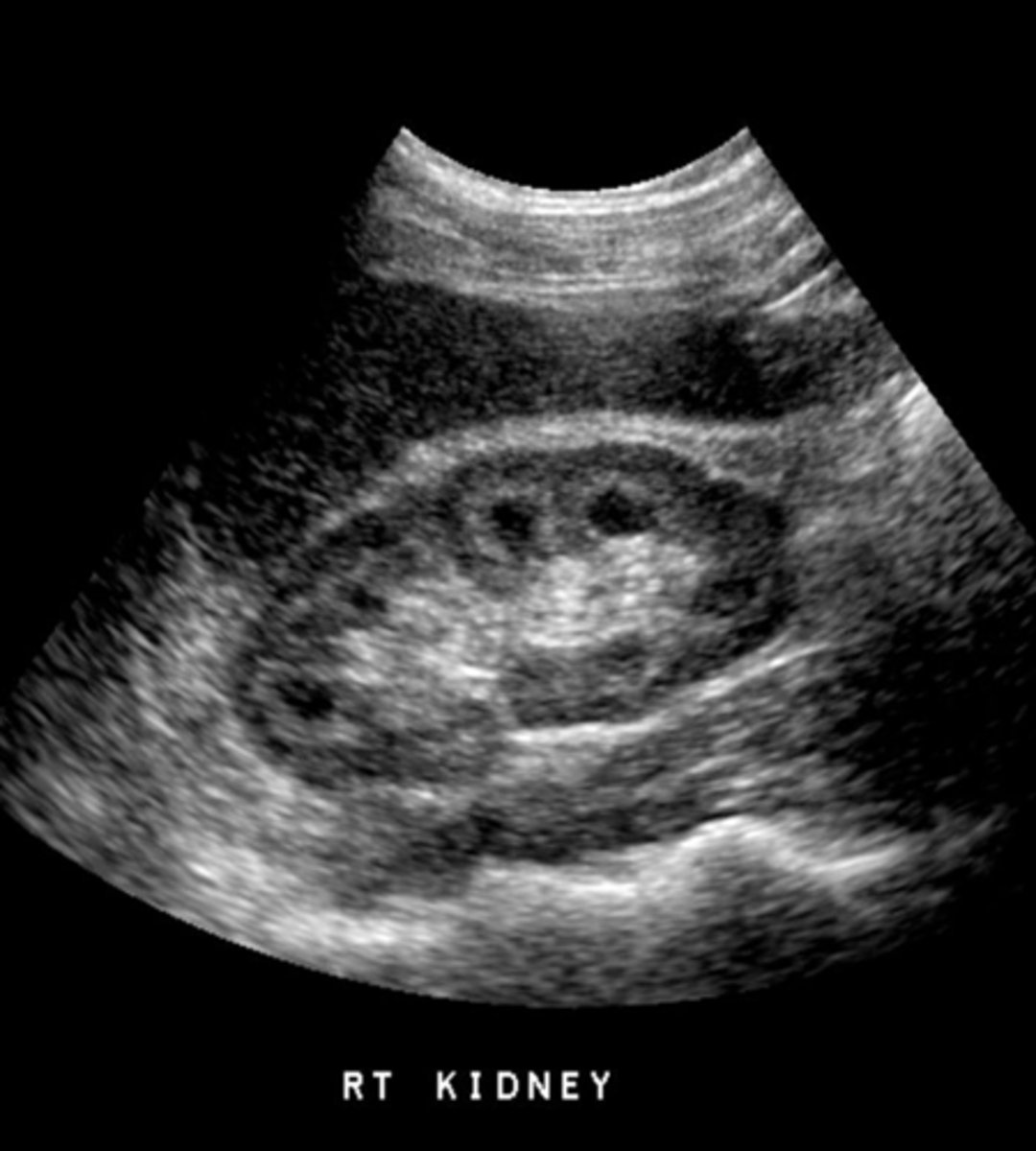
Medullary cystic disease is also called:
medullary sponge kidney (MSK)
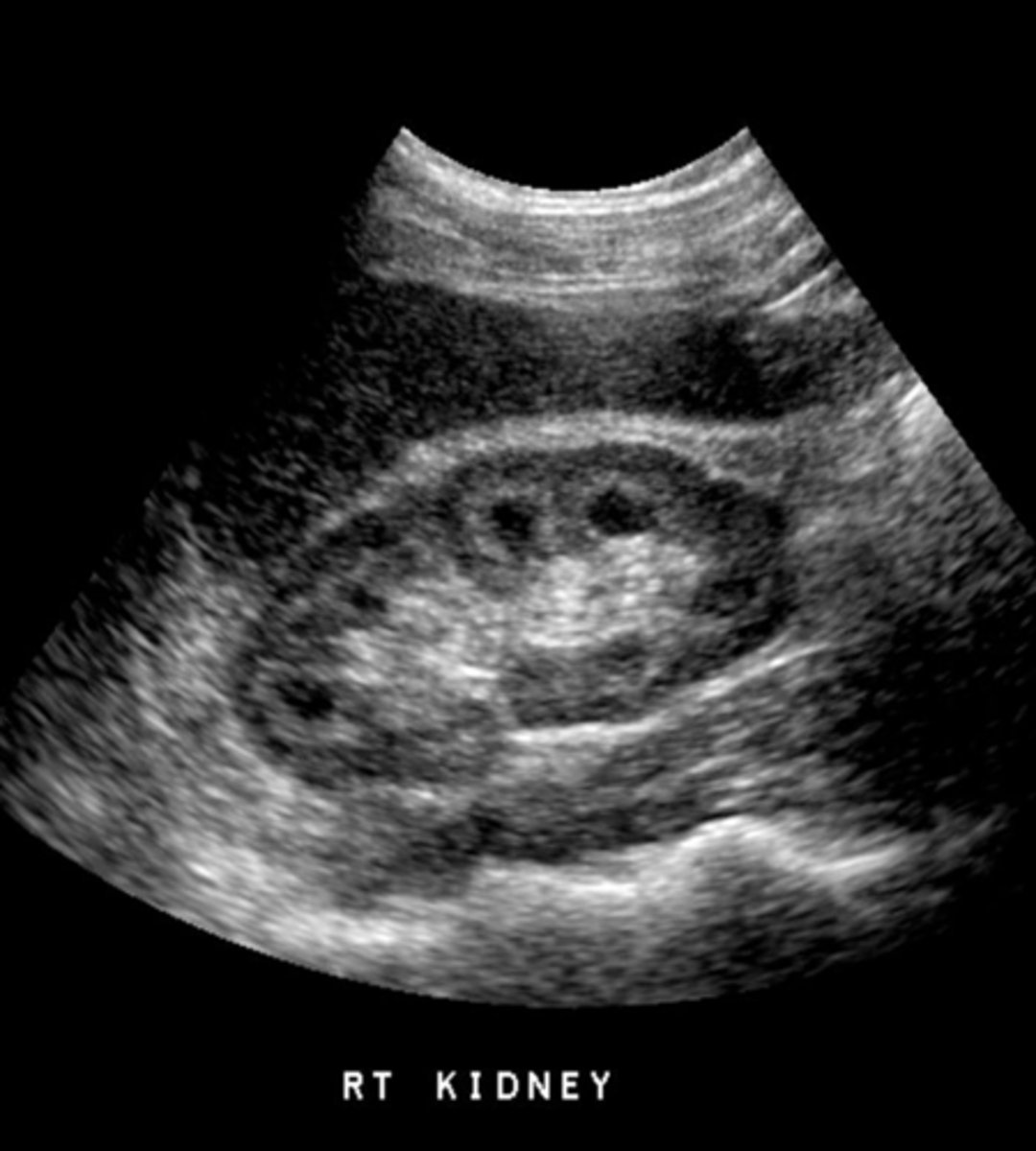
MSK is a development anomaly that occurs in the medullary pyramids and consists of ___ dilation of the distal collecting ___
fusiform; ducts
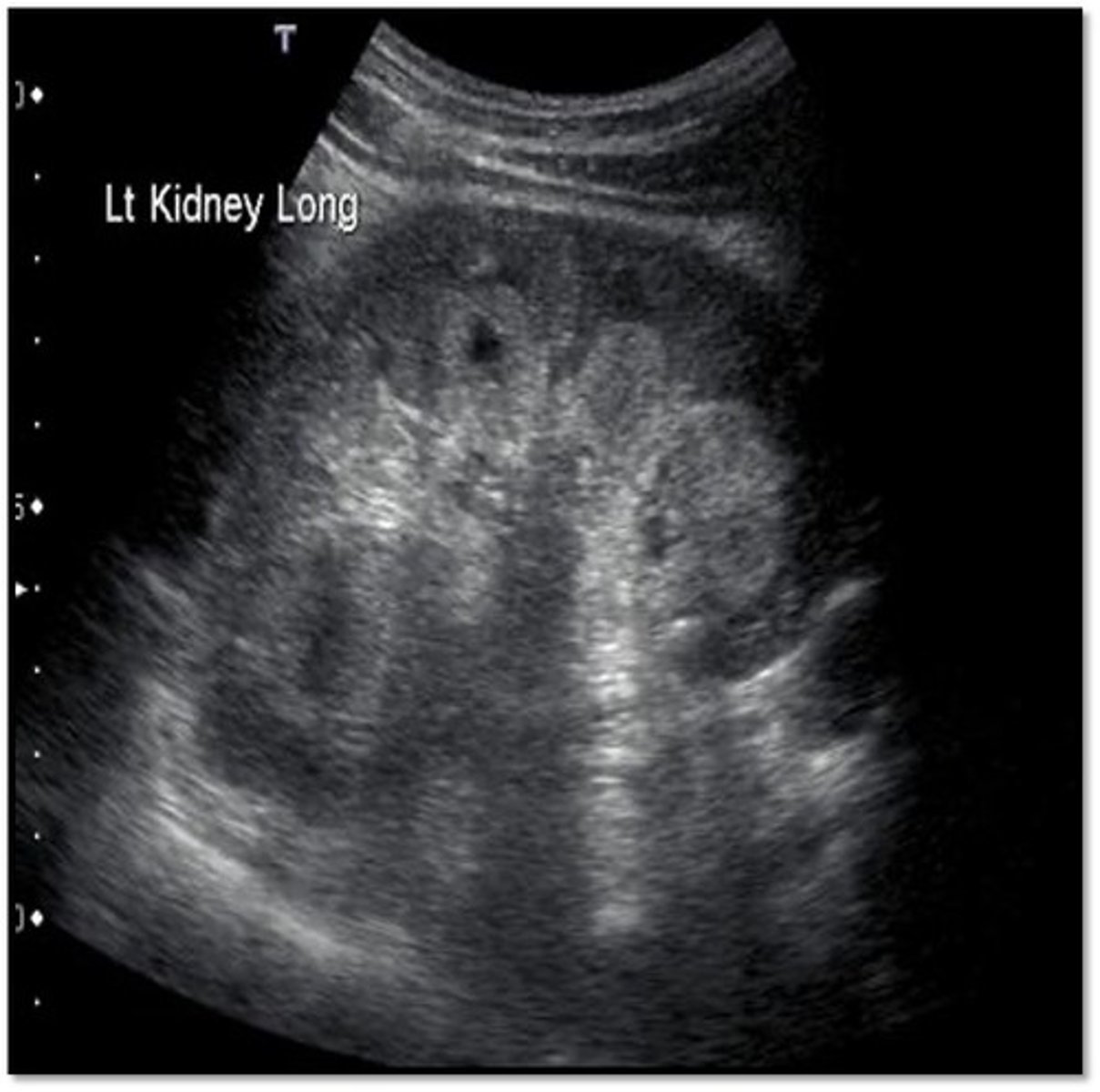
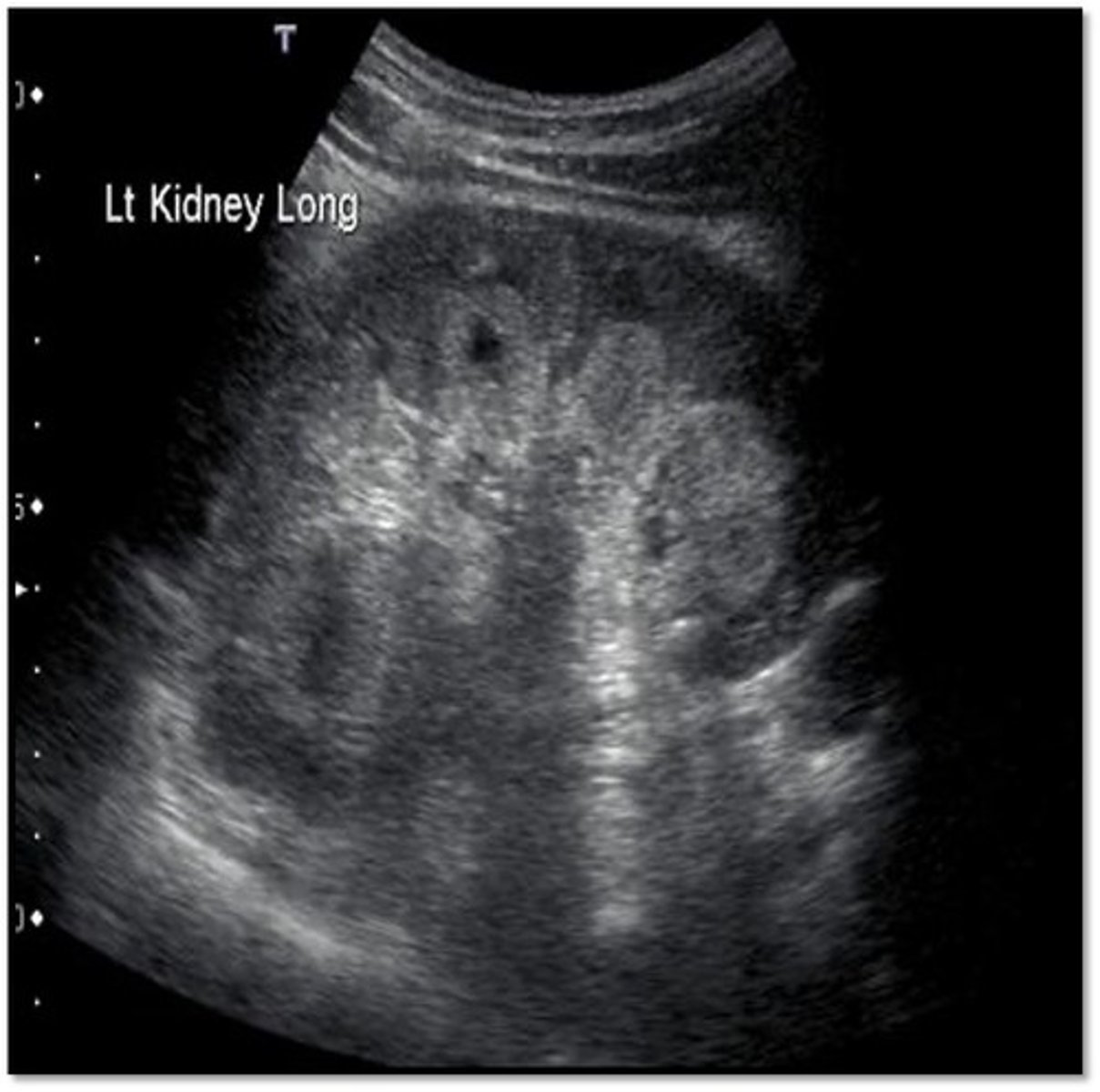
MSK causes ___ and ___
urine stasis; stone formation
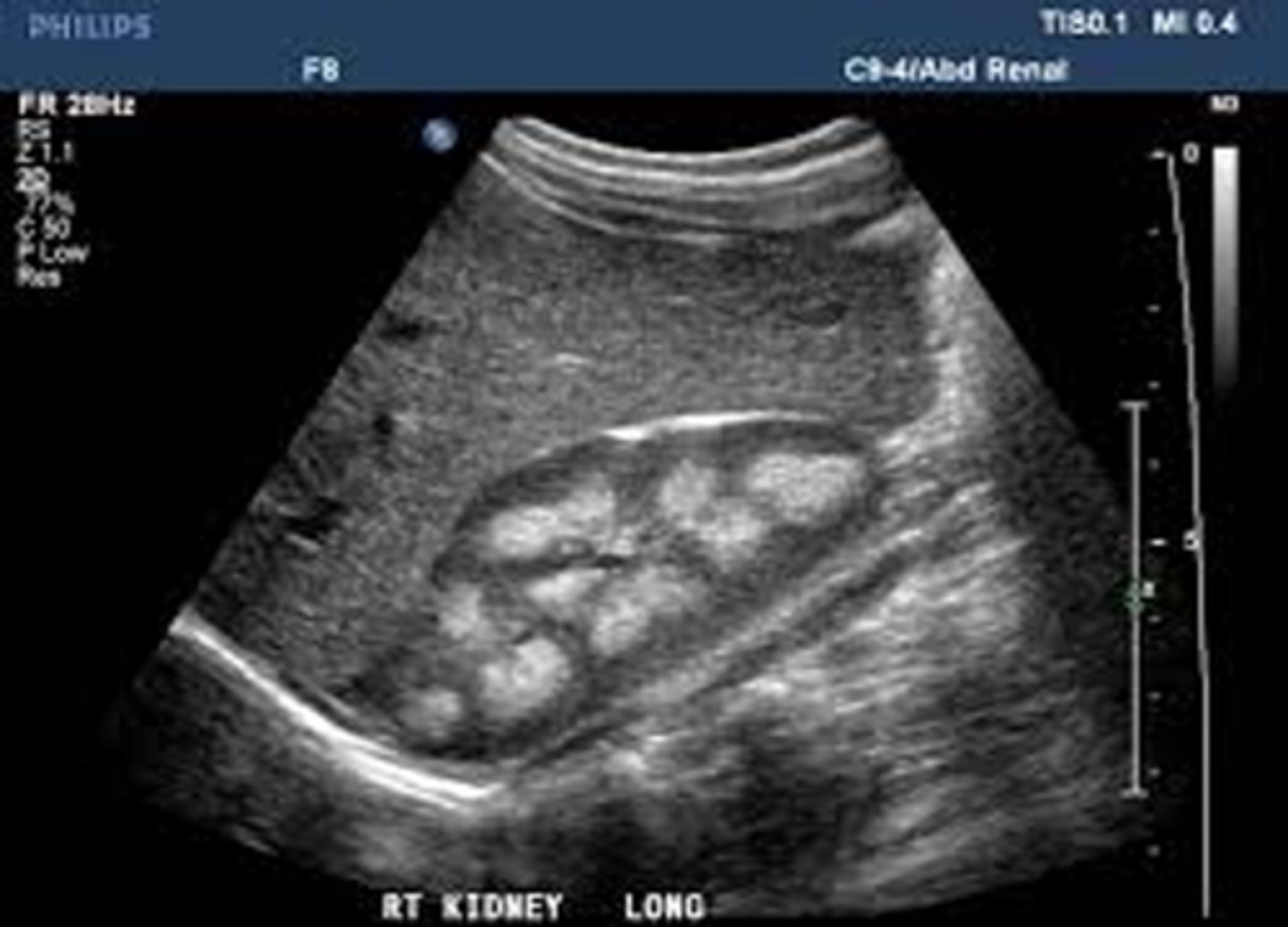
MSK is ___ and has an unknown ___
nonhereditary; etiology
What diseases is MSK associated with?
- Caroli's disease
- PKD
- Beckwith-Wiedemann
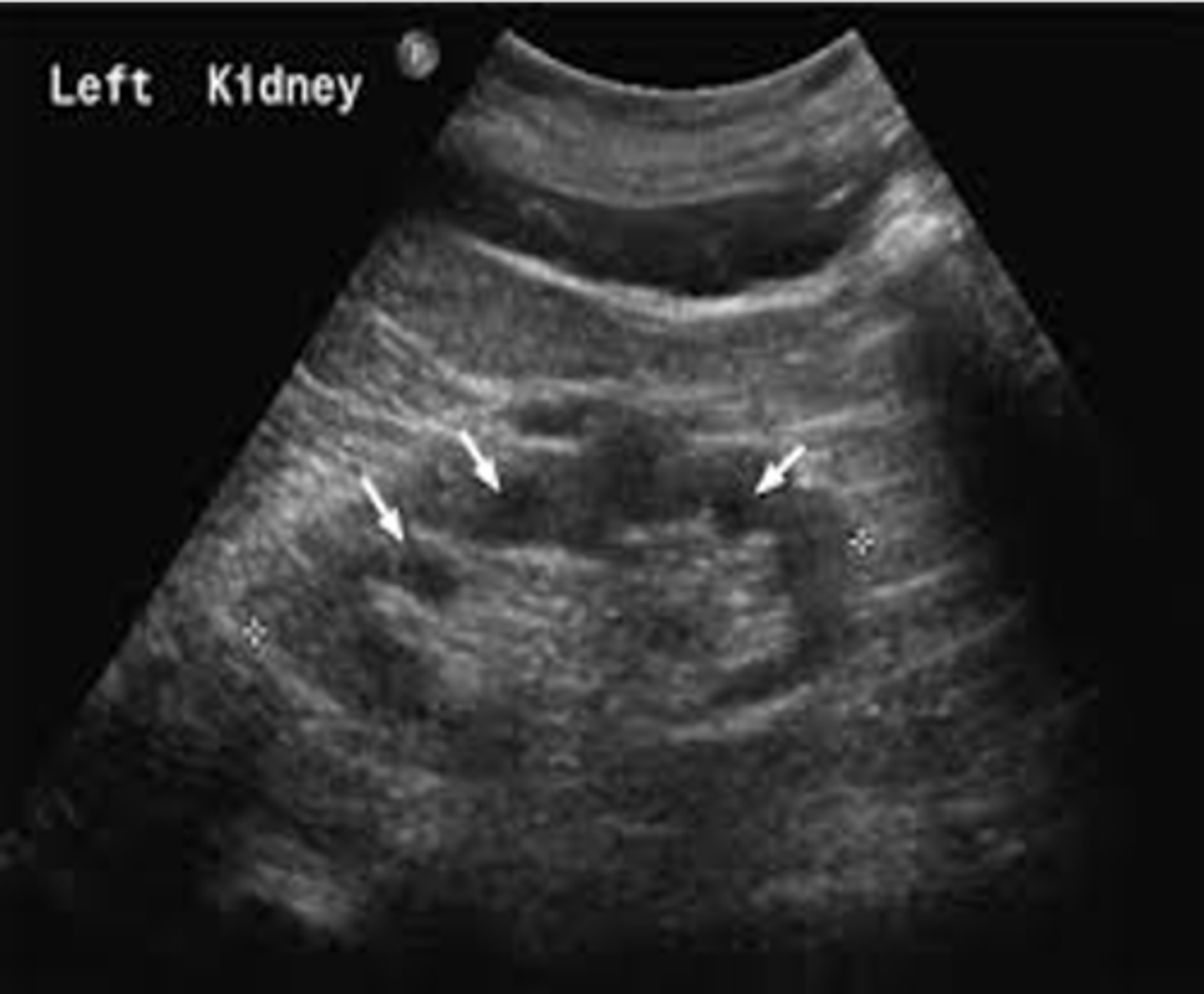
Nephronophthisis (NPH) is autosomal ___
recessive
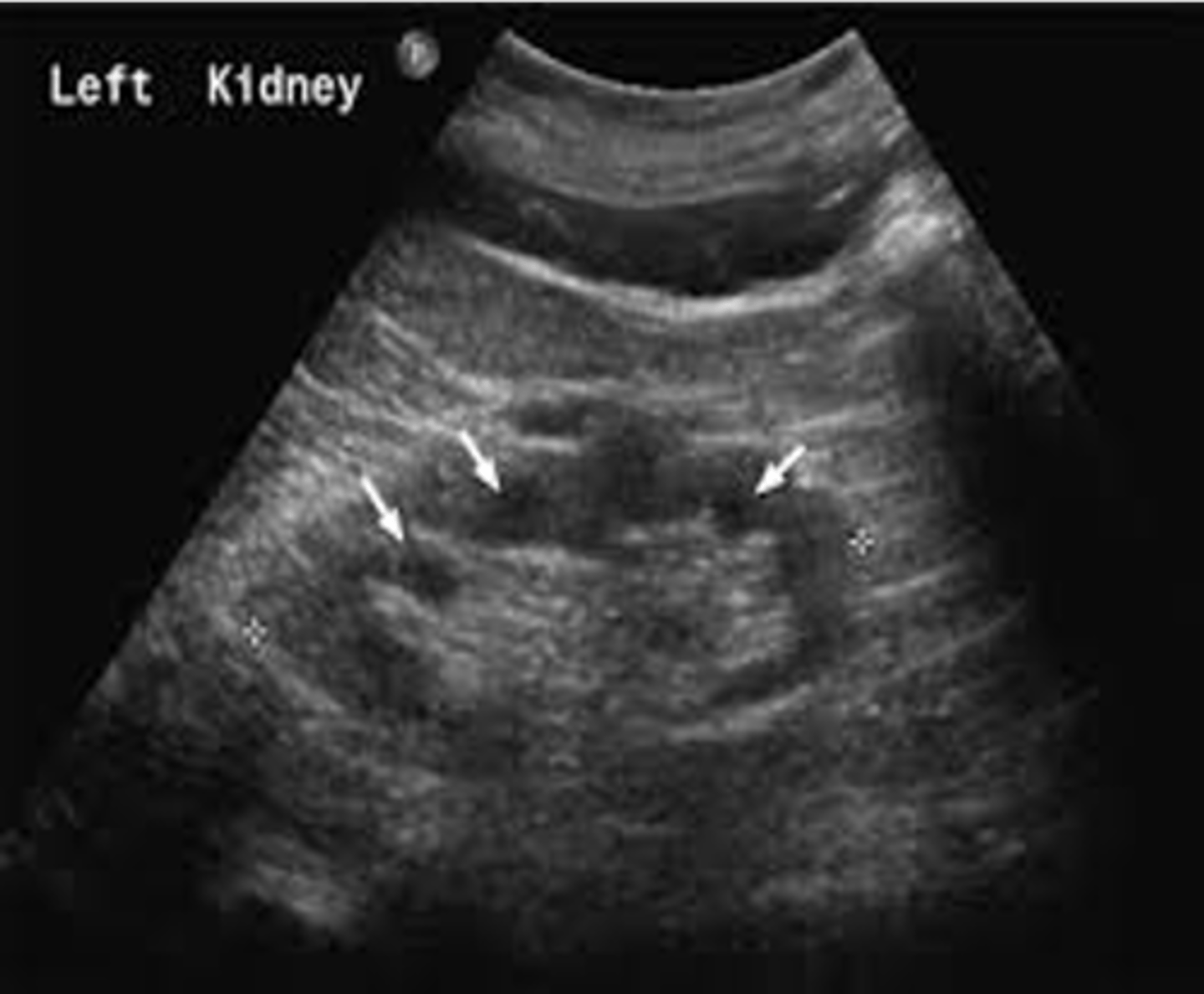
