VCE Health and Human Development QUESTIONS BANK 2025 ( 149 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS )
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
behavioural determinants
actions or patterns of living of an individual or a group that impact on health
name three behavioural determinants
tobacco use
dietary choices
levels of physical activity
bilateral aid
aid given from one country to another with consultation to ensure that the aid meets the needs of the targeted population
example of bilateral aid
Australia giving money to Indonesia to build schools
biological determinants
factors relating to the structure of cells, tissues and systems of the body and how adequately they function
name three biological determinants
genetics
body weight
cholesterol levels
biomedical model of health
a medical model of care practiced by doctors and health professionals; focuses on the diagnosis, treatment and cure of illness or disease once symptoms appear
strengths of the biomedical model of health (4)
advances in technology and research
effective treatment
extends life expectancy
improves quality of life
limitations of the biomedical model of health (4)
costly, due to reliance on professional health workers and technology
doesn't always promote good health
not every condition can be treated
not always affordable
burden of disease
a measure of the impact of disease and injuries on individuals or populations; specifically it measure the gap between current health status and an ideal situation where everyone lives to an old age free of disease and disability; measured in a unit called DALY
determinants of health (def)
factors that raise or lower a level of health in a population or individual; help to explain or predict trends in health and differences in health
determinants of health (4)
biological
physical environment
social
behavioural
disability adjusted life year (DALY)
a measure of burden of disease; one DALY equals one year of life lost due to premature death (YLL) and time lived with illness, disease or injury (YLD)
emergency aid
rapid assistance given to people or countries in immediate distress to relieve suffering during and after man-made or natural emergencies or disasters
example of emergency aid
warehouse of emergency supplies in Brisbane that are ready to be flown out in the event of a crisis
food security
adequate access to affordable, nutritious, culturally appropriate and safe food regularly through non-emergency sources
global health
the health of populations in a world wide context that goes beyond the needs of individual countries; it is about an international collaborative approach to achieving equality in health for all people worldwide
health
'a complete state of physical, social and mental wellbeing, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity' (WHO, 1946)
health adjusted life expectancy (HALE)
a measure of burden of disease based on life expectancy at birth, but including an adjustment for time spent in poor health; it is the number of years in full health that a person can expect to live, based on current rates of ill health and mortality
health status
an individual's or a population's overall health, taking into account various aspects such as life expectancy, amount of disability and levels of disease risk factors
human development
creating an environment in which people can develop to their full potential and lead productive, creative lives according to their needs and interests; it is about expanding people's choices and enhancing capabilities, having access to knowledge, health and a decent standard of living, and participating in the life of their community and decisions affecting their lives
human development index
a tool developed by the United Nations to measure and rank countries' levels of social and economic development
