Tissue Histology and Types
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards contain key terms and definitions related to histology and types of tissues, offering a review of essential concepts for examination.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Histology
The study of normal structures of tissues.
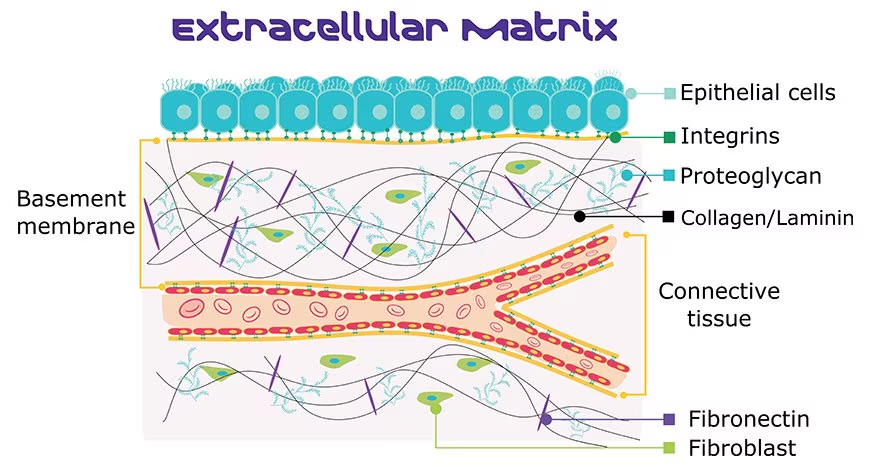
Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
Ground Substance & Protein Fibers. The material surrounding cells in a tissue composed of substances in liquid, gel, or solid forms. provide strength to resist stretching and compression and holds cells in place.
Epithelial Tissue
A type of tissue that consists of tightly packed cells that cover and line body surfaces and cavities. provides protection immune defenses, secretion of hormones and oils , transport and sensation. Avascular Tissue and fairly impermeable.
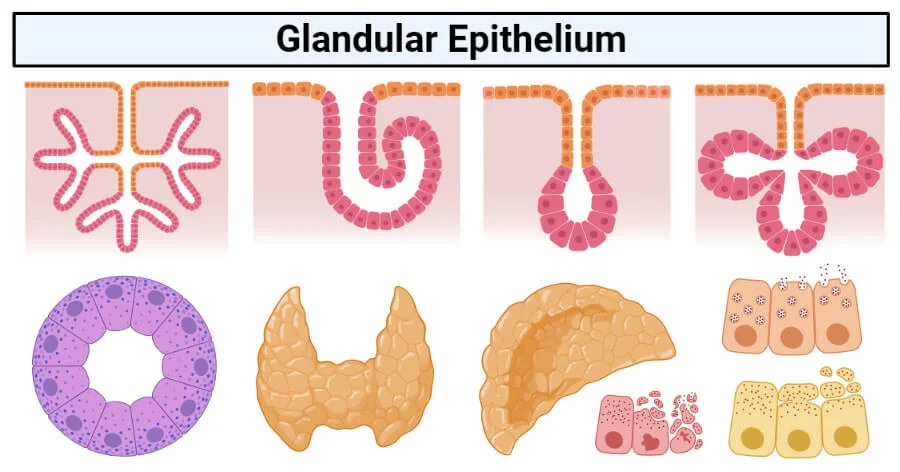
Glandular Epithelia
Epithelia specialized for secretion, including endocrine and exocrine glands.
