physical chemistry
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MSOP 1014 - the science of medicines
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
define molarity
moles of solute dissolved in 1L of solution
define normality
gram equivalent weight of solute dissolved in 1L of solution
define molality
moles of solute per kilogram of solvent
mole fraction
moles of solute / total number of moles
define milliequivalent (mEQ)
concentration of an ion in solution
what is a molecular equation?
an equation with reactants and products written as molecular substances
what is a complete ionic equation?
an equation where soluble ionic compounds are written as separate ions
what is a net ionic equation?
an equation where soluble ionic compounds are written as separate ions and spectator ions are cancelled
define an electrolye
a substance that dissociates into ions
define a non-electrolyte
a substance that does not dissociate into ions
what is a hydronium ion?
H3O+
define an acid according to the arrhenius theory
a substance that releases H+ into water
define a base according to the arrhenius theory
a substance that releases OH- into water
what is the exception to the arrhenius theory?
NaHCO3 (is a base though does not release H+)
what is an acid according to the bronsted-lowry theory?
a substance that donates a proton
what is a base according to the bronsted-lowry theory?
a substance that accepts a proton
what is an amphoteric substance?
a substance that can act either as an acid or a base
what is self-ionisation?
when a molecule reacts with itself to give ions
what is the ionic product of water (Kw)?
[H3O+][OH-]
give the value of Kw at 25C
1×10^-14
give the value of Kw at 37C
2.5×10^-14
what happens to [H+] ([H3O+]) with acids and bases according to bronsted-lowry?
acids increase concentration, bases decrease concentration
give the equation for pH by hydronium ion concentration (for a strong acid)
pH = -log10[H3O+]
give the equation for hydronium ion concentration by pH value
[H3O+] = 10^-pH
give the equation for pOH by hydroxide ion concentration (for a strong base)
pOH = -log10[OH-]
the higher the Ka value, the ___ the acid
stronger
the lower the pKa value, the ___ the acid
stronger
[H3O+][OH-] = …
Kw
pH + pOH = …
pKw
the higher the Kb value, the ___ the base
stronger
the lower the pKb value, the ___ the base
stronger
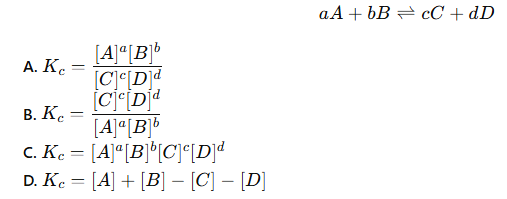
which of these is the correct equation for the equilibrium constant (Kc)?
B
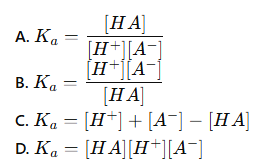
which of these is the correct equation for the acid dissociation constant (Ka)?
B
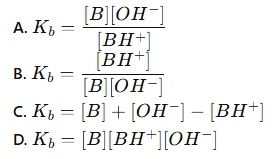
which of these is the correct equation for the base dissociation constant (Kb)?
B
what is the bronsted-lowry definition of a polyprotic acid?
an acid that can donate more than one proton
Ka x Kb = …
Kw
pKa x pKb = …
pKw
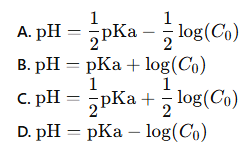
which of these is the correct equation for the pH of a weak acid using the initial molarity of the weak acid
A
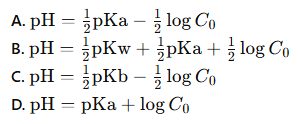
which of these is the correct equation for the pH of a weak base using the initial molarity of the weak base
B
what salt is formed from a weak base and a strong acid?
an acidic salt
what salt is formed from a weak acid and a strong base?
a basic salt
what salt is formed from a strong acid and a strong base?
a neutral salt
what salt is formed from a weak acid and a weak base?
a neutral salt
what is meant by %ionisation
ratio of the concentration of ionised molecules to the concentration of all molecules in solution
which of these is the correct equation for the percentage ionisation of a weak acid?
which of these is the correct equation for the percentage ionisation of a weak acid