Nephronophthisis (NPH) appears sonographically as small ___ kidneys with multiple cysts measuring less than ___
echogenic; 2 cm
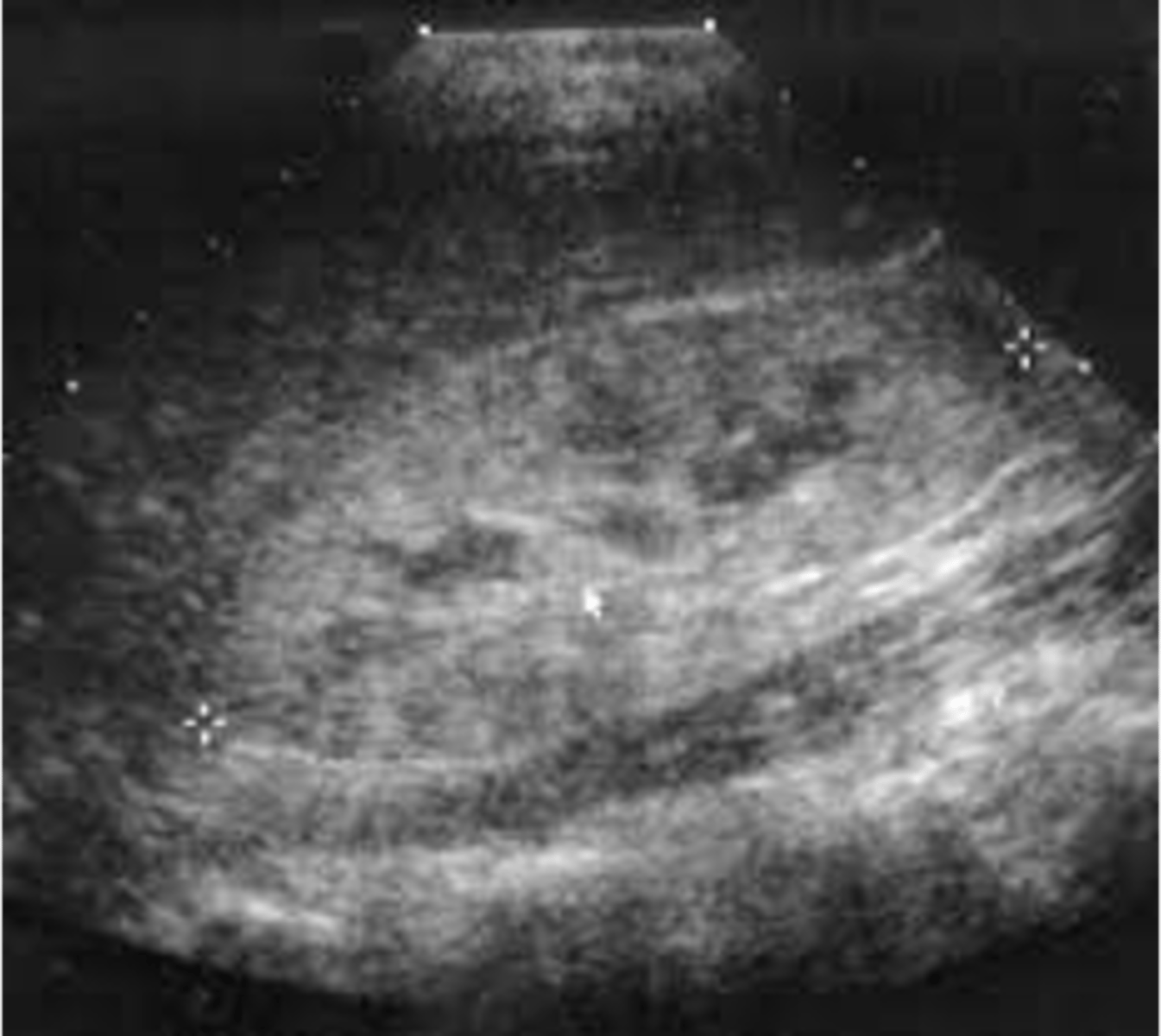
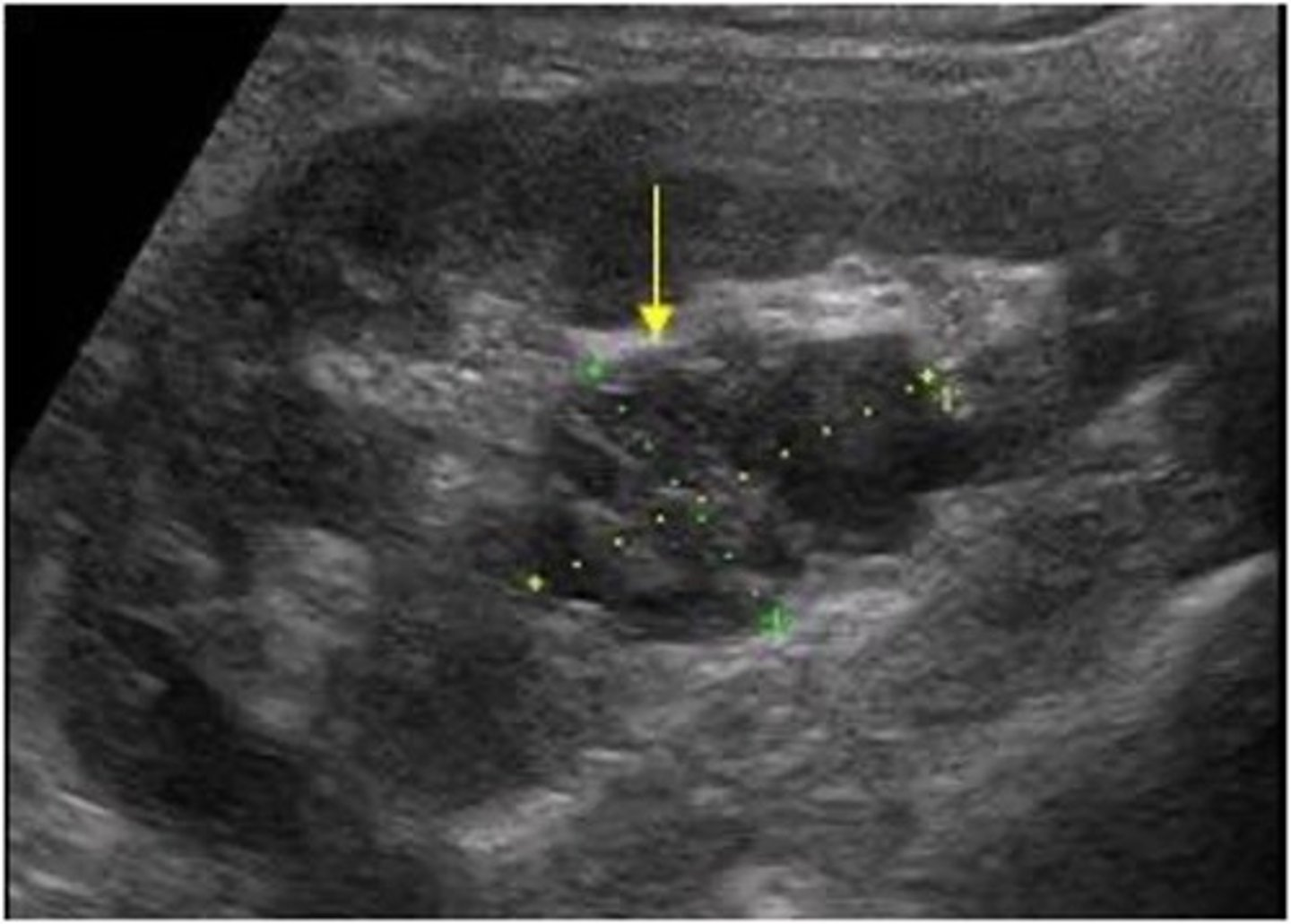
Cystic nephroma is a ___ cystic mass that is ___
multiloculated; benign
Cystic nephroma does not communicate with the renal ___
pelvis
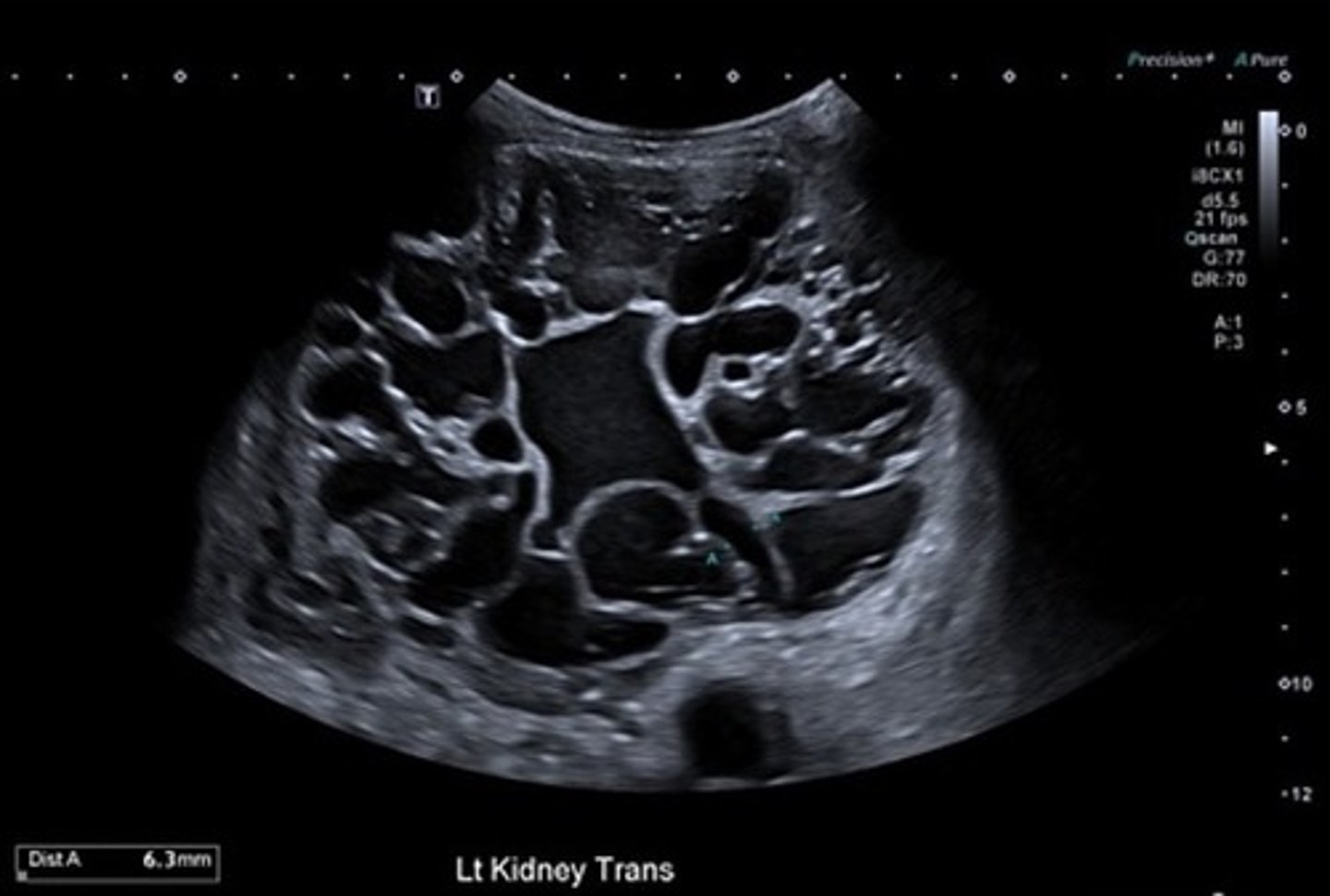
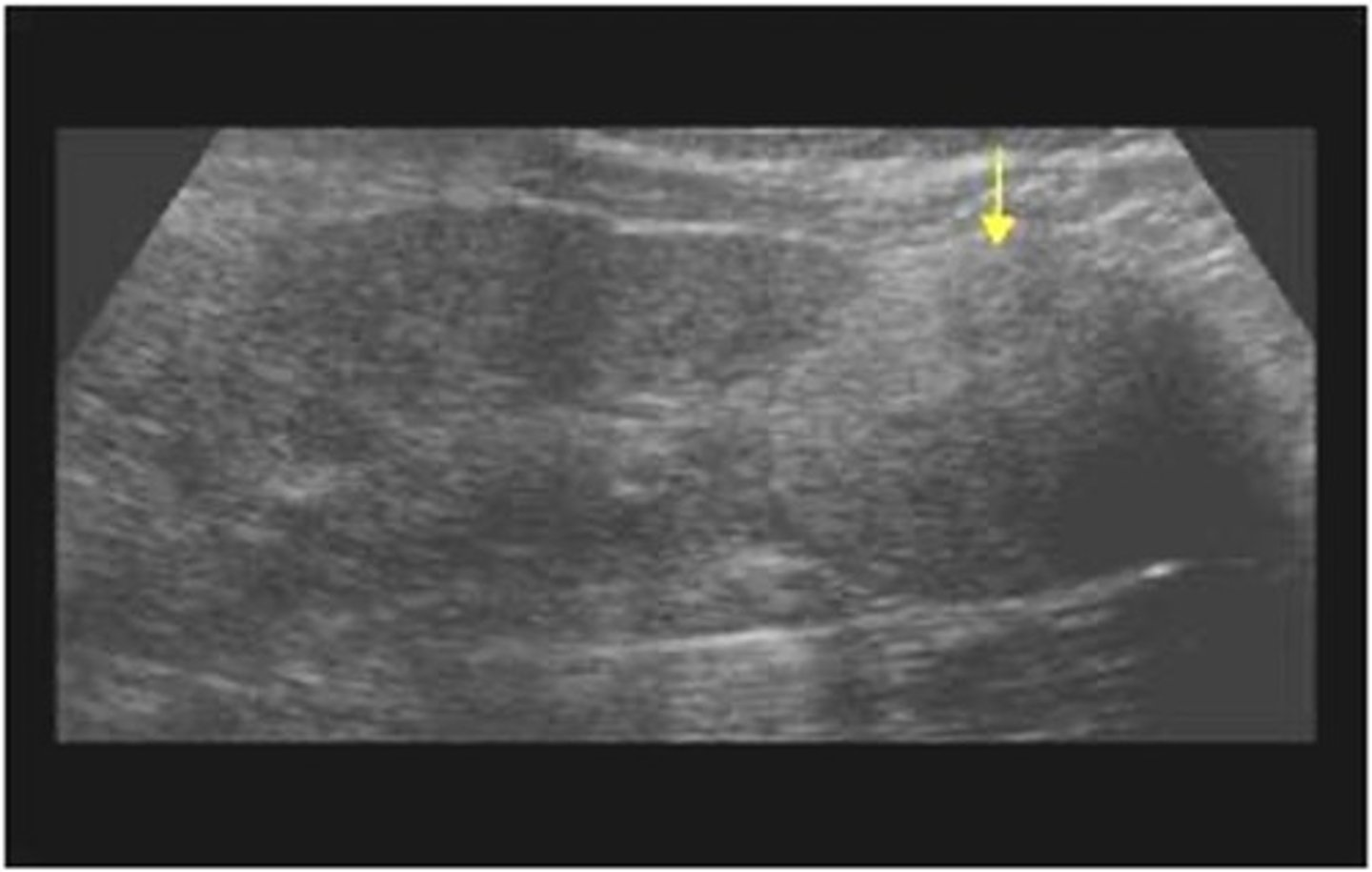
What is the most common of all kidney tumors?
renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
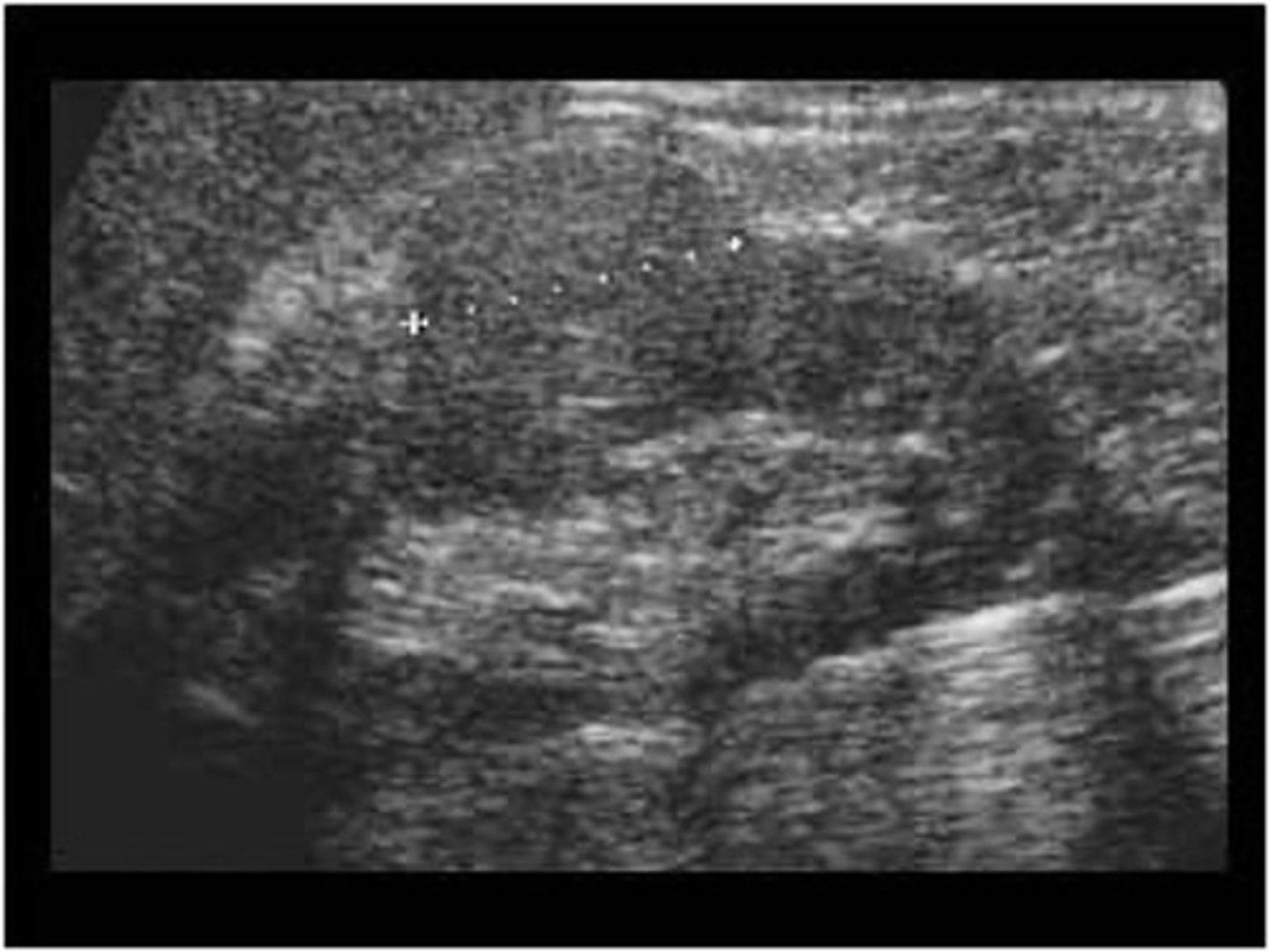
RCC is more common in ___ older than ___
males; 70
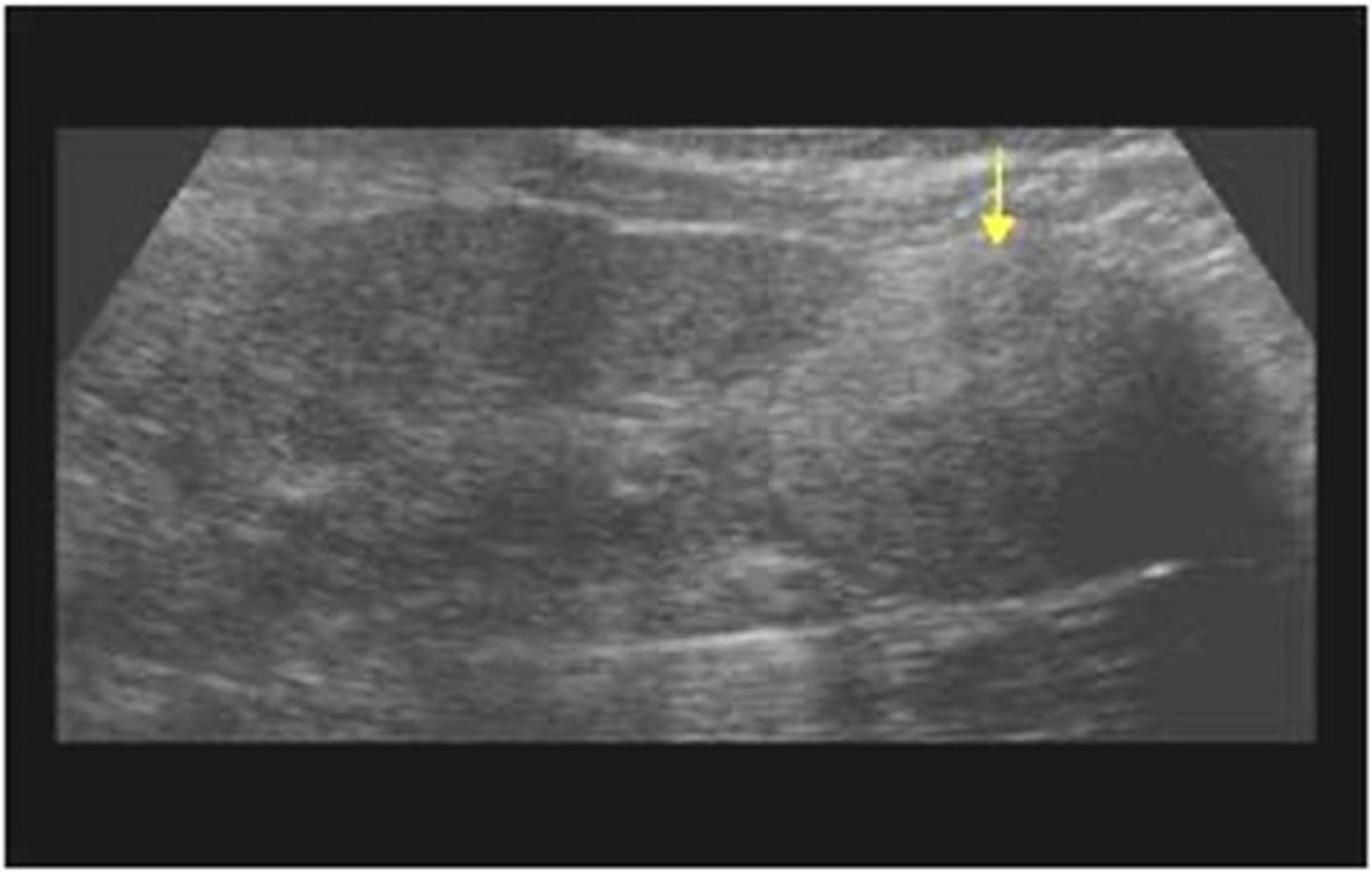
RCC is associated with ___ and ___
von hippel-lindau disease; chronic dialysis
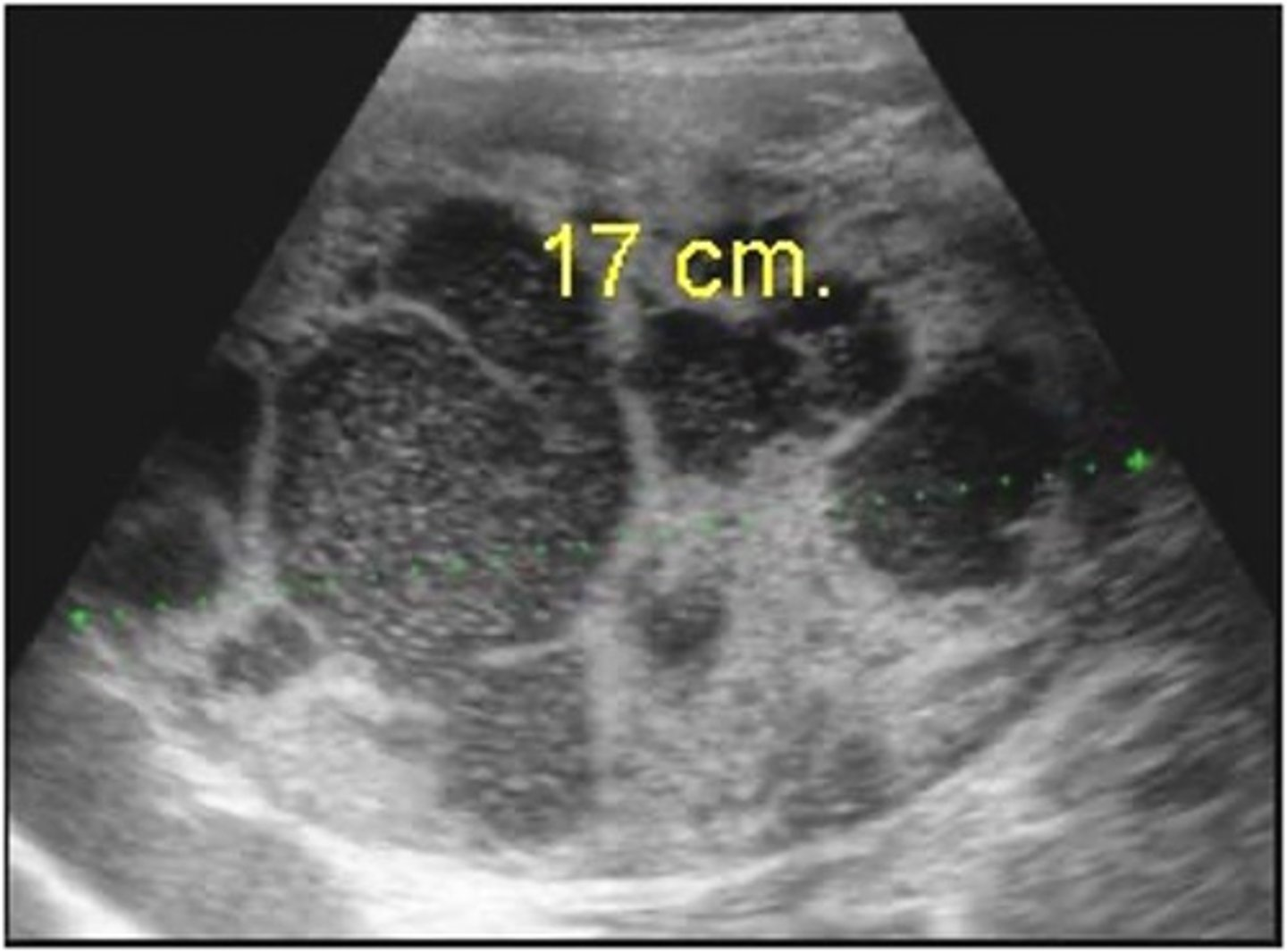
What are symptoms of RCC?