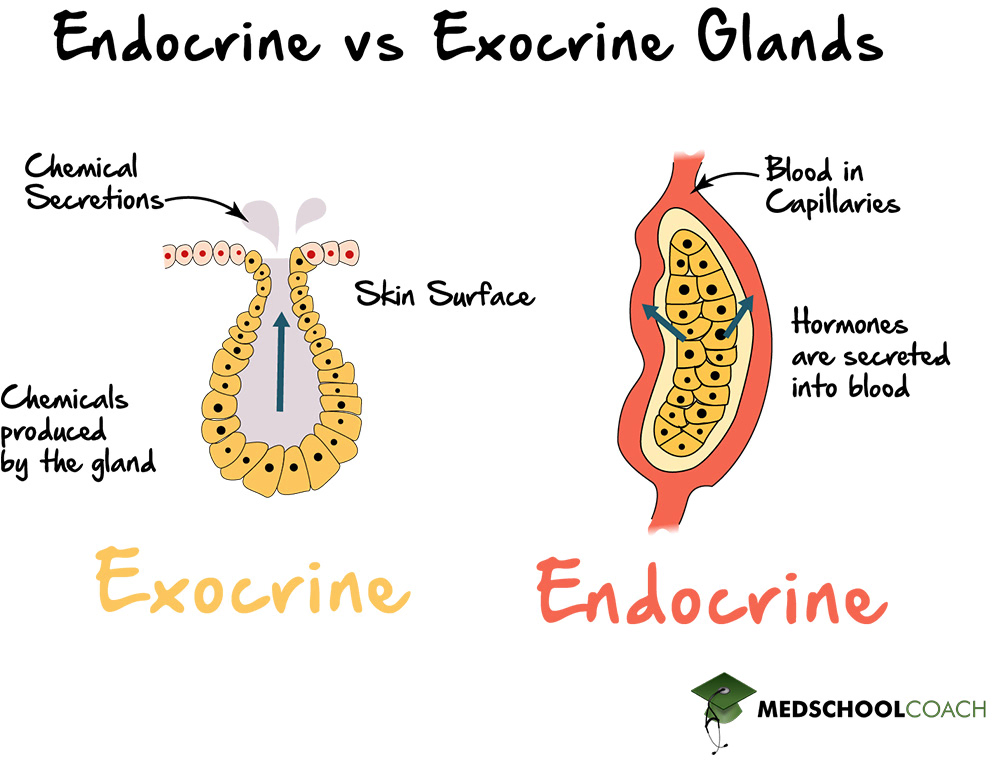
Endocrine Glands
Glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream without ducts. ex: thyroid, pituitary, ovary
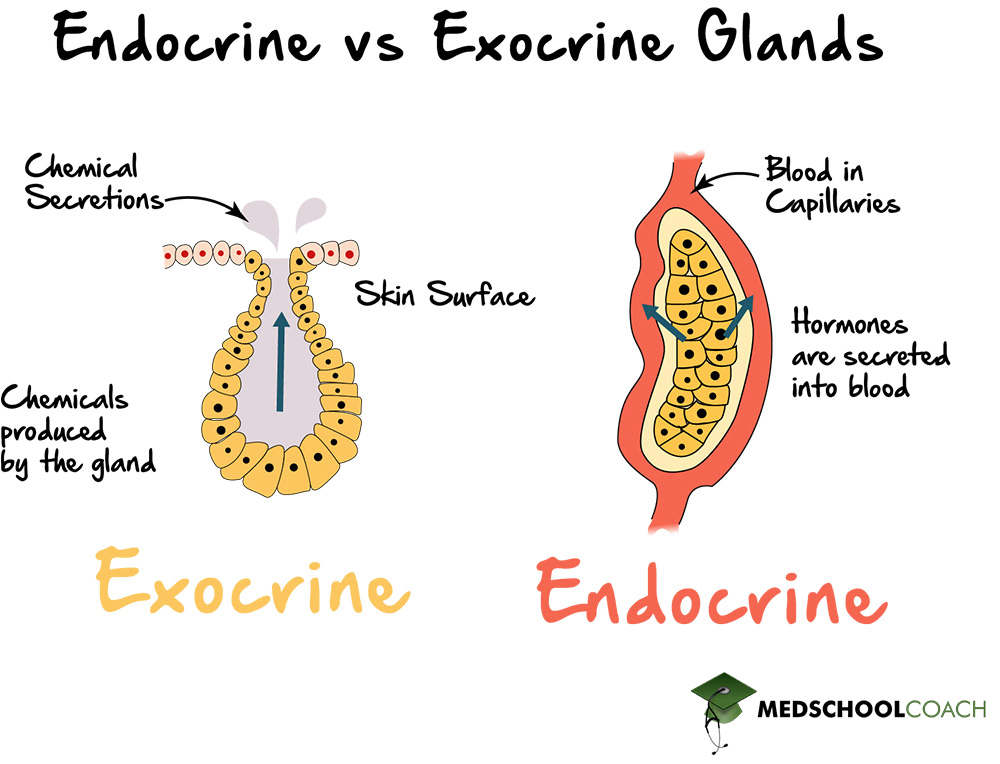
Exocrine Glands
Glands that have ducts and secrete substances with local effects. ex: sweat and salivary glands
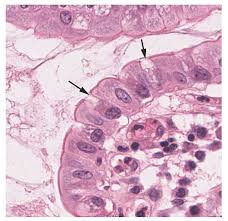
Goblet Cells
unicellular and secrete mucus for digestive and respiratory tracts. protects underlying epithelia
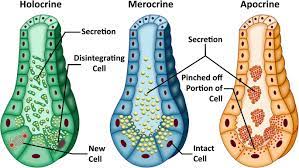
Merocrine Secretion
A type of exocrine secretion where products are released via exocytosis without loss of cell integrity, such as in sweat and salivary glands.
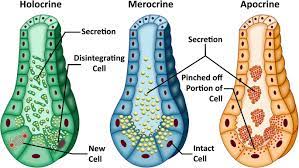
holocrine secretion
A type of exocrine secretion where entire cells disintegrate to release their substance, such as in sebaceous glands.
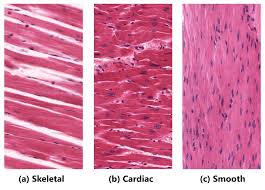
