Comprehensive Tests & Measures in Physical Therapy: Balance, Vital Signs, and ROM
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Purpose of Tests & Measures
Establish baseline @ initial evaluation (TUG, BERG Balance, 6 min walk, standard balance battery), track progress, guide treatment
Validity
Does the test measure what it should?
Reliability
Consistent results across testers/time
Intra Reliability
Within tester (mistakes)
Inter Reliability
Between testers (mistakes)
Standardization
Using the same method for accuracy
Heart Rate (HR)
60-100 bpm
Respiratory Rate (RR)
12-18 breaths/min
Blood Pressure (BP)
90/60 - 120/80 mmHg (above 120/80 is prehypertension)
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
95-100%
Temperature
97-99 degrees F (37 degrees C avg)
BP PROCESS
1. Pulse (Brachial) 2. Line Cuff Up w/ brachial 3. Stethoscope Bell on artery 4. Pump it up >180 mm/Hg 5. Deflate it (Rate is an art)
Timed Up & Go (TUG)
<12 sec normal, >13.5 fall risk, 12
Berg Balance Scale (BBS)
0-56; <45 = Fall Risk
6-Minute Walk
500(1640ft)-700m (2300ft) typical adult; declines with age
Gait Speed
1.0-1.4 m/s; <0.8 m/s = risk
Manual Muscle Testing (MMT)
0-5 scale (poor intra+inter reliability)
Standard Balance Test
Not for geriatrics; Can show which side is weaker or stronger; Stand for 30 seconds on both legs eyes open/closed; On one right/left leg eyes closed/open; Left/Right foot in front eyes closed/open
30s Sit to Stand
Measures lower body strength, functional mobility, and risks of falling
Average Score for 30s Sit to Stand by Age and Gender
60-64 Men <14, Women <12; 65-69 Men <12, Women <11; 70-74 Men <12, Women <10; 75-79 Men <11, Women <10; 80-84 Men <10, Women <9; 85-89 Men <8, Women <8
Fall Risk Assessment
Any score below the average for that age group and gender is considered fall risk.
Mytomes
Key muscle groups by spinal level
Dermatomes
Skin sensation regions
Reflexes
normal, hypo, or hyperactive
Range of Motion (ROM) checks
Assessment of joint movement capabilities.
Strength Quick Checks
Brief assessments of muscle strength.
EOC
8 weeks
Reassess
4 weeks
Initial Evaluation
The first assessment of a patient's condition.
Diagnosis
Identification of a disease or condition.
Physical Limitations
Restrictions in physical capabilities.
Assess: Qual/Quan
Evaluation of qualitative and quantitative aspects.
ROM (goniometer)
Measurement of joint angles using a goniometer.
Strength (MMT)
Muscle strength assessment using Manual Muscle Testing.
Balance (30s balance)
Assessment of balance over a 30-second period.
Functional Outcomes
Results related to a patient's ability to perform daily activities.
Pt: Walking, transfers
Patient's ability to walk and transfer (6m WT, Gait Speed).
Ot: ADL's
Occupational therapy assessments of Activities of Daily Living.
Both: Fall Risk
Assessment of risk of falling (TUG, Berg BT).
OIAN (Origin Insertion Action Nerve)
A method to describe muscles' anatomy and function.
Shoulder Flexion
0 - 180 degrees of shoulder movement.
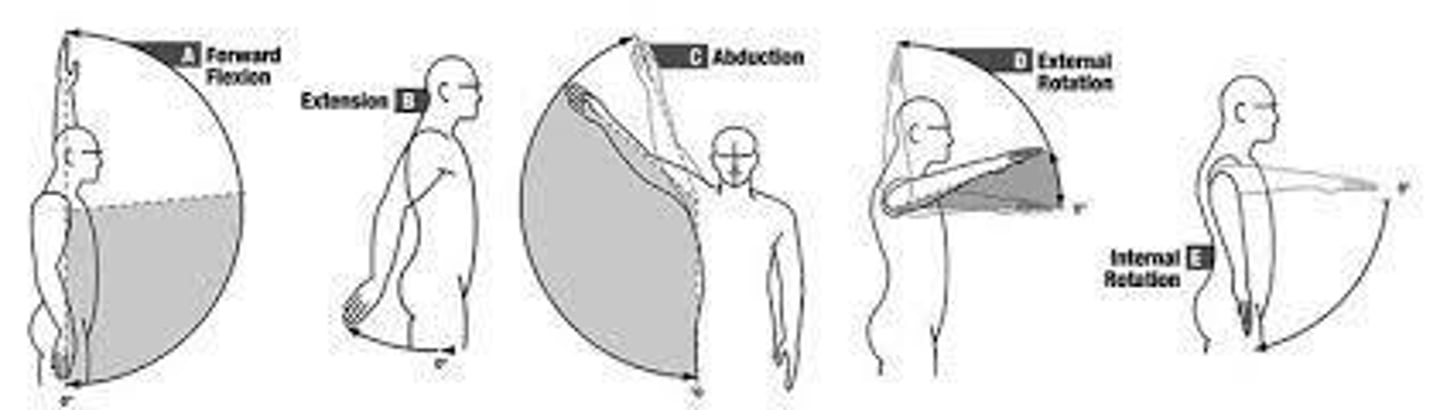
Shoulder Extension
0 - 60 degrees of shoulder movement.
Shoulder Abduction
0 - 180 degrees of shoulder movement.
Shoulder Internal Rotation
0 - 70 degrees of shoulder movement.
Shoulder External Rotation
0 - 90 degrees of shoulder movement.
Cervical Spine Flexion
0 - 45 degrees of neck movement.
Cervical Spine Extension
0 - 45 degrees of neck movement.
Cervical Spine Lateral Flexion
0 - 45 degrees of neck movement.
Cervical Spine Rotation
0 - 60 degrees of neck movement.
Hip Flexion
0 - 120 degrees of hip movement.
Hip Extension
0 - 30 degrees of hip movement.
Hip Abduction
0 - 45 degrees of hip movement.
Hip Adduction
0 - 30 degrees of hip movement.
Hip Internal Rotation
0 - 45 degrees of hip movement.
Hip External Rotation
0 - 45 degrees of hip movement.
Knee Flexion
0 - 135 degrees of knee movement.
Knee Extension
0 degrees (neutral) of knee movement.
Knee Hyperextension
Up to 10 degrees in some individuals.