- hematuria
- flank pain
- palpable mass
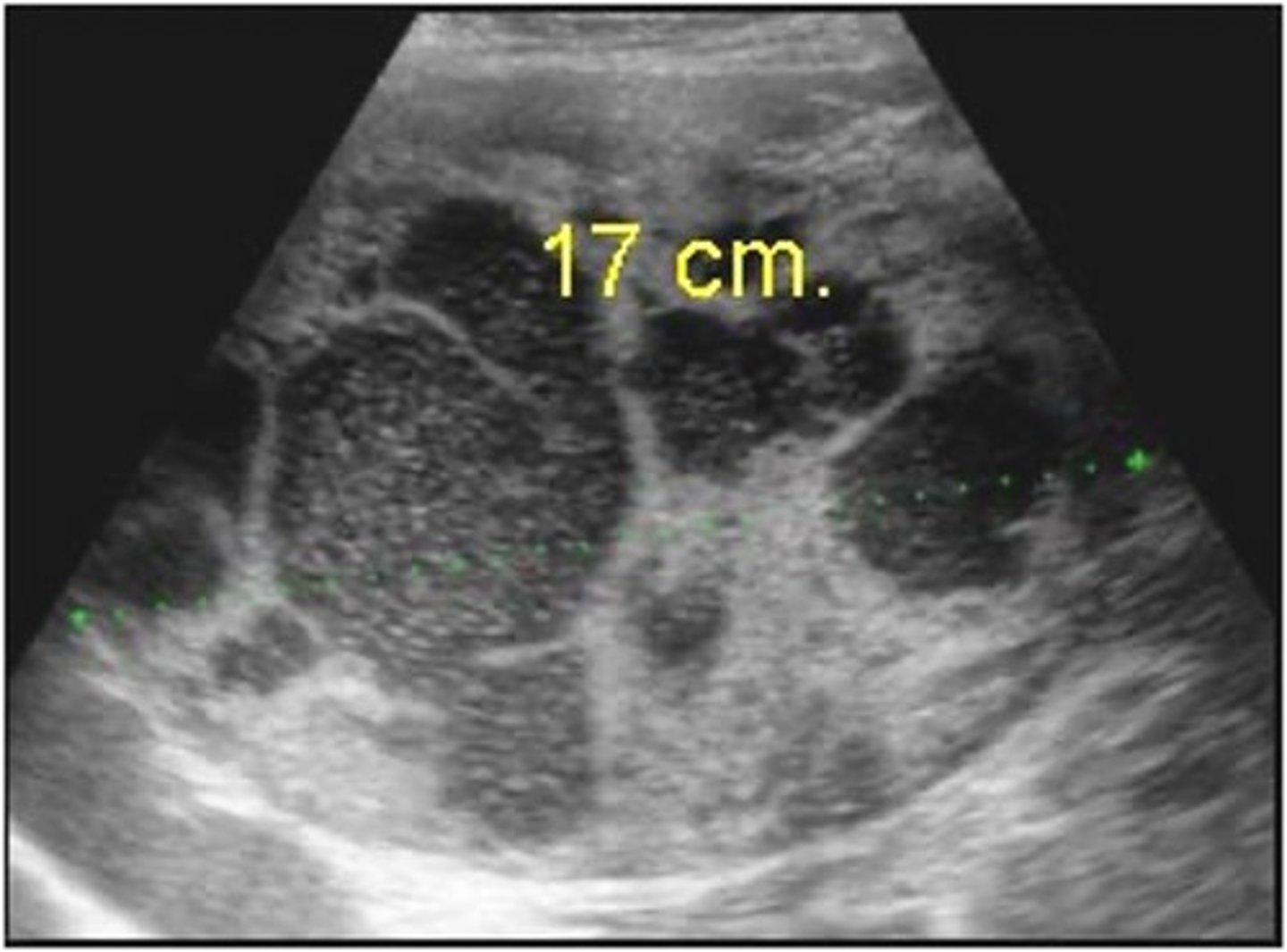
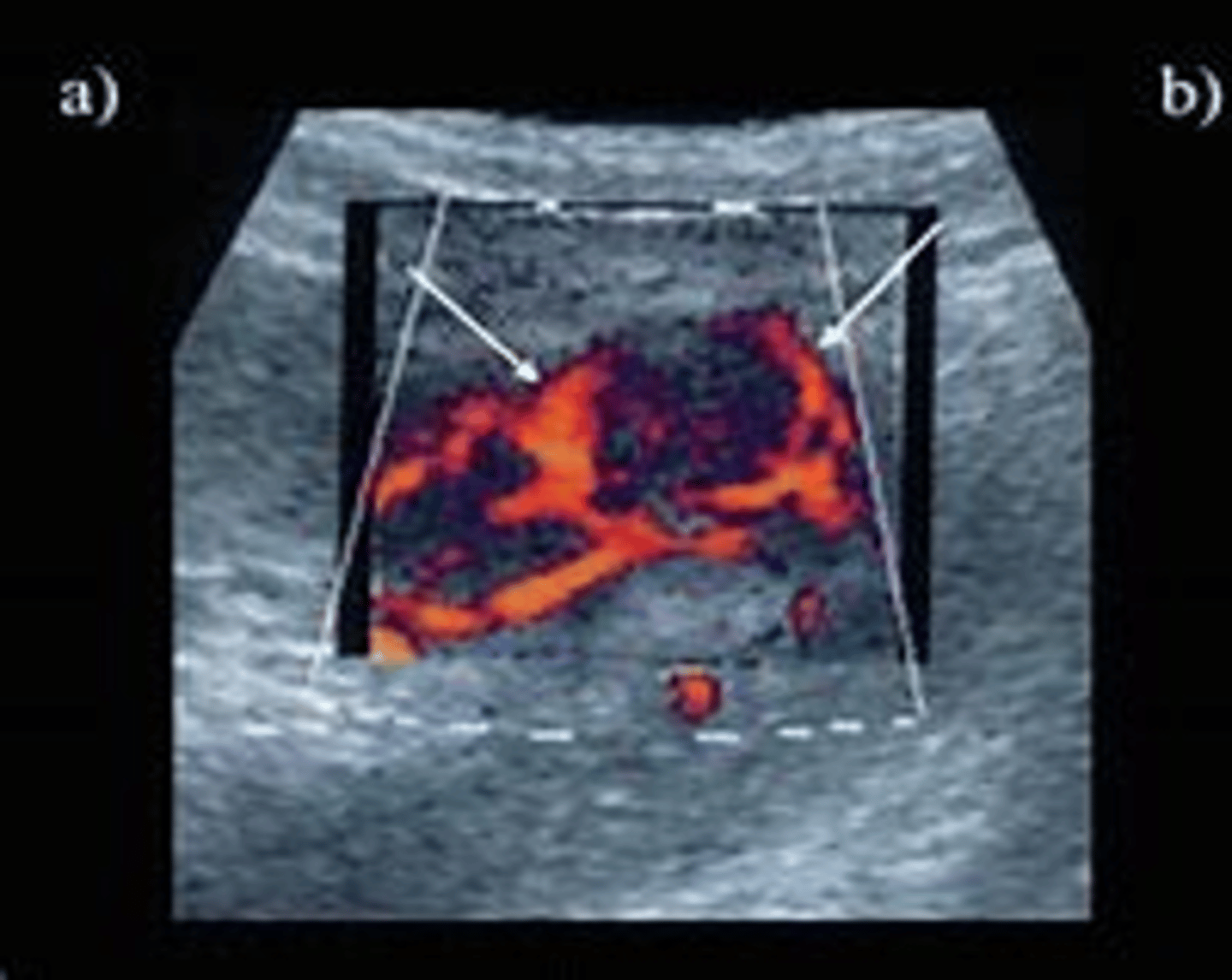
How does RCC appear sonographically?
Record
- heterogeneous with hemorrhage and necrosis
- isoechoic or hyperechoic
- can be cystic
- basket sign

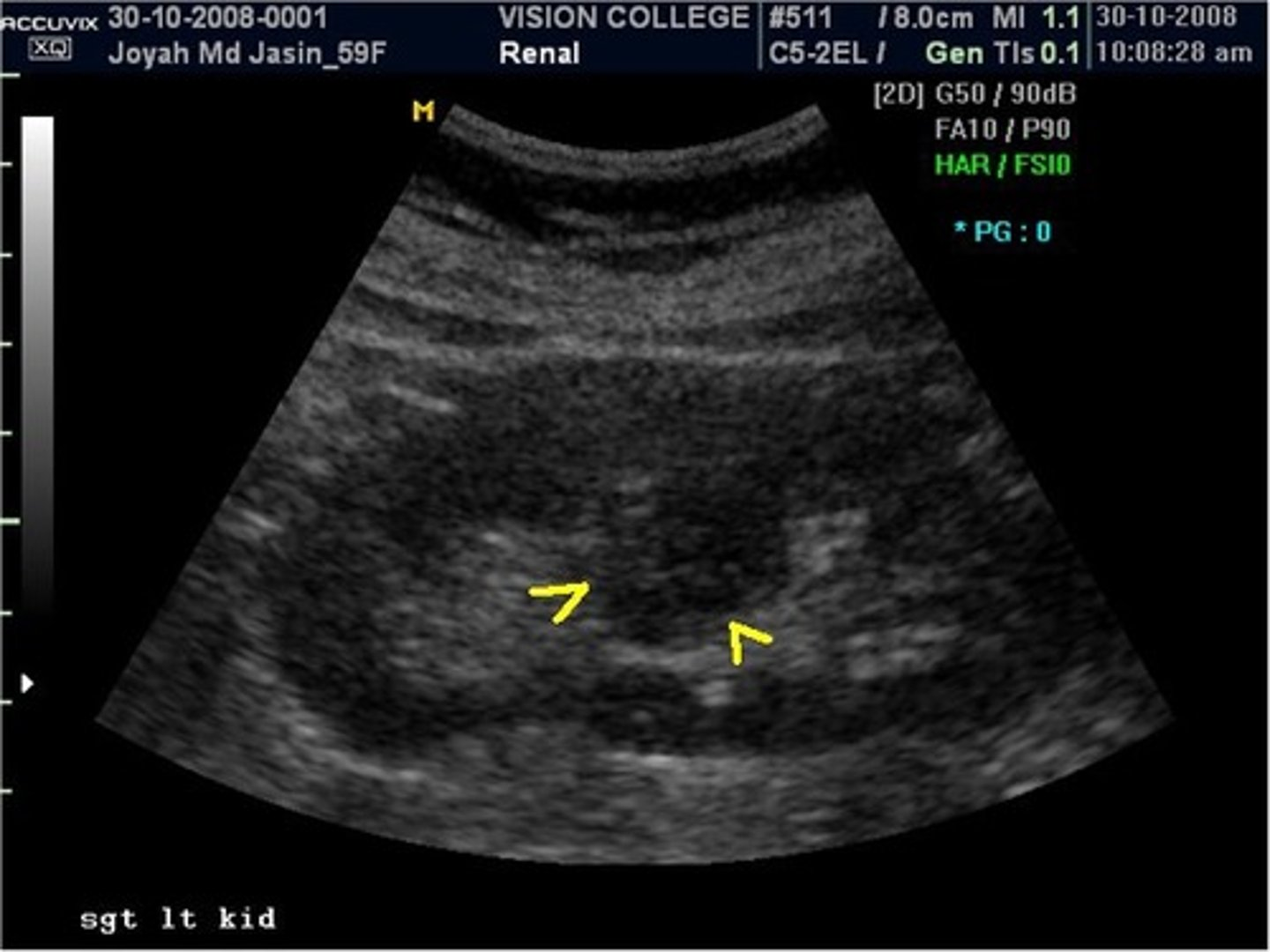
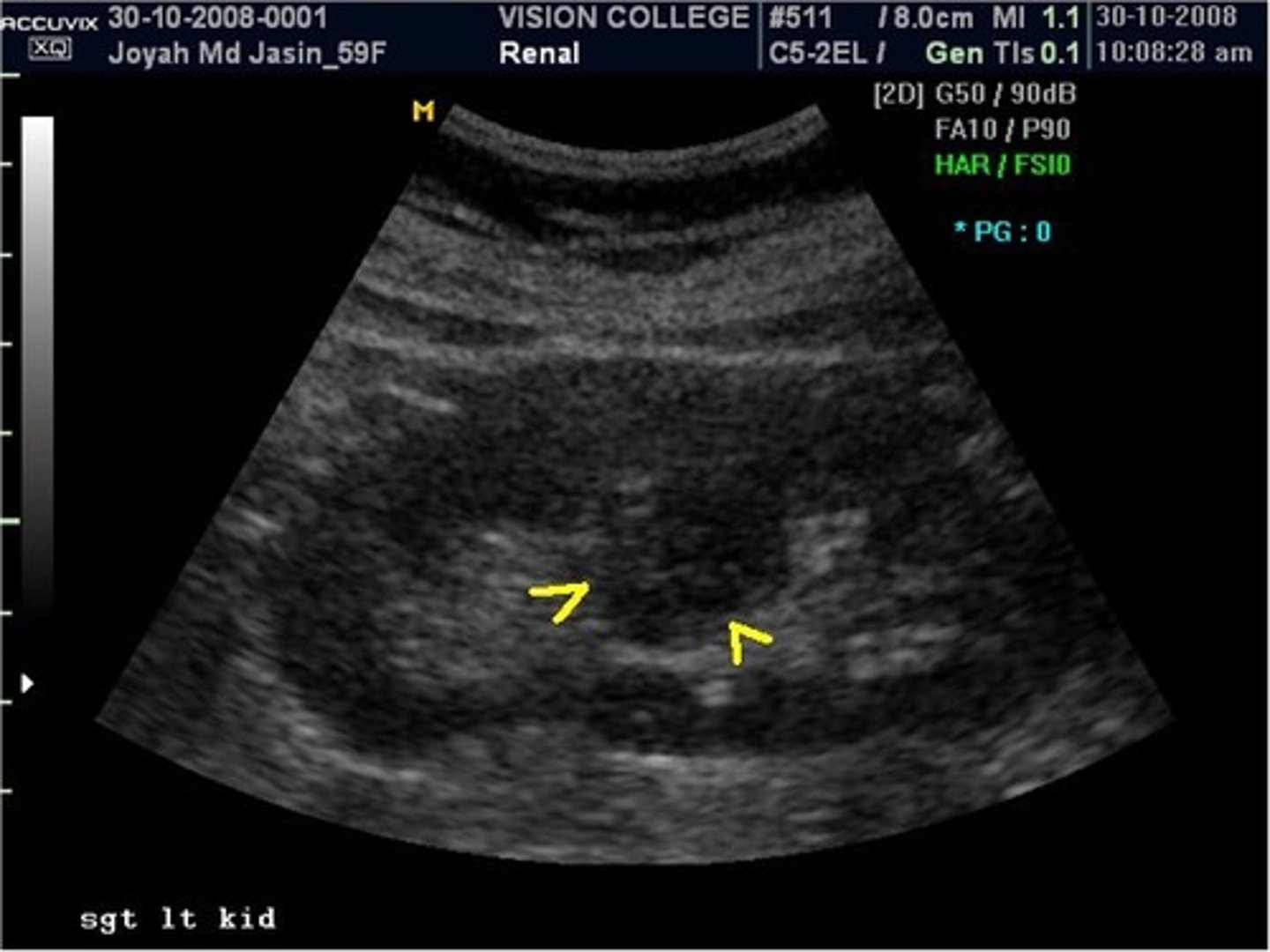
RCC has a similar appearance to what normal renal variant?
column of bertin
Grading RCC:
Grade I- ___ to kidney
Grade II- spread to ___, but within ___
Grade III- spread to ___, ___, and regional ___
Grade IV- invasion of neighboring ___
- confined
- perinephric fat; Gerota's fascia
- renal vein; IVC; lymph nodes
- structures
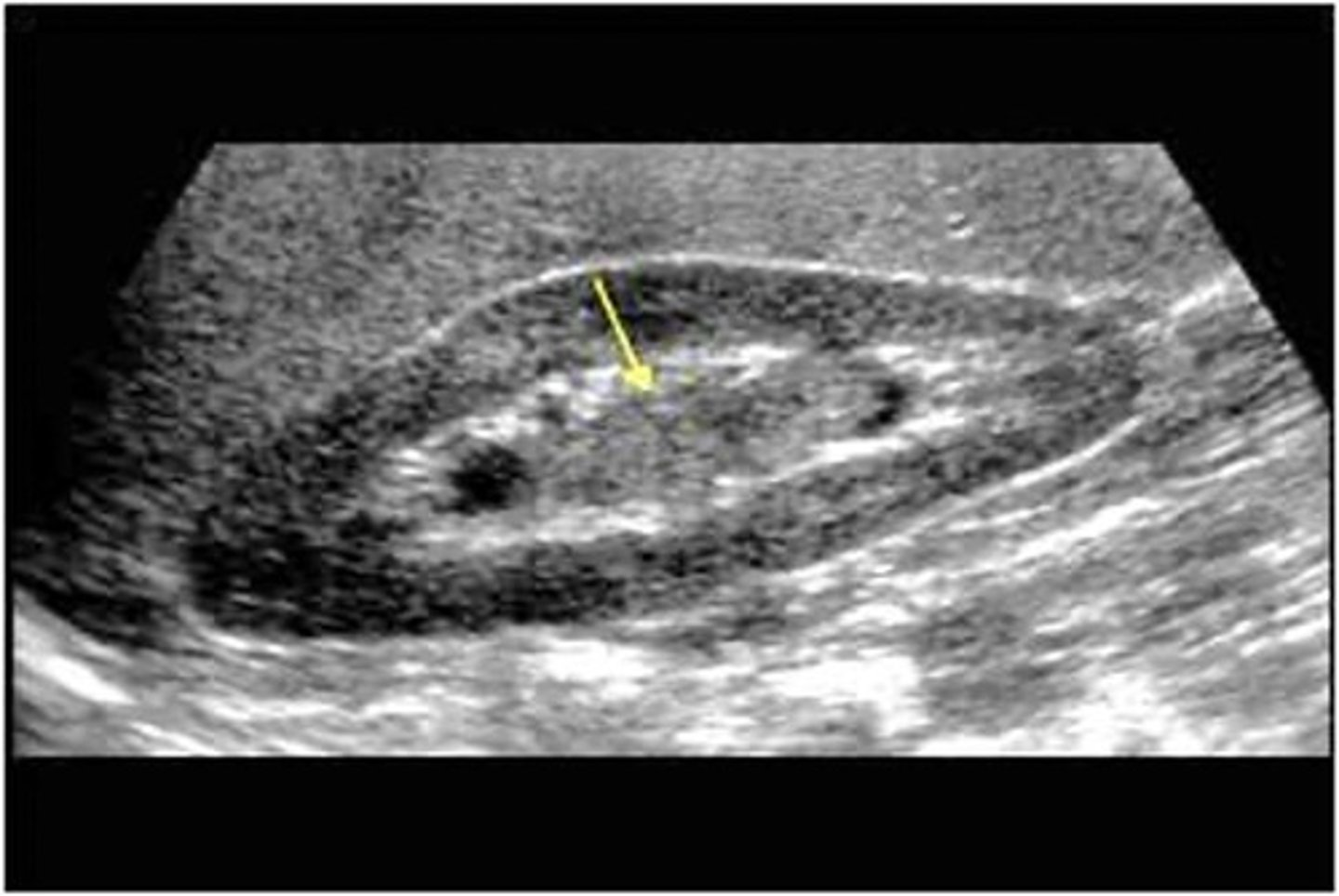
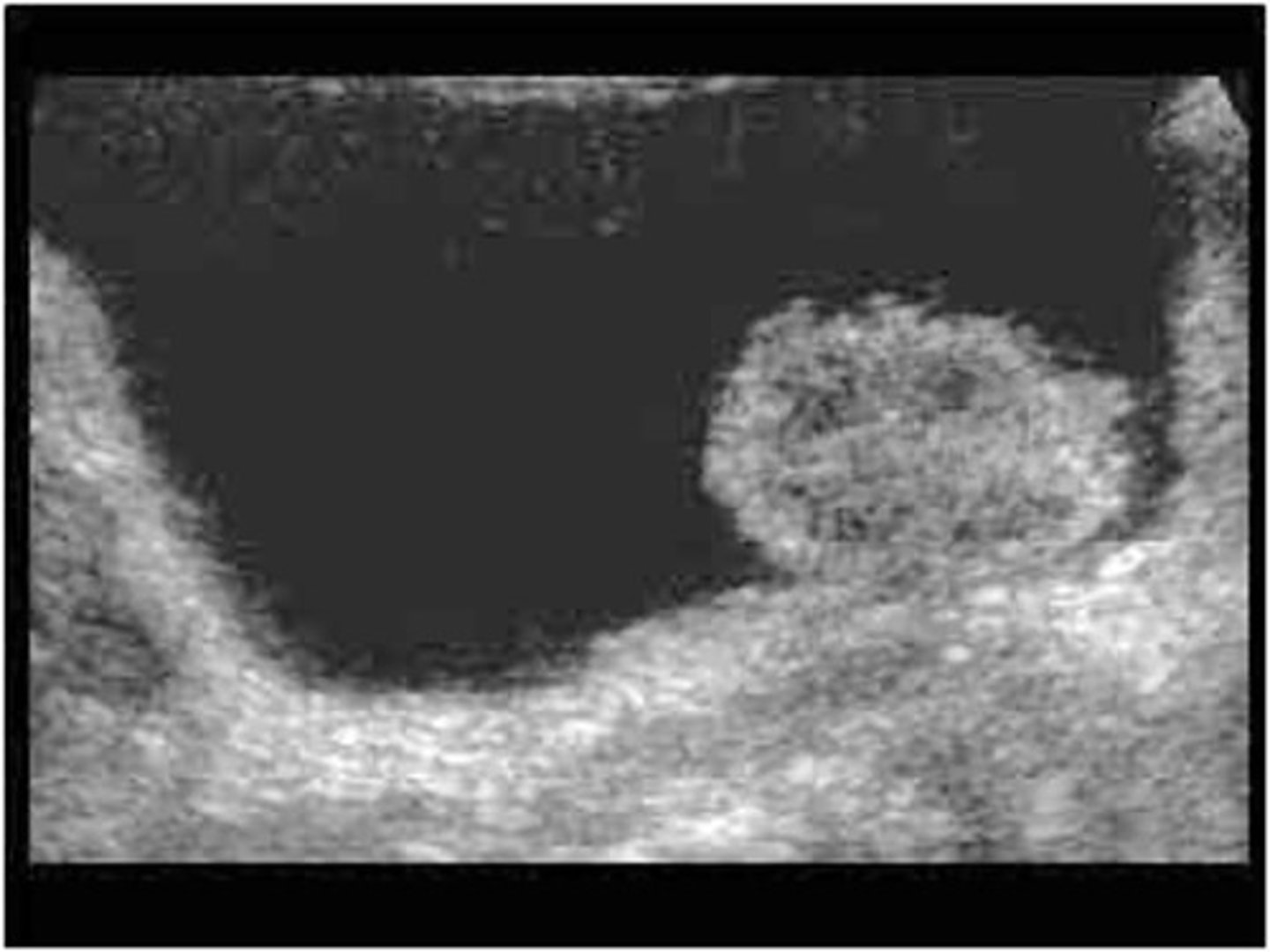
Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) is a tumor of the renal ___
pelvis
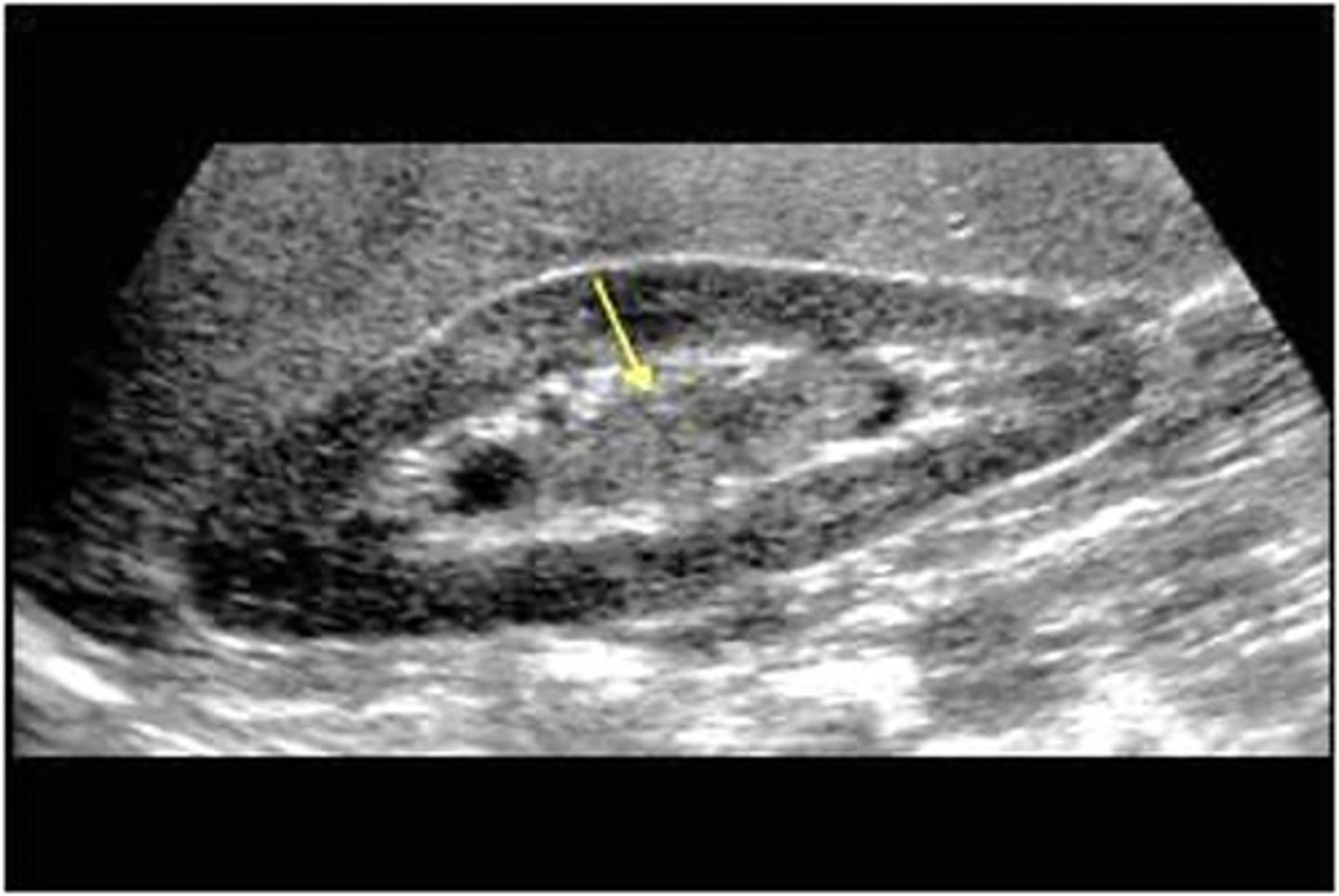
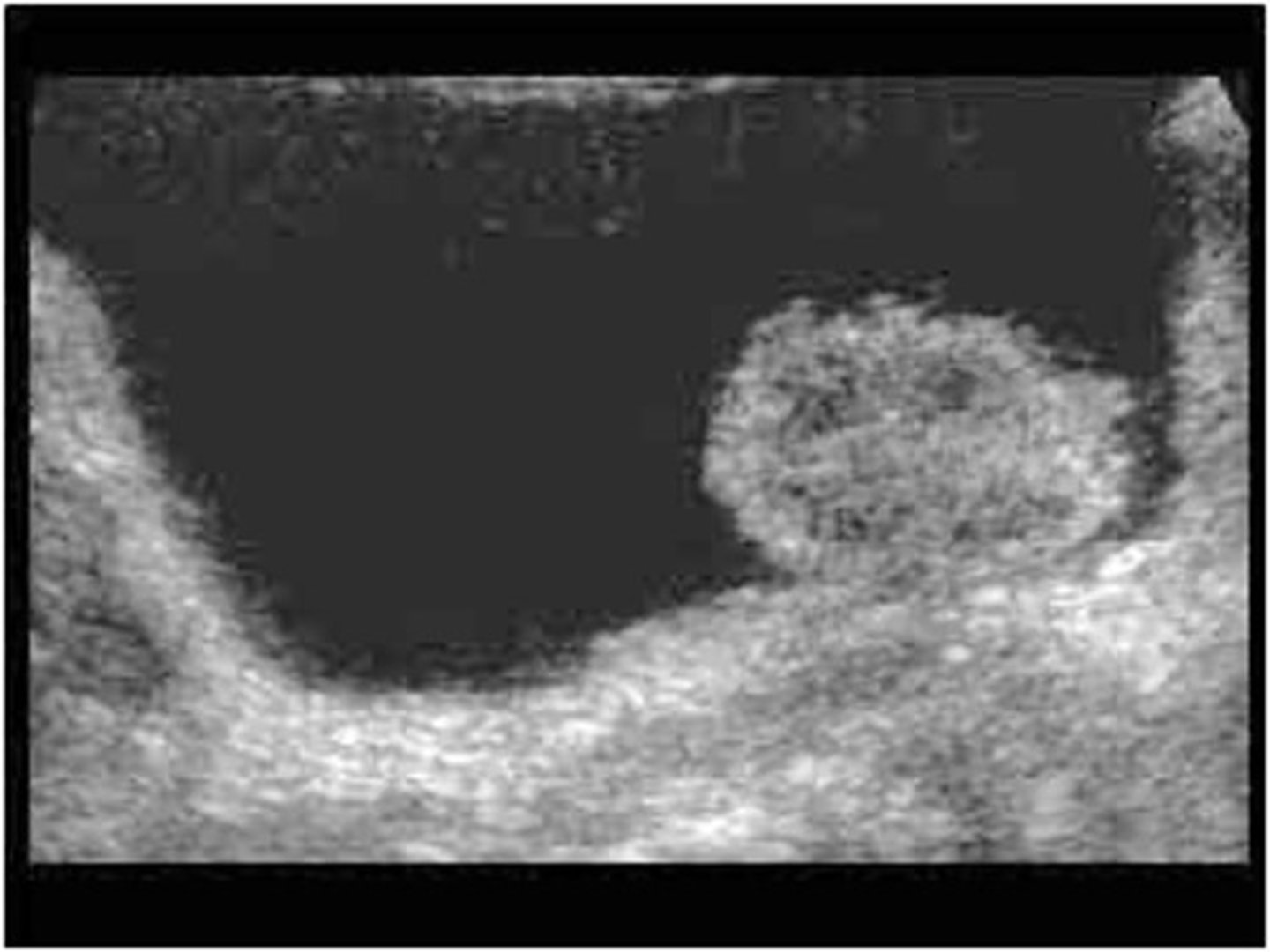
TCC is more frequently found in the ___
bladder
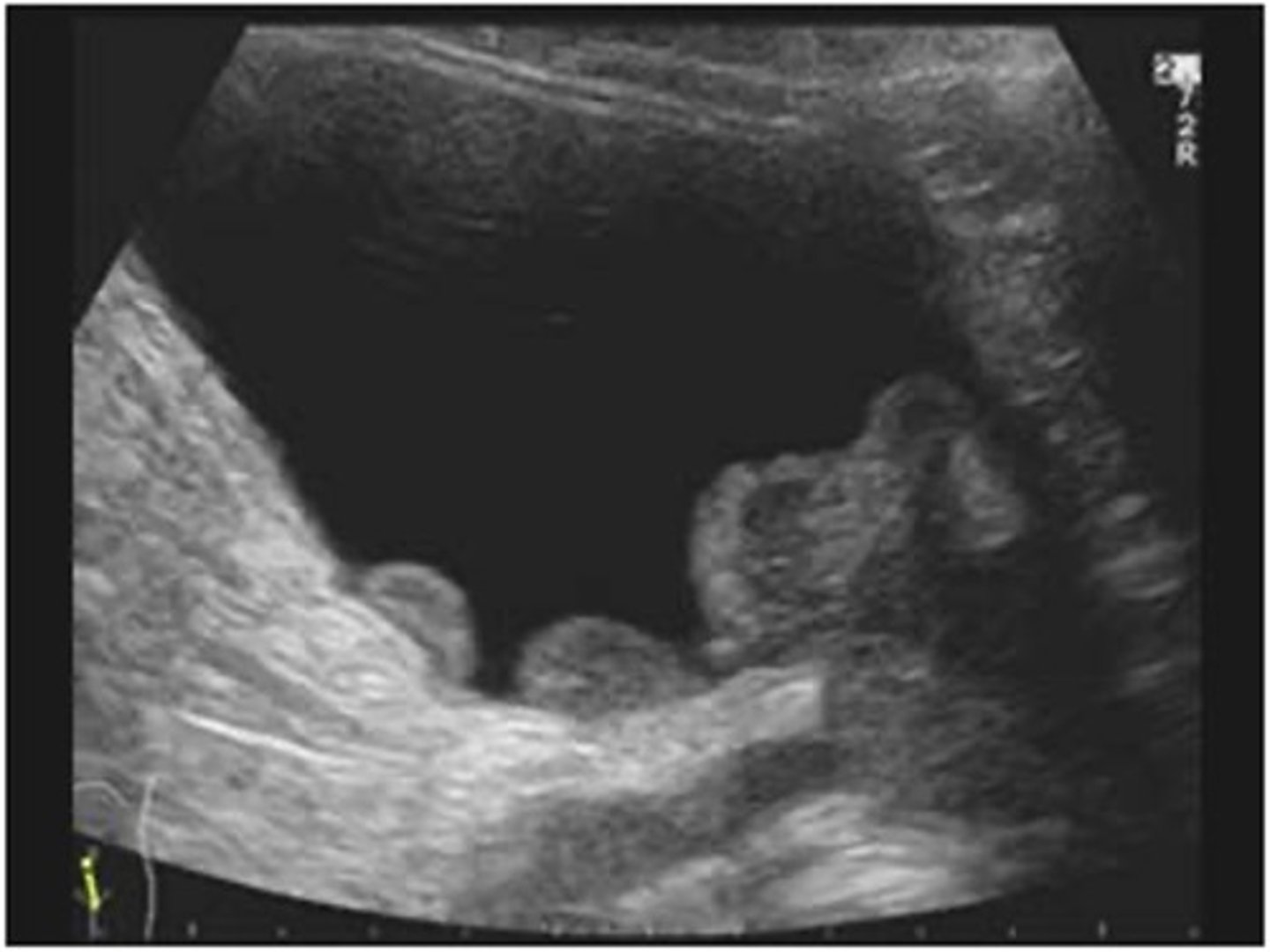
TCC is more common in ___
older males