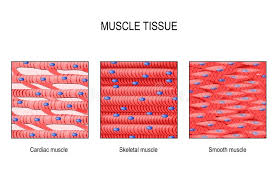
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is striated and under voluntary control.
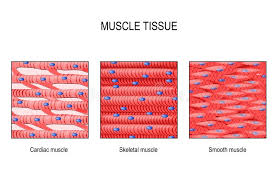
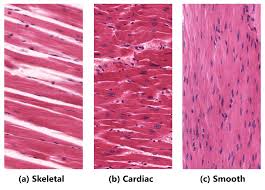
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
A type of muscle tissue that is striated and involuntary, found in the heart.
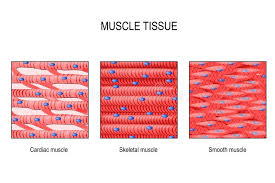
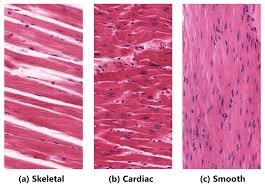
Smooth Muscle Tissue
A non-striated, involuntary muscle tissue found in the walls of hollow organs.
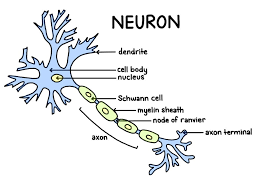
Neurons
Cells in nervous tissue capable of transmitting nerve impulses. They consist of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. They send and receive messages.
Neuroglial Cells
Support cells in nervous tissue that do not conduct impulses.
Regeneration
The process of replacing damaged or dead cells with the same type of cells.
