Chapter 7 Bio-Rad
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
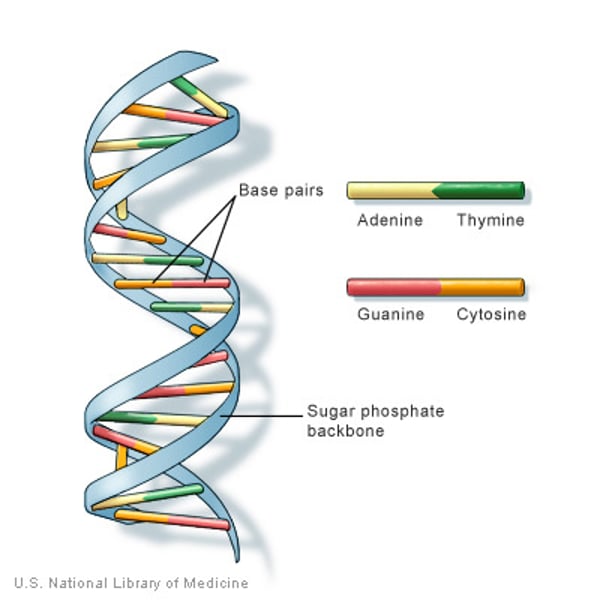
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information. It is a long molecule composed of smaller molecules. It is composed of 6 different smaller molecules (Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine, Adenine, Deoxyribose, Phosphate Group).
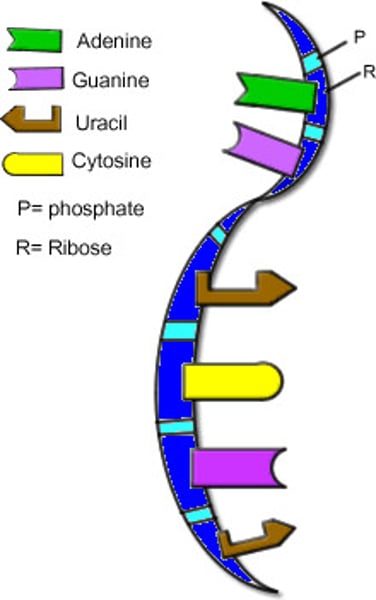
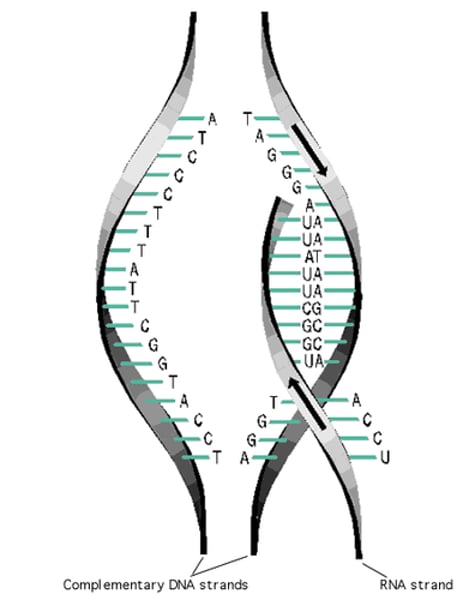
RNA
A single-stranded nucleic acid that passes along genetic messages
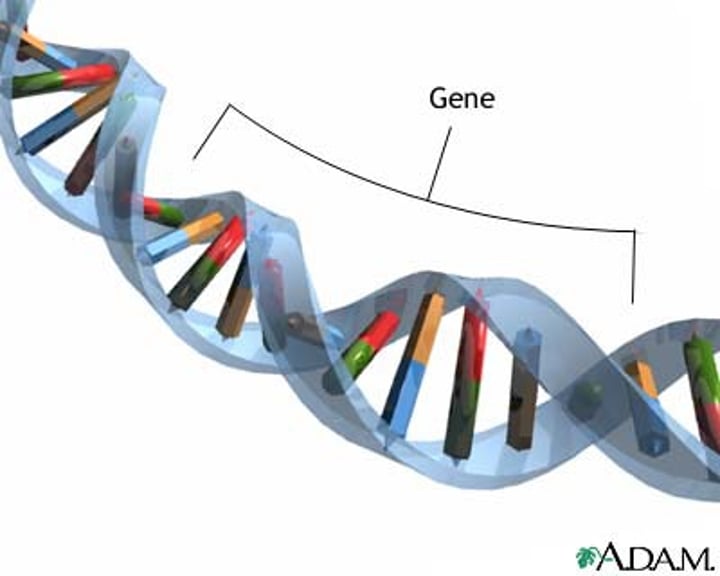
Gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a polypeptide or RNA molecule
Thymine
a compound that is one of the four constituent bases of nucleic acids. A pyrimidine derivative, it is paired with adenine in double-stranded DNA.
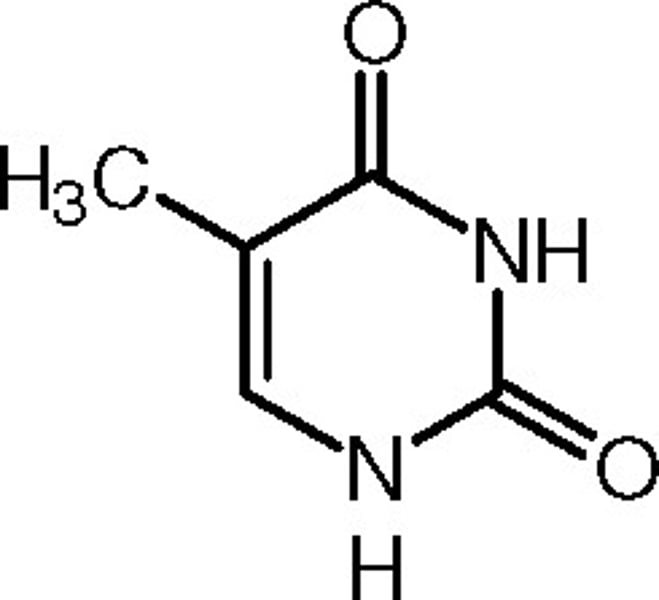
Cytosine
The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA
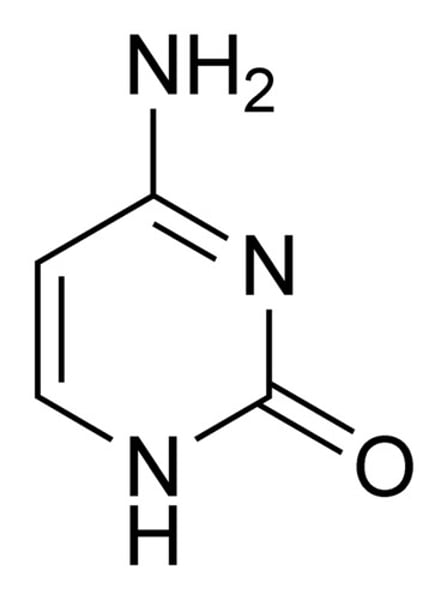
Guanine
The base that pairs with Cytosine in DNA
DNA replication
The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself.
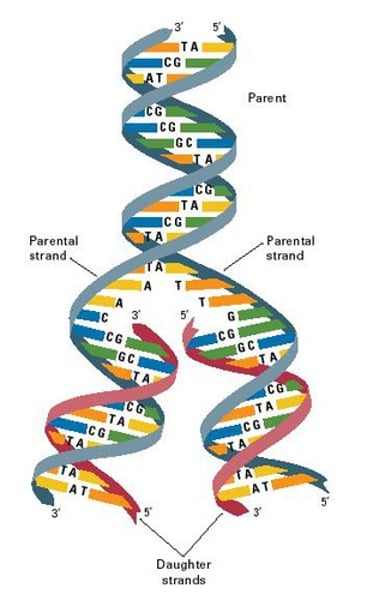
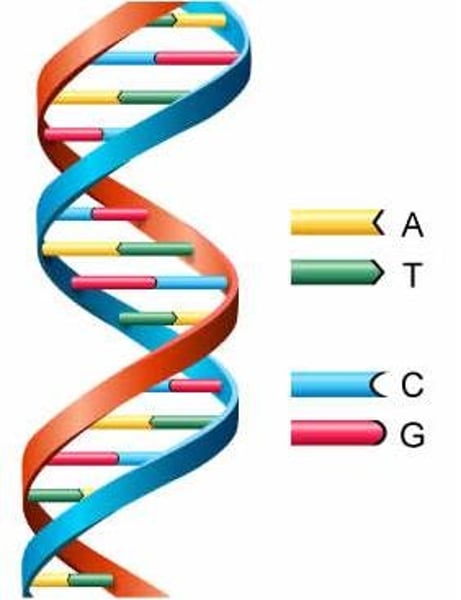
Double Helix
The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape.
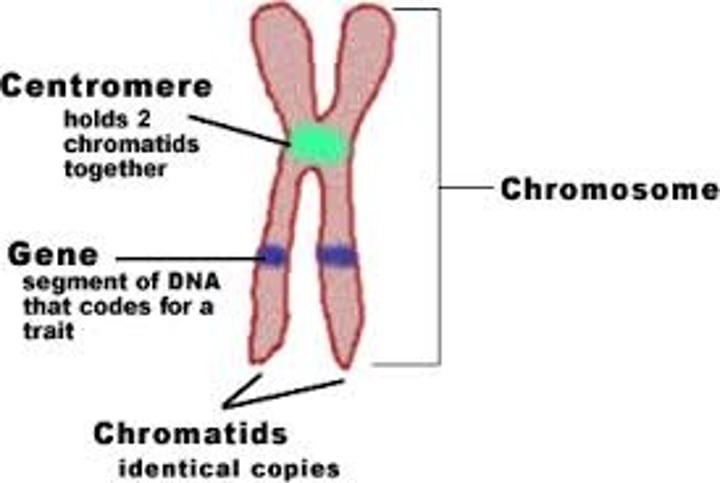
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
