Option B.3+ B.4: Mental preperation and Physiological skills training
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
arousal
is an alertness or state of reediness (continum ranging from deep sleep to intense alertness) of the body for an action
It is neutral and can be triggered by both pleasant/positive and unpleasant/negative situations
It is how motivated/interested/excited an athlete is prior to and throughout the performance
2 types of arousal
cognitive; thought processes
somatic ; body responses eg. sweat+ hr
3 arousal theories
drive reduction theory
inverted u hypothesis
catastrophe theory
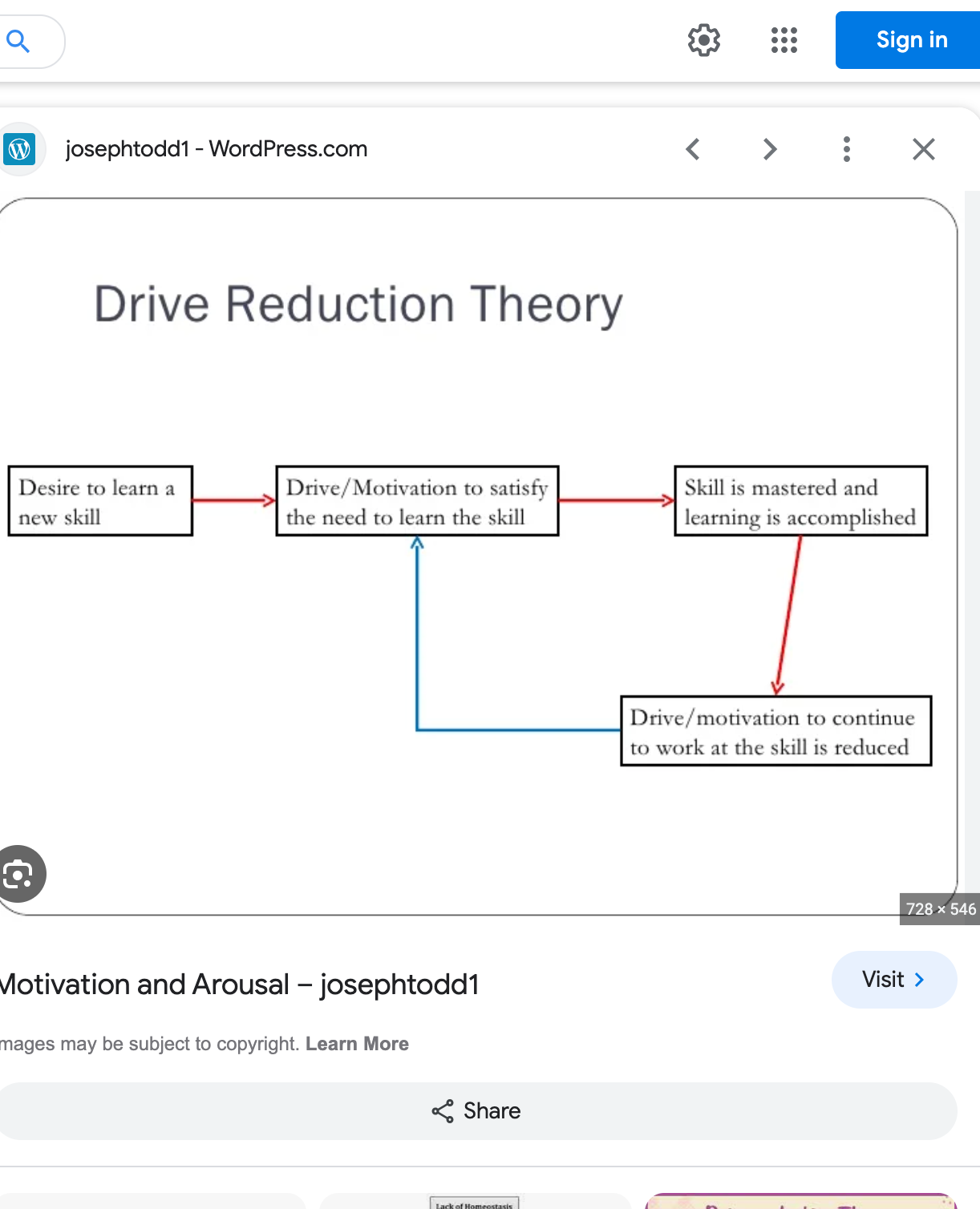
drive reduction theory + diagram
says humans are motivated to reduce the state of tension caused when certain biological needs are not satisfied.
