MCAT Biochemistry Chapter 1
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Amino Acid functional groups
Carboxyl and amino group
R group
Determines chemical properties of amino acid
Proteinogenic amino acids
Have the R group, caroxyl, amino group all bonded to one alpha carbon
Chiral/stereogenic AA
All, except glycine
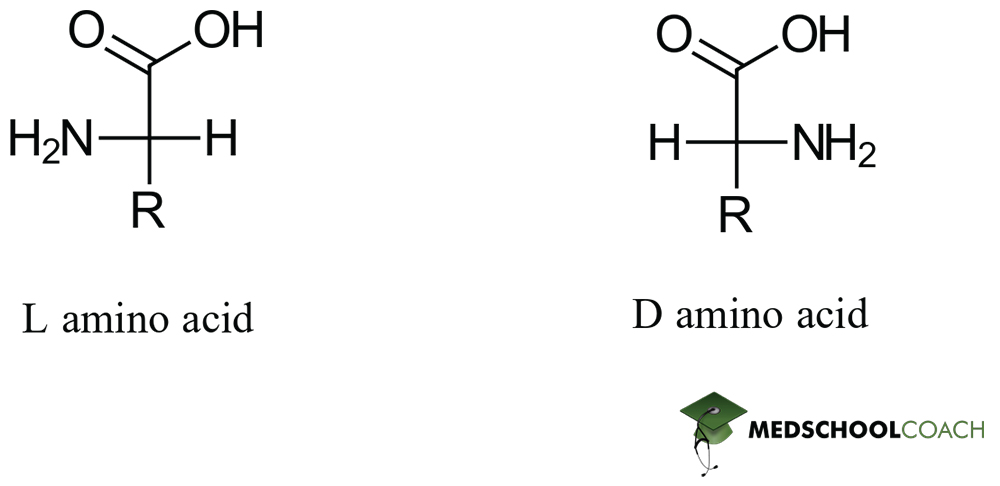
Configuration of AA
All L
All S except for cysteine
Non polar, nonaromatic AA
Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline
Aromatic AA
Tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine
Polar AA
Serine, cysteine, threonine, glutamine, asparagine,
Acidic AA, negatively charged
Aspartate, glutamate
Basic AA, postively charged
Arginine, lysine, histidine
Hydrophobic AA
Interior proteins
Alanine, leucine, isoleucine, valine, phenylalanine
Hydrophilic AA
Exterior proteins
Histidine, arginine, lysine, glutamate, aspartate, asparagine, glutamine
Site directed mutagenesis W53Y
53rd amino acid tryptophan mutated to tyrosine
Most acids in the body are
Deprotonated
Arginine postive charge
Delocalized across guanidine
Histidine protonation
Imidizole, can be protonated in acidic conditions
Proline flexibility
Decreased due to cyclic formation
Arginine and glutamine amine groups
Are not protonated with pH changes
Serine and threonine
Very polar hydroxyl group
Cysteine
Less electronegative than oxygen
Amphoteric amino acids
Can donate or accept protons due to acidic carboxylic group, basic amino group
pKa
pH when half would be protonated
pH > pKa
More deprotonated molecules
pH < pKa
More protonated molecules
All AA have at least_ pKa’s
Ionizable AA have _
2; 3
pKa1
Carboxyl, 2
pKa2
Amino group, 9, 10
At an acidic pH, amino acids are usually __
At a basic pH, amino acids are usually __
positive, negative
Zwitterions
Amino acids at physiologic pH, has both positive and negative charge
pI
Isoelectric point, when molecule is electrically neutral
When pH is near pKa, solution
Acts as a buffer
At pI, solution
Is very sensitive to changes in pH
pI for amino acids without an ionizable side chain
Approximately 6
When pH is below pKa1
Amine and carboxyl group are protonated
When pH is above pKa2
Amine and carboxyl group are deprotonated
When pH is around pI
Amine is protonated, carboxyl is deprotonated
pI is typically equal to
(pKa1+ pKa2)/2
pI for acidic amino acids equals
(pKa of R group + pKa of carboxyl group)/2
pI for basic amino acids equals
(pKa of R group + pKa amine group)/2
pI of acidic amino acid
below 6
pI of basic amino acid
above 6
Residues
Amino acid subunits, make up peptides
Oligopeptide
Polypeptide
Under 20 residues
Over 20 residues
Peptide bond
Formed by a condensation/dehydration/acyl substitution rxn between amino and carboxyl group
Peptide bond formation
electrophilic carboyl attacks nucleophilic amino group
Hydroxyl of carboxylic acid becomes water, is removed
Amide group resonance
Has delocalized pi electrons, the C=O double bond can switch to a C-O single bond and C=N double bond
Limits rotation
Peptides are synthesized from
N to C terminus, by ribosomes
Peptide bond breakers
Hydrolysis by trypsin at C terminus of R, K and by chymotrypsin at C terminus of F, W, Y
Adds OH to carbonyl and H to amide
Primary structure of peptides
Amino acid sequence from N to C
Secondary structure of peptides
Hydrogen bonds between R groups, making alpha helixes, beta sheets
Alpha helix
H bond between carbonyl oxygen and amide hydrogen 3 residues apart, with side chains facing out
Beta sheets
H bond between amino acids across from each other
Can be parallel, antiparallel
Turns
Join secondary structures together
Beta are most common, between amino acids 3 residues apart
Proline in secondary structures
Causes kinks, usually in turns and at the beginning of alpha helices that cross the cell membrane
Rare in beta sheets
Fibrous proteins
Sheets or long strands
Globular proteins
Spherical
Tertiary structures of peptides
3-D structure determined by h-phobic and h-philic interactions of R groups and acid-base interactions
Salt bridges and Disulfide bonds
Salt bridge
Hydrogen and ionic bond
Disulfide bond
Oxidation bond between two cysteins, loss of 2 electrons and protons
Form loops, curlier hair has more bonds
Protein formation
Secondary structure form, moten globules form in intermediate states, collapse into tertiary structures
Denaturation
Loss of tertiary structure, loss of function
Solvation layer
Solvent molecules surrond the solute
Water molecules rearrange to maximize hydrogen bonding, nonspontaneous due to less disorder and decreased entropy
Entropy in h-philic R groups
Increased, spontaneous, more stable
Max stability
H-phobic R groups are away from water
H-philic R groups are interacting with water
Quaternary peptide structure
Only with multiple peptide chains
Brings catalytic sites together
Induces cooperativity - changes in one subunit can influence the other
Quaternary peptide formation
Smaller globular peptide subunits aggregate, reduces surface area
Conjugated proteins
Function/delivery location determined by prosthetic groups
Lipoprotein: ___ prosthetic group
Glycoprotein: ___ prosthetic group
Nucleoprotien: ___ prosthetic group
Lipid; carbohydrate; nucleic acid
Hemoglobin
4 pyrrole (heterocyclic aromatic) rings
Nitrogen of each ring attaches to central Fe
Denaturation occurs through
Heat - increases energy, decreases bonds between amino acids and hydrophobic interactions
Solutes - urea, SDS interfere with h-bonds, noncovalent bonds
CM
Concentration when half the species is denatured
TM
Melting point when half the species is denatured