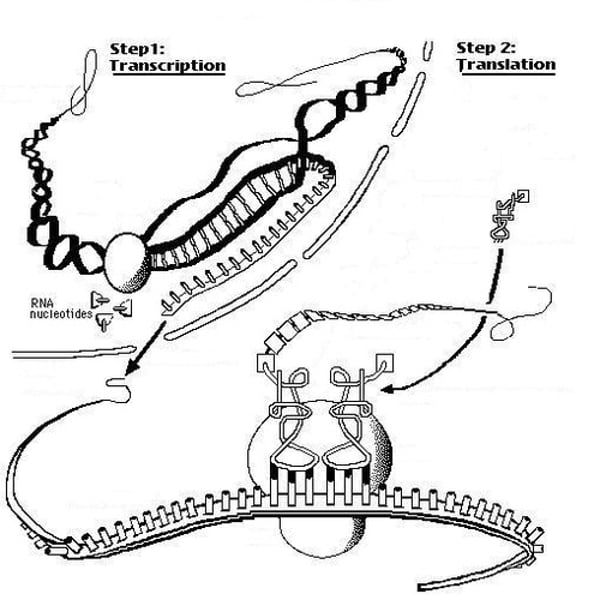
protein synthesis
the formation of proteins by using information contained in DNA and carried by mRNA
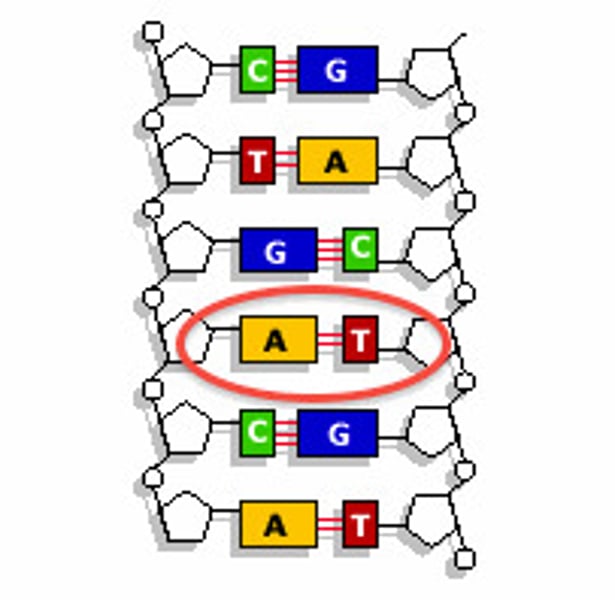
Adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine in DNA
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA
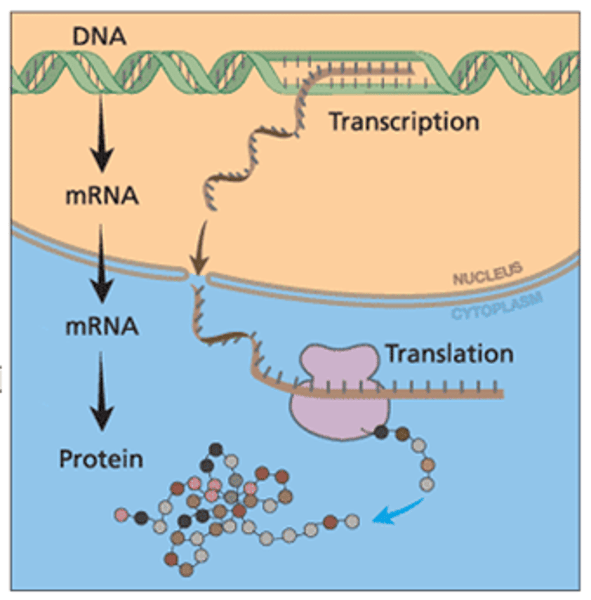
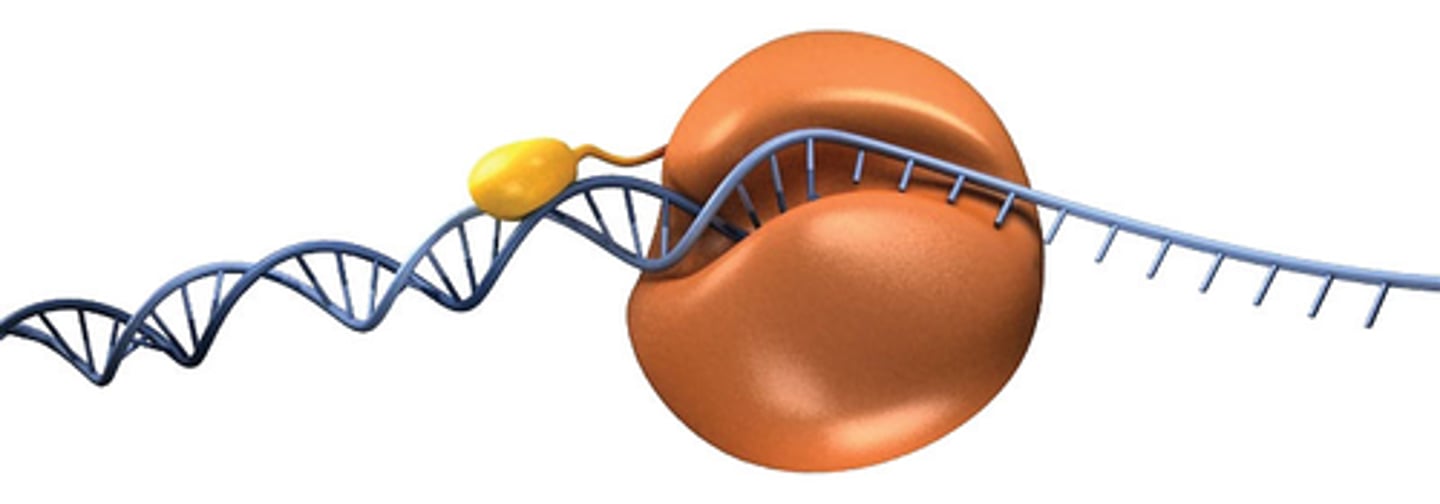
Transcription
the proccess of copying a section of dna in order to make proteins
Translation
process that decodes mRNA to produce a protein strand
Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment

DNA Polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
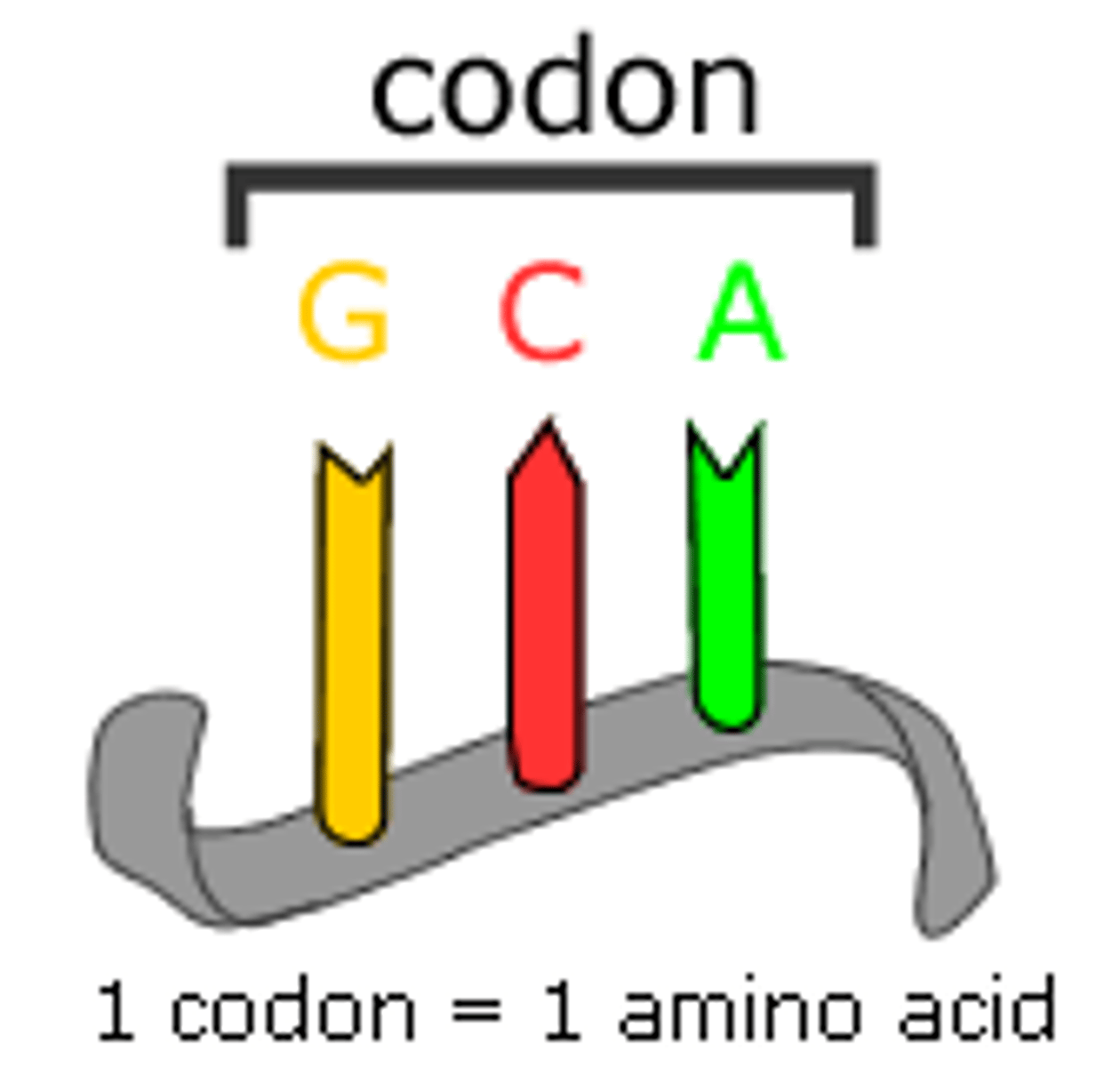
Codon
three-nucleotide sequence on messenger RNA that codes for a single amino acid
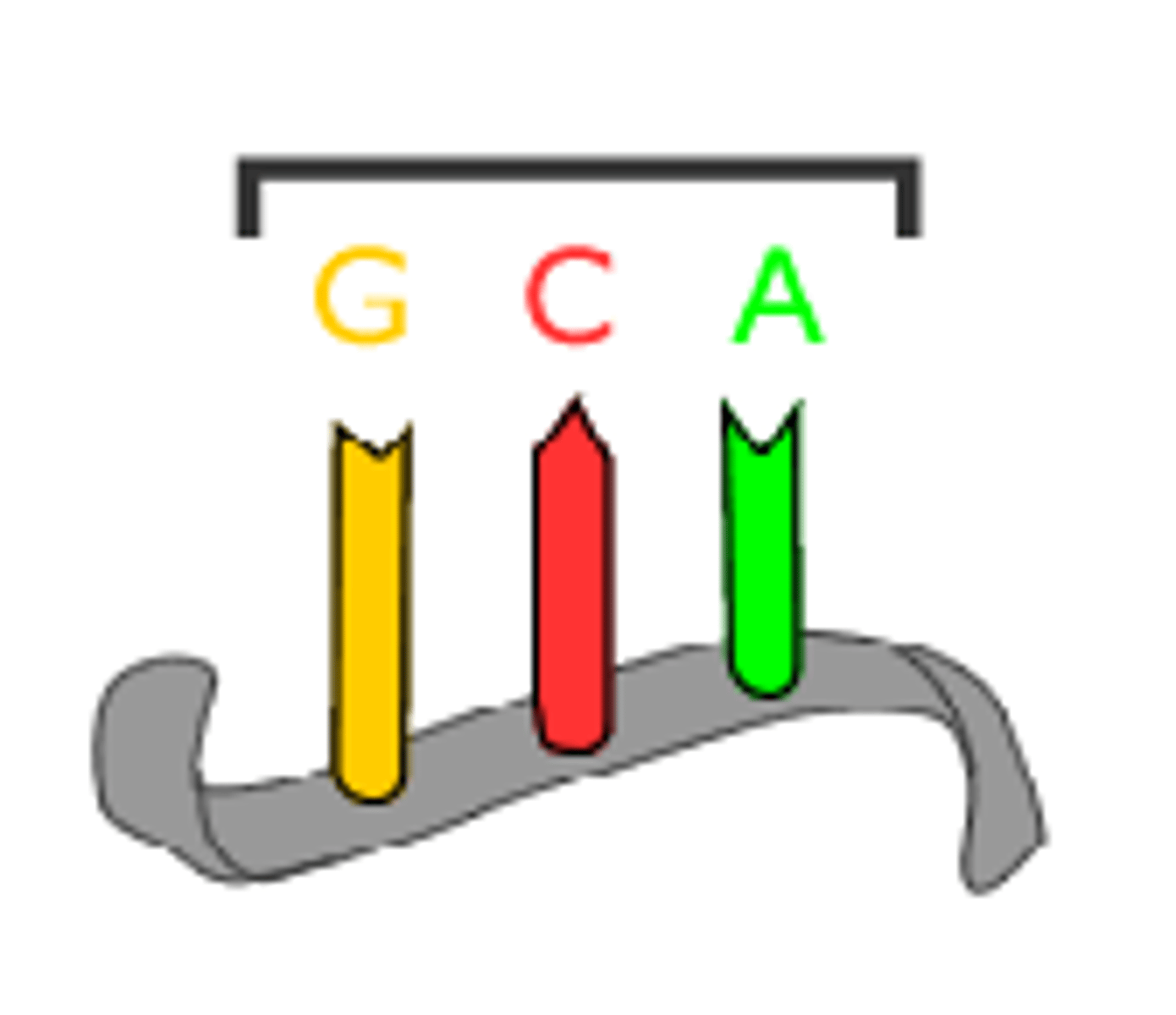
DNA Triplet
a sequence of three nucleotides eg. ATC, that codes for a particular amino acid
Polypeptide
A polymer (chain) of many amino acids linked together by peptide bonds.
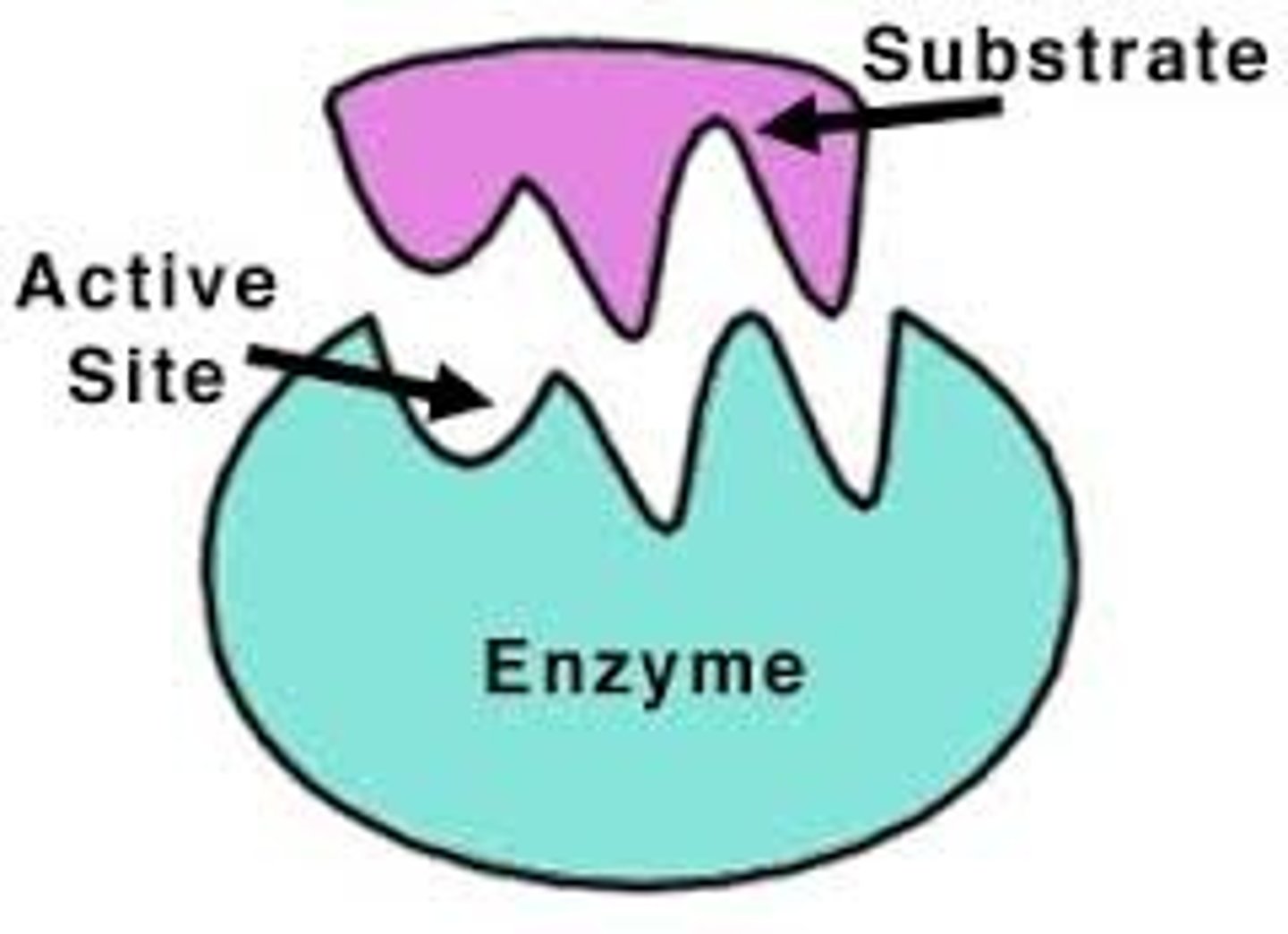
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
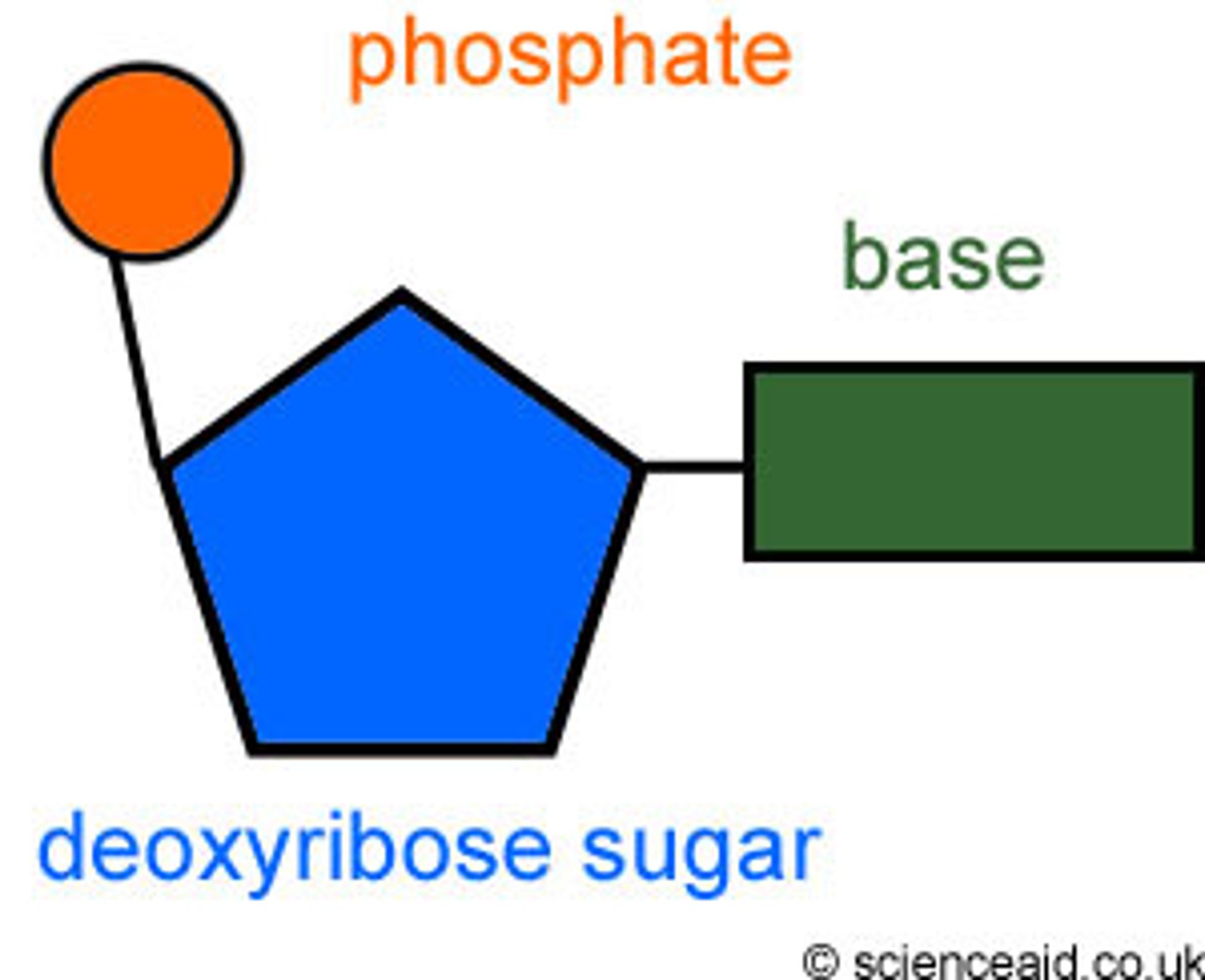
Nucleotide
Monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Complementary base pairing
Hydrogen bonding between particular pyrimidines and purines. Adenine & Thymine. Cytosine & Guanine.