Fibrosis
The process of scar tissue formation, where fibroblasts produce collagen to repair tissue. results in scar tissue
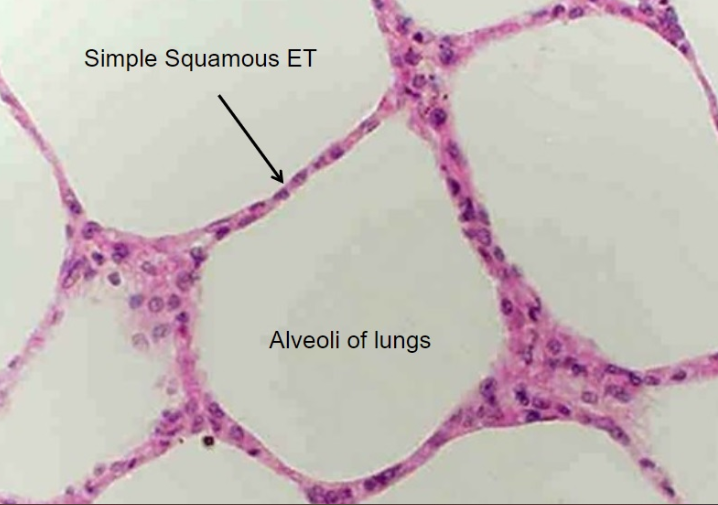
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A single layer of flat cells that facilitates diffusion, found in air sacs of lungs and line blood vessels. good for rapid diffusion
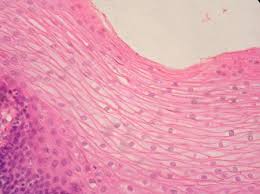
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Multiple layers of cells that protect underlying tissues from abrasion, found in skin, mouth, and throat.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
A single layer of cube-shaped cells that functions in secretion and absorption, commonly found in glands and kidney tubules.
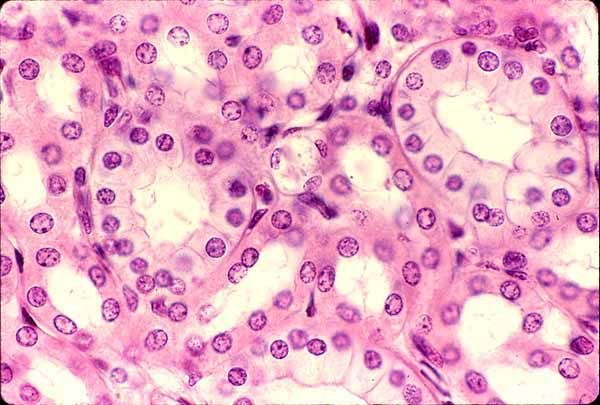
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
rare in humans. lines ducts of sweat glandsand mammary glands, providing protection and some secretion.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
A single layer of column-shaped cells that aids in absorption and secretion, typically found in the digestive tract and uterus. often has microvili to increase surface area for absorption.
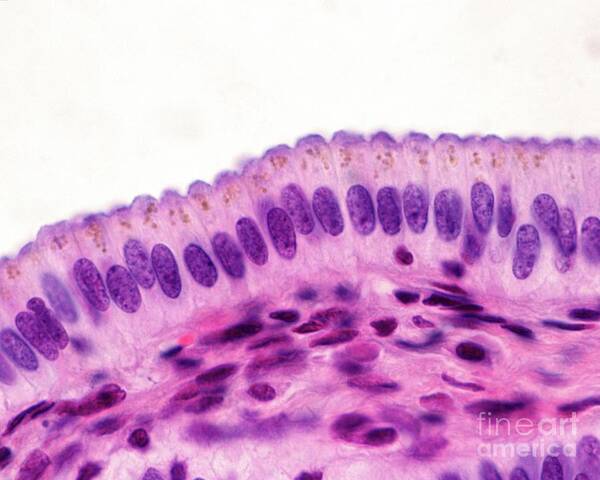
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
multiple layers of column-shaped cells that are rare in humans found in male urethra, cornea, and ducts of salivary glands
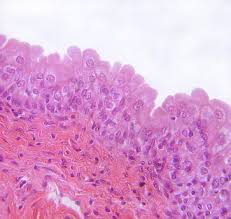
Transitional Epithelium (stratified weird)
A type of epithelium consisting of multiple layers of cells that can stretch, found primarily in the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra, allowing for flexibility and expansion. basal cell layers are cuboidal and the upper layers are flattened or dome-shaped.
