Chapter 5: Histology- Cellular Junctions, Glands, and Membranes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Tight junction
zipper-like, interlocking linkage between two adjacent cells by transmembrane cell-adhesion protein
Seals off intercellular space, making it difficult for substance to pass between cells
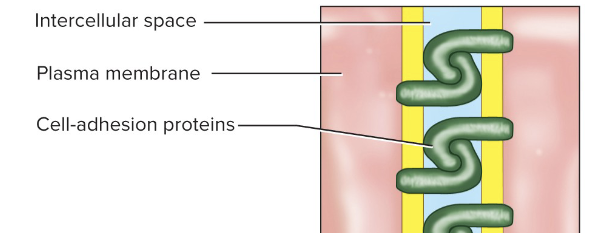
Desmosome
patch that holds cells together (like a clothing snap)
Keeps cells from pulling apart—resists mechanical stress
Hook-like, J-shaped proteins arise from cytoskeleton
Hemidesmosome
half-desmosome that anchors basal cells of an epithelium to an underlying basement membrane
Epithelium cannot easily peel away from underlying tissues
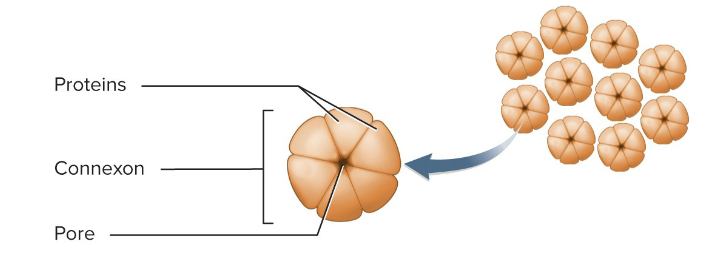
Gap (communicating) junction
formed by ring-like connexons
Connexon consists of six transmembrane proteins arranged like segments of an orange around water filled pore
Ions, nutrients, and other small solutes pass between cells