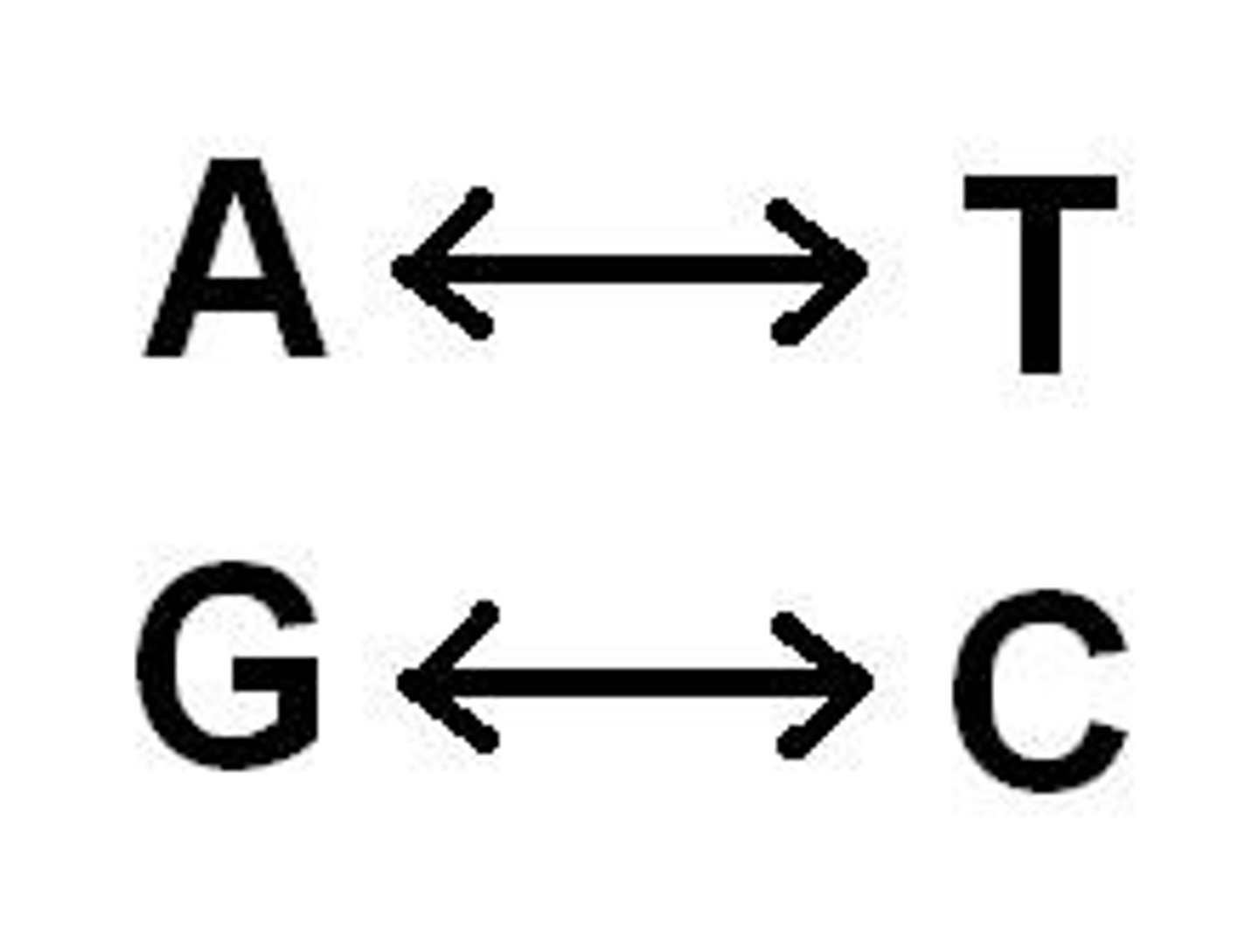
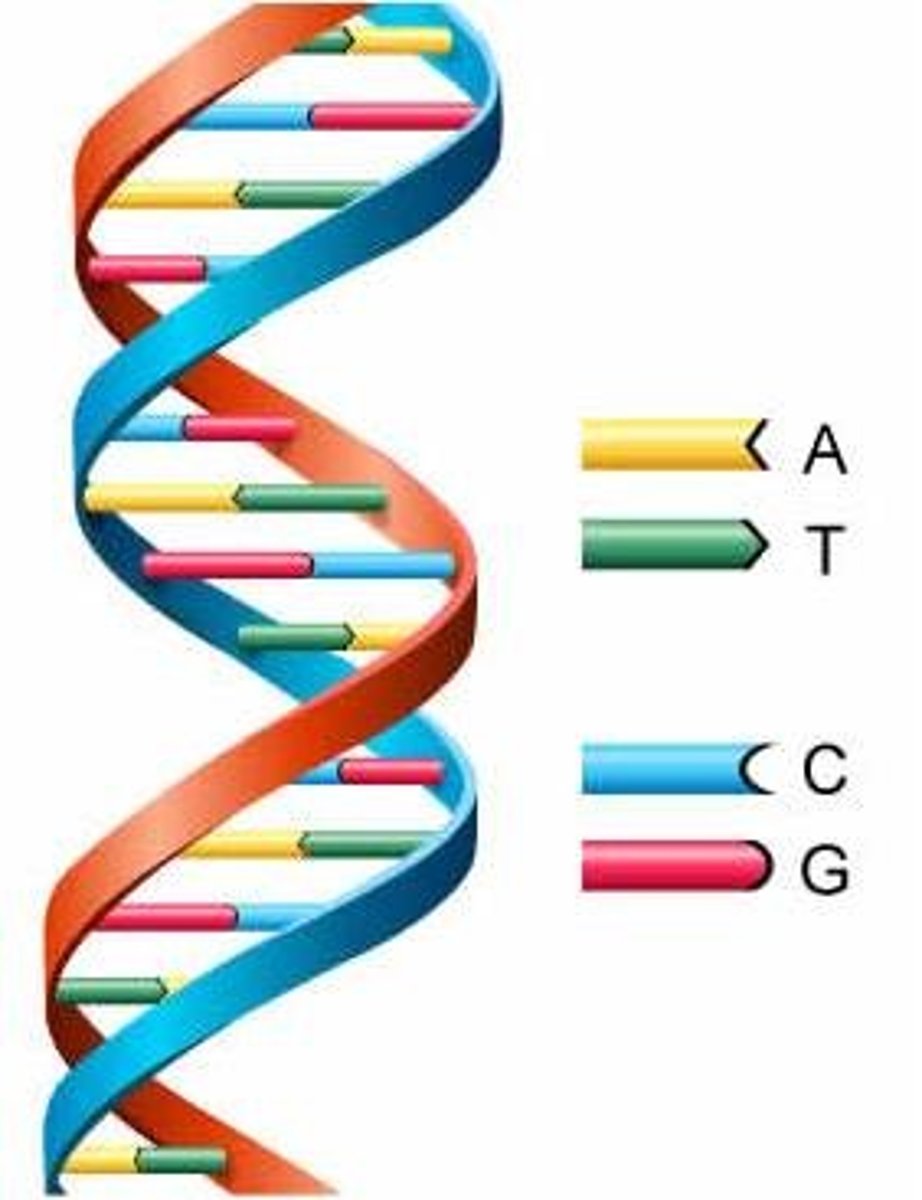
Double helix
The form of native DNA, referring to its two adjacent polynucleotide strands wound into a spiral shape.
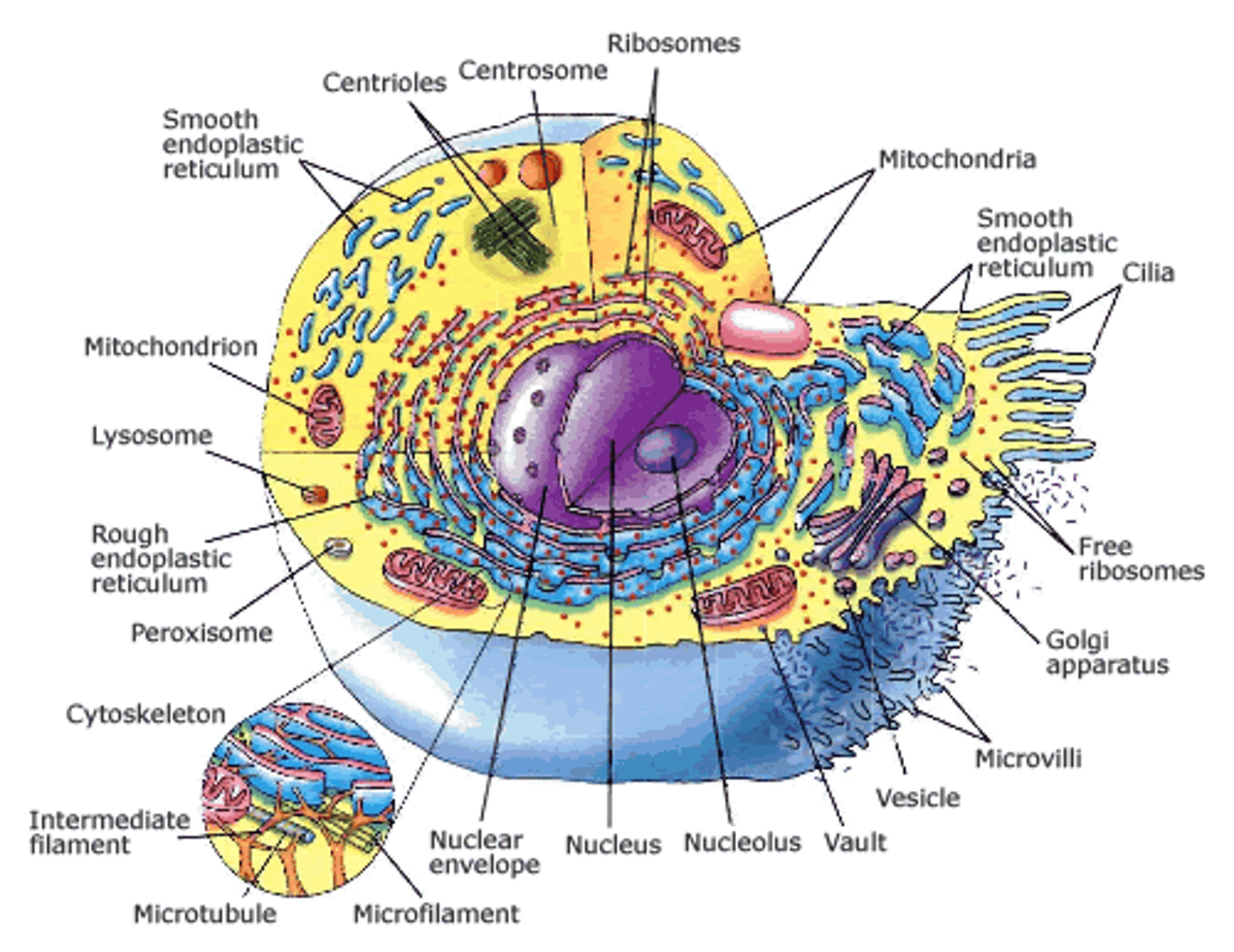
Eukaryotic
A cell characterized by the presence of a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes can be unicellular (protists) or multicellular (fungi, plants and animals).
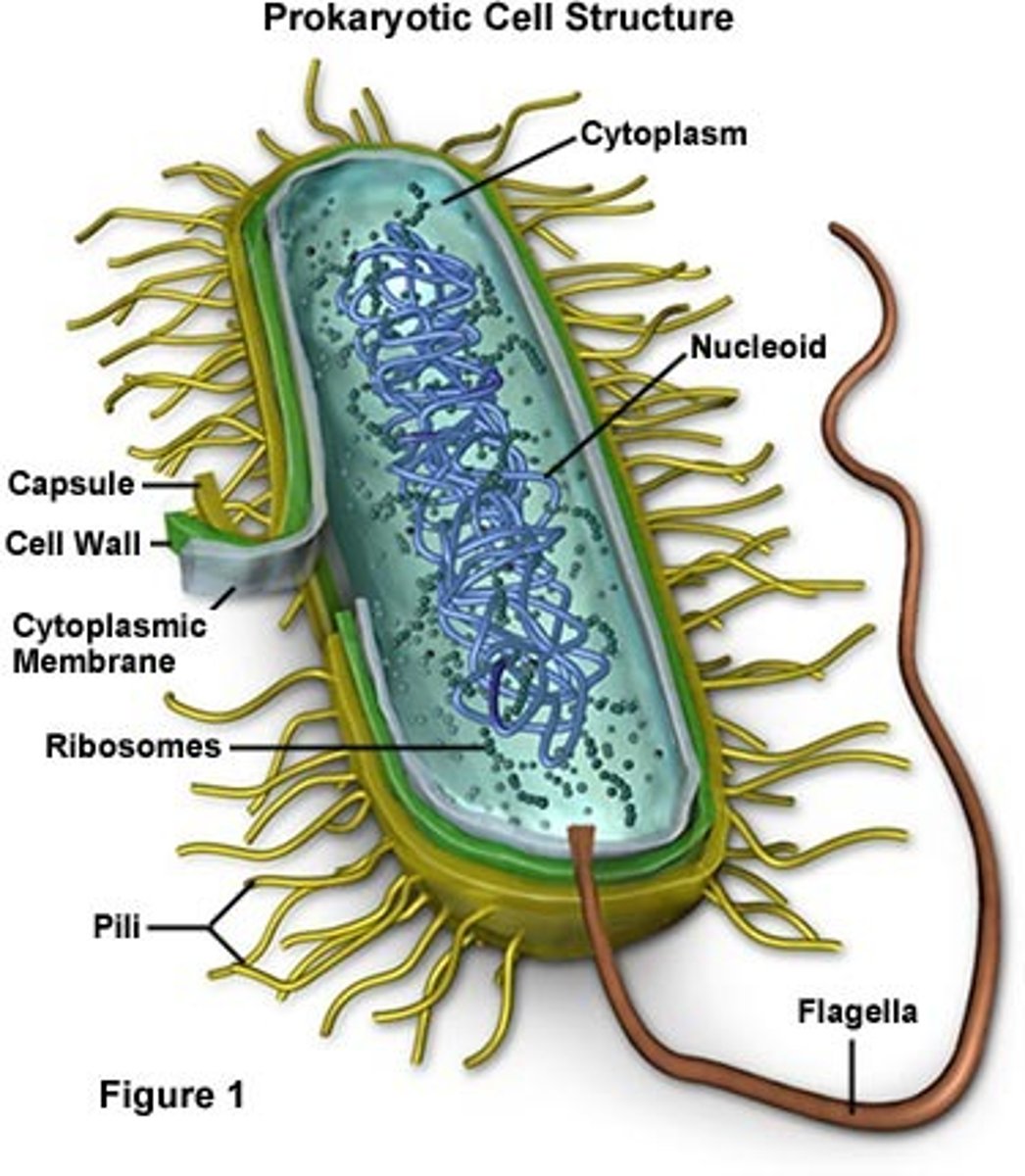
Prokaryotic
An organism whose cells do not have an enclosed nucleus, such as bacteria. Pro NO
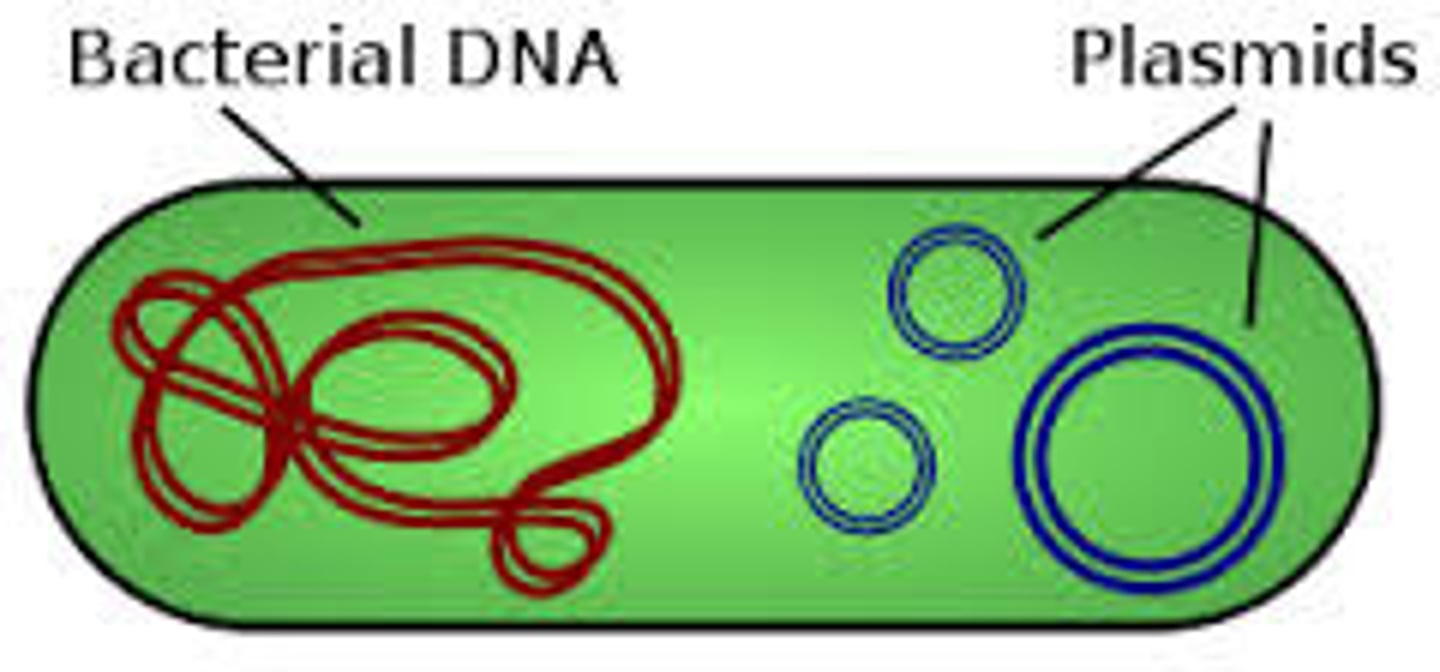
Circular chromosome
Often accompanied by smaller rings of DNA called plasmids