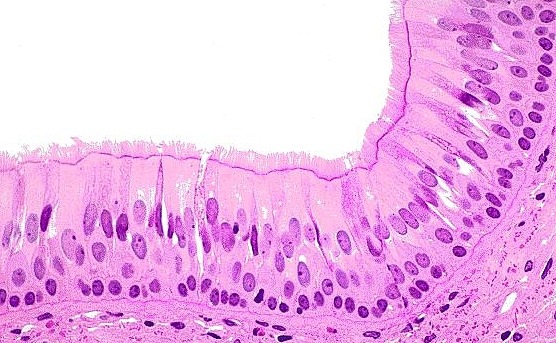
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
A type of epithelial tissue that appears to have multiple layers due to varying cell heights but is actually a single layer of cells, often found lining the respiratory tract and containing cilia to help move mucus. Found in Trachea and respriratory passages, it helps trap and move particles out of the airways.
Ground Substance
makes up most of extracellular matrix ECM . Made up of extracellular fluid aka interstital fluid, proteoglycans, GAGs, CAMs, and protien fibers.
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
polysaccharides in ECM. ex: chondroitin sulfate (cartilage) and hyaluronic acid
Proteogycans
macromolecules in the extracellular matrix, consisting of a protein core with glycosaminoglycan side chains. They play a crucial role in regulating the movement of water and nutrients within tissues.
Cell-Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
Made up of different glycoproteins that bind surface protein and maintain architecture of tissues
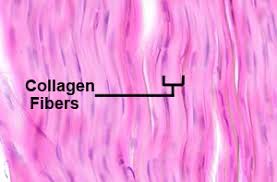
Collagen Fibers
Protein fiber that is resistant to tension and pressure. 20-25% of all proteins in the body. (white, fibrous)
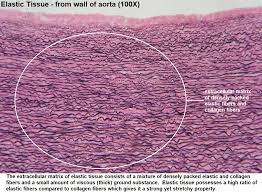
Elastic Fibers
protein fibers that provide elasticity and resilience to tissues, allowing them to withstand stretching. (yellow)
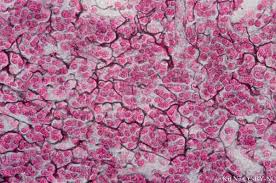
Reticular Fibers
thin, web-like protein fibers that provide a supportive framework for soft tissues and organs. meshwork
carcinogens
substances that are known to cause cancer by altering cellular metabolism or damaging DNA.
carcinoma
a type of cancer that originates in epithelial tissues, such as skin or lining of organs.
basal cell carcinoma
a common type of skin cancer that arises from basal cells in the epidermis. It typically manifests as a growth on sun-exposed areas. basement membrane slows the spread of cancerous cells, making it less aggressive than other skin cancers.
Connective Tissue (CT)
A type of tissue that connects tissues to one another, consists of scattered cells in an ECM, and provides support, protect and transport substances. very vascular
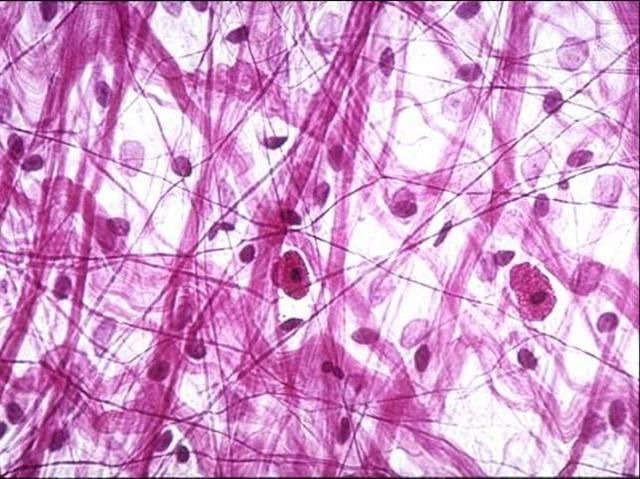
loose connective tissue areolar
a type of connective tissue characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and cells in the extracellular matrix, providing flexibility and support.
dense regular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that has tightly packed collagen fibers arranged in parallel, providing strength and resistance to tension in one direction.
