UWORLD Biostats USMLE Step 2 CK
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
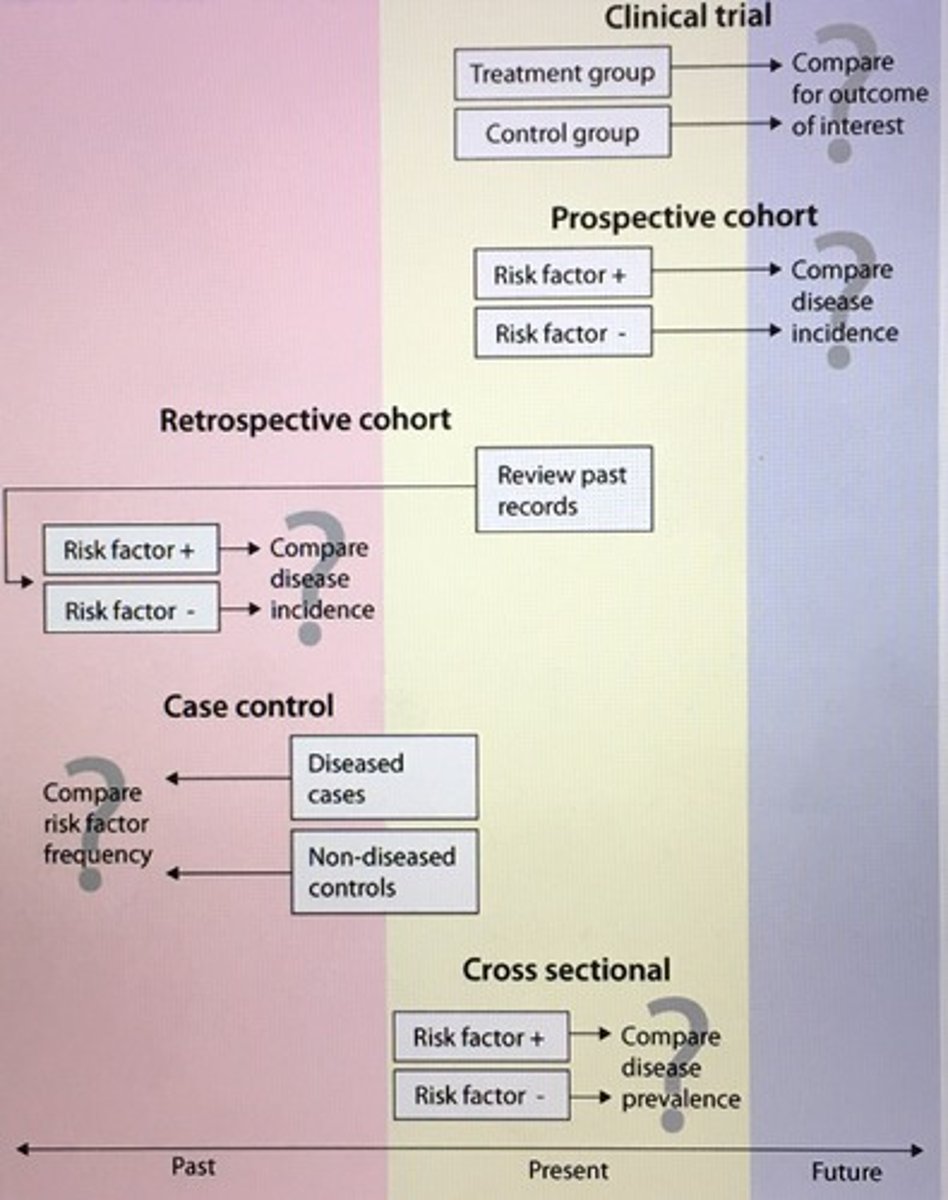
The main measure of association in case-control study design in which the exposure of people with the disease (cases) is compared to the exposure of those without the disease (controls).
Exposure odds ratio
__ or external validity pertains to the applicability of study results to other populations (the results of a study in middle-aged woman would not be expected to be applicable to elderly men).
Generalizability
The __ hypothesis is always the statement of no relationship between the exposure and the outcome.