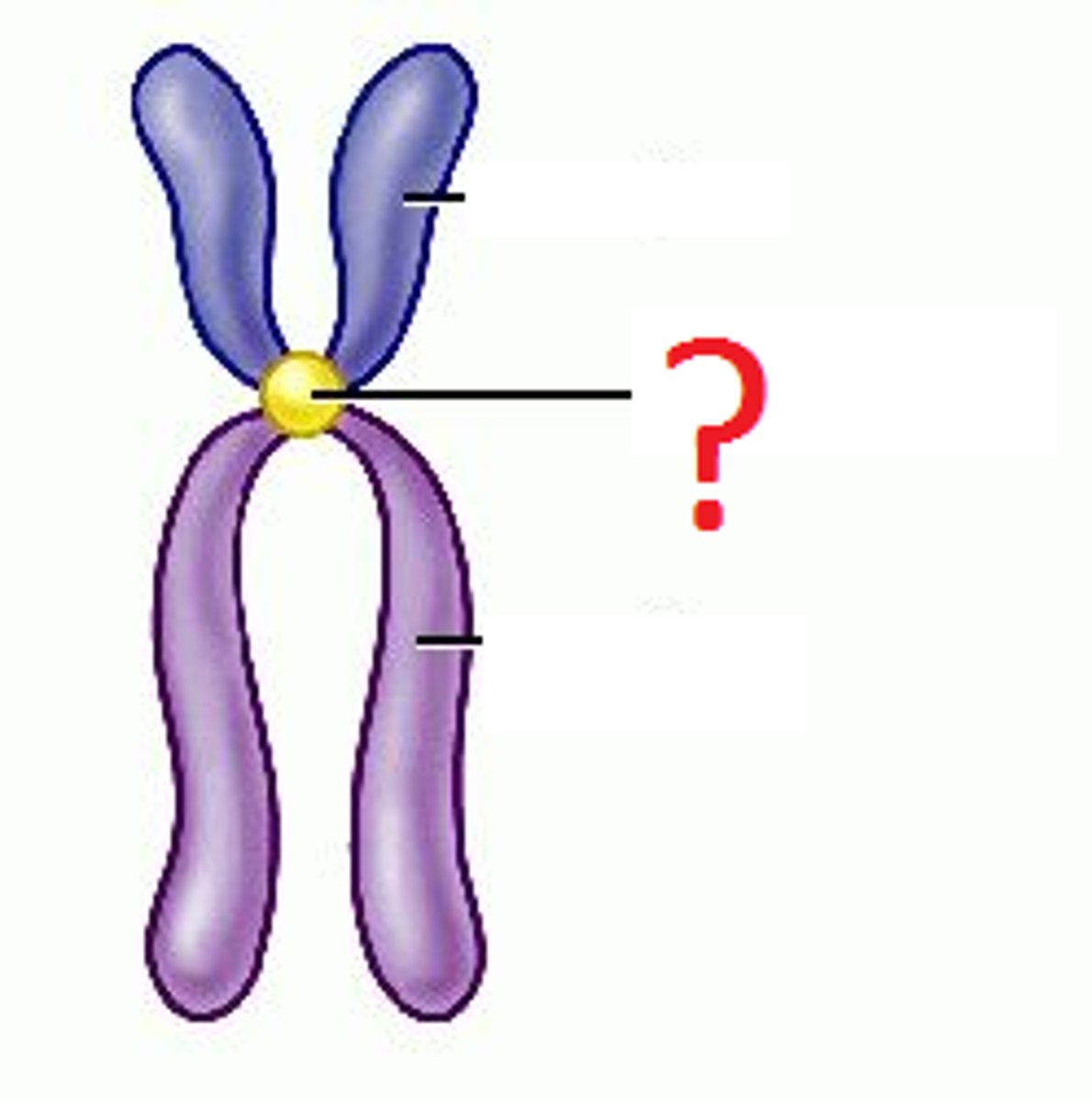
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
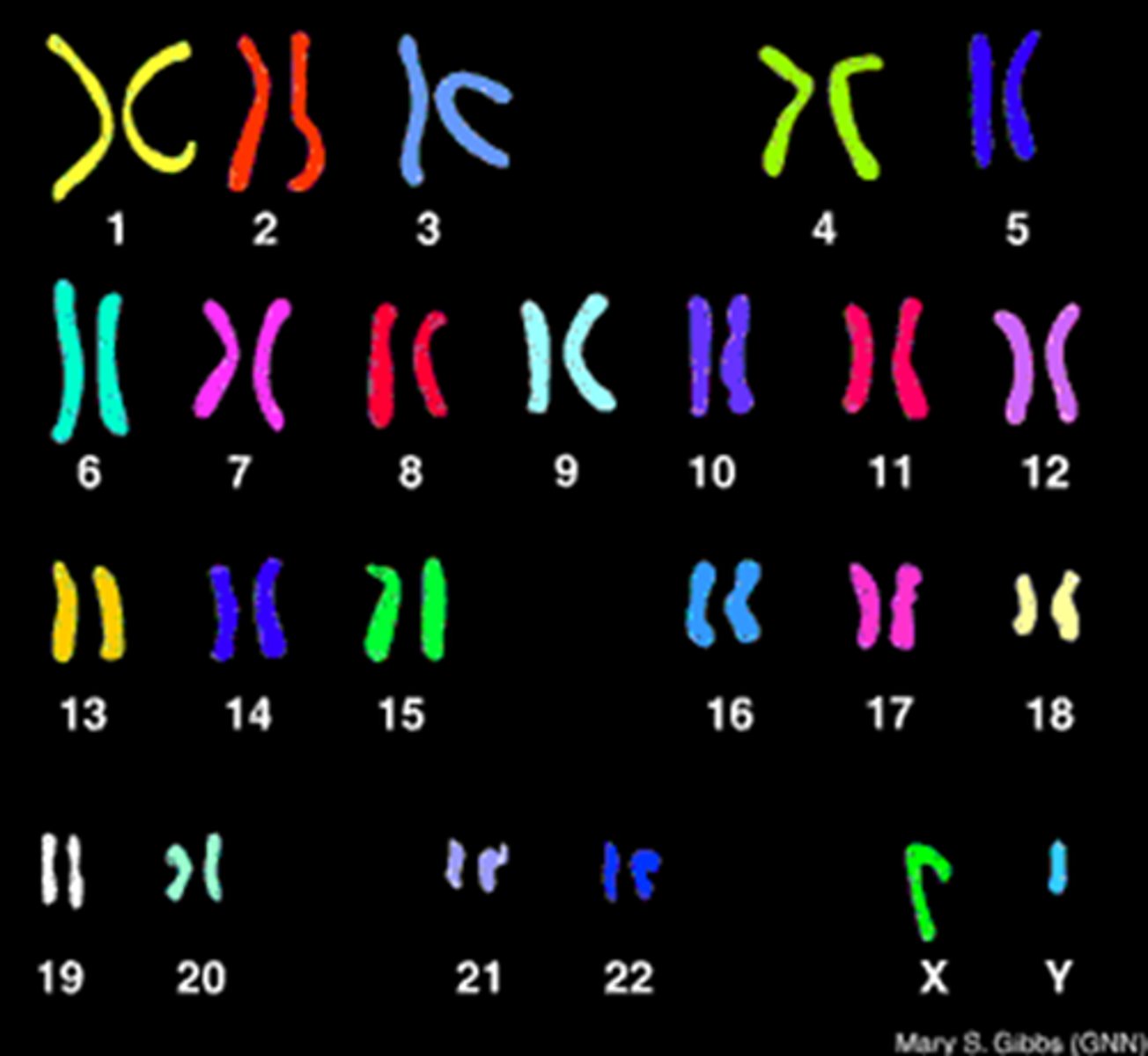
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
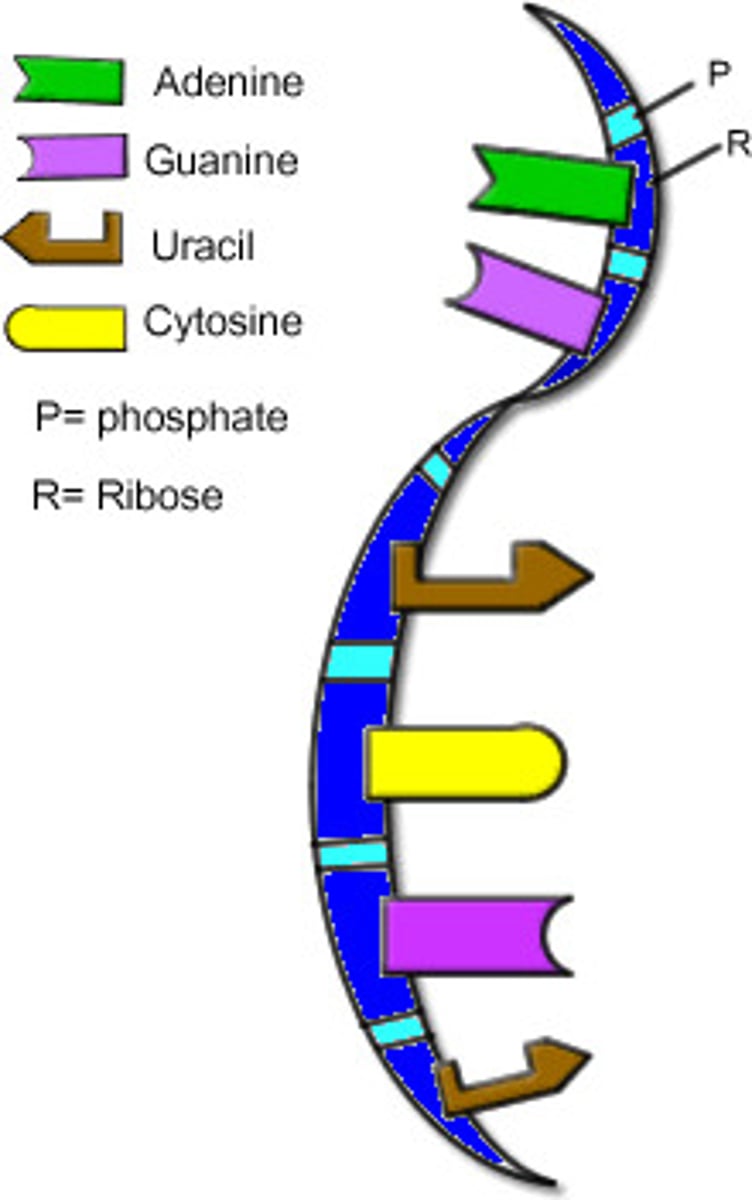
mRNA
A type of RNA, synthesized from DNA, that attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm and specifies the primary structure of a protein.
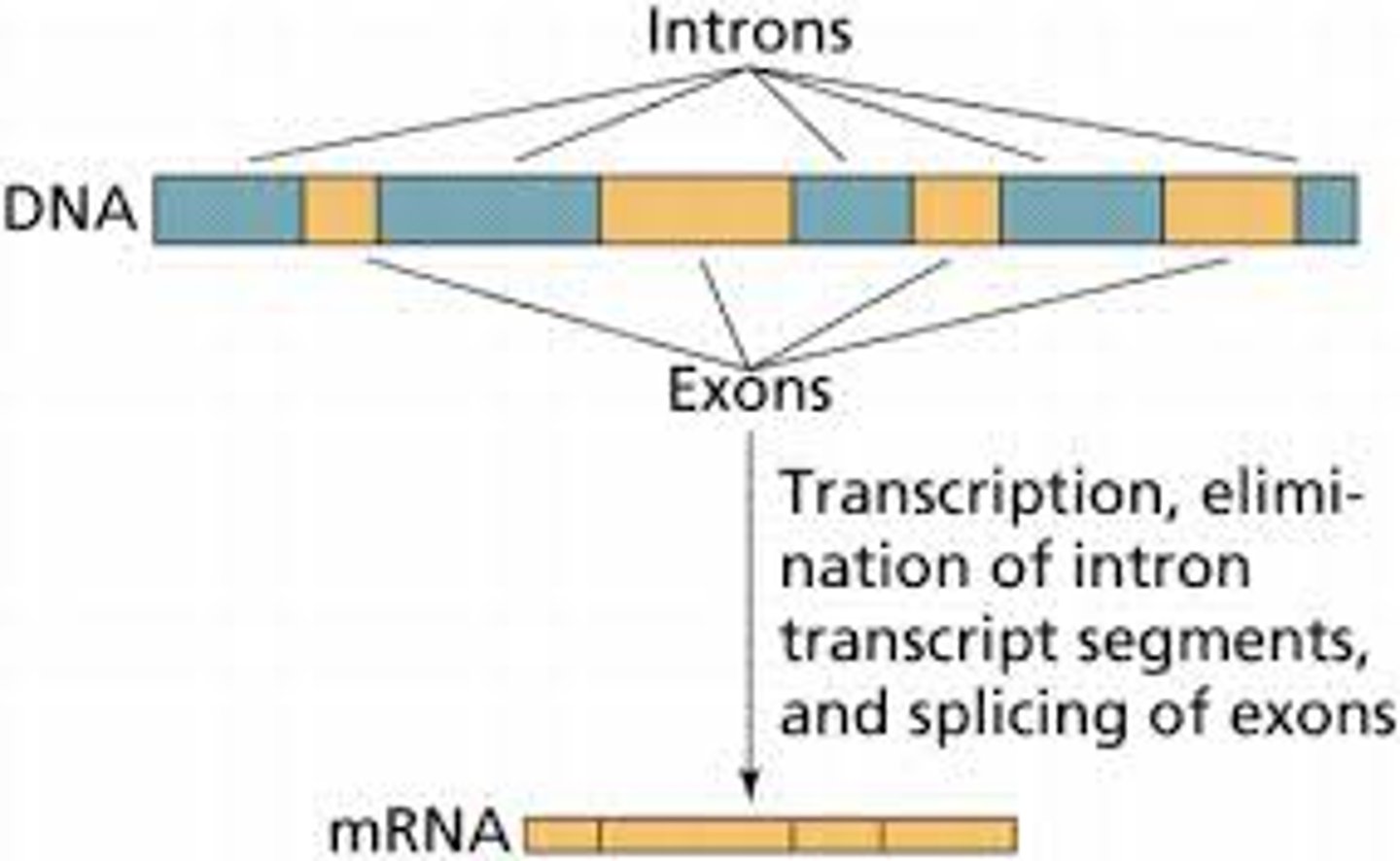
Exon
A segment of a DNA or RNA molecule containing information coding for a protein or peptide sequence.
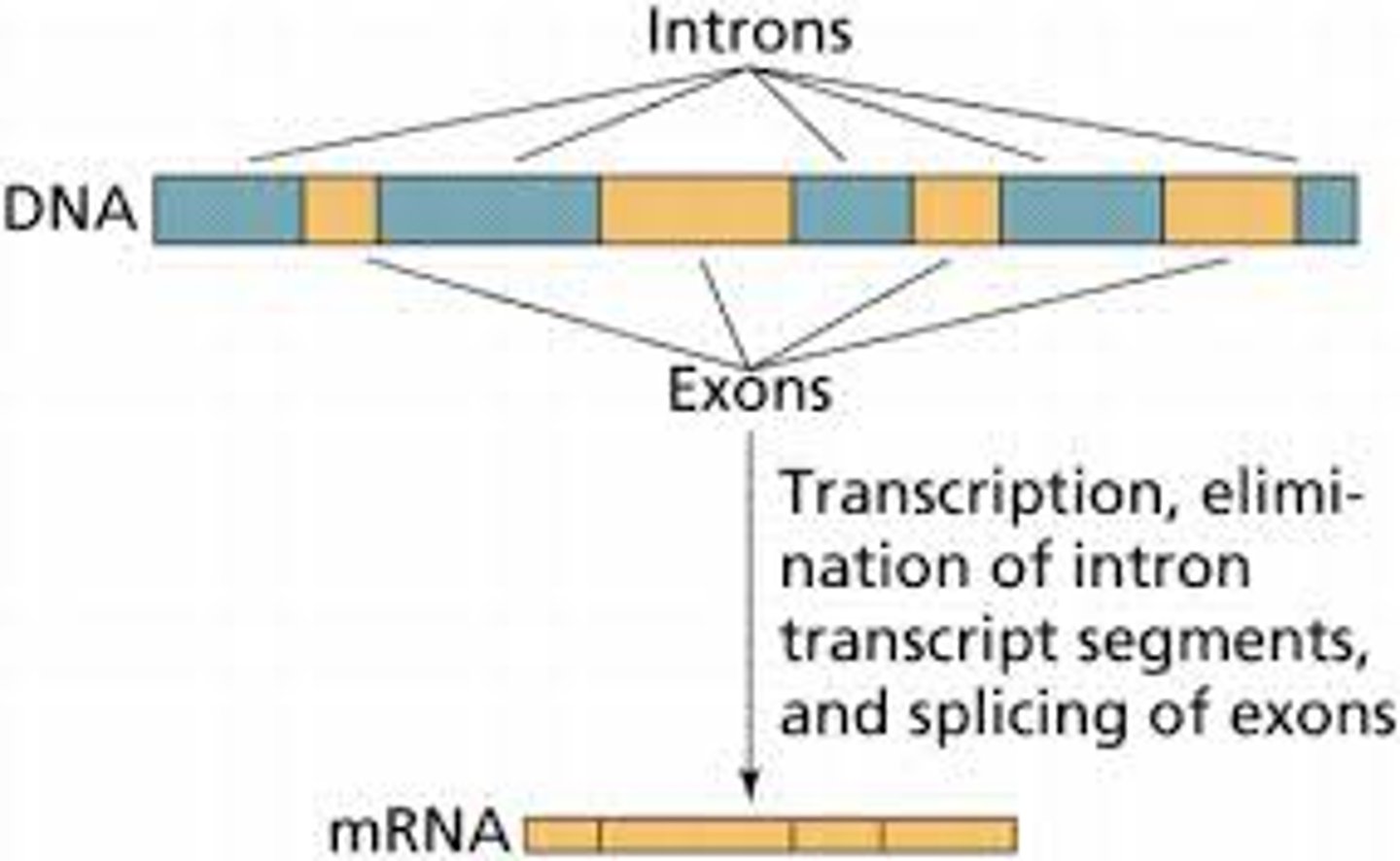
Intron
A noncoding, intervening sequence within a eukaryotic gene.