single statistic based on four indicators:
life expectancy at birth
mean years of schooling (for those over 25)
mean expected years of schooling (for children of school entrance age)
gross national income (GNI) per capita
and three dimensions:
health
education
living standards
life expectancy
an indication of how long a person can expect to live; it is the number of years of life remaining to a person at a particular age if death rates do not change
mental dimension of health
state of wellbeing in which the individual realises his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community
limitations of the human development index (HDI)
limitations of the WHO mortality strata
- doesn't take female mortality rates, a vulnerable population, into account
- doesn't measure human development, only mortality rates
- broad strata
- lacks detail
name three aspects of the mental dimension of health
self-esteem
thought patterns
stress levels
morbidity
refers to ill health in an individual and the levels of ill health in a population or group
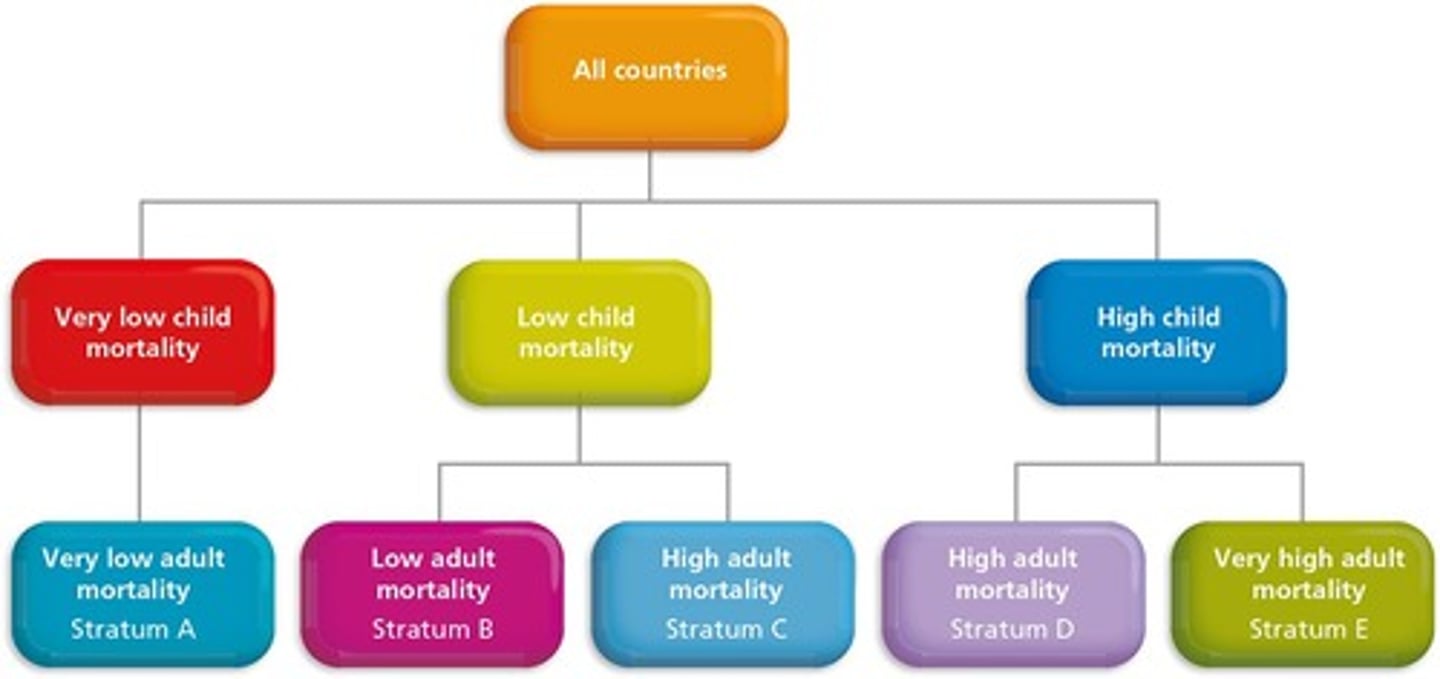
WHO mortality strata
classifies countries in one of five mortality strata based on the mortality rates of children (0-5) and adult males (19-59)
multilateral aid
combined donations from a number of countries is distributed as aid by an international organisation (World Bank, United Nations, World Health Organisation)
example of multilateral aid
World Bank running a immunisation program in Zambia
NGO aid
aid given by organisations that are independent to the government; often focused on long-term, community based projects that fill the gaps in bilateral and multilateral aid
Ottawa Charter definition of health promotion
'the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health' (WHO, 1998)
Ottawa Charter strategies for health promotion
advocate
enable
mediate
physical dimension of health
relates to the efficient functioning of the body and it's systems, and includes the physical capacity to perform tasks and physical fitness
name three aspects of the physical dimension of health
body weight
energy levels
immune system
physical environment determinants
the physical surroundings in which we live, work and play, including natural and man made infrastructure
name three physical environment determinants
air quality
climate/climate change
housing
prevalence
the number or proportion of cases of a particular disease or condition present in a population at a given time
social determinants
aspects of society and the social environment that impact on health
name three social determinants
socioeconomic status (SES)
occupation/unemployment
social exclusion
social dimension of health
being able to interact with others and participate in the community in both an independent and cooperative way
name three aspects of the social dimension of health
friends
family
productive relationships
social model of health
an approach to healthcare that attempts to address the broader influences on health (cultural, environmental, social and economic) rather than the disease or injury itself
key principles of the social model of health (5)
addresses the broader determinants of health
involves intersectoral collaboration
acts to reduces social inequities
acts to enable access to healthcare
empowers individuals and communities
sustainability (def)
'...meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.' (UN, 1987)
types of sustainability (3)
environmental
economic
social
U5MR
under five mortality rate: the number of deaths of children under 5 years of age per 1000 live births
values that underpin Australia's health system (7)
effective
efficient
responsive
accessible
safe
continuous
sustainable
build up of plaque on the walls of the blood vessels
atherosclerosis
MDG 1 (name + purpose + why?)
eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
purpose:
reduce the proportion of people living on less than US$1 a day; achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all (including women and young people); reduce the proportion of people suffering from hunger
why?
lack of income leads to lack of access to food, health care and education; poverty results in high morbidity and mortality rates from preventable causes; lack of income reduces the capacity for a country to develop its economy
MDG 2 (name + purpose + why?)
achieve universal primary education
purpose:
access to education for males and females; improve literacy and numeracy skills; promote the skills and knowledge necessary to engage in health promoting behaviour
why?
literacy = employment = income; understanding of health promotion
MDG 3 (name + purpose + why?)
promote gender equality and empower women
purpose:
raise the SES of women through education; greater decision making power for themselves, their communities and their countries
why?
access to higher paid/safer employment; take better care of families; pass knowledge onto children
MDG 4 (name + purpose + why?)
reduce child mortality
purpose:
reduce U5MR
why?
preventable through existing, inexpensive means
MDG 5 (name + purpose + why?)
improve maternal health
purpose:
reduce the number of deaths of women that occur due to pregnancy and childbirth; increase access to reproductive services
why?
reducing risk of complications reduces MMR, enables women to continue in caregiving role, women are better able to take care of themselves and their children
MDG 6 (name + purpose + why?)
combat HIV/AIDs, malaria and other diseases
purpose:
reduce the morbidity/mortality rates from HIV/AIDs, malaria and other diseases
why?
HIV can be reduced through education and behaviour change; anti-retroviral drugs enable people to continue working; simple/cost-effective methods can reduce transmission of malaria
MDG 7 (name + purpose + why?)
ensure environmental sustainability
purpose:
improve lives of slum dwellers; protect valuable natural resources; increase access to clean water/basic sanitation
why?
to not compromise the abilities of future generations to meet their own needs; clean water/sanitation reduces spread of malaria/diarrhoea; reduces slum dwellers risk of malnutrition, disease and injury/violence
MDG 8 (name + purpose + why?)
develop a global partnership for development
purpose:
ensure trade agreements don't discriminate; provide aid through Official Development Assistance (ODA); reduce debt; access to essential drugs; access to new technologies
why?
develop economy; better meet the needs of population; allocate funds to health services and infrastructure; treatment of conditions; gain information from technology
optimal health
the best level of health that an individual can realistically achieve
health indicators
statistics that give information on the health status of groups and populations
mortality rate
the proportion of the population who die in a one year period, per 100,000
infant mortality rate
rate of deaths of infants between birth and their first birthday, per 1000 live births
maternal mortality rate
rate of deaths of pregnant women or who die within the first 42 days after giving birth/having a termination, per 100,000 live births
incidence
the number of NEW cases of a disease during a specified period of time
protective factors
determinants that reduce the risks of lifestyle related conditions or are otherwise beneficial to health
risk factors
determinants that increase the risks of lifestyle related conditions or are otherwise harmful to health
SES
socioeconomic status, based on occupation, income and education
variations in health status in Australia
males
Indigenous Australians
rural and remote populations
people of low SES backgrounds
males (stats)
more likely to die at every lifespan stage, life expectancy 5 years less
Indigenous Australians (stats)
life expectancy 11 years less, twice the infant mortality
Syndrome X
collection of disease that gives an increase of six times the average rate of premature death; includes heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, renal (kidney) failure
people of low SES backgrounds (stats)
lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality
rural and remote populations (stats)
lower life expectancy, higher mortality rates
why are NHPAs selected?