Null
In case-control study, is the outcome is uncommon in the population, the __ is a close approximation of the relative risk. "rare disease assumption"
Odds ratio
- when disease is rare, disease incidence typically low, the odds ratio OR approximates the relative risk RR
Correlation coefficient -1.0 and +1.0
r = + means increase one variable means increase in other
r = - means increase in one means decrease in the other
r = 0 means no correlation

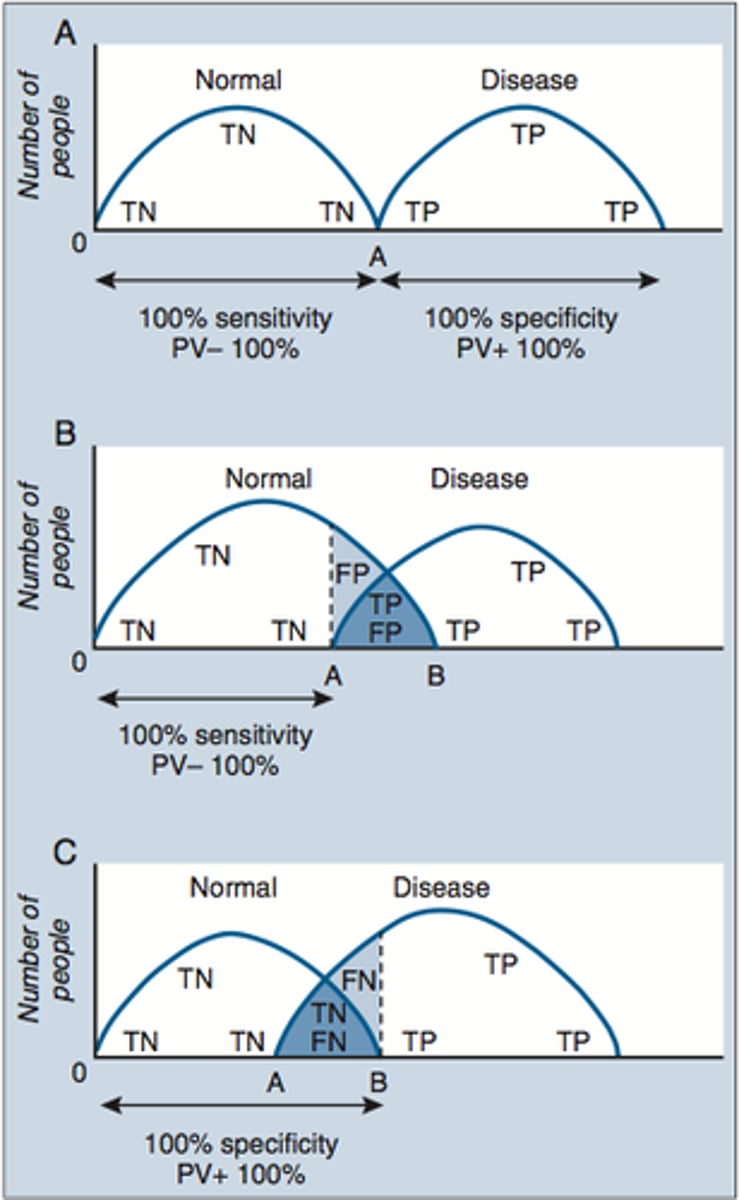
Distribution curves sensitive and specificity compare TN and TP.