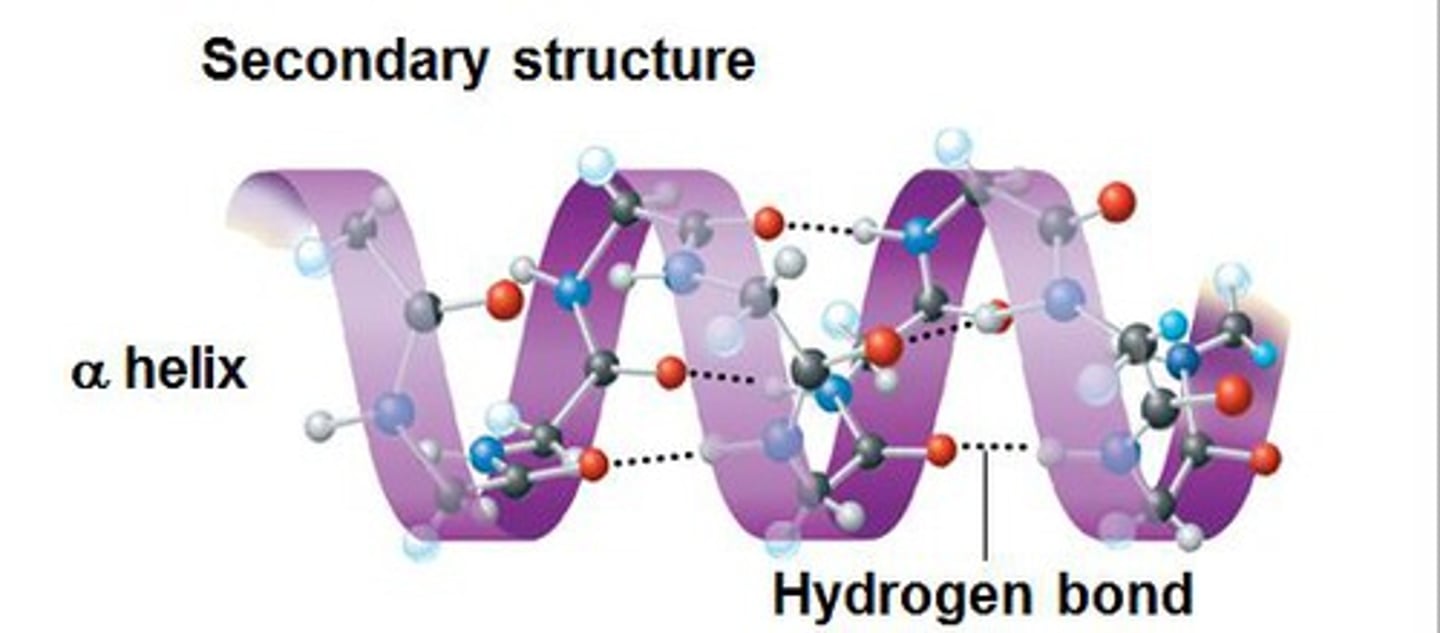
Alpha helix
A spiral shape constituting one form of the secondary structure of proteins, arising from a specific hydrogen-bonding structure.
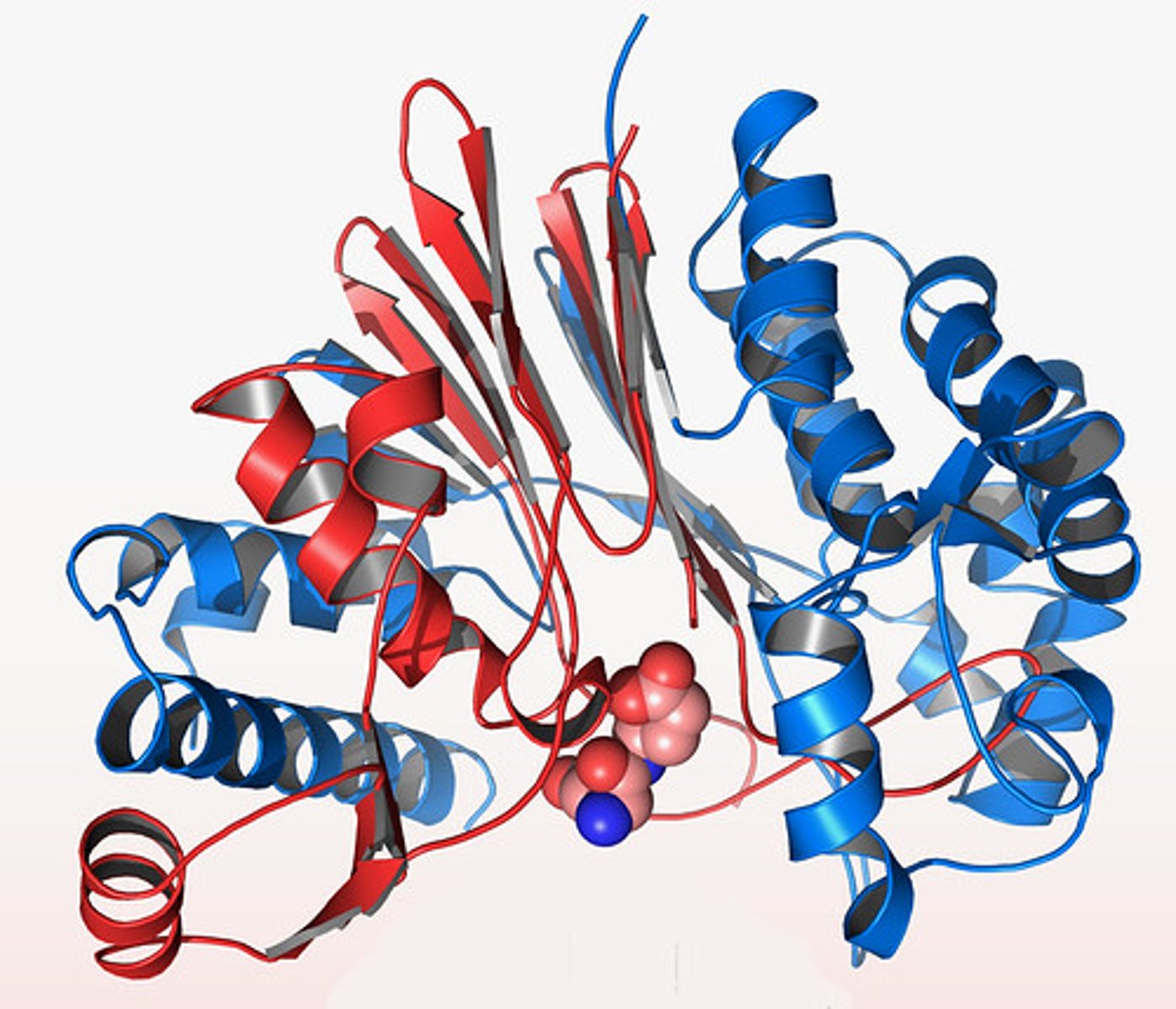
Tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
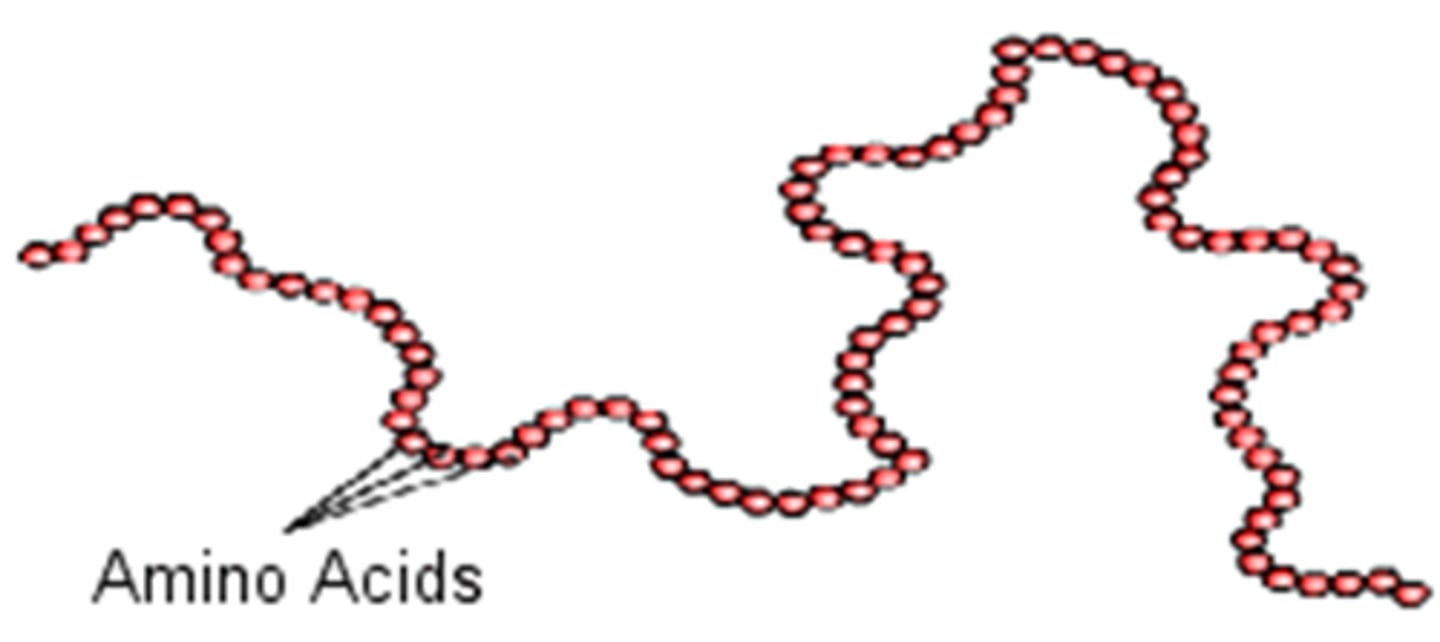
Primary structure
The first level of protein structure; the specific sequence of amino acids making up a polypeptide chain.

Quaternary structure
The fourth level of protein structure; the shape resulting from the association of two or more polypeptide subunits.
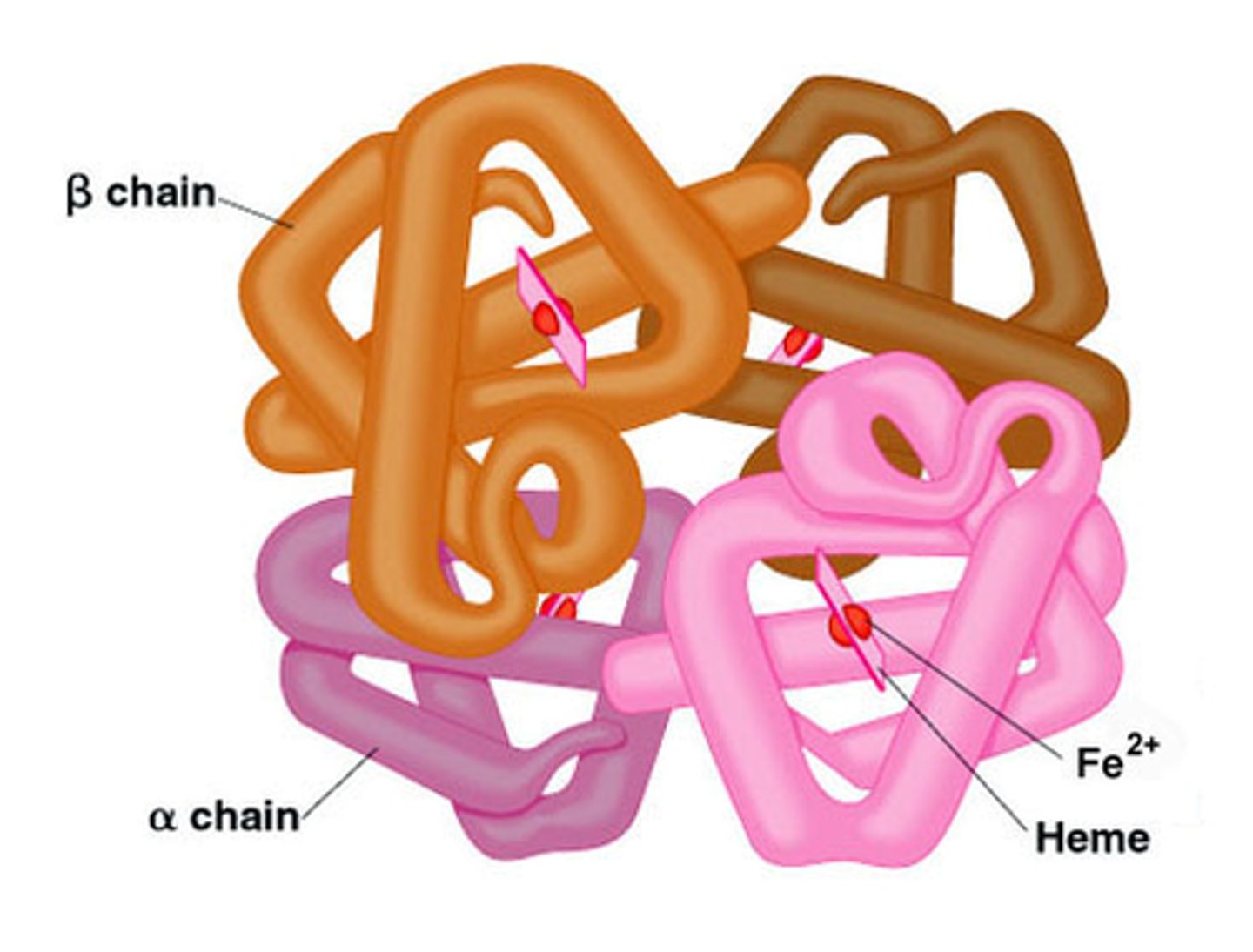
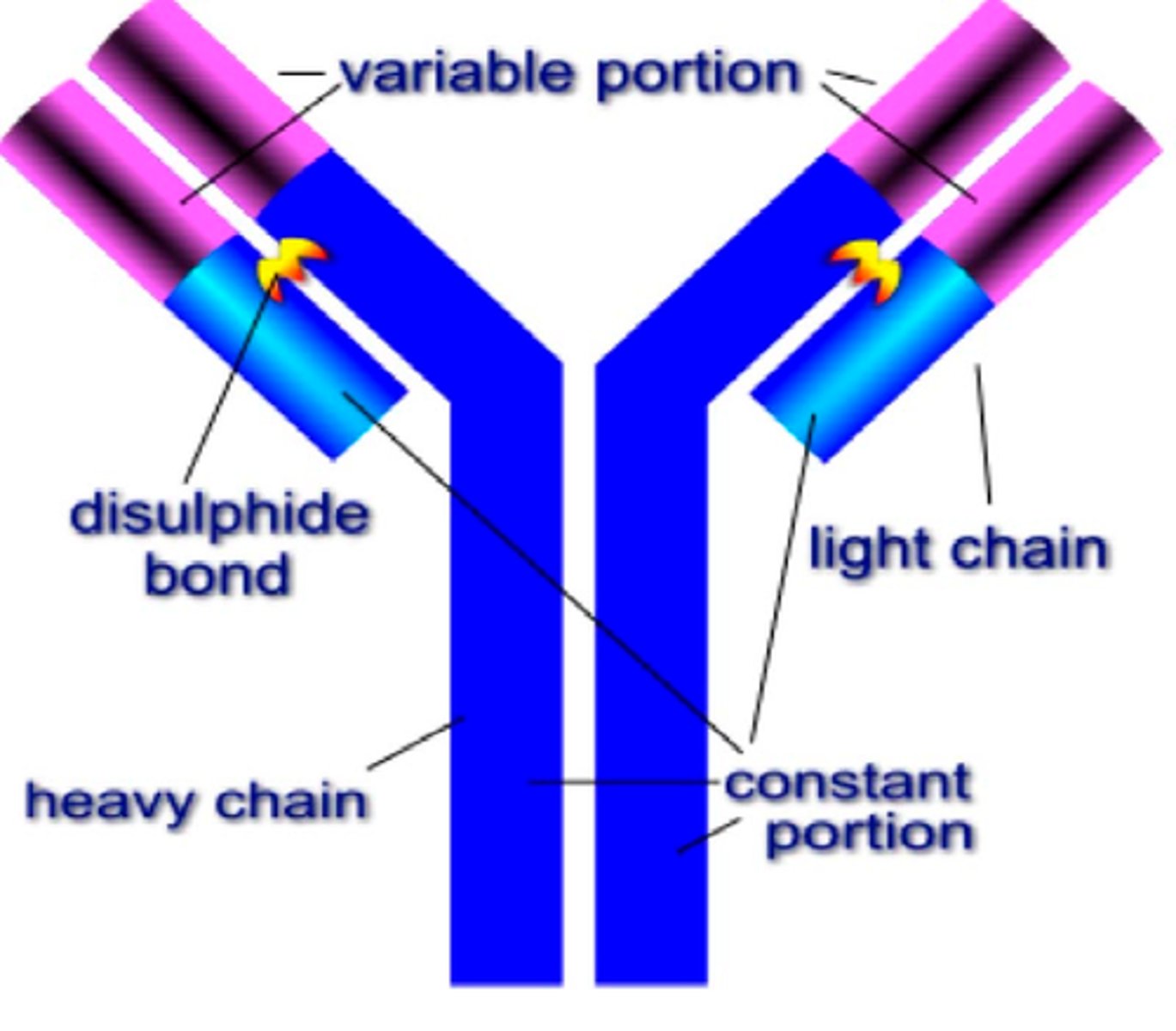
Antibodies
Specialized proteins that aid in destroying infectious agents
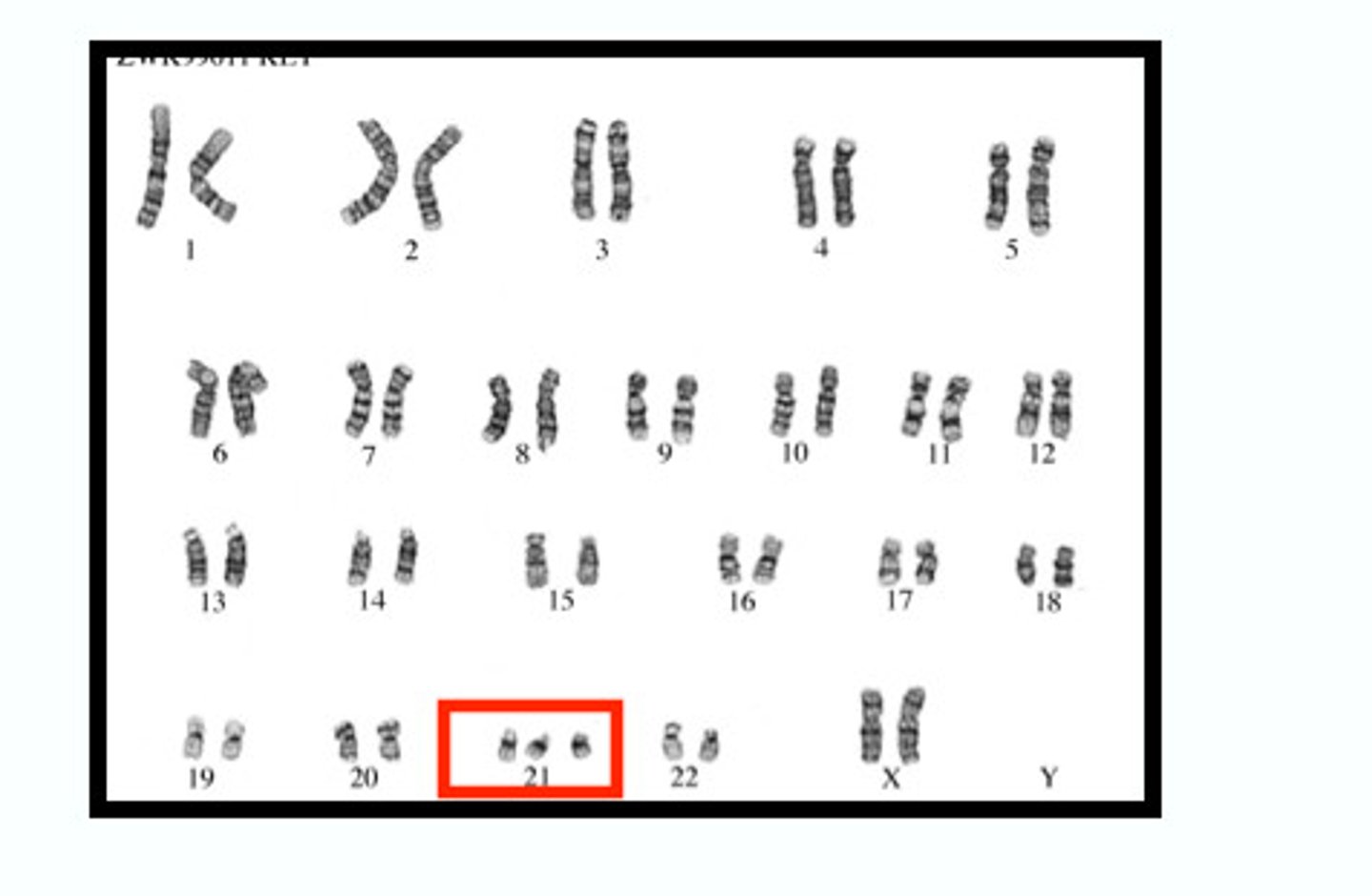
Down syndrome