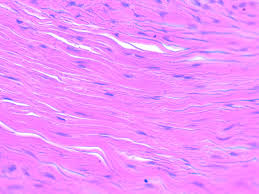
dense irregular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue with collagen fibers arranged irregularly, providing strength and support in multiple directions.
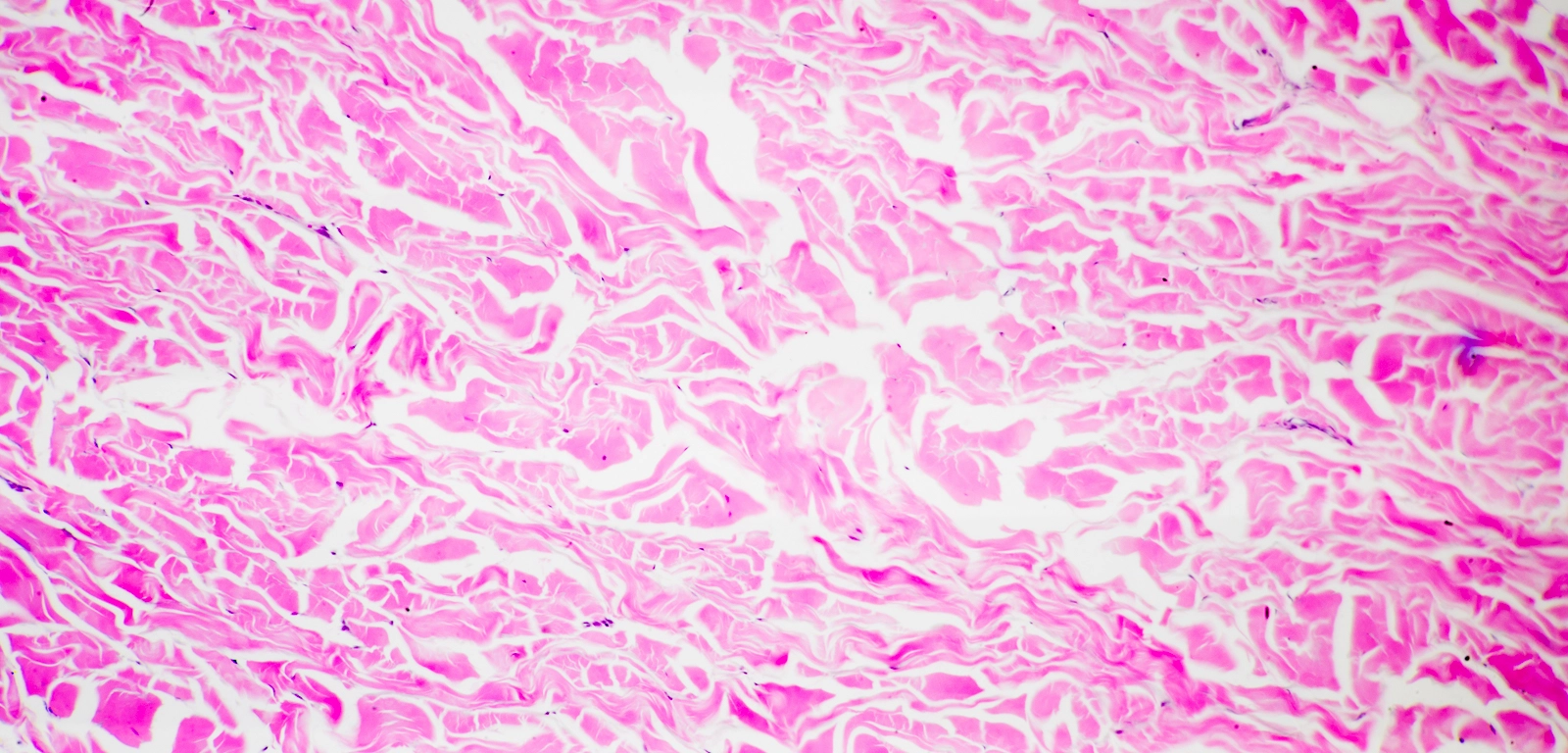
reticular connective tissue
A type of connective tissue composed of a network of reticular fibers and cells, providing structural support and a framework for organs such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
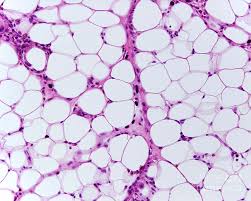
adipose connective tissue
A type of connective tissue that stores fat, providing insulation and cushioning to the body, as well as serving as an energy reserve.