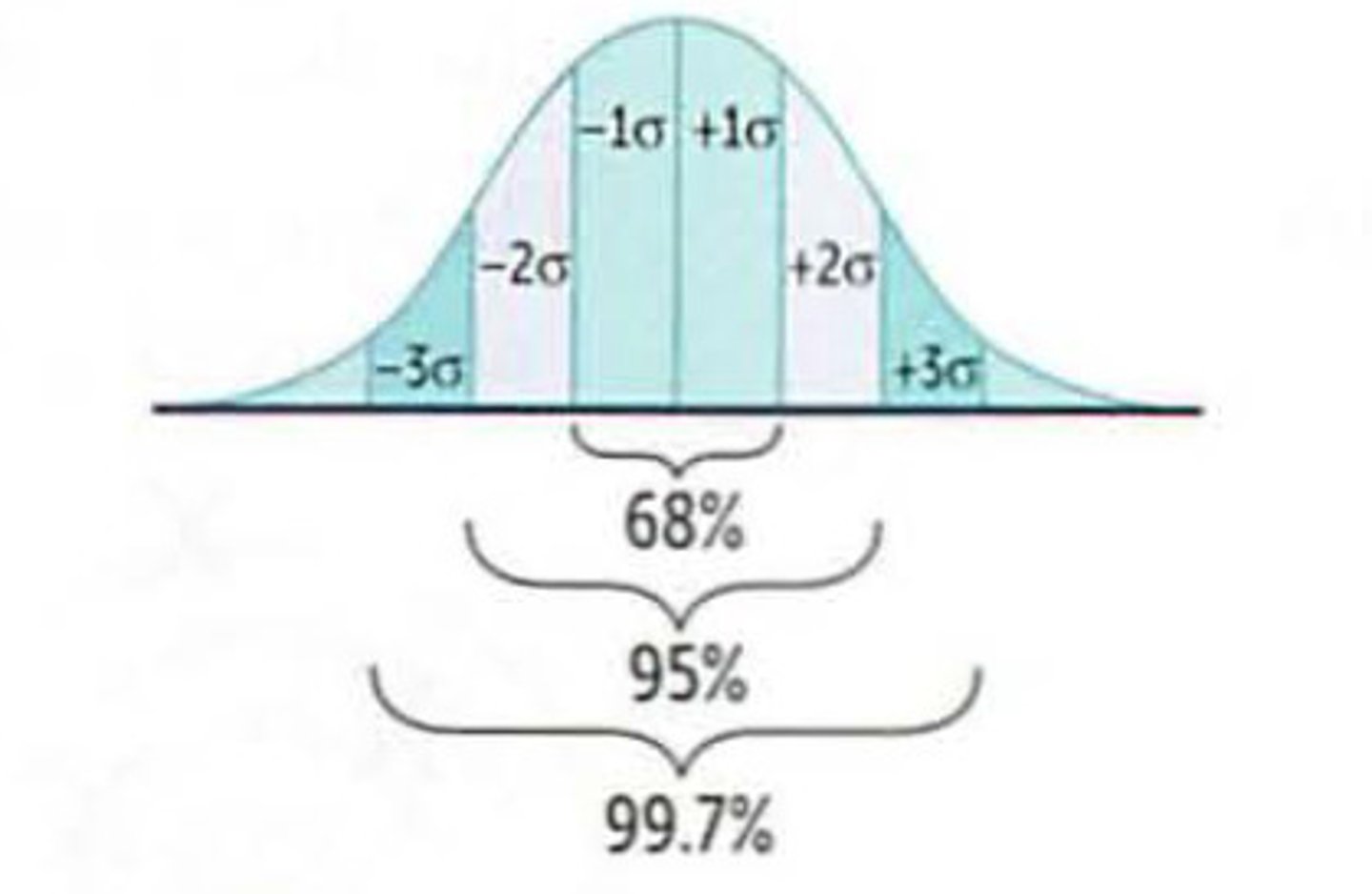
Standard deviation of normal distribution
∂ = standard deviation
68% of all values w/in 1 SD from mean
95% of all values w/in 2 SD
99.7% of all values within 3 SD
___ is design is best for determine the incidence of a disease. Comparing the incidence of the disease in 2 populations (with and without a given risk factor) allows for the calculation of relative risk.