A condition of mild to severe intellectual disability and associated physical disorders caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21
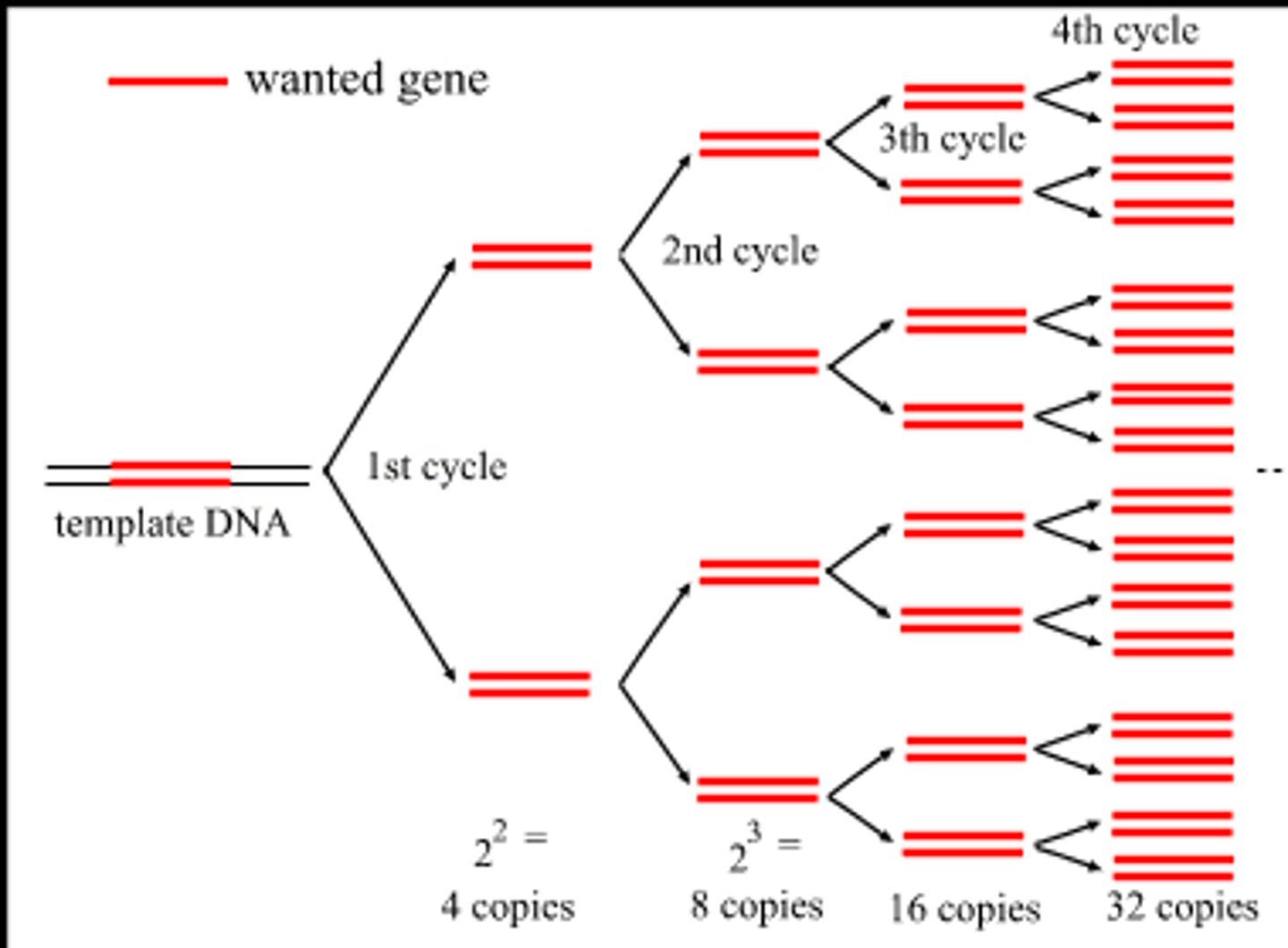
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
A technique for amplifying DNA in vitro by incubating with special primers, DNA polymerase molecules, and nucleotides.
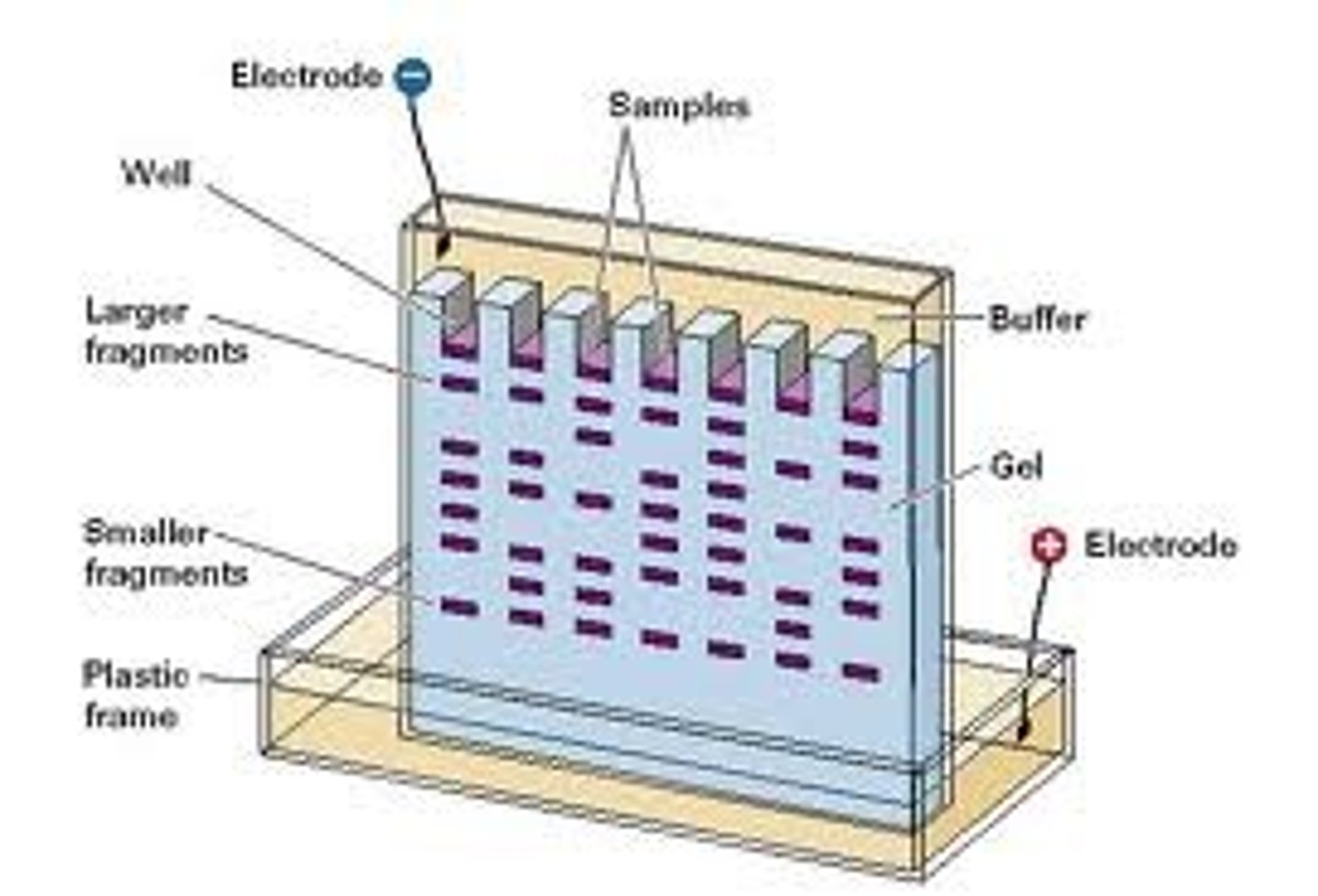
Gel Electrophoresis
A process where DNA fragments are separated according to size using electrical charges
DNA sequence
The sequence, or order, in which the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T) are arranged in a gene or a DNA fragment, or in an organism's genome.
Genome
All the genetic information in an organism; all of an organism's chromosomes.
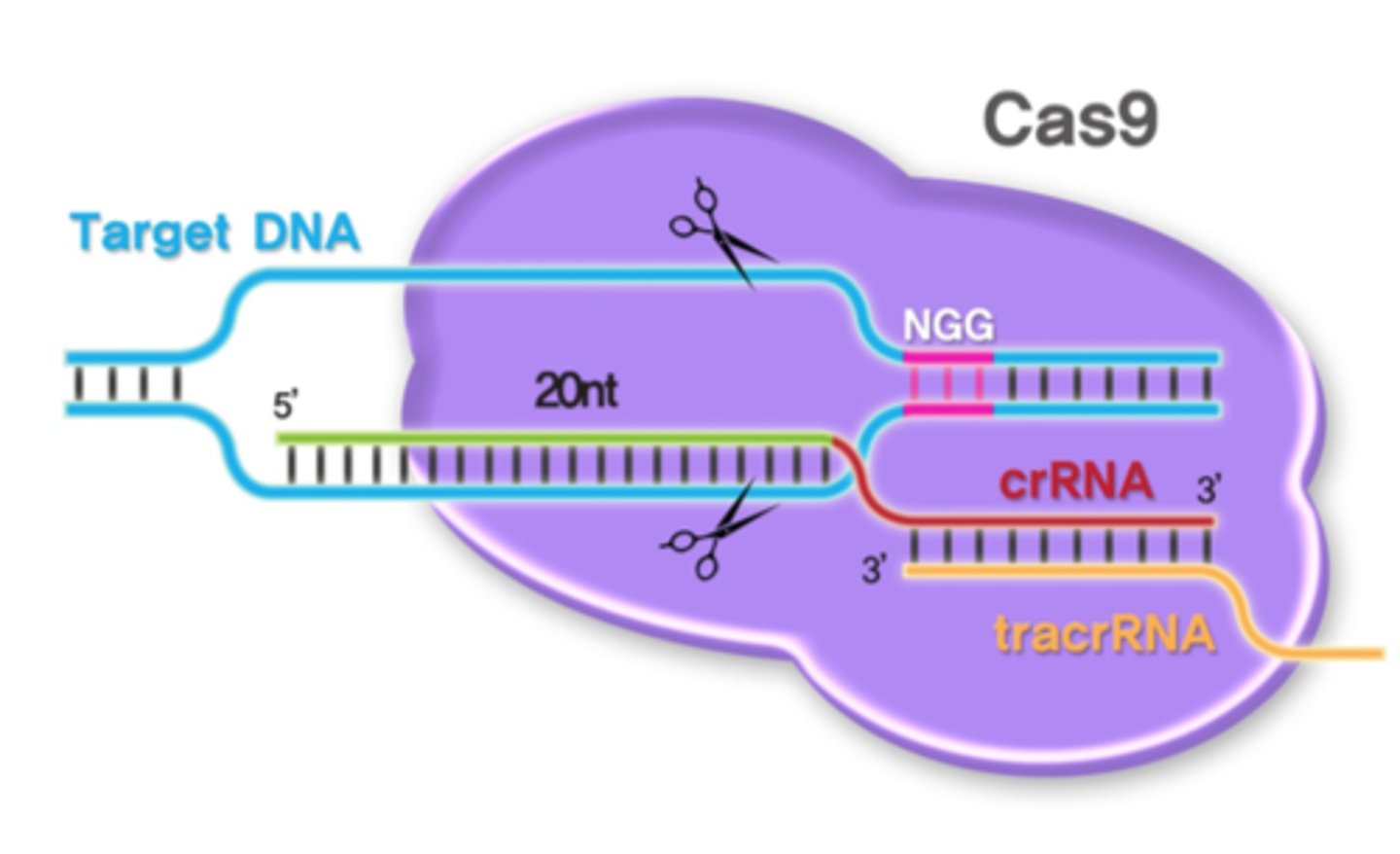
CRISPR/Cas9
A revolutionary gene editing technique derived from the immune system of simple prokaryotes.