Located in cardiac and smooth muscle, embryonic tissue, lens and cornea
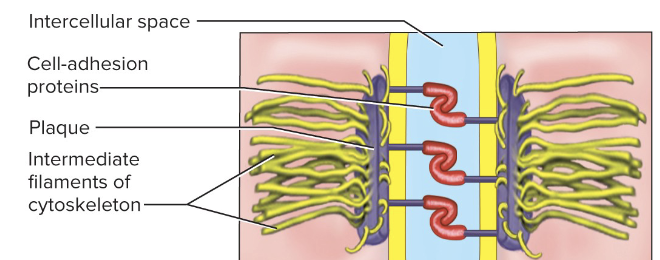
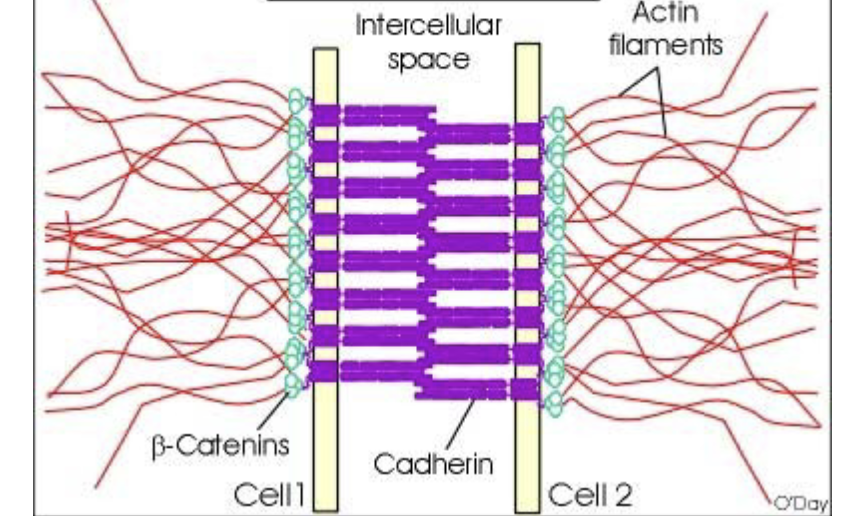
Adherens junction
Adherens junctions hold cells together via cadherins. Intracellularly, these proteins are connected to actin filaments that form a belt around the cell—provide stability to tissues
not as impermeable as tight junctions
glands
cell or organ that secretes substances for use elsewhere in the body or releases them for elimination from the body
Usually composed of epithelial tissue in a connective tissue framework and capsule
Secretion
product useful to the body
Excretion
waste product
Exocrine glands
maintain their contact with surface of epithelium by way of a duct
Surfaces can be external (e.g., sweat, tear glands) or internal (e.g., pancreas, salivary glands)
Endocrine glands
have no ducts; secrete hormones directly into blood