Cohort
__ exposure and outcome are measured simultaneously at a particular point of time (snapshot study).
Cross-section study
- prevalence study
- exposure and outcomes measured simultaneously
- surveys
___ is used to compare proportions. A 2x2 table may be used to compare the observed values with the expected values.
Chi-square test
Common types of systemic error in statistical studies
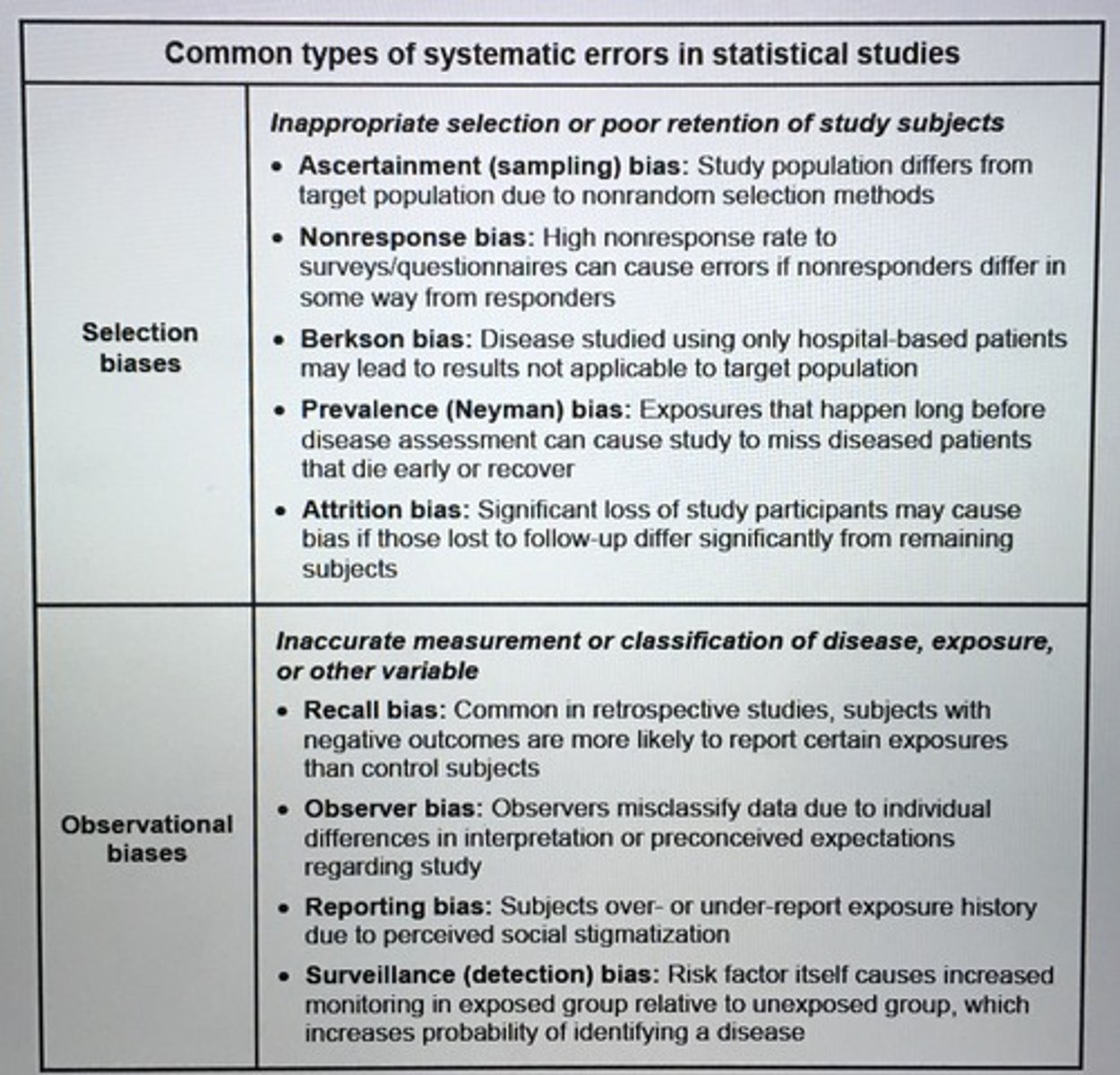
Loss to follow-up in prospective studies ceases potential for ___ bias.
Attrition bias, subtype of selection bias
Methods to control confounding.
Design stage: matching, restriction, randomization
analysis: stratified analysis, statistical modeling
___ when an external variable positively or negatively impacts the effect of a risk factor on the disease of interest.
Effect modification
___ can be applied to both disease pathogenesis and exposure to risk modifiers. Exposure to risk factors and the initial steps in disease pathogenesis sometimes occur years before clinical manifestations are evident.