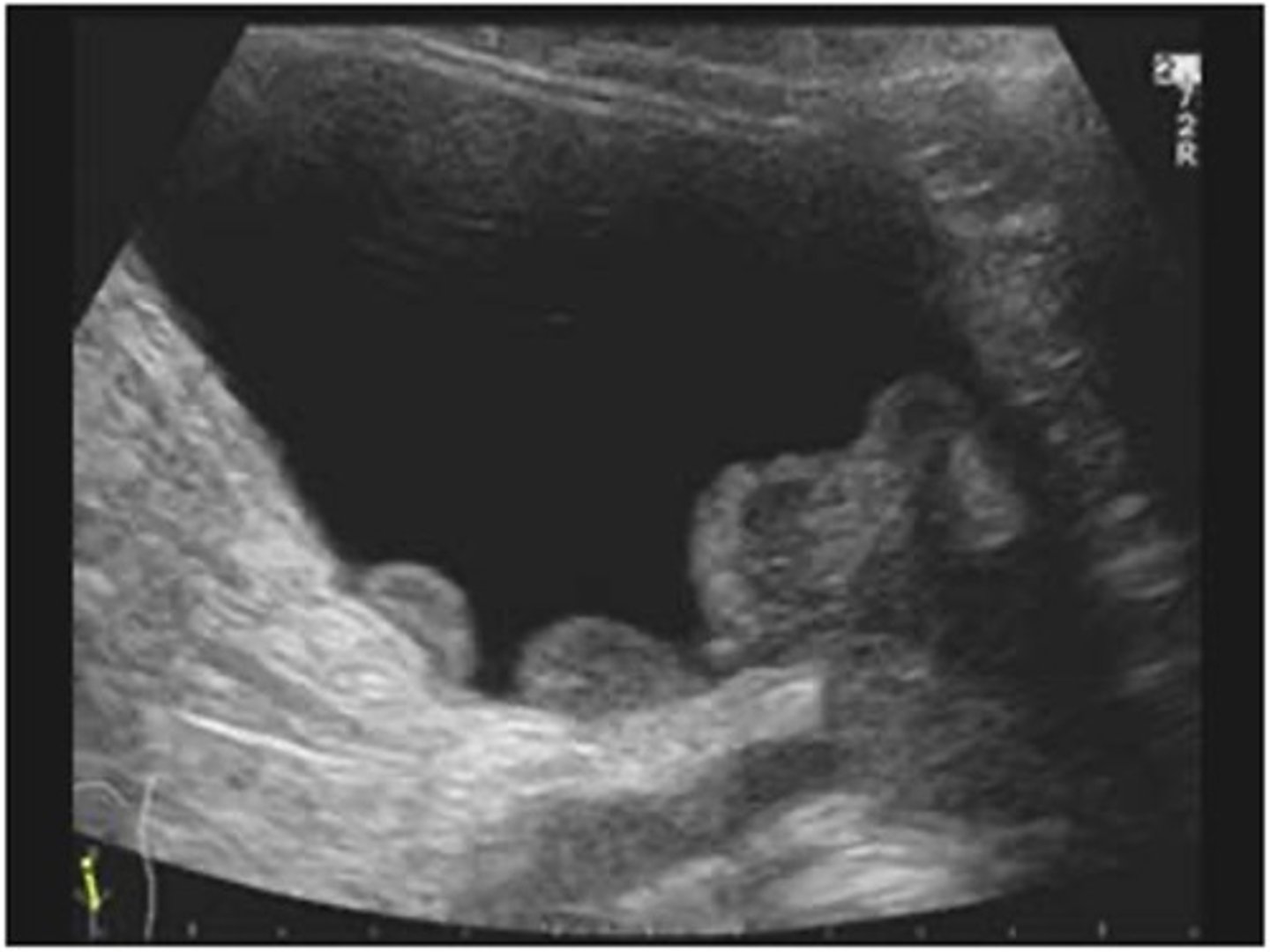
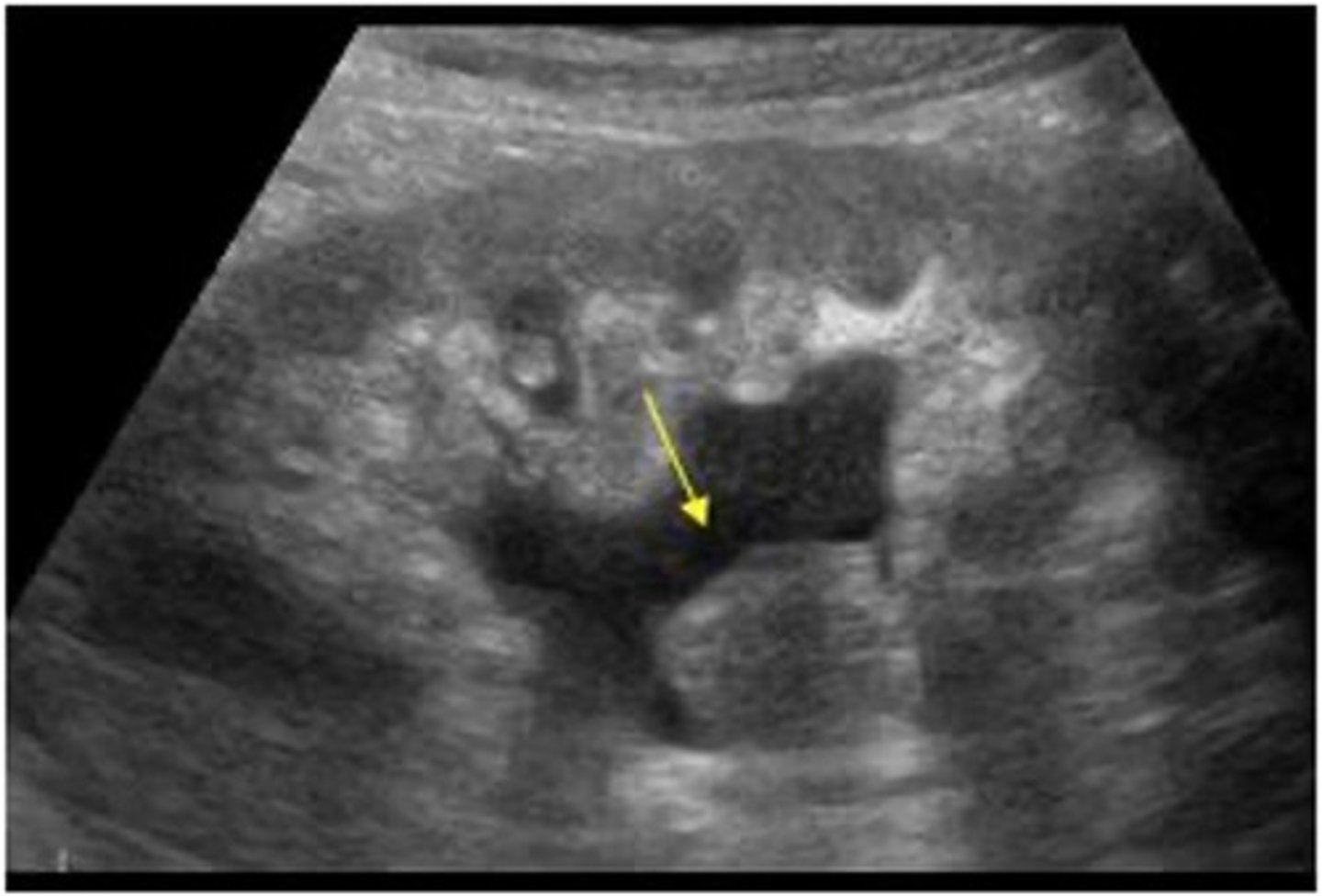
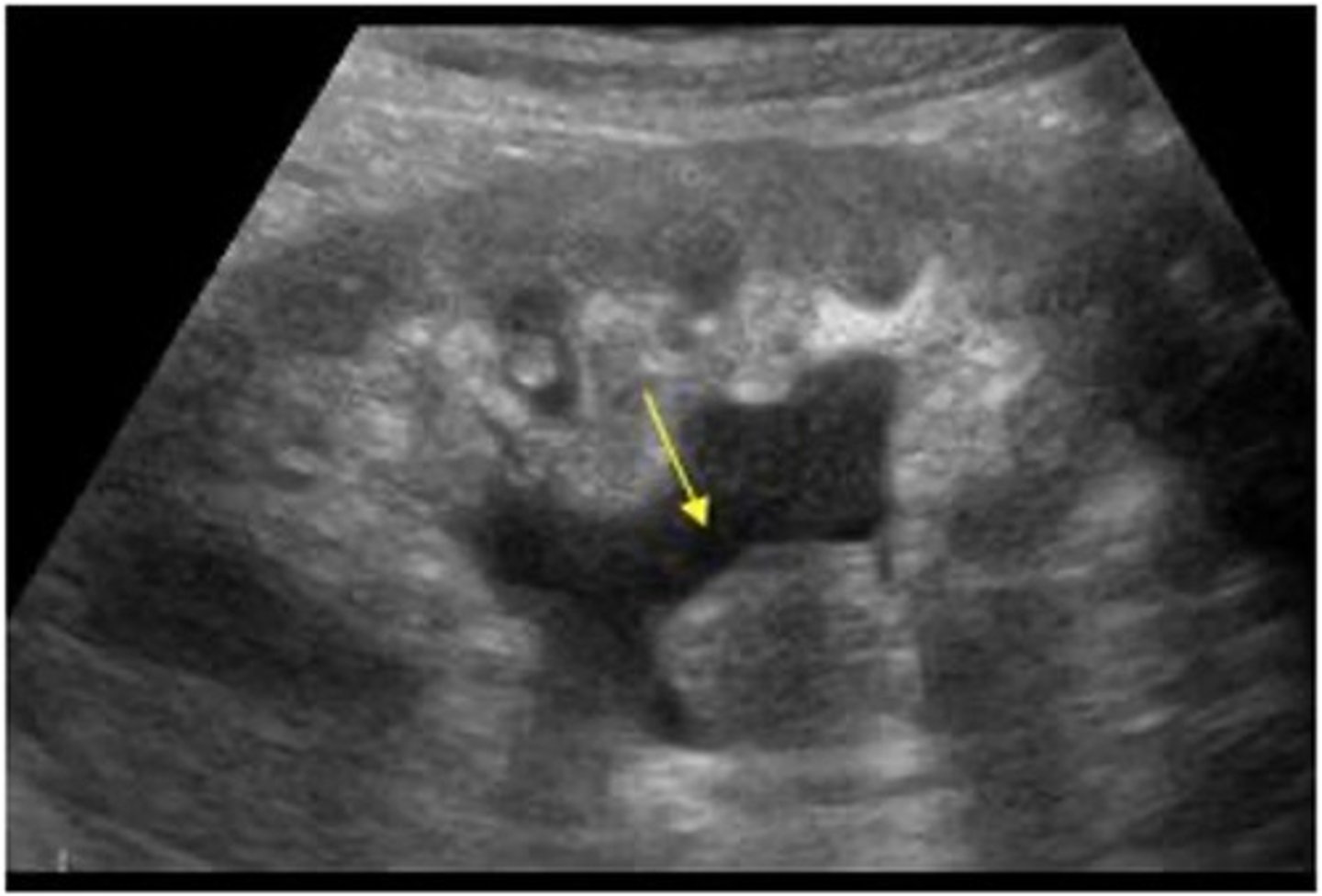
What is the sonographic appearance of TCC?
- hypoechoic mass within the collecting system
- low vascularity
Renal lymphoma is typically a ___ process
secondary
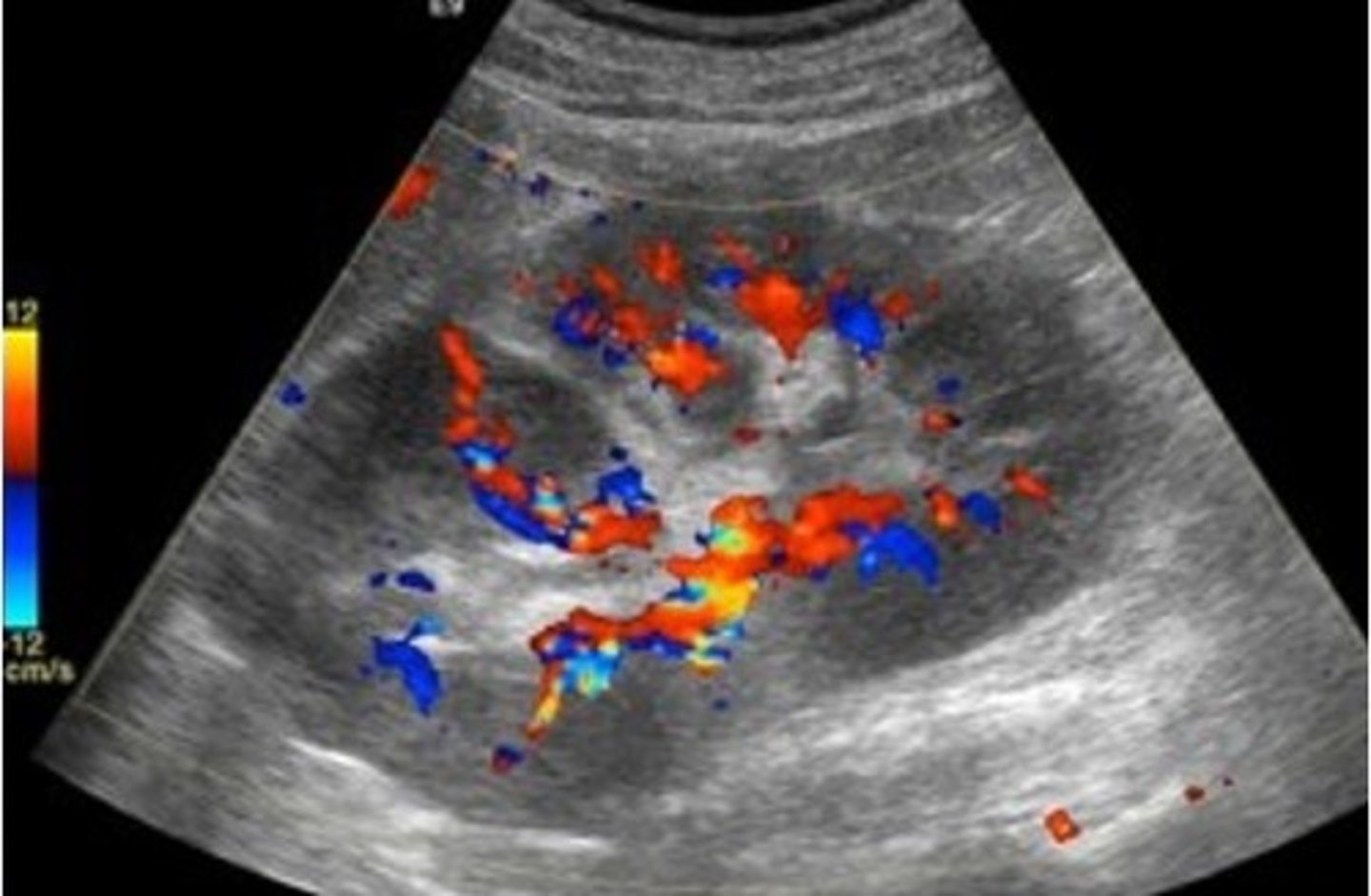
Which is more common: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma or Hodgkin lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
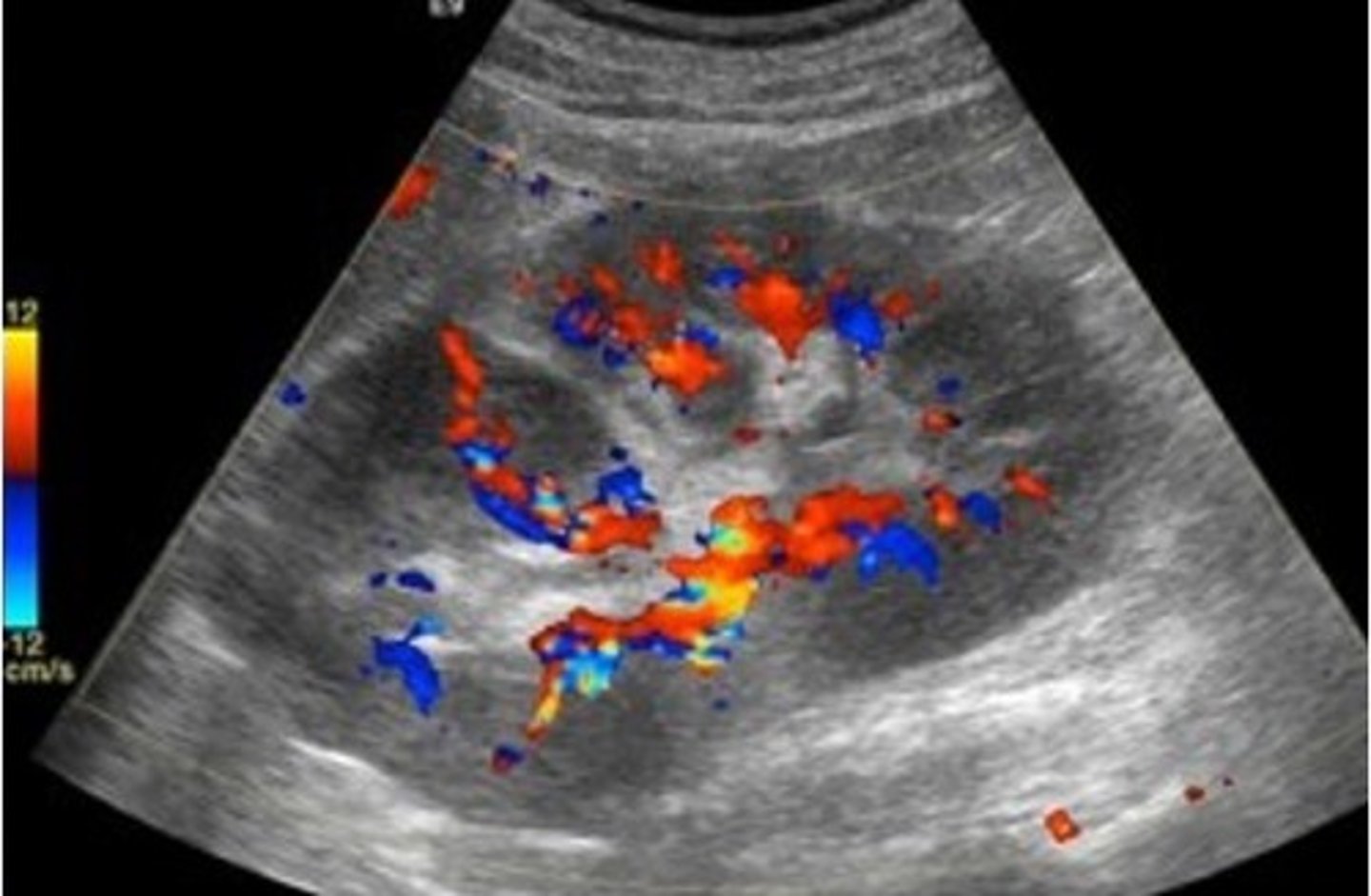
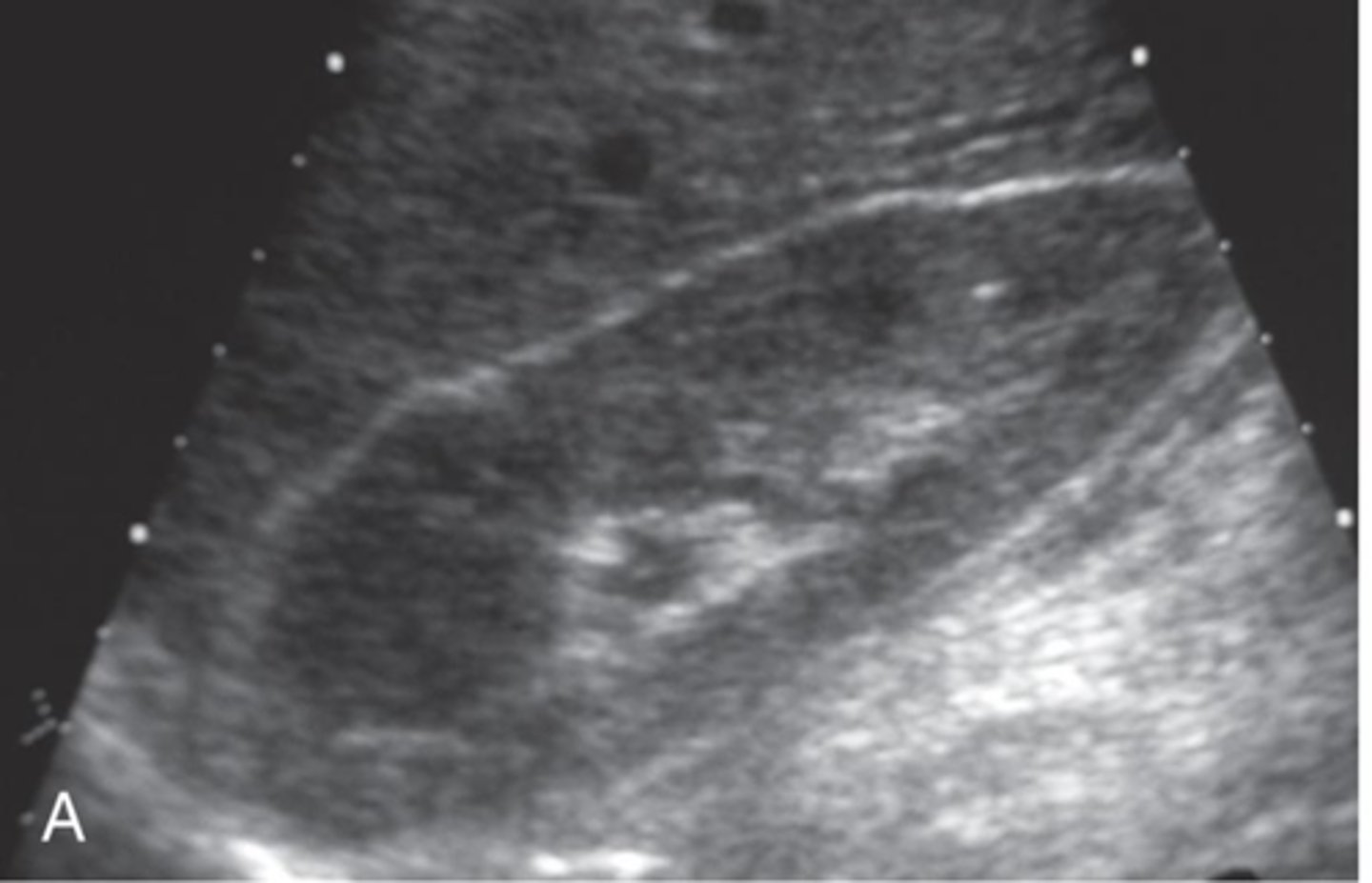
Lymphoma is more common as a ___ invasion with multiple ___
bilateral; nodules
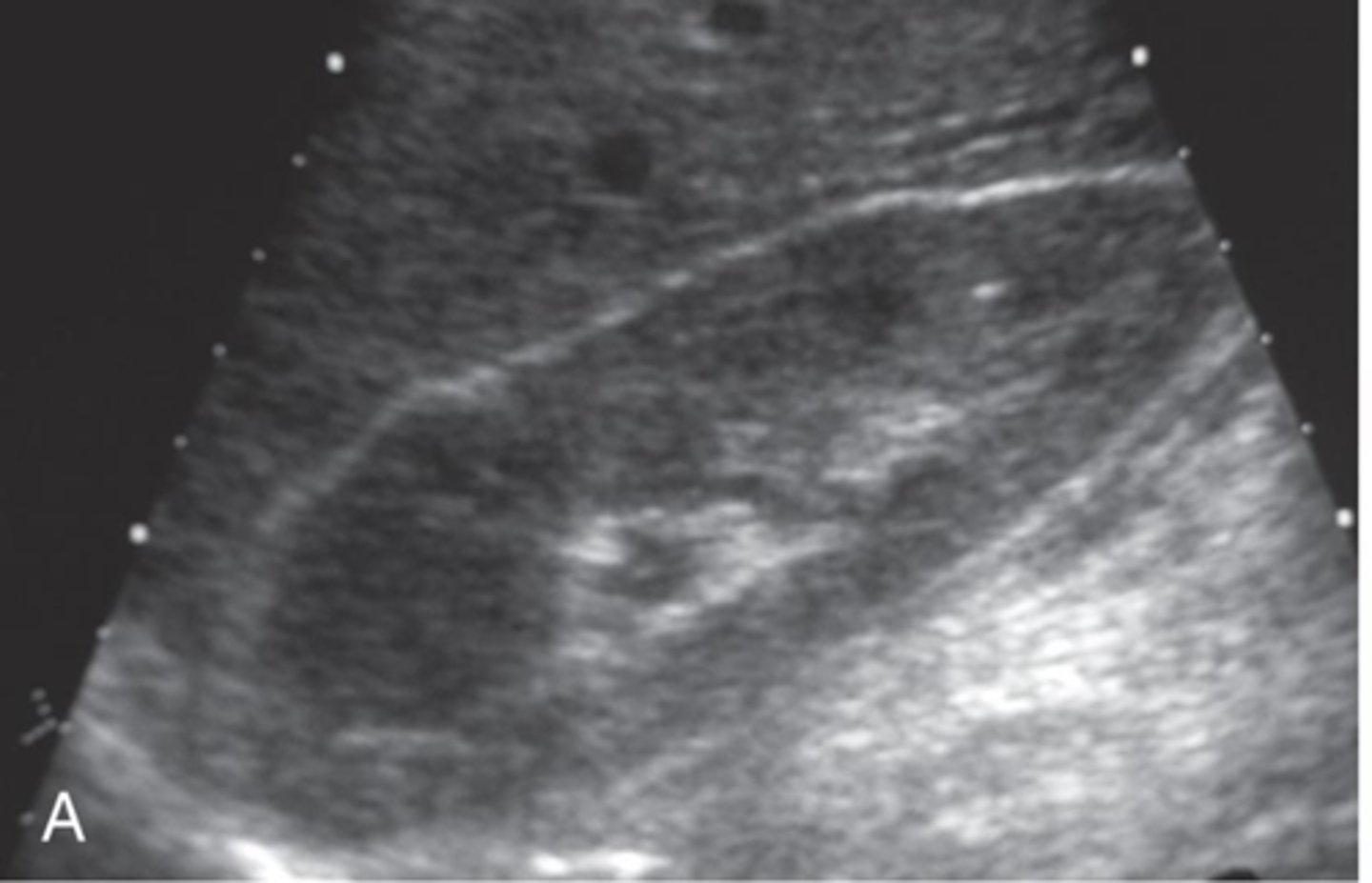
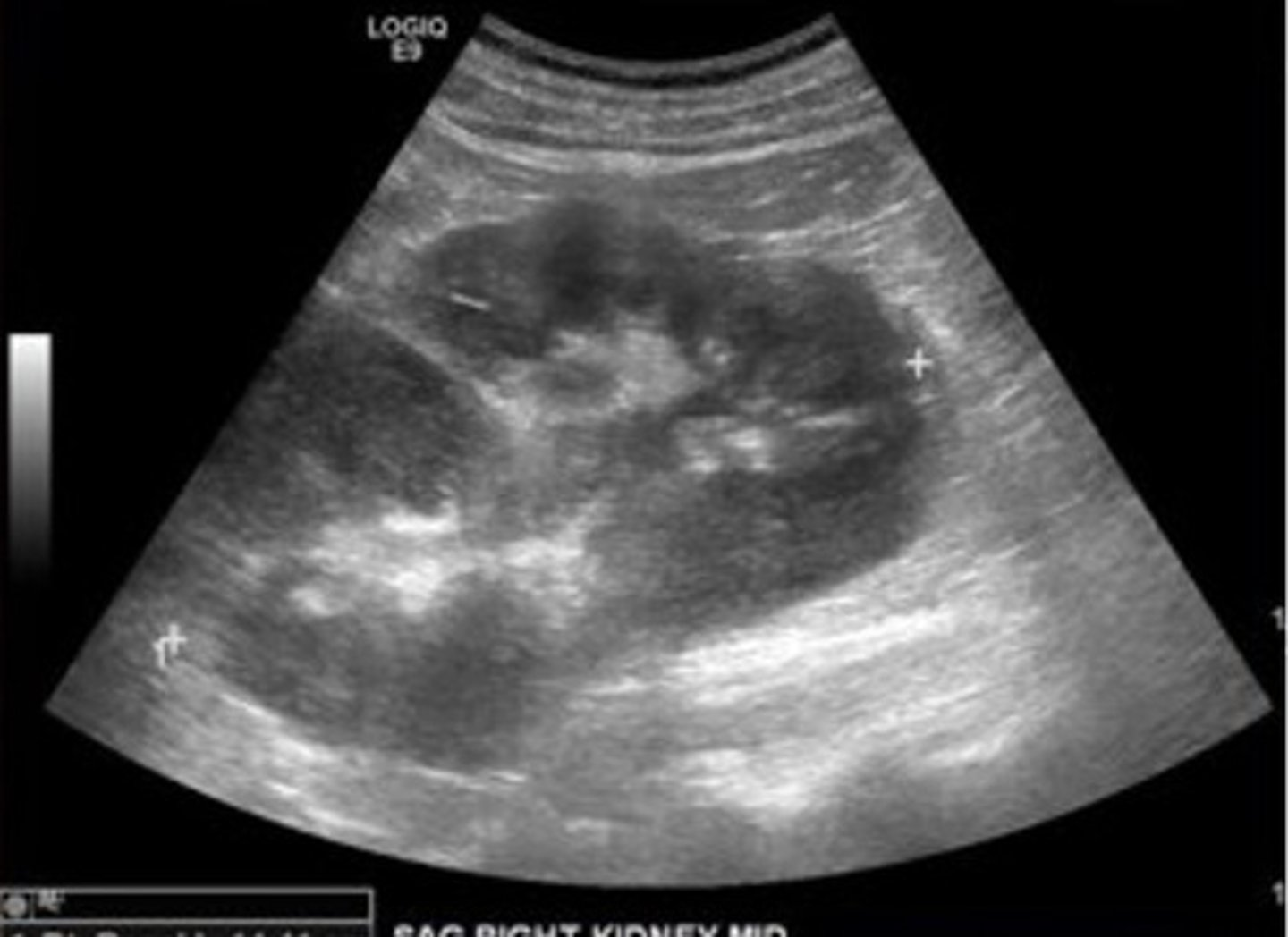
Renal lymphoma sonographic features include ___ kidneys with ___ outlines, multiple ___ masses, and enlarged retroperitoneal ___
enlarged; irregular; hypoechoic; lymph nodes
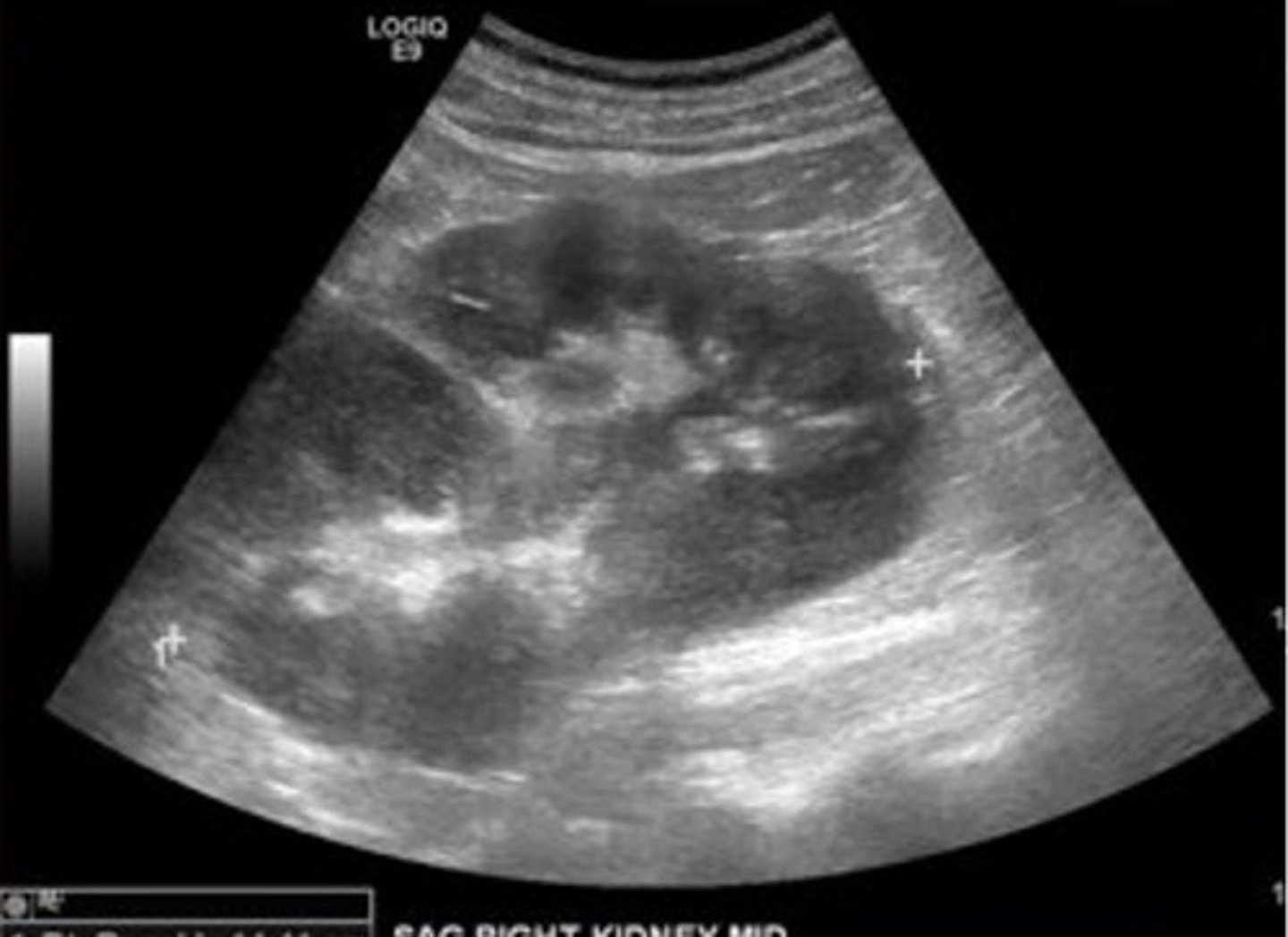
Metastases to the kidneys are relatively common, occurring ___ in the course of the disease
late
What are the most common primary malignancies that metastasize to the kidneys?