Examples: thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary glands
Hormones
chemical messengers that stimulate cells elsewhere in the body
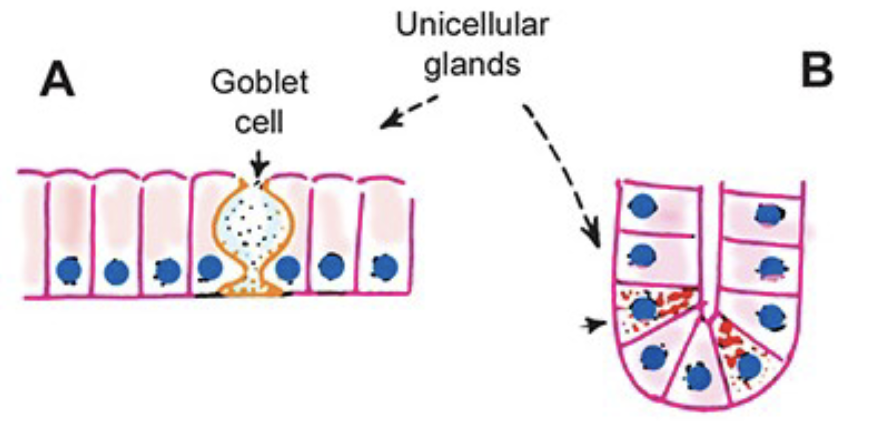
Unicellular glands
found in an epithelium that is predominantly non-secretory
Can be exocrine or endocrine
Examples: mucus-secreting goblet cells in trachea or endocrine cells of stomach
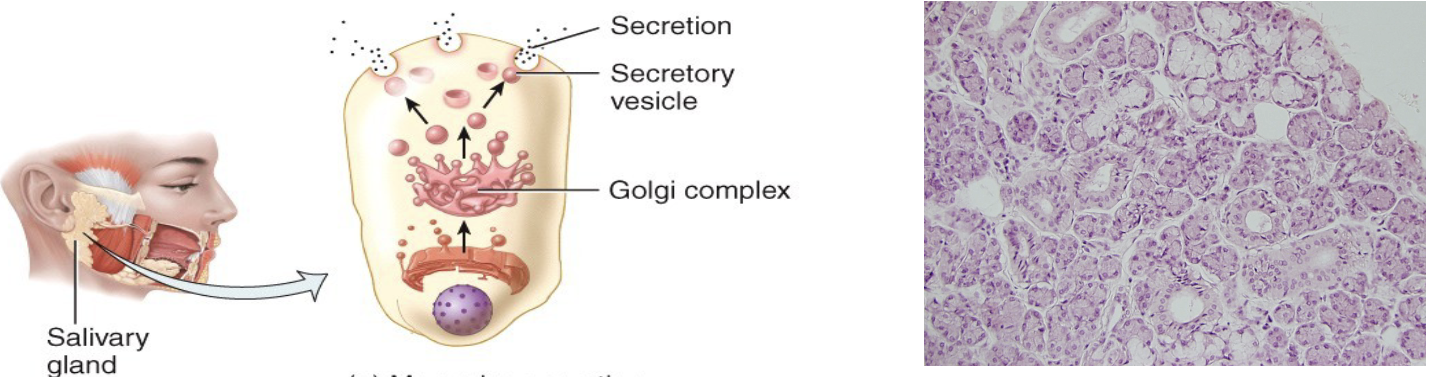
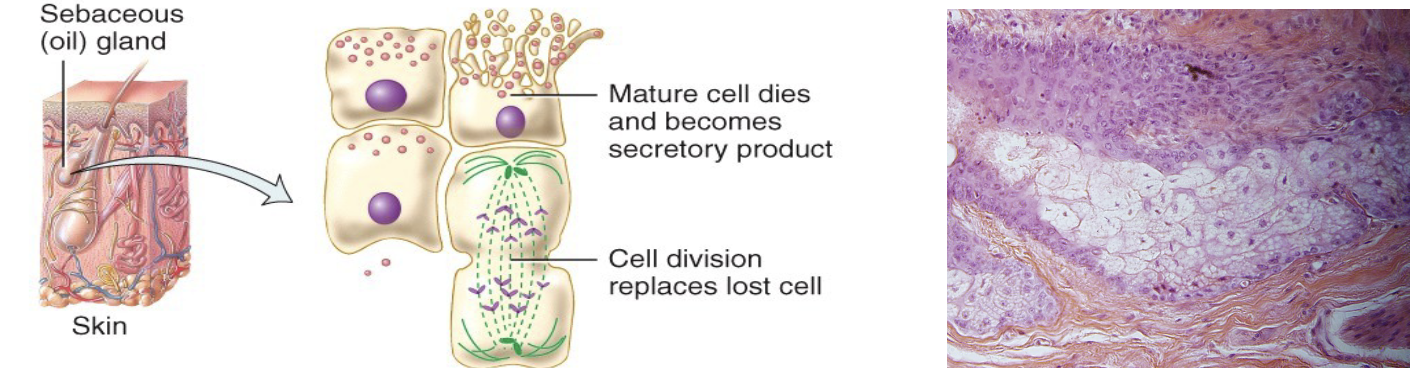
merocrine secretion
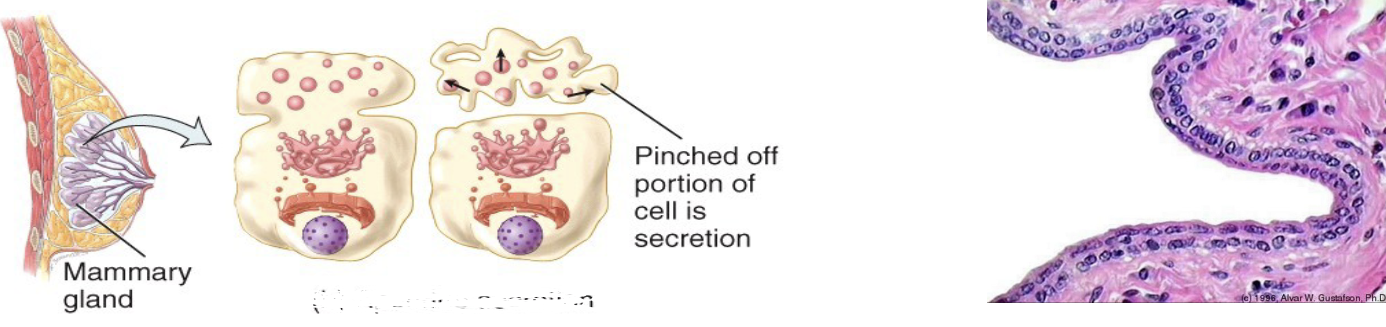
Apocrine secretion
holocrine secretion
membranes
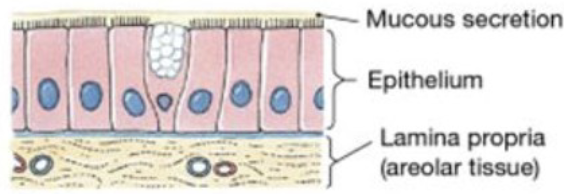
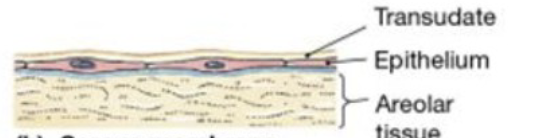
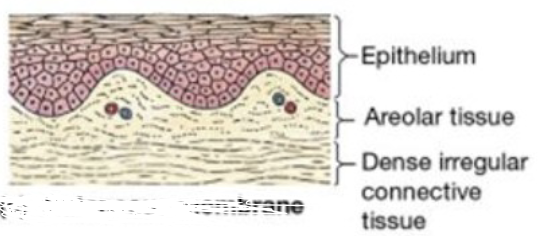
superficial epithelium sheet + underlying connective layer (called lamina propria)
cover and protect
what are the four types of membrane?
Serous, Mucous, Cutaneous, Synovial membrane
Mucous Membrane
serous membrane
Cutaneous Membrane
Synovial membrane