they contribute significantly to the burden of disease
the conditions are preventable
potential to reduce health inequalities between population groups
potential for a range of strategies to be implemented
direct costs to the community (3)
implementing health promotion programs
Medicare
the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme
direct costs to the individual (5)
ambulance transport
diagnostic tests not covered by Medicare
doctor and specialist fees
surgery or hospital fees
pharmaceuticals
indirect costs to the community (3)
lost productivity
lost taxation revenue
social security payments
indirect costs to the individual (3)
transport costs
loss of income
need for home help
intangible costs to the community (3)
loss of community participation
emotional toll on family/friends
intangible costs to the individual (4)
loss of social participation
loss of self-esteem
pain and suffering
stress
obesity (def + program)
carrying excess body weight in the form of fat, BMI over 30
The Shape Up Australia Campaign (Federal Government); puts Shape Up logo on credible products, website offers resources
cardiovascular health
health of the heart and blood vessels, cardiovascular disease (hypertension, coronary heart disease)
The Heart Foundation Tick (The Heart Foundation); organisations who fit certain health criteria and pay a fee display the logo, enables consumers to select healthier food choices within categories
asthma
airways become inflamed and narrow, inhibiting breathing, when contact is made with a trigger (pollen, exercise, dust)
The Sensitive Choice Program (National Asthma Council Australia); low allergen products display a blue butterfly logo for a fee
injury prevention and control
the adverse effects on the body caused by a range of events, accidental (drowning/sporting/workplace) or intentional (attempted suicide/violence)
The National Road Safety Strategy 2011-2020 (The Australian Transport Council); aims to cut road tolls by at least 30% by 2020 by achieving four key objectives: safe roads, safe speeds, safe vehicles and safe people
cancer control
a general term for a number of difference conditions characterised by the uncontrolled mutation and growth of cells threatening to damage the other areas of the body, types focused on include: prostate cancer, breast cancer in females, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, melanoma, non-melanoma, cancer of the cervix and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Sunsmart (Cancer Council Victoria and VicHealth); promotes awareness of the dangers of UV radiation through prevention campaigns such as Slip, Slop, Slap, Seek and Slide, advocates for policy change and uses evidence to back up claims
diabetes mellitus
chronic condition that causes blood glucose to be unable to be utilised correctly by the body, types include type 1, type 2 and gestational, can lead to blindness and kidney failure
Life! Taking Action on Diabetes (Victorian State Government); aims to prevent or aid in the early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in Victorians over 50 and Aboriginals/Torres Strait Islanders, runs media campaigns, a website and a $50 eight month lifestyle change course for those at high risk
mental health
state of wellbeing in which the individual realises his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community; most common mental illnesses are anxiety and depression
Youthbeyondblue; encourages people to seek help and reduces stigma through work with schools, workplaces and community groups, promotes key messages: LOOK for the signs and symptoms, LISTEN to your friends experiences, TALK about what's going on and SEEK HELP together
dementia
used to describe over 100 conditions that are characterised by progressive and irreversible loss of brain function (language, personality, attention), types include: Alzheimer's, vascular dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies and fronto temporal dementia
Your Brain Matters (Alzheimer's Australia); offers information about preventable risk factors (Brain/Body/Heart), BrainyApp allows people to assess their current risk levels and take steps to reduce that risk
arthritis and musculoskeletal conditions
used to describe over 100 conditions including osteoarthritis, back problems and osteoporosis
Bone Health For Life (Jean Hailes for Women's Health); offers information and a quiz on treatment/diagnosis/prevention of osteoporosis, GPs can access information and activities about bone health promotion
macronutrients
required in large amounts
protein
fats
carbohydrates (including fibre)
micronutrients
required in small amounts
vitamins
minerals
LDL
low density lipoproteins, bad cholesterol
HDL
high density lipoproteins, good cholesterol
carbohydrates (function + 2 food sources)
converted into glucose to provide fuel for energy
potatoes
bread
fibre (function + 2 food sources)
regulates the functioning of the digestive system
bran flake cereal
fruit
protein (function + 2 food sources)
growth, maintenance and repair of body cells, fuel for energy
eggs
beef
water (function + 2 food sources)
many functions within the body e.g. temperature regulation
water
fruit
calcium (function + 2 food sources)
stored in the bones, blood, muscles and intracellular fluid, aids in achieving peak bone mass
milk
salmon
phosphorus (function + 2 food sources)
works with calcium to ossify bones
milk
eggs
sodium (function + 2 food sources)
regulates fluids (water/blood) in the body
table salt
olives