Latency period
Calculate risk.
Divide the number of disease subjects by the total number of subjects (all the people at risk)
Risk = probability of getting a disease over a certain period of time
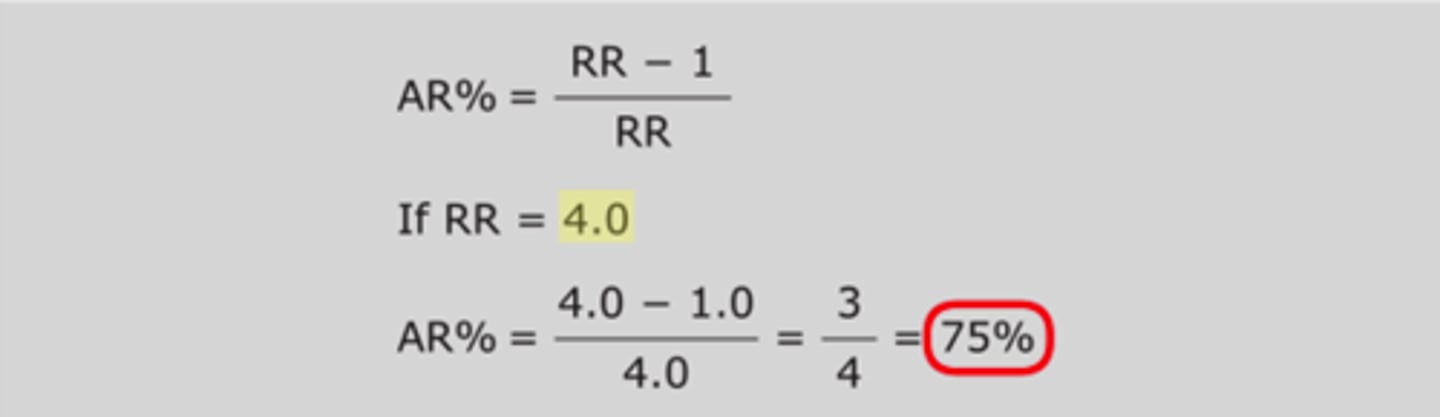
Calculate attributable risk percent (ARP).
Excess risk in population that can be explained by exposure to particular risk factor
ARP = (RR - 1)/RR
Biostats 2x2 table
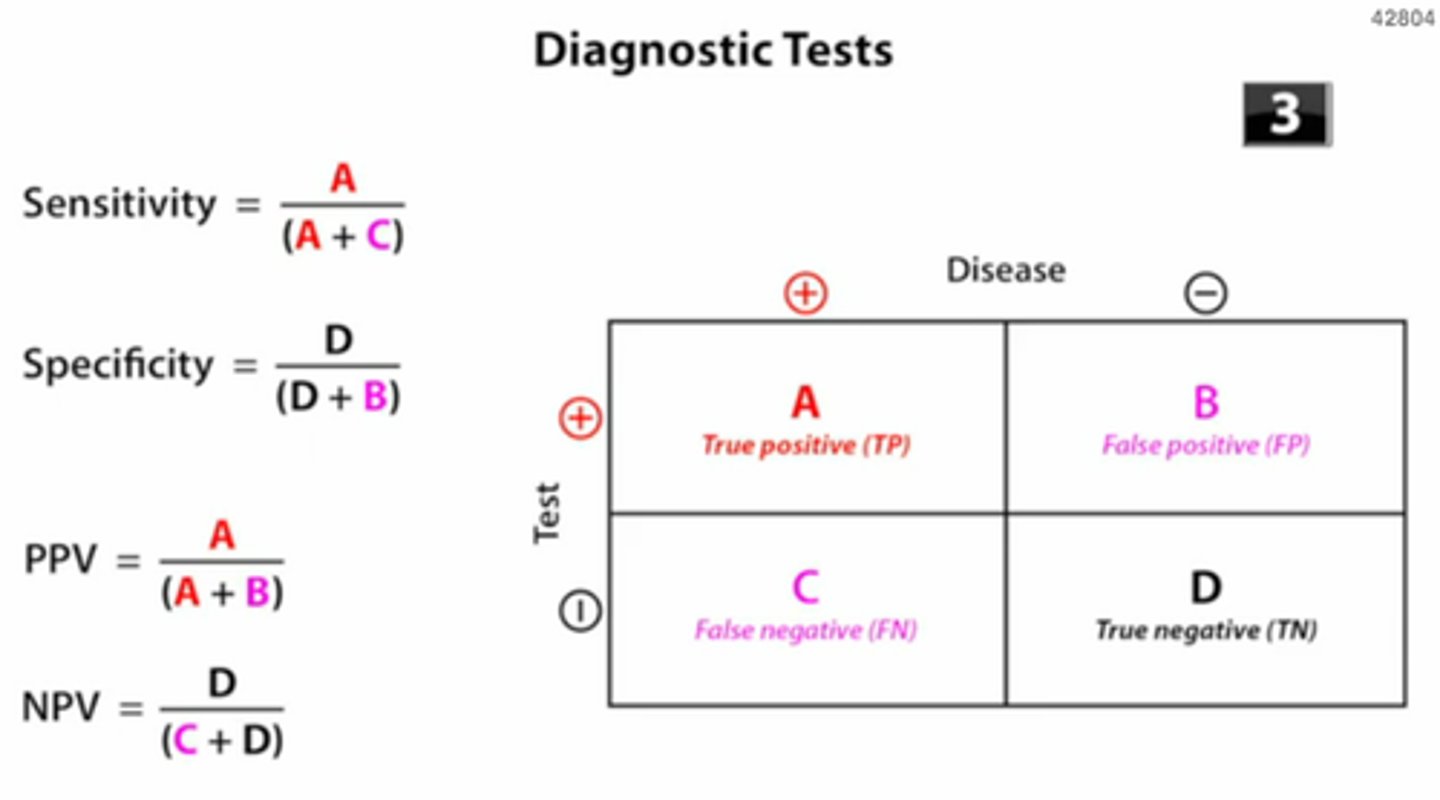
___ is said to be successful when a similarity of baseline characteristics of the patients in the treatment and placebo group is seen.
Randomization
Different study designs
Hazard ratios
Ratio > 1 the tx group had higher event rate
Ratio < 1 the tx group had lower event rate

___ design studies involve randomization to different interventions with additional study of 2 or more variables.
Factorial design
ex: study design that has 3 different drug interventions (metoprolol, ramipril, amlodipine) and 2 different variable BP endpoints
Continuity of care for medications at the time of transition of care, between inpatient and outpatient facilities and within inpatient facilities, is potential source of medical error. Interventions that target ___ and ___ appear to be the most effective in improving the quality of patient care.
Pharmacy personnel and high-risk patients
___ is statistical method that is commonly employed to compare the means of 2 groups of subjects.
two-sample t test
The typical example of ___ bias is prolongation of apparent survival in patients to whom a test is applied, without changing the prognosis of the disease.
Lead-time bias
A ___ test gives similar result on repeat measurements.
Reliable test
- reliability is maximal when random error is minimal
___ is the measure of random error. The tighter the confidence interval, the more ___ the results.
Precision
- increasing the sample size increases precision
___ bias occurs when the investigator's decision is adversely affected by knowledge of the exposure status.
Observer bias
If a test result is negative, the probability of having the disease is ___.
= 1 - NPV
False positive ratio = ___.
= 1 - specificity
False negative ratio = ___.
= 1 - sensitivity
Normal distribution curve
central tendency are equal: mean = median = mode

Number needed to treat (NNT) is defined as the number of people that need to receive a treatment to prevent 1 additional adverse event. It is calculated as the ___.
Inverse of the absolute risk reduction (ARR)
NNR = 1/ARR
__ is the tendency of the study population to affect the outcome since they are aware that they are being studied.
Hawthorne effect
With an INC in prevalence, the PPV will [INC/DEC] and NPV will [INC/DEC].
PPV INC = Prevalence
NPV DEC