brings into consideration the reduction in motivation as performance changes not just as arousal increases so does perf
the inverted U hypothesis
as arousal increases so does performance until and optimum where performance will decrease
issues with inverted u
optimal arousal always occurs at the mid-point of the curve
assumes you cannot recover after optimum arousal
where are optimum arousal levels dependent on
skill level: beginners= lower arousal levels(will have lower peak also as cannot perform well)
sport= archery lower arousal levels
personality= extrovert higher arousal levels
fine/gross skill= fine lower arousal lvels
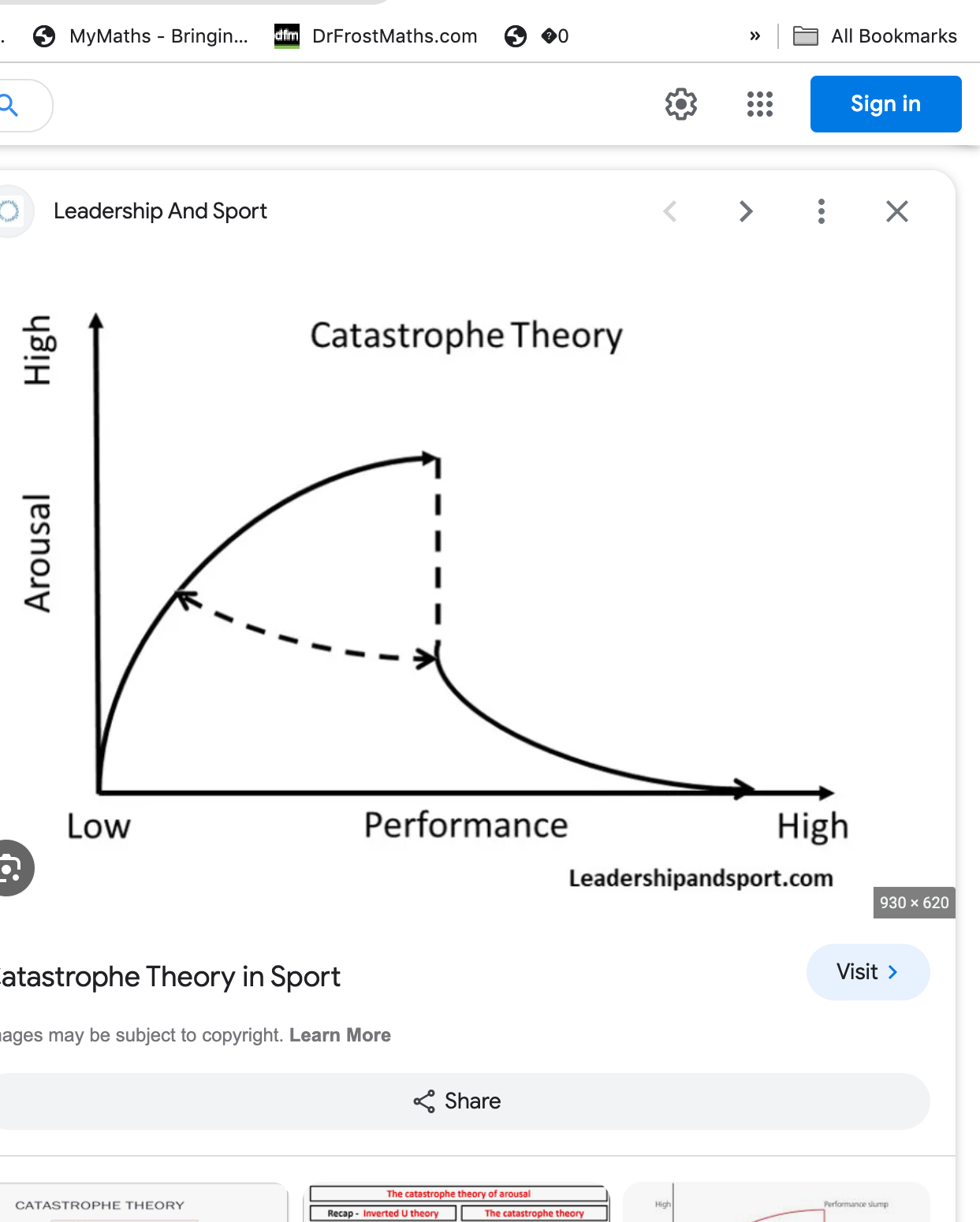
catastrophe theory
arousal increases performance until an optimum.
if over arousal occurs 2 things may happen
1- arousal levels drop slightly due to somatic anxiety however performer returns to optimum arousal (eg via pos self talk)
-arousal levels drop rapidly, due to cognitive and somatic anxiety and the performer will not be able to recover : catasrophe!