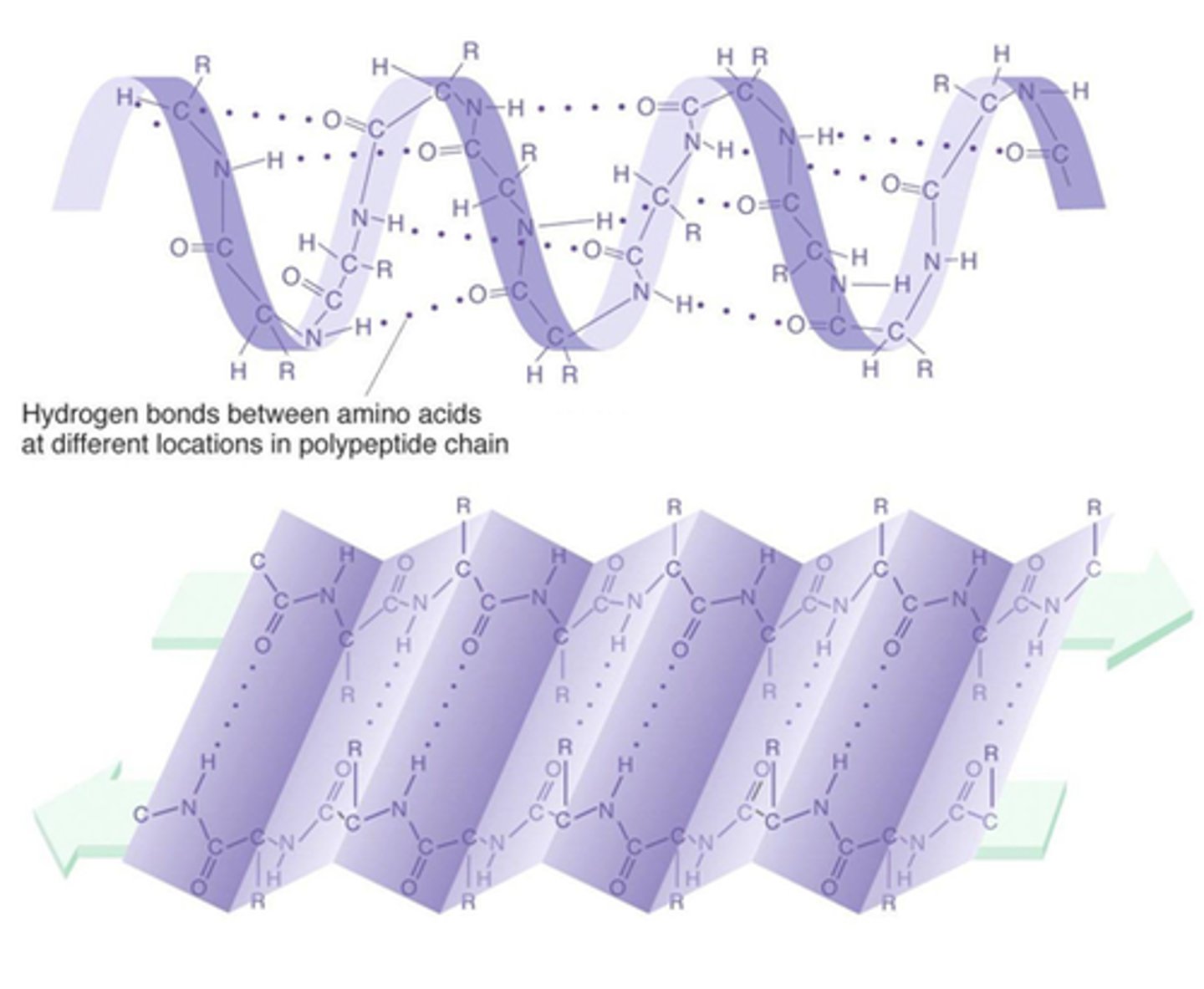
Secondary structure
Regions of repetitive coiling or folding of the polypeptide backbone of a protein due to hydrogen bonding between constituents of the backbone (not the side chains).
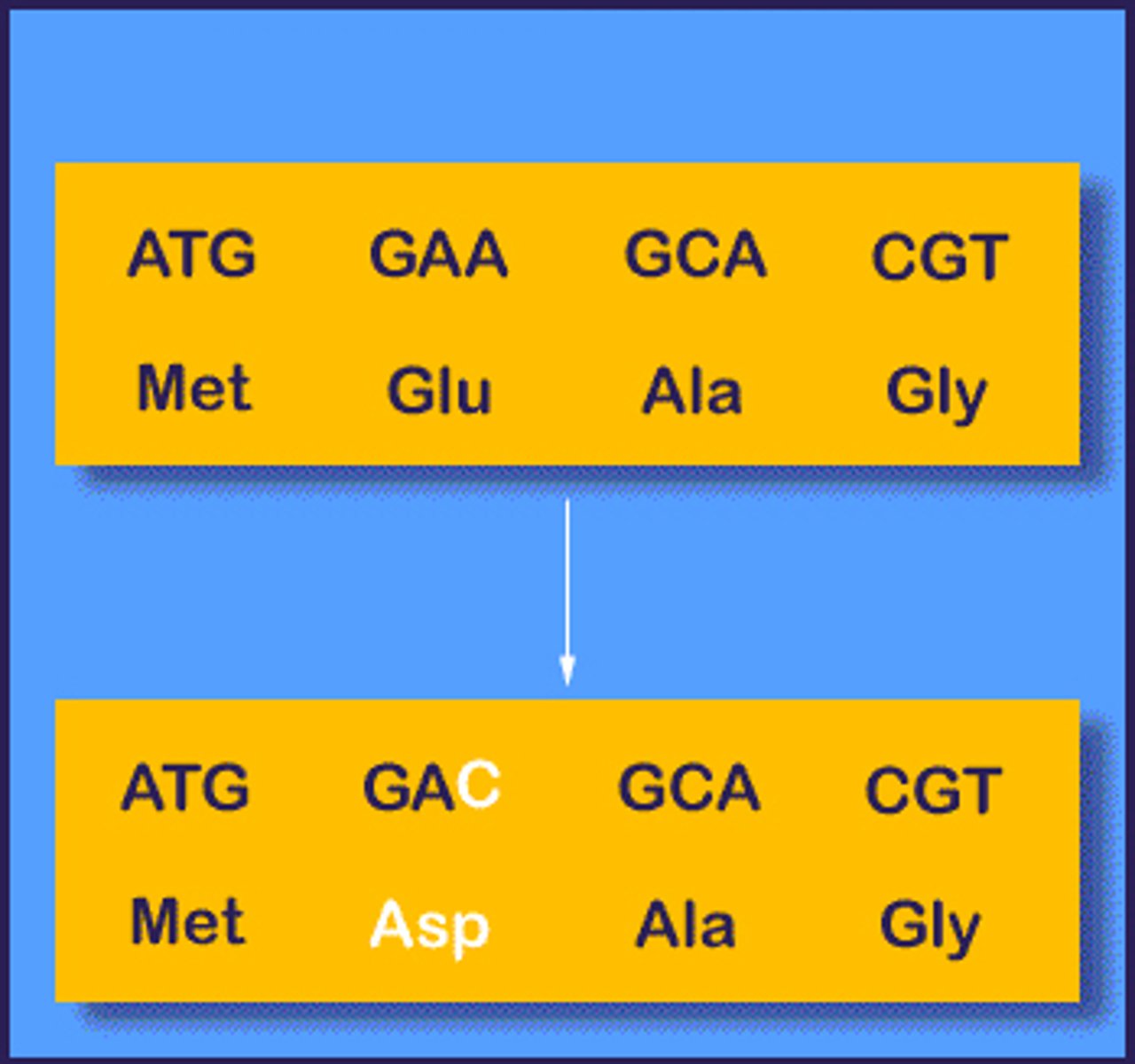
missense mutation
A point mutation in which a codon that specifies an amino acid is mutated into a codon that specifies a different amino acid.
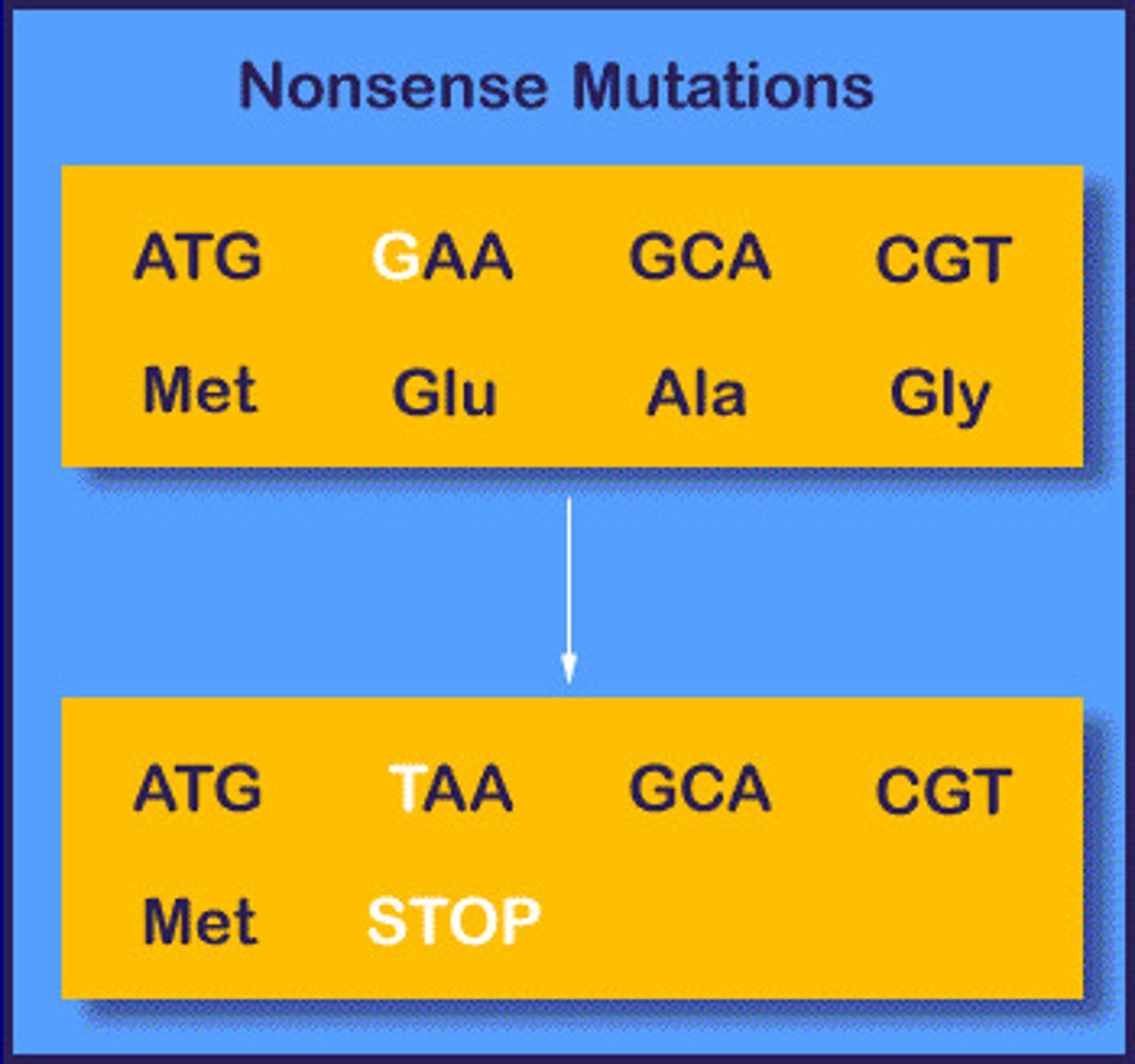
nonsense mutation
A mutation that changes an amino acid codon to one of the three stop codons, resulting in a shorter and usually nonfunctional protein.
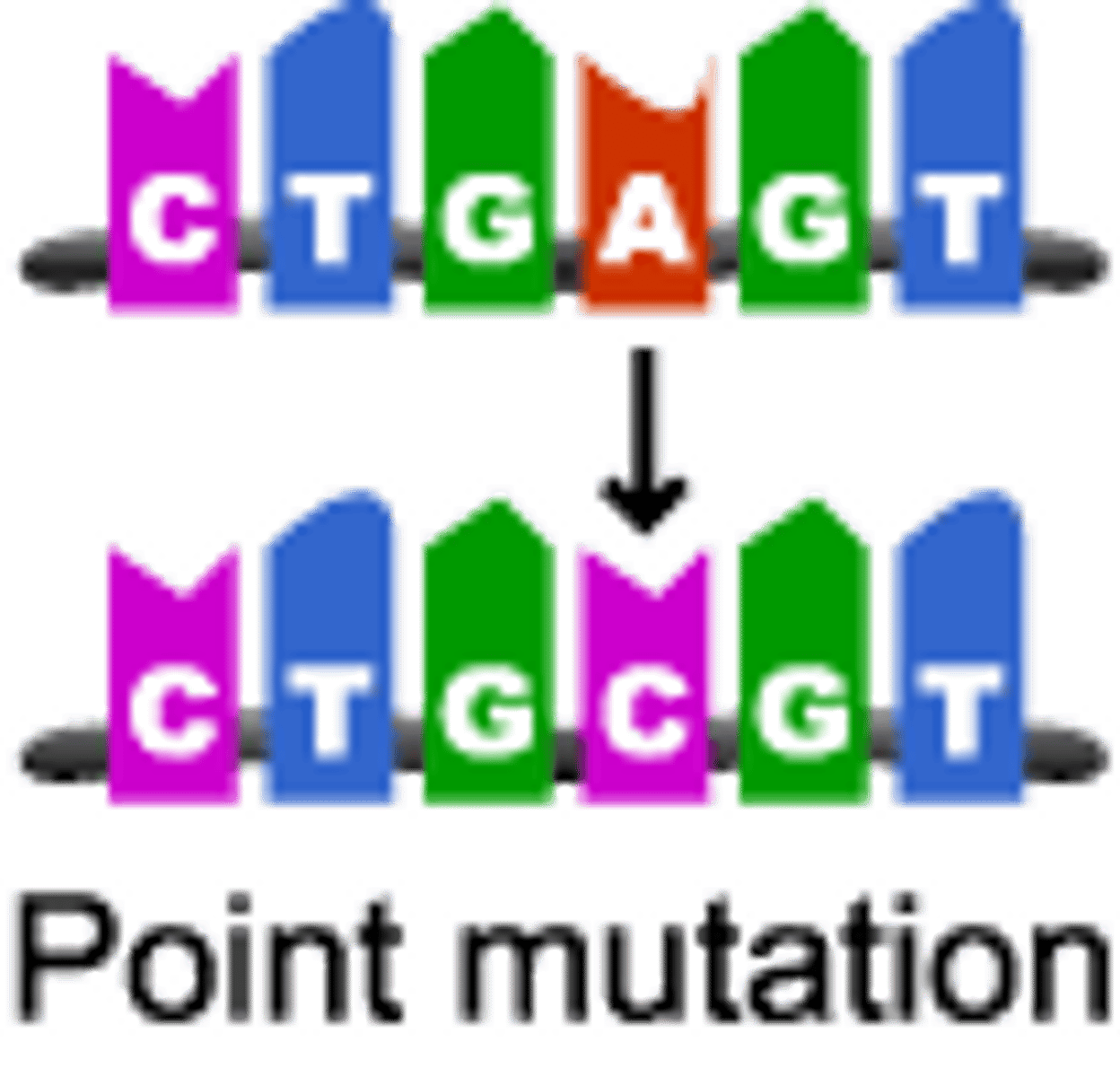
point mutation
gene mutation in which a single base pair in DNA has been changed
deletion mutation
a change in the base sequence of a gene that results from the loss of one or more base pairs in the DNA

insertion mutation
a mutation in which one or more nucleotides are added to a geneinse

BLAST
In bioinformatics, BLAST (basic local alignment search tool) is an algorithm and program for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as the amino-acid sequences of proteins or the nucleotides of DNA and/or RNA sequences
Bioinformatics
application of mathematics and computer science to store, retrieve, and analyze biological data
Protein Data Bank (PDB)
An international database that archives the data describing the three-dimensional structure of nearly all macromolecules for which structures have been published.
