Concepts of Health, Illness, and Wellness in Nursing
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Man
A bio-psycho-socio-spiritual human being.
Illness
State of diminished physical or mental functioning.
Internal Variable
Factors affecting illness behavior from within.
Biological Being
Man shares similarities with other humans biologically.
Psychological Being
Man's psychological experience is unique to each individual.
Social Being
Man shares some social characteristics with others.
Spiritual Being
Man shares spiritual aspects with all humans.
Perception of Symptoms
Influences how one experiences and responds to illness.
Nature of Illness
Main physical feature or type of illness experienced.
Unified Whole
Man's parts are interdependent and interrelated.
Greater Whole Concept
Man's essence exceeds the sum of his parts.
Major Attributes of Human Being
Characteristics defining human capacity and behavior.
Coping Abilities
How a person adjusts to illness influences response.
External Variable
Factors affecting illness behavior from outside influences.
Visibility of Symptoms
Visible symptoms increase likelihood of seeking assistance.
Family Formation
Family structure influences health-seeking behavior.
Territoriality
Tendency to maintain personal space and boundaries.
Verbal Symbols
Language aids in cultural development and communication.
Human Needs
Essential for well-being and motivation for behavior.
Basic Human Needs
Common needs shared by all individuals.
Culture & Values
Teach health maintenance and illness recognition.
Economic Variable
Economic factors influence health treatment access.
Health Care Accessibility
Proximity to services affects health care utilization.
Stage 1: Symptom Experience
Initial recognition of feeling unwell without diagnosis.
Stage 2: Assumption of Sick Role
Adopting a sick role after symptom acknowledgment.
Stage 3: Medical Care Contact
Seeking medical help for illness confirmation.
Traditional Health Definition
Health defined by presence or absence of disease.
Florence Nightingale's Definition
Health is utilizing one's abilities to the fullest.
WHO Health Definition
Health is a state of complete well-being.
Health
Complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
Illness
Deviation from normal health with symptoms.
Dependent Patient Role
Client relies on professionals for treatment.
Recovery & Rehabilitation
Stage where symptoms subside and status improves.
Emotional Response to Illness
Ability to maintain daily tasks and fitness.
Fear
Expectation of harm or unpleasantness.
Over Dependence
Excessive reliance on others during illness.
Intellectual Wellness
Effective learning and personal development.
Anxiety
Emotional response leading to insomnia and fatigue.
Hope
Expectation for a long and healthy life.
Anger & Hostility
Emotions related to frustration and unpleasant situations.
Clinical Model of Health
Narrow interpretation focusing on disease absence.
Wellness
State of well-being and self-responsibility.
Role Performance Model
Health defined by fulfilling societal roles.
Well-Being
Subjective perception of vitality and fulfillment.
Physical Wellness
Regaining original health status post-illness.
Spiritual Wellness
Belief in a unifying force for meaning.
Occupational Wellness
Balance between work and leisure satisfaction.
Daily Decision Making
Choices in nutrition, stress, and fitness.
Preventive Health Care
Actions taken to prevent disease and promote health.
Emotional Health
Management of emotions and coping strategies.
Dynamic Process of Wellness
Continuous growth and adaptation in health.
Symptoms of Illness
Physical and psychological signs indicating health issues.
Health Continuum
Measurement of well-being on a spectrum.
Physiological Systems
Body functions related to health and disease.
Client Helplessness
Feelings of powerlessness during illness.
Adaptive Model
Health as a creative process; disease is maladaptation.
Eudaimonistic Model
Health as realization of full potential.
Agent-Host-Environment Model
Disease results from interactions among agent, host, environment.
Illness-Wellness Continuum
Ranges from optimal health to premature death.
Health-Illness Continua Model
Scale measuring perceived wellness; health and illness spectrum.
Health Status
Individual's health state at a specific time.
Health Beliefs
Personal concepts about health, factual or not.
Environmental Wellness
Ability to promote health in the community.
Social Wellness
Ability to interact successfully with others.
Emotional Wellness
Ability to manage stress and express emotions.
High-Level Wellness
Healthy lifestyle maintained in a favorable environment.
Emergent High-Level Wellness
Knowledge of health but struggles due to challenges.
Protected Poor Health
Sick but receiving proper medical care.
Poor Health
Sick without access to healthcare or support.
Roy Adaptation Model
Views person as an adaptive system.
Self-Actualization
Realization of one's full potential, per Maslow.
Dynamic Interactive Elements
Agent, Host, and Environment in health models.
Wellness Measures
Assessments of health status and quality of life.
Health Perception
Individual's view of their own health.
Quality of Life
Standard of living influenced by health measures.
Stress Management
Techniques to cope with stress effectively.
Goal-Directed Behavior
Actions aimed at achieving personal health goals.
Satisfying Relationships
Healthy interactions contributing to overall wellness.
Maladaptation
Failure to adapt leading to health issues.
Health Promotion
Activities aimed at improving community health standards.
Disease Prevention
Identifying risk factors to avoid health issues.