- RCC of contralateral kidney
- carcinoma of lungs or breast
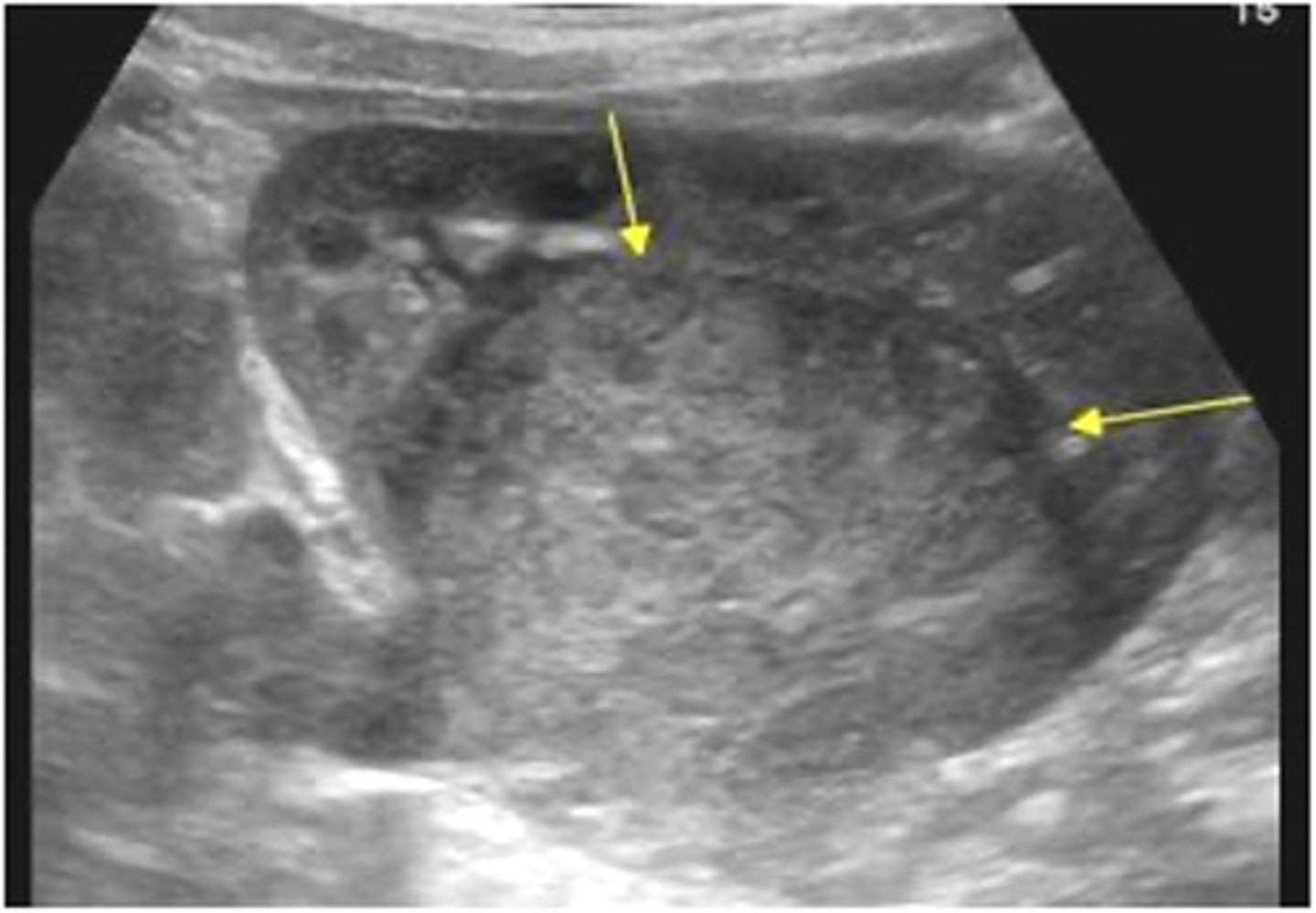
What is the most common abdominal malignancy in children?
nephroblastoma
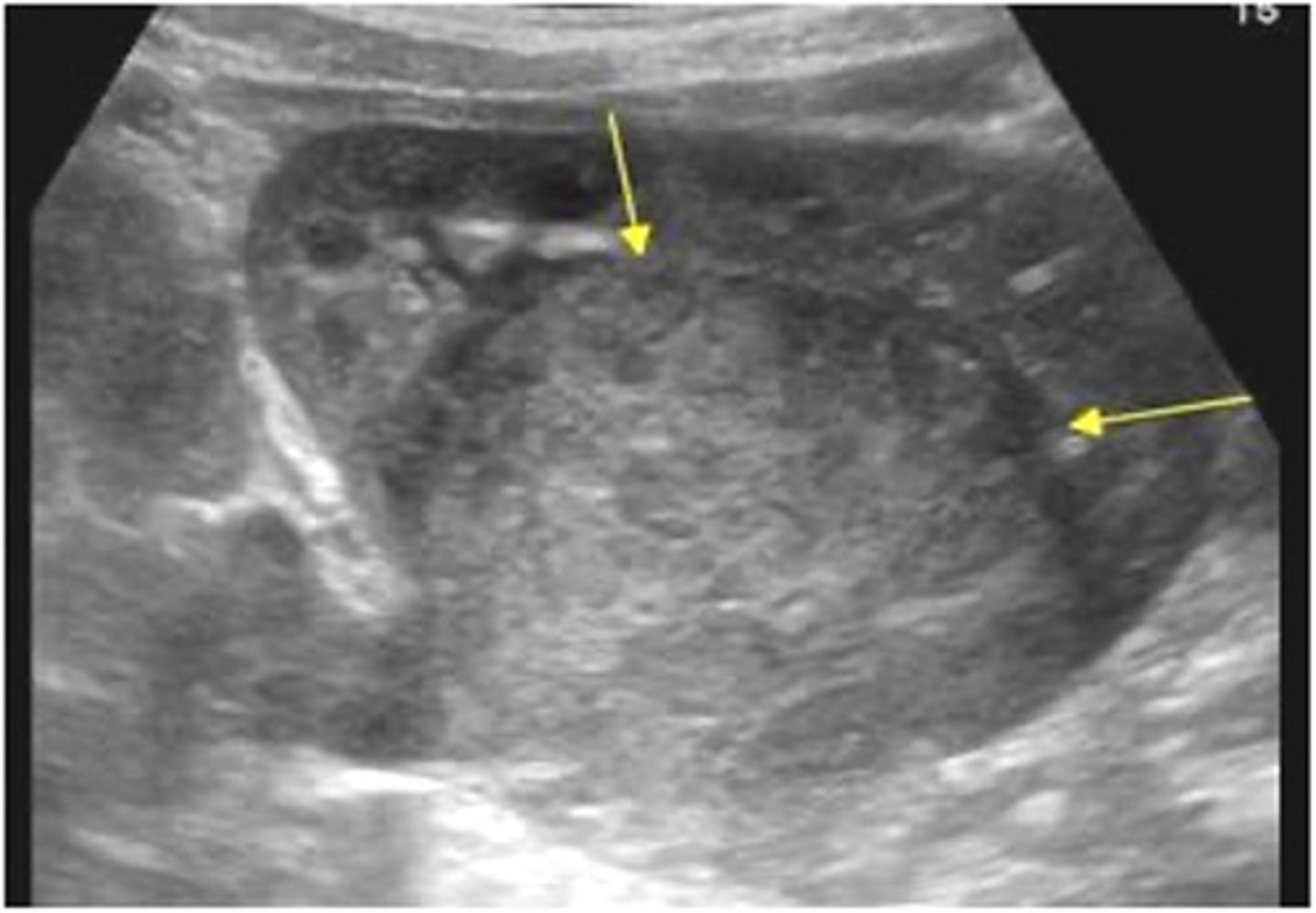
What is another name for nephroblastoma?
Wilms tumor
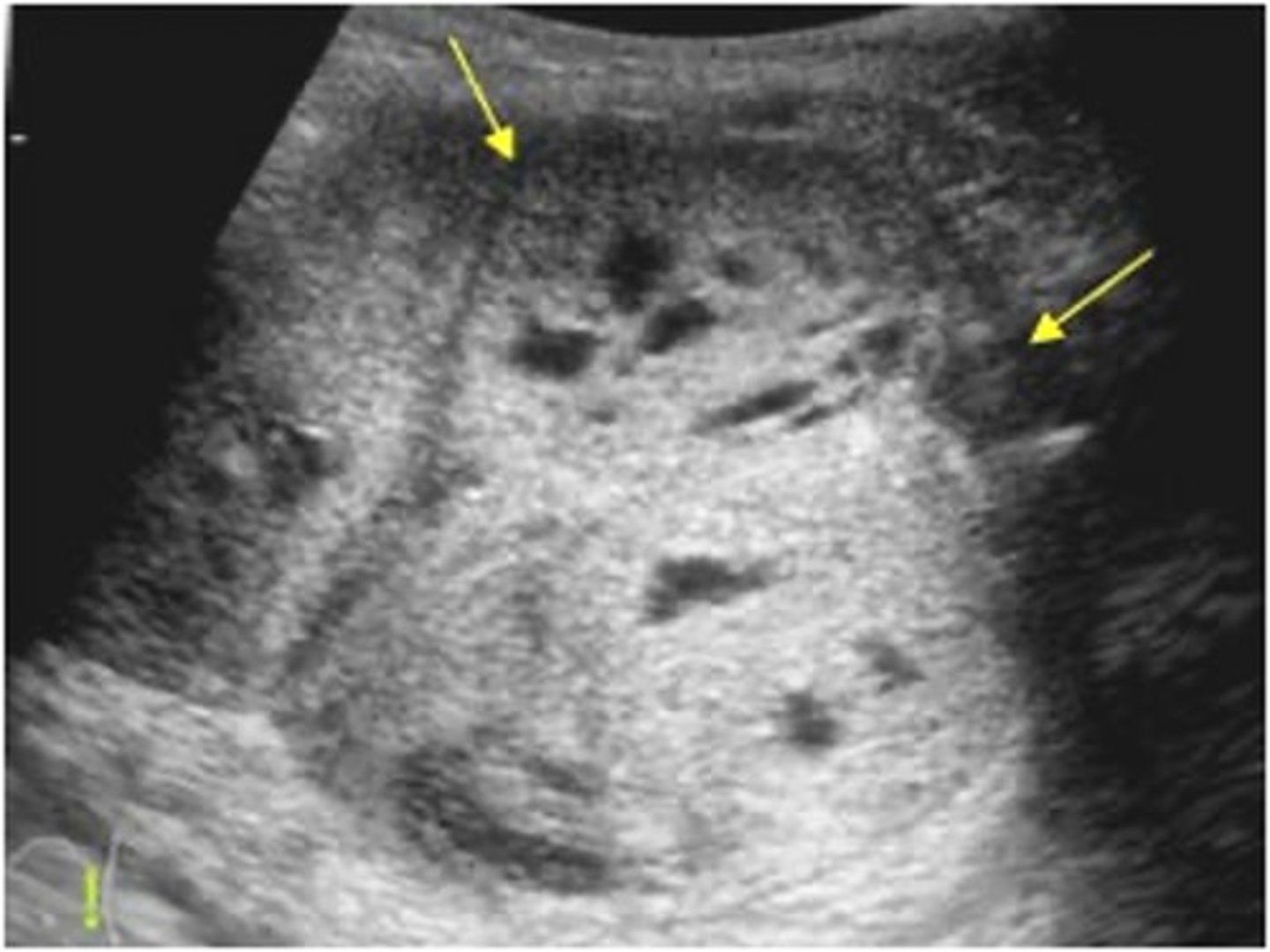
Nephroblastoma is typically found in children ages ___
2-5
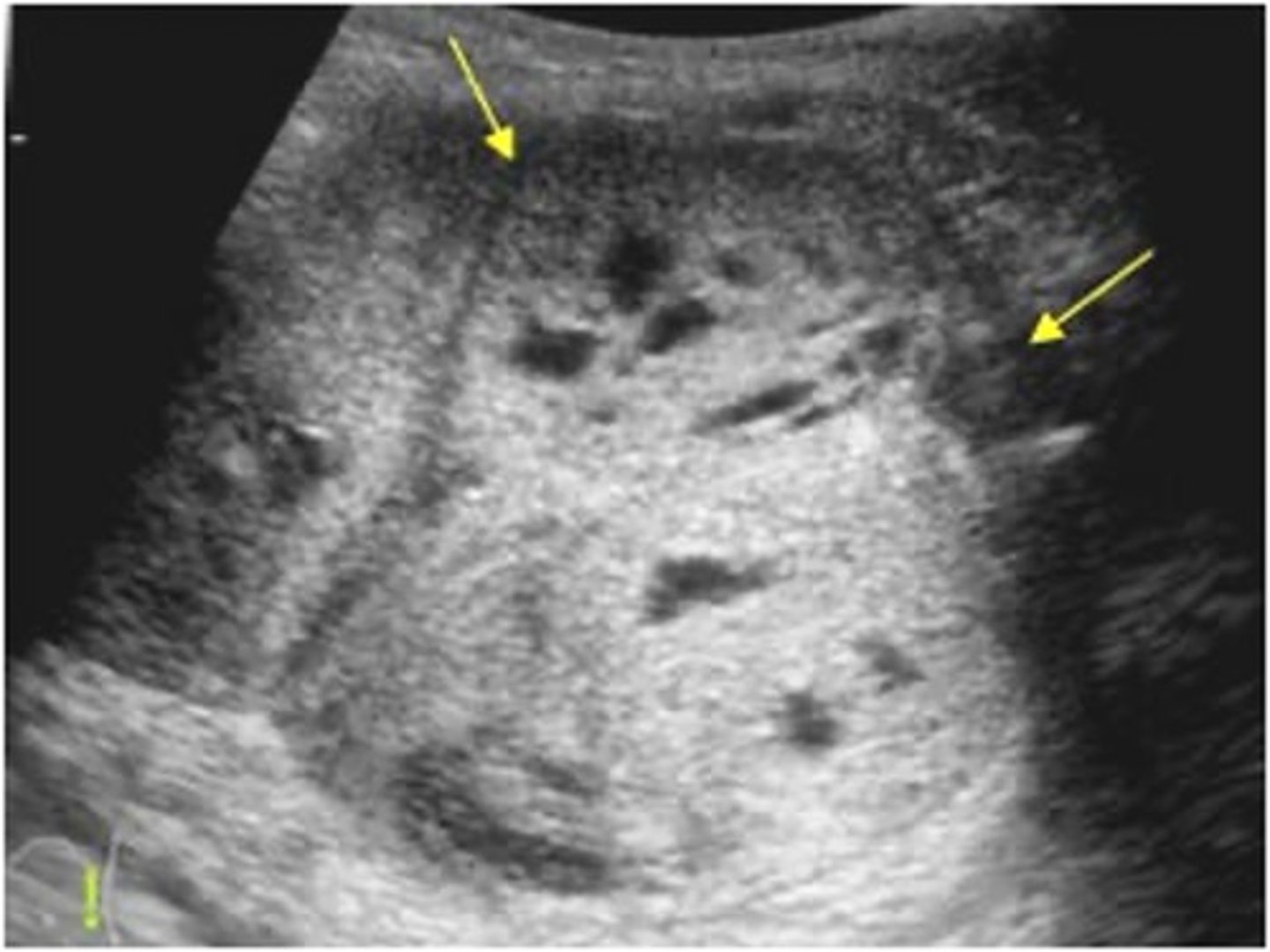
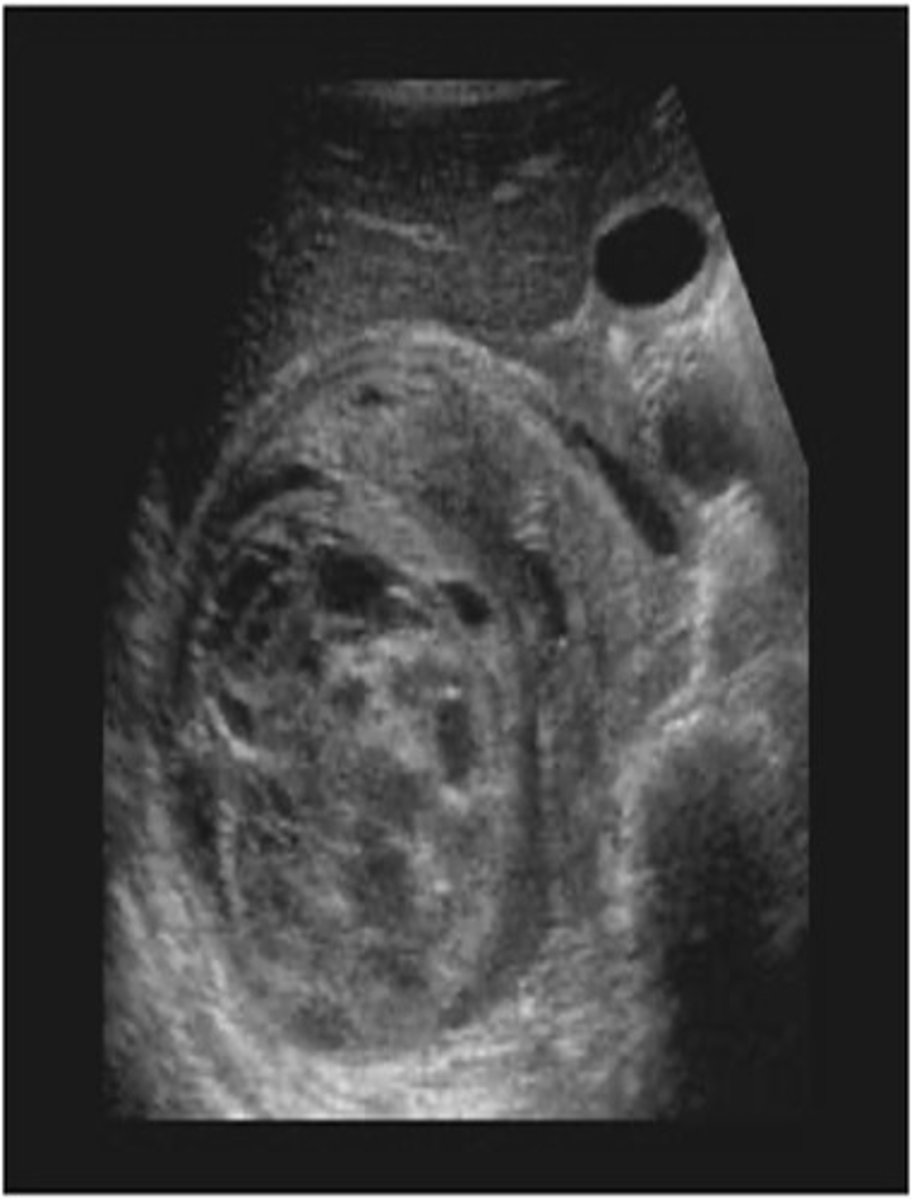
What are symptoms of nephroblastoma?