positive emotions in sport
excitement, relief, pride
lead to an increase in performance due to increase confidence and motivation
excitement masks pain
relief calms nerves
negative emotions in sport
anxiety, anger, guilt, boredom, shame
leads to a decrease in performance due gto decreasing confidence and motivation
how do emotions affect performance
significantly
regular change in emotions= regular change in performance
high trait anxiety more likely to be emotional
the effect of negative moods in performance
will prime us to remember negative memories of past failures and therefoore reduces confidence to perform
learned helplessness(attribute to stable internal factors)
the effect of positive moods in performance
will prime us to remeber positive memories of past sucess and therefore increase our confidence to perform
increased descision making
anxiety
a negative emotion of apprehension and tension which includes irrational thoughts, worry, fear of failure
2 types of anxiety
trate/ innate anxiety: inherited, likely to be anxious in a wide range of situations
state anxiety: situation specific, before an event eg. penalty
temporary, drops significantly once comp begins
cognitive anxiety + what can lead to
negative thoughts/perceptions/ worrys about performance
attentional narrowing(can be + or-) fixed on ball so loose player
loss of concentartion
somatic anxiety and responses
normally comes as a result of cognitive
sweating, muscle tension, naseau, increased hr
2 ways anxiety is measured
SCAT test for trait anxiety
CSAI-2R state anxiety
Scat test
find out which competitors are likely to become too anxious in a competitive situation.
Four factors are related to competitive anxiety:-
Individual differences in how performers interact with different situations - some events are more important than others and therefore cause more anxiety
The different types of anxiety (state and trait) that a performer experiences
A specific anxiety trait that only occurs in competitive situations.
The competition itself, which involves interaction between the performer's personality traits, their own competitive trait anxiety and the specific situation involved
CSAI-2R
Measured three components: cognitive, somatic, self-efficacy.
Given out before competition but more than once, such as a week before, a day before, and half an hour before this.
Enables researchers to discover baseline levels of anxiety and compare it with pre-competition levels to see if they differ.
stress
Stress is a process that involves one's perception of an imbalance between the demands of the environment and one's response capability, under conditions where failure to meet the demands
causes of stress
failure to perform at expected level
high staking games
large crowd/ whose in it eg.home/away
stress responses
anxiety, fear, inability to focus as of overthinking, muscle tension
stress process in sports
1. Cause of stress (environmental demand/event).
2. Stress response (persons reactions; fight or flight?) physical
3. Stress experience (psychological interpretation)
4. Actual behaviour (outcome).
Psychological skills training(PST)
the systematic and consistent practice of mental or physiological skills.
unique to individual(depending on sport+pyscological state)
PST skills
psychological qualities that need to be developed
PST methods
tools used to help develop PST skills
common misconceptions of pst training
just for elite athletes/problem athletes
does not provide quick fix solutions
3 phases of a PST program
Education: clarifies what psychological skills are+ benefits, why doing it+ how long going to take, commitment from both athlete and pyschologist
Acquisition:developing stratagies + skills specific for athelete + context of why they work so athlete can self regulate actions in context of their environment and emotions
Practice: to autonimate skills into performance situations
benefits of pst
– Self-confidence
– Motivation
– Concentration
– Skill acquisition
– Emotional control
goal setting
increases self confidence motivation and task persistence
types of goal
outcome
performance
process
outcome goals
have a specific result, does not consider how achieved just wether it is or not. involves comparison with other performers
eg.i want to win the game
good long term goal
performance goals
involves comparison with own performances
eg. scored 1 goal last time, want to score 2 this time
process goals
Things that need to be done to achieve desired outcomes, improving techniques
eg.practing tackling 20 times this session
SMARTER goals
Specific (clear+precise, use data is poss)
Measurabe(know if achieved or not)
Achievable (possible to)
Realistic(within reach but not impossible)
Time(clear deadline ie short/longterm)
Evaluate (reflection on achievment eg what worked)
Re-do= if unsucessull, reasses+ adjust to help sucess
mental imagrey+ uses
formation of a mental picture of when a skill was performed sucessfully in the past which considers feelings and emotions. inclides mental rehersal
– Improve Technique
– Whilst Injured
– Learning a New Skill
– Motivational Issues
mental rehersal
going through the movements of a task before the events
2 types of mental imagrey
internal/external
internal imagrey
emotions/feelings of doing a skill from within
external imagrey
image placed in an environment, watching yourself do it
issues when inventing imagrey skills
– Using all the Senses
– Internal or External Imagery
– Imagery Control
relaxation/somatic stress managment techniques
-arousal regulation, reducing s+c anxiety
progressive muscular relaxation techniques
breathing techniques
biofeedback
breathing techniques
also known as centering
focus of breathing, directs attention away from stress causer
biofeedback
measurement of phsiological responses to stressm such a HR recorder, know when getting stressed so can prevent/ start to put measures in places
progressive muscular relaxation
active muscle tensioning followed by releasing
-if employed too close to competition may lead to under arousal
self talk techniques
-concentration, attention, motivation
positive/neg self talk
thought stopping
positive/ negself talk
optimistic approach/pess
replaces negative talk w positive thoughts ab performance/ neg thoughts decrease performance
-used to focus on tactic,overcome poor technique / can lead to reduction in perf
thought stopping
recognition of when you startto have negative thoughts + using a cue, action or word to redirect attention to positive thoughts eg. snap out of it