Vaccines
A preparation that prevents a person from contracting a specific disease
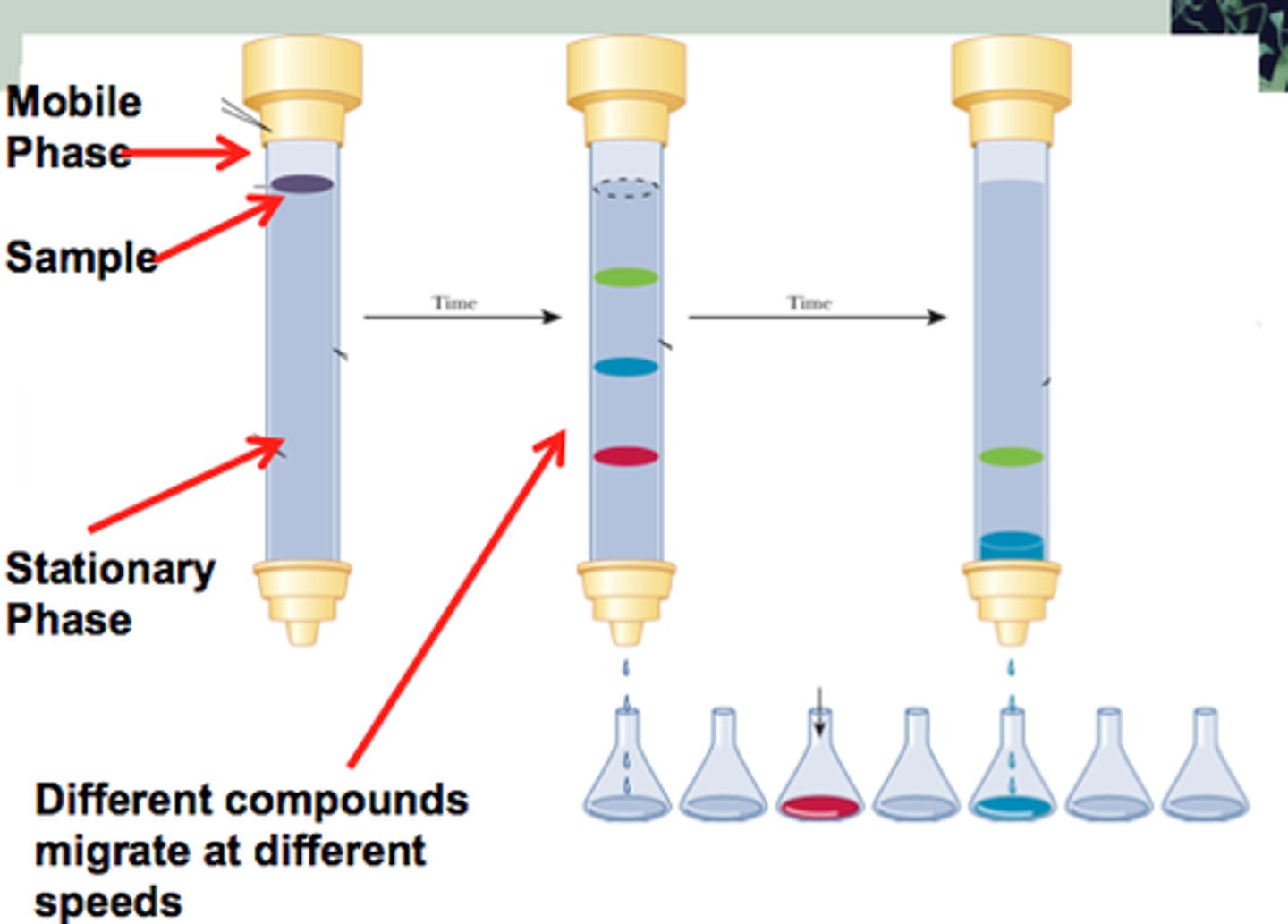
Chromotography
A physical process used to determine what type of substances have been mixed together
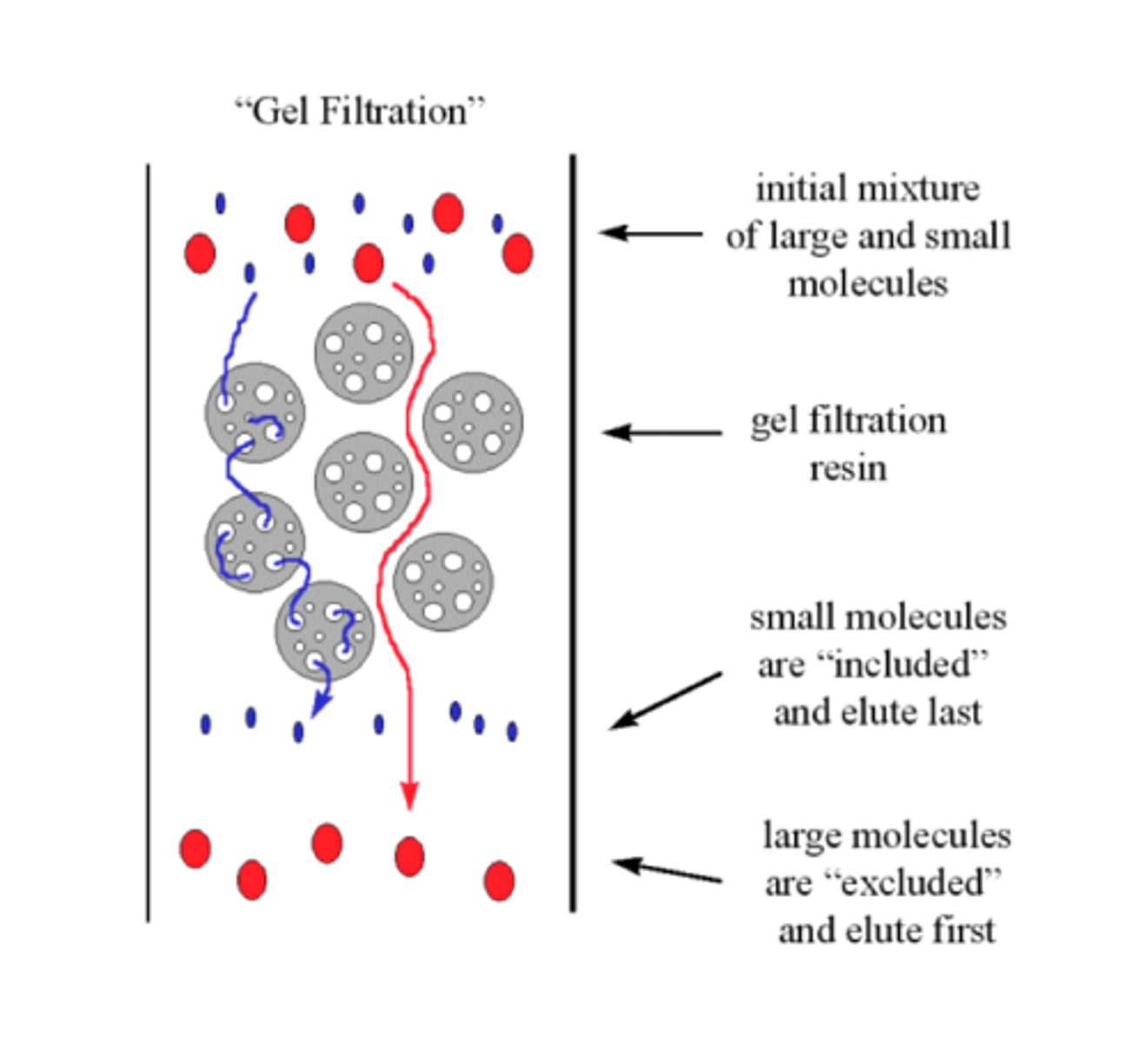
size exclusion chromatography
relies on porous beads; larger molecules elute first because they are not trapped in small pores
phobic
fear

recombinant
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources
protein electrophoresis
differentiates between protein fractions
affinity
an attraction to

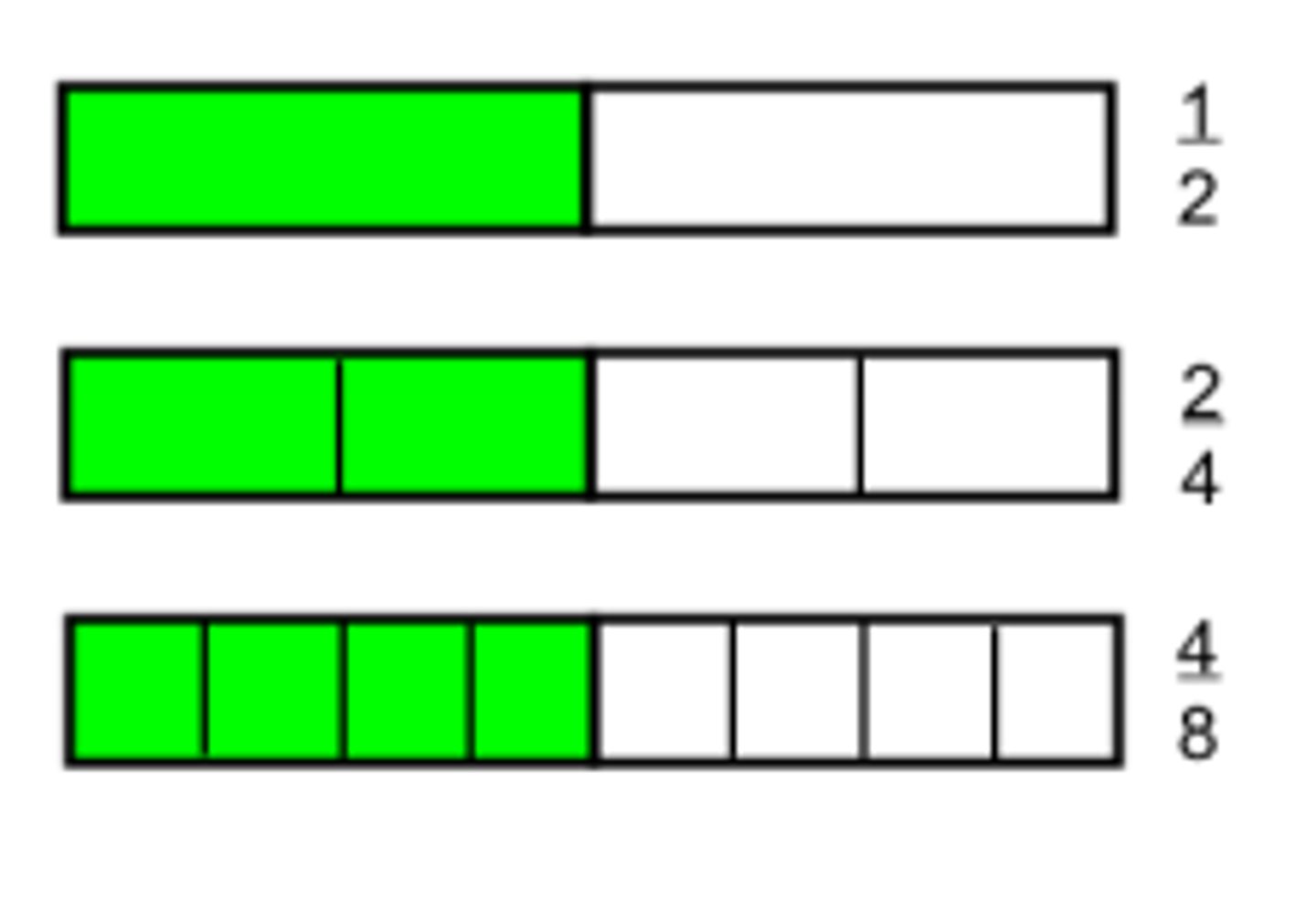
fraction
part of a whole

Cations
positively charged ions

Anion
negative ion
eluted
remove (an adsorbed substance) by washing with a solvent, especially in chromatography.
GenBank
NCBI database of sequences

Accesion Number
Unique identifier used in NCBI database
NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information)
An agency established in 1988 as a national (US) resource for molecular biology information. NCBI creates public databases, conducts research in computational biology, develops software tools for analyzing genome data, and disseminates biomedical information to better understand molecular processes affecting human health and disease.
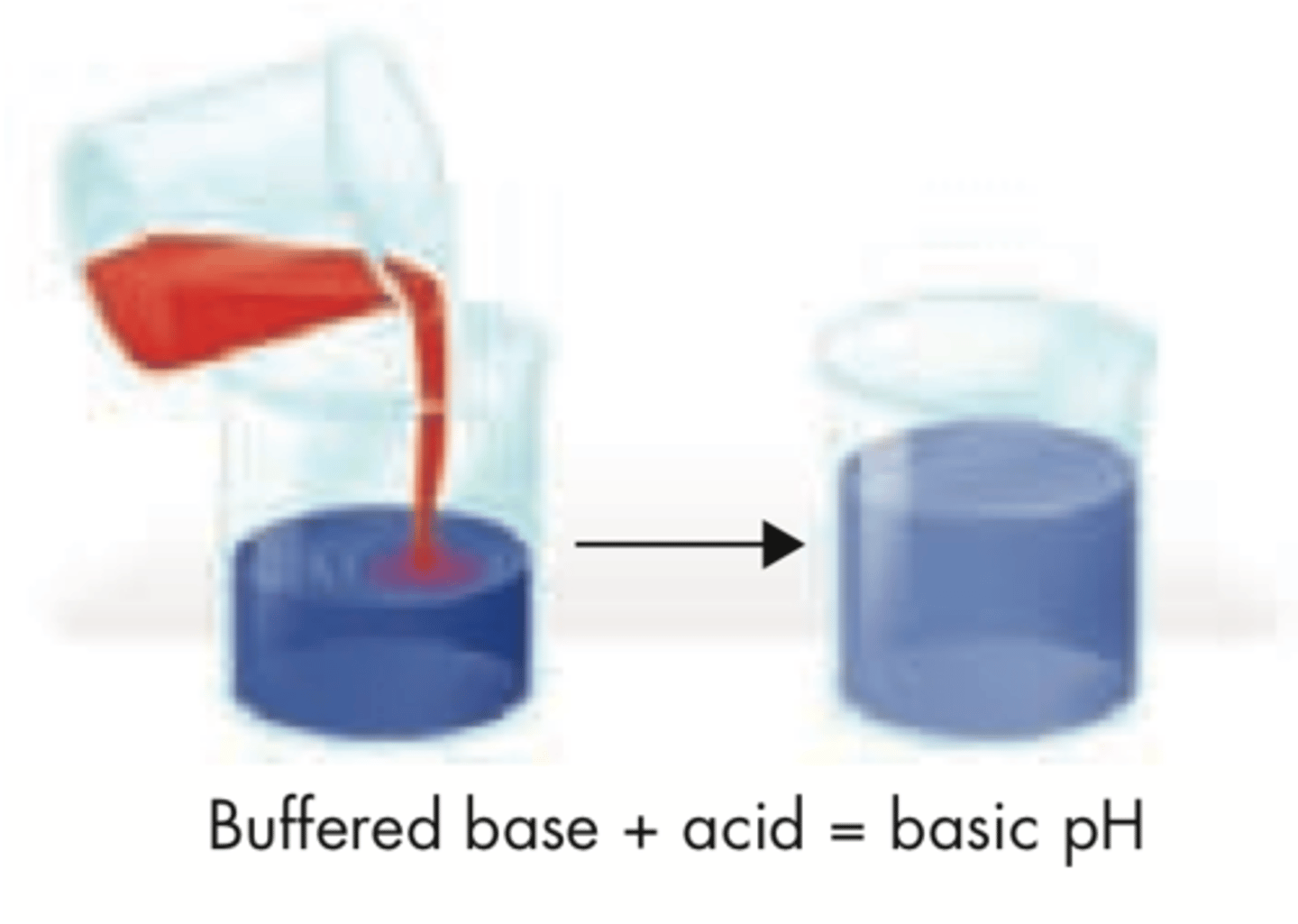
Buffer
compound that prevents sharp, sudden changes in pH
colorimetric assay
Measure with color test
assay
to test, analyze

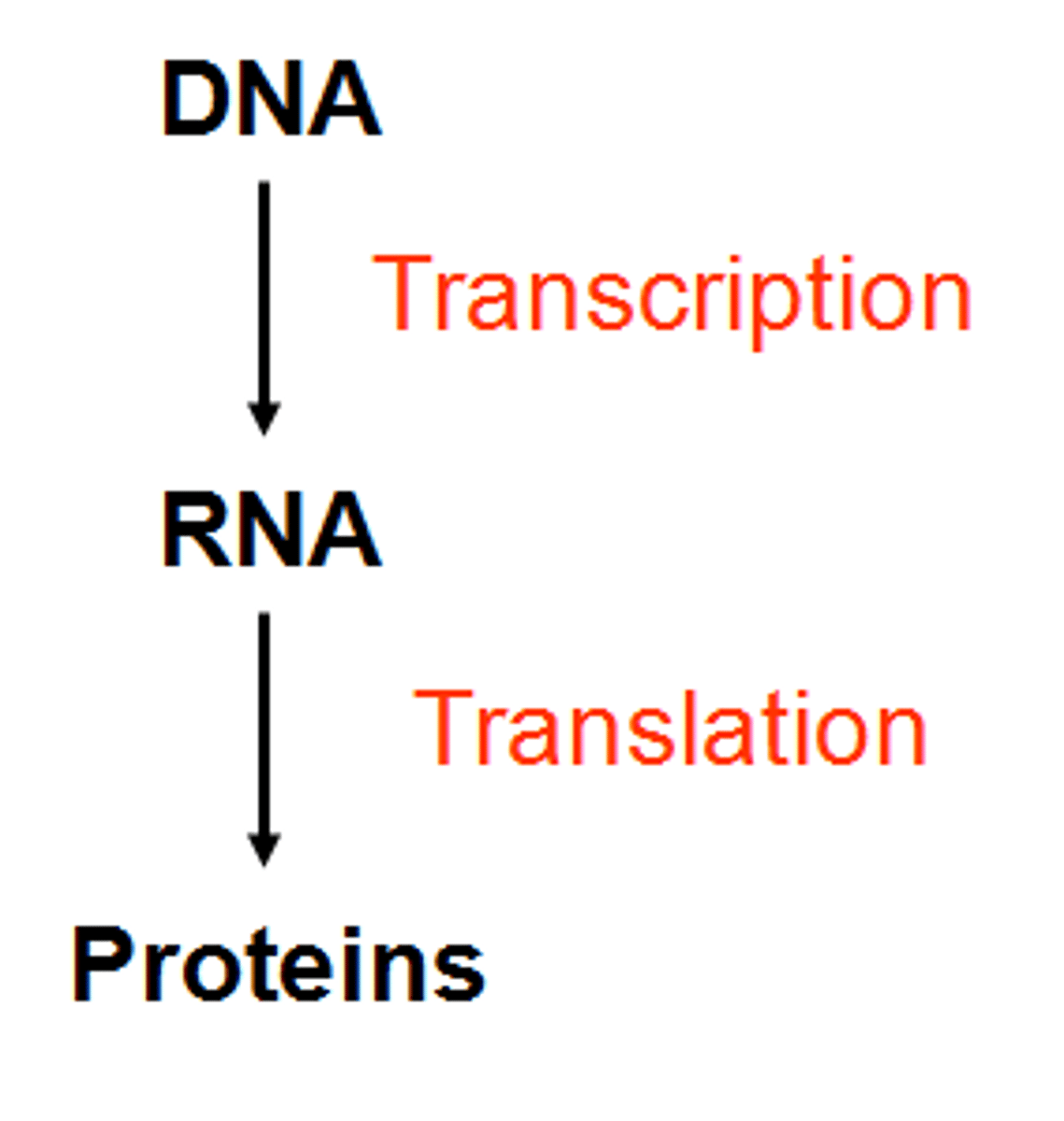
Central Dogma of Biology
DNA -> RNA -> Protein