Hot-Cold System
Cultural belief balancing food qualities for health.
Health Behavior
Actions to maintain well-being and prevent illness.
Health Axis
Range from peak wellness to death.
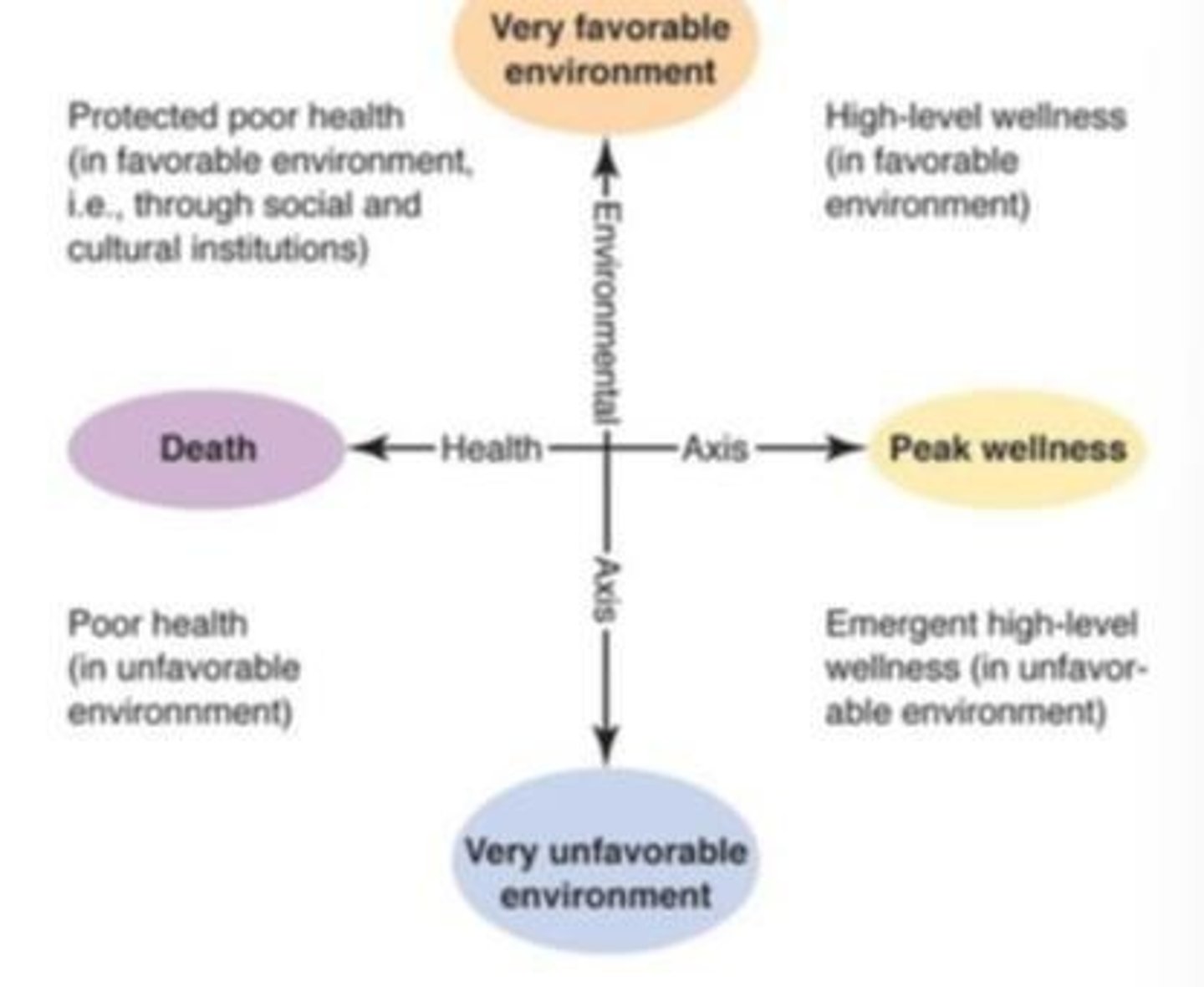
Environmental Axis
Range from very favorable to very unfavorable.
Wellness Quadrants
Framework for understanding health influences.
Internal Variables
Nonmodifiable factors affecting health outcomes.
Biological Dimension
Genetic and biological factors influencing health.
Support Systems
Family and friends aid recovery from illness.
Genetic Makeup
Influences biological traits and disease susceptibility.
Genomics
Study of genetics and environmental health interactions.
Psychological Dimension
Mental factors impacting health and wellness.
Health Beliefs Model
Predicts engagement in health promotion activities.
Mind-Body Interaction
Connection between mental state and physical health.
Emotional Responses
Stress affects physical health and immune function.
Health Locus Model
Belief in control over health outcomes.
Internals
Individuals who believe health is self-determined.
Externals
Individuals who believe health is controlled externally.
Stress Management Techniques
Methods like meditation improve health outcomes.
Cognitive Dimension
Mental processes influencing health decisions.