- abdominal flank mass
- hematuria
- fever
- anorexia
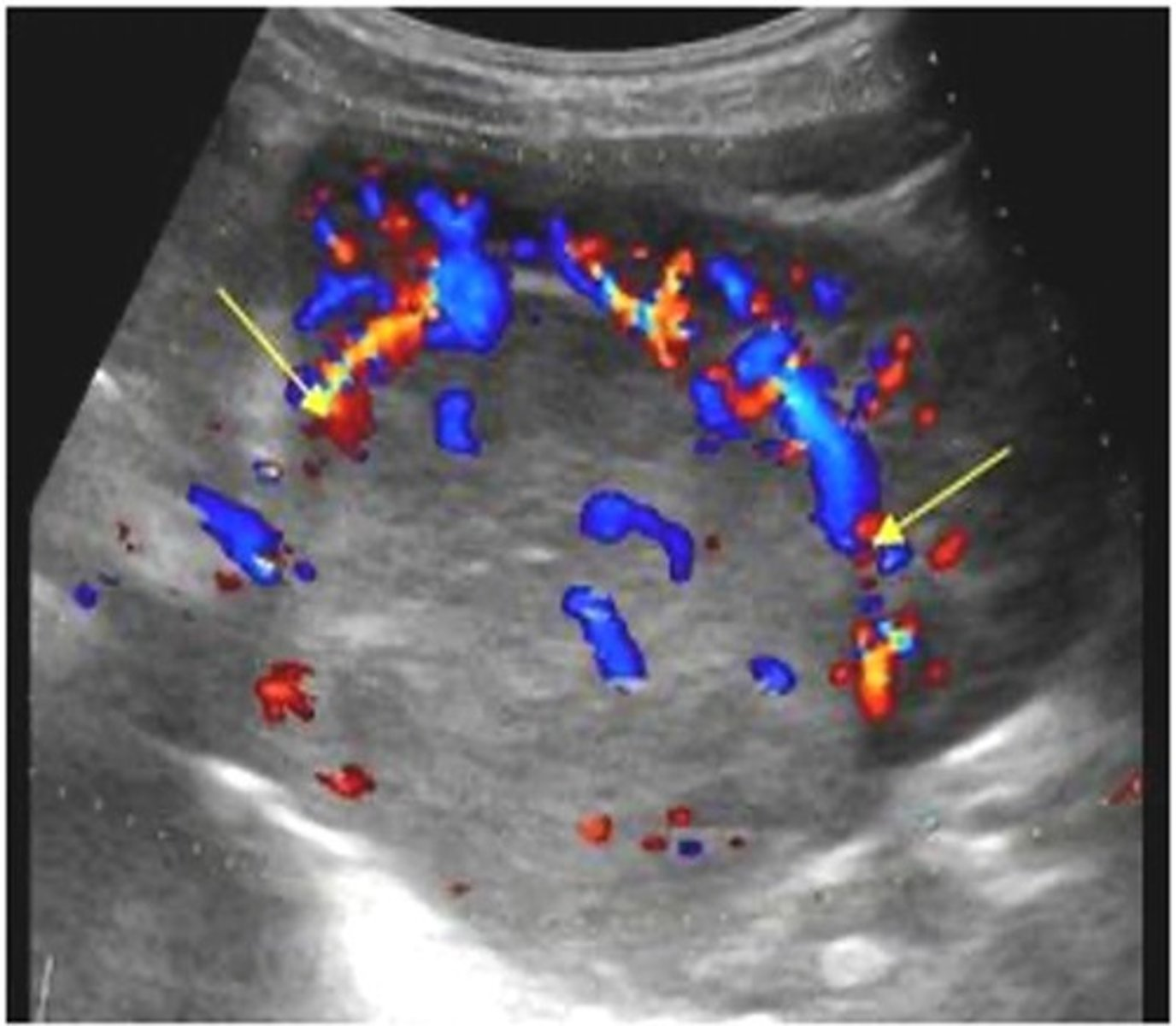
Nephroblastoma may be found with ___ obstruction with findings of leg edema, varicocele, or Budd-Chiari syndrome
venous
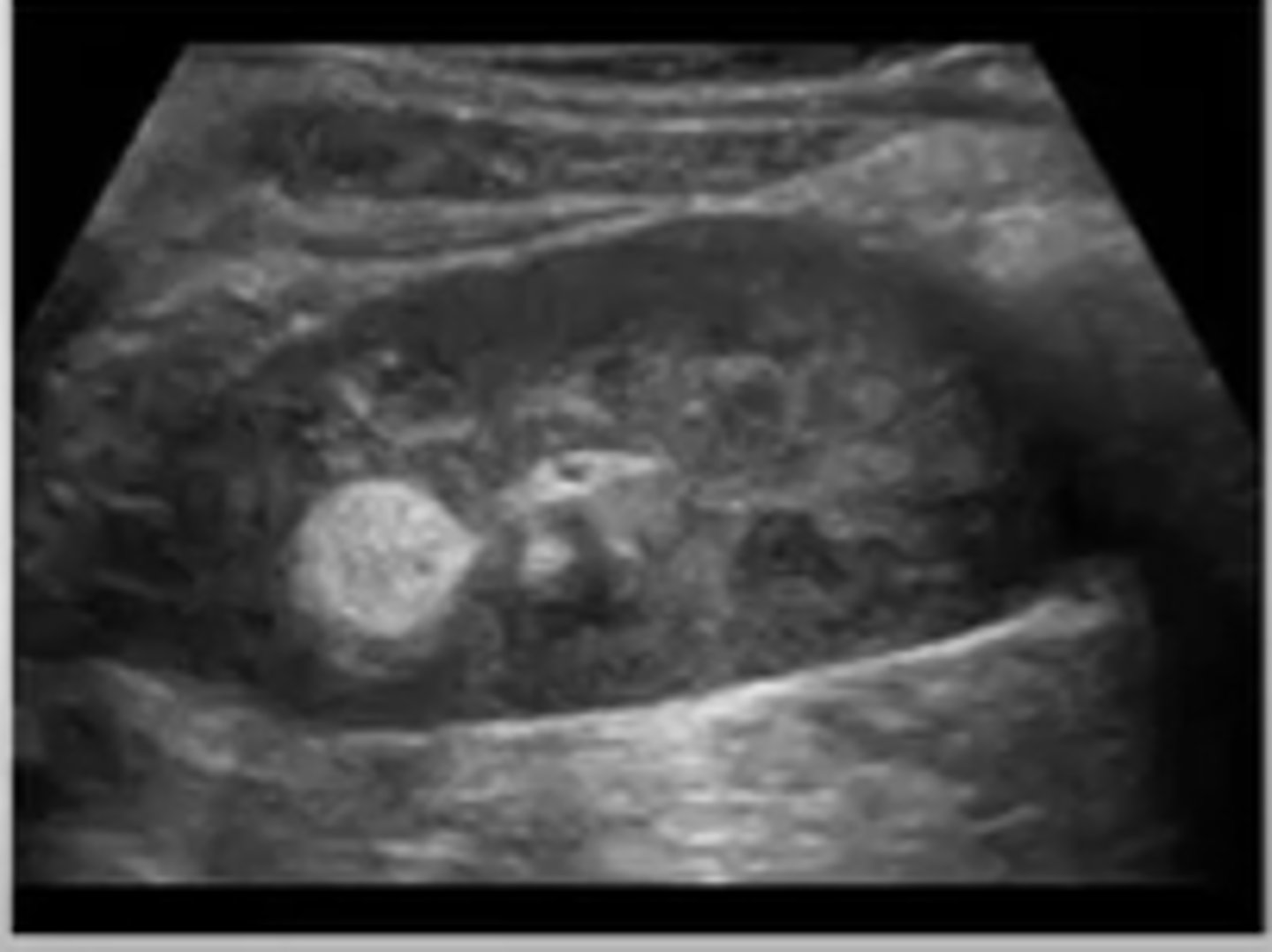
What is the most common benign renal tumor?
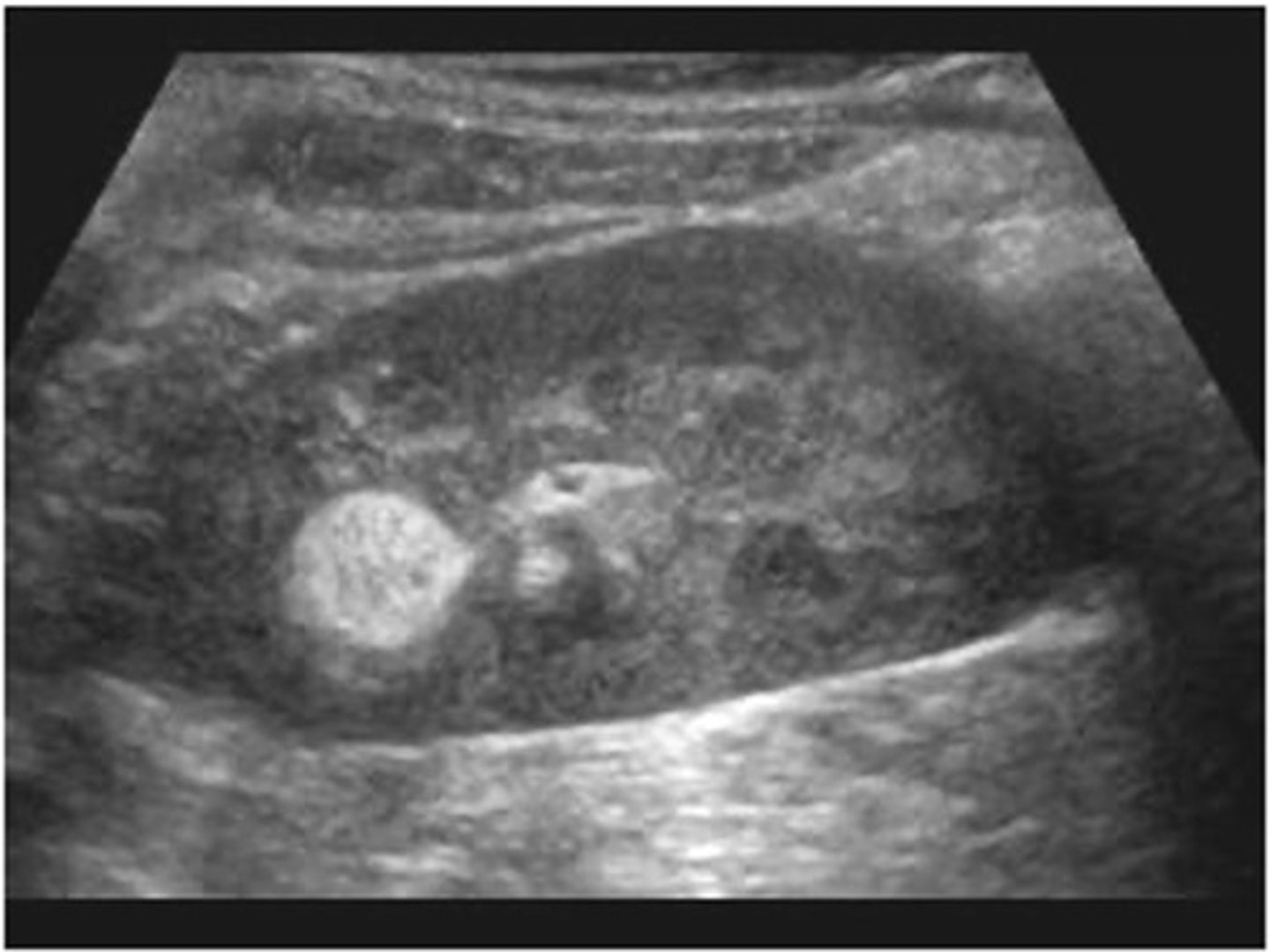
renal angiomyolipoma (AML)
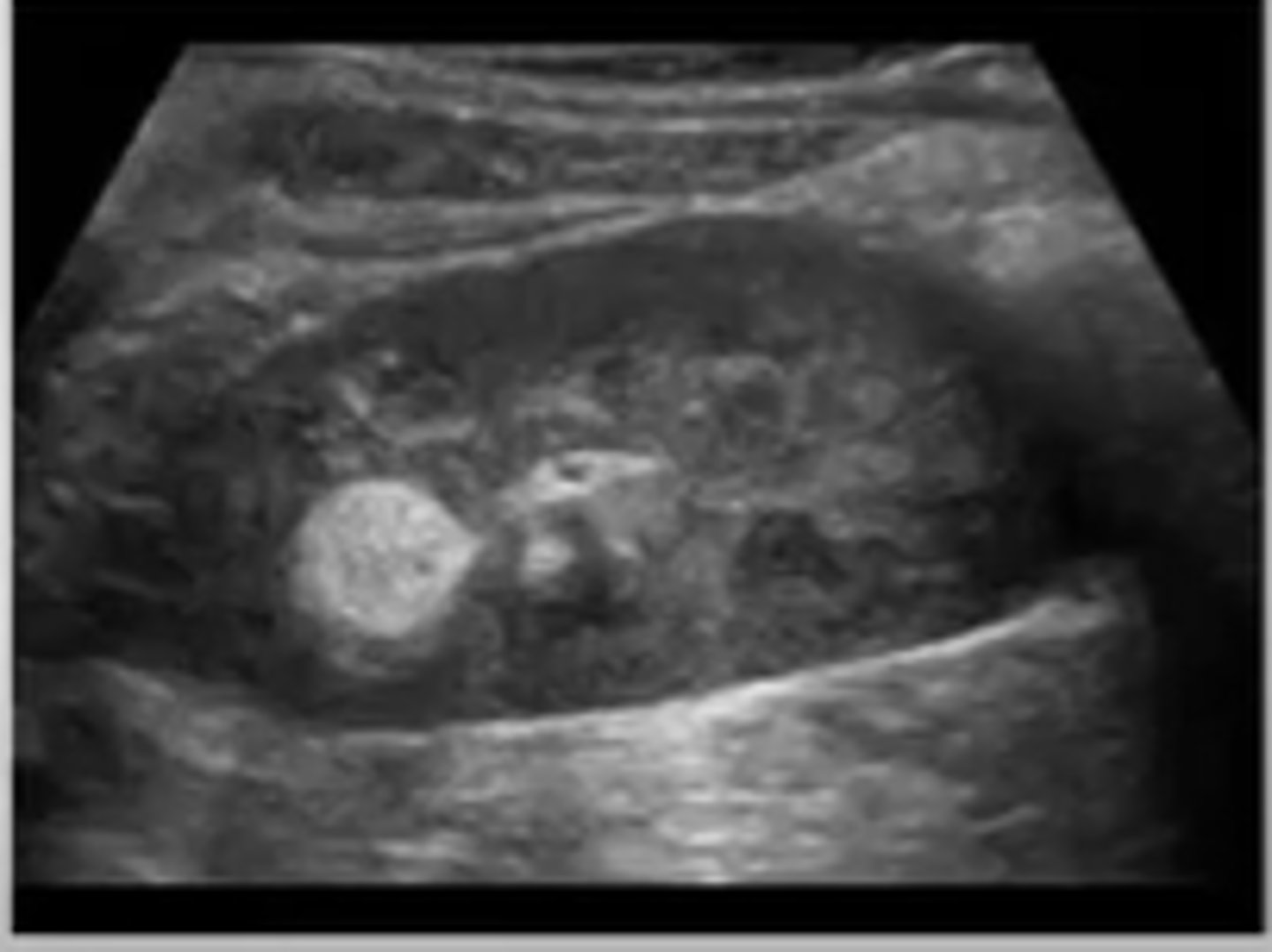
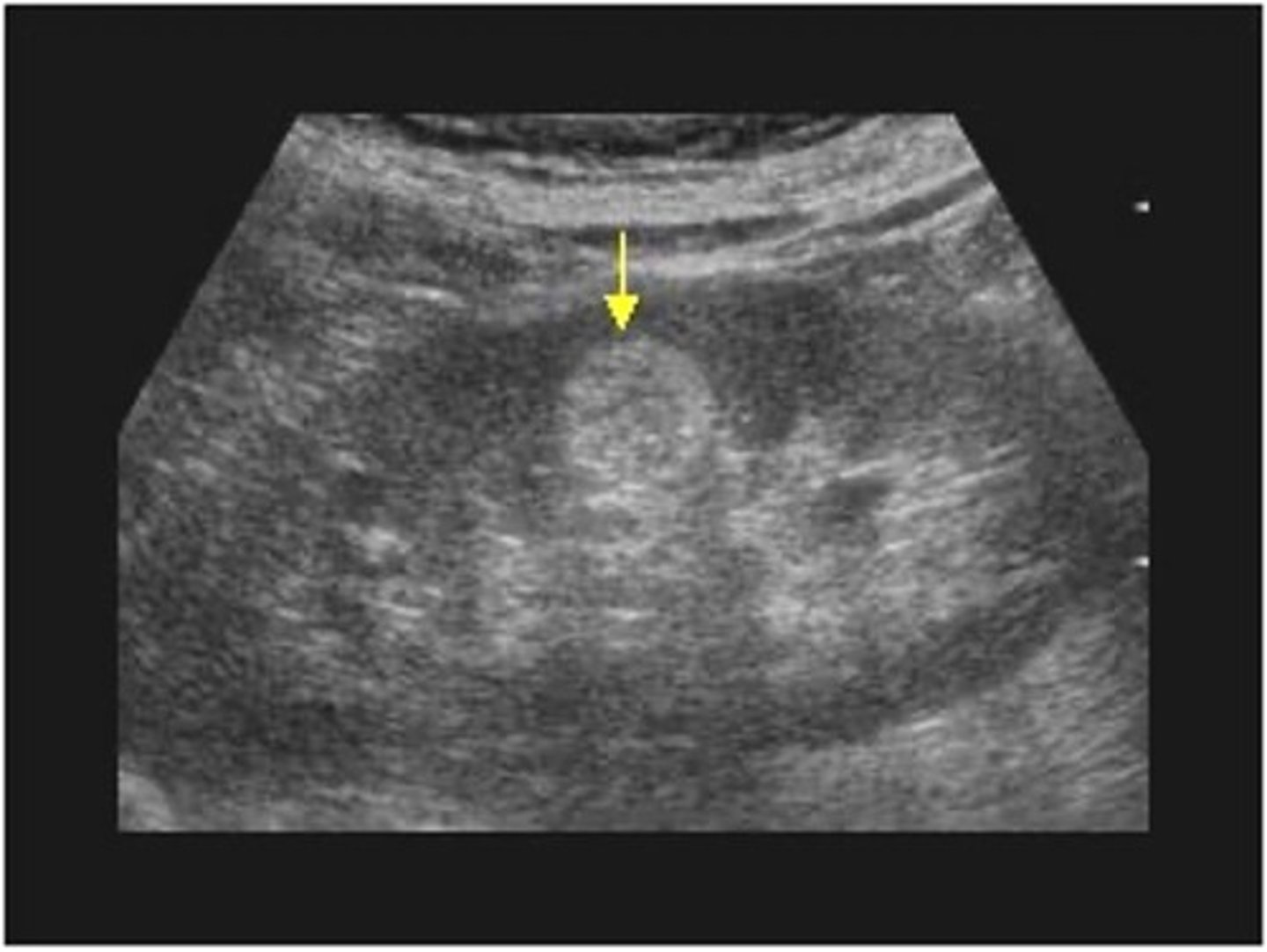
Renal angiomyolipoma (AML) is composed of ___, ___, and ___
fat; muscle; blood vessels
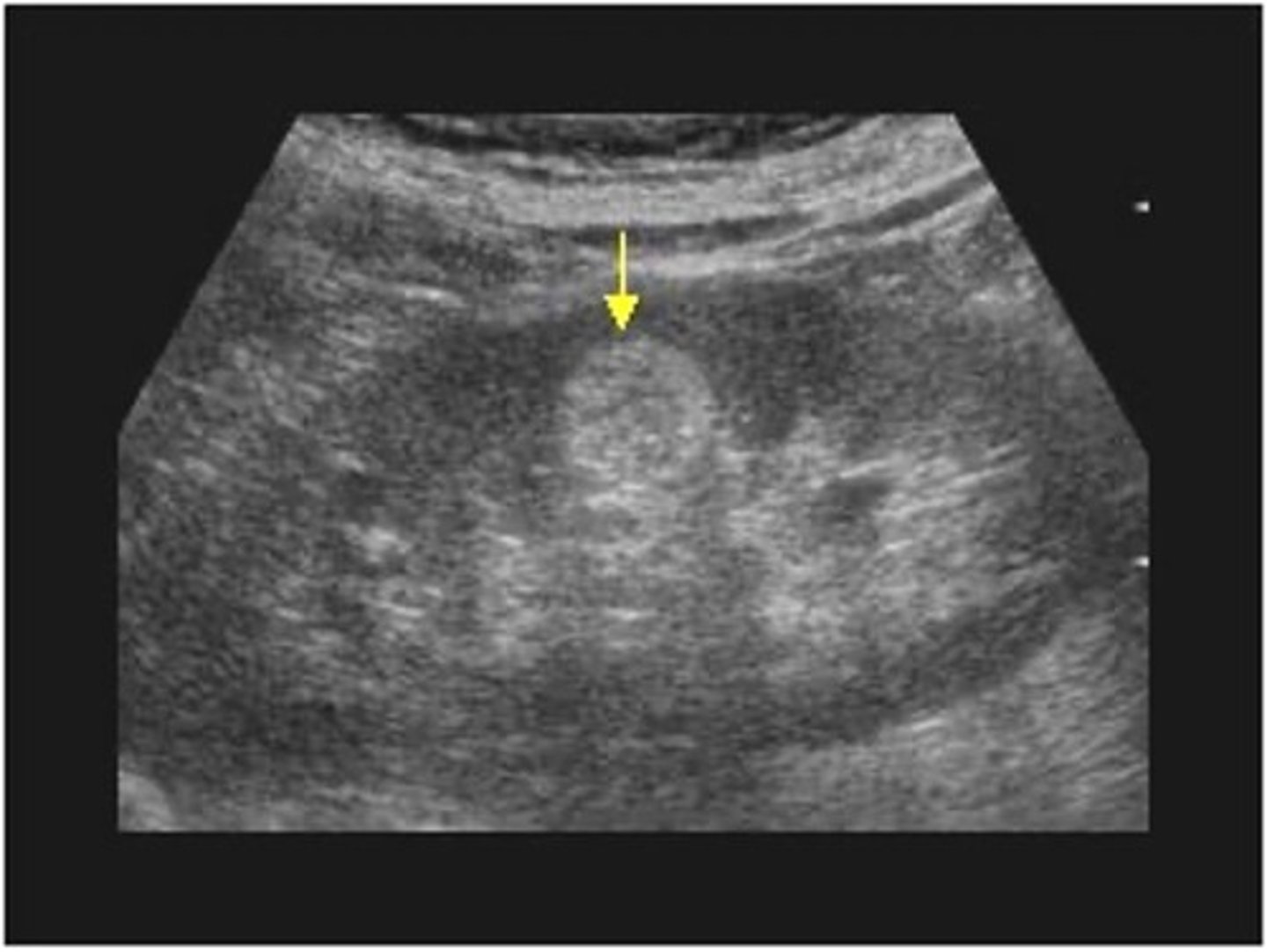
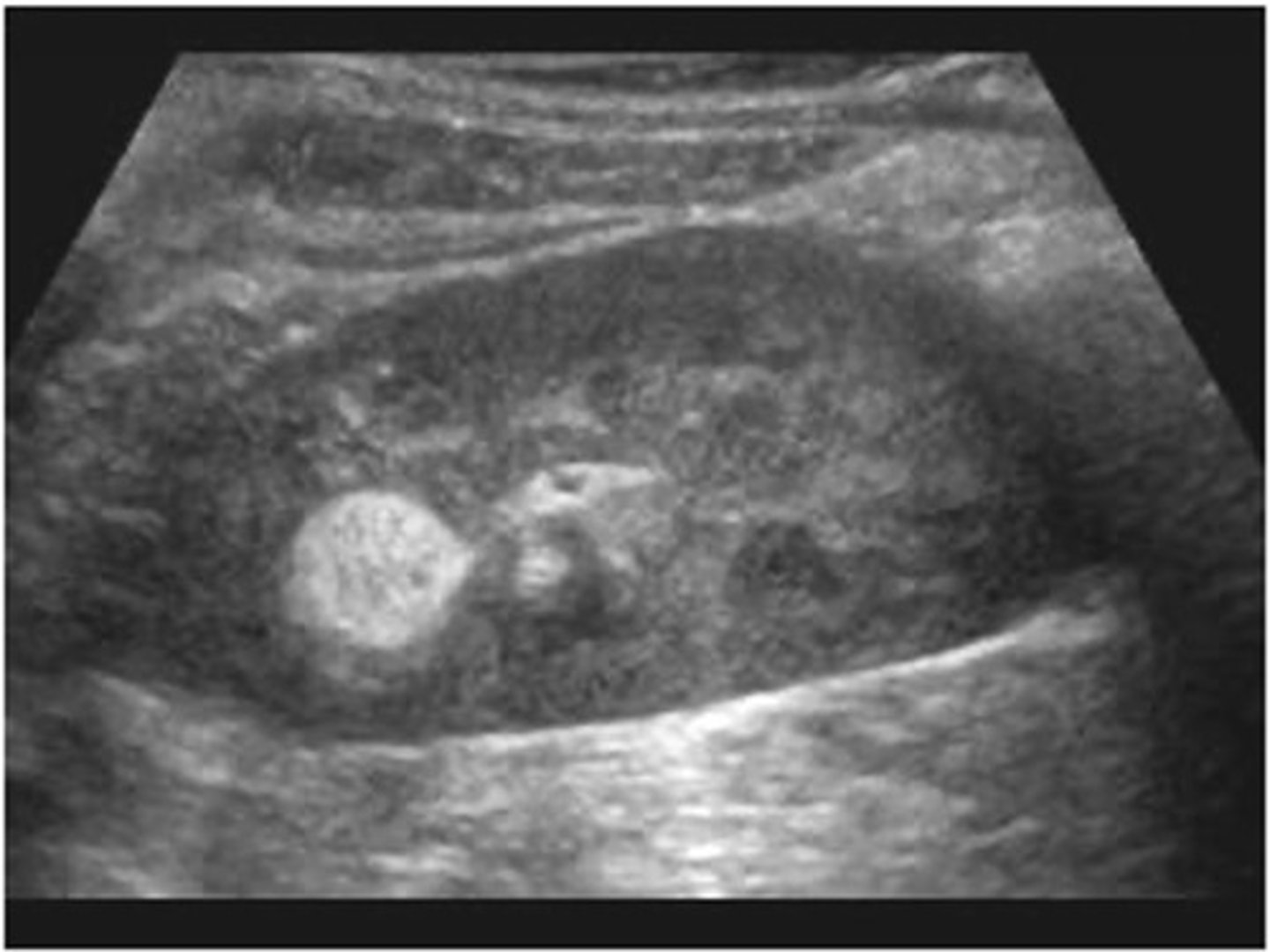
Sonographically, renal angiomyolipoma (AML) appears ___
hyperechoic
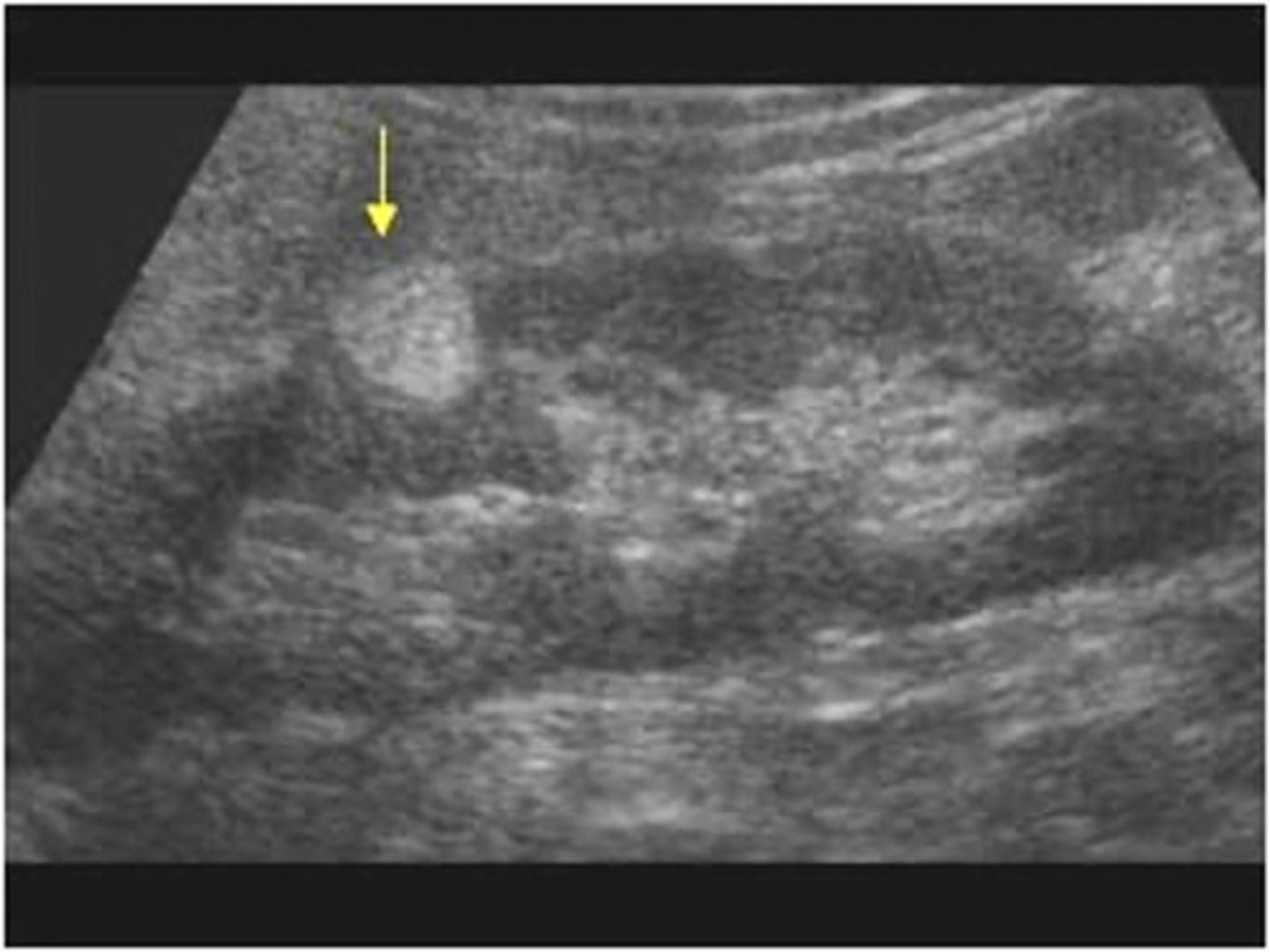
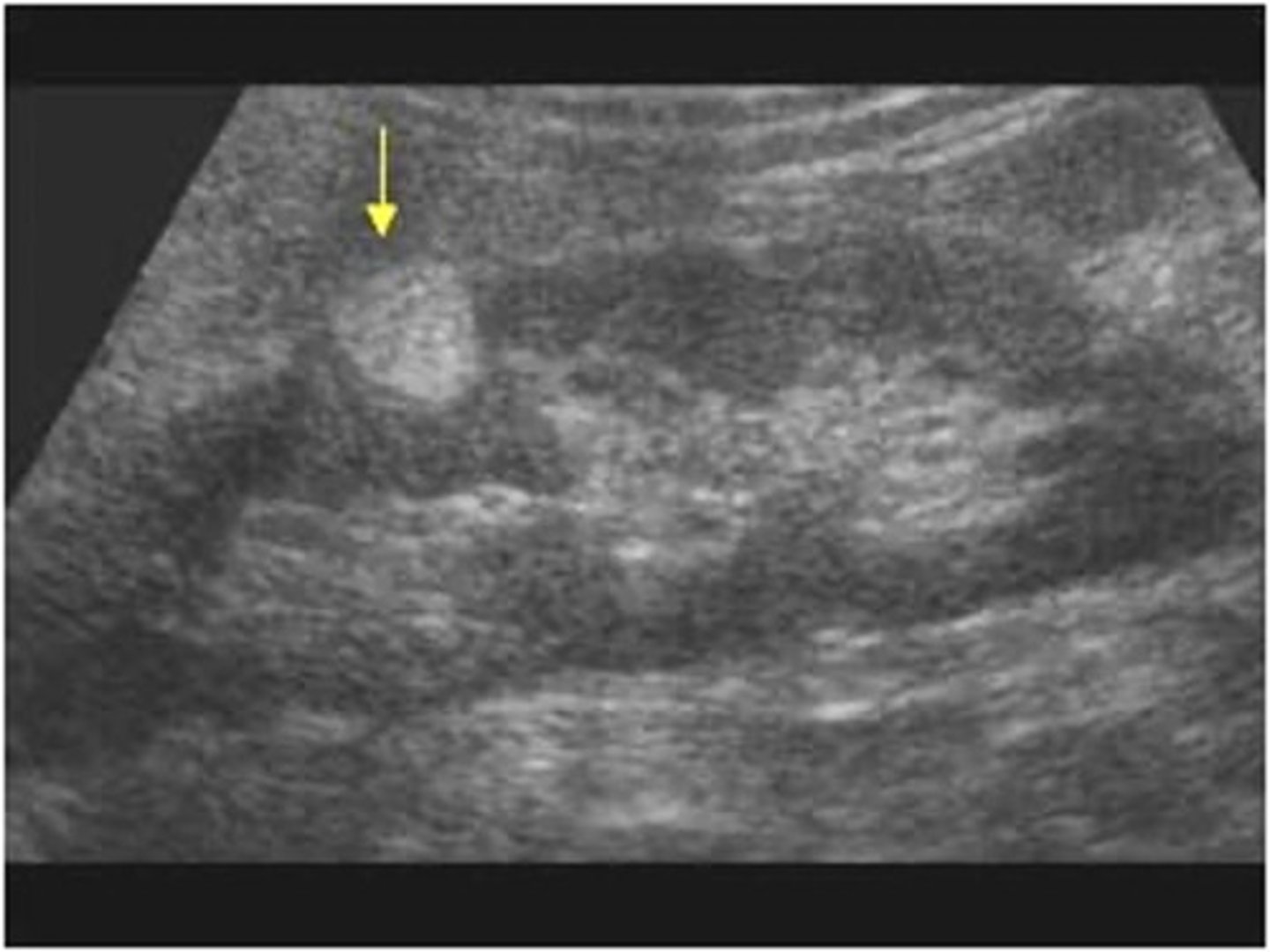
Angiomyolipoma (AML) occurrence:
80% in ___
80% in ___
80% in ___
females; right kidney; patients with tuberous sclerosis
Renal adenomas and oncocytomas are ___ and ___
uncommon; benign
Adenomas are ___
hypovascular
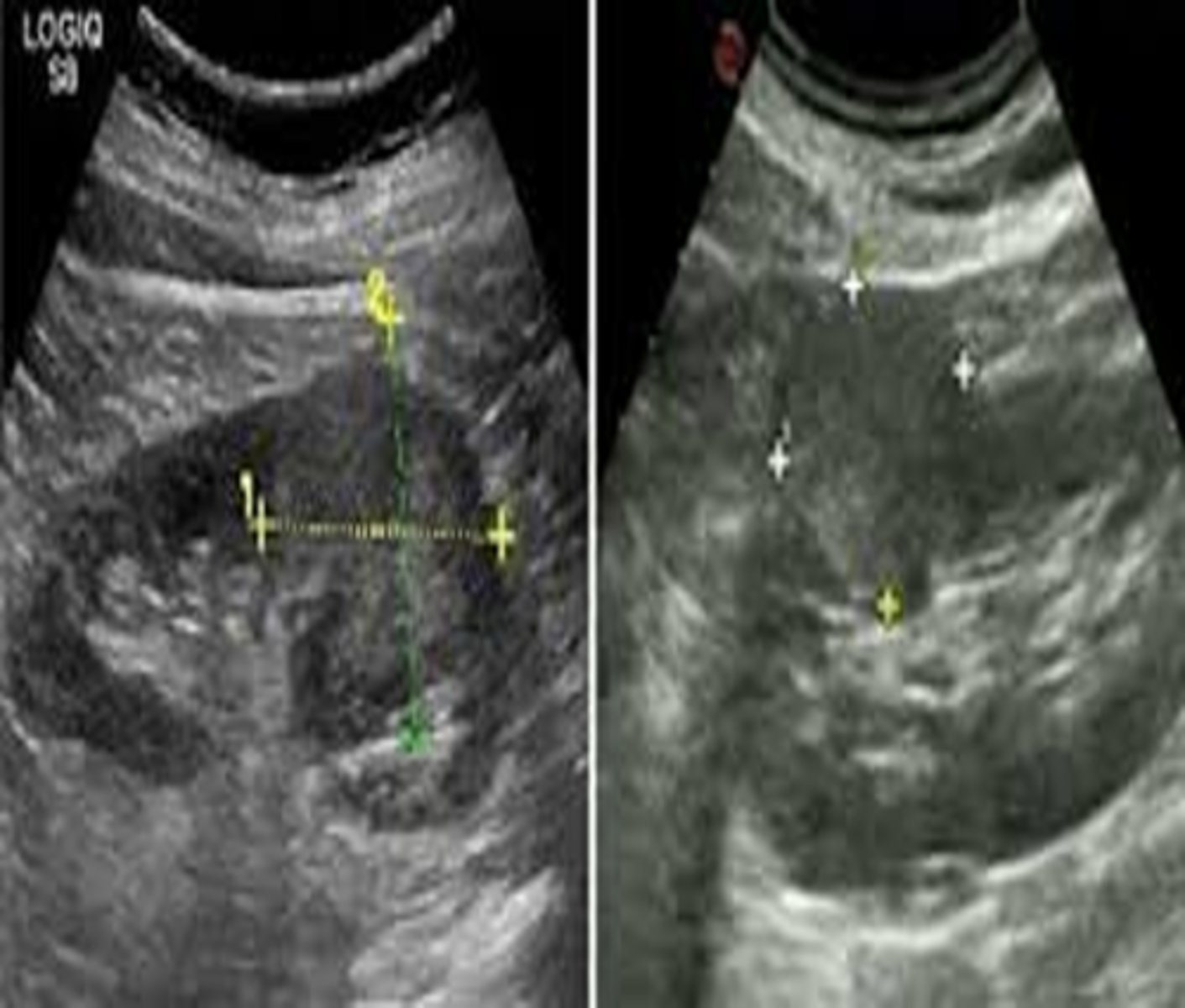
Oncocytomas resemble a ___ ___ pattern with a central ___
spoke wheel; scar
Lipomas consist of ___
fat
Lipomas are more common in ___
females
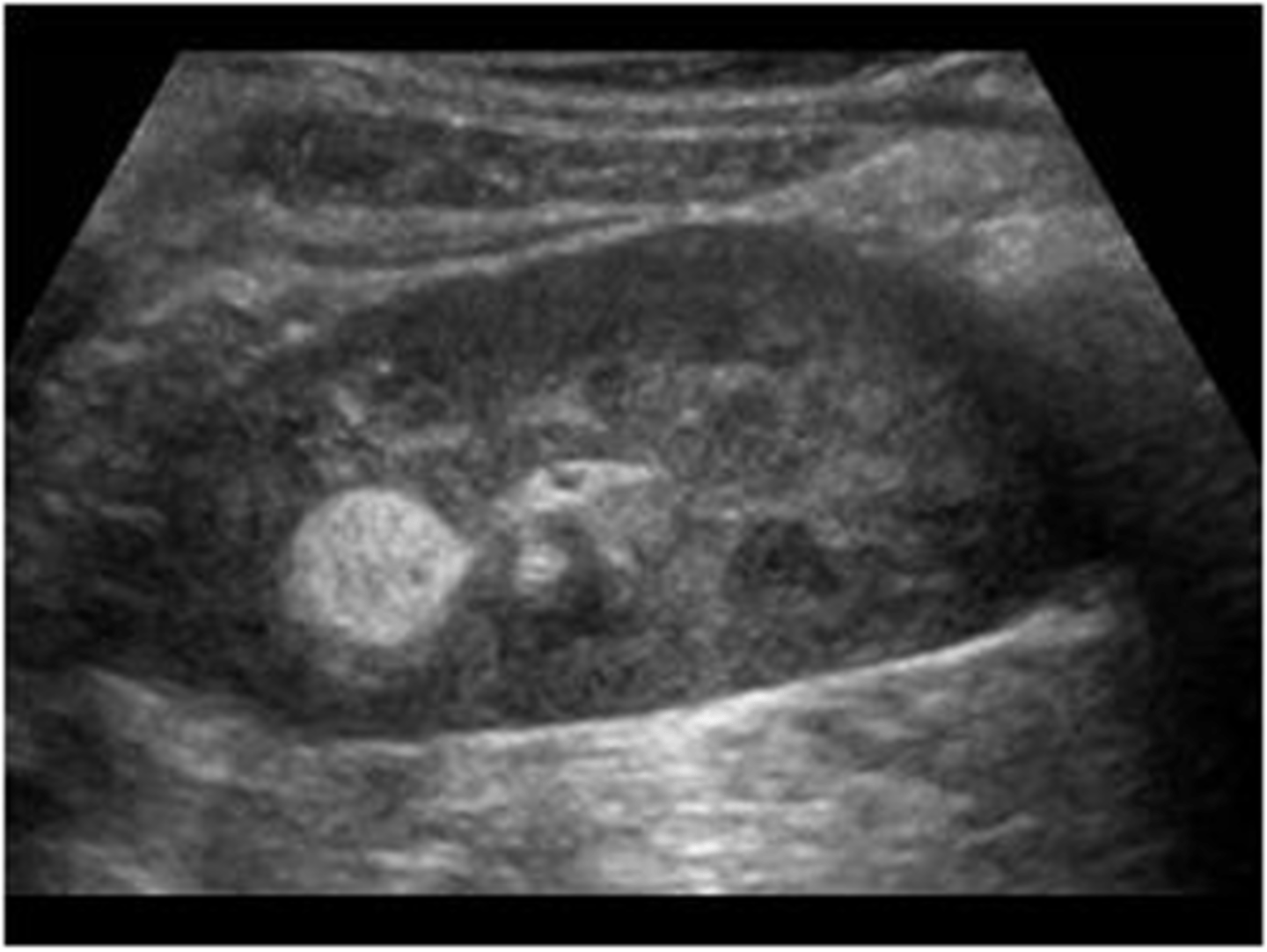
Sonographically, lipomas appear well-defined and ___
echogenic
Lipomas can appear ___
anywhere
Intrinsic renal disease can be classified into two groups:
1. produces increased ___ echoes; caused by deposition of collagen and fibers
2. produces loss of anatomic ___ and inability to distinguish ___ from ___
cortical
detail; cortex; medulla
Intrinsic renal disease group 1 includes
- interstitial nephritis
- acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
- amyloidosis
- diabetic nephropathy
- systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- myeloma
Intrinsic renal disease group 2 includes
- chronic pyelonephritis
- renal tubular ectasia
- acute bacterial nephritis
End stage intrinsic disease leads to ___
atrophy
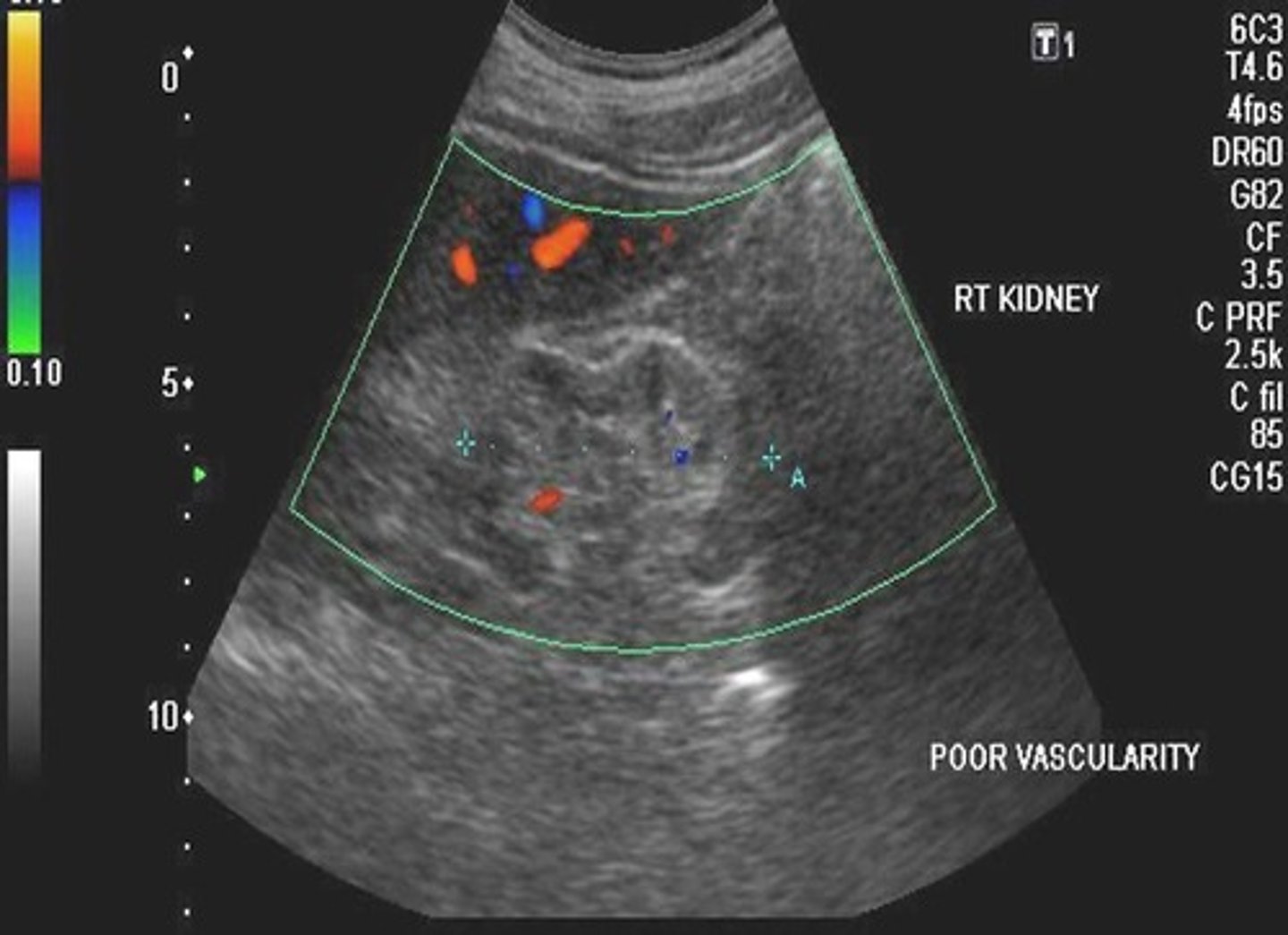
In acute glomerulonephritis, ___ and/or ___ of cellular elements occurs in the glomeruli
necrosis; proliferation
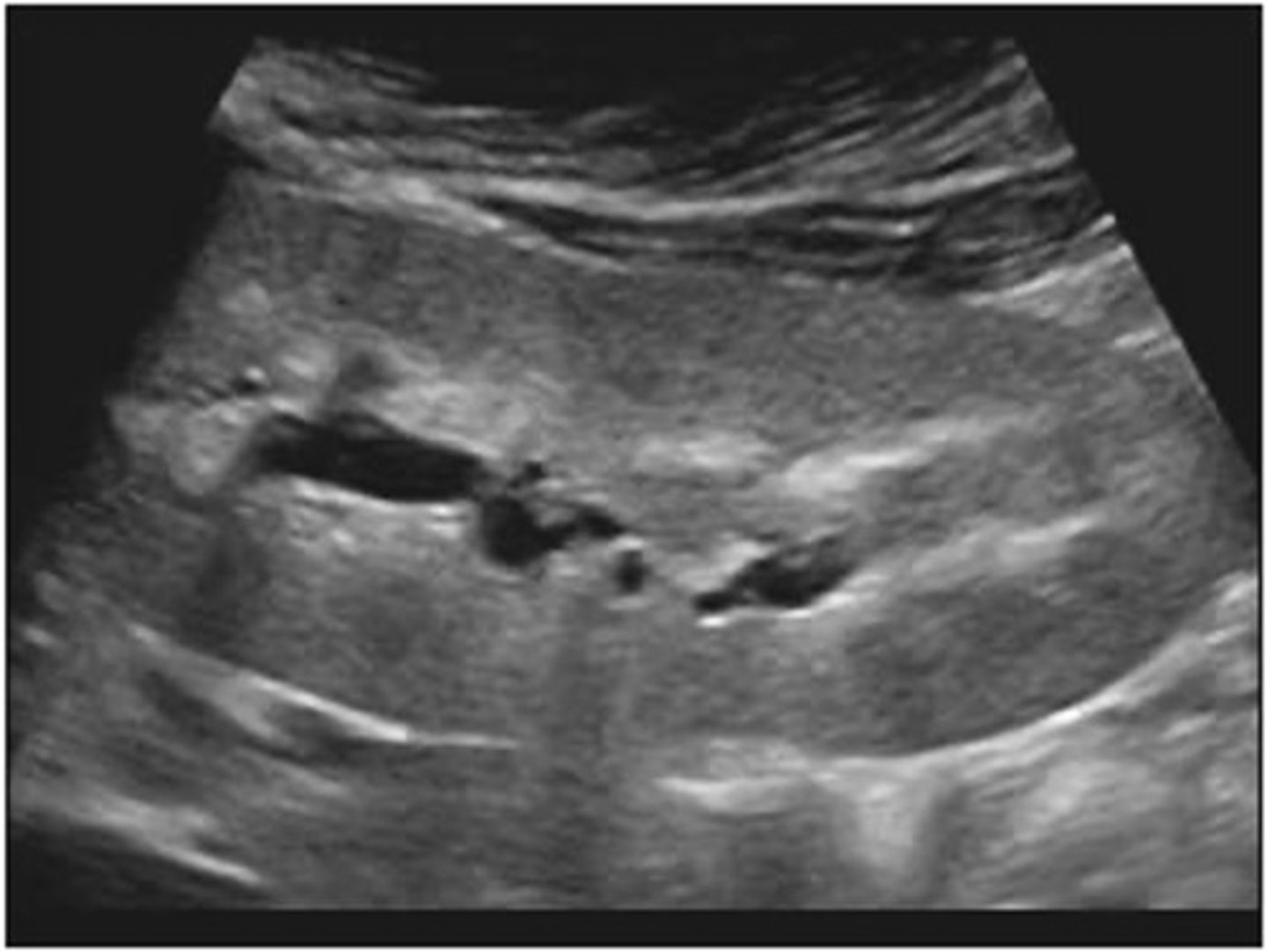
The end result of acute glomerulonephritis is ___, poorly ___ kidneys
enlarged; functioning
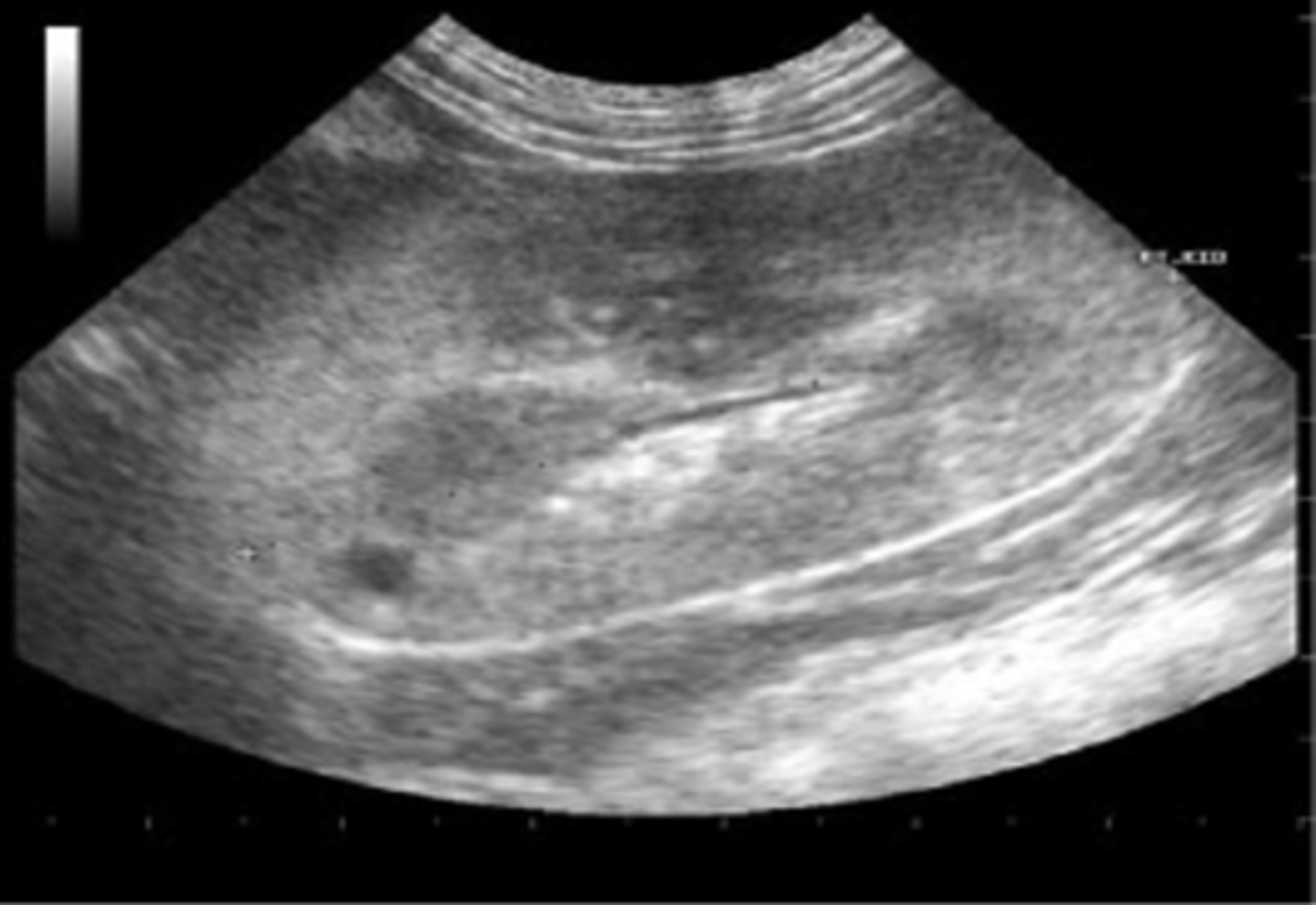
Acute glomerulonephritis is seen sonographically with increased ___ echoes
cortical
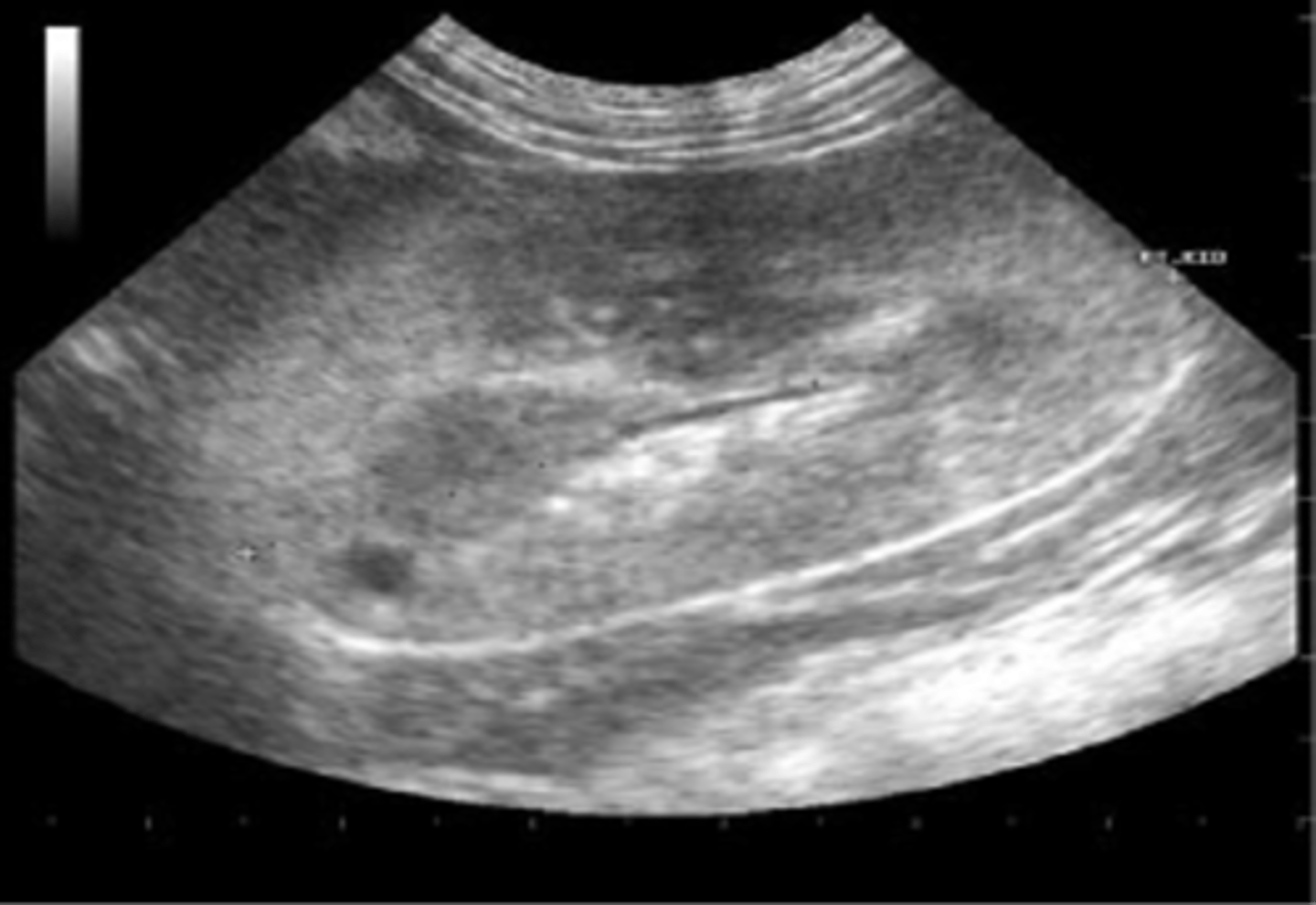
What are symptoms of acute glomerulonephritis?
- nephrotic syndrome
- hypertension
- anemia
- peripheral edema
Acute interstitial nephritis is associated with the infectious processes of ___ and ___, or as an ___ to certain drugs
scarlet fever; diphtheria; allergic reaction
What are symptoms of acute interstitial nephritis?
- uremia
- proteinuria
- hematuria
- rash
- fever
- eosinophilia
Acute interstitial nephritis causes ___ and ___ kidneys
enlarged; mottled
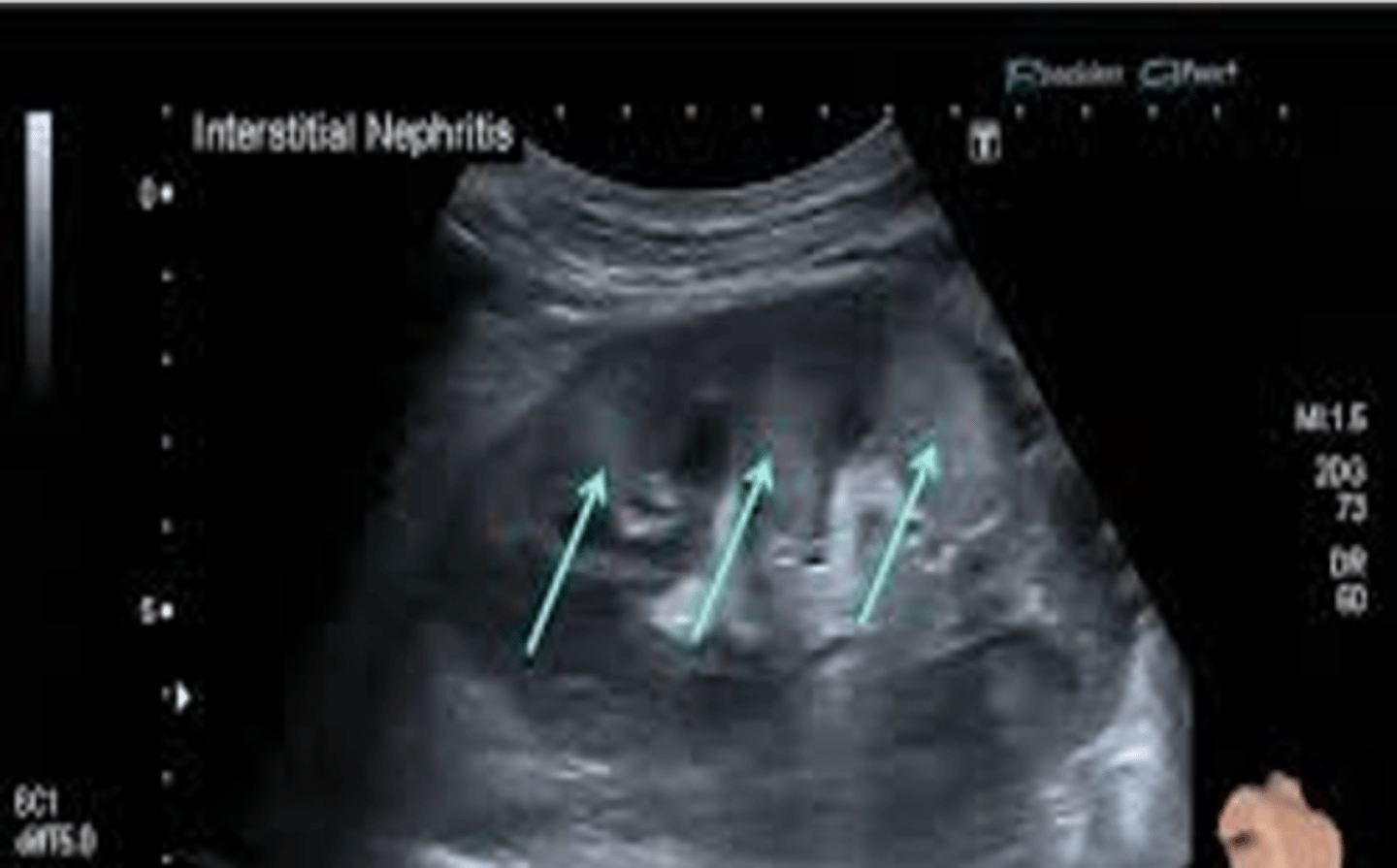
Sonographically, acute interstitial nephritis appears with increased ___ ___
cortical echogenicity
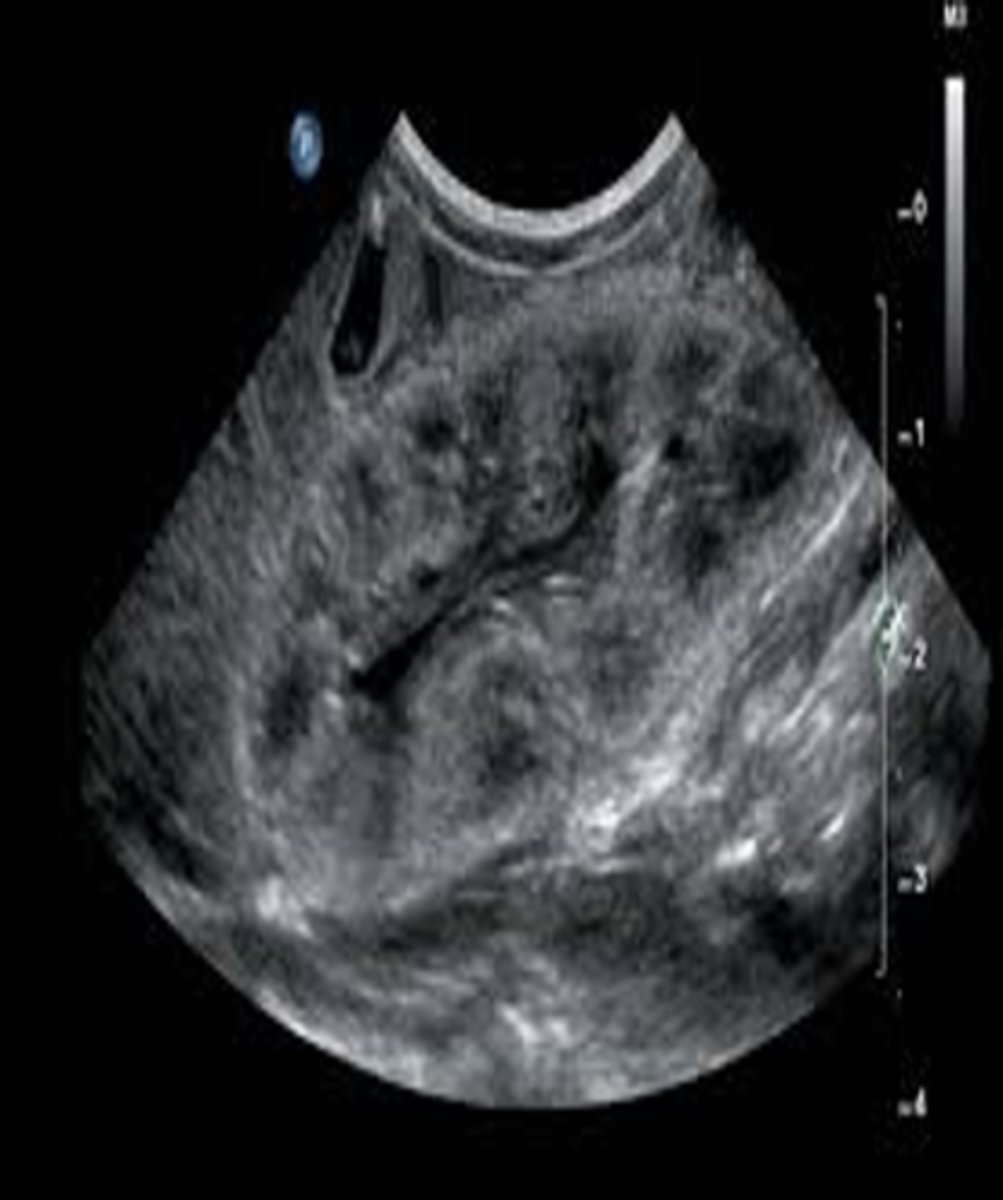
Lupus nephritis is an ___ disorder that causes ___, ___, ___, renal vein ___, and renal ___
autoimmune; hematuria; proteinuria; hypertension; thrombosis; insufficiency
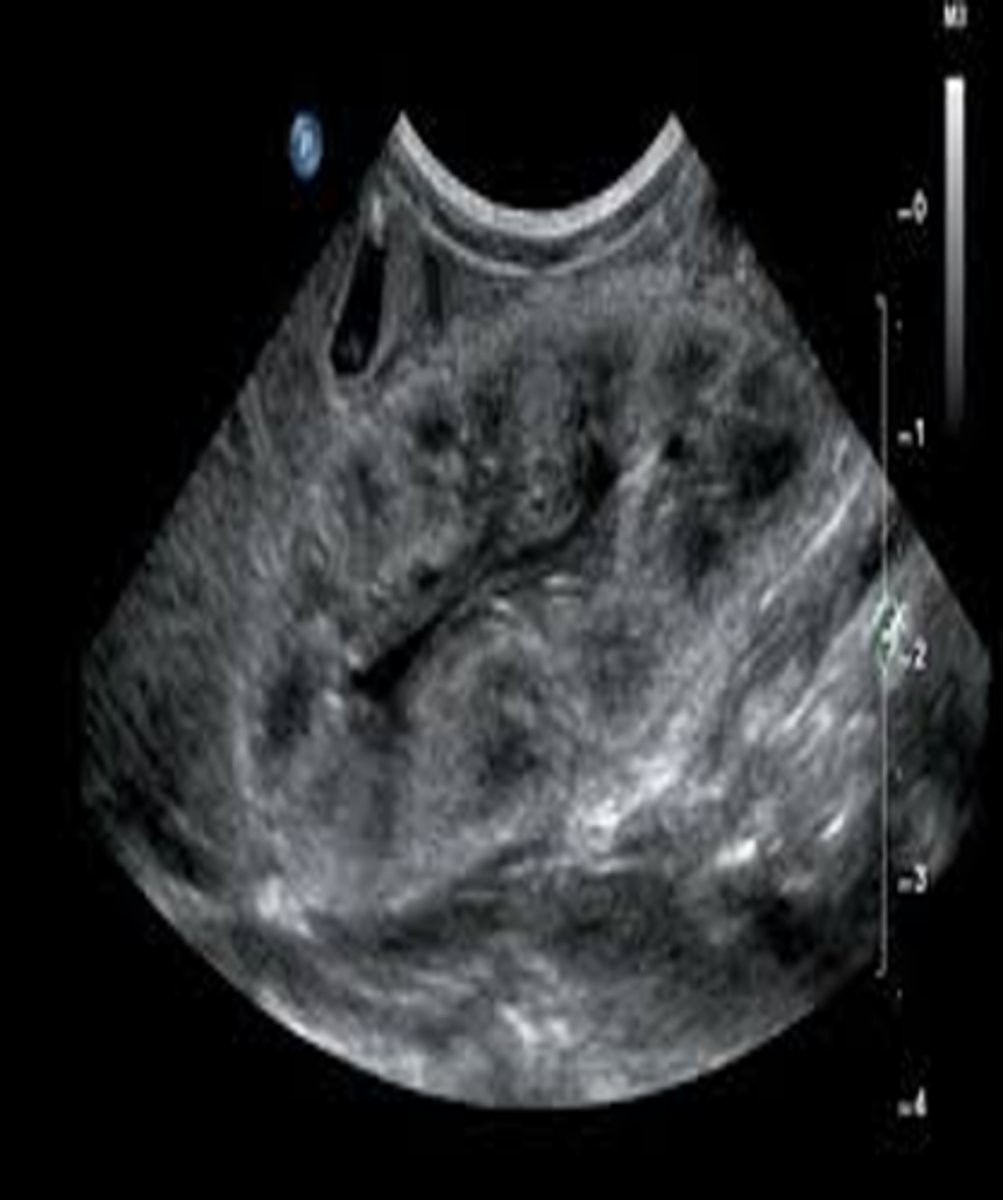
Lupus nephritis appears sonographically with increased ___ and renal ___
echogenicity; atrophy
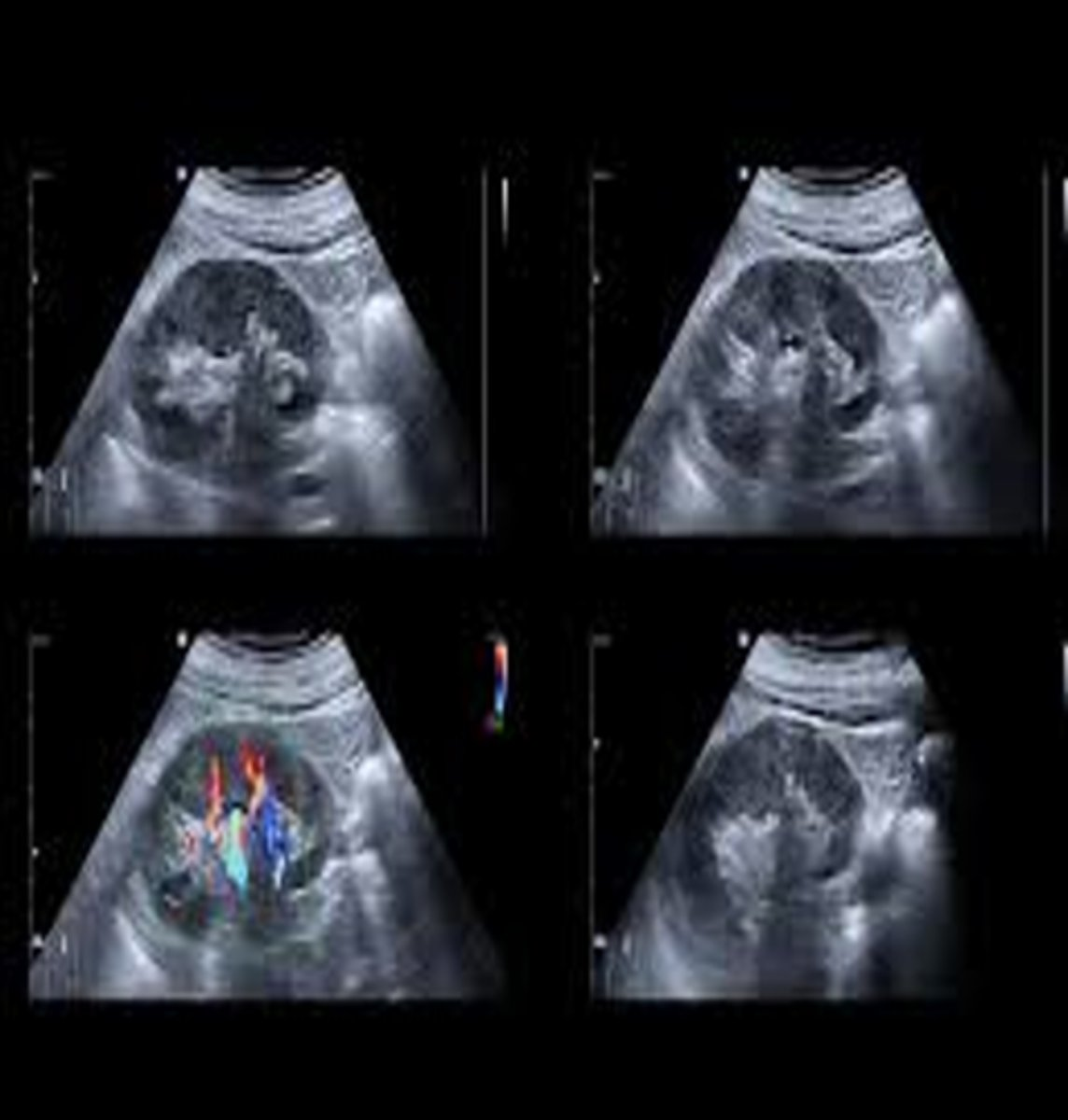
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) causes unexplained ___ and ___ resulting in renal ___
uremia; azotemia; dysfunction
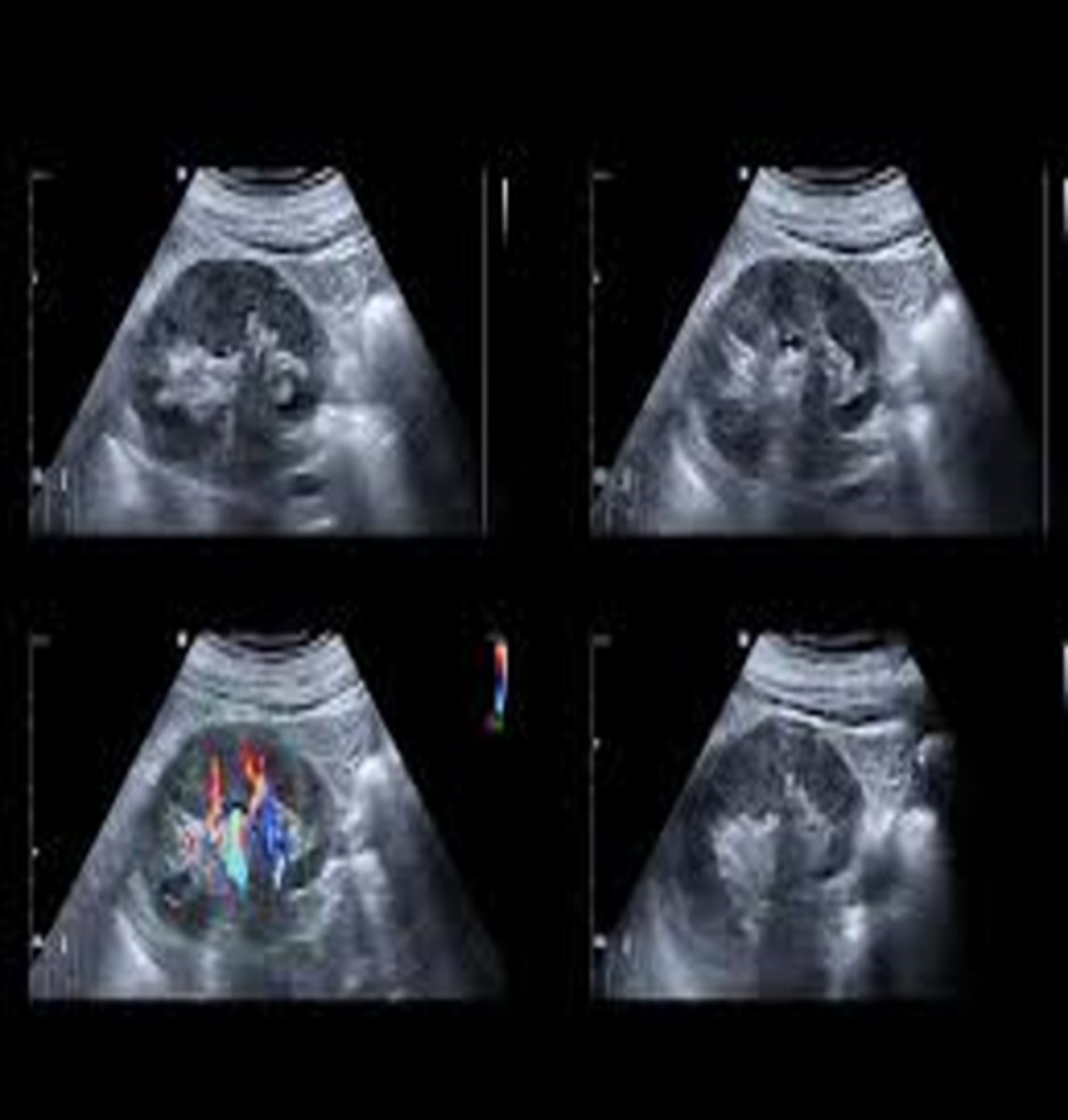
Sonographically, a patient with AIDS will have ___ kidneys that may be ___
echogenic; enlarged
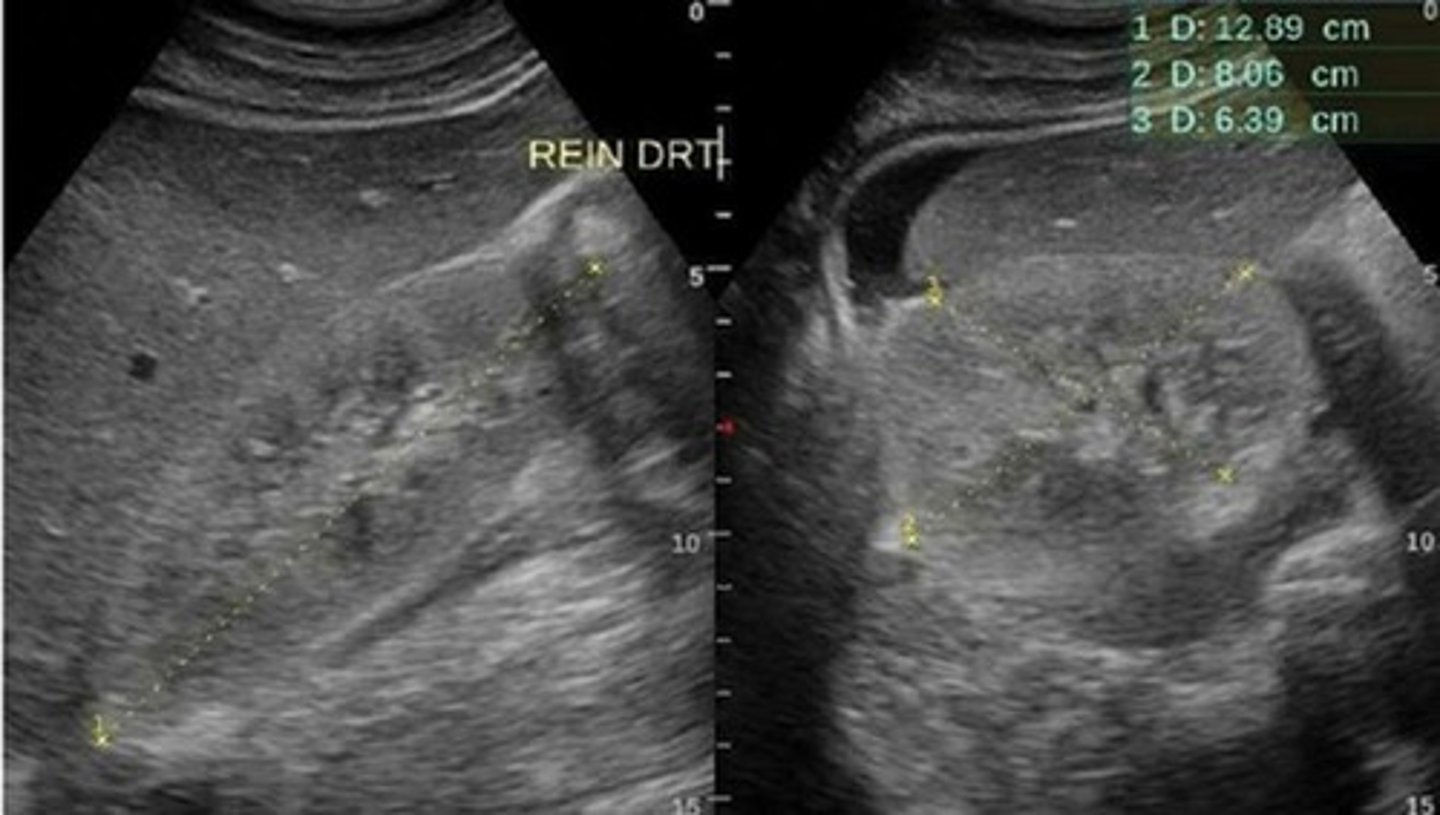
Sickle cell nephropathy causes ___, renal vein ___, papillary ___, and ___
glomerulonephritis; thrombosis; necrosis; hematuria
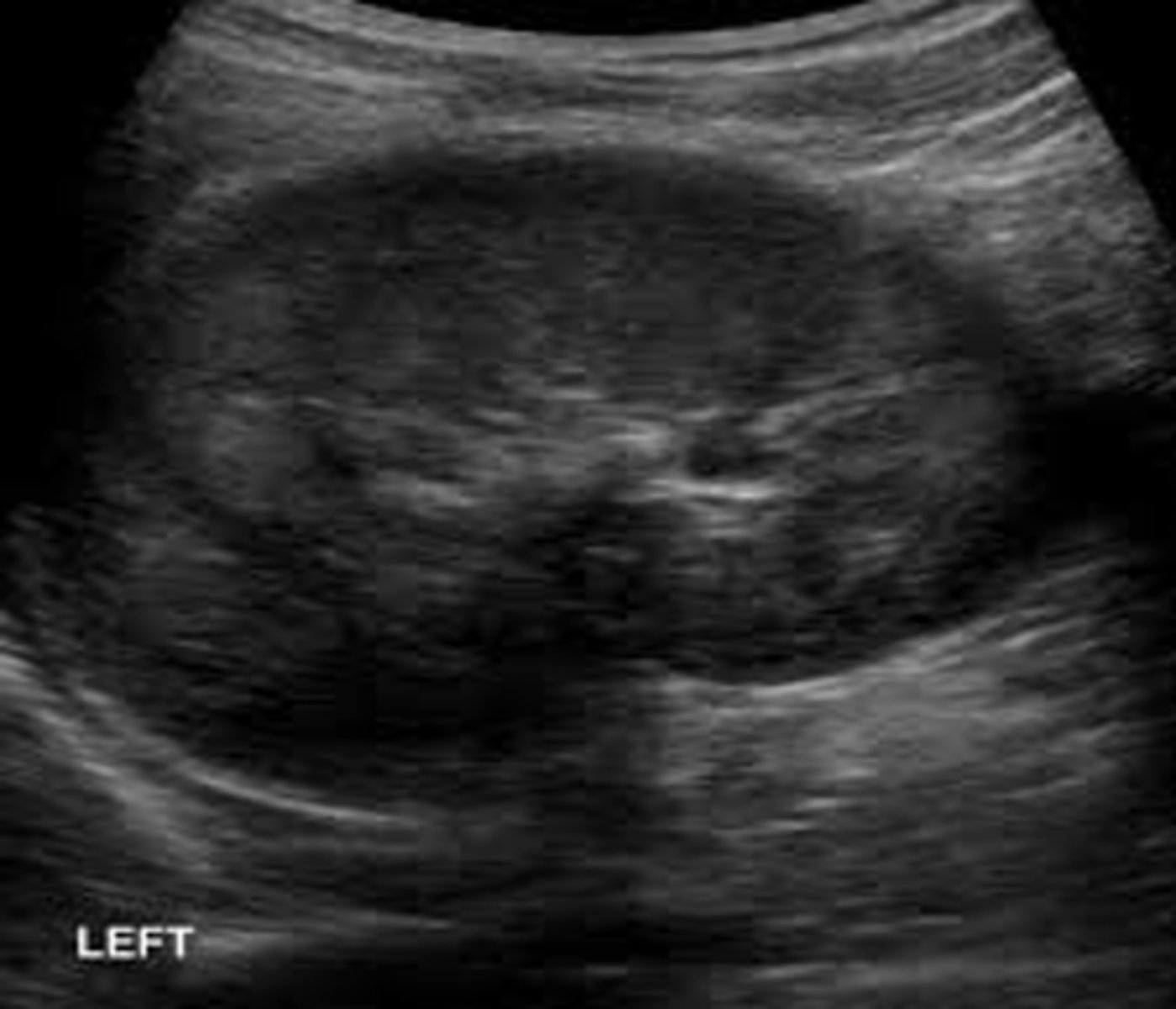
Renal papillary necrosis (RPN) is caused by ___, ___, ___, and other diseases
sickle cell; diabetes; kidney transplant
What has an important role in necrosis?
ischemia
What are symptoms of renal papillary necrosis (RPN)?
- hematuria
- flank pain
- dysuria
- fever
- hypertension
- acute renal failure (ARF)
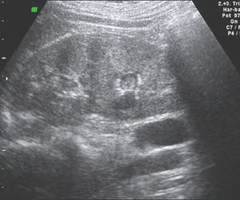
Sonographically, renal papillary necrosis (RPN) appears as round or triangular ___ spaces at the ___ junction
fluid; corticomedullary
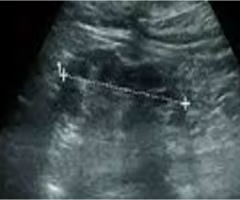
Renal atrophy is a ___ loss of renal tissue with preservation of ___ anatomy
uniform; intrarenal
What occurs secondary to renal atrophy?
renal sinus lipomatosis
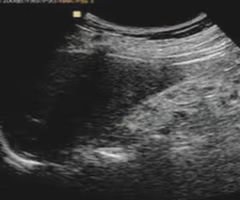
With renal atrophy, kidneys appear ___ with a highly ___ sinus and a thin cortex
enlarged; echogenic
Acute renal failure (ARF) is a sudden ___ in kidney function that results in retention of ___ products and imbalance of electrolytes and fluids
decline; waste
Prerenal failure is caused by ___ of the kidney
hypoperfusion
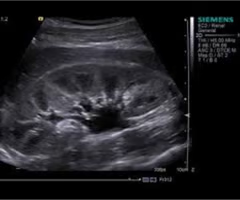
Postrenal failure results from ___ obstruction and is ___
outflow; reversible
An extremely large echogenic renal sinus that appears to engulf the entire renal parenchymal outline suggests:
lipomatosis
Adult polycystic disease may be characterized by all except which of the following?
The involved kidneys are small and extremely echogenic
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis can have all of the following sonographic findings except:
Decreased renal size
In cases of nephrocalcinosis, calcium deposits are usually located in the:
medulla