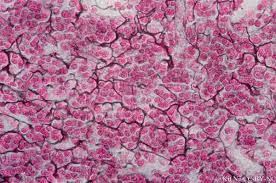
cartilage connective tissue (specialized)
A type of connective tissue that is more flexible than bone, providing support and cushioning to joints, and is found in structures like the nose, ears, and between vertebrae.
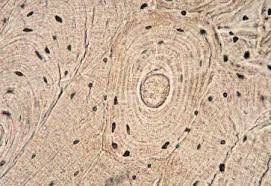
bone specialized c.t.
A type of specialized connective tissue that provides structural support and protection to the body, consisting of a hard matrix mineralized with calcium phosphate and collagen fibers.
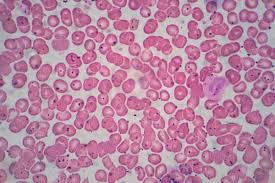
blood specialized c.t.
A type of specialized connective tissue that circulates throughout the body, consisting of red and white blood cells suspended in plasma, and is crucial for transportation of nutrients, gases, and waste.
hypertrophic obesity
A type of obesity characterized by the enlargement of adipocytes, resulting in an increased fat mass and storage within the body.
hypercellular obesity
A type of obesity marked by an increase in the number of adipocytes, leading to higher overall fat mass and potential health risks.
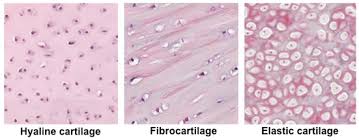
hyaline cartilage
A type of cartilage characterized by a smooth, glassy appearance, providing support and flexibility in structures such as the nose, trachea, and joints.
fibrocartilage
A tough and dense type of cartilage that provides support and absorbs shock in joints, found in areas like the intervertebral discs and knee menisci.
elastic cartilage
A type of cartilage that is flexible and resilient, containing abundant elastic fibers, found in structures such as the external ear and epiglottis.
hemopoiesis
The process of blood cell formation that occurs primarily in the bone marrow, producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
osteoarthritis
A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage and underlying bone, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. glucosamine slows this degeneration.
membranes
are thin layers of tissue that cover surfaces, line cavities, and separate organs, often serving protective and functional roles.
serous membranes
are membranes that produce a watery fluid, reducing friction between organs and body cavities. They line closed cavities and cover organs. line periotoneal, pericardial and pleural cavities
synovial membranes
are specialized connective tissue membranes that line the cavities of joints and produce synovial fluid to lubricate and nourish cartilage.
The secretory cells of sebacous glands fill with secretions then rupture to release their contents. what is this type of secertion?
Holocrine secretion
gland has no ducts to carry its secretion so it releases it directly in ecf. what type of gland is this?
endocrine gland
what is the function of microvilli for epithelium?
Microvilli increase the surface area of epithelial cells, enhancing absorption and secretion, particularly